A closed system of the heart/blood. Function: The heart pumps blood. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body
|
|
|
- Morris Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At all times, blood is contained within the vessels or heart Function: Deliver oxygen and nutrients and re move carbon dioxide and other waste products
3 Location Thorax: between the lungs & inferior to the mediastinum Orientation Apex (5cm) is pointed toward the left hip Superior surface lies on the diaphragm Base (9 cm) is towards the right shoulder Lies anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Size About the size of your fist Weighs less than 1 pound Shape Hollow & cone shaped
4
5
6 Pericardium Double walled sac containing the heart & the roots of the greater vessels Two walls: fibrous pericardium & serous pericardium Functions to protect the heart & lubricate the heart Fibrous pericardium is loose and superficial Functions: Protect the heart Anchor the heart to its surrounding structures (diaphragm & greater vessels) Prevents overfilling of the heart with blood Serous membrane (pericardium) is deep to the fibrous pericardium and composed of two layers Visceral pericardium Next to heart; also known as the epicardium Parietal pericardium Outside layer that lines the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium Serous fluid fills the space between the layers of pericardium The fluid is pale yellow, translucent, & benign in nature ( functionless)
7 Three layers Epicardium Outside layer This layer is the visceral pericardium Produces pericardial fluid Connective tissue layer Lubricates the motion between the inner and outer layers of the pericardium Often infiltrated with fat, in older people Myocardium Middle layer Mostly cardiac muscle arranged in circular/spiral bundles This arrangement is what links all the structures of the heart together Collagen & elastin connective tissues form the fibrous skeleton of the heart Creates additional support where the great vessels issue from the heart/ around the heart valves Over time, these area become stretched out from the continual stress of blood pumping Connective tissue cannot carry electrical impulses - limits the direct spread of action potential across cardiac tissue
8 Endocardium Inner layer Endothelium Thin, white sheet of epithelial tissue Lines the entire surface of the circulatory system, down to the interior surfaces of the capillaries Label it all!
9 Right and left side act as separate pumps Four chambers & two major separations Atria Thin walled & small à blood just flows down Receiving chambers: blood enters the heart Right atrium: receives deoxygenated blood from: Superior vena cava Returns blood from the body that is superior from the diaphragm Inferior vena cava Returns blood from the body that is inferior from the diaphragm Coronary sinuses Collects blood that drains from the myocardium itself Left atrium: receives oxygenated blood from: Left & right pulmonary veins This makes up most of the heart s base Transports blood back to the heart, from the lungs
10 Atria The right and left atria are separated by the interatrial septum Fossa ovalis: small shallow depression that marks where the foramen ovale had existed in the fetal heart Auricles: small flaps that increase atrial volume distinguishing feature of atria Bundles of muscle in atria are specifically called pectinate muscles look like they have been raked with a comb
11 Ventricles Makes up most of the mass of the heart Discharging chambers: blood leaves the heart Right ventricle: pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries Makes up most of the anterior surface of the heart Left ventricle: pumps (propels) oxygenated blood through the aorta out through the body (systemic circulation) Makes up most of the posteroinferior surface Trabeculae carneae: irregular ridges in the internal walls of the muscle layer crossbars Papillary muscles: conelike muscle bundles Play a role in valve function
12
13 Interventricular septum Separates the two ventricles Interatrial septum Separates the two atria
14 Systemic circulation Blood flows from the left side of the heart through the body tissues and back to the right side of the heart Left side of the heart systemic circuit pump Blood leaves the left side of the heart to smaller arteries attached to body tissues to provide nutrients and gases. Pulmonary circulation Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back to the left side of the heart Right side of the heart pulmonary circuit pump Starts as Oxygen poor/carbon dioxide rich blood in the right atrium/ventricle OPPOSITE: Pulmonary veins carry OXYGEN RICH blood back to the L.A.
