Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
|
|
|
- Darcy Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The muscular layer of blood vessels is the A) tunica intima. B) tunica externa. C) tunica media. D) tunica intima. E) tunica adventitia. 2) Compared to veins, arteries A) are more elastic. B) have less smooth muscle in their tunica media. C) have a smooth endothelium. D) have thinner walls. E) lose their shape when cut. Answer: A 3) The blood vessels that carry blood at the highest pressure are the A) arteries. B) arterioles. C) veins. D) venules. E) capillaries. Answer: A Page 1 of 26
2 4) The blood vessels that have only a tunica intima are the A) arteries. B) arterioles. C) veins. D) venules. E) capillaries. 5) Which of the following blood vessels hold the greatest volume of blood? A) arteries B) arterioles C) capillaries D) venules E) veins 6) Blood flow has the highest velocity in the A) arteries. B) arterioles. C) capillaries. D) venules. E) veins. Answer: A 7) Thick-walled vessels with a large degree of distensibility are called arteries. A) coronary B) pulmonary C) elastic D) muscular E) arteriolar Page 2 of 26
3 8) The brachial artery would be classified as a(n) artery. A) anastomotic B) elastic C) conducting D) large E) muscular 9) The outermost layer of the arterial wall is the A) endothelium. B) tunica intima. C) tunica externa. D) tunica media. E) serosa. 10) Which of the following is lesser amount? A) the normal blood volume of the arterial system B) the normal blood volume of the venous system Answer: A 11) The vessels that permit exchange of materials between the cells and the blood are termed A) capillaries. B) arterioles. C) arteries. D) venules. E) veins. Answer: A Page 3 of 26
4 12) Plasma proteins that remain in the blood capillaries help A) maintain the osmotic pressure of the blood. B) decrease the osmotic pressure of the blood. C) maintain the hydrostatic pressure of the blood. D) decrease the hydrostatic pressure of the blood. E) increase the osmotic pressure of the blood. Answer: A 13) Blood flow through the cardiovascular system is affected by A) pressure differences. B) the viscosity of the blood. C) the amount of friction in the blood vessels. D) the length and diameter of the blood vessels. E) all of the above 14) Which of the following conditions would completely stop all NET filtration? A) Blood hydrostatic pressure forces fluid from the capillary into the interstitial space. B) Blood osmotic pressure moves fluid from the interstitial space into the capillary. C) The blood hydrostatic pressure and the blood osmotic pressure are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. 15) As blood travels from the aorta toward the capillaries the A) pressure increases. B) resistance increases. C) flow increases. D) viscosity increases. E) all of the above Answer: B Page 4 of 26
5 16) Blood pressure increases with A) increased cardiac output. B) increased peripheral resistance. C) increased blood volume. D) B and C only E) all of the above 17) The one-third of the systolic pressure added to diastolic pressure is called the A) critical closing pressure. B) mean arterial pressure. C) pulse pressure. D) blood pressure. E) circulatory pressure. Answer: B 18) Which of the following is faster? A) blood flow along the walls of a blood vessel B) blood flow in the center of a large vessel Answer: B 19) Which of the following is a normal pressure within capillaries? A) mm Hg B) mm Hg C) 5 10 mm Hg D) mm Hg E) mm Hg Answer: A Page 5 of 26
6 20) Which of the following is the top number in a blood pressure reading? A) diastolic pressure B) systolic pressure C) pulse pressure D) mean arterial pressure E) blood osmotic pressure Answer: B 21) Transport mechanisms used by capillaries include A) diffusion. B) filtration. C) osmosis. D) all of the above E) none of the above Answer: D 22) Swelling of a tissue is due to A) trauma to the blood. B) constriction of vessels. C) release of bone fragments. D) increased permeability of capillaries. E) filtration. Answer: D 23) Blood moves forward through veins A) because the pressure in the veins is lower than in the arteries. B) with the aid of contractions of skeletal muscles. C) with the aid of changes in cavity pressure. D) A and B only E) all of the above Page 6 of 26
7 24) Which of the following has the greatest effect on blood flow? A) HR B) SV C) peripheral resistance D) vessel length E) adipose tissue 25) In which of the following would the resistance be least? A) a vessel 10 microns in diameter B) a vessel 1 mm in diameter C) a vessel 1 cm in diameter 26) In which of the following would the rate of blood flow be greatest, assuming the same pressure? A) a vessel 10 microns in diameter B) a vessel 1 mm in diameter C) a vessel 1 cm in diameter Answer: A 27) The third and fourth heart sounds are caused by A) resistance. B) opening valves. C) closing valves. D) viscosity. E) turbulence. Page 7 of 26
