ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY: A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PANCHAKARMA
|
|
|
- Christine Shauna Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
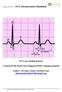
1 INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: ) (October, 2017) 5(10) ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY: A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PANCHAKARMA Rosy Malik 1, Swati S. Deshpande 2, VinayKumar K.N 3 1 PG 2 nd Year PG Scholar, 2 Head of Department, 3 Reader, SKAMCH&RC, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India malikrose2000@yahoo.com ABSTRACT The heart is an electrical organ, and its activity can be measured non-invasively. The wealth of information is related to the electricall patterns and the geometry of the heart tissue. ECG is the stan- test is of great dard tool used in a wide-range of medical evaluations. For Ayurvedic physicians, This value as it may serve as diagnostic test for knowing status of heart e.g. in Hridroga, Sthoulya, Prameha and Medorogas especially before posting a patient for Panchakarma. ECG should be per- formed with due concentration to each Panchakarma procedure. Keywords: Heart, ECG, Hridroga, Panchakarma INTRODUCTION Electrocardiography is diagnostic tool, used for diagnosis of various ailments; especially related to heart (a vital organ). Due to force produced by the cardiac pump, blood circu- lates in each and every cell of the body. In heart, atria work as turbochargers, myocar- dium required for mechanical systole and pace maker cells work as electrical systole. Electrical impulse (wave of depolarisation) picked up by placing electrodes on patient. The voltage change is sensed by measuring the current change across 2 electrodes (A positive electhe electri- trode and a negative electrode). If cal impulse travels towards the positive electrode this results in a positive deflection and if the impulse travels away from the positive electrode this results in a negative deflection. So this way electrical potential is recorded 1. As cardiac disorders are very common nowa- days, so it should be a routine investigation in the protocol of pareeksha in every Ayurvedic hospital. Before implementing ECG in Panchakarma, one should be able to assess ECG for that pur- here. As pose ECG Examination is explained if we are administering particular Panchakarma to the indicated disease (As Virechana & Basti Karmaa are indicated
2 hridroga 2,3 ), it will help to assess the improvement in disease i.e. before and after the procedure. And if particular Panchakarma is contraindicated in a specific disease and according to avastha, it is required to administer the any of Panchakarma (as Vamana Karma in Gulma, Chardi and Hridroga 4 ), physician can plan extent of shodhana to be given as Mridu or Madhya depending upon ECG changes. Electrode Placement: Six are chest electrodes 5 ; V1 to V6 and Four are limb electrodes 6, which are place on right arm (red colour), left arm (yellow colour), left leg (green colour) and right leg (black colour). The right leg electrode is a neutral or dummy lead. Leads and what they tell you: Limb leads look at the heart in the coronal plane. avl, I, V5, V6 = anterior and left side of heart. II, III and avf = inferior side of heart. avr, V1 and V2 = right side of the heart. V2 to V4 = Antero-septal. V1 and V2 = posterior (for reciprocal changes).v1-v6 = extensive Anterior. What do the components represent 7? P wave = Depolarisation or contraction of atria. QRS complex= Depolarisation or contraction of ventricles. T = Repolarisation of the ventricles. Repolarisation of atria is not recorded on graph. PR interval = Conduction time from atrium to ventricles. QRS interval = Time taken by impulse to spread through ventricles, QT interval = Total electrical activity of ventricles. RR interval = Ventricular heart rate and Pulse rate. PP interval = Atrial contraction rate. ST segment = interval between ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation. PR segment = It represents the duration of the conduction from the A-V node to the bundle of His. Interpreting the ECG ECG should be interpreted as follows: pain pre-op chest pain or routine pre op Any previous or subsequent ECGs Is it part of a serial ECG sequence? In which case it may be numbered Calibration Rate Rhythm Axis Elements of the tracing in each lead Calibration First of all one should check that ECG is calibrated correctly i.e. Height; 10mm = 1mV. Look for a reference pulse which should be the rectangular looking wave somewhere near the left of the paper. It should be 10mm (10 small squares) tall. Paper speed should be 25mm/s. 25 mm (25 small squares / 5 large squares) equals one second. Following are the normal ranges: P wave = sec (2-2.5mm) PR interval = sec (3-5mm) PR segment = 0.10 sec (2-3mm appx.) QRS complex width = sec (2-3mm ) QRS complex amplitude = sec (5-30mm) QT interval = sec (9-10mm) ST segment = sec (0.5-1mm) T wave amplitude = 0.20 (5 mm in limb leads), 0.4 sec (10mm in chest leads) T wave width = 0.12sec-0.16sec (3-4mm) IAMJ: OCTOBER,
