The Cardiovascular Exam Sources: UST-FMS Med1 Lecture (October 8, 2014), Mosby s, KaiMM notes, Netter s Anatomy, Berne and Levy Physiology
|
|
|
- Walter Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MED 1: Cardivascular Exam Bambam2017 The Cardivascular Exam Surces: UST-FMS Med1 Lecture (Octber 8, 2014), Msby s, KaiMM ntes, Netter s Anatmy, Berne and Levy Physilgy MOSBY S NOTES Heart: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Cne-shaped 12 cm lng, 8 cm wide, 6 cm AP diameter Brader upper prtin: BASE Narrwer lwer tip: APEX Area verlying the heart: PRECORDIUM Lies in the mediastinum, t the left f midline, just abve the diaphragm, and is cradled between the medial and lwer brders f the lungs Psitined behind the sternum and the cntiguus parts f the 3rd t 6th cstal cartilages In a tall persn: heart tends t hang vertically and psitined mre centrally In a stcky r shrt persn: heart tends t be mre left and hrizntally Dextrcardia: heart n the right Situs Inversus: heart and stmach n the right, liver n the left Structure Fur chambers: tw atria and tw ventricles Pericardium: tugh, duble-walled, fibrus sac encasing the heart; has 2 layers with fluid inside prviding fr easy, lw frictin mvement Epicardium thin utermst muscle layer Mycardium thick muscular layer Endcardium innermst layer, lines the chambers and valves Cardiac Septum divides the heart int left and right Atrium small, thin-walled Ventricle large, thick-walled Primary muscle mass f the heart: ventricles Surface Anatmy Anterir: RV Left: LV Right: RA Psterir: LA Valves AV Valves: Mitral and Tricuspid Mitral (left): 2 cusps Tricuspid (right): 3 cusps Semilunar Valves: Artic and Pulmnary (bth have 3 cusps) Artic: between Left ventricle and Arta Pulmnary: between right ventricle and pulmnary artery UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 1
2 Ask patient t lie dwn and remve his/her T-shirt. Intrduce yurself t the patient. We shuld always d CV exam with the patient lying. We stay n the right side f the patient. WE DO IT IN THIS SEQUENCE: 1. General Survey 2. Vital signs 3. JVP 4. Cartid pulse 5. Peripheral pulse 6. Precrdial Exam Just fr this afternn, we ll start with precrdial exam. We expse nly the area we want t examine. The heart is in the middle, pinting t the left. QRS cmplex the spread f stimulus t the ventricles (ventricular deplarizatin), usually less than 0.10 s ST segment and T wave the return f stimulated ventricular muscle t a resting state (ventricular replarizatin) U wave a small deflectin smetimes seen just after the T wave QT interval the time elapsed frm the nset f ventricular deplarizatin until the cmpletin f ventricular replarizatin. Interval varies with cardiac rate R cardiac brder: RA Mst anterir prtin: RV L cardiac brder: LV Mst psterir chamber: LA (when it enlarges, it will push anterir structures frward) The Flw f Bld 1. SVC and IVC 2. RA 3. Tricuspid valve 4. RV 5. Pulmnic valve 6. Pulmnary artery 7. Lungs (t be xygenated) 8. Pulmnary veins 9. LA 10. Mitral valve 11. LV 12. Artic valve 13. Arta In essence, there are 2 simultaneus circulatin: (1) pulmnary and (2) systemic. Our heart as a pump has t be deplarized. There is electrical and mechanical event. Cnductin f Impulse SA nde (pacemaker): lcated in the wall f RA AV nde: lcated at the atrial septum Bundle f His Purkinje fibers: in the ventricular mycardium Ventricular cntractin starts at the apex t the base MOSBY S NOTES ECG The heart is autnmus An intrinsic electrical cnductin system enables it t cntract within itself Electrcardigram: graphic recrding f the electrical activity f the heart; deplarizatin and replarizatin P wave the spread f stimulus thrugh the atria (atrial deplarizatin) PR interval the time frm initial stimulatin f the atria t initial stimulatin f the ventricles, usually 0.12 t 0.20 s UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 2
3 PRECORDIAL EXAMINATION INSPECTION Lk at the chest and check fr any defrmity: Pectus excavatum Sternum naka-uka papalb Pectus carinatum sternum prtruding ut These defrmities may be assciated with heart prblems PALPATION MOSBY S NOTES PALPATION Suggested sequence: apex left sternal brder base dwn t the right sterna brder epigastrium r axilla (depending n circumstances) Apical Impulse: n mre than 1cm, gentle and brief, nt lasting as lng as systle Check the back, there is usually slight thracic Kyphsis If there s n kyphsis Straight back syndrme (assciated with heart prblems) Check the precrdium fr visible pulsatins. Adynamic: n visible pulsatins Dynamic: 1 visible pulse Hyperdynamic: 2 r mre visible pulse Check visible pulsatins at eye level r use