Urinary system disorders Chapter 29
|
|
|
- Pearl Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urinary system disorders Chapter 29 1
2 The Nephron Anatomy 2
3 Physiology 1.25 L per minute blood flow 25% of Cardiac Output Kidney compensates if one is lost - 2 weeks 3
4 Urine Formation 1. Filtration 2. Reabsorption w Diffusion w Osmosis w Active Transport 3. Secretion w Diffusion w Osmosis w Active Transport 4. Excretion 4
5 Glomerular Filtration w Driven by pressure through glomerular membrane 5
6 Glomerular Filtration w Through 3 Selectively Permeable Layers w Capillary endothelium w Basement membrane w Epithelium of Bowman s capsule w podocytes 6
7 Glomerular Filtration w Basement Membrane w Selective Filter w Slightly porous w Repels proteins (negative charge) w Allows only water, ions, and small molecules 7
8 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Angiotensinogen Renin Angiotensin I ACE Vasoconstriction Efferent Arterioles Systemic Arteries Angiotensin II Aldosterone Release 8
9 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 9
10 Renal Cystic Disease w Fluid filled sacs or Dilated nephrons w Four types w Simple kidney cysts w Acquired cystic disease w Medullary sponge kidney w Polycystic kidney disease w Result of tubular obstruction w Enlarging cysts w Compresses vessels and renal tissue 10
11 Polycystic Kidney Disease w Autosomal dominant disorder characterized by multiple bilateral grapelike cysts that enlarge and replace functioning kidney tissue w Grossly enlarged kidneys w Slowly progressive w Destruction of renal tissue 11
12 Polycystic Kidney Disease w Complications w Pain from enlarging cysts w Hematuria from bleeding into a cyst w Pyelonephritis from ascending UTI w Hypertension due to compression of intrarenal blood vessels and activation of R-A-A System w End stage renal failure after age 40 12
13 Polycystic Kidney Disease w Diagnosis and Treatment w Ultrasonography w Abdominal CT scanning w Supportive treatment w Control hypertension w Prevention of ascending UTIs w Dialysis and Transplant 13
14 Obstruction w Urine accumulates behind blockage w Infection w Damage due to backpressure w Classification w Site of obstruction w Degree of obstruction w Duration of obstruction 14
15 Obstruction w Site of Obstruction w Renal Pelvis w Ureter w Bladder and Urethra 15
16 Obstruction w Common Causes of Obstruction w Stones (Renal Calculi) w Pregnancy w Ureteral Stricture w Prostatic Hyperplasia or Cancer 16
17 Obstruction w Mechanisms of Damage w Stasis of urine w infection w stone formation w Back pressure w interferes with blood flow w destroys renal tissue w kidney atrophies 17
18 Obstruction w Back Pressure (location is important) w Urethral Obstruction w Accommodated in the bladder w Mild discomfort, Frequency w Bladder or Ureter Obstruction w More severe w Pressure can irreversibly stretch the ureters and renal pelvis w (hydroureter & hydronephrosis) w May alter tubular transport and compromises blood flow to the kidney 18
19 Hydronephrosis 19
20 Obstructive Disorders w Clinical Features w Vary depending on site, cause and rapidity of onset w Pain w UTIs w Indications of Renal Dysfunction w Hypertension 20
21 Kidney Stones w Most Common Cause of Obstruction w Nephrolithiasis stone within the kidney w Urolithiasis stone anywhere in the urinary system w Calcium Stones are Most Common w Theories of Stone Formation? w Calcium: idiopathic, hypercalciuria, alkaline urine w Struvite: from urease-producing bacteria, acidic urine w Contributing Factors w immobilization w bone disease w vitamin D intoxication w decreased fluid intake 21
22 Staghorn Kidney Stones 22
23 Renal Colic w Pain that accompanies urinary obstruction caused by kidney stones w Symptoms: acute, intermittent, excruciating, upper quadrant/flank pain that may radiate to other areas; nausea/vomiting; cool, clammy skin 23
24 Lower Urinary Tract Obstruction w Neurogenic bladder often due to injury of urinary system or neurologic dysfunction w Dyssynergia : dyscoordination of the detrusor muscles of the bladder and the external urethral sphincter muscles w Detrusor hyperreflexia: AKA overactive bladder. Lesions above C2, pontine micturation center, upper motor neuron disease, Guillain-Barre w Detrusor areflexia: muscle fails to contract in response to the stretch of filling urine. MS, spinal lesion below S1, lower motor neuron disorder 24