3 Rate If the heart rate is regular, Count the number of small squares between R waves i.e. the RR interval in large squares. Simple formula for rate is; Rate = 1500/ small squares b/w RR or 300/ large squares b/w RR (5 small squares = 1 large square) 1 small square = 0.04sec, so 1500 small squares or 300 large sequare = 60 sec or 1 min.rate below 60/min is bradycardia. Rate above 100/min is tachycardia.so small squares b/w 2 R waves is normal Rhythm Is the rhythm regular? The easiest way to tell is to take a sheet of paper and line up. One edge with the tips of the R waves on the rhythm strip. Mark off on the paper the positions of 3 or 4 R wave tips. Move the paper along the rhythm strip so that your first mark lines up with another R wave tip. See if the subsequent R wave tips line up with the subsequent marks on your paper. If they do line up, the rhythm is regular. If not, the rhythm is irregular. Count R waves in 15 large squares, and multiply by 20 ( As 15 large square = 3 sec and 3 20=60 sec i.e. 1 min.) this represent rate in irregular rhythm. So here HR = 5 20=100/min (appx.) Clinically by palpating Pulse is ventricular rate. Atrial rate can be seen only on ECG. As one can see in this image; Total Heart block as Atrial Rate = 100/min, Ventricular Rate = 30/min. Axis 8 Electrical axis of heart is examined in Lead I & III of limb leads. Normally QRS complex are predominantly upward in both of these leads Left Axis Deviation: For example, in this image; Prominent R wave in lead I and Negative deflection in lead III. Right Axis Deviation: For example, in this image; Prominent R wave in lead III and Negative deflection in lead I. Axis deviation For detecting axis deviation, lead I& III should be seen. One should remember, for left axis deviation: Left Leaves and for right axis deviation: Right Reaches Examples of Left Axis Deviation are; Left Venticular Hypertrophy, Left Bundle Branch Block, Inferior wall Infarct. Examples of Right Axis Deviation are; Right Ventricular Hypertrophy, Right Bundle Branch Block, Anterior wall Infarct. Elements of the tracing in each lead By tracing the elements for each lead, one can easily diagnose a case, depending upon the changes seen in ECG, can be understood by following points: Atrial Hypertrophy Atrial hypertrophy is diagnosed with contour of P IAMJ: OCTOBER,
4 wave seen best in Lead II. P wave presents depolarisation of both left and right atria. Initial part (non - shaded) presents right atrium depolarisation, as SA node start depolarisation first here. Later (shaded) part represent left atrium. In left atrium hypertrophy, 2nd component is delayed and prominent. So we get wide and notched P wave, wider than 2.5 small squares. Since it is common in mitral wall diseases, it is termed as P mitrale. In right atrial hypertrophy, Initial component is prominent. P wave is tall and peaked, taller than 2.5 small squares. Since it is common in Pulmonary hypertension, it is termed as P Pulmonale. Normal Ventricular Complexes Ventricular enlargement is diagnosed from patterns and amplitudes of QRS complexes in Chest leads from V1 to V6. This is the normal pattern of QRS complexes in chest leads. The lead V1 shows small R wave and deep S wave. As we proceed from V1 to V6, height of R wave progressively increases and depth of S wave progressively decreases. Somewhere in V3 and V4, R wave and S wave both becomes equal. This way in V6 tall R wave and very small or absent S wave. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Pattern remains the same but amplitude of waves increases. So we have to measure amplitude of V1 or V2 whichever is larger and V5 or V6 whichever is larger. If any of these is more than 25mm; SV1 or RV6 i.e SV1 25 or RV6 25. Or if there addition is more than 35 mm i.e SV1 + RV6 35. Left ventricular hypertrophy is usually be associated with Left Axis Deviation. P Mitrale may be seen. So, one should also look Left Axis Deviation if there are Left Atrium Hypertrophic changes in ECG. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Here pattern and amplitude is opposite to normal. So there is prominent R wave in V1 or V2 or deep S wave in V5 or V6. The Criteria for diagnosis is RV1 7 or SV6 7.Or if there addition is more than 10 mm i.e RV1 + SV6 10 Right ventricular hypertrophy may or may not be associated with Right Axis Deviation. And often there will be P Pulmonale of Right Atrium Hypertrophy. So, one should also look Right Axis Deviation if there are Right Atrium Hypertrophic changes in ECG. Bundle Branch Block When width of QRS complex is 3small squares or more that is more than 0.12 sec in any of the lead Bundle Branch Block is diagnosed RBBB & LBBB RSR or M Shape pattern with broad QRS comlex 3mm in right chest leads i.e V1 &V2, it suggests RBBB. RSR or M Shape pattern with broad QRS comlex 3mm in left chest leads i.e V5 &V6, it suggests IAMJ: OCTOBER,
5 LBBB. At the same time opposite chest leads will display wide and slurred S wave. Accompanying T wave in wave in opposite direction. In LBBB, R wave is absent in opposite lead i.e. V1. RBBB may also be associated with Right Axis Deviation. LBBB will always be associated with Left Axis Deviation (In I and avl left sided leads). Myocardial Infarction 9 Three basic changes in the lead facing infracted wall: 1) Elevation of ST segment indicative of zone of injury. 2) Inversion of T wave indicates of surrounding ischemic zone. 3) A deep and wide Q wave indicative of zone of infarct or dead muscle. The diagnosis is supported by reciprocal changes in the leads facing opposite wall i.e. Depression of ST segment and tall upright T wave. Acute Myocardial Ischemia Criteria for diagnosing is the J point should be depressed at least 1mm. The ST segment should be horizontal or downward slopping comparing to infarction state where it is upward slopping. Only if J point is more than 2mm then even if ST segment is upward slopping, Acute Ischemia is diagnosed. Ischemic changes are never seen in V1 & V2. As ST segment depression in V1 & V2 indicates right ventricular hypertrophy with strain and in true posterior wall infarctions. Non Acute Myocardial Ischmia Commonest change is slightest ST segment depression and T wave inversion or flattening of T wave. Remember if these changes are with tall R wave or S wave then it is ventricular hypertrophy with strain. Read ECG in sequence so that no diagnosis get skipped 1. avr should be inverted 2. Calculate heart rate 3. P wave morphology should be studied which is most prominent in lead II, If it is more than 2mm wide or tall then left or right atrial hypertrophy may be present Inverted P wave indicates nodal rhythm 4. PR interval, normally it is 3-5mm If it is increased to 5 mm or more, it is 1 st degree AV block In such a case, note there dropped beats suggesting 2 nd degree heart block. If PR interval is less than 3mm, look for slurring of R waves in leads I and V6, to rule out WPW syndrome 5. QRS complex Look at lead I & III for axis deviation (remember left leaves, right reaches) Then measure QRS interval, in leads in which it is most wide and clear, generally it is 2-2.5mm wide If it is more than 3mm, study if it is LBBB or RBBB 6. Then look for pathological Q wave, in anterior, inferior or chest leads IAMJ: OCTOBER,
6 A Q wave deeper than 1mm or wider than 1mm or more than 1/3 rd of R wave is considered as significant 7. Chest leads Study the pattern of QRS complexes from V1 to V6 If pattern is normal i.e. Deep S wave in V1 to tall R wave in V6 then measure SV1 and RV6 to rule out LVH If pattern is changed then look for the criteria of RVH or RBBB 8. ST segment & T wave If ST segment is elevated or depressed, the pattern must be studied and clinically correlated to myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, Pericarditis and ventricular strain patterns ST segment depressions are basically of three types: (i) Strain (in right and left ventricular hype r- trophy) with T wave inversion (ii) Digitalis (mirror image of check mark) with T wave flattening Ischemia and Infarct with T wave changes with respect to time ST elevation (not mandatory in all leads, always concave upward never convex upward) Remember in pericarditis; ST elevation (reciprocal changes are absent) with T wave elevation 9. T wave inversion is seen in (i) Abnormal conduction (intraventricular e.g. LBBB, Total heart block, WPW etc.) (ii) Strain in LVH &RVH (iii) Myocardial