white light (flash it tangentially) Apex L lwer parasternum and Epigastrium Midprecrdium 2 nd ICS, left parasternum 2 nd ICS, right parasternum Thrills Fr thrills, sensatin is like the ball f yur hand. Thrill is a palpable murmur (at least grade 4) turbulent flw Landmarks Midsternum Parasternum Midclavicular line (d nt use the nipple) Anterir axillary line Midaxillary line Psterir axillary line Angle f Luis (palpate frm suprasternal ntch, slide yur finger dwn): 2 nd rib is attached MOSBY S NOTES THRILL fine, palpable, rushing vibratin, a palpable murmur; usually ver the base r right r left 2 nd ICS; lcate in terms f ICS, relatinship t midsternal, midclavicular, r axillary lines While palpating precrdium, use the ther hand t palpate the cartid artery just medial r belw the angle f the jaw. The cartid pulse and S1 are practically synchrnus. UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 3
4 The murmur f grade IV level r mre can be felt. The sensatin is called the thrill, It can be appreciated in systle r diastle. The fllwing are cmmn: Timing Lcatin Prbable Cause Systle Suprasternal ntch Artic stensis and/r 2 nd and 3 rd right ICS Suprasternal ntch Pulmnic stensis and/r 2 nd and 3 rd left ICS 4 th left ICS Apex VSD Mitral regurgitatin Left lwer sternal Tetralgy f Fallt brder Left upper sternal PDA brder, ften with extensive radiatin Diastle Right sternal brder Artic regurgitatin Aneurysm f ascending arta Apex Mitral stensis Apex beat When the heart cntracts, it will rtate cunterclckwise, hitting the chest t prduce the apex beat. Characterize the apex beat: lcatin, amplitude, diameter, duratin Ask the patient t exhale, then hld his/her breath; s that the lungs wn t cver the apex beat Or put the patient n left lateral decubitus Hw t reprt Apex beat: The apex beat is palpable ver the 5 th ICS MCL, 8.5 cm frm MSL. Fund n nly 1 ICS, apprx. 1cm in diameter. Amplitude is very small. If yu can feel the apex beat during the whle systle, that is a sustained apex beat. This means that LV is hypertrphied. If LV is dilated, the apex beat will g t left and dwn. Lifts LA lift (at the 3 rd ICS L parasternum): dilated LA PA lift (at the 2 nd ICS L parasternum): dilated PA Dilated arta (2 nd ICS, R parasternum) Fr apex beat, d nt use PMI. It s nt always LV that prduces the PMI. Apex beat Heaves RV heave (left lwer parasternum r ver epigastrium): dilated/hypertrphied RV LV heave (apical area, very strng): dilated RV Mst lateral palpable ventricular impulse Patient shuld be sitting Mid left thrax (10 cm frm MSL) Level f 4 th t 5 th ICS, LMCL Only feel it within ne ICS (< 2.0 cm); if mre than 1, the apex beat is diffuse Nt mre than 1 ½ fingertips wide Small and feels like a gentle tap Only feel it transiently UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 4
5 AUSCULTATION Auscultatry Areas MOSBY S NOTES CARDIAC CYCLE 1. Mitral Valve: Apex, 5 th ICS MCL 2. Tricuspid Valve: Left lwer parasternum, 4 th ICS 3. Pulmnic Valve: Left parasternum, 2 nd ICS 4. 2 nd Pulmnic Valve: Left sternal brder, 3 rd ICS 5. Artic Valve: Right parasternum, 2 nd ICS Ideal Stethscpe Largest ear tips pssible Adjustable head pieces Vinyl tubing Nt mre than 25 cms 3/16 internal diameter Shallw large diameter bell Smth stiff, thin diaphragm The Cardiac Cycle 1. Isvlumetric cntractin a. Because systemic pressure is always HIGHER than ventricular pressure, ventricles build pressure by cntracting b. N mvement f bld c. Cntractin against clsed valve = builds up pressure 2. Rapid ejectin a. Rapid mvement f bld upn pening f artic valve b. LV pressure drps -> artic & pulmnic valve will clse (S2) 3. Isvlumetric relaxatin a. Atria cannt build up pressures as high as ventricles Nt pressure builders b. They need the ventricles t actively relax c. When ventricular pressure drps and becmes less than atrial pressure, mitral & tricuspid valves pen 4. Rapid filling phase a. During ventricular systle, large amunts f bld accumulate in the right and left atria because f the clsed A-V valves. b. Therefre, as sn as systle is ver and the ventricular pressures fall again t their lw diastlic values, the mderately increased pressures that have develped in the atria immediately push the AV valves pen and allw bld t flw rapidly int the ventricles. 5. Slw filling phase a. When pressures between atria and ventricles equilibriate 6. Atrial deplarizatin a. Cause atrial cntractin and eject any residual bld Systle: ventricles cntract, ejecting bld frm the LV int the arta and frm the RV int the pulmnary artery Diastle: the ventricles dilate, an energyrequiring effrt that draws bld int the UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 5