15 Coronary circulation Shortest circulation within the body Blood flow within the vessels of the heart itself Ensures adequate oxygen supply for the heart muscle itself to function The vessels are the coronary arteries & cardiac veins Coronary arteries are the only source of blood supply for the actual myocardium Myocardium is too thick to allow for diffusion of nutrients and gases Delivery of nutrients and gases are specifically accomplished by the left and right coronary arteries (arising from the base of the aorta)
16 Coronary circulation The left C.A. runs towards the left side of the heart, branching into the interventricular artery, supplies blood to the interventricular septum & the anterior walls of both ventricles Then, that blood travels to the posterior walls of the left ventricle via the circumflex artery. The right C.A. runs along the right side of the heart, branching in two: Marginal artery serves the myocardium of the lateral part of the right side of the heart Posterior interventricular artery runs to the heart apex and supplies the posterior ventricular walls
17 Coronary circulation Arterial supply of the heart varies considerably Each person can have different anastomoses (merging points) of arteries These create different networks/routes of blood delivery to the heart This also explains how arterial blockages don t always stop the heart from working completely, unless. Complete blockage of a coronary artery leads to tissue death and heart attack Coronary arteries provide pulsing, intermittent blood flow to the heart Actively deliver blood when the heart is relaxed Ineffective when the ventricles are contracting Compressed by the contracting heart muscles Entrances to the coronary arteries are partly blocked by the flaps of the open aortic semilunar valve Even though the heart only represents 1/200 of body weight, it requires 1/20 of blood supply With the left ventricle using most of that blood supply
18 Valves allow blood to only flow in one direction (prevent backflow) Four valves: Between the atria & ventricles: AV valves Anchored in place by chordae tendinae: heart strings Open during heart relaxation and closed during ventricular contract Bicuspid (mitral): left side of the heart Tricuspid: right side of the heart Between ventricles & an artery: semilunar valves Closed during heart relaxation & open during ventricular contract Pulmonary semilunar valve: between the right ventricle & the pulmonary artery Aortic semilunar valve: between the left ventricle & the aorta
19 Arteries: Aorta: leaves the left ventricle Brings oxygenated blood out to the body Pulmonary artery: leaves the right ventricle Veins Brings deoxygenated blood to the lungs Superior & inferior vena cava: enters the right atrium Brings deoxygenated blood into the heart Pulmonary veins (there are four): enters the left atrium Brings oxygenated blood into the heart
20 Superior & Inferior venae cavae bring blood into the right atrium From the right atrium, blood travels through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle Blood leaves the right ventricle, passing through the semilunar valve into the pulmonary trunk The pulmonary trunk splits into the left/right pulmonary arteries that carry blood into the lungs
21 Oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is dropped off Oxygen rich blood travels back to the heart through the four pulmonary veins Blood enters the left atrium, travels through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle From the left ventricle, blood leaves the heart via the aortic semilunar valve and ultimately the aorta allowing the blood to travel through the body. Simple, no?
22 Blood in the heart chambers does not nourish the myocardium The heart has its own nourishing circulatory system consisting of Coronary arteries branch from the aorta to supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood Cardiac veins drain the myocardium of blood Coronary sinus a large vein on the posterior of the heart, receives blood from cardiac veins Blood empties into the right atrium via the coronary sinus
23
24 Intrinsic conduction system (nodal system) Heart muscle cells contract, without nerve impulses, in a regular, continuous way Special tissue sets the pace Sinoatrial node = SA node ( pacemaker ) Impulse generating tissue that keeps the regular contractions of the heart It s a group of cells called myocytes positioned by the top of the right atrium It s a muscle cell that contains some parts of the contractile unit Atrioventricular node = AV node, is at the junction of the atria and ventricles Serves as a backup for the SA node (pacemaker) Ensures there is a mild delay (0.12 seconds) in the contraction of ventricles to ensure that there is actually enough blood to pump out of the ventricles
25 Special tissue sets the pace (continued) Atrioventricular bundle = AV bundle (bundle of His), is in the interventricular septum Transmits impulses from the AV node to the apex of the heart Purkinje fibers extend out of the AV bundle This bundle of cells is important because it s regular rate of impulse messaging is beats per minute Bundle branches are in the interventricular septum Purkinje fibers spread within the ventricle wall muscles Distribute the impulses to the walls of ventricles actually allowing cardiac muscle contraction to happen Atrial fibrillation: the muscles of the atria quiver instead of regularly contract Physiological cause: overwhelming, disorganized impulses from the SA node or AV node miscommunication Increases stroke risk up to 7x because blood may pool in atria or clot
