Origins of the Segmental Arteries in the Aorta: An Anatomic Study for Selective Catheterization with Spinal Arteriography
|
|
|
- Anissa Morris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , April 2005 Origins of the Segmental Arteries in the Aorta: An Anatomic Study for Selective Catheterization with Spinal Arteriography Satoru Shimizu, Ryusui Tanaka, Shinichi Kan, Sachio Suzuki, Akira Kurata, and Kiyotaka Fujii BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The segmental arteries, which include the posterior intercostal, subcostal, and lumbar arteries, are gateways for performance of selective spinal arteriography of the thoracolumbar level. We performed a cadaveric study to clarify the anatomic relationship between the origins of the segmental arteries in the aorta and the vertebral column. METHODS: Five adult cadaveric aortas with intact thoracolumbar spines were dissected under magnification. In each specimen, nine pairs of posterior intercostal arteries, one pair of subcostal arteries, and four pairs of lumbar arteries were examined in detail. RESULTS: The origin of the posterior intercostal arteries in the upper thoracic level was situated at most about two levels caudal to the feeding level, whereas the origins in the lower levels were just caudal to the corresponding levels. The position of the bilateral orifices of the segmental arteries in the axial plane of the aorta was on the medial side at the thoracic levels, whereas it was on the dorsal side at the lumbar level. The horizontal distance between the orifices in the lumen of aorta was found to be wider at the thoracic level than the lumbar level, and the longitudinal distance was higher at the lower level, corresponding to the height of the vertebra. CONCLUSION: Understanding the 3D relationship of the initial segment of the segmental arteries with reference to the aorta and vertebral column is necessary for performance of the selective spinal arteriographic examination rationally by using a two-dimensional fluorescent display. Received May 9, 2004; accepted after revision July 16. From the Departments of Neurosurgery (S. Shimizu, R.T., S. Suzuki, A.K., K.F.) and Radiology (S.K.), Kitasato University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan. Address reprint requests to Satoru Shimizu, MD, Department of Neurosurgery, Kitasato University School of Medicine, Kitasato, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan; Satoru4756@ aol.com American Society of Neuroradiology Selective spinal arteriography is indicated for evaluation of vascular malformations or vascular tumors of the spinal cord, spinal meninges, or vertebral column, as well as for endovascular intervention (1). Although less invasive imaging techniques have been developed, it is still a useful method because of the high resonance. Below the cervical level, the segmental arteries that originate from the descending aorta, and which consist of the posterior intercostal artery and subcostal artery at the thoracic level and the lumbar artery at the lumbar level, are the gateways to obtain images of the vasculature in this region (2, 3). The anatomy of the branches of the segmental arteries, especially the radiculomedullary artery represented by the artery of Adamkiewicz, has been well documented (4 7). However, the anatomy of the segmental arteries in the proximal region, including the orifices in the aorta, has received less attention, despite the necessity to access the region in selective spinal arteriography (8). Our purpose was to perform a cadaveric study to clarify the anatomic relationship between the origins of the segmental arteries in the aorta and the vertebral column, from the standpoint of catheterization for selective spinal arteriography. Methods Five adult cadaveric aortas with intact thoracolumbar spines were examined. No specimens had aortic disease or deformity of the spinal column except one with marked atherosclerosis and an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Microscopic exposure of the segmental arteries by removal of the surrounding fat tissue was performed, with care taken to preserve the anatomic relationship to the aorta. One of the specimens was dissected following perfusion of the aorta with colored silicone. After observation of the course of each artery, the anterior wall of the aorta was removed and the orifices of the arteries were identified. Axial and longitudinal locations of the orifices with reference to the spine were examined at each level, and longitudinal and horizontal distances between the orifices were measured by using a divider and a caliper. Also, axial and 922
