6/5/2010. Outline of Talk. Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Metaplastic / reactive changes. Problems in Biopsies/Curettages
|
|
|
- Edmund Bartholomew Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline of Talk Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Problems in Biopsies/Curettages Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Papillary metaplasia Arias Stella / clear cell / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Joseph Rabban MD MPH Associate Professor Atypical changes in endometriosis Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma Minimal Diagnostic Criteria Atypical Hyperplasia (WHO System) Diagnostic Criteria Kurman et al. Cancer 1985; Architecture: Gland Fusion Loss of Endometrial Stroma Expansive Labrynthine Pattern Atypical Cytology: Enlarged nuclei Round, oval nuclei Vacuolated chromatin Nucleoli Loss of polarity 1
2 Outline of Talk Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Papillary metaplasia Arias Stella / clear cell / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis Clinical Correlation Red Flags in EMB with Benign Findings Post-menopausal patient Thickened endometrial stripe on ultrasound Uterine mass on imaging Prior history of atypical hyperplasia or cancer Morphologic Red Flags in EMB with Benign Findings: Foamy histiocytes in endometrial stroma Atypical hyperplasia Endometrioid adenocarcinoma Abundant necrosis Degenerative or neoplastic origin Is sampling representative of target? Outline of Talk Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis 2
3 Mucinous Change in Endometrium Mucinous endometrium with gland complexity Intracytoplasmic mucin without gland complexity Within spectrum of normal endometrium In degenerating endometrium (breakdown) Mucinous endometrium with gland complexity Possibly tip of the iceberg of adenocarcinoma Risk of unsampled cancer Risk in EMB: unsampled adenocarcinoma (up to 64% to 100%) Typically low grade Mucinous or endometrioid adenocarcinoma Confined to endometrium Risk is a function of architectural complexity Cribriform pattern, rigid pseudolumens Microglandular pattern Villous / papillary pattern Extensive glandular budding Nucci et al. Mod Pathol 1999; 12:1137 Vang et al. Int J Surg Pathol 2003; 11: 261 Mucinous proliferation in EMB Mucinous proliferation in EMB 3
4 Architectural complexity raises further concern despite lack of cytologic atypia EMB: Mucinous proliferation Hysterectomy: Mucinous adenocarcinoma Architectural complexity raises further concern despite lack of cytologic atypia Architectural complexity raises further concern despite lack of cytologic atypia 4
5 Architectural complexity raises further concern despite lack of cytologic atypia Foamy stromal histiocytes raise further concern Foamy stromal histiocytes raise further concern EMB: Mucinous proliferation with foamy histiocytes Hysterectomy: Mucinous adenocarcinoma 5
6 Recommended Diagnosis: Differential Diagnosis of Mucinous Glands in EMB Complex mucinous glandular proliferation. Comment: Discuss risk of unsampled cancer. Provide references: Nucci et al. Mod Pathol 1999; 12:1137 Vang et al. Int J Surg Pathol 2003; 11: 261 Normal endocervical mucosa Endocervical adenocarcinoma, intestinal type Non-GYN mucinous adenocarcinoma Colorectal/upper GI Pancreas Lung Endocervical adenocarcinoma, intestinal type Signet ring colorectal / gastric cancer in EMB 6
7 Outline of Talk Microglandular hyperplasia-like changes in EMB Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis Endocervix with MGH Typical MGH Atypical MGH MGH-like uterine adenocarcinoma Typically mucinous or endometrioid cancer MGH-like change is at surface/periphery Often post-menopausal patients MGH involving endocervical polyp Typical MGH of Endocervix 7
8 Atypical MGH of Endocervix Solid MGH of Endocervix Solid / sheet like pattern (mimic clear cell carcinoma) Reticular pattern ( mimic yolk sac tumor) Myxoid stroma (creates pseudoinfiltrative appearance) Mitoses (<1 per 10 hpf) Mild atypia Young et al. Am J Surg Pathol 1989: 13:50 Solid MGH of Endocervix MGH-like Endometrial Adenocarcinoma Clinical Post-menopausal age Not linked to exogenous hormone use Morphology Mucinous or endometrioid adenocarcinoma Grade 1, Stage 1A MGH-like changes at tumor surface / periphery Zaloudek et al. Int J Gyn Pathol 1997; 16: 52 Young et al. Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:
9 Mucinous adenocarcinoma with MGH-like surface MGH-like proliferation Mucinous adenocarcinoma with MGH-like surface MGH-like proliferation 9
10 Mucinous adenocarcinoma with MGH-like surface Mucinous adenocarcinoma with MGH-like surface MGH-like carcinoma is deceptive in EMB MGH-like morphology: benign or malignant? 10
