Case report of a 45-year old female Fabry disease patient carrying two alphagalactosidase
|
|
|
- Katrina Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 DOI /s z CASE REPORT Case report of a 45-year old female Fabry disease patient carrying two alphagalactosidase A gene mutation alleles Daniel Oder 1,2, Dorothee Vergho 1,2, Georg Ertl 1,2, Christoph Wanner 1,2 and Peter Nordbeck 1,2* Open Access Abstract Background: X-chromosomal inheritance patterns and generally rare occurrence of Fabry disease (FD) account for mono-mutational hemizygous male and heterozygous female patients. Female mutation carriers are usually clinically much less severely affected, which has been explained by a suggested mosaicism in cell phenotype due to random allele shutdown. However, clinical evidence is scarce and potential additional effects in female gene carriers, which might account for specific clinical characteristics such as less severe chronic kidney disease, are yet unknown. Case presentation: This article reports on a 45 year old female patient carrying the two alpha-galactosidase A gene mutations c.416a > G, p.n139s in exon 3 and c.708g > C, p.w236c in exon 5, but still showing only mild organ manifestations. Conclusion: This current case highlights the importance of careful clinical characterization in patients with Fabry disease, who may show additional rare constellations and, therefore, are in need of personalized medicine. The impact of potential additional protective effects exceeding the presence of a non-pathogenic GLA allele in female gene carriers requires further investigation. Keywords: Fabry disease, Cryptogenic stroke, Pain, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Chronic kidney disease Background Anderson-Fabry disease (FD) is a rare, X-chromosomal inherited lysosomal storage disorder resulting from currently over 800 known pathogenic alpha-galactosidase A gene (GLA) mutations [1, 2]. Recent focus has been set on understanding mutation-specific clinical characteristics and outcome, which might eventually lead to a clinically relevant sub-classification of FD, such as into classical, non-classical, late onset and/or organ-specific variants [3 6]. While most X-linked diseases only cause phenotypical manifestations in male patients with females usually being completely unaffected carriers [7, 8], FDfemales may develop manifestations to a specific extent, which are usually much less severe in terms of clinical * Correspondence: nordbeck_p@ukw.de 1 Department of Internal Medicine I and Comprehensive Heart Failure Center (CHFC), University Hospital Würzburg, Oberdürrbacher Str. 6, D Würzburg, Germany 2 Fabry Center for Interdisciplinary Therapy (FAZIT), University Hospital Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany symptoms compared to respective men [2, 9, 10]. This is attributed to the fact that women nearly always present a heterozygous GLA genotype including one further, nonpathologically affected allele. However, the definite underlying mechanisms ultimately leading to somewhat less morbidity in female FD patients are still under debate. A potential impact of skewed X-inactivation has been supposed central, leading to random transcriptional silencing of one of both X chromosomes in every cell, eventually leading to the typical findings of female genetic mosaicism [8, 11, 12]. Due to the marked variance of FD regarding clinical symptoms, there is high interest to characterize the impact of genotypes in order to embrace patients individualized additive therapeutic needs aside from enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and improve mechanistic knowledge regarding genotype-phenotype pathophysiology The Author(s). Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 Page 2 of 6 Table 1 General- and Fabry-associated characteristics, biomarkers, renal function and quality of life of the index patient Variables Index patient Reference values Demographics Age at first visit (years) 44 Body-mass-index (kg/m2) 20.7 Biomarkers Lyso-Gb3 (ng/ml) 30.2 <0.9 α-gal A (nmol/min/mg protein) NT-proBNP (pg/ml) (agedependent) hs-tnt (pg/ml) < Renal Serum-Creatinine (mg/dl) Cystatin C (mg/l) GFR DTPA Clearance (ml/min) Fabry associated Angiokeratoma Cornea verticillata Impaired sweating Vertigo Tinnitus Frequent diarrhea Constipation Abdominal pain Abdominal cramps Nausea/vomiting Medication ERT Agalsidase beta Beta blocker ACEi/ARBs Ca-blockers Diuretics ASA/OAC Quality of life (SF-36 questioner) Physical functioning 75 Role physical 0 Bodily pain 100 General health 45 Vitality 20 Social functioning 12.5 Table 1 General- and Fabry-associated characteristics, biomarkers, renal function and quality of life of the index patient (Continued) Role emotional 100 Mental health 48 Physical component summary score Mental component summary score Abbreviations: α-gal Aalpha-galactosidase A enzyme activity, ACEi angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ARBs Angiotensin II receptor antagonists, ASA/OAC acetylsalicylic acid/oral anticoagulation therapy, ERT enzyme replacement therapy, GFR glomerular filtration rate, hs-tnt high-sensitive troponin T, NT-proBNP N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide Methods All patients attending the Fabry Center for Interdisciplinary Therapy (FAZIT) Wurzburg, Germany, undergo a standardized comprehensive clinical, laboratory and imaging examination with special focus on Fabry-related impairments and organ involvement. Cardiac imaging modalities include standard twodimensional echocardiography, as well as speckle tracking analysis, and cardiac magnetic resonance tomography (MRI), both beneficial for indirect quantification