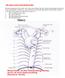
2 AJNR: 26, April 2005 SEGMENTAL ARTERY ORIGINS 923 FIG 1. (Continued on next page).
3 924 SHIMIZU AJNR: 26, April 2005 FIG 2. Photographs of specimens of a cadaveric aorta. A, Left anterior oblique view of the inner lumen of the thoracic aorta shows the locations of the orifices (arrows) of the posterior intercostal arteries. The longitudinal distances between adjacent orifices are shorter in the upper level, and orifices on the left at this level are situated in a higher position than those on the right side, depending on the curve of the aortic arch. B and C, Pins are placed in the initial segment of the segmental arteries at the thoracic (B) and lumbar (C) levels to show the direction of each vessel. Differences in direction of the initial segment between the spinal levels can be seen, with a medial course where the aorta is lying to the left of the spinal column, but the course is dorsolateral where the aorta is anterior to the spinal column. longitudinal directions of the initial segment of the segmental arteries just after passing from the orifice were recorded. Results The descending aorta began on the left side of the fourth thoracic vertebra as a continuation of the aortic arch. It was situated on the left side of the spinal column in the upper thoracic region and descends anteromedially to become situated anterior to the lumbar column, a little left of the midline. The descending aorta ended just below the fourth lumbar vertebra by dividing into the two common iliac arteries (Fig 1A). Nine pairs of posterior intercostal arteries, one pair of subcostal arteries, and four pairs of lumbar arteries arose from the aspect of the descending aorta, adjacent to the spinal column (Fig 1B G). The posterior intercostal arteries passed from the third to the 11th intercostal spaces, the subcostal arteries run below the 12th rib, and the lumbar arteries ran from the first to the fourth vertebral bodies, respectively, corresponding to each segmental level. The origin of the most cephalad segmental arteries branching from the aorta, the third posterior intercostal arteries, was situated at the level between the fifth and sixth thoracic vertebra, and that of the most caudal, the fourth lumbar arteries, was situated in the middle portion at the height of the fourth lumbar vertebral body. The origin of the cephalad posterior intercostal arteries was situated about two segmental levels at most below their feeding levels (Fig 1C and D), whereas the segmental arteries originate just below the corresponding vertebra except for the last two FIG 1. Photographs of specimens of a cadaveric aorta with intact thoracolumbar spine. A, Anterior view shows the whole aorta, which is situated on the left side of the spinal column at the upper thoracic levels and descends medially to be situated anterior to the lumbar column, a little to the left of the midline. This specimen has an abdominal aortic aneurysm. B D, Anterior (B), right lateral (C), and left lateral (D) views of the thoracic aorta show the course of the posterior intercostal arteries (PIAs). In the lateral views, white and black numbers indicate the levels of the posterior intercostal arteries and thoracic vertebrae, respectively. The arteries at the upper thoracic levels, originating below the corresponding feeding levels, run upward, whereas those of the middle to lower thoracic levels originate just below the feeding levels and ascend for a short distance. On the right side, the initial segment runs straight after branching from the aorta, whereas that on the left exhibits angulation just distal to the origin. E G, Anterior (E), right lateral (F), and left lateral (G) views of the lumbar aorta show the lumbar arteries (LAs) originating at the levels of the corresponding vertebrae. The first two lumbar arteries run upward, whereas the last two run almost horizontally. The first lumbar artery on the left is absent in this specimen. IVC indicates inferior vena cava. H, Left anterior view of the lower thoracic level after vertebrectomy shows the common origin of the 10th and 11th posterior inercostal arteries (PIAs). The major trunks can be identified.
