Always changing & growing up
|
|
|
- James Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Always changing & growing up Always Changing Boy s Guide
2 Questions about puberty? Try talking with your dad or with another adult you trust, like your older brother, grandfather, uncle, mom, coach, doctor or nurse. Asking questions about private stuff isn t always easy, but here are some tips that might help: Remember, it s normal to feel awkward or embarrassed. If your dad seems busy, just say, There s something I d like to ask you about when you have time. This way you won t keep putting off the discussion. You don t have to learn everything at once. One question at a time is a great way to start. Show your dad or other trusted adult this booklet, and ask him to look through it with you. Contents What s happening? 4 Growing up and out 6 Feeling good in your skin 10 Healthy hair 12 No sweat! 14 The way it works 16 Glossary
3 What s happening? This is a booklet about growing up. Now that you re growing up, you ll probably notice that your body is changing in all sorts of ways. You ll notice changes in the way you look and also in the way you feel. This is because you re going through a stage called puberty. This is an exciting time it s when you start to change from being a boy to becoming a man. Puberty for boys usually starts between the ages of 10 and 17, and lasts for a few years. Everyone is different, though, and it doesn t matter when you start your body will decide when the time is right. Don t worry These changes won t suddenly happen overnight. You ll notice that some happen quickly, but others take place slowly over a few years. New words? All the words in orange bold type are defined in the glossary on pages 22 and 23. This booklet will tell you about all the changes to expect during puberty. It will also answer many of the questions you might want to ask. Just remember that puberty is a normal and healthy part of life and it happens to everyone! 4 5
4 Growing up & out Puberty starts when a gland just beneath the front of your brain the pituitary gland sends a signal for your body to start making some special chemicals. One of these chemicals or hormones is called testosterone, and it is produced in your testicles. Testosterone is responsible for many of the changes that are beginning to happen. Females have a different hormone responsible for their body changes. It s called estrogen. You ll know you are starting to go through puberty when you suddenly start to grow taller. You will also notice that your muscles will develop, your chest will become broader, and you ll probably start to gain weight. Don t worry if your friends seem to be growing more quickly than you. You ll soon catch up. Don t worry Some of these changes don t sound like a great deal of fun who wants body odor, oily hair and pimples? But they are all normal, and can be managed with good hygiene habits. Remember, your body is your responsibility. Treat it with respect. Boys go through many changes during puberty. The main ones are: Your body grows taller. Your muscles develop and your chest gets broader. Your body may sweat more and you will develop body odor. Your hair may become more oily. Your skin may become oily and pimples may develop. Hair starts to grow under your arms, on your legs, in the pubic area around the base of your penis, on your face and sometimes on your chest. Your voice begins to sound deeper and may crack as you talk. Your penis and testicles become bigger and sperm begins to be produced. How do I get my parents to accept that I m almost an adult? Even preteens feel grown up, so you may resent the fact that your parents still see you as a child. When you disagree with them about being ready for new responsibilities, talking honestly with them about your disagreement is the only way to resolve it. Puberty can be difficult for parents, too. Be patient as you prove you re ready for more responsibility, and negotiate with your parents for more freedom. 6 7
5 Body growth Is it normal to put on weight during puberty? Definitely. An adult man has a broader and more muscular body than a young boy. Puberty is not a good time to limit the amount of food you eat. You are meant to put on weight during puberty because your body is growing. As long as you eat healthy and stay active, there shouldn t be any need to worry about your weight. You are likely to put on more weight than your body needs only if you eat too many fatty and sugary foods and don t get enough exercise. Help I think I m growing breasts. Don t worry, you re not turning into a girl. It s normal for boys to have some swelling around the breasts and nipples. This area can also feel a bit sore. It won t last for long and will soon go away. Why do some parts of the body mature more quickly than others? Growth of the testicles is typically the earliest sign of puberty, but body changes can occur in a different order and still be normal. There s also a wide range of individual differences in the growth of other parts of the body feet, hands, shoulders, legs, etc. Many different growth patterns are normal; everybody and every body is unique. How tall will I be? It s difficult to predict, but height is usually determined by heredity how tall your parents and grandparents are. If both parents are tall, chances are you will be tall. If both parents are short, you may be shorter. But this is not always true everybody is different. Occasionally, a boy will continue