8 28) Edema would be likely to form when A) the concentration of protein in the blood increases. B) hemorrhage occurs. C) the heart is an insufficient pump. D) blood hydrostatic pressure at the capillary decreases. E) the blood hydrostatic pressure in a capillary is equal to the blood osmotic pressure. 29) Which of the following will cause a decrease in blood pressure? A) increased levels of aldosterone B) increased levels of angiotensin II C) increased blood volume D) increased levels of ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) E) increased levels of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) Answer: D 30) Which of the following changes will result in increased nutrient delivery to a specific tissue? A) increased blood volume B) increased vessel diameter C) increased blood pressure D) decreased peripheral resistance E) relaxation of precapillary sphincters 31) Baroreceptors that function in the regulation of blood pressure are located in the A) left ventricle. B) brain stem. C) carotid sinus. D) common iliac artery. E) all of the above Page 8 of 26
9 32) Blood pressure in the systemic arteries is greatest during A) atrial systole. B) ventricular systole. C) ventricular diastole. D) atrial diastole. E) none of the above Answer: B 33) Angiotensin increases blood pressure by A) increasing peripheral resistance. B) promoting the release of renin. C) inhibiting aldosterone. D) promoting the excretion of sodium. E) inhibiting ADH. Answer: A 34) Which of the following factors is most likely to result in an increase in blood pressure? A) decreased blood flow to the kidneys B) decreased volume of body fluids C) increased excretion of sodium D) increased excretion of water E) increased excretion of potassium Answer: A 35) causes a direct increase in blood volume. A) Renin B) Erythropoietin C) ADH D) ACTH E) Angiotensin Page 9 of 26
10 36) Which of the following is greater? A) blood pressure when sympathetic stimulation to the heart increases B) blood pressure when parasympathetic stimulation to the heart increases Answer: A 37) When a capillary bed decreases in blood flow due to locally high oxygen levels, it is caused by A) intercellular chemicals. B) angiotensin. C) autoregulation. D) neural mechanisms. E) endocrine mechanisms. 38) Blood pressure is lowest in which of the following structures? A) arteriole B) artery C) capillary D) vein E) venule Answer: D 39) The baroreceptor reflex causes changes in A) blood pressure. B) stroke volume. C) heart rate. D) peripheral resistance. E) all of the above Page 10 of 26
11 40) Pulse pressure is the difference between A) the heart at rest and the heartbeat. B) elastic rebound and elastic recoil. C) circulatory pressure and blood pressure. D) blood pressure and osmotic pressure. E) systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. 41) A decrease in vessel diameter is called A) heart action. B) vasoconstriction. C) vasodilation. D) viscosity. E) peripheral resistance. Answer: B 42) Which of the following affects blood pressure indirectly by altering blood volume? A) neural factors B) venous return C) endocrine factors D) changing blood glucose concentration Answer: D Diff: 3 43) In response to hemorrhage, there is A) decreased vasomotor tone. B) increased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart. C) mobilization of the venous reserve. D) A and C only E) all of the above Learning Outcome: 13.4 Page 11 of 26
12 44) Symptoms of shock include A) hypotension. B) rapid, weak pulse. C) decreased urine formation. D) acidosis. E) all of the above Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is greater? A) heart rate normally B) heart rate during cardiovascular shock Answer: B Learning Outcome: ) Which is a branch of the pulmonary trunk? A) right coronary artery B) left coronary artery C) pulmonary artery D) left common carotid artery E) brachiocephalic artery Learning Outcome: ) The celiac artery provides blood to the A) brain. B) diaphragm. C) liver and spleen. D) large intestine. E) suprarenal glands. Page 12 of 26
13 48) Which of the following supplies blood to parts of the intestinal tract? A) phrenic arteries B) superior mesenteric artery C) lumbar artery D) middle sacral artery E) celiac artery Answer: B 49) An important artery that supplies blood to the brain is the A) external carotid. B) subclavian. C) vertebral. D) brachiocephalic. E) maxillary. 50) Blood from the face returns to the heart by way of the A) vertebral vein. B) axillary vein. C) brachiocephalic vein. D) internal jugular vein. E) external jugular vein. 51) The pulse point on the wrist is actually the artery. A) brachial B) radial C) ulnar D) antebrachial E) cubital Answer: B Page 13 of 26
