A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
|
|
|
- Melinda French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor Volume 4, Issue 11, Review Article ISSN A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz Ali Riyasat Ali 1*, Pentewar R.S, Gholve S.B, Sugave R.V, Bhosle P.H, Shaikh F.E. Department of Pharmaceutics, Channabasweshwar Pharmacy College, Latur, Maharashtra, India. Article Received on 14 Sept 2015, Revised on 05 Oct 2015, Accepted on 27 Oct 2015 *Correspondence for Author Sayyed Sarfaraz Ali Riyasat Ali Department of Pharmaceutics, Channabasweshwar Pharmacy College, Latur, Maharashtra, India. ABSTRACT The most convenient method of drug delivery System is oral route which is due to patient's compliance, it's reliability, ease of administration and flexibility of formulation. Gastro retentive drug delivery system has lot of advantages and applications which include significance of prolong gastric residence time of drug and improve bioavailability, reduce drug wastage, enhance solubility of those drugs specifically that are poorly soluble in high ph environment. The another important physiology is that gastro retention facilitate local drug delivery to the stomach & proximal small intestine. This technology has novel approach for those drugs which have narrow absorption window in Gastric intestinal tract. Gastro retentive drug delivery system is designs in such a way that it must retain in stomach for prolonged time & release active drug and hence, thereby provide sustainable and long time input of drug to the upper part of Gastric intestinal tract. Enormous amount of attention has been generated towards this novel technology since, from last few decades owing to their potential usefulness to improve solubility & bioavailability thereby targeting site specific release. Ultimately, enhancing their therapeutic outcome. This technique has a innovative approach for those drugs having narrow absorption window in gastric intestinal tract. Owing to it's reliability, we can consider the significant applicability of gastro-retentive drug delivery in future days. Keywords: Gastro-retentive drug delivery, Solubility, Gastric residence, Bioavailability. INTRODUCTION Development of oral controlled release dosage form quiet few decades ago due to it's considerable merits which include ease of administration patient compliance and it's Vol 4, Issue 11,
2 flexibility in formulation. Simultaneously, this methodology has several physiological difficulties such as inability to restrain and locate the controlled drug delivery system within desired region of gastric intestinal tract due to variable gastric motility and it's emptying time. The average gastric emptying time is 2-3 hour through stomach and the upper part of intestine which can be resulting in incomplete drug release from the drug delivery system leading to reduced efficacy of administered dose.[1] Therefore, control of placement of drug delivery in a specific region of gastric intestinal tract offers advantage for a variety of important drugs characterized by narrow absorption window & stability complication in gastro intestinal tract. [2] The dosage form of gastro-retentive drug delivery system may remain in gastric environment for several hour and hence significantly prolong the gastric residence time of drug. Prolong gastric retention results in enhancement of bioavailability, reduction in drug wastage and improvement of poorly soluble drugs. Thus this innovative approach is suitable for local drug delivery to the stomach and proximal small intestine. It facilitates the novel products with suitable therapeutic activity and the numerous benefits for the patient. [3] Figure 1: Schematic representation of inter-digestive motility Need of study [4-9] 1. Low density dosage form causes buoyancy in gastric fluid. 2.Dosage form with high density which is retained at the bottom of stomach. 3.Bioadhesion to stomach mucous. 4.Expansion by swelling to a large size which restricts emptying to the dosage form through the pyrolic sphincter. 5.Concomitant administrations of drugs causes slow motility of gastric intestinal tract. Vol 4, Issue 11,
3 Physiology of Stomach [10-11] The Migrating Myloelectric cycle is divided into four phases which described by Wilson and Washington as follows: 1. Phase I: Also known as basal phase lasts from 40 to 60 minutes with rare contractions. 2. Phase II: Also known as preburst phase lasts for 40 to 60 minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. As the phase progresses the intensity and frequency also increases gradually. 3.Phase III: Also known as burst phase lasts for 4 to 6 minutes. It includes intense and regular contractions for short period. 4. Phase IV: lasts for 0 to 5 minutes and occurs between phases III and I of 2 consecutive cycles. Figure 2: Diagram of human stomach Advantages [12-13] Used in the stomach for local action. To treat peptic ulcer. Employed for the drug delivery with narrow absorption window in small intestine. Dosing frequency reduced. Bioavailability of the drug improved Applied for those drugs which are unstable in intestinal fluids. Maintain the systemic drug concentration within the therapeutic window. Site specific drug delivery is possible. Disadvantages [13] It needs high levels of stomach fluids, for the system to float. Stability /Solubility problem drugs are not suitable. Vol 4, Issue 11,
