LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
|
|
|
- Chrystal Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 1 GRADE 7 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development. MATERIALS: 1. HANDOUT: The Male Reproductive System: How Does it Work 2. HANDOUT: Male Reproductive System 3. ANSWER KEY SLIDE: Male Reproductive System 4. SLIDE: Male Reproductive System 5. HANDOUT: The Female Reproductive System: How Does it Work 6. HANDOUT: Female Reproductive System 7. ANSWER KEY SLIDE: Female Reproductive System 8. SLIDE: Female Reproductive System 9. CARDS: Reproduction 10. HANDOUT: When I Was Your Age 11. SLIDE: Menstrual Cycle 12. SLIDE: Sperm Production 13. SLIDE: Conception 14. SLIDE: Implantation INTRODUCTION: Students need to be able to identify the basic components of the human reproductive system and to describe how they function in order to discuss human sexuality. This lesson provides them with an overview of human sexual anatomy and physiology, menstruation, sperm production, conception and fertilization. 1
2 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 APPROACHES/STRATEGIES: A. GROUND RULES (5-10 min) Ensure ground rules are established before beginning this lesson. For classes that have already established ground rules, quickly reviewing them can promote a successful lesson. B. MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM DIAGRAMS (20 min) Students identify the basic parts of the human reproductive system and describe how they function. 1. Distribute the handout Male Reproductive System: How does it Work, and the Male Reproductive System handout. 2. Ask students to label and colour the diagram according to the instructions. You may choose to do this activity together with the students using a slide of the handout and coloured markers while student volunteers read from the Male Reproductive System: How Does it Work? handout. 3. Ask students to correct their diagram s using the slide of the Male Reproductive System answer key. 4. Repeat the same process using the: a. Female Reproductive System handout, b. Female Reproductive System: How Does it Work? c. Female Reproductive System Slide, and d. Female Reproductive System answer key. C. REPRODUCTION CHAIN (20-40 min) Students demonstrate a basic understanding of the male and female reproductive physiology. This is a review of grade 5 Human Sexuality. 1. Draw a Y shaped continuum on floor using tape or chalk (ensure the line can be removed once the activity is complete). Label one part of the top of the Y MALE, the other FEMALE, and the bottom CONCEPTION, FERTILIZATION & PREGNANCY as in the example below. MALE FEMALE CONCEPTION, FERTILIZATION & PREGNANCY 2
3 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 2. Using the Reproduction cards, give one card per student until all cards are distributed. 3. Have students arrange themselves in the proper order along the Y continuum. Ask the students to sit down along the lines once they feel that they are in the correct order. 4. Go through the cards together, and make corrections according to this answer key and the Menstrual Cycle, Sperm Production, Conception & Implantation slides. MALE axis (sperm production) 1. Sperm made in testicles 2. Sperm matures in epididymis 3. Sperm travel up vas deferens 4. Sperm mix with seminal fluid to make semen 5. Sperm leave the penis (ejaculation) Teachers may consider colour coding the lines of the Y and the cards into three sets: Male, Female, and Conception & Fertilization. This will help students place themselves. For example, the BOY axis could be purple, and the cards outlining sperm production could be printed on purple paper. FEMALE axis (menstrual cycle) 1. Lining of uterus is shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) 2. Lining of uterus thickens with blood 3. Ovulation occurs (egg released from ovary) 4. Egg travels through fallopian tube 5. Egg enters the uterus 6. Egg dissolves if unfertilized 7. Lining of uterus is shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) FERTILIZATION, CONCEPTION and IMPLANTATION axis 1. Sperm enters vagina. 2. Sperm travels up the vaginal canal. 3. Sperm meets egg in the outer portion of the fallopian tube (fertilization). 4. Fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus. 5. Fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. 6. Fertilized egg uses lining of the uterus for nourishment. 7. Fertilized egg takes nine months to grow completely into a full-term baby 5. Debrief this activity using the following questions: What else do you know about menstruation? It can begin as early as 8 and as late as 16. Usually one egg is released each menstrual cycle. If more than one egg is released, and if they are fertilized, it means a woman may have a multiple 3