25 Urinary Tract Obstruction w Compensatory hypertrophy: the functional side increases in size and makes up for the loss of function on the other side. Due to w Obligatory growth: due to growth hormone w Compensatory growth: hormones unknown w Postobstructive diuresis:large increase in excretion of urine after obstruction is removed 25
26 Urge incontinence: I feel like I need to go but the bladder is not as full as it feels, maybe nervous or inflammatory stimulus Stress incontinence: weak muscles and fascia so coughing, laughing, jumping results in urine leaks Overflow incontinence: bladder is just too full to hold that much urine, you waited too long to void Functional incontinence: urinary system and nerves going to and from it work, but you are cognitively demented (Alzheimer s) 26
27 Urinary Tract Infections w Etiology w Escherichia coli (E. coli) w Any microorganism that has contaminated or colonized in the urethra, vaginal or perineal area can cause an UTI 27
28 Urinary Tract Infections Acute Cystitis Lower UTI of the bladder Symptoms: increased frequency of urination, burning & pain on urination, lower abdominal discomfort Also associated with urethritis or vaginitis Acute Pyelonephritis Upper UTI that affects the tubules and interstitium of the kidneys Bacterial infection caused by catheterization and urinary instrumentation, vesicoureteral reflux, pregnancy, neurogenic bladder 28
29 Urinary Tract Infections w Host Defenses w Washout phenomenon w Protective mucin layer of the bladder and urethra w Estrogen may play a role in women w Local immune response w IgA as an antibacterial defense w Prostatic secretions in men w Genetic polymorphism increases E. coli ability to attach in some women 29
30 Urinary Tract Infections Women Shorter urethra Urethra proximity to openings of vagina and rectum leads to easy contamination Hormonal and anatomical changes during puberty and sexual activity contribute to UTI Common during pregnancy Men Longer urethra Prostatic secretions help protect from UTI until age 50 when prostatic hypertrophy leads to obstruction and UTI 30
31 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) w Nonbacterial infectious cystitis: viral, fungal, chlamydia w Interstitial cystitis: cause??? unknown, though several theories have been put forward (these include autoimmune theory, nerve theory, mast cell theory, leaky lining theory, infection theory and a theory of production of a toxic substance in the urine. Other theories are neurologic, allergic, genetic and stress-psychological w Manifestations w Most common in women 20 to 30 years old w Bladder fullness, frequency, small urine volume, chronic pelvic pain w Treatment w No single treatment effective, symptom relief 31
32 Glomerulonephritis w Bilateral inflammation of the glomeruli w Most common cause of chronic renal failure w Uncertain cause but immune mechanism is likely (Type 2 cell lysis Strep A ab, Type 3 SLE immune complex) w Injury to Glomeruli (Glomerulopathies) w Allows Proteins to enter tubules with filtrate w Proteinuria w Allows RBC s to enter tubules with filtrate w Hematuria 32
33 Glomerular Disorders w Increased glomerular capillary permeability and loss of negative ionic charge barrier result in passage of plasma proteins into the urine w Resulting hypoalbuminemia encourages plasma fluid to move into the interstitial spaces w Edema 33
34 Structure of the Glomerulus w Glomerular capillaries and Bowman s capsule are both made of epithelial cells sitting on a basement membrane w They are so tightly attached to each other that they share one basement membrane w The epithelial cells of Bowman s capsule stand up from the basement membrane on foot processes, leaving pores between the feet for filtration Urine Epithelial cell Foot processes Basement membrane Blood in capillary 34
35 Immune Damage to the Glomerulus Antibodies to glomerular basement membrane proteins Circulating immune complexes lodge in glomerular membrane 35
36 Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis w The most common form of glomerulonephritis w Follows infections caused by strains of group A Strep w Inflammatory response due to an immune reaction w Capillary membrane swells w Becomes permeable to plasma proteins and cells w Also called post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis w Occurs 7 12 days post infection w Oliguria is first sign followed by proteinuria and hematuria w Approximately 95% full recovery - spontaneously 36