6 ventricles as the atria cntract Heart Sunds S1, lubb : clsure f AV valves S2, dubb : clsure f semilunar valves, has 2 cmpnents; A2(artic valve clsure) and P2 (pulmnary valve clsure) S3: ventricular filling/ diastle S4: atrial cntractin Generalities Pressures in the RV, RA and PA are LOWER than the left side f the heart The events ccur slightly LATER n the right side than n the left side; thus heart sunds smetimes have tw cmpnents E.g. A2 and P2: split S2 (physilgic) The simultaneus muscular tensin and flw f bld give bdy t the sunds The sunds are best heard in the directin f bld flw S1 (1 st Heart Sund) Etilgy Clsure f mitral valve Clsure f tricuspid valve Ejectin int the artic rt Quality (apex) Lud High pitch Timing Cincides with the apex beat Hw t Identify S1 frm S2 S1 Cincides with apex upstrke S1 is heard immediately befre cartid upstrke S1 with shrter interval frm S2 Apex - S1 luder than S2 Base - S2 luder than S1, S2 splits n inspiratin Factrs affecting the ludness f S1 Rate f rise f LV pressure Timing f MV clsure in relatin t nset f ventricular cntractin Psitin f the MV at the beginning f ventricular cntractin The mre pen the mitral valve is at the end f diastle, the luder the S1(parang pint. Kapag binuksan m ng malaki, malakas ang kalabg pag padabg mng sinara) The strnger the LV cntracts, the luder the S1 Splitting f S1: usually ver tricuspid area S2 (2 nd Heart sund) Etilgy Initiatin f diastle Sudden deceleratin f frward flw during artic and pulmnary valve clsure Best heard at the base f the heart Nrmally widens n inspiratin Physilgic Splitting When a persn inhales, the intrathracic pressure becmes mre NEGATIVE increases the bld returning t the right side f the heart. Therefre in SYSTOLE, mre bld is present in the right atrium LONGER time is needed fr bld t empty frm the right atrium t the right ventricle Cmpnent delayed is the pulmnic cmpnent UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 6
7 JUGULAR VENOUS PULSE Use internal jugular vein which is behind SCM (external jugular vein may als be used) S3 (3 rd Heart sund) Rapid filling sund Early filling gallp sund Occurs at the end f the rapid expansin phase f the ventricle Heard best at r near the apex Heart best with bell applied with light pressure Physilgic S3: due t increase in velcity f ventricular expansin (tachycardia, nervusness) Pathlgic S3: lss f cmpliance/distensibility (heart failure) Lk fr maximal mvement f that clumn f bld In getting JVP, use the RIGHT jugular vein because it reflects right atrial pressure REMINDERS IN TAKING THE JVP: 1. Patient must be seated at Measure the highest angulatin 3. Put ruler hrizntally 4. Put ruler vertically at angle f Luis 5. Height will be yur JVP 6. Use cm mark 7. Use white light S4 (4 th Heart Sund) Atrial gallp, presystlic gallp, S4 gallp rarely physilgical cmmnly pathlgical - decreased distensibility r cmpliance f the LV During atrial Cntractin best heard with the use f bell at the apex with the patient n left lateral decubitus Murmurs Abnrmal sunds Pericardial frictin rub Prsthetic Valve sunds Pacemaker sunds UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 7
8 JVP Wavefrms Murmurs 1. a wave -reflects the slight rise in atrial pressure that accmpanies atrial cntractin. a. It ccurs just befre the first heart sund and befre the cartid pulse. 2. x descent -starts with atrial relaxatin. It cntinues as the right ventricle, cntracting during systle, pulls the flr f the atrium dwnward 3. v wave - secnd elevatin a. The tricuspid valve is clsed, the chamber begins t fill, and right atrial pressure begins t rise again. 4. y descent -secnd trugh a. When the tricuspid valve pens early in diastle, bld in the right atrium flws passively int the right ventricle and right atrial pressure falls again. Lw JVP Dehydratin, Diarrhea, Bld lss High JVP Maneuvers Sme murmurs are affected by maneuvers t change intensity f murmurs. These are the fllwing maneuvers: 1. Respiratry variatins 2. Valsalva maneuver 3. Pstural changes 4. Exercise 5. Pharmaclgic agents 6. Pst premature beat 7. Transient arterial cclusin Vlume verlad Increased RV pressure Increased vascular resistance Obstructin t utflw Pulmnary hypertensin Any increase in pulmnary pressure Tricuspid stensis Increased pressure in RA which reflects RV pressure Right heart failure OPENING SNAP Occurs in mitral stensis Occurs earlier than S3 1st heart sund accentuated T distinguish if S3 r OS Sft S1 - S3 Lud S1 OS Valsalva maneuver frceful attempt t exhale a clsed glttis after taking a nrmal breath 2 part prcess: straining and relaxatin Mst murmurs diminish in intensity dut t decreased ventricular filling and cardiac utput except MVP UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 8