4 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 pregnancy (twins, etc.). If twins are a result of two eggs being fertilized, they are called fraternal twins. Identical twins happen when a fertilized egg splits into two before cells begin dividing. Eggs can live hours from the time of ovulation. Girls need to be aware of good hygiene (using pads, etc.) to ensure healthy practices during menstruation. Cramps can be a part of menstruation, and can be alleviated using wellness methods like exercise or a hot water bottle. For severe cramps, your doctor may give medication. What else do you know about sperm production? Sperm cells mature at about years of age. Sperm production and ejaculation first happens around ages Wet dreams are ejaculations that occur while sleeping. It is normal to experience these, or not to experience these. As many as two million sperm can be released during each ejaculation. Sperm can live inside a female s body 3 to 7 days from the time of ejaculation. Will a pregnancy occur every time sexual intercourse occurs? No. Pregnancy only happens if a sperm fertilizes an egg and if the fertilized egg implants in the uterine wall. This can happen if intercourse takes place when a female is ovulating. Women are most likely to become pregnant if intercourse happens around the middle of the menstrual cycle. The length of the menstrual cycle is different for each woman, so it is difficult to predict. Students may have different views concerning nocturnal ejaculation. It is important to be sensitive to these views, but to reassure students that wet dreams are a normal occurrence during puberty. Keep in mind that students with differing abilities may have very different interpretations of the menstrual cycle, menstrual bleeding, ejaculation, etc. This may be very scary or very funny to them and it is important for the teacher to anticipate different reactions. Keep explanations concrete and use simple visuals where possible. What do menstruation and sperm maturation make possible? Menstruation and sperm maturation are 4
5 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 indications that a person can produce a baby. It is important to remember that ovulation occurs before bleeding; therefore a girl can get pregnant before her first period. Although the body is capable of producing a baby once menstruation and sperm maturation occur, why would most people wait until they are much older to have a baby? Discuss issues surrounding the need to be emotionally, educationally or financially ready to parent. There are health problems for the baby and the mother that are associated with an early pregnancy such as babies with low birth weight. Students considered high risk or with differing abilities may benefit from more instruction about fetal development and parenting. For example: Have each student evaluate whether or not he/she is ready (has the skills and desire) for parenting. Recognize and acknowledge those goals that they would like to achieve before parenting. List with students persons whom they know and respect who do not have children. Create a realistic budget for a couple with a child. Have students compare this budget to their current income. Discuss other factors which might increase expenses even further, such as an extended illness. Go to a local department store or use advertisements and price a pre-made list of essential items one would need for a baby. D. WHEN I WAS YOUR AGE (5 min today, 30 min homework, 5 min next class) Students begin to build a support network to help them cope with puberty. 1. Distribute the When I Was Your Age handout for students to complete as a homework assignment. 2. Explain that students can complete this interview with a parent or supportive adult. 3. Allow students to work in partners or small groups to brainstorm a list of questions they would like to ask a supportive adult regarding the adolescent experience, and choose the three best questions to use as interview questions. If time permits, groups could share their chosen questions with the rest of the class. 4. Dedicate time to debrief this activity during the next lesson. 5
6 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 Although adolescents challenge their parents ideas, they want to hear their parents opinions and values. A survey conducted with Canadian teenagers found the teens saw their parents as their role models when it came to sexuality and sexual health, not celebrities from movies, television, music or sport 2. Many personal values are learned and reinforced at home. Invite students to discuss this topic with their family and encourage open dialogue. QUESTION BOX (10min) Have students fill out questions and address them next class. TAKE IT HOME Students complete the When I Was Your Age handout. Keep in mind that all students do not live in a traditional family nor do they have equal opportunities for open discussion within their family. Although it is best for students to complete this assignment with a supportive parent or guardian, it may not be possible. Be sensitive to the needs of your students. SELF REFLECTION During the lesson, were: Ground rules being followed? Good practices established regarding group work and discussion? What will you change for future classes with this group? What will you change for future use of this lesson? 6
7 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 STUDENT ASSESSMENT During the lesson, did students: Knowledge: Identify the basic parts of the human reproductive system? Describe the process of sperm production? Describe the process of menstruation? Describe how pregnancy can occur? Skills: Participate in class discussion and exemplify listening and appropriate speaking skills? Attitudes: Begin to articulate that menstruation and sperm production are signs that a person is capable of reproduction? Accept that menstruation and sperm production are positive, healthy aspects of puberty? 1. Alberta Education. (2002). Health and life skills guide to implementation: Kindergarten to grade 9. Retrieved from 2. Frappier, J.Y., Kaufmen, M., Baltzer, F., Elliott, A., Lane, M., Pinzon, J., et al. (2008). Sex and sexual health: A survey of Canadian youth and mothers. Paediatr Child Health (1): Retrieved from 7