4 AJNR: 26, April 2005 SEGMENTAL ARTERY ORIGINS 925 TABLE 1: Horizontal distances between orifices of the segmental arteries in the lumen of the aorta from five cadaveric specimens Artery and Level Distance (mm) Posterior intercostal (9.83) (11.17) (17.22) (15.34) (11.20) (10.47) (11.73) (11.25) (10.14) Subcostal (6.72) Lumbar (7.56) (6.74) (8.96) (14.12) Note. Data are the range. Numbers in parentheses are the mean. TABLE 2: Longitudinal distances between orifices of the segmental arteries in the lumen of the aorta from five cadaveric specimens Distances (mm) FIG 3. Schematic drawing shows the locations of the orifices of the segmental arteries in the aorta relative to the spine (left) and the directions (arrows) of the initial segment in axial sections at each level (right). The directions of the initial segment are nearly parallel to the coronal plane in the upper thoracic (Th) region and are dorsolateral in the lumbar (L) region. lumbar arteries. The levels of origin of the third and fourth lumbar arteries were at the centers of the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae, respectively (Fig 1E G). Each segmental artery ran upward to reach the middle region of the corresponding vertebral body, so the ascending course was more apparent in the upper thoracic region. As a result of the location of the origin, the arteries in the upper thoracic level, the third to sixth, ran upward markedly to reach the corresponding feeding levels, whereas the arteries in the middle to lower thoracic and lumbar levels ran upward for only a short course until the middle portion of the vertebra and then almost horizontally. The courses of the arteries in the initial segment were different in the upper thoracic level on the right side than in the other regions. In the former, the initial segment ran straight after branching from the aorta (Fig 1B and C), whereas the latter showed angulation just distal to the origin (Fig 1D). One of the specimens showed absence of segmental arteries at four levels (the third and fourth posterior intercostal arteries, the subcostal artery on the right, and the first lumbar artery on the left) and common origins of adjacent posterior intercostal arteries in two regions (the third and fourth, and the 10th and 11th) on the left side (Fig 1H). Obliteration of the orifices of the arteries due to atherosclerosis was observed at three levels. The positions of the orifices in the axial plane of the aorta were on the medial side at the thoracic level, but on the dorsal side at the Artery and Level Right Left Posterior intercostal (6.45) (10.66) (11.84) (16.75) (12.43) (15.84) (14.07) (14.43) (20.33) (21.50) (24.23) (25.84) (23.38) (22.70) (25.52) (23.00) 11 Subcostal (23.84) (27.27) Subcostal lumbar (32.44) (30.79) Lumbar (27.92) (27.79) (26.32) (28.28) (27.99) (29.83) Note. Data are the range. Numbers in parentheses are the mean. lumbar level (Fig 2A C). The locations and directions of the origin of the arteries are schematically illustrated in Fig 3. Horizontal and longitudinal distances among the orifices of the arteries in the lumen of the aorta are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. The horizontal distance was wider at the thoracic level than the lumbar level, and the longitudinal distance was greater at the lower level, corresponding to the heights of vertebrae. Discussion The segmental arteries have three major trunks: lateral (posterior intercostal artery or lumbar artery), middle (muscular and dorsal branches), and medial (radicular artery, radiculomedullary artery, or radiculopial artery) (Fig 1H). They supply intercostal muscle and fat, the caudal aspect of the intervertebral foramen, and the nerve roots and spinal cord, respec-
5 926 SHIMIZU AJNR: 26, April 2005 FIG 4. A and B, Selective arteriograms of the posterior intercostal arteries (PIA) on the right (A) and left (B) show arteries arising on the right side of the thoracic aorta, and the left one runs posterior to the aorta. Arrowheads indicate the orifices of the arteries; arrows, the lateral rim of the aorta. Th indicates thoracic vertebra. (Figure 4 continues.) tively (4). Selective catheterization of the initial segment of the segmental arteries is important to assess the branches by sufficient opacification, and the present study revealed some anatomic points for adequate catheterization. The orifices of the segmental arteries are situated on the right side (medial side) in the inner lumen of the aorta in the upper thoracic level, and the position gradually changes to the dorsal side from the cephalad to the caudal level, and finally the orifices are situated on the dorsal aspect of the aorta. Experienced neuroradiologists have described that all of the orifices can be found by moving the catheter tip upward or downward straight along the aorta after identification of one orifice (8); however, in the present study, we showed that the course for seeking the longitudinally neighboring orifices was not straight but twisted. The directions of the initial segment of the segmental arteries just after branching from the aorta are nearly parallel to the coronal plane at the upper thoracic level, and dorsolateral at the lumbar level, running to the surface of the vertebral bodies. Differences in location of the orifices in the axial plane and direction of the initial segment at each level contributed to the anatomic relationships between the spinal column and aorta. The aorta is situated on the left side of the spinal column in the upper thoracic level and descends anteromedially to ride on the lumbar spinal column. Thus, the arteries reach the vertebra by the nearest course from each origin. Dissociation of the levels between the origin of segmental arteries and their corresponding vertebral column is apparent at the upper thoracic level, with the third to sixth posterior intercostal arteries. In the human embryo, segmental arteries belonging to each somite arise from the dorsal aorta at about 3 weeks of age, and their origins are situated at the same levels (9). The dissociation may be the result of relatively greater longitudinal growth of the vertebral column as compared with the aorta in later development. The distances between the orifices on both sides are wider at the upper thoracic than the lumbar level, and the longitudinal distances between neighboring levels increase from cephalad to caudal, depending on the increments in height of vertebrae. At the upper thoracic level, the longitudinal distance is shorter. The distance is longer on the left than on the opposite side, due to the origins of cephalad arteries at the end of the aortic arch being situated at a higher position on the left side. The long mean horizontal distance between the last lumbar arteries and the