to grow or get another growth spurt in his late teens. Does a lot of body hair mean you have more testosterone? No, testosterone is the hormone that starts the body hair growing. How much hair you have is determined by your racial/ethnic group and heredity. Voice As you mature, your voice will deepen. You may experience your voice cracking or changing pitch in mid-sentence. That s because your vocal cords are growing and changing just like the rest of you. Don t worry If you have some questions, it s always good to talk to someone. The best person is probably your dad or your mom. But if you don t feel comfortable talking to them, choose another older person you trust an uncle, a friend s parent, a teacher or coach, a school nurse. You could also talk to an older brother or friends at school, if they ve already experienced some of the changes of puberty themselves. 8 9
6 Feeling good in your skin During puberty the oil glands in your skin become more active, producing excess amounts of an oily substance called sebum. Skin care is especially important during this time. Acne What is it? Acne ( pimples ) is a natural occurrence. It starts when the skin s pores become blocked with dead skin cells and sebum, which slows down or stops the flow of sebum to the skin surface. Bacteria can then develop in the clogged pore, causing a pimple. Doctors describe acne as: Mild A few pimples on the face, back or chest. Most teenagers usually experience this type of acne. It can be treated with products bought from a supermarket or pharmacy. Moderate Around 20 to 60 small- to medium-size pimples over the face, back or chest. It can be treated by a family doctor. Severe This type of acne is rare and is treated by a family doctor or specialist (dermatologist). Tips n Tricks For taking care of your skin: Help prevent acne by establishing a twice-daily cleansing routine with a medicated acne wash or cleanser. Don t be afraid to ask for help. Take good care of your general health and well-being. Don t squeeze, pick or pop pimples. This can make them worse and cause scarring. Be patient. Don t expect acne to disappear overnight. Body hair, facial hair and shaving Hair will start to grow under your arms, on your legs, in the pubic area around the base of your penis, on your face and perhaps on your chest. At some point you ll probably want to start shaving the hair on your face, but that will be your decision. Some men like to shave off the fine hair that grows first. Others prefer to wait until the hair becomes darker and thicker. It may be some time before you ll need to shave every day. When will I shave? It depends on how soon your facial hair appears and how thick it becomes, as well as your personal preference. Generally, heavy facial hair doesn t develop until later in puberty, maybe not until you re 16 or older
7 Healthy hair Just as you look after your skin, you should also look after your hair and scalp. Healthy hair is all about choosing the right hair care products and using them right. Nourish and protect your hair Develop a routine for taking care of your hair, just as you do for your skin. It s simple: just use a good shampoo, followed by a conditioner, every time you wash your hair. A good shampoo not only cleans your hair, it can also help protect your hair from damage and can nourish it too. A conditioner untangles your hair and makes it easier to manage. It can also help keep it moisturized and protect it from damage. Did you know? We have about 5 million hairs all over our body and 100,000 hairs on our head. Hair grows more during the day than at night and more in summer than in winter. Most people lose between 50 and 150 hairs from their head every day. If hair were not replaced as it is shed, we d be completely bald in 1,000 days. Tips for healthy hair: Shampooing is good for your hair because it helps remove deposits, such as dirt, sebum and styling products. Shampoo your hair regularly (daily if you want to) instead of using soap. Shampoos are made specifically to clean hair. If your hair looks or feels dirty between shampoos, you may need to shampoo more often. Massage conditioner into your hair with your fingertips, so the conditioner can spread throughout your hair. This will help keep your hair healthy looking and strong. If you re a young African-American man, your hair may tend to be dry and delicate. You can protect your hair by shampooing and conditioning it less often, and styling it gently with a wide-tooth comb. If your hair is cut very short, use a sunscreen on your scalp or wear a hat to protect against 12 the harmful effects of the sun. 13
8 No sweat! Another body change during puberty is that your sweat glands produce more sweat (perspiration). Perspiration is normal and important it helps your body regulate its temperature. You have two different kinds of sweat glands. The first type eccrine glands produce perspiration that is clear and odorless. These glands start working at birth. The second type apocrine glands become active only when you start puberty. They produce a different kind of perspiration that can smell unpleasant when it comes in contact with bacteria on the skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Tissue Pores Hair Shafts Sebaceous Gland Eccrine Gland Apocrine Gland There are four different kinds of products: Underarm deodorants counteract odor and help you smell good. Anti-perspirants reduce perspiration and underarm wetness to help prevent odor before