26 Contraction is initiated by the sinoatrial node Sequential stimulation occurs Force cardiac muscle depolarization in one direction from atria to ventricles Once SA node starts the heartbeat Impulse spreads to the AV node Then the atria contract At the AV node, the impulse passes through the AV bundle, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers Blood is ejected from the ventricles to the aorta and pulmonary trunk as the ventricles contract
27 Tachycardia rapid heart rate over 100 beats per minute Bradycardia slow heart rate less than 60 beats per minutes
28 Atria contract simultaneously Atria relax, then ventricles contract Systole = contraction Usually describes left ventricle contraction: cardiomyocytes Diastole = relaxation Happens after systole; allows the heart to refill with blood Cardiac cycle events of one complete heart beat Mid- to- late diastole blood flows from atria into ventricles Ventricular systole blood pressure builds before ventricle contracts, pushing out blood Early diastole atria finish refilling, ventricular pressure is low
29 Left atrium Right atrium Left ventricle Right ventricle Ventricular filling Atrial contraction Isovolumetric Ventricular contraction phase ejection phase Isovolumetric relaxation Mid-to-late diastole (ventricular filling) Ventricular systole (atria in diastole) Early diastole
30 Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped by each side (ventricle) of the heart in one minute Stroke volume (SV) Volume of blood pumped by each ventricle in one contraction (each heartbeat) Usually remains relatively constant About 70 ml of blood is pumped out of the left ventricle with each heartbeat Heart rate (HR) Averages: 75 beats per minute CO = HR SV CO = HR (75 beats/min) SV (70 ml/beat) CO = 5250 ml/min Starling s law of the heart the more the cardiac muscle is stretched, the stronger the contraction Changing heart rate is the most common way to change cardiac output
31 Increased heart rate Sympathetic nervous system is stimulated Crisis Low blood pressure Hormones Epinephrine released in stressful situations (adrenaline) Thyroxine used to increase metabolism Exercise Decreased blood volume Decreased heart rate Parasympathetic nervous system is activated in reaction to a sympathetic stimulation High blood pressure or blood volume Decreased venous return
32 Transport blood to the tissues and back Carry blood away from the heart Arteries Arterioles Exchanges between tissues and blood Capillary beds Return blood toward the heart Venules Veins
33 Three layers (tunics) Tunica intima Endothelium one layer of cells Have direct contact with blood Tunica media Smooth muscle In larger arteries, there may be elastic tissue Controlled by sympathetic nervous system Tunica externa Mostly fibrous connective tissue (collagen) Anchors blood vessels to body organs
34 Walls of arteries are the thickest Lumens of veins are larger Larger veins have valves to prevent backflow Skeletal muscle milks blood in veins toward the heart Walls of capillaries are only one cell layer thick to allow for exchanges between blood and tissue Most arterial blood is pumped by the heart
35 Capillary beds consist of two types of vessels Vascular shunt vessel directly connecting an arteriole to a venule True capillaries exchange vessels Oxygen and nutrients cross to cells Carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products cross into blood
36 Aorta Largest artery in the body Leaves from the left ventricle of the heart Regions of the Aorta Ascending aorta leaves the left ventricle Left & right coronary arteries leave here to supply blood to the heart Aortic arch arches to the left Thoracic aorta travels downward through the thorax Abdominal aorta passes through the diaphragm into the Abdominopelvic cavity
37 Arterial branches of the aortic arch (BCS) Brachiocephalic trunk splits into the Right common carotid artery Right subclavian artery Left common carotid artery splits into the Left internal and external carotid arteries Left subclavian artery branches into the Vertebral artery In the axilla, the subclavian artery becomes the axillary artery à brachial artery à radial and ulnar arteries LabelingExercisesII/activityApplet7.html
38 Arterial branches of the thoracic aorta Intercostal arteries supply the muscles of the thorax wall Other branches of the thoracic aorta supply the Lungs (bronchial arteries) Esophagus (esophageal arteries) Diaphragm (phrenic arteries)
39 Arterial branches of the abdominal aorta Celiac trunk is the first branch of the abdominal aorta. Three branches are Left gastric artery (stomach) Splenic artery (spleen) Common hepatic artery (liver) Superior mesenteric artery supplies most of the small intestine and first half of the large intestine Left and right renal arteries (kidney) Left and right gonadal arteries Ovarian arteries in females serve the ovaries Testicular arteries in males serve the testes Lumbar arteries serve muscles of the abdomen and trunk
40 Arterial branches of the abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric artery serves the second half of the large intestine Left and right common iliac arteries are the final branches of the aorta Internal iliac arteries serve the pelvic organs External iliac arteries enter the thigh à femoral artery à popliteal artery à anterior and posterior tibial arteries
41