11 MGH-like morphology: depends on sampling MGH-like Findings in EMB Recommended Approach: Use caution before reporting endocervical MGH in EMB especially in post-menopausal women Unless clear cut evidence of endocervical tissue associated with the MGH-like changes: Report as MGH-like proliferation Comment on sampling issue and DDX Outline of Talk Squamous Metaplasia in EMB Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis Squamous metaplasia (non-morular) Morular squamous metaplasia Keratin granulomas outside of uterus 11
12 Squamous differentiation in benign EMB Squamous differentiation in malignant EMB Squamous Metaplasia (non-morular) in EMB Isolated, focal, scattered distribution? reactive to irritation, trauma, infection No significance on its own Differential diagnosis: Placental site nodule Extension of cervical dysplasia/carcinoma Endometrial squamous cell carcinoma Ichthyosis uteri Placental Site Nodule Epithelioid cells embedded in hyaline nodule Positive keratin, inhibin, PLAP 12
13 Endometrial Extension of Cervical HSIL Myometrial Invasion by Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Ichthyosis Uteri Rare benign alteration Stratified proliferation of benign squamous cells replacing endometrium Associated with: chronic endometritis heat ablation of endometrium Squamous Squamous Placental Ichthyosis Metaplasia Dysplasia Site Nodule Uteri Distribution Focal Diffuse Atypia None Present None None Mitoses None/rare Present None None Hyaline stroma Present 13
14 Morular metaplasia in EMB Morular metaplasia in EMB Well-defined circumscribed solid round nests Squamous differentiation (cytologically bland) Fill and expand underlying existing glands Central necrosis common Most common: Less common: atypical hyperplasia grade 1 adenocarcinoma hyperplasia atypical polypoid adenomyoma Significance Risk of subsequent carcinoma: 5% of morules in non-atypical hyperplasia 19% of morules in atypical endometrium Interpretation: Lin et al Mod Pathol 2009; 22: 167 Based on the surrounding glands non-atypical hyperplasia or proliferative pattern? atypical hyperplasia? adenocarcinoma? Not based on the morule itself Crowded glands + squamous morules 14
15 Diagnosis Depends on Glandular Epithelium Not Squamous Cells Differential Diagnosis of Morular Metaplasia Atypical Polypoid Adenomyoma Epithelioid Uterine Smooth Muscle Tumor Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor Uterine PEComa Cervical Squamous Dysplasia/Cancer Atypical Polypoid Adenomyoma Unique Clinical Entity Typically years old Lower uterine segment Exophytic/polypoid growth Limited recurrent potential Local excision Polypoid glandular proliferation Foci of atypical hyperplasia Myoid / fibromyoid stroma Squamous morules Central necrosis Atypical Polypoid Adenomyoma 15
16 Atypical endometrium in APA Morules in APA Morules in APA Myoid stroma in APA 16
17 Differential Diagnosis of Morular Metaplasia Epithelioid Leiomyoma Atypical Polypoid Adenomyoma Epithelioid Uterine Smooth Muscle Tumor Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor Uterine PEComa Rare! Cervical Squamous Dysplasia/Cancer Epithelioid Leiomyoma Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor 17
18 Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor Uterine PEComa HMB45 Uterine PEComa Desmin Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas Granulomatous peritonitis admixed with Keratin Anucleate squamous cells No adenocarcinoma Patients with endometrioid adenocarcinoma Uterus (or uterine APA) Ovary Tube Significance: None (in the absence of adenocarcinoma in granuloma) Do not upstage AJCC/FIGO based on this alone 18
19 Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas Other Origins of Peritoneal Keratin Granulomas GYN endometrioid adenocarcinoma Ruptured ovarian teratoma squamous epithelium spilled into peritoneum Spilled amniotic fluid (vernix caseosa peritonitis) traumatic C-section Peritoneal squamous metaplasia without granulomas Intraperitoneal renal-dialysis 19
20 Vernix Caseosa Peritonitis ( reaction to spilled amniotic fluid) Squamous Metaplasia of Peritoneum Peritoneal dialysis Peritonitis Hosfield et al. Int J Gyn Pathol 2008; 27: 465 Outline of Talk Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis Atypical Hyperplasia / Grade 1 Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma Surgery Management Options Non-surgical: High Dose Progestin Pre-menopausal desiring fertility Poor surgical candidate 20