6 AJNR: 26, April 2005 SEGMENTAL ARTERY ORIGINS 927 Fig 4 continued. C and D, Lumbar arteriograms at the upper (C) and lower (D) levels show that the first two lumbar arteries (LAs) arise just below the corresponding vertebrae, whereas the last two arteries arise in the middle regions of the vertebrae. Th indicates thoracic vertebra; L, lumbar vertebra. short mean longitudinal distance between the right third and fourth lumbar arteries are influenced by the high position of the fourth lumbar artery, between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae. Although the roadmap method is popular to facilitate catheterization, its application is difficult in cases that require selective arteriography for large numbers of segmental arteries, because specification of the feeding artery of vascular malformation, time, large amounts of contrast medium and x rays are needed. Understanding the 3D relationship of the initial segments of segmental arteries close to the aorta and spine is thus very important to determine the level of the spine corresponding to the artery of interest (Fig 4). Finally, the presence of unusual anatomic relationships between the segmental arteries and the aorta, due to variation or pathologic conditions (atherosclerosis and elongation of the aorta, fracture and abnormal alignment of the spinal column), should be borne in mind in clinical practice. Conclusion The three-dimensional anatomy of the initial segment of the segmental arteries at each spinal level needs to be taken into consideration for performance of selective spinal arteriography. Understanding the spatial relationships may be helpful to conduct examinations that require fluoroscopic guidance in as short a period as possible, thus minimizing the contrast medium needed. Acknowledgments The authors thank Professor Albert L. Rhoton, Jr., and Ronald Smith, MS, Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida, for providing some of the specimens. References 1. Stevens JM, McAllister VL. The spine: methods of examination. In: Grainger RG, Allison D, eds. Grainger & Allison s Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging 3rd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1997: Jinkins JR. Atlas of Neuroradiologic Embryology, Anatomy, and Variants. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000: Moore KL. Clinically Oriented Anatomy 3rd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; 1992: Alleyne CH Jr, Cawley CM, Shengelaia GG, et al. Microsurgical anatomy of the artery of Adamkiewicz and its segmental artery. J Neurosurg 1998;89: Lazorthes G, Gouaze A, Zadeh JO, et al. Arterial vascularization of the spinal cord: recent studies of the anastomotic substitution pathways. J Neurosurg 1971;35:
7 928 SHIMIZU AJNR: 26, April Rodriguez-Baeza A, Muset-Lara A, Rodriguez-Pazos M, et al. The arterial supply of the human spinal cord: a new approach to the arteria radicularis magna of Adamkiewicz. Acta Neurochir 1991;109: Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, Raybaud C. Surgical Neuroangiography Vol. 3: Spinal and Spinal Cord Arteries and Veins. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1990: Djindjian R, Hurth M, Houdart R, Laborit G, Julian H, Mamo H. Angiography of the Spinal Cord: The Technique of Angiography of the Spinal Cord. Paris: Masson et Cie; 1970: Patten BM. The development of the heart. In: Gould SE, ed. Pathology of the Heart and Blood Vessels 3rd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher; 1968:20 90
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
THE SEGMENTAL ARTERIES
 HAEMANGIOMA OF A VERTEBRAL BODY TREATED BY LIGATION OF THE SEGMENTAL ARTERIES Report of a Case T. BUCKNILL, J. W. JACKSON, H. B. S. KEMP, STANMORE, ENGLAND, and B. E. KENDALL, LONDON, ENGLAND hoot The
HAEMANGIOMA OF A VERTEBRAL BODY TREATED BY LIGATION OF THE SEGMENTAL ARTERIES Report of a Case T. BUCKNILL, J. W. JACKSON, H. B. S. KEMP, STANMORE, ENGLAND, and B. E. KENDALL, LONDON, ENGLAND hoot The
Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Research of thoracolumbar spine lateral vascular anatomy and imaging
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 69, No. 3, pp. 128 133 Copyright 2010 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Research of thoracolumbar spine lateral vascular anatomy and imaging
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 69, No. 3, pp. 128 133 Copyright 2010 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Research of thoracolumbar spine lateral vascular anatomy and imaging
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
 Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Multidetector CT has enlarged our view of human vascular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.H. Heo Y.J. Cho S.H. Sheen M.S. Hong S.M. Cho S.H. Park 3D Reconstructions of Spinal Using CT Angiography: Applications in Minimally Invasive Spinal Procedures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.H. Heo Y.J. Cho S.H. Sheen M.S. Hong S.M. Cho S.H. Park 3D Reconstructions of Spinal Using CT Angiography: Applications in Minimally Invasive Spinal Procedures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs
 Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs A CADAVER AND RADIOLOGICAL STUDY S. W. Suh, V. U. Shingade, S. H. Lee, J. H. Bae, C. E. Park, J. Y. Song From the University
Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs A CADAVER AND RADIOLOGICAL STUDY S. W. Suh, V. U. Shingade, S. H. Lee, J. H. Bae, C. E. Park, J. Y. Song From the University
In the Last Three Lectures We Already Discussed the Importance of the Thoracic Cage.