of intramural fibrosis as prominently seen in advanced Fabry cardiomyopathy [13 15]. Investigations also include a thorough investigation of the kidneys including biopsy if suitable, central and peripheral nervous system including brain MRI, skin biopsy, and assessment of sweating capacity, and psychic factors, including assessment of quality of life using SF-36. Case presentation In late 2015, a 45-year-old female patient with genetically proven FD approached FAZIT for specialized clinical evaluation and therapy induction. Molecular gene analysis revealed the atypical situation of a heterozygous female patient carrying two different haplotype variants c.416a > G, p.n139s in exon 3 and c.708g > C, p.w236c in exon 5, one on each X- chromosomal allele which both have previously been described as potentially pathogenic [16, 17]. Due tothelowfrequencyofpathogenicgla mutations in the population, comparable respective cases are extremely rare. The initial suspicion for FD in this index patient was raised during a routine ophthalmologist checkup leading to the discovery of Fabryspecific depositions in her cornea at young age of six years. Later on, it was revealed that not only her mother, but also her brother are both affected by the same mutational variant (c.708g > C, p.w236c in exon 5), which was in both relatives clinically related to Fabryassociated acral pain, myocardial hypertrophy, and renal
3 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 Page 3 of 6 dysfunction. In addition, the index patient s brother suffered from young-aged stroke at age 45 years and now receives hemodialysis due to end-stage chronic kidney disease. Her grandfather from maternal site is anticipated to have been affected by FD, suffering from fatal end-stage kidney disease at his early forties. Unfortunately, the index patient s 74 years old father refused to undergo genetic analysis. As the index patient never subjectively suffered from any health problems, neither doctors were consulted nor medication taken until the event of young-aged cryptogenic stroke at the age of 44 years. As a result of stroke, she attended FAZIT for clinical examination and initiation of life-time ERT. At FAZIT she denied any acral pain or gastrointestinal claims besides of frequent diarrhea. Sweating capacity was reported mildly reduced, but only attracted her attention in hot summer months (Table 1). Alphagalactosidase A (α-gal A) enzyme activity was measured reduced (0.26 nmol/min/mg protein in leucocytes; reference: ) and plasma lyso-gb3 was elevated (30.2 ng/ml; reference: 0.9). The body-mass-index (20.5 kg/m 2 ), resting blood pressure (100/82 mmhg) and heart rate (80 bpm) were all in normal ranges, with sinus rhythm and no signs of cardiac hypertrophy or ischemia in neither resting, nor exercise electrocardiograms (ECG). (Table 2) Physical capacity in exercise ECG was sufficient, reaching a maximal heart rate of 133 bpm, 75 % of the age-predicted optimum of 176 bpm at 125 W. No spontaneous cardiac arrhythmia was detectable in Holter monitoring, or evocable in exercise stress test. The cardiac biomarker high-sensitive troponin T was inconspicuous for cardiac involvement (<5 pg/ml; reference: 0 14). N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide was slightly elevated (325 pg/ml; reference: <125), which might be a hint on an early stage cardiac involvement. This suspicion from blood biomarkers was supported by findings in standard cardiac imaging, revealing borderline septal and posterior wall thickness of 11 mm and a visually determined concentric left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy with prominent papillary muscles but physiologically preserved LV ejection fraction (68 %) in echocardiography. The normalized LV mass was 66.7 g/m 2, normalized end-systolic volume 26.0 ml/m 2, normalized end-diastolic volume 75.9 ml/ m 2, normalized stroke volume 49.9 ml/m 2, and the cardiac index 3.19 l/min/m 2 in cardiac MRI with minimal intramural left ventricular late gadolinium enhancement, as seen in early stage Fabry cardiomyopathy (Fig. 1a/b) [15, 18]. In order to more evidently investigate the possible presence of mild fibrotic scar tissue, twodimensional echo speckle tracking was performed, allowing inferences on myocardial muscle rigidity and stiffness in an 18 segment model. The result revealed a mild pathologic peak systolic strain in the posterior- Table 2 Cardiac features and imaging modalities results in the index patient Variables Index patient Cardio-vascular Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) 115 Diastolic blood pressure (mmhg) 75 Heart rate (bpm) 68 Cardiac stress test maximal heart rate (bpm) 133 maximal watts (watts) 75 Echocardiography LVEF (%) 68 IVSd (mm) 11 LVPWd (mm) 11 LVMI (g/m 2 ) 88 E/A 1.3 E/E 10 DT (ms) 155 Speckle tracking strain [%] global strain basal strain mid strain apical strain septal strain lateral strain Speckle tracking strain rate [S 1 ] global strain rate 1.50 basal strain rate 1.24 mid strain rate 1.25 apical strain rate 2.17 septal strain rate 1.61 lateral strain rate 1.49 Cardiac MRI LGE (/no) normalized LVM (g/m 2 ) 66.7 normalized ESV (ml/m 2 ) 26.0 normalized EDV (ml/m 2 ) 75.9 normalized SV (ml/m 2 ) 49.9 CI (l/min/m 2 ) 3.19 LVEF (%) 65.7 Abbreviations: DT deceleration time, IVSd interventricular septum thickness in end-diastole, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction in %, LVMI left ventricular mass index in echocardiography, LVPWD left ventricular posterior wall thickness in end-diastole, normalized EDV normalized end-diastolic volume in cardiac MRI, normalized ESV normalized end-systolic volume in cardiac MRI, normalized LVM normalized left ventricular mass in cardiac MRI, normalized SV normalized stroke volume in cardiac MRI