21 High dose Progestin Therapy High dose Progestin Therapy Oral progestin or progesterone-releasing IUD Down-regulates ER Success in 60-70% patients May take up to 9-12 months to achieve success Interval 3 month surveillance samplings Progestin Start Atypia EMB EMB EMB 3 months 6 months 9 months No atypia Successful No Surgery Progestin Start Atypia Atypia High dose Progestin Therapy EMB EMB EMB 3 months 6 months 9 months Atypia Cancer Pathology of Interval Samples on Progestin What do we need to report? Presence or absence of atypical findings Comparison to original EMB and prior surveillance EMB Quantity of atypia: More / same / less Quality of atypia: Worse / same / less Hysterectomy 21
22 Pathology of Interval Samples on Progestin Pathology of Interval Samples on Progestin Progestin effects on atypia / cancer Reduction in architectural complexity Reduction in cytologic atypia Reduction in quantity of abnormalities Successful end point: No residual atypical findings Decidualized stroma Sparse, atrophic benign glands Atypical Architecture Crowding Papillary / branching Fusion Cribriform Atypical Cytology Nucleoli Coarse chromatin Any 1 feature: Residual Disease Wheeler et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2007; 31: 988 Residual Disease on High dose Progestin Therapy Residual Disease on High dose Progestin Therapy Progestin Start EMB EMB EMB Progestin Start EMB EMB EMB 3 months 6 months 9 months 3 months 6 months 9 months continue Progestin 40% will be successful unlikely successful 40% will be successful unlikely successful Hysterectomy Wheeler et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2007; 31:
23 Successful Progestin 6 months Complex atypical hyperplasia No residual gland crowding Successful Progestin 6 months No gland crowding, irregular shapes or cytologic atypia Residual Disease in Interval Samples on Progestin Pre Treatment Progestin, 3 months Progestin, 10 months Any 1 Feature Atypical Architecture Crowding Papillary / branching Fusion Cribriform Atypical Cytology Nucleoli Coarse chromatin may not be present Wheeler et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2007; 31:
24 Residual Disease in Interval Samples on Progestin Complex Atypical Hyperplasia 36 y woman desires fertility preservation May not fullfill WHO criteria for atypia May look like benign polyp or crowding May look cytologically bland BUT..patient needs continued therapy Residual Progestin-treated atypical 4 months Residual Progestin-treated complex atypical 4 months atypical nuclei non-atypical nuclei 24
25 Residual Progestin-treated complex atypical months Residual crowding without cytologic atypia is still abnormal and requires continued therapy Squamous metaplasia in residual disease on Progestin Squamous metaplasia in residual disease on Progestin 25
26 Squamous metaplasia in residual disease on Progestin Squamous metaplasia in residual disease on Progestin Morules do not express hormone receptors Reporting Surveillance EMB on Progestin Residual Progestintreated hyperplasia ER PR Avoid a premature message of success WHO criteria may not be met by abnormalities that still require treatment. 26
27 Reporting Surveillance EMB on Progestin Decidualized Stroma: A Red Flag in Otherwise Benign Non-secretory EMB If no residual disease: be descriptive If residual disease persists If it meets WHO criteria for atypia/cancer Residual treated adenocarcinoma Residual treated atypical hyperplasia Compare to prior EMB If it does not meet WHO criteria Residual treated atypical glandular proliferation Comment and compare to prior EMB Common reasons to have decidualized stroma: Contraception (oral or IUD) Hormone replacement therapy Treatment of atypia / cancer Outline of Talk Alterations in Endometriosis Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis Proliferative / architectural alteration: Hyperplasia with or without atypia Polypoid endometriosis Borderline mucinous tumor Adenocarcinoma (Endometrioid / Clear Cell) Adenosarcoma / Endometrial stromal tumor Non-proliferative / cytologic alteration: Nuclear atypia without hyperplasia 27
28 Endometriosis May Give Rise to Adenocarcinoma Atypia May be Seen in Transition to Cancer Atypical Hyperplasia May Arise in Endometriosis Clinical Significance of Atypia in Endometriosis When There is No Cancer and No Hyperplasia? Non-proliferative endometriosis with: Variable Nuclear Enlargement Variable Nuclear Shapes Nucleoli Hobnail Pattern Clear Cytoplasm 28
29 Atypia without hyperplasia in endometriosis Atypical Endometriosis (without hyperplasia) Atypical cytology: Nuclear enlargement Nucleocytomegaly Hyperchromasia Tiny nucleoli Significance: Smudged / degenerative chromatin None Follow up advised Seidman et al. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1996;15:1 Czernobilsky et al. Obstet Gynecol 1979; 53:318 Atypical Endometriosis: Nucleoli Atypical Endometriosis: Smudged chromatin 29