 -This Lecture Will Revise what we took in the last three lectures and will introduce the concept of the chest cavity ( Thoracic Cavity ) In the Last Three Lectures We Already Discussed the Importance of
-This Lecture Will Revise what we took in the last three lectures and will introduce the concept of the chest cavity ( Thoracic Cavity ) In the Last Three Lectures We Already Discussed the Importance of
Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept
 www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 15: 363-368, 2009 Letter to the Editor Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept M. KOMIYAMA Department of Neurosurgery, Osaka City General Hospital;
www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 15: 363-368, 2009 Letter to the Editor Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept M. KOMIYAMA Department of Neurosurgery, Osaka City General Hospital;
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22,
 JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
Intercostal Muscles LO4
 Intercostal Muscles LO4 4 List the structures, from superficial to deep, in an intercostal space. Describe their relationships to each other, to the associated neurovascular bundle and to the pleural cavity.
Intercostal Muscles LO4 4 List the structures, from superficial to deep, in an intercostal space. Describe their relationships to each other, to the associated neurovascular bundle and to the pleural cavity.
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
MD Bones & Joints of the Back. A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle
 Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
Anatomy Lecture #19 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THORAX April 3, 2012
 Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study
 Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study Bina.K.Katariya 1*, Priyank Bhabhor 2, H.R.Shah 3. 1, 2 Third year resident, 3 Additional Professor, Department of anatomy, B.J.Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Accessory Renal Arteries: A Cadaveric Study Bina.K.Katariya 1*, Priyank Bhabhor 2, H.R.Shah 3. 1, 2 Third year resident, 3 Additional Professor, Department of anatomy, B.J.Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam
 Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center
 Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center Leo Happel disclosed no financial relationships Vascular Lesions of the Spinal Cord The vast majority
Leo Happel, PhD Professor, Neurology, Neurosurgery, Physiology, and Neuroscience LSU Health Science Center Leo Happel disclosed no financial relationships Vascular Lesions of the Spinal Cord The vast majority
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin
 PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
VARIANT ORIGIN OF RENAL ARTERIES AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION
 VARIANT ORIGIN OF RENAL ARTERIES AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION Krunal Chauhan,*Shweta J. Patel, Rashvaita K. Patel, Mehta C.D. and Maunil Desai Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Surat,
VARIANT ORIGIN OF RENAL ARTERIES AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION Krunal Chauhan,*Shweta J. Patel, Rashvaita K. Patel, Mehta C.D. and Maunil Desai Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Surat,
Surgical anatomy of the juxta dural ring area
 J Neurosurg 89:250 254, 1998 Surgical anatomy of the juxta dural ring area SUSUMU OIKAWA, M.D., KAZUHIKO KYOSHIMA, M.D., AND SHIGEAKI KOBAYASHI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School
J Neurosurg 89:250 254, 1998 Surgical anatomy of the juxta dural ring area SUSUMU OIKAWA, M.D., KAZUHIKO KYOSHIMA, M.D., AND SHIGEAKI KOBAYASHI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
The descending thoracic aorta morphological characteristics
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2016; 3(22): 186-191 10.1515/arsm-2016-0031 Malik S., Bordei P., Rusali A., Iliescu D. M. The descending thoracic aorta morphological characteristics Faculty of Medicine, Ovidius
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2016; 3(22): 186-191 10.1515/arsm-2016-0031 Malik S., Bordei P., Rusali A., Iliescu D. M. The descending thoracic aorta morphological characteristics Faculty of Medicine, Ovidius