8 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 HANDOUT THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: HOW DOES IT WORK? On your diagram of the male anatomy, label and colour the internal and external organs according to the instructions below. Vocabulary words that need to be written on the diagram have been italicized. Start at the lower right hand side of your diagram. This special sac that houses the two testicles, is called the scrotum. Colour the scrotum in blue pencil crayon. The scrotum is a sac of loose skin divided into two parts. Each part contains a testicle, epididymis (the small kidney shaped gland at the top of the scrotum), and the end of the vas deferens. Label the three words epididymis, testicle, and scrotum at the lower right hand side of your diagram. Colour the epididymis purple. Each testicle contains tiny tubes that are continuously creating sperm throughout a man s life. When puberty occurs, sperm move to the epididymis to mature. The vas deferens allows the sperm to move up to the seminal vesicle. Follow the vas deferens tube up to the top of the diagram. Colour the entire vas deferens dark green, but be sure to stop colouring as the vas deferens tube enters the penis. The large egg-shaped organ in the centre of your diagram is the bladder. This organ stores urine until it can be expelled from the body. It is not considered part of the reproductive system. Label the bladder, but leave it uncoloured. As the vas deferens curves around the top of the bladder and back down again, it passes the seminal vesicle. This gland is oblong-shaped, and is located behind the bladder on your diagram. The seminal vesicle produces fluids that activate sperm. Colour it light blue. The prostate gland is located just below the bladder. It supplies most of the liquid that combines with the sperm prior to ejaculation. When a man is sexually aroused to the point of orgasm, the fluid from the prostate gland combines with the sperm to make semen. Strong muscle contractions in and around the prostate gland contract rapidly to force the semen out of the urethra. Colour the prostate gland orange. Just under the prostate gland rests a very small round gland called the Cowper s gland. This gland secretes a fluid that removes any acidity from the urethra just before ejaculation. This ensures that the sperm have the best chance of living! 1
9 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 HANDOUT The tube leading from the various glands down the length of the penis is called the urethra. The urethra is the special passageway that allows urine to be voided from the bladder, and allows semen to travel out of the body during sexual intercourse. Both urine and semen cannot be in the urethra at the same time. During an erection, a small valve at the entrance from the bladder seals it off. Colour the urethra light green. The organ in which the urethra is housed is called the penis. The penis has spongy tissues containing small blood vessels and nerves. During sexual arousal, the spongy tissue fills with blood, and the penis hardens. This is called an erection. An erection is a necessary part of human reproduction. It allows the man to insert his penis into the woman s vagina, which enables semen to reach the egg inside the woman s reproductive system. At the very tip of the penis is the glans, which is the head of the penis. This part of the male reproductive system may or may not be covered by foreskin. If the male is circumcised, the foreskin will not cover the glans. Some parents may choose not to circumcise their son, while other parents do. Colour the area of the glans yellow. 2
10 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 MALE ANATOMY HANDOUT 13. 1
11 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 MALE ANATOMY SLIDE & ANSWER KEY Foreskin 1
12 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM HANDOUT THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: HOW DOES IT WORK? On your diagram of the female anatomy, label and colour the internal and external organs according to the instructions below. Vocabulary words that need to be written on the diagram have been italicized. Start at the very bottom of your diagram. The opening leading up into the internal reproductive system is called the vagina. The vagina is a soft, muscular elastic tube. Its inner lining is soft and moist. During sexual arousal, the walls of the vagina secrete a lubricant to assist in intercourse. The vagina also functions as the birth canal for a baby, and allows menstrual flow to exit the body from the uterus. Colour the vagina dark blue. The uterus is a pear shaped organ about the size of a woman s fist that stretches to house the baby, placenta and amniotic fluid during pregnancy. It is very strong, muscular and stretchable! Colour the uterus pink. At the top of the vagina is the cervix which is the bottom of the uterus. This is slightly open in women who are not pregnant, but is plugged during pregnancy to avoid infection. When a baby is ready to be born, the cervix opens to a diameter of 10 cm. Colour the cervix purple. The thick tissue inside the entire uterus is the uterine lining. If fertilization does not occur, this lining is shed every month. This is called menstruation, the process by which the uterus