37 Glomerulonephritis w Rapidly progressing glomerulonephritis w Antiglomerular basement membrane disease (Goodpasture syndrome: glomerulonephritis and hemorrhaging of the lungs), autoimmune Type II hypersensitivity reaction w Chronic glomerulonephritis, diabetes mellitus, SLE 37
38 Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis w Unknown cause w Perhaps - immunologic mechanism w Immune complex: Strep A w Anti-glomerular membrane: Goodpasture s w Rapidly progressive w Treatment w Plasmapheresis w Immunosuppressive drugs 38
39 IgA Nephropathy w Primary glomerulonephritis w IgA containing immune complexes w Unknown cause w Possible defect in IgA molecule w Slowly progressive w No known treatment 39
40 Nephritic Syndrome w Glomerular disorders in which inflammatory process damages the glomerular membrane w Mild protein loss w Red and white blood cells escape into the urine w Hematuria with red and white cell casts w Hemodynamic changes can decrease permeability of glomerular membrane and decreases the GFR w Low proteinuria 40
41 Nephritic Syndrome w Complications w Renal Failure w Pulmonary edema w Heart failure w Hypertension 41
42 Nephrotic Syndrome w Collection of clinical findings associated with glomerular disease characterized by marked proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia and edema w Increased glomerular permeability causes massive loss of plasma proteins w proteinuria w Edema is common w Hypoalbuminemia allows plasma to leak into tissues w Reduced intravascular volume lowers GFR triggering Angiotensin II and Aldosterone which increase sodium and water retention 42
43 Nephrotic Syndrome w Other proteins lost in urine: Immunoglobulins and complement à immune suppression Clotting and anti-clotting proteins à thrombosis Proteins that carry other blood components à imbalances in blood components; altered drug dosages 43
44 Nephrotic Syndrome Glomerular Damage Permeability to Protein Proteinuria > 3.5 g/24hr Hypoproteinemia (Albumin < 3 g/100ml) Compensatory Protein Synthesis including Lipoproteins Plasma Osmotic Pressure Hyperlipidemia Plasma leaks into tissues Plasma Volume GFR ñ Na / Water Retention EDEMA Aldosterone 44
45 Nephrotic Syndrome w Complications w Malnutrition w Infection w Coagulation disorders w Thromboembolic vascular occlusion w Accelerated atherosclerosis w Acute renal failure 45
46 Nephrotic Syndrome w Treatment w Correct underlying cause w Diuretics 46
47 Nephrotic Syndrome w Membranous glomerulonephritis:one of the more common forms of nephrotic syndrome. Caused by immune complexes binding to the glomerular basement membrane w Focal glomerulosclerosis: common in kids, scarring of some of the glomeruli, there are several genetic causes w Minimal change disease (lipoid nephrosis): in kids, cause is idiopathic, diffuse loss of (podocyte) foot processes., vacuolation, and growth of microvilli on the visceral epithelial cells. 47
48 Tubulointerstitial Disorders w Damage to tubules and surrounding tissues w Generally due to: w Pyelonephritis w Toxic substances such as medications or ischemic injury w Urinalysis is neither nephrotic nor nephritic in Character w Mild Proteinuria ( < 1 gm/day ) 48
49 Renal Failure w Inability of kidney to maintain homeostasis and eliminate nitrogenous wastes w Decline in GFR leading to azotemia w Creatinine w Urea w Generally a decline in urine output w Oliguria = < 500 ml/day w Anuria = < 100 ml/day w Non-oliguric failure is possible 49
50 Acute Renal Failure w Sudden interruption of renal function w Classified as prerenal, postrenal & intrarenal w Often reversible if treated early w Three phases w Oliguric phase w Diuretic phase w Recovery phase 50
51 Acute Renal Failure w Oliguric phase w Lasts for a few days to several weeks w Urine output drops to below 400 ml/day w Patient may become fluid overloaded w Cellular injury and necrosis of kidney w Diuretic phase w Lasts days to weeks w Kidneys become unable to conserve sodium & water w Urine output increases 51
52 Acute Renal Failure w Recovery Phase w Lasts 3 to 12 months w Renal function gradually returns to normal 52
53 Acute Renal Failure w Prerenal failure: most common w Caused by diminished blood blow to the kidney w Kidney becomes ischemic w Damages kidney tubules 53