it starts. Deodorants/ Anti-perspirants do the job of both a deodorant AND an anti-perspirant. Body sprays, with cologne-like fragrances you can apply to your body, help you smell good everywhere. Wash regularly especially after exercise! To stay looking and feeling your best, take a bath or shower at least once a day. Any time you get sweaty, you should bathe more often. For odor protection, use body wash or soap. Then grab some clean clothes (body odor stays on clothes) and apply deodorant to help keep body odor away. If you are concerned about underarm wetness, try a deodorant/anti-perspirant that not only fights odor but wetness, too. Did you know? Females have more apocrine glands than males. All your eccrine glands working at maximum output could produce about 10.5 quarts of perspiration a day! You have about 2.5 million sweat glands all over your body, except on your lips and ears. A lot of apocrine glands are located under your arms, so many people use underarm deodorants 14 or anti-perspirants to control the smell. 15
9 The way it works The reason you have a reproductive system is because it provides the sperm needed to fertilize a female s egg, which then can grow to be a baby. During puberty the levels of the hormone testosterone in your body begin to rise. This causes your penis and testicles to get bigger and the testicles to produce sperm. The testicles cannot make sperm before puberty. Sperm duct Penis Urethra Foreskin Scrotum Epididymis One of two testicles Bladder One of two seminal vesicles Prostate gland Anus Sperm are the male reproductive cells, in the same way that the eggs inside a woman are the female reproductive cells. (The sperm and the egg need to meet to make a baby.) Sperm look like tadpoles, with what appear to be a head and a tail. Sperm are made in the testicles which hang outside your body in a sac (scrotum) just beneath your penis.the testicles make a lot of sperm about 1,000 sperm per second. Sperm are stored in the epididymis, which is the tube you can feel at the back of each testicle. Sperm are damaged or killed by heat. Because of this, the penis and scrotum hang outside your body to keep the sperm cooler than your body temperature. If you become cold, you may notice that your penis and scrotum shrink. They are drawing themselves closer to your body to keep warm. When you are hot, they will hang loose, away from your body. Sperm are released from the testicles and epididymis and move through the sperm ducts toward the penis. Along the way, sperm mix with fluid so they can move more easily. The sperm and this fluid are now called semen. It is whitish and sticky. The sperm are too tiny to see a drop of semen the size of the period at the end of this sentence would contain more than 1,000 sperm. Semen leaves the penis through the urethra. This is the tube that runs through the middle of your penis. Urine also leaves the body through the urethra, but never at the same time as semen. One of your testicles may be higher than the other. This is normal. No one is perfectly the same on both sides. Generally the right one is slightly higher than the left one
10 Erections When a boy or man is sexually excited, or sometimes for no reason at all, his penis becomes harder and stands away from his body. This is called an erection. Do men stop having erections when they get older? No. Healthy males of all ages, from babies to old men, can get erections. The difference is that only after puberty do males produce sperm and semen. Then they produce sperm for the rest of their lives. Why does it get hard? It gets hard because the blood vessels in the penis fill with blood when you get excited. It doesn t have any muscles in it, which is why you can t move it around very much. You can get an erection any time your penis is touched or rubbed, you have happy or exciting thoughts, or if you see someone attractive. There are lots of causes for erections, even if you aren t thinking about girls or sex. You can get an erection for no reason at all, even when you don t want to have one, which might take you by surprise! You might notice a ridge down the back of each testicle. This is normal. What you feel is the epididymis where the sperm is stored. There is an epididymis down the back of each testicle. If you find any other lumps, you should visit your doctor to get a full checkup. But don t worry it s the same for all boys and men. And don t worry that someone will notice erections are The average ejaculation generally contains more than 40 million sperm. not as noticeable as you think. Try to ignore the erection, and it will go away on its own. Does it matter what size your penis is? Not at all! Penises do vary in length and shape from person to person, but not as much as you may think. Remember, the size of your penis has nothing to do with how manly you are or whether you can become a father. What is circumcision? This minor surgical procedure, usually performed soon after birth, removes all or part of the foreskin of the penis. The operation is not usually considered medically necessary, but often it is performed for religious or cultural reasons, or because it makes it easier to keep the penis clean. To help prevent the growth of bacteria, uncircumcised boys and men should wash under the foreskin every day. Ejaculation Sometimes semen spurts out of the penis. This is called an ejaculation. It happens when muscles at the base of the penis start to expand and contract (tighten). This pushes the semen through the urethra and out through the tip of the penis. But this won t happen every time you have an erection