9 Classificatin f Murmurs 1. Systlic Murmurs a. Systlic Ejectin murmurs i. Prduced by bld flwing frward thrugh a semilunar valve ii. starts with final cmpnent f S1 iii. crescend - decrescend iv. finishes befre S2 v. PULMONIC & AORTIC STENOSIS b. Systlic Regurgitant Murmurs i. Prduced by retrgrade flw frm a high pressure area thrugh sme abnrmal pening int an area f lwer pressure ii. always start with S1 if early iii. iv. always g t r beynd S2 if late predminantly high pitch and blwing when sft CAROTID PULSE Pulse: Remember RCV (rate, cntur, vlume) 2. Diastlic Murmurs a. Diastlic Atriventricular Valve Murmurs i. lw pitch ii. rumbling iii. starts with an pening snap iv. after shrt crescend, it is decrescend, fllwed by crescend t S1 (presystlic accentuatin) b. Diastlic Semilunar Valve Murmurs i. Begins with S2 ii. decrescend iii. blwing 1. Pulmnary Regurgitatin 2. Artic Regurgitatin a. Sit the patient up b. Lean patient frward c. Press hard with diaphragm during held expiratin d. "Lub kitah" UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 9
10 PERIPHERAL PULSES Simultaneus Radial and Femral (t detect artic cartatin) Ppliteal: Use tw hands Brachial(d nt use thumb!) Drsalis Pedis Radial Psterir tibialis: encircle yu fingers n the medial mallelus Femral: press deeply belw the inguinal ligament midway between the ASIS and symphysis pubis UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 10
11 The Auscultgram Whatever yu cannt draw, write (e.g. yung precrdium, lagay ny sa baba) At the apex, luder si S1 At the base, luder si S2 Between S1 and S2 are systlic events. S1 split heard best n tricuspid. Left has higher pressure, s M1 is taller than T1. S2 split heard best at pulmnic, heard at inspiratin (indicate). Pulmnic sfter than artic. Fr JVP, write the measurement. Nrmally the a-wave is higher. Fr CAP, nrmally upstrke is rapid and at S1. Gradually it will decline. UST-FMS Batch 2017 Sectin D [amfv] 11
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
NSB603 Introduction to Cardiothoracic Nursing
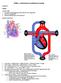 NSB603 Intrductin t Cardithracic Nursing Lecture 1a HEART OBJECTIVES Describe pathphysilgy f heart failure, CAD, angina/mi List Rx fr angina/mi Evaluate effectiveness f interventins HEART PATHWAY Frm Bdy
NSB603 Intrductin t Cardithracic Nursing Lecture 1a HEART OBJECTIVES Describe pathphysilgy f heart failure, CAD, angina/mi List Rx fr angina/mi Evaluate effectiveness f interventins HEART PATHWAY Frm Bdy
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st. Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
Exercise Physiology CardioRespiratory Trimester 2. Exercise Physiology Cardiorespiratory Study Guide
 Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Cairns Base Hospital Emergency Department Part 1 FACEM MCQs
 airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session CVS Blood pressure monitoring Taking upper body pulses
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin CVS Bld pressure mnitring Taking upper bdy pulses Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylr-Jnes and Ms C Tierney Aims and Objectives Aim: Fr the student t be able t take a
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin CVS Bld pressure mnitring Taking upper bdy pulses Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylr-Jnes and Ms C Tierney Aims and Objectives Aim: Fr the student t be able t take a
CARDIAC CYCLE CONTENTS. Divisions of cardiac cycle 11/13/13. Definition. Badri Paudel GMC
 CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
Cardiovascular System Chapter 8 1 Cardiovascular System Functions: pump saturated oxygenated blood into arterial system cells pump desaturated deoxygenated blood to lungs via veins for reoxygenation Heart
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Sydney University Graduate Medical Program Year 1. Heart Sounds Session
 2 Sydney University Graduate Medical Prgram Year 1 Heart Sunds Sessin 2016-2017 Dr Andrew Cggins Emergency Medicine Cnsultant Simulatin Centre Instructr Westmead Hspital 1 Cardivascular OSCE Initial Examinatin
2 Sydney University Graduate Medical Prgram Year 1 Heart Sunds Sessin 2016-2017 Dr Andrew Cggins Emergency Medicine Cnsultant Simulatin Centre Instructr Westmead Hspital 1 Cardivascular OSCE Initial Examinatin
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
HEALTH ASSESSMENT. Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc.
 HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
Cardiac Examination. Pediatrics Clinical Examination
 Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Pediatrics Clinical Examination Symptoms of Cardiovascular Affection: Cardiac Examination 1. Perinatal history: Maternal DM, cyanosis, respiratory distress 2. Symptoms of lung congestion: Poor interrupted
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and
 This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
CARDIOLOGY. Dr.G.Bhanu Prakash
 CARDIOLOGY Dr.G.Bhanu Prakash CVD signs: Enlarged heart, swelling f the ankles r legs, unusual/ excess weight gain, wunds that d nt heal well. CVD symptms: Chest discmfrt (pain, pressure, squeezing, heaviness,
CARDIOLOGY Dr.G.Bhanu Prakash CVD signs: Enlarged heart, swelling f the ankles r legs, unusual/ excess weight gain, wunds that d nt heal well. CVD symptms: Chest discmfrt (pain, pressure, squeezing, heaviness,
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Toe-Touch Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Non Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
Leicester Medical School
 Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
Leicester Medical School THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Overview The cardiovascular examination should include the following: - General inspection from the end of the bed. - General examination
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing. 5. Intensity 2. Shape. 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum intensity
 Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
Definition Items in description of Timing Shape Location of maximum intensity Murmur Sounds made by turbulence in the heart or blood stream. 1. Timing 5. Intensity 2. Shape 6. Pitch 3. Location of maximum
Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System. James G. Laws D.O. MACOI
 Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System James G. Laws D.O. MACOI An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation
Physical Exam Of The Cardio- Vascular System James G. Laws D.O. MACOI An Important Part Of The Physical Exam Of The Cardio-Vascular System That Is Commonly Overlooked Is? 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 1. Palpation
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
LESSON 10: NEITHER PLANT NOR ANIMAL
 LIFE IN GENERAL LESSON 10: NEITHER PLANT NOR ANIMAL READING & RESEARCH Read KSE Fungi and Lichens, p. 55. Read USE Fungi, pp. 284-285. Read DSE Fungi, p. 315. DEFINITIONS Define the fllwing terms, nting
LIFE IN GENERAL LESSON 10: NEITHER PLANT NOR ANIMAL READING & RESEARCH Read KSE Fungi and Lichens, p. 55. Read USE Fungi, pp. 284-285. Read DSE Fungi, p. 315. DEFINITIONS Define the fllwing terms, nting
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hockey Selection Camp August 16-19, 2018
 2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Label Diagram #1 (Pg. 664)
 Chapter 18 The Cardiovascular System 18.1 Heart Anatomy The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Oxygen rich vs. Oxygen Poor Heart is a transport system consisting of two side-by-side pumps Right side receives
Chapter 18 The Cardiovascular System 18.1 Heart Anatomy The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Oxygen rich vs. Oxygen Poor Heart is a transport system consisting of two side-by-side pumps Right side receives
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits:
 1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
o hold ankle (first uninvolved, then involved) o hold 4 seconds
 Prtcl fr Cx Technique Hands-On Prtins f Curses step by step instructins fr treating patients with Cx Distractin Decmpressin Adjustment & Manipulatin Prtcl I and II Instructins Lumbar Spine prepared by
Prtcl fr Cx Technique Hands-On Prtins f Curses step by step instructins fr treating patients with Cx Distractin Decmpressin Adjustment & Manipulatin Prtcl I and II Instructins Lumbar Spine prepared by
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
efferent fibers from t.. Heart Surface anatomy and heart sounds -Dry lecture -Gray s 169,
 A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
current, and acting like
 Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
Heart 10 IV. HEART PHYSIOLOGY - How the heart beats. How the heart depolarizes the myocardium, which leads to a contraction. A) INTRINSIC CONTROL - Heart controls its own rhythm. HOW? The presence of gap
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 18. Bdy Fluids and Circulatin Bld: A special cnnective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system f man and ther vertebrates cnsisting f fluid matrix, plasma and frmed elements.