54 Acute Renal Failure w Intrinsic failure (intrarenal failure) w Damage to the filtering structures of the kidney w May be nephrotoxic, inflammatory or ischemic 54
55 Acute Renal Failure w Postrenal failure w Bilateral obstruction to urine outflow 55
56 Acute Renal Failure Causes of Acute Renal Failure Prerenal Hypovolemia Decreased vascular filling Heart failure Vasoconstrictive drugs Postrenal Bilateral ureteral obstruction Bladder outlet obstruction Intrinsic (ATN) Prolonged ischemia Nephrotoxins Acute renal disease 56
57 Acute Renal Failure w Complications w Infection w Heart failure w Hypertensive crisis w Electrolyte imbalance w Diagnostic test findings w Elevated BUN, creatinine and potassium w Abnormal urinalysis 57
58 Acute Renal Failure w Treatment w Reverse the cause w Electrolyte and I.V. therapy 58
59 Acute Tubular Necrosis w Intrarenal acute renal failure w Injury to the nephron s tubular segment w Resulting from ischemia or nephrotoxic injury 59
60 Acute Tubular Necrosis w Causes w Ischemic injury w Hypotension w Trauma, hemorrhage, dehydration w Shock w Nephrotoxic injury w Toxic chemical ingestion or inhalation w Hypersensitivity reaction to antibiotics etc. 60
61 Acute Tubular Necrosis w Pathophysiologic Changes w Decreased urine output, hyperkalemia and elevated renal function tests w Complications w Heart failure w Pulmonary edema w Anorexia and vomiting 61
62 Acute Tubular Necrosis w Diagnostic test findings w Abnormal urinalysis w Abnormal blood tests of renal function w Treatment w Reverse cause w Long term fluid management 62
63 Chronic Renal Failure w End result of gradual tissue destruction and loss of renal function w Occasionally due to acute destruction of kidney w Fatal without treatment w Nephron damage is progressive and permanent w Relatively asymptomatic until 75% loss of nephrons 63
64 Chronic Renal Failure w w w w Diminished renal reserve w Nephrons are working as hard as they can w GFR is 50 89% of normal Renal insufficiency w Nephrons can no longer regulate urine density w GFR is 20 50% of normal Renal failure w Nephrons can no longer keep blood composition normal w GFR is 5 20% of normal End-stage renal disease w GFR is Less than 5% of normal 64
65 Chronic Renal Failure w As GFR decreases azotemia and uremia develops w Azotemia = accumulated nitrogenous wastes in blood w Early asymptomatic sign of renal failure w Elevated BUN w Uremia = urea and other nitrogenous wastes increase in blood w Constellation of symptoms due to systemic complications attributed chronic renal failure (increased BP, edema, nausea, vomiting, neurological problems due to toxic levels of nitrogenous wastes) w These appear when azotemia becomes significant 65
66 Chronic Renal Failure w Renal filtering function decreases w Altered fluid and electrolyte balance w Acidosis, hyperkalemia, salt wasting, hypertension w Wastes build up in blood w Increased creatinine and BUN w Toxic to CNS, RBCs, platelets w Kidney metabolic functions decrease w Decreased erythropoietin w Decreased Vitamin D activation 66
67 Chronic Renal Failure These are not usually seen in Acute Renal Failure Body System Hematologic Cardiovascular Gastrointestinal (GI) Musculoskeletal Neurologic Body fluids Genitourinary Manifestations Anemia, bleeding tendencies, immunocompromised Hypertension, CHF, pulmonary edema, arrhythmias Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, GI bleeding Muscle weakness, bone pain, spontaneous fractures Headache, anorexia, lethargy, delirium, coma, seizures Metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia Impotence, amenorrhea, loss of libido 67
68 Chronic Renal Failure w Causes w Endocrine disease (diabetes) w Chronic glomerular disease (glomerulonephritis) w Chronic infection w Congenital anomalies w Vascular disease (hypertension etc.) w Obstruction w SLE 68
69 Chronic Renal Failure w Treatment w Low protein, high calorie, fluid restricted diet w Medications w Dialysis w Kidney transplant 69
70 Acute Renal Failure (ARF) 70
71 Chronic Renal Failure 71
72 Tumors w Renal tumors w Renal adenomas w Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) w Bladder tumors w Transitional cell carcinoma w Gross, painless hematuria w Most common in males older than 60 years w Chronic heavy smokers 72
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Renal pathophysiology.