4 Those drugs which undergo extensive first pass metabolism are not suitable candidates. Irritant effect drugs restricts the applicability. Factors affecting gastric retention [14-16] 1.pH of the stomach The particle size must be in the range of 1 to 2 mm to pass through the pyloric valve into the small intestine. The stomach ph in fasting state is ~1.5 to 2.0 and in fed state is 2.0 to Gastric Emptying The rate of gastric emptying depends mainly on viscosity, volume, and caloric content of meals. Determination gastric emptying time is possible with nutritive density of meals. a. Density: Dosage forms which have a low density than that of gastric fluid experience floating behavior and therefore gastric retention. A density of <1.0 gm/cm3 needs to exhibit floating property. b. Size and shape of dosage unit: During the digestive phase the smaller units get emptied from the stomach and the larger units during the housekeeping waves in fed conditions. c. Food Fed and Unfed State: Food intake, the nature of the food, caloric content, and frequency of feeding has a profound impact on the gastric retention. The presence/absence of food in the stomach influences the gastric retention of the dosage form. d. Gender: Mean ambulatory gastric retention in males (3.4±0.4 hours) is less as compared with their age and race matched female counterparts (4.6±1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface. e. Age : People those over 70 years have a significantly longer gastric retention. f. Miscellaneous: Biological factors such as age, body mass index, gender, posture, and diseased states influence gastric emptying the effect of buoyancy, posture, and nature of meals on the gastric emptying process have impact on the gastric emptying rate. APPROACHES TO ACHIEVE GASTRIC RETENTION 1.High density (sinking) system or non- floating drug delivery system The formulation of dosage forms with the density that should exceed density of normal stomach content (~ gm/cm3) involve in this technique. Preparations of these formulations by coating drug on a heavy core or mixed with inert materials such as iron powder, barium sulphate, zinc oxide and titanium oxide etc [13]. The materials increase Vol 4, Issue 11,
5 density by up to gm/cm3. A density near to 2.5 gm/cm3 are essential for specific prolongation of gastric residence time. [19] Figure 3: Schematic localization of an intragastric floating and high density system in the stomach. 2.Floating drug delivery systems Floating drug delivery systems is one of the significant approaches to achieve gastric retention to obtain enough drug bioavailability. [20] This delivery systems is desirable for drugs with an absorption window in the upper small intestine. [21] It has a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period and thus, drug is released at desired rate. Residual system is emptied from the stomach after release of drug. Therefore it result in an improved gastric retention time and a better control of the fluctuation in plasma drug concentration. The major requirements for floating drug delivery system are [13] It must release contents at desirable rate to serve as a reservoir. It should maintain specific gravity lower than gastric contents ( gm/cm3). Cohesive gel barrier should be formed. 3. Hydro dynamically balanced systems Hydro dynamically balanced systems are initially designated by Sheth and Tossounian. [24] These are single-unit dosage form, containing one or more gel-forming hydrophilic polymers.for the development of these systems Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydroxethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, polycarbophil, polyacrylate, polystyrene, agar, carrageenans or alginic acid are commonly employed as excipients. [25-26] In hydrodynamically balanced system capsule the polymer is mixed with Vol 4, Issue 11,
6 drugs and administered. When capsule shell comes in contact with water get dissolves and mixture swells to form a gelatinous barrier, which imparts buoyancy to dosage form in gastric juice for a long period. [26] Figure 4. Hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS). 4. Bioadhesive or Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems These systems are used as a delivery device within the human to improve drug absorption in a site-specific manner. Bio adhesive polymers are used and may adhere to the epithelial surface in the stomach. [30] Thus, they enhance the prolongation of gastric retention. On the basis of adhesion a dosage form can stick to the mucosal surface by different mechanism as follows: [31-32] 1) On the basis of wetting theory, ability of bioadhesive polymers to spread and develop intimate contact with the mucous layers. 2) The physical entanglement of mucin strands the flexible polymer chains, or an interpenetration of mucin strands into the porous structure of the polymer substrate proposed by diffusion theory. 3) The bioadhesion is due to secondary forces such as Vander Waal forces and hydrogen bonding suggested by absorption theory. 4) Attractive electrostatic forces between the glycoprotein mucin net work and the bio adhesive material proposed by the electron theory, 5. Expandable, unfold able and swell able systems In stomach the dosage form will withstand gastric transit if it is large than pyloric sphincter. The dosage form must be small enough to be swallowed, does not cause gastric obstruction. Thus, their configurations are required to develop an expandable system to prolong gastric retention time. [33-34] Vol 4, Issue 11,