30 Atypical Endometriosis Clear cytoplasm Hobnail Pattern Mucinous change in Endometriosis Tubal (Ciliated) Metaplasia in Endometriosis Not Atypical 30
31 Squamous Metaplasia in Endometriosis Squamous Metaplasia in Endometriosis: Consider Extra Sampling to Exclude Cancer Atypical endometriosis and inflammation: Reactive etiology? Atypical endometriosis and inflammation: Reactive etiology? 31
32 Atypical endometriosis and inflammation: Reactive etiology? Atypia without hyperplasia in endometriosis Differential Diagnosis Reactive atypia Serous carcinoma in endometriosis Clear cell carcinoma in endometriosis Severe atypia + brisk mitoses in endometriosis Serous Carcinoma Severe atypia + brisk mitoses in endometriosis Serous Carcinoma p53 32
33 Clear cytoplasm + papillary buds + nuclear atypia in endometriosis Need to exclude Clear Cell Carcinoma Clear cell carcinoma arising in endometriosis Atypia without hyperplasia in endometriosis Endometriosis Adenocarcinoma Check how much of tissue is sampled Peritoneal biopsy or Oophorectomy? Consider additional sampling to exclude cancer 33
34 Recommended Diagnosis: Outline of Talk Atypical endometriosis. Comment: No hyperplasia or cancer Advise follow-up References: Seidman et al. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1996;15:1 Czernobilsky et al. Obstet Gynecol 1979; 53:318 Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia Arias Stella / hobnail change Evaluating hormonally treated atypia/cancer Atypical changes in endometriosis 34
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience
 Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions
 Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Page # 1. Endometrium. Cellular Components. Anatomical Regions. Management of SIL Thomas C. Wright, Jr. Most common diseases:
 Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Case 3 - GYN. History: 66 year old, routine Pap test. Dr. Stelow
 Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS
 ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
Disclosure. Case. Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix. I have nothing to disclose
 Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Endometrial hyperplasia vs. Intraepithelial neoplasia. Martin Chang, MD PhD FRCPC Pathology Update Friday November 9, 2012
 Endometrial hyperplasia vs. Intraepithelial neoplasia Martin Chang, MD PhD FRCPC Pathology Update Friday November 9, 2012 Disclosure No relevant financial conflicts to declare. Case 1 Gland crowding Gland
Endometrial hyperplasia vs. Intraepithelial neoplasia Martin Chang, MD PhD FRCPC Pathology Update Friday November 9, 2012 Disclosure No relevant financial conflicts to declare. Case 1 Gland crowding Gland
Endometrial pathology. Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England
 Endometrial pathology Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England Case 1 Female age 35 Case 1 Proliferative endometrium Case 2 Female age 38 Case 2 Secretory endometrium Dating endometrium Assessed on the
Endometrial pathology Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England Case 1 Female age 35 Case 1 Proliferative endometrium Case 2 Female age 38 Case 2 Secretory endometrium Dating endometrium Assessed on the
OUTLINE. Case History 1/28/2013. Endometrial Neoplasia, Including Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia (EIN)
 Endometrial Neoplasia, Including Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia (EIN) TEXAS SOCIETY OF PATHOLOGISTS ANNUAL MEETING Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Brigham and Women
Endometrial Neoplasia, Including Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia (EIN) TEXAS SOCIETY OF PATHOLOGISTS ANNUAL MEETING Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Brigham and Women
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo. Case Discussions. 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC
 BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus
 Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000
 Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
05/07/2018. Types of challenges. Challenging cases in uterine pathology. Case 1 ` 65 year old female Post menopausal bleeding Uterine Polyp
 Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
 Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Index. Cytoplasm, nonepithelial malignant tumor features 70
 Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Parasitism as a potential contributor to massive clam mortality at the Blake Ridge Diapir methane-hydrate seep
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231960327 Parasitism as a potential contributor to massive clam mortality at the Blake Ridge