 Renal pathophysiology basa.konecna@gmail.com Outline Intro basic structure & physiology Nephrotic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Acute renal failure Chronic kidney disease Gross structure and location Kidney
Renal pathophysiology basa.konecna@gmail.com Outline Intro basic structure & physiology Nephrotic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Acute renal failure Chronic kidney disease Gross structure and location Kidney
1. Disorders of glomerular filtration
 RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Renal Disease. Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs
 Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Thambi, M. (2017). Acute Kidney Injury. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. AKI This
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Thambi, M. (2017). Acute Kidney Injury. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. AKI This
Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders
 Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders Objectives: Congenital Kidney Disorders, Obstructive Kidney Disorders and Kidney cancer. Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial Disorders Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney
Renal and Urinary Tract Disorders Objectives: Congenital Kidney Disorders, Obstructive Kidney Disorders and Kidney cancer. Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial Disorders Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Chapter 23. Micturition and Renal Insufficiency
 Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
HTN, retenopathy, edema, encephalopathy
 ARF Uremic syndrom Uremic syndrome (uremia) is a serious complication of CRF & ARF. It occurs when urea and other waste products build up in the body because the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. These
ARF Uremic syndrom Uremic syndrome (uremia) is a serious complication of CRF & ARF. It occurs when urea and other waste products build up in the body because the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. These
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Pediatric GU Dysfunction
 Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Urinary System. Dr. Thorson
 Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Chapter 14 The Urinary System. Anatomy
 Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Chapter 14 The Urinary System Anatomy 14.1 Overview Role in removal of wastes to maintain homeostasis Acts as filtering system of the blood Produces urine Removes wastes, maintains ph, electrolyte composition,
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013 10 questions on this outline on Exam 7 Urinary System performs: Maintains
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Urology Revised: 11/2013 10 questions on this outline on Exam 7 Urinary System performs: Maintains
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
The Excretory System
 The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
Pathophysiology. Renal basic structure / function. Page 1. JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, ,
 Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 17 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 17 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test. c. Kidneys have three protective layers d. The adrenal gland is located deep within the kidney
 Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test 1. Which of the following is a function of the urinary system? a. Regulates water b. Regulates balance of acids, bases, and electrolytes c. Filters waste from
Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test 1. Which of the following is a function of the urinary system? a. Regulates water b. Regulates balance of acids, bases, and electrolytes c. Filters waste from
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. Dr Boldizsár CZÉH
 THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Bladder Schistosomes. Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection.
 Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
KIDNEY FAILURE. What causes kidney failure People who are most at risk for kidney failure usually have one or more of the following causes:
 KIDNEY FAILURE Your kidneys are a pair of organs located toward your lower back. One kidney is on each side of your spine. They filter your blood and remove toxins from your body. Your kidneys send toxins
KIDNEY FAILURE Your kidneys are a pair of organs located toward your lower back. One kidney is on each side of your spine. They filter your blood and remove toxins from your body. Your kidneys send toxins
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney:
 Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists. Lesson 12.1 Objective. Chapter 12 Urinary Pathologies. Urinary System (cont. Urinary System. (cont d.
 Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Lesson 12.1 Objective Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the urinary system. Chapter 12 Urinary Pathologies 2 Urinary System Urinary
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Lesson 12.1 Objective Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the urinary system. Chapter 12 Urinary Pathologies 2 Urinary System Urinary
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests. Amelyn R.
 Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pear-shaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman s capsule
 Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered
 URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
A&P of the Urinary System
 A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System. Short Answer. Figure 15.1
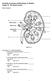 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Clinical Significance of ARF. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency. Case - Acute Renal Failure. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency
 Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Urinary tract pathology Renal syndromes Acute nephritic syndrome syndrome includes oliguria hematuria proteinuria edema hypertension typically occurs
 Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Head of Paediatric Department BBH Rawalpindi
 Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Head of Paediatric Department BBH Rawalpindi Acute Post streptococcal Glomerulonephritis Sudden onset of Gross hematuria Edema Hypertension Renal insufficiency Cause of AGN Post
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Head of Paediatric Department BBH Rawalpindi Acute Post streptococcal Glomerulonephritis Sudden onset of Gross hematuria Edema Hypertension Renal insufficiency Cause of AGN Post
Unit 15: The Urinary System
 Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