7 1) for oral intake a small configuration, 2) an expanded gastroretentive form. a. Swellable systems Figure 5. Swellable system. b. Unfolding system Unfolding takes place due to mechanical shape memory i.e. the gastroretentive dosage form (GRDF) is fabricated in a large size and is folded into a pharmaceutical carrier e.g. a gelatin capsule, for convenient intake. Figure 7: Different geometric shapes of unfolding systems. 6. Super porous hydrogel systems These swellable systemsvaries enough from the traditional types to have separate classification. For improvement of gastric retention time super porous hydrogels of average pore size >100 micro meter, swelling to the equilibrium size within a minute due to rapid water uptake by capillary wetting through numerous interconnected open pores. [35] Large size swelling are intended to have enough mechanical strength to withstand pressure. Vol 4, Issue 11,
8 Figure 6: Superporous hydrogels. 7. Magnetic Systems This method is to improve the gastric retention time which is based on the principle that the dosage form contains a small internal magnet which is placed on the abdomen over the position of the stomach. However,the external magnet must be positioned with a degree of precision. [32] MECHANISM OF GASTRORETENTIVE DOSAGE FORMS [18] Figure 8. Various forms of gastroretentive systems; (a) Floating gastro-retentive drug delivery systems; (b) Swelling gastro-retentive drug delivery systems; (c) Bioadhesive gastroretentive drug delivery systems; (d) High-density gastro retentive drug delivery systems. To gain the dosage form in the stomach as a way of improving the retention time numerous attempts have been made. Some of these attempts consist of introducing floating dosage forms mucoadhesive systems, high-density systems, modified shape systems, gastricemptying delaying devices.. Most commonly used dosage forms are the floating system. Floating drug delivery systems have a bulk density less than gastric fluids thus, remain Vol 4, Issue 11,
9 buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. As the system is floating on the gastric, the drug is released slowly at the desired rate. Thereafter, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. This results in an enhanced GRT and a better control of the fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. A minimal gastric content essential to allow the proper achievement of the buoyancy retention principle, a minimal level of floating force (F) is required to keep the dosage form reliably buoyant on the surface of the meal. Measurement of the floating force kinetics, a novel apparatus for determination of resultant weight has been reported. Operation carried out with the apparatus by measuring continuously the force equivalent to F (as a function of time) that is required to maintain the submerged object. The object floating possible if F is on the higher positive side. This device helps in optimizing FDDS with respect to stability and durability of floating forces generated to prevent the demerits of unforeseeable intragastric buoyancy capability variations. F = F buoyancy - F gravity = (Df - Ds) gv--- (1) Where, F= total vertical force, Df = fluid density, Ds = object density, v = volume and g = acceleration due to gravity. g = acceleration due to gravity. Figure 9: Mechanism of floating systems (a) Swelling system (c) Gas generating system Types of floating drug delivery system [36] It can be divided into two systems. 1. Effervescent systems 2. Non-effervescent systems. 1. Effervescent Systems. Vol 4, Issue 11,
10 A. Volatile liquid containing systems. a) Intragastric floating gastrointestinal drug delivery system. In this systems floating can be made in the stomach because of floatation chamber, which may be a vacuum or filled with gas, while the encapsulation of drug reservoir inside a microporus compartment carried out. Figure 10 : Intra gastric floating gastrointestinal drug delivery device. b) Inflatable gastrointestinal delivery systems [39] Incorporation of inflatable chamber which contains liquid ether that gasifies at body temperature to cause the chamber to inflate in the stomach. Fabrication of these system by loading the inflatable chamber with a drug reservoir, which can be a drug, impregnated polymeric matrix, then encapsulated in a gelatin capsule. The capsule dissolves to release the drug reservoir together with the inflatable chamber after oral administration. Inflation occur automatically and retains the drug reservoir compartment in the stomach. From the reservoir the drug continuously released into the gastric fluid. Figure 11 : Inflatable gastrointestinal delivery system c) Intragastric osmotic ally controlled drug delivery systems It is composed of an osmotic pressure, controlled drug delivery device and an inflatable floating support in a biodegradable capsule. The capsule in the stomach, quickly Vol 4, Issue 11,