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231960327 Parasitism as a potential contributor to massive clam mortality at the Blake Ridge
6/3/2010. Outline of Talk. Lobular Breast Cancer: Definition of lobular differentiation. Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies
 Outline of Talk Lobular Breast Cancer: Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies Definition of lobular differentiation Variants of LCIS that: carry risk for unsampled invasive cancer mimic DCIS
Outline of Talk Lobular Breast Cancer: Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies Definition of lobular differentiation Variants of LCIS that: carry risk for unsampled invasive cancer mimic DCIS
The incidence of cervical adenocarcinoma (ADC) has
 Cervical Adenocarcinoma of Human Papillomavirus Positive and Human Papillomavirus Negative Tumors Edyta C. Pirog, MD, PhD Context. Cervical adenocarcinomas span a diverse group of tumors with several distinct
Cervical Adenocarcinoma of Human Papillomavirus Positive and Human Papillomavirus Negative Tumors Edyta C. Pirog, MD, PhD Context. Cervical adenocarcinomas span a diverse group of tumors with several distinct
Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma
 THE 1999 LONG COURSE ON PATHOLOGY OF THE UTERINE CORPUS AND CERVIX Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Steven G. Silverberg, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
THE 1999 LONG COURSE ON PATHOLOGY OF THE UTERINE CORPUS AND CERVIX Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Steven G. Silverberg, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
3/24/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Mixed Epithelial Endometrial Carcinoma. ISGyP Endometrial Cancer Project
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Intravascular Endometrium Mimicking Vascular Invasion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland.
 UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
PAPILLARY PROLIFERATION OF THE ENDOMETRIUM: A BENIGN LESION SIMULATING ADENOCARCINOMA.
 PAPILLARY PROLIFERATION OF THE ENDOMETRIUM: A BENIGN LESION SIMULATING ADENOCARCINOMA. Teresa Pusiol, Maria Grazia Zorzi, Doriana Morichetti U.O. Anatomia Patologica Ospedale S. Maria del Carmine Rovereto
PAPILLARY PROLIFERATION OF THE ENDOMETRIUM: A BENIGN LESION SIMULATING ADENOCARCINOMA. Teresa Pusiol, Maria Grazia Zorzi, Doriana Morichetti U.O. Anatomia Patologica Ospedale S. Maria del Carmine Rovereto
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
 SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial Stromal Tumors
 Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Low-grade serous neoplasia. Robert A. Soslow, MD
 Low-grade serous neoplasia Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org Outline Orientation Ovarian tumor overview Non serous borderline tumors Serous borderline tumors Clinical summary Morphologic description
Low-grade serous neoplasia Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org Outline Orientation Ovarian tumor overview Non serous borderline tumors Serous borderline tumors Clinical summary Morphologic description
EU guidelines for reporting gynaecological cytology
 EU guidelines for reporting gynaecological cytology Amanda Herbert Guy s & St Thomas Foundation NHS Trust 5th EFCS Annual Tutorial, Trondheim, Norway 28 th May 1 st June 2012 EU guidelines aim to harmonize
EU guidelines for reporting gynaecological cytology Amanda Herbert Guy s & St Thomas Foundation NHS Trust 5th EFCS Annual Tutorial, Trondheim, Norway 28 th May 1 st June 2012 EU guidelines aim to harmonize
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon. Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology
 Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Received, June 29, 1904; accepted for publication
 THE AMEBICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1964 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 42, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. CARCINOMA IN SITU OF THE ENDOMETRIUM ISABELLE A. BUEHL, M.D., PRANK VELLIOS, M.D.,
THE AMEBICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1964 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 42, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. CARCINOMA IN SITU OF THE ENDOMETRIUM ISABELLE A. BUEHL, M.D., PRANK VELLIOS, M.D.,
What s (new) and Important in Reporting of Uterine Cancers Katherine Vroobel The Royal Marsden
 What s (new) and Important in Reporting of Uterine Cancers Katherine Vroobel The Royal Marsden Maastricht Pathology 2018 Wednesday 20 th June Endometrioid adenocarcinoma High grade carcinomas (common)