Ishchemia (symmetr i- cal & pointed like an arrow head) and (iv) Chronic Pericarditis (generalized) T waves are pathological if they are more than 10mm tall in chest leads or more than 5mm tall in limb leads; associated ST segment changes are very important A tall T wave in chest leads can be a reciprocal change toward inferior wall infarct A tall T waves in most of the leads is hall mark of hyperkalemia DISCUSSION Every individual should undergo regular health check-up once in a year (ECG included in it) to know status of once health. ECG test should be performed when person is at rest and breathing normally. Moving, talking or shivering may distort the test results so in most of the hospitals a towel is placed over chest after applying leads to keep the patient at warm and still. avr should always be inverted except in dextrocardia or it implies limb leads are wrongly connected, so a repeat ECG should be taken in such a case after assuring leads are connected properly. If Q wave is only present in lead III, it may indicate, high diaphragm; so take a fresh ECG again with deep inspiration, if Q wave is non pathognomic it may reduce in size or disappear. This physiologic Q wave will appear in expiration. Bradycardia and cardiac hypertrophy are physiologic in athletics or persons who do exercise more than 1hour. If ECG is normal and Clinically MI (Myocardial Infarction) is there, repeated ECGs should be taken as it may take minutes to hours to manifest during MI. Even ECG serves to decide degree of severity e.g. in Myocardial Ischemia, Heart Block severity of disease can be estimated. As cardiac disorders are common these days so ECG should be performed as regular check IAMJ: OCTOBER,
7 up as Ashtavidha and Dashvidha Pareeksha are performed in Ayurvedic Hospitals. Patient suffering with Amlapitta, Anaha, Adhmana may present angina like symptoms many a times, that time ECG may serve as good differential diagnostic tool. If performed as a prior investigation before posting a patient for Panchakarma procedure, this may help to reduce number of vyapadas related to Panchakarma. As Vamana Karma is contraindicated in Hridroga 10 and Virechana & Basti Karmas are especially indicated in Hridroga 11,12,So ECG assessment plays essential role here. Panchakarma procedures e.g Vamana Karma even though contraindicated in Hridroga but can be practiced if patient s condition demands it 13, extent of shuddhi can be decided depending on degree of disease and ECG may help in such situations. If ECG is indicative of pathological condition, further investigations such as: Cardiac markers e.g. Troponin I or T, TMT or Stress Test, Echocardiography, Angiography, CT heart, MRI heart, Electrolytes, Calcium levels etc. should be advised depending upon condition. CONCLUSION ECG examination can be proved to be boon for Panchakarma practice, as it will reduce Panchakarma Vyapadas. As if there are abnormal changes in person s ECG who is posted for Vamana Karma, procedure can be cancelled or stopped and / or modified depending upon the condition. ECG will be helpful for assessing effect of Virechana Karma and Basti Karma procedures for Hridroga patients, if performed before and after the procedures. Also further tests can be recommended or patient can be referred to the higher centres whose ECG shows suspicion of major cardiac ailments. So this way ECG examination as a routine tool will lead to safe Panchakarma practice. REFERENCES 1. Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 13, Reprint-2014, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 16, Reprint-2014, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 27, Reprint-2014, Page no Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Dr. C.C. Chatterjee, Human Physiology, th, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 8, Reprint-2014, Page no IAMJ: OCTOBER,
8 11. Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 13, Reprint-2014, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 16, Reprint-2014, Page no Agnivesha, Acharya Charaka, Ayurvedadipika 27, Reprint-2014, Page no Source of Support: Nil Conflict Of Interest: None Declared How to cite this URL: Rosy Malik Et Al: Electrocardiography: A Diagnostic Tool In Panchakarma. International Ayurvedic Medical Journal {online} 2017 {cited October, 2017} Available from: IAMJ: OCTOBER,
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG
 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals. Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