14 52) After passing the axilla, the axillary artery becomes the A) radial artery. B) ulnar artery. C) brachial artery. D) subclavian artery. E) digital artery. 53) In the forearm, the brachial artery becomes the A) radial artery. B) ulnar artery. C) antebrachial artery. D) subclavian artery. E) both A and B 54) The basilar artery gives off the arteries. A) circle of Willis B) anterior cerebral C) external carotid D) internal carotid E) posterior cerebral 55) The internal carotids and the basilar artery are interconnected by an anastomosis called the A) common carotid artery. B) cerebral ring. C) circle of Willis. D) external carotid artery. E) none of the above Page 14 of 26
15 56) The divides the aorta into a superior thoracic aorta and an inferior abdominal aorta. A) pericardium B) mediastinum C) diaphragm D) peritoneum E) pleura 57) Near the level of vertebra L4, the aorta branches to form the A) common carotid arteries. B) common iliac arteries. C) femoral arteries. D) popliteal arteries. E) tibial arteries. Answer: B 58) The lumbar arteries are A) paired and travel in the intercostal spaces. B) paired and found in the lower abdomen. C) multiple in number and found exiting the posterolateral abdominal aorta. D) single branches of the abdominal aorta. E) none of the above 59) The vessel that receives blood from below the diaphragm is the A) internal jugular vein. B) external jugular vein. C) superior vena cava. D) inferior vena cava. E) coronary sinus. Answer: D Page 15 of 26
16 60) Small veins of the brain empty into the A) coronary sinuses. B) dural sinuses. C) circle of Willis. D) external jugular vein. E) vertebral veins. Answer: B 61) The is superficial and runs along the medial upper limb. A) digital vein B) cephalic vein C) axillary vein D) brachial vein E) basilic vein 62) After receiving the internal jugular vein, the subclavian vein becomes the A) cephalic vein. B) vena cava. C) axillary vein. D) brachiocephalic vein. E) external jugular vein. Answer: D 63) The fusion of the brachiocephalic veins forms the A) inferior vena cava. B) superior vena cava. C) cephalic vein. D) subclavian vein. E) iliac vein. Answer: B Page 16 of 26
17 64) The two common iliac veins form the A) femoral vein. B) internal iliac vein. C) inferior vena cava. D) lumbar vein. E) common iliac vein. 65) Which of the following is a remnant of a fetal blood vessel? A) hepatic portal B) ligamentum arteriosum C) ductus arteriosus D) umbilical artery Answer: B Learning Outcome: ) Elderly individuals are more prone to suffer from than younger individuals. A) hypertension B) venous thrombosis C) arteriosclerosis D) problems with the conducting system of the heart E) all of the above Learning Outcome: ) Factors that increase the risk of atherosclerosis include A) smoking. B) lack of exercise. C) high-fat diets. D) obesity. E) all of the above 0 Page 17 of 26
18 68) Vicki has a disabled posterior pituitary. What type of cardiovascular affects might you expect? A) decreased blood volume B) increased blood pressure C) peripheral vasoconstriction D) increased numbers of red blood cells E) all of the above Answer: A 0 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications Matching Questions 1) Match the blood vessels in the first column with the characteristic in the second column. 1. artery A. controls blood pressure 2. arteriole B. most permeable 3. capillary C. largest lumen 4. venule D. drains tissues 5. vein E. thickest wall Answer: 1-E, 2-A, 3-B, 4-D, 5-C 2) Match the arteries in the first column with the major regions they supply in the second column. 1. internal carotid A. posterior abdominal wall 2. phrenic B. upper digestive tract 3. renal C. brain 4. celiac D. diaphragm 5. lumbar E. kidney Answer: 1-C, 2-D, 3-E, 4-B, 5-A Page 18 of 26
19 Fill in the Blank Questions 1) The blood vessels whose walls are thin enough to allow the exchange of gases between the blood and tissues are. Answer: capillaries 2) drain fluid from the interstitial spaces back into the general circulation. Answer: Lymphatic vessels 3) Strong, elastic blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called. Answer: arteries 4) The smallest vessels of the arterial system are called. Answer: arterioles 5) Blood flowing out of a capillary bed first enters vessels called. Answer: venules 6) The force that pulls water INTO a capillary is called pressure. Answer: osmotic 7) Diastolic pressure plus one-third of the pulse pressure equals. Answer: mean arterial pressure 8) The force that pushes fluid out of the capillaries is called pressure. Answer: hydrostatic 9) The term refers to the pressure in the arterial side of the cardiovascular system. Answer: blood pressure Page 19 of 26