42 Superior and inferior vena cava enter the right atrium of the heart Superior vena cava drains the head and arms Inferior vena cava drains the lower body Veins draining into the superior vena cava Radial and ulnar veins à brachial vein à axillary vein These veins drain the arms Cephalic vein drains the lateral aspect of the arm and empties into the axillary vein Basilic vein drains the medial aspect of the arm and empties into the brachial vein Basilic and cephalic veins are jointed at the median cubital vein (elbow area)
43 Veins draining into the superior vena cava Subclavian vein receives Venous blood from the arm via the axillary vein Venous blood from skin and muscles via external jugular vein Vertebral vein drains the posterior part of the head Internal jugular vein drains the dural sinuses of the brain Left and right brachiocephalic veins receive venous blood from the Subclavian veins Vertebral veins Internal jugular veins Brachiocephalic veins join to form the superior vena cava à right atrium of heart Azygous vein drains the thorax
44 Veins draining into the inferior vena cava Anterior and posterior tibial veins and fibial veins drain the legs Posterior tibial vein à popliteal vein à femoral vein à external iliac vein Great saphenous veins (longest veins of the body) receive superficial drainage of the legs Each common iliac vein (left and right) is formed by the union of the internal and external iliac vein on its own side Right gonadal vein drains the right ovary in females and right testicle in males Left gonadal vein empties into the left renal vein Left and right renal veins drain the kidneys Hepatic portal vein drains the digestive organs and travels through the liver before it enters systemic circulation Left and right hepatic veins drain the liver
45
46 Internal carotid arteries divide into Anterior and middle cerebral arteries These arteries supply most of the cerebrum Vertebral arteries join once within the skull to form the basilar artery Basilar artery serves the brain stem and cerebellum Posterior cerebral arteries form from the division of the basilar artery These arteries supply the posterior cerebrum Circle of Willis Anterior and posterior blood supplies are united by small communicating arterial branches Result complete circle of connecting blood vessels called cerebral arterial circle or circle of Willis
47
48 Pulse Pressure wave of blood Monitored at pressure points in arteries where pulse is easily palpated Pulse averages beats per minute at rest
49 Normal human range is variable Normal mm Hg systolic mm Hg diastolic Hypotension Low systolic (below 110 mm HG) Often associated with illness Hypertension High systolic (above 140 mm HG) Can be dangerous if it is chronic
50 BP is blood pressure BP is affected by age, weight, time of day, exercise, body position, emotional state CO is the amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle per minute PR is peripheral resistance, or the amount of friction blood encounters as it flows through vessels Narrowing of blood vessels and increased blood volume increases PR BP = CO PR
51 Neural factors Autonomic nervous system adjustments (sympathetic division) Renal factors Regulation by altering blood volume Renin hormonal control Temperature Heat has a vasodilating effect Cold has a vasoconstricting effect Chemicals Various substances can cause increases or decreases Diet
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
The Cardiovascular System
 11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Cardiovascular System
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
The Cardiovascular System. Preview of Heart Action. The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
 The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System. Chapter 18 & 19
 Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
- what other structures, besides the heart, does the mediastinum contain?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) An Introduction to the Cardiovascular System - read the paragraphs under this heading on page 580 The Heart is a Four Chambered Organ describe
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Heart pumps blood Blood vessels circulate blood to all parts of the
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Heart pumps blood Blood vessels circulate blood to all parts of the
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
The Heart. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS:
 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
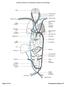 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Vascular System Part One
 Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system 1 Essential Question: How does the structure of the heart allow it to function in pumping blood? 2 Function? 3 Location of Heart 4 Heart coverings double sac of serous membrane pericardium
Cardiovascular system 1 Essential Question: How does the structure of the heart allow it to function in pumping blood? 2 Function? 3 Location of Heart 4 Heart coverings double sac of serous membrane pericardium
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) HEART P1 OF 5
 BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) HEART P1 OF 5 1. Heart Functions a. Generates pressure that propels blood thru blood vessels. (Tissue perfusion.) b. Separates oxygenated
BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) HEART P1 OF 5 1. Heart Functions a. Generates pressure that propels blood thru blood vessels. (Tissue perfusion.) b. Separates oxygenated
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