11 disintegrates to release the intragastric osmotic ally controlled drug delivery device. Formation of inflatable support inside stomach and a deformable hollow polymeric bag that contains a liquid that gasifies at body temperature to inflate the bag. The osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery equipment having two components; drug reservoir compartment and an osmotic ally active compartment. Enclosed drug reservoir compartment by a pressure responsive collapsible bag, which is impermeable to vapors and liquid. The osmotic ally active Compartment contains an osmotically active salt which is enclosed within a semi permeable membrane. Absorption of water in the GI fluid is continuously through the semi permeable membrane into osmotic ally active compartment to dissolve the osmotically active salt. Creation of an osmotic pressure which acts on the collapsible bag and in turn activate the drug reservoir compartment to reduce its volume and activate the drug release of a drug solution formulation through the delivery orifice. The floating support is prepared to contain a bio-erodible plug that erodes after a predetermined time to deflate the support. [36,38] Figure 12: Intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery system d.effervescent (gas generating) systems Figure 13: Drug release from effervescent (gas generating) systems. Vol 4, Issue 11,
12 Achievement of floatability is possible by generation of gas bubbles. These buoyant systems uses matrices made up of swellable polymers such as polysaccharides (e.g. chitosan), effervescent components (e.g. sodium bicarbonate, citric acid or tartaric acid). [29] The ratio of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate generation of gas is reported to be 0.76: 1. [18] In this system carbon dioxide is released which leads to the formulation to float in the stomach. Several techniques and materials that have been employed are a mixture of sodium alginate and sodium bicarbonate, multiple unit floating dosage forms that generate gas when ingested, floating mini capsules with a core of sodium bicarbonate, lactose and polyvinyl pyrrolidone coated with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and floating system based on ion exchange resin technology etc. [17] Figure 14: Gas generating system: Schematic monolayer drug delivery system (a) Bilayer gas generating system, with (c) or without (b) semipermeable membrane. 2 Non-effervescent Systems Production of non-effervescent floating drug delivery systems from gel-forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides or matrix forming polymers like polyacrylate, polycarbonate, polystyrene and polymethacrylate. Mixing of drug with a gel forming hydrocolloid which results in contact with gastric fluid after oral administration and sustain a relative integrity of shape and a bulk density. [23] The air trapped by the swollen polymer confers buoyancy. Excipients employed include hydroxypropyl methylcellulose polyacrylates, polyvinyl acetate, carbopol, agar, sodium alginate, calcium chloride, polyethylene oxide and polycarbonates. [17] Vol 4, Issue 11,
13 A. Colloidal gel barrier systems Sheath and Tossounian in 1975 first designed hydro-dynamically balanced system. It contains drug with gel forming hydrocolloids meant to remain buoyant on stomach contents. Incorporation of a high level of one gel forming highly swell able cellulose type hydrocolloids e.g. HEC, HPMC,NaCMC, Polysaccharides and matrix forming polymers such as polycarbophil, polyacrylates and polystyrene, incorporated either in tablets or in capsules. Once they came in contact with gastric fluid, the hydrocolloid in the system hydrates and forms a colloidal gel barrier. The maintenance of a density by air trapped with the swollen polymer less than unity which leads to buoyancy to this dosage forms. [36] Figure 15 : colloidal gel barrier system B.. Microballoons / Hollow microspheres Loading of Microballoons / hollow microspheres with drugs in their other polymer shelf were produced by simple solvent evaporation technique. [27] For prolongation of the gastric retention time of the dosage form. Commonly used polymers are polycarbonate, cellulose acetate, calcium alginate, Eudragit S, agar etc. drug Drug release from dosage form and it's buoyancy are dependent on quantity of polymers, the plasticizer polymer ratio and the solvent utilized for formulation. The microballoons floated continuously over the surface of an acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for >12 hours. [17] As hollow microspheres has combine benefit of multiple-unit system and good floating, hence these are considered the most promising buoyant systems. Vol 4, Issue 11,