20 10) refers to the factors that oppose blood flow in the cardiovascular system. Answer: Total peripheral resistance 11) are the distinctive sounds heard during the measurement of blood pressure. Answer: Korotkoff's sounds 12) The instrument used to determine blood pressure is the. Answer: sphygmomanometer 13) is the regulation of blood flow at the tissue level. Answer: Autoregulation 14) In, the wall of an artery becomes thicker and tougher. Answer: arteriosclerosis Learning Outcome: 13.4 Page 20 of 26
21 15) The condition known as is characterized by the formation of fatty plaques in the lining of arteries. Answer: atherosclerosis Learning Outcome: ) The largest blood vessels are the. Answer: venae cavae 17) Supply the name of the missing vein: liver,, inferior vena cava. Answer: hepatic vein 18) Supply the name of the missing vein: cephalic vein, subclavian vein,. Answer: brachiocephalic vein 19) The vessel that carries blood to the arm and shoulder is called the. Answer: subclavian artery 20) The vessel that supplies blood to the head and neck is the. Answer: common carotid artery 21) The second branch off of the aortic arch is the. Answer: left common cartoid artery Page 21 of 26
22 Page 22 of 26 22) The vessels that supply blood to the diaphragm are the arteries. Answer: phrenic 23) The vessel that supplies blood to the brain and spinal cord is called the. Answer: vertebral artery 24) The vessel that supplies blood to the liver, stomach, and spleen is called the. Answer: celiac artery 25) The vessel that supplies blood to the pancreas, small intestine, and most of the large intestine is called the. Answer: superior mesenteric artery 26) The vessel that supplies blood to the arm and shoulder is the. Answer: subclavian artery 27) The vessel that branches to form a right common carotid artery and a right subclavian artery is the. Answer: innominate artery or brachiocephalic artery 28) The vessel that supplies blood to the muscles of the upper arm is the. Answer: brachial artery 29) The small intestine and most of the large intestine receive blood from the. Answer: superior mesenteric artery 30) The lower part of the large intestine, including the rectum, receives blood from the. Answer: inferior mesenteric artery
23 31) Ovaries or testes receive a blood supply from the. Answer: gonadal arteries 32) The kidneys receive blood from the. Answer: renal arteries 33) The branch of the common iliac artery that serves the leg is the. Answer: external iliac artery 34) The vessel that collects blood from the overlying structures of the head and neck is the. Answer: external jugular vein 35) Blood from the inside of the cranium is drained by the. Answer: internal jugular vein Page 23 of 26
24 36) The receives blood from the kidney. Answer: renal vein 37) Blood is drained from the liver by the. Answer: hepatic vein 38) In a fetus, blood from right atrium skips the right ventricle by passing through the. Answer: foramen ovale Learning Outcome: 13.8 Essay Questions 1) Tom loves to soak in hot tubs and whirlpools. One day, he decides to raise the temperature in his hot tub as high as it will go. After a few minutes in the very warm water, he feels faint, passes out, and nearly drowns. Luckily, he is saved by an observant bystander. Explain what happened physiologically. Answer: In response to the high temperature of the water, Tom's body shunted more blood to the superficial veins to decrease body temperature. The dilation of the superficial veins caused a shift in blood to the arms and legs and resulted in a decreased venous return. Because of the decreased venous return, the cardiac output decreased and less blood with oxygen was delivered to the brain. This caused Tom to feel lightheaded and faint, nearly causing his demise. Diff: 2 0 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications Page 24 of 26
25 Labeling Exercises Using the figure above, identify the labeled part. 1) Label A: Answer: Ascending aorta Learning Outcome: ) Label B: Answer: Superior vena cava Learning Outcome: ) Label C: Answer: Right pulmonary arteries Learning Outcome: ) Label D: Answer: Right pulmonary veins Learning Outcome: ) Label E: Answer: Inferior vena cava Learning Outcome: 13.6 Page 25 of 26
26 6) Label F: Answer: Descending aorta Learning Outcome: ) Label G: apillary Learning Outcome: ) Label H: Answer: Alveolus Learning Outcome: ) Label I: Answer: Left pulmonary veins Learning Outcome: ) Label J: Answer: Left pulmonary arteries Learning Outcome: ) Label K: Answer: Pulmonary trunk Learning Outcome: ) Label L: Answer: Aortic arch Learning Outcome: 13.6 Page 26 of 26
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Vascular System Part One
 Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Types of Blood Vessels
 Chapter 21 Peripheral Circulation and Regulation 21-1 Types of Blood Vessels Capillaries: site of exchange with tissue Arteries in dif. Types & sizes Elastic Muscular Arterioles Veins: thinner walls than