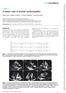
4 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 Page 4 of 6 Fig. 1 Index patient simagingfeaturesofcardiaca-c and brain d-e involvement at FAZIT baseline visit. Please note that morphologic and late gadolinium enhancement cardiac MRI a-b reveals mild hypertrophy and marginal fibrotic scar tissue with only minimal intramural late gadolinium enhancement detectable. In two-dimensional speckle tracking c peak systolic strain is mildly reduced, visualizing in loco typico early stage Fabry cardiomyopathy in the posterior-lateral and antero-lateral walls (bull s eye method). Brain MRI d-e shows residual lesions (encircled) due to previously suffered cryptogenic stroke lateral and anterior-lateral wall segments visualized by speckle tracking bull s eye(fig.1c)hinting on a very early stage of cardiomyopathy [14]. Renal function was completely preserved, with a 99-Technetium DTPA clearance of 90 ml/min, a serum-creatinine of 0.80 mg/dl (reference: ), and cystatin-c of 0.76 mg/l (reference: ), with no prove of pathologic proteinuria in spot or collecting urine. Brain MRI revealed residual lesions due to the previously suffered stroke (Fig. 1d/e), Health related quality of life was accessed by the SF-36 questionnaires and revealed reduced physical (41.61 out of 100) and mental component summary scores (35.17 out of 100) reflecting both somatic and mental impact on the index patient s subjective well-being. By rules of genetic penetrance, in this particular case the index patient conducts one of her pathogenic GLA alleles to all of her biological descendants. Thus both of her children, an 11 year old daughter and her 8 year old son underwent genetic analysis for FD (Centogene AG,
5 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 Page 5 of 6 Rostock, Germany), both presenting the c.708g > C, p.w236c mutation in exon 5. α-gal A enzyme activity was reduced in her daughter (0.20 nmol/min/mg protein in leucocytes) and highly reduced in the index patient s son (0.03 nmol/min/mg protein in leucocytes). Lyso- Gb3 was 8.1 ng/ml in the index patient s daughter and not determined in her son. Interestingly, her son already claims about stinging pain occurring in situations of bodily stress and during infections even though he is at very young age. Female mutation carriers usually present milder phenotypes than comparable males, which might be explained due to compensatory effects of the second, nonpathologically affected allele. In rare cases of homozygous female patients classical FD is to be expected. In this regard, Rodríguez-Marí and colleagues reported about a young female patient, who was found homozygous for the Q279R GLA mutation and presented a classics Fabry-phenotype with cardiac and neurological organ involvement, reduced α-gal A activity, Fabry-associated angiokeratoma, a reduced sweating capacity and acral pain, which started at young age of 8 years [19]. In contrast, all three female homozygous patients (p.arg118cys variant) published by Susana Ferreira and colleagues did not develop a classical Fabry phenotype, highlighting the impact of mutation-specific factors in FD [20]. However, contradictory to both mentioned reports, the index patient of the current study was found homozygous with not one and the same, but two different GLA mutations in each of her alleles. Regarding our index patient, family pedigree, laboratory data, and clinical manifestations give a mixed picture regarding disease patterns. While young-aged stroke gives evidence for neurological manifestations, further organ involvement was minimal with only very mild cardiac and no renal impairments detectable. Comparing her clinical course to her brothers, much less severe manifestations were found. This could indicate that there might not be an additive effect of two independent pathogenic GLA alleles, questioning the anticipated clinical impact of skewed X-inactivation leading to silence of the index patient s second pathogenic allele. It might instead be speculated that there could be so far unknown additional modifying effects in females, preventing severe clinical courses including e.g. chronic renal disease. These assumptions remain limited due to the scarce comprehensive data about p.n139s available in literature, discussing this respectively novel mutation being of pathogenic impact [17]. However, long-term results remain to be evaluated in order tojudgeonclinicalseverityandoutcomeovertime. Both of the index patient s children are likely to develop organ involvement as seen in their biological relatives. As therapeutic effects of ERT have been reported to be most beneficial when started before organ injury is detectable [21, 22], it is to be discussed whether and when the index patient s children should start receiving ERT, particularly in the light of the high prevalence of young-aged stroke in the family pedigree. Conclusion In summary, this current case highlights the importance of careful clinical characterization in patients with Fabry disease, who may show additional uncommon constellations and are thus in need of personalized medicine. The impact of potential additional protective effects exceeding the presence of a non-pathogenic GLA allele in female gene carriers require further investigation. Abbreviations α-gal A, alpha-galactosidase A; ERT, enzyme replacement therapy; FAZIT, Fabry Center for Interdisciplinary Therapy Würzburg; FD, Fabry disease; GLA, alphagalactosidase A encoding gene; LV, left ventricle of the heart. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung of the Federal Republic of Germany (BMBF 01EO1504 MO2 to Peter Nordbeck and Christoph Wanner). We thank Mrs. Irina Turkin for her long-standing dedicated work at FAZIT. Authors contributions Conception and design: DO, PN; analysis and interpretation of data: DO, DV, GE, CW, PN; drafting the article: DO, PN; revising the article: DO, DV, GE, CW, PN. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests Potential conflicts of interest: DO received travel assistance from Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts, and Shire Plc., Dublin, Ireland. DV received travel assistance from Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts, and Shire Plc., Dublin, Ireland. GE reports no competing interest. CW received travel assistance, speaker s/advisory board honoraria, and research support from Genzyme and Shire. PN received travel assistance, speaker s/advisory board honoraria, and research support from Genzyme and Shire. Consent for publication Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available. Ethics approval and consent to participate The investigations were approved by the local ethics committee of the University Hospital Würzburg, Bavaria, Germany. Received: 19 January 2016 Accepted: 15 June 2016 References Desnick RJ, Brady R, Barranger J, Collins AJ, Germain DP, Goldman M, Grabowski G, Packman S, Wilcox WR. Fabry disease, an under-recognized multisystemic disorder: expert recommendations for diagnosis, management, and enzyme replacement therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(4): Froissart R, Guffon N, Vanier MT, Desnick RJ, Maire I. Fabry disease: D313Y is an alpha-galactosidase A sequence variant that causes pseudodeficient activity in plasma. Mol Genet Metab. 2003;80(3): Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010;5: Lin HY, Chong KW, Hsu JH, Yu HC, Shih CC, Huang CH, Lin SJ, Chen CH, Chiang CC, Ho HJ, et al. High incidence of the cardiac variant of Fabry disease revealed by newborn screening in the Taiwan Chinese population. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009;2(5): van der Tol L, Smid BE, Poorthuis BJ, Biegstraaten M, Deprez RH, Linthorst GE, Hollak CE. A systematic review on screening for Fabry disease:
6 Oder et al. BMC Medical Genetics (2016) 17:46 Page 6 of 6 prevalence of individuals with genetic variants of unknown significance. J Med Genet. 2014;51(1): Morey C, Avner P. Genetics and epigenetics of the X chromosome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1214:E Elstein D, Schachamorov E, Beeri R, Altarescu G. X-inactivation in Fabry disease. Gene. 2012;505(2): MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 60 obligate carrier females. J Med Genet. 2001;38(11): MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 98 hemizygous males. J Med Genet. 2001;38(11): Dobrovolny R, Dvorakova L, Ledvinova J, Magage S, Bultas J, Lubanda JC, Elleder M, Karetova D, Pavlikova M, Hrebicek M. Relationship between X- inactivation and clinical involvement in Fabry heterozygotes. Eleven novel mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene in the Czech and Slovak population. J Mol Med. 2005;83(8): Maier EM, Osterrieder S, Whybra C, Ries M, Gal A, Beck M, Roscher AA, Muntau AC. Disease manifestations and X inactivation in heterozygous females with Fabry disease. Acta Paediatr. 2006;95(451): Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;16(3): Kramer J, Niemann M, Liu D, Hu K, Machann W, Beer M, Wanner C, Ertl G, Weidemann F. Two-dimensional speckle tracking as a non-invasive tool for identification of myocardial fibrosis in Fabry disease. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(21): Weidemann F, Ertl G, Wanner C, Kramer J. The Fabry cardiomyopathy - diagnostic approach and current treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(4): Davies JP, Eng CM, Hill JA, Malcolm S, MacDermot K, Winchester B, Desnick RJ. Fabry disease: fourteen alpha-galactosidase A mutations in unrelated families from the United Kingdom and other European countries. Eur J Hum Genet. 1996;4(4): Havndrup O, Christiansen M, Stoevring B, Jensen M, Hoffman-Bang J, Andersen PS, Hasholt L, Norremolle A, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Kober L et al. Fabry disease mimicking hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: genetic screening needed for establishing the diagnosis in women. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010;12(6): Linhart A, Kampmann C, Zamorano JL, Sunder-Plassmann G, Beck M, Mehta A, Elliott PM, European FOSI. Cardiac manifestations of Anderson-Fabry disease: results from the international Fabry outcome survey. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(10): Rodriguez-Mari A, Coll MJ, Chabas A. Molecular analysis in Fabry disease in Spain: fifteen novel GLA mutations and identification of a homozygous female. Hum Mutat. 2003;22(3): Ferreira S, Ortiz A, Germain DP, Viana-Baptista M, Caldeira-Gomes A, Camprecios M, Fenollar-Cortes M, Gallegos-Villalobos A, Garcia D, Garcia- Robles JA, et al. The alpha-galactosidase A p.arg118cys variant does not cause a Fabry disease phenotype: data from individual patients and family studies. Mol Genet Metab. 2015;114(2): Germain DP, Charrow J, Desnick RJ, Guffon N, Kempf J, Lachmann RH, Lemay R, Linthorst GE, Packman S, Scott CR, et al. Ten-year outcome of enzyme replacement therapy with agalsidase beta in patients with Fabry disease. J Med Genet. 2015;52(5): Weidemann F, Niemann M, Breunig F, Herrmann S, Beer M, Stork S, Voelker W, Ertl G, Wanner C, Strotmann J. Long-term effects of enzyme replacement therapy on fabry cardiomyopathy: evidence for a better outcome with early treatment. Circulation. 2009;119(4): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness
 Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease
 Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Heart disease. Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS
 Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D.
 FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
Fabry Disease and the Kidneys
 Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Long-Term Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Fabry Cardiomyopathy Evidence for a Better Outcome With Early Treatment
 Long-Term Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Fabry Cardiomyopathy Evidence for a Better Outcome With Early Treatment Frank Weidemann, MD*; Markus Niemann*; Frank Breunig, MD; Sebastian Herrmann;
Long-Term Effects of Enzyme Replacement Therapy on Fabry Cardiomyopathy Evidence for a Better Outcome With Early Treatment Frank Weidemann, MD*; Markus Niemann*; Frank Breunig, MD; Sebastian Herrmann;
Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease
 Open access To cite: Liu D, Oder D, Salinger T, et al. Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease. Open Heart 2018;5:e000803. doi:10.1136/
Open access To cite: Liu D, Oder D, Salinger T, et al. Association and diagnostic utility of diastolic dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis in patients with Fabry disease. Open Heart 2018;5:e000803. doi:10.1136/
Yin-Hsiu Chien, 1 Ni-Chung Lee, 1 Shu-Chuan Chiang, 1 Robert J Desnick, 2 and Wuh-Liang Hwu 1
 Fabry Disease: Incidence of the Common Later-Onset α-galactosidase A IVS4+919G A Mutation in Taiwanese Newborns Superiority of DNA-Based to Enzyme-Based Newborn Screening for Common Mutations Yin-Hsiu
Fabry Disease: Incidence of the Common Later-Onset α-galactosidase A IVS4+919G A Mutation in Taiwanese Newborns Superiority of DNA-Based to Enzyme-Based Newborn Screening for Common Mutations Yin-Hsiu
Annalisa Sechi 1*, Gaetano Nucifora 2, Gianluca Piccoli 3, Andrea Dardis 1 and Bruno Bembi 1
 Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation
 Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation Ana Baptista, Pedro Magalhães, Sílvia Leão, Sofia Carvalho, Pedro Mateus, Ilídio Moreira Centro Hospitalar
Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation Ana Baptista, Pedro Magalhães, Sílvia Leão, Sofia Carvalho, Pedro Mateus, Ilídio Moreira Centro Hospitalar
Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT
 Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT Mean change to month 18 in mitt patients (all randomized, treated patients with amenable mutations); LVMi decreased significantly (95% CI does
Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT Mean change to month 18 in mitt patients (all randomized, treated patients with amenable mutations); LVMi decreased significantly (95% CI does
This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 relating to business,
 American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Migalastat Monotherapy Phase 3 Data N November b 15 15, 2014 Safe Harbor This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Migalastat Monotherapy Phase 3 Data N November b 15 15, 2014 Safe Harbor This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis
 Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis D. Berliner, N. Deubner, W. Fenske, S. Brenner, G. Güder, B. Allolio, R. Jahns, G. Ertl, CE. Angermann, S. Störk for
Copeptin in heart failure: Associations with clinical characteristics and prognosis D. Berliner, N. Deubner, W. Fenske, S. Brenner, G. Güder, B. Allolio, R. Jahns, G. Ertl, CE. Angermann, S. Störk for
Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 10 years treatment
 Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From
 Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From Significant Burden of Disease And Impaired Quality of Life Raymond Wang, M.D. Children s Hospital of Orange County Division of
Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From Significant Burden of Disease And Impaired Quality of Life Raymond Wang, M.D. Children s Hospital of Orange County Division of
Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO PhD European Society of Cardiology 2012
 Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Relative Apical Sparing of Longitudinal Strain Using 2- Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography is Both Sensitive and Specific for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Dr. Dermot Phelan MB BCh BAO
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies
 Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
Highlights from EuroEcho 2009 Echo in cardiomyopathies Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ESC Congress 2010 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy To determine the differences
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced
 A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
Online Appendix (JACC )
 Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare X-linked lysosomal storage
 High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Clinical Blood Biomarker for Staging Cardiomyopathy in Fabry Disease Nora Seydelmann, MD; Dan Liu, MD; Johannes Kr amer, MD; Christiane Drechsler, MD; Kai Hu, MD; Peter Nordbeck,
High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Clinical Blood Biomarker for Staging Cardiomyopathy in Fabry Disease Nora Seydelmann, MD; Dan Liu, MD; Johannes Kr amer, MD; Christiane Drechsler, MD; Kai Hu, MD; Peter Nordbeck,
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder. Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: preliminary results.
 Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis
 : A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report
 Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New?
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry
 JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page:
 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines
 The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines Fakhr Alayoubi, Msc,R Ph President of SCCP Cardiology Clinical Pharmacist Assistant Professor At King Saud University King Khalid University Hospital Riyadh-KSA 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA
The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines Fakhr Alayoubi, Msc,R Ph President of SCCP Cardiology Clinical Pharmacist Assistant Professor At King Saud University King Khalid University Hospital Riyadh-KSA 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women
 Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Efficacy and safety of enzyme-replacementtherapy with agalsidase alfa in 36 treatment-naïve Fabry disease patients
 Tsuboi and Yamamoto BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology (2017) 18:43 DOI 10.1186/s40360-017-0152-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of enzyme-replacementtherapy with agalsidase alfa in 36 treatment-naïve
Tsuboi and Yamamoto BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology (2017) 18:43 DOI 10.1186/s40360-017-0152-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Efficacy and safety of enzyme-replacementtherapy with agalsidase alfa in 36 treatment-naïve
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure
 The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM
 What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
2011 HCM Guideline Data Supplements
 Data Supplement 1. Genetics Table Study Name/Author (Citation) Aim of Study Quality of life and psychological distress quality of life and in mutation psychological carriers: a crosssectional distress
Data Supplement 1. Genetics Table Study Name/Author (Citation) Aim of Study Quality of life and psychological distress quality of life and in mutation psychological carriers: a crosssectional distress
Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease?
 Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease? Michelle Michels MD, PhD Center of Inherited Cardiovascular Diseases Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands No disclosures What is phenotype negative
Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease? Michelle Michels MD, PhD Center of Inherited Cardiovascular Diseases Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands No disclosures What is phenotype negative
Utility of Echocardiography
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Beyond- Echo Hawaii 2018 Lawrence Rudski MD FRCPC FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Cardiology and Azrieli Heart Center Jewish General Hospital, McGill
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Beyond- Echo Hawaii 2018 Lawrence Rudski MD FRCPC FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Cardiology and Azrieli Heart Center Jewish General Hospital, McGill
Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome
 Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome G. Deswarte, AS. Polge, N. Lamblin, A. Millaire, M. Richardson, C. Bauters,
Rest and Exercise Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Determinants of Exercise Peak Gradient and Predictors of Outcome G. Deswarte, AS. Polge, N. Lamblin, A. Millaire, M. Richardson, C. Bauters,
Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females
 Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Heart Failure in Women: Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre
 Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Heart Failure in Women: More than EF? Dr Goh Ping Ping Cardiologist Asian Heart & Vascular Centre Overview Review pathophysiology as it relates to diagnosis and management Rational approach to workup:
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography
 Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 5 RAAS inhibitors should be avoided if possible in patients with obstructive HCM Influence of RAAS inhibition on outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Katrin Witzel,
The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern
 CASE REPORT The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern Koya Ono 1, Go Ishimaru 2, Miho Hayashi 3,YuanBae 4, Takashi Ito 4, Toshiyuki Izumo
CASE REPORT The Imaging Diagnosis of Less Advanced Cases of Cardiac Amyloidosis: The Relative Apical Sparing Pattern Koya Ono 1, Go Ishimaru 2, Miho Hayashi 3,YuanBae 4, Takashi Ito 4, Toshiyuki Izumo
XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, October 2017, Budapest, Hungary
 XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, 12-14 October 2017, Budapest, Hungary Ružica Maksimović MRI in Myocarditis Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Centre for Radiology and
XVth Balkan Congress of Radiology Danubius Hotel Helia, 12-14 October 2017, Budapest, Hungary Ružica Maksimović MRI in Myocarditis Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Centre for Radiology and
Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase beta) Prior Authorization Criteria:
 Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Could care really be personalized: Genes, biomarkers or just one size fits all? Aldo P Maggioni Florence, Italy
 Could care really be personalized: Genes, biomarkers or just one size fits all? Aldo P Maggioni Florence, Italy Could care really be personalized: genes, biomarkers or just one size fits all? Aldo P. Maggioni,
Could care really be personalized: Genes, biomarkers or just one size fits all? Aldo P Maggioni Florence, Italy Could care really be personalized: genes, biomarkers or just one size fits all? Aldo P. Maggioni,
UPDATES IN MANAGEMENT OF HF
 UPDATES IN MANAGEMENT OF HF Jennifer R Brown MD, MS Heart Failure Specialist Medstar Cardiology Associates DC ACP Meeting Fall 2017 Disclosures: speaker bureau for novartis speaker bureau for actelion
UPDATES IN MANAGEMENT OF HF Jennifer R Brown MD, MS Heart Failure Specialist Medstar Cardiology Associates DC ACP Meeting Fall 2017 Disclosures: speaker bureau for novartis speaker bureau for actelion
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping
 HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
HFPEF Echo with Strain vs. MRI T1 Mapping Erik Schelbert, MD MS Director, Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assistant Professor of Medicine Heart & Vascular Institute University of Pittsburgh Disclosures
Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function
 Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Kara, Y. Paksoy, C. Erol,
Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Kara, Y. Paksoy, C. Erol,
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain. V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen
 HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration SINE Wave Curve On Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients
 Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients Juan Carlos Plana, MD, FACC, FASE Co-Director, Cardio-Oncology Center Section of Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Cardiovascular
Advanced Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Chemotherapy Patients Juan Carlos Plana, MD, FACC, FASE Co-Director, Cardio-Oncology Center Section of Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Cardiovascular
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy
 Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
Role of CMR in heart failure and cardiomyopathy Hajime Sakuma Department of Radiology, Mie University Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) LGE MRI can demonstrate site of necrosis, fibrosis or deposition
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Fabry s disease
 Chorzy trudni nietypowi/case report Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Fabry s disease Kardiologia Polska 2010; 68, 8: 929 934 Copyright Via Medica ISSN 0022 9032 Obrazowanie serca za
Chorzy trudni nietypowi/case report Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Fabry s disease Kardiologia Polska 2010; 68, 8: 929 934 Copyright Via Medica ISSN 0022 9032 Obrazowanie serca za
Selective Cardiac Myosin Activators in Heart Failure
 Selective Cardiac Myosin Activators in Heart Failure John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Selective Cardiac Myosin Activators in Heart Failure John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: case report and literature review
 Yin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2016) 2:25 DOI 10.1186/s41016-016-0045-4 CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY CASE REPORT CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia:
Yin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2016) 2:25 DOI 10.1186/s41016-016-0045-4 CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY CASE REPORT CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION Subdural hemorrhages in acute lymphoblastic leukemia:
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT
 HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT Division of Inherited Cardiac Diseases Heart Center for the Young and Athletes A Dpt of Cardiology University of Athens ASYMPTOMATIC
HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT Division of Inherited Cardiac Diseases Heart Center for the Young and Athletes A Dpt of Cardiology University of Athens ASYMPTOMATIC
What s new in the 2017 heart failure guidelines. Prof.Dr.Mehmet Birhan YILMAZ, FESC, FACC, FHFA
 What s new in the 2017 heart failure guidelines Prof.Dr.Mehmet Birhan YILMAZ, FESC, FACC, FHFA Key points to remember 2017 guidelines recommend using natriuretic peptides as biomarkers to screen for heart
What s new in the 2017 heart failure guidelines Prof.Dr.Mehmet Birhan YILMAZ, FESC, FACC, FHFA Key points to remember 2017 guidelines recommend using natriuretic peptides as biomarkers to screen for heart
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
Heart.org/HFGuidelinesToolkit
 2017 /H/HFS Focused Update of the 2013 F/H 6.3.1 Biomarkers for Prevention: Recommendation OR LOE Recommendation a For patients at risk of developing HF, natriuretic peptide biomarker-based screening followed
2017 /H/HFS Focused Update of the 2013 F/H 6.3.1 Biomarkers for Prevention: Recommendation OR LOE Recommendation a For patients at risk of developing HF, natriuretic peptide biomarker-based screening followed
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
HFpEF, Mito or Realidad?