What s (new) and Important in Reporting of Uterine Cancers Katherine Vroobel The Royal Marsden Maastricht Pathology 2018 Wednesday 20 th June Endometrioid adenocarcinoma High grade carcinomas (common)
May 2017 TSL workshops. EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses
 May 2017 TSL workshops EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses CASE 1 28 yr old female with menorrhagia. Well diff endometrioid adenocarcinoma (back ground complex hyperplasia) 4 Non-atypical endometrial
May 2017 TSL workshops EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses CASE 1 28 yr old female with menorrhagia. Well diff endometrioid adenocarcinoma (back ground complex hyperplasia) 4 Non-atypical endometrial
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis
 In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
They Do Look Alike : Mimics of Prostate Cancer in Biopsy Samples
 They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
Glandular lesions in cervical cytology. Margareta Strojan Fležar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia
 Glandular lesions in cervical cytology Margareta Strojan Fležar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia 2nd PANNONIA CONGRESS OF PATHOLOGY, SIÓFOK, HUNGARY, 17-19 MAY
Glandular lesions in cervical cytology Margareta Strojan Fležar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia 2nd PANNONIA CONGRESS OF PATHOLOGY, SIÓFOK, HUNGARY, 17-19 MAY
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual Combination
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
Endosalpingiosis. Case report
 Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Case 1. Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno
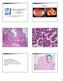 Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives
 Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Wendy L Frankel. Chair and Distinguished Professor
 1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation
 Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation May Yu Director of Cytology Laboratory Service Department of Anatomical & Cellular Pathology Prince of Wales Hospital Cervical
Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation May Yu Director of Cytology Laboratory Service Department of Anatomical & Cellular Pathology Prince of Wales Hospital Cervical
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi. Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat. Ahmad Al-Tarefe
 5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
5 Mousa Al-Abbadi Ola Al-juneidi & Obada Zalat Ahmad Al-Tarefe Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) AUB is a very common scenario or symptom where women complain of menorrhagia (heavy and/or for long periods),
GYN (Glandulars) Still Difficult After All These Years! Dina R Mody, MD Director of Cytology Laboratories and fellowship Program Methodist Hospital
 GYN (Glandulars) Still Difficult After All These Years! Dina R Mody, MD Director of Cytology Laboratories and fellowship Program Methodist Hospital and Bioreference Labs (Houston) Department of Pathology
GYN (Glandulars) Still Difficult After All These Years! Dina R Mody, MD Director of Cytology Laboratories and fellowship Program Methodist Hospital and Bioreference Labs (Houston) Department of Pathology
Morphologic Clues and Pitfalls for High Grade Lesions in Cervical Cytology
 Morphologic Clues and Pitfalls for High Grade Lesions in Cervical Cytology Ritu Nayar, MD Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL, USA Disclosures Editor, Cervical Cytology Bethesda
Morphologic Clues and Pitfalls for High Grade Lesions in Cervical Cytology Ritu Nayar, MD Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago, IL, USA Disclosures Editor, Cervical Cytology Bethesda
Maturation Index 3/29/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Gynecologic Cytology. Normal Maturation of Squamous Epithelium : :
 Gynecologic Cytology Fadi W. Abdul Karim, MD MEd Department of Anatomic Pathology Vice Chair Education RT PLMI Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Ohio Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Gynecologic Cytology Fadi W. Abdul Karim, MD MEd Department of Anatomic Pathology Vice Chair Education RT PLMI Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Ohio Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Hitting the High Points Gynecologic Oncology Review
 Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology
 New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Mody. Atypical Glandular Cells(TBS 2001) Adenocarcinoma In Situ(TBS 2001)
 Glandular Lesions in Cervicovaginal Cytology Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College of Cornell