rids itself of its old lining, and prepares for the possibility of conception the following month. About 14 days after ovulation, the body begins to shed the uterine lining, which is made up of blood and fluid. This is commonly called a period. Colour the uterine lining red. Follow the tube out of the uterus to the right on your diagram. This is called the fallopian tube. The fallopian tube carries the egg from the ovary down to the uterus. This journey usually takes about three days. Usually, conception (joining of the sperm and egg) occurs in the fallopian tube. Colour both fallopian tubes on the diagram orange. The finger-like structures at the end of the fallopian tube are called fimbria. The internal, very tiny hair like structures inside the fallopian tube are called cilia. The cilia help the egg move down the fallopian tube from the ovary. 1
13 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM HANDOUT Two egg-shaped organs on either side of the uterus are the ovaries. These are the female counterparts to the male testicles. An ovary is about the size of an almond. When a woman is born, the ovaries already contain all the ova (eggs) she will ever produce. There are up to 400,000 ova. Unlike the testicles, ovaries only house eggs. They don t produce them. The ovary releases one ovum (a single egg) each month. This process is called ovulation. When the ovary releases the egg it travels down the fallopian tube, with help from cilia. If a sperm does not fertilize the egg, it will not adhere to the uterus wall. As a result, menstruation will occur. Colour each ovary light brown, and label your diagram on the left side. 2
14 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 FEMALE ANATOMY HANDOUT 1
15 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 FEMALE ANATOMY SLIDE & ANSWER KEY 1
16 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Lining of the uterus shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) Ovulation occurs (egg [ovum] released from ovary) Lining of uterus thickens with blood 1
17 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Egg (ovum) travels through fallopian tube Egg (ovum) enters the uterus Egg (ovum) dissolves if unfertilized Lining of uterus shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) 2
18 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Sperm made in testicles Sperm mature in epididymis Sperm travel up vas deferens Sperm mix with seminal fluid to make semen 3
19 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Sperm leave the penis (ejaculation) Sperm enters vagina Sperm travels up the vaginal canal 4
20 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Sperm meets egg (ovum) in the outer portion of the fallopian tube (fertilization) Fertilized egg (ovum) travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus Fertilized egg (ovum) attaches itself to the lining of the uterus 5
21 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CARDS Fertilized egg (ovum) uses lining of the uterus for nourishment Fertilized egg (ovum) takes nine months to grow completely into a full-term baby 6
22 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 HANDOUT Student Name: Parent/Adult Support: WHEN I WAS YOUR AGE At times, you may feel as if you re the only one who feels the way you do. It may help to remember that everyone has gone or will go through puberty. Although every generation of teenagers has its own special set of concerns, some feelings and experiences are the same for teenagers of every generation. Do you ever wonder what puberty was like for your parents or grandparents or other supportive adults in your life? In Class Work with a partner or small group to brainstorm a list of questions to ask a parent, grandparent or supportive adult about what life was like as a teenager. From your list, choose the three best questions the ones you are most interested in and the ones most likely to encourage your subject to open up. Write these three questions in the blanks provided. Have your teacher review the questions before you go home. At Home Share this handout with a parent or supportive adult, and ask that person if you can complete it together. Schedule about a half an hour with the adult for the interview. Give the adult this handout so that they can think about the answers before the interview. Interview the adult using the questions provided. Both you and the adult sign the tear-off slip at the bottom of the page when the interview is complete. This tear-off slip can be handed in to show that you have completed the activity (Tear off and hand in this slip only) We completed the When I Was Your Age interview. Student Adult 1
23 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 MENSTRUAL CYCLE SLIDE 1
24 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 SPERM PRODUCTION SLIDE 1
25 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 CONCEPTION SLIDE 1
26 GRADE 7 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 1 IMPLANTATION SLIDE 1
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook
 Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Puberty and Reproduction
 Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway
 Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Human Reproduction & Anatomy Breakaway Image courtesy of Dream Design at Free Digital Photos Kim Graybill/FamilyConsumerSciences.com Page 1 Challenge #1: Who Do I Belong To? Male? Female? Both? Neither?