14 Figure 16: Formulation of floating hollow microsphere or microballoon C. Alginate beads Development of a multiple-unit floating system based on cross-linked beads by Talukdar and Fassihi. [22] They were prepared by using Ca2+ and low methoxylated pectin and sodium alginate. Usually, sodium alginate solution is dropped into aqueous solution of calcium chloride and causes the precipitation of calcium alginate. Separation of these beads and dried by air convection and freeze drying, causing the formulation of a porous system, which can sustain a floating force for over 12 hrs. It improve gastric retention time more than 5.5 hrs [17,28] D.Microporous compartment system Microporous compartment system is based on the principle of the encapsulation of a drug reservoir inside a microporous compartment with pores along its top and bottom walls. [29] The walls of the apparatus were completely sealed to present any direct contact of the gastric surface with the undissolved drug. In the stomach the floatation chamber containing entrapped air leads to the delivery system to float in the gastric fluid. [13] E. Raft Forming GF System Raft forming systems have received much attention for drug delivery for gastrointestinal infection and disorders. The basic principle in the raft formation includes the formation of viscous cohesive gel in contact with gastric fluids, where in each portion of the liquid swells forming a continuous layer called a raft. This raft floats on gastric fluids due to low density created by the formation of CO2. Usually, this system ingredients includes a gel forming agents and alkaline bicarbonates which is responsible for formation of CO2 to prepare the system less dense and float on gastric fluids. [37] Vol 4, Issue 11,
15 Figure 17: Barrier formed by the raft forming system Applications of Floating Drug Delivery Systems [40] 1. Enhanced Bioavailability The bioavailability of riboflavin CR-GRDF is significantly enhanced in comparison to the administration of non-grdf CR polymeric formulations. There are numerous different approaches, related to absorption and transit of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract, that act concomitantly to influence the magnitude of drug absorption. 2. Sustained drug delivery Oral CR formulations are encountered with problems such as gastric residence time in the GIT. These problems can be overcome with the Hydro dynamically balanced systems which can remain in the stomach for prolong periods and have a bulk density <1 as a result of which they can float on the gastric contents. Passing from the pyloric opening is prohibited because these systems are relatively larger in size. 3. Site specific drug delivery systems These systems are specifically benefits for drugs that are significantly absorbed from the proximal part of the small intestine.the controlled, slow delivery of drug to the stomach provides sufficient local therapeutic levels and restricts the systemic exposure to the drug. This decreases side effects that are caused by the drug in the systemic circulation. However,the prolonged gastric availability from a site directed delivery system may reduce the dosing frequency. Eg: Furosemide and Riboflavin. 4. Absorption enhancement Drugs with poor bioavailability due to site specific absorption from the upper part of the GIT are potential candidates to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems, thereby maximizing their absorption. Vol 4, Issue 11,
16 5. Minimized adverse activity at the colon Retention of the drug in the HBS systems at the stomach minimizes the amount of drug that reaches the colon. Thus, undesirable activities of the drug in colon may be prevented. This Pharmacodynamic aspect provides the rationale for gastric retention dosage form formulation for beta-lactam antibiotics that are absorbed only from the small intestine, and whose presence in the colon leads to the development of microorganism s resistance. 6. Reduced fluctuations of drug concentration Fluctuations in drug effects are reduced and prevention of concentration dependent adverse effects that are associated with peak concentrations. This feature is specifically important for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index. Future potential of floating drug delivery system [41] From several recent publications it is evident that floating dosage form offers various futures potential. The decrease in fluctuations in the plasma level of drug results from delayed gastric emptying. We can deliver the drugs efficiently that have poor bioavailability because of their limited absorption to the upper gastrointestinal tract thereby enhancing their absorption and improving their absolute bioavailability. It is beneficial for the treatment of gastric and duodenal cancers as buoyant delivery system. The floating concept can be utilized for various anti-reflux formulations. Development of a