 HFpEF, Mito or Realidad? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology/Population Health Associate Chief for Academic Affairs -- Cardiology Montefiore-Einstein Medical Center Bronx, NY
HFpEF, Mito or Realidad? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology/Population Health Associate Chief for Academic Affairs -- Cardiology Montefiore-Einstein Medical Center Bronx, NY
Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease. Investor Webcast May 2018
 Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease Investor Webcast May 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease Investor Webcast May 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
 9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD
 Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures
 Euroecho Kopenhagen Echo in Resynchronization in 2010 E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD December 10, 2010 Ziekenhuis Oost Limburg Genk University Hasselt
Euroecho Kopenhagen Echo in Resynchronization in 2010 E/Ea is NOT an essential estimator of LV filling pressures Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD December 10, 2010 Ziekenhuis Oost Limburg Genk University Hasselt
Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0959-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation Saori Yamamoto 1,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0959-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation Saori Yamamoto 1,
Fabry disease is a rare X-linked metabolic disorder caused by
 ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function:
 Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function: results of the SHIFT echocardiography
Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function: results of the SHIFT echocardiography
Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report
 1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
LCZ696 A First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor
 The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
Congestive Heart Failure: Outpatient Management
 The Chattanooga Heart Institute Cardiovascular Symposium Congestive Heart Failure: Outpatient Management E. Philip Lehman MD, MPP Disclosure No financial disclosures. Objectives Evidence-based therapy
The Chattanooga Heart Institute Cardiovascular Symposium Congestive Heart Failure: Outpatient Management E. Philip Lehman MD, MPP Disclosure No financial disclosures. Objectives Evidence-based therapy
HeFSSA Practitioners Program 2017 Theme The Patient Journey: Feel Good and Live Long. Case Study 2
 HeFSSA Practitioners Program 2017 Theme The Patient Journey: Feel Good and Live Long Case Study 2 HEART FAILURE WITH MID-RANGE EJECTION FRACTION TREATMENT OPTIONS CLINICAL CASE MEDICAL HISTORY 59-year-old
HeFSSA Practitioners Program 2017 Theme The Patient Journey: Feel Good and Live Long Case Study 2 HEART FAILURE WITH MID-RANGE EJECTION FRACTION TREATMENT OPTIONS CLINICAL CASE MEDICAL HISTORY 59-year-old
BIOAUTOMATION, 2009, 13 (4), 89-96
 Preliminary Results оf Assessment of Systolic and Diastolic Function in Patients with Cardiac Syndrome X Using SPECT CT Tsonev Sv. 1, Donova T. 1, Garcheva M. 1, Matveev M. 2 1 Medical University Sofia
Preliminary Results оf Assessment of Systolic and Diastolic Function in Patients with Cardiac Syndrome X Using SPECT CT Tsonev Sv. 1, Donova T. 1, Garcheva M. 1, Matveev M. 2 1 Medical University Sofia
Supplementary Online Content. Abed HS, Wittert GA, Leong DP, et al. Effect of weight reduction and
 1 Supplementary Online Content 2 3 4 5 6 Abed HS, Wittert GA, Leong DP, et al. Effect of weight reduction and cardiometabolic risk factor management on sympton burden and severity in patients with atrial
1 Supplementary Online Content 2 3 4 5 6 Abed HS, Wittert GA, Leong DP, et al. Effect of weight reduction and cardiometabolic risk factor management on sympton burden and severity in patients with atrial
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey
 J Inherit Metab Dis (2012) 35:891 898 DOI 10.1007/s10545-011-9447-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey Machtelt G. Bouwman & Saskia M. Rombach
J Inherit Metab Dis (2012) 35:891 898 DOI 10.1007/s10545-011-9447-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey Machtelt G. Bouwman & Saskia M. Rombach
Misdiagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever in patients with Anderson Fabry disease
 Clin Genet 2013: 83: 576 581 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01940.x
Clin Genet 2013: 83: 576 581 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01940.x
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging. Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology
 Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy With Hemodynamically Unstable Ventricular Arrhythmia Atypical Presentation
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hemant Chaturvedi* Department of Cardiology, Non-Invasive Cardiology, Eternal Heart Care Center & research Institute, Rajasthan, India Received: September 15, 2015; Published: October
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hemant Chaturvedi* Department of Cardiology, Non-Invasive Cardiology, Eternal Heart Care Center & research Institute, Rajasthan, India Received: September 15, 2015; Published: October
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Identification of patients with heart failure and PREserved systolic Function : an Epidemiologic Regional study
 Identification of patients with heart failure and PREserved systolic Function : an Epidemiologic Regional study Dr. Antonio Magaña M.D. (on behalf I-PREFER investigators group) Stockholm, Sweden, August
Identification of patients with heart failure and PREserved systolic Function : an Epidemiologic Regional study Dr. Antonio Magaña M.D. (on behalf I-PREFER investigators group) Stockholm, Sweden, August