12 Lead ECG. Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept.
 12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
ECG CONVENTIONS AND INTERVALS
 1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
Introduction to Electrocardiography
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012
 Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012 Session 2: 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals 101 Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Though for Today Mastery is not something that strikes in an instant, like a thunderbolt,
Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012 Session 2: 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals 101 Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Though for Today Mastery is not something that strikes in an instant, like a thunderbolt,
DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES
 PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1
 If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
ECG (MCQs) In the fundamental rules of the ECG all the following are right EXCEP:
 ECG (MCQs) 2010 1- In the fundamental rules of the ECG all the following are right EXCEP: a- It is a biphasic record of myocardial action potential fluctuations. b- Deflection record occurs only during
ECG (MCQs) 2010 1- In the fundamental rules of the ECG all the following are right EXCEP: a- It is a biphasic record of myocardial action potential fluctuations. b- Deflection record occurs only during
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice. Presented By: Cynthia Webner, BSN, RN, CCRN-CMC. Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC
 12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice NTI 2009 Preconference Session 803 Presented By: Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC 1 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals: The Starting Place for Linking
12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice NTI 2009 Preconference Session 803 Presented By: Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC 1 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals: The Starting Place for Linking
Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D.
 Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG. Jakub Dorożyński
 Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
1 st Degree Block Prolonged P-R interval caused by first degree heart block (lead II)
 AV Heart Blocks 1 st degree A condition of a rhythm, not a true rhythm Need to always state underlying rhythm 2 nd degree Type I - Wenckebach Type II Classic dangerous to the patient Can be variable (periodic)
AV Heart Blocks 1 st degree A condition of a rhythm, not a true rhythm Need to always state underlying rhythm 2 nd degree Type I - Wenckebach Type II Classic dangerous to the patient Can be variable (periodic)
Electrocardiogram ECG. Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University
 Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
Paediatric ECG Interpretation
 Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
5- The normal electrocardiogram (ECG)
 5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH. General. Heart Rate. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
Basic electrocardiography reading. R3 lee wei-chieh
 Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
12 LEAD EKG BASICS. By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC
 12 LEAD EKG BASICS By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC ECG Review Waves and Intervals P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria QRS complex: right and left ventricular
12 LEAD EKG BASICS By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC ECG Review Waves and Intervals P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria QRS complex: right and left ventricular
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
ECG Interpretation. Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction
 ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series
 ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
also aid the clinician in recognizing both the obvious and subtle abnormalities that may help guide therapy.
 Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1:
 ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1: The first 20 strips are for teaching various abnormalities of the morphology of the waves of the ECG. Strips 21 and following are for teaching some abnormalities
ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1: The first 20 strips are for teaching various abnormalities of the morphology of the waves of the ECG. Strips 21 and following are for teaching some abnormalities
Lab Activity 24 EKG. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias. Conduction
 Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
ECG. Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13
 ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Section V. Objectives
 Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Ekg pra pr c a tice D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Ekg practice D.HAMMOUDI.MD Anatomy Revisited RCA (Right Coronary Artery) Right ventricle Inferior wall of LV Posterior wall of LV (75%) SA Node (60%) AV Node (>80%) LCA (Left Coronary Artery) Septal wall
Ekg practice D.HAMMOUDI.MD Anatomy Revisited RCA (Right Coronary Artery) Right ventricle Inferior wall of LV Posterior wall of LV (75%) SA Node (60%) AV Node (>80%) LCA (Left Coronary Artery) Septal wall
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
ECG interpretation basics
 ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know. Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series
 ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
12 Lead ECG Interpretation: Color Coding for MI s
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation: Color Coding for MI s Anna E. Story, RN, MS Director, Continuing Professional Education Critical Care Nurse Online Instructional Designer 2004 Anna Story 1 Objectives review
12 Lead ECG Interpretation: Color Coding for MI s Anna E. Story, RN, MS Director, Continuing Professional Education Critical Care Nurse Online Instructional Designer 2004 Anna Story 1 Objectives review
Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina Non ST segment Elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST segment Elevation MI (STEMI)
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
3/26/15 HTEC 91. EKG Sign-in Book. The Cardiac Cycle. Parts of the ECG. Waves. Waves. Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2)
 EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
The ABC of Pediatric ECG
 The ABC of Pediatric ECG Mohamed Hamdan, MD, FAAP, FACC Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, NY, USA Consultant Pediatric Cardiologist & Co-Director
The ABC of Pediatric ECG Mohamed Hamdan, MD, FAAP, FACC Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, NY, USA Consultant Pediatric Cardiologist & Co-Director
All About STEMIs. Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC. Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager.
 All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
Understanding basics of EKG
 Understanding basics of EKG By Alula A.(R III) www.le.ac.uk Topic for discussion Understanding of cellular electrophysiology Basics Rate Rhythm Axis Intervals P wave QRS ST/T wave Abnormal EKGs Understanding
Understanding basics of EKG By Alula A.(R III) www.le.ac.uk Topic for discussion Understanding of cellular electrophysiology Basics Rate Rhythm Axis Intervals P wave QRS ST/T wave Abnormal EKGs Understanding
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
INTRODUCTION TO ECG. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com EKG Rounds Handouts available at http://www.drstultz.com January 5, 2004 David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 Overview of Topics How to read an EKG Normal EKG Determination
http://www.dilbert.com EKG Rounds Handouts available at http://www.drstultz.com January 5, 2004 David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 Overview of Topics How to read an EKG Normal EKG Determination
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Left posterior hemiblock (LPH)/
 ECG OF THE MONTH Left Postero-inferior Depolarization Delay Keywords Electrocardiography Intraventricular conduction delay, Inferoposterior hemiblock, Left posterior fascicular block, Left posterior hemiblock
ECG OF THE MONTH Left Postero-inferior Depolarization Delay Keywords Electrocardiography Intraventricular conduction delay, Inferoposterior hemiblock, Left posterior fascicular block, Left posterior hemiblock
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced. Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA
 2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes
 Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field.
 A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field. Let s talk, prep and placement. Try to shoot for quality, consistency and no artifact! (looking sometimes for 1 or 2 mm changes)
A few new tools for better detection and understanding of STEMIs in the field. Let s talk, prep and placement. Try to shoot for quality, consistency and no artifact! (looking sometimes for 1 or 2 mm changes)
15 16 September Seminar W10O. ECG for General Practice
 15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
Electrocardiography. Hilal Al Saffar College of Medicine,Baghdad University
 Electrocardiography Hilal Al Saffar College of Medicine,Baghdad University Which of the following is True 1. PR interval, represent the time taken for the impulse to travel from SA node to AV nose. 2.
Electrocardiography Hilal Al Saffar College of Medicine,Baghdad University Which of the following is True 1. PR interval, represent the time taken for the impulse to travel from SA node to AV nose. 2.
ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES
 Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
- why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave?
 Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director
 December 2018 ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director To obtain best results Select Slide Show from the ribbon at the top of your PowerPoint screen Select From Beginning on the
December 2018 ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director To obtain best results Select Slide Show from the ribbon at the top of your PowerPoint screen Select From Beginning on the
Acute Coronary Syndromes. Disclosures
 Acute Coronary Syndromes Disclosures I work for Virginia Garcia Memorial Health Center, Beaverton, OR. Jon Tardiff, BS, PA-C OHSU Clinical Assistant Professor And I am a medical editor for Jones & Bartlett
Acute Coronary Syndromes Disclosures I work for Virginia Garcia Memorial Health Center, Beaverton, OR. Jon Tardiff, BS, PA-C OHSU Clinical Assistant Professor And I am a medical editor for Jones & Bartlett
3/4/2018. March Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology. Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves
 March 2018 Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves Frontal view Limb leads: I, II, III, avl, avf, (avr) Horizontal
March 2018 Martina Frost, PA C Desert Cardiology Electricity moving towards/away from electrode create downward/upward directions of waves Frontal view Limb leads: I, II, III, avl, avf, (avr) Horizontal
12 Lead EKG. The Basics
 12 Lead EKG The Basics Objectives Demonstrate proper 12 EKG lead placement Determine electrical axis Identify ST and T wave changes as they relate to myocardial ischemia Describe possible complications
12 Lead EKG The Basics Objectives Demonstrate proper 12 EKG lead placement Determine electrical axis Identify ST and T wave changes as they relate to myocardial ischemia Describe possible complications
ECG WORKBOOK. Rohan Jayasinghe
 ECG WORKBOOK Rohan Jayasinghe Contents Preface vii Foreword viii Acknowledgements ix The author x Reviewers xi Section 1 Basics of the ECG 1 Section 2 ECG-based diagnosis: pathology by ECG 21 Section 3
ECG WORKBOOK Rohan Jayasinghe Contents Preface vii Foreword viii Acknowledgements ix The author x Reviewers xi Section 1 Basics of the ECG 1 Section 2 ECG-based diagnosis: pathology by ECG 21 Section 3
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology
 Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants
 Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants A Ship in the Harbor is Safe But that is not what ships are built for. Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Cardiovascular
Relax and Learn at the FARM 2012: Session 8: 12 Lead ECG 401: ECG Variants A Ship in the Harbor is Safe But that is not what ships are built for. Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Cardiovascular
Myocardial Infarction. Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline )
 Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Electrical System Overview Electrocardiograms Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning Values To Memorize Calculating Rates
 Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
Disclosures. STEMI:To Call or Not to Call. Disclosures 9/18/2017. Alternate Title: Hey Doc, If you re not doing anything Saturday Night
 STEMI:To Call or Not to Call Disclosures No financial disclosures September, 2017 Frederick James Trip Meine III MD, FACC, FSCAI Cape Fear Heart Associates, Wilmington, NC Disclosures Alternate Title:
STEMI:To Call or Not to Call Disclosures No financial disclosures September, 2017 Frederick James Trip Meine III MD, FACC, FSCAI Cape Fear Heart Associates, Wilmington, NC Disclosures Alternate Title:
Pathologic ECG. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 Pathologic ECG Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze the morphology and
Pathologic ECG Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze the morphology and
EKG. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 EKG Danil Hammoudi.MD What is an EKG? The electrocardiogram (EKG) is a representation of the electrical events of the cardiac cycle. Each event has a distinctive waveform, the study of which can lead to
EKG Danil Hammoudi.MD What is an EKG? The electrocardiogram (EKG) is a representation of the electrical events of the cardiac cycle. Each event has a distinctive waveform, the study of which can lead to
BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG
 BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of cardiac electrical activity. The electrical activity is readily detected by electrodes attached to the skin. After the
BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of cardiac electrical activity. The electrical activity is readily detected by electrodes attached to the skin. After the