11 Wet dreams Sometimes you can ejaculate when you are asleep. This is called a nocturnal emission, more commonly known as a wet dream. It happens without you knowing about it, and it s not necessarily because you are dreaming about sex. You may notice that your pajamas or sheets feel wet or sticky when you wake up. This is nothing to worry about most boys have wet dreams. I have been having wet dreams for a while now. Will they ever stop? You will experience wet dreams less frequently after your body has gone through puberty. Generally, as you grow older, you will have more control over your body. Some boys experience wet dreams regularly, while others have very few. It is nothing to worry about. When do I need to wear a jockstrap? This is a personal decision. As your body changes, you may be more comfortable with an athletic supporter when you swim or participate in other sports. In some sports, boys and men wear a plastic cup to protect their genitals. It can be very painful to be hit on the penis and testicles. Check with a parent, your coach, or a physical education teacher if you have questions. What is jock itch? Jock itch is a skin infection caused by a fungus. Its symptoms can include a scaly, itchy rash in the genital area. To help avoid jock itch, wear clean cotton underwear and loose-fitting pants. Don t use anyone else s towels or clothes. Jock itch can be treated with anti-fungal medications available at the drug store without a prescription. You may want to ask a parent, coach, physical education teacher or school nurse to help you choose the right product. If the rash continues, see your doctor
12 Glossary apocrine glands Sweat glands (mostly under the arms and in the genital area) that produce perspiration that can mix with bacteria to cause body odor. Apocrine glands become active atpuberty. circumcision A medical or religious procedure in which a doctor or clergy member cuts away the foreskin from the penis. Circumcision is usually performed during the first few days of a baby s life. eccrine glands Sweat glands (all over the body) that produce clear, odorless perspiration. Eccrine glands are active at all ages. ejaculation Forceful release of semen from the penis. erection Hardening of the penis. estrogen Female hormone, produced in the ovaries, that is responsible for many of the changes that take place in females during puberty. foreskin This fold of skin covers the end of the penis. A boy who has been circumcised has had his foreskin removed. hormones Special chemicals that regulate the growth and activity of body tissues and organs. penis The male reproductive organ, also used for urinating. pituitary gland A small gland beneath the front of the brain, that is responsible for triggering the production of hormones that start puberty. puberty Stage of life when human males and females become capable of reproduction. sebum An oily substance (from the sebaceous glands) that helps keep skin moist. During puberty, too much sebum may contribute to acne. semen A sticky fluid that contains sperm and various other secretions. sperm The male reproductive cell. testicles The male reproductive glands, which produce sperm and the male hormone testosterone. testosterone The male hormone that is responsible for many of the changes that take place in males during puberty. urethra A canal that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males the urethra is also the passageway for semen. wet dream The ejaculation of semen out of the penis during sleep. This is also called a nocturnal emission
13 Want to know more about puberty? Check out Lots of activities, games and answers to your health questions. Online movies and more on puberty, health and lots of other topics. These materials have been reviewed by the American Association for Health Education and accepted as educationally appropriate P&G
always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide
 always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 3 Body Growth 5 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making 10 Physical Activity 11 Sweat 12
always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 3 Body Growth 5 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making 10 Physical Activity 11 Sweat 12
always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide
 always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 2 Body Growth 4 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making 10 Physical Activity 11 Sweat 12
always changing AND GROWING UP boy s guide CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 2 Body Growth 4 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making 10 Physical Activity 11 Sweat 12
Everything You Need To Know About Puberty MALE GUIDE
 CHANGING and GROWING UP Everything You Need To Know About Puberty MALE GUIDE CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 3 Body Growth 5 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making
CHANGING and GROWING UP Everything You Need To Know About Puberty MALE GUIDE CONTENTS Puberty Introduction Changes That Happen to Boys 3 Body Growth 5 Skin Care 6 Hair Care 8 Smile Care 9 Decision Making
What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells
 What s Happening? What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells Or start to make egg cells What is Puberty?