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 18. Bdy Fluids and Circulatin Bld: A special cnnective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system f man and ther vertebrates cnsisting f fluid matrix, plasma and frmed elements.
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Knee Class Fremont Physical Therapy
 Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Medication Guide SIGNIFOR [sig-na-for] (pasireotide) Injection
![Medication Guide SIGNIFOR [sig-na-for] (pasireotide) Injection Medication Guide SIGNIFOR [sig-na-for] (pasireotide) Injection](/thumbs/77/75048581.jpg) Medicatin Guide SIGNIFOR [sig-na-fr] (pasiretide) Injectin Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start using SIGNIFOR and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
Medicatin Guide SIGNIFOR [sig-na-fr] (pasiretide) Injectin Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start using SIGNIFOR and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
Heart and Neck Vessels
 CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
CHAPTER 12 Heart and Neck Vessels ANATOMY The precordium is the area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels. The heart extends from the second to the fifth intercostal space, and from
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
How do you interpret these radiographs and what are your clinical concerns?
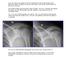 A 39 year-ld man presents t the ED cmplaining f severe left shulder pain fllwing a fight. He admits t having "a few beers" and cannt recall exactly hw the injury ccurred. He exhibits limited range f mtin
A 39 year-ld man presents t the ED cmplaining f severe left shulder pain fllwing a fight. He admits t having "a few beers" and cannt recall exactly hw the injury ccurred. He exhibits limited range f mtin
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Fitness & Weight Training I Manual School Year Revised, Spring 2008
 1 Fitness & Weight Training I Manual 2007-2008 Schl Year Revised, Spring 2008 2 Part! REVIEW MATERIAL. TERMINOLOGY: Vlume The number f sets & reps used in a particular wrkut r phase, i.e. 3 sets f 10 repetitins.
1 Fitness & Weight Training I Manual 2007-2008 Schl Year Revised, Spring 2008 2 Part! REVIEW MATERIAL. TERMINOLOGY: Vlume The number f sets & reps used in a particular wrkut r phase, i.e. 3 sets f 10 repetitins.
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Perfrmed Ultrasund (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echcardigraphy (RCE) Page 1 f 10 07/16 Australasian Sciety fr Ultrasund in Medicine PO BOX 943, Crws Nest NSW 1585, SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA
Certificate in Clinician Perfrmed Ultrasund (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echcardigraphy (RCE) Page 1 f 10 07/16 Australasian Sciety fr Ultrasund in Medicine PO BOX 943, Crws Nest NSW 1585, SYDNEY, AUSTRALIA
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th. Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
Postoperative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Care WITH meniscus repair:
 Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet
 Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION OF THE HEART
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Check ut the Cardilgy_Flash_Cards fr a nice summary f ECG. Electrical Cnductin f the Heart The Cardiac Cycle Hemdynamics Mycardial Perfrmance Valvular Dysfunctin The Micrcirculatin
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Check ut the Cardilgy_Flash_Cards fr a nice summary f ECG. Electrical Cnductin f the Heart The Cardiac Cycle Hemdynamics Mycardial Perfrmance Valvular Dysfunctin The Micrcirculatin
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
- what other structures, besides the heart, does the mediastinum contain?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2008) CMG Archives --()-- IMPORTANT
 HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2008) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
HYPERTENSION AN OVERVIEW Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2008) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Active elbow motion is when your own muscles move the elbow back and forth.
 Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Understanding your thumb osteoarthritis
 Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