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report. K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs, B Odion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Abnormal Pattern Of Brachial Plexus Formation: An Original Case Report K Oluyemi, O Adesanya, D Ofusori, C Okwuonu, V Ukwenya, F Om'iniabohs,
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
An Anomalous Case of A. Subclavia Dextra Rising from Arcus Aortae as the Last Branch. Hiroshi Hanai, Atsuko Ryumon, Kenji Kamakura
 An Anomalous Case of A. Subclavia Dextra Rising from Arcus Aortae as the Last Branch By Hiroshi Hanai, Atsuko Ryumon, Kenji Kamakura and Seiji Kaneko Department of Anatomy, Osaka Dental College, Osaka
An Anomalous Case of A. Subclavia Dextra Rising from Arcus Aortae as the Last Branch By Hiroshi Hanai, Atsuko Ryumon, Kenji Kamakura and Seiji Kaneko Department of Anatomy, Osaka Dental College, Osaka
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
Relation of Paralumbar Nerves and Conus Medullaris to the Vertebrae of Swamp Buffaloes
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 37 : 41-46 (2003) Relation of Paralumbar Nerves and Conus Medullaris to the Vertebrae of Swamp Buffaloes Narong Chungsamarnyart, Worawut Rerkamnuaychoke and Nati Nilnophakoon ABSTRACT
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 37 : 41-46 (2003) Relation of Paralumbar Nerves and Conus Medullaris to the Vertebrae of Swamp Buffaloes Narong Chungsamarnyart, Worawut Rerkamnuaychoke and Nati Nilnophakoon ABSTRACT
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Surgical anatomy of the juxtadural ring area
 Surgical anatomy of the juxtadural ring area Susumu Oikawa, M.D., Kazuhiko Kyoshima, M.D., and Shigeaki Kobayashi, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine, Matsumoto, Japan
Surgical anatomy of the juxtadural ring area Susumu Oikawa, M.D., Kazuhiko Kyoshima, M.D., and Shigeaki Kobayashi, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine, Matsumoto, Japan
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Pulmonary vascular anatomy & anatomical variants
 Review Article Pulmonary vascular anatomy & anatomical variants Asha Kandathil, Murthy Chamarthy Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA Contributions:
Review Article Pulmonary vascular anatomy & anatomical variants Asha Kandathil, Murthy Chamarthy Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA Contributions:
Variations In Branching Pattern Of Coeliac Trunk
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. IV (Nov. 2015), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Variations In Branching Pattern Of Coeliac
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. IV (Nov. 2015), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Variations In Branching Pattern Of Coeliac
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Congenital Absence of IVC with Azygous Continuation
 Congenital Absence of IVC with Azygous Continuation M. J. Rauf ( Departments of Radiology, Liaquat National Postgraduate Medical Center, Karachi. ) K. R. Makhdoomi ( Departments of Vascular Surgery, Liaquat
Congenital Absence of IVC with Azygous Continuation M. J. Rauf ( Departments of Radiology, Liaquat National Postgraduate Medical Center, Karachi. ) K. R. Makhdoomi ( Departments of Vascular Surgery, Liaquat
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
SAMPLE EDITION PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION. Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines
 Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
LECTURE -I. Intercostal Spaces & Its Content. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Date:
 LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study
 Original article: Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study 1Dr.VaishaliBondge*, 2 Dr. Ashok Khade, 3 Dr. P.H.Shingare 1Assistant Professor, Grant Medical College, Mumbai,
Original article: Variations of median nerve and musculocutaneous nerve: Cadeveric study 1Dr.VaishaliBondge*, 2 Dr. Ashok Khade, 3 Dr. P.H.Shingare 1Assistant Professor, Grant Medical College, Mumbai,
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR
 cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla
 Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