Glandular Lesions in Cervicovaginal Cytology Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College of Cornell
5/26/2016. Pelvic Serous Carcinoma: 2014 W.H.O. Update. Outline of Talk. Changes to 2014 WHO system for pelvic serous tumors
 Pelvic Serous Carcinoma: 2014 W.H.O. Update Outline of Talk Practical Implications for Pathologists Changes to 2014 WHO system for pelvic serous tumors High grade serous carcinoma versus low grade serous
Pelvic Serous Carcinoma: 2014 W.H.O. Update Outline of Talk Practical Implications for Pathologists Changes to 2014 WHO system for pelvic serous tumors High grade serous carcinoma versus low grade serous
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
5/2/2018. Low Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. High Grade Dysplasia of GI Tract. Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues
 Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
Dysplasia in Gastrointestinal Tract: Practical Pearls and Issues Arief Suriawinata, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Department of Pathology and
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Conflict of Interest 9/7/2018. Dr. Mody 1. None with vendors of cytology equipment/testing/vaccines Amirsys (now Elsevier)
 Glandular Lesions in Cervicovaginal Cytology: Patterns, Pitfalls and Bethesda Updates Dina R Mody, MD Director of Cytology Laboratories Houston s Methodist Hospital and Bioreference Laboratory The Ibrahim
Glandular Lesions in Cervicovaginal Cytology: Patterns, Pitfalls and Bethesda Updates Dina R Mody, MD Director of Cytology Laboratories Houston s Methodist Hospital and Bioreference Laboratory The Ibrahim
intraepithelial neoplasia: a premalignant lesion?
 J Clin Pathol 1986;39:22-28 Cervical glandular atypia associated with squamous intraepithelial neoplasia: a premalignant lesion? LJR BROWN, M WELLS From the Department of Pathology, University ofleeds,
J Clin Pathol 1986;39:22-28 Cervical glandular atypia associated with squamous intraepithelial neoplasia: a premalignant lesion? LJR BROWN, M WELLS From the Department of Pathology, University ofleeds,
CME/SAM. KRAS Mutations in Mucinous Lesions of the Uterus
 AJCP / Original Article KRAS Mutations in Mucinous Lesions of the Uterus Mai He, MD, PhD,,2 Cynthia L. Jackson, PhD, 2,3 Rebecca Buell Gubrod, MD,,2 Virginia Breese, 3 Margaret Steinhoff, MD,,2 W. D. Lawrence,
AJCP / Original Article KRAS Mutations in Mucinous Lesions of the Uterus Mai He, MD, PhD,,2 Cynthia L. Jackson, PhD, 2,3 Rebecca Buell Gubrod, MD,,2 Virginia Breese, 3 Margaret Steinhoff, MD,,2 W. D. Lawrence,
What really matters When and Why. Pathology of Uterine Mesenchymal Lesions. Nafisa Wilkinson London
 What really matters When and Why Pathology of Uterine Mesenchymal Lesions Nafisa Wilkinson London Patient centred approach immunohistochemistry Histological diagnosis Next generation sequencing Genetic
What really matters When and Why Pathology of Uterine Mesenchymal Lesions Nafisa Wilkinson London Patient centred approach immunohistochemistry Histological diagnosis Next generation sequencing Genetic
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Index 179. Genital tract contaminants, 17, 20, 22, 150 papilloma virus-infected cells, 47 squamous cells, sources of, 7
 Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology. Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT
 Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT Case 1 History: 50 year old woman with a uterine mass
Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT Case 1 History: 50 year old woman with a uterine mass
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
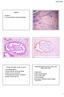 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Female genital tract II.
 Female genital tract II. Pathology of the uterine corpus Lilla Madaras 2 nd Department Of Pathology Semmelweis University Budapest 9 th April 2018 Anatomy 2 The normal endometrium Histology Regulation
Female genital tract II. Pathology of the uterine corpus Lilla Madaras 2 nd Department Of Pathology Semmelweis University Budapest 9 th April 2018 Anatomy 2 The normal endometrium Histology Regulation
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
4/12/2018. MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, Jesse K. McKenney, MD
 MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours. Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh
 Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate
 Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Cytyc Corporation - Case Presentation Archive - March 2002
 FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