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Chapter 16 Endocrine and Reproductive Health
 Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Note Taking Lesson 2 The Male Reproductive System Directions: Use the following outline to help organize your notes as you read through the lesson. Key Concept Consider and Reconsider Before reading the
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Transformation Information elearning Kit Combined Program Lesson Plan Page 1. LESSON TITLE: Combined Program
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this animated activity, students will go more in depth about changes that happen to both males and females during puberty. The Coach re-introduces Ted Testosterone,
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth
 Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Revised January 2017 Reproductive Anatomy, Conception, Pregnancy, and Birth Lesson Goals Explain the Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproduction Systems Review Proper Vocabulary for the
Purpose. Teaching notes. Procedure. 2. Give each group a bingo card and counters. 4. Explain any words students are unsure of.
 Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
Reproductive bingo Activity: Key Messages Males and females have different reproductive parts, each of which has an important function. It is important to use the correct terminology for reproductive parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
DESCRIBING THE MALE AND FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS & THEIR FUNCTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to describe male and female sexual and reproductive systems including body parts
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy
 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: Students
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
NAKED How to understand teenagers x 6 min. minutes
 NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
NAKED How to understand teenagers 2007 6 x 6 min. minutes Program Synopsis: This innovative series of six, six-minute documentaries hears from teens about various issues confronting them at puberty. Breasts,
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Session 4_Girls. Learning about my body: Reproductive system
 Session 4_Girls Learning about my body: Reproductive system Rationale Pubertal changes begin around 9-10 years in girls and around 11 years for boys. Acknowledging the mental, emotional, and physical changes
Session 4_Girls Learning about my body: Reproductive system Rationale Pubertal changes begin around 9-10 years in girls and around 11 years for boys. Acknowledging the mental, emotional, and physical changes
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty
 Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Puberty For Boys Male Anatomy and Physical Changes During Puberty 70 minutes Preparing To Teach About Puberty - Teacher Guide Anatomy Review - Teacher Guide Bernie (male
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6. Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty
 TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
TEACHER GUIDE GROWING UP AND LIKING IT 2-Hour Assembly/Health Lesson Science-To-Go! Program Grades: 5-6 Growing Up and Liking It: Pondering Puberty Description Hour 1: Learn the science inside a changing
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Reading Preview. The Menstrual Cycle Days 1-4 Menstrual discharge. Days 5-13 Developing Egg. Hormones control growth and development.
 Section 2 The Male and Female Reproductive s 2 The Male and Female Reproductive s Objectives After this, students will be able to D.7.2.1 Define sexual reproduction. D.7.2.2 Describe the structures and
Section 2 The Male and Female Reproductive s 2 The Male and Female Reproductive s Objectives After this, students will be able to D.7.2.1 Define sexual reproduction. D.7.2.2 Describe the structures and
Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017
 Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 5th grade,
Proposed Revisions for the 5th Grade S.H.A.R.E. Sexuality, Health, and Responsibility Education Curriculum Revised February 15, 2017 Sexual and Reproductive Anatomy NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of 5th grade,
Structure and Function
 Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology)
 Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Lecture Series: Puberty
 Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18
 Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
Review and Resources Grades 4-6, Lesson #18 Time Needed 50-60 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Recognize the definitions of at least 90% of the vocabulary introduced in the unit.
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Science Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which
Class X Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Science Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Chapter 18. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Year Five. God loves me in my changing and development. 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5
 Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Downloaded from Organisms Reproduce
 Organisms Reproduce Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus
Organisms Reproduce Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
2 - male hormones/ female system
 2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
2 - male hormones/ female system May 7, 2012 5:08 PM I) Testosterone: main androgen (male sex hormone) A) Intro to Testosterone: -steroid hormone produced by interstitial cells in testes -produced in response
The Female Reproductive System
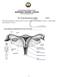 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