Chapter 21 Peripheral Circulation and Regulation 21-1 Types of Blood Vessels Capillaries: site of exchange with tissue Arteries in dif. Types & sizes Elastic Muscular Arterioles Veins: thinner walls than
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
The Cardiovascular System. Preview of Heart Action. The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
 The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Heart. Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node. Lymphatic. system Arteriovenous anastomosis. (exchange vessels)
 Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Cardiovascular System
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Contents. Page 1. Homework 11 Chapter Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11
 Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
The Cardiovascular System
 11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes. Pulmonary Circulation H E A R T. Systemic Circulation
 The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
Anatomy of the Blood Vessels
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated. B.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated. B.
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Heart pumps blood Blood vessels circulate blood to all parts of the
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Heart pumps blood Blood vessels circulate blood to all parts of the
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
Chapter 21. Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulation INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated.
Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulation INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated.
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
ANATOMY OF BLOOD VESSELS
 BIOLOGY 212: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************************** ANATOMY OF BLOOD VESSELS ********************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 212: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************************** ANATOMY OF BLOOD VESSELS ********************************************************************************************************
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE. There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood
 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
A closed system of the heart/blood. Function: The heart pumps blood. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body
 A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System 1 The Heart Major organ of the cardiovascular system 2 What is the mediastinum? The mediastinum is the space between the lungs, where the heart is located. The heart is divided into
Cardiovascular System 1 The Heart Major organ of the cardiovascular system 2 What is the mediastinum? The mediastinum is the space between the lungs, where the heart is located. The heart is divided into
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels
 CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Chapter 21. Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 Openstax: Chapter 20 Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter 21 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 21, you will be able to: 1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels based on their
Chapter 21 Openstax: Chapter 20 Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter 21 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 21, you will be able to: 1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels based on their
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties!
 Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 1! Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 1! Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow. Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD
 Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Biology 232 Final. 7. Which of the following lists the elements of the heart s conduction system in the correct order? Name
 Biology 232 Final Name 1. The heart is located within the: a) mediastinum b) pleural cavity c) pericardial cavity 2. Which of the following is not part of cardiac muscle histology: a) striations b) intercalated
Biology 232 Final Name 1. The heart is located within the: a) mediastinum b) pleural cavity c) pericardial cavity 2. Which of the following is not part of cardiac muscle histology: a) striations b) intercalated
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Chapter 21! Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulation! Blood Vessels and Circulation!
 Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
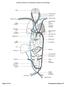 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Which Artery am I? I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm.
 I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