What s Happening? What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells Or start to make egg cells What is Puberty?
Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6
 Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6 Lesson 5: Body Awareness for Boys (to run concurrently with Body Awareness for Girls) If gender-
Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6 Lesson 5: Body Awareness for Boys (to run concurrently with Body Awareness for Girls) If gender-
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin.
 Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin. Puberty begins two years earlier for girls than for boys. For most girls,
Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin. Puberty begins two years earlier for girls than for boys. For most girls,
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information.
 Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty
 Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
penis and testicles below the belt
 below the belt penis and testicles Here are some tips on taking care of and enjoying your parts if you have a penis and testicles (balls, testes). Not everyone experiences or relates to their penis and
below the belt penis and testicles Here are some tips on taking care of and enjoying your parts if you have a penis and testicles (balls, testes). Not everyone experiences or relates to their penis and
b o ys Growing Up g i r l s how your body changes
 g i r l s how your body changes NHS South of Tyne and Wear b o ys Growing Up girls Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust 2 boys and girls
g i r l s how your body changes NHS South of Tyne and Wear b o ys Growing Up girls Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust 2 boys and girls
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal Stories will not be
 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal Stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal Stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
Structure and Function
 Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
are some questions. level and Group similar of discussion. the class. somewhere! Avoid offering 1. Is ways to make mean, it means that the a healthy
 Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
The key word when it comes to
 The key word when it comes to puberty is change. Your body is changing, your feelings are changing, and your relationships with those around you are changing. You re growing up and becoming an adult. This
The key word when it comes to puberty is change. Your body is changing, your feelings are changing, and your relationships with those around you are changing. You re growing up and becoming an adult. This
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1)
 What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1) What is Puberty? I understand why I go through puberty and what happens to me during this time. I feel confident in dealing with the challenges puberty will bring and
What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1) What is Puberty? I understand why I go through puberty and what happens to me during this time. I feel confident in dealing with the challenges puberty will bring and
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Males Grade 5. Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information.
 Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. Males Grade 5 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. Males Grade 5 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
DAY 1. Slides 4-16 (60 minutes) Background Knowledge Vocabulary access compare valid product(s) service(s) avoid reduce behavior personal risk
 Males Grade 5 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal Stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question
Males Grade 5 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal Stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
All Play All Play All Play All Play. All Play All Play All Play All Play
 All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
Lecture Series: Puberty
 Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Sexual Feelings. Having sexual feelings is not a choice, but what you do with your feelings is a choice. Let s take a look at this poster.
 Sexual Feelings It may be your first instinct to deny that your child will ever have sexual feelings. You may even do everything in your power to suppress those feelings if they do surface. You won t succeed
Sexual Feelings It may be your first instinct to deny that your child will ever have sexual feelings. You may even do everything in your power to suppress those feelings if they do surface. You won t succeed
Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6
 Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6 Lesson 3: Changes at Puberty Target Group: Grades 5 and 6 Suggested Time: 60 minutes Learning Goals:
Teaching Puberty: You Can Do It! Human Development & Sexual Health Curriculum Support for Grades 5 and 6 Lesson 3: Changes at Puberty Target Group: Grades 5 and 6 Suggested Time: 60 minutes Learning Goals:
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
For EXtra Special BoYs
 For EXtra Special BoYs A Guide to 47,XXY, Klinefelter syndrome Acknowledgements This is an official publication of axys association for X and Y variations. Additional information available at www.axysinfo.org.
For EXtra Special BoYs A Guide to 47,XXY, Klinefelter syndrome Acknowledgements This is an official publication of axys association for X and Y variations. Additional information available at www.axysinfo.org.