12 LEAD EKG & CXR INTERPRETATION.
 12 LEAD EKG & CXR INTERPRETATION www.cherylherrmann.com cherrmann@frontier.com Audio Product Recording discount for participants $60 Nonparticipants = $190 o Get CEs and manual https://catalog.vyne.com
12 LEAD EKG & CXR INTERPRETATION www.cherylherrmann.com cherrmann@frontier.com Audio Product Recording discount for participants $60 Nonparticipants = $190 o Get CEs and manual https://catalog.vyne.com
What the ECG is about
 What to expect from the ECG 00 The electricity of the heart 00 The shape of the ECG 00 The ECG electrical pictures 00 The shape of the QRS complex 00 Making a recording practical points 00 How to report
What to expect from the ECG 00 The electricity of the heart 00 The shape of the ECG 00 The ECG electrical pictures 00 The shape of the QRS complex 00 Making a recording practical points 00 How to report
How to Read an Athlete s ECG. Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC
 How to Read an Athlete s ECG Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC Athlete s EKG Vagotonia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia First degree AVB ST-elevation Tall T waves Increased chamber size Left ventricular
How to Read an Athlete s ECG Sanjay Sharma BSc (Hons), MD, FRCP, FESC Athlete s EKG Vagotonia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia First degree AVB ST-elevation Tall T waves Increased chamber size Left ventricular
Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG. ECG Recording. J Point. Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive System. Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP
 The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP SA Node Intranodal Pathways AV Junction AV Fibers Bundle of His Septum Bundle Branches Purkinje System Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive
The Fundamentals of 12 Lead EKG Dr. E. Joe Sasin, MD Rusty Powers, NRP SA Node Intranodal Pathways AV Junction AV Fibers Bundle of His Septum Bundle Branches Purkinje System Reviewing the Cardiac Conductive
6/19/2018. Background Athlete s heart. Ultimate question. Applying the International Criteria for ECG
 Applying the International Criteria for ECG Interpretation in Athletes to a preparticipation screening program DAVE SIEBERT, MD, CAQSM ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF FAMILY MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
Applying the International Criteria for ECG Interpretation in Athletes to a preparticipation screening program DAVE SIEBERT, MD, CAQSM ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF FAMILY MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
CORONARY ARTERIES HEART
 CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
The ECG in healthy people
 The ECG in healthy people The normal cardiac rhythm 3 The heart rate 3 Extrasystoles 7 The P wave 7 The PR interval The QRS complex 3 The ST segment 29 The T wave 33 The QT interval 42 The ECG in athletes
The ECG in healthy people The normal cardiac rhythm 3 The heart rate 3 Extrasystoles 7 The P wave 7 The PR interval The QRS complex 3 The ST segment 29 The T wave 33 The QT interval 42 The ECG in athletes
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss. Objectives
 10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012
 Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
Blocks & Dissociations. Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline )
 Blocks & Dissociations Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline ) Objectives Who are Wenckebach and Mobitz? Review SA and AV Blocks AV Dissociations: learning who s the boss and why 2 nd degree SA Block:
Blocks & Dissociations Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline ) Objectives Who are Wenckebach and Mobitz? Review SA and AV Blocks AV Dissociations: learning who s the boss and why 2 nd degree SA Block:
ECG pre-reading manual. Created for the North West Regional EMET training program
 ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
Abnormalities Caused by Left Bundle Branch Block
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 12-17-2010 Abnormalities Caused by Left Bundle Branch
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Physician Assistant Studies, Department 12-17-2010 Abnormalities Caused by Left Bundle Branch
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Reading Assignment. Chapter 5 (p17-30)
 Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (III) THE ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (III) THE ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin Recording and analysis of the 12-lead ECG is part of the basic medical assessment performed for every
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (III) THE ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin Recording and analysis of the 12-lead ECG is part of the basic medical assessment performed for every
at least 4 8 hours per week
 ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
Chapter 2 Practical Approach
 Chapter 2 Practical Approach There are beginners in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis who are fascinated by a special pattern (e.g., a bundle-branch block or a striking Q wave) and thereby overlook other
Chapter 2 Practical Approach There are beginners in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis who are fascinated by a special pattern (e.g., a bundle-branch block or a striking Q wave) and thereby overlook other
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline
 Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