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Core knowledge content
 Core knowledge content Puberty There are 3 periods of rapid growth: conception to birth, birth to the 1 st birthday and puberty. Puberty is the stage of development when a person changes from a child to
Core knowledge content Puberty There are 3 periods of rapid growth: conception to birth, birth to the 1 st birthday and puberty. Puberty is the stage of development when a person changes from a child to
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
HUMAN REPRODUCTION Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember: Asexual reproduction:
Key Concepts Guide. Rev. March 2015 Page 1 of 13
 Key Concepts Guide Key concepts are main ideas. They convey big-picture ideas. Birth control is good at preventing pregnancy and Everyone has the right to say who touches their body and how are both key
Key Concepts Guide Key concepts are main ideas. They convey big-picture ideas. Birth control is good at preventing pregnancy and Everyone has the right to say who touches their body and how are both key
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8
 THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8 You may find you are getting a lot of questions from your students about a variety of topics. They are asking these questions because their bodies and minds are changing,
THE ANSWER BOX: GRADES 7 AND 8 You may find you are getting a lot of questions from your students about a variety of topics. They are asking these questions because their bodies and minds are changing,
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
What are Varicoceles?
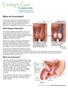 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education
 Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education Dear Parent/Guardian: Grade 6 students will be receiving 4 hours of instruction from one of our district Sexual Health Education teachers soon. The classroom
Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education Dear Parent/Guardian: Grade 6 students will be receiving 4 hours of instruction from one of our district Sexual Health Education teachers soon. The classroom
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring
 Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
Quiz: Evolution Human Reproduction Why Reproduce? In order to ensure the continuation of the species and the continuation of life in general by producing offspring Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Remember:
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Purpose. Teaching notes. Procedure. 2. Give each group a bingo card and counters. 4. Explain any words students are unsure of.
 Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
What You Need to Know about a Vasectomy
 What You Need to Know about a Vasectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a vasectomy is how it works what you can expect what to do after the procedure Please
What You Need to Know about a Vasectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a vasectomy is how it works what you can expect what to do after the procedure Please
Questions??????? Things you may have questions about:
 Puberty 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and
Puberty 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and
GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6. Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty
 TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses. 1) Physical
 You are considering taking feminizing hormones, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. It is very important
You are considering taking feminizing hormones, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. It is very important
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2
 PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT. Fourth Grade Boys
 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Fourth Grade Boys PUBERTY Stage of growth and development that marks the beginning of the change from childhood to adulthood Usually starts between the ages of 11 and 17 Starts earlier
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Fourth Grade Boys PUBERTY Stage of growth and development that marks the beginning of the change from childhood to adulthood Usually starts between the ages of 11 and 17 Starts earlier
Chapter 18. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development.
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Non-gonococcal urethritis. Looking after your sexual health
 Non-gonococcal urethritis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Non-gonococcal urethritis Urethritis is inflammation (pain, redness or soreness) of the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body).
Non-gonococcal urethritis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Non-gonococcal urethritis Urethritis is inflammation (pain, redness or soreness) of the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body).
What do I need to know about HIV and sex? What are my responsibilities and choices?
 Patient and Family Education HIV: Teens and Sex This handout has information about sex and HIV. This handout answers common questions you might ask about sex. It is important for you to talk to your parents
Patient and Family Education HIV: Teens and Sex This handout has information about sex and HIV. This handout answers common questions you might ask about sex. It is important for you to talk to your parents
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Table of Contents 1) What external and internal genital organs does a girl have and what is their function? ) Where does the bag o
 Table of Contents 1) What external and internal genital organs does a girl have and what is their function?..................1 2) Where does the bag of water (embryonic sac) surrounding a baby in its motherõs
Table of Contents 1) What external and internal genital organs does a girl have and what is their function?..................1 2) Where does the bag of water (embryonic sac) surrounding a baby in its motherõs
Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete
 Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete Children Their development is our future! Children are the touchstone of a healthy and sustainable society. How a culture or society treats its youngest
Transitional Phases in childhood Dr Jeané Cloete Children Their development is our future! Children are the touchstone of a healthy and sustainable society. How a culture or society treats its youngest
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information.
 Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Sexual Side Effects for Gay and Bisexual Men Changes in a man s sex life are common and can be managed.
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Sexual Side Effects for Gay and Bisexual Men Changes in a man s sex life are common and can be managed. Even without prostate cancer, getting older can cause changes
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Sexual Side Effects for Gay and Bisexual Men Changes in a man s sex life are common and can be managed. Even without prostate cancer, getting older can cause changes
Puberty. You re growing UP OK! Growing up means that you will experience lots of changes.
 Puberty Growing up means that you will experience lots of changes. You will grow and mature in your own way and at your own pace. Somewhere between the ages of about 8 and 16 puberty will begin. Puberty
Puberty Growing up means that you will experience lots of changes. You will grow and mature in your own way and at your own pace. Somewhere between the ages of about 8 and 16 puberty will begin. Puberty
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary
 X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat, severe acne
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat, severe acne
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses.
 You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
CHEMOTHERAPY. What should I expect?
 CHEMOTHERAPY What should I expect? WHAT IS CHEMOTHERAPY? Chemotherapy is treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy
CHEMOTHERAPY What should I expect? WHAT IS CHEMOTHERAPY? Chemotherapy is treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy
YOUR CHANGING BODY. A Catholic Booklet About Puberty For Girls
 Created in collaboration with the Lewis University College of Nursing and the Diocese of Joliet Family Life Committee 2011 Material reflects USCCB Guideline Formation in Chaste Living and Diocese of Joliet
Created in collaboration with the Lewis University College of Nursing and the Diocese of Joliet Family Life Committee 2011 Material reflects USCCB Guideline Formation in Chaste Living and Diocese of Joliet
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be
 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
UNIT 1 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS Structure 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning and Concept of Male Reproductive System 1.2.1 External Reproductive Organs 1.2.2 Internal
UNIT 1 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS Structure 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning and Concept of Male Reproductive System 1.2.1 External Reproductive Organs 1.2.2 Internal
Radiotherapy for breast cancer. Cancer Services Information for patients
 Radiotherapy for breast cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet will tell you about radiotherapy treatment for breast cancer and the side effects that you may experience
Radiotherapy for breast cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet will tell you about radiotherapy treatment for breast cancer and the side effects that you may experience
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
always changing and growing up girl s guide
 always changing and growing up girl s guide Puberty Contents Puberty 1 Body Growth 7 Breast Growth 8 Skin Changes 10 Hair Changes 11 Perspiration 12 Vaginal Discharge 14 Your Period 15 Feminine Protection
always changing and growing up girl s guide Puberty Contents Puberty 1 Body Growth 7 Breast Growth 8 Skin Changes 10 Hair Changes 11 Perspiration 12 Vaginal Discharge 14 Your Period 15 Feminine Protection
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
Client Information for Informed Consent FEMINIZING MEDICATIONS FOR TRANSGENDER CLIENTS
 Client Information for Informed Consent FEMINIZING MEDICATIONS FOR TRANSGENDER CLIENTS Before using medications to transition and feminize, you need to know the possible advantages, disadvantages and risks
Client Information for Informed Consent FEMINIZING MEDICATIONS FOR TRANSGENDER CLIENTS Before using medications to transition and feminize, you need to know the possible advantages, disadvantages and risks
Know your Acne. Acne. Causes Of Acne. Published on: 7 Nov 2010
 Published on: 7 Nov 2010 Know your Acne Acne All of us have glands that produce oil to keep our skin from becoming dry and flaky. However, sometimes, our oil glands overproduce! This is what commonly causes
Published on: 7 Nov 2010 Know your Acne Acne All of us have glands that produce oil to keep our skin from becoming dry and flaky. However, sometimes, our oil glands overproduce! This is what commonly causes
Sexuality Information For Teachers
 Sex and sexuality : What s the difference? When many people hear the word sexuality, they often hear only the first syllable. However, sexuality is not the same as sex. Sexuality includes everything that
Sex and sexuality : What s the difference? When many people hear the word sexuality, they often hear only the first syllable. However, sexuality is not the same as sex. Sexuality includes everything that