controlled release system for the drugs, which are potential to treat the Parkinson s disease. CONCLUSION In the gastrointestinal tract the drug absorption is a highly variable procedure and prolong gastric retention of the dosage form which provides extension for the absorption time. Floating drug delivery system promises to be a potential approach for gastric retention. As there are numerous of difficulties to be worked out to achieve prolonged gastric retention, a large number of industries are focusing toward commercializing this approaches. An significant feature to take into account is physiology of the stomach. Important parameter considered is the time when the drug is taken during or apart from the meal. A real challenge to pharmaceutical technology is to develop an efficient gastroretentive dosage form. Retention of drug in stomach for prolong duration which is not compatible with physiology of stomach. All these Gastro retentive drug delivery systems such as high density, floating, Vol 4, Issue 11,
17 expandable or unfoldable or swelling, super porous, bioadhesive, magnetic systems etc. are important and present their own advantages and disadvantages. Future expectation are more with these dosage form as they have great importance. Thus, it will lead to improved efficiencies of various types of pharmacotherapy. Therefore, we can conclude that these dosage form has a vital role to play in future and it's potential to provide improved results. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The author wish to express his gratitude to the faculty members of Channabasweshwar Pharmacy college, Latur, India. Author's statements competing interest The author declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCE 1. Rouge N, Buri P, Doelker E. Drug absorption sites in the gastrointestinal tract and dosage forms for site specific delivery. Int J Pharm., 1996; 136: Singh BN and Kim KH. Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J. Control. Release., 2000; 63: Ali J, Arora S, Khar RK. Floating drug delivery System: A Review. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech., 2005; 06(03): E372-E Deshpande AA, Shah NH, Rhodes CT, Malick W. Development of a novel controlledrelease system for gastric retention. Pharm Res., 1997; 14: Davis SS, Stockwell AF, Taylor MJ. The effect of density on the gastric emptying of single and multiple unit dosage forms. Pharm Res., 1986; 3: Lehr CM. Bioadhesion technologies for the delivery of peptide and protein drugs to the gastrointestinal tract. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst., 1994; 11: Groning R, Heun G. Oral dosage forms with controlled gastrointestinal transit. Drug Dev Ind Pharm., 1984; 10: Groning R, Heun G. Dosage forms with controlled gastrointestinal passage studies on the absorption of nitrofurantion. Int J Pharm., 1989; 56: Klausner EA, Lavy E, Friedman M, Hoffman A. Expandable gastroretentive dosage forms. J Control Release., 2003; 90: Vol 4, Issue 11,
18 10. Wilson CG, Washington N. The stomach: its role in oral drug delivery. In: Rubinstein MH, ed. Physiological Pharmacetical: Biological Barriers to Drug Absorption. Chichester, UK: Ellis Horwood., 1989; Desai S, Bolton S. A floating controlled release drug delivery system: in vitro- in vivo evaluation. PharmRes., 1993; 10: Debjit Bhowmik., Chiranjib B., Margret Chandira., Jayakar B., Sampath Kumar K.P., Floating Drug Delivery System-A Review, Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2009; 1(2): Vyas S. P., Roop K. Khar., Controlled Drug Delivery: Concepts and Advances, Vallabh Prakashan, Wells J. Pharmaceutical Preformulation. Pharmaceutics: The Science Of Dosage Form Design. M.E. Aulton, Eds, 3 rd Edinburg London: Melbourne And Newyork,1988,P Rajput GC., Majmudar FD., Patel JK, Patel KN., Thakor RS., Rajgor NB. Stomach Specific Mucoadhesive Tablets As Controlled Drug Delivery System A Review Work, International Journal on Pharmaceutical and Biological Research., 2010; 1(1): Chawla G, Gupta P, Koradia V, Bansal AK. Gastroretention: A Means to Address Regional Variability in intestinal drug Absorption, Pharmaceutical technology, July 2003; 27(2): Garg R, Gupta GD. Progress in controlled gastroretentive delivery systems. Trop. J Pharm Res., 2008; 7(3): Garg S, Sharma S. Gastroretentive drug delivery systems. Business Briefing: Pharmatech., 2003; Clarke GM, Newton JM, Short MD. Gastrointestinal transit of pellets of differing size and density. Int J Pharm., 1993; 100(13): Sing BN, Kim KH. Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J Control Rel., 2000; 63: Sungthongjeen S, Paeratakul O, Limmatvapirat S, Puttipupathachorn S. Preparation and in-vitro evaluation of multiple-unit floating drug delivery system based on gas formation technique. Int J Pharm., 2006; 324: Talukdar R, Fassihi R. Gastroretentive delivery systems: hollow beads. Drug Dev Ind Pharm., 2004; 30: Hilton AK, Deasy PB. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of an oral sustained release floating dosage form of amoxicillin trihydrate. Int J Pharm., 1992; 86: Vol 4, Issue 11,
19 24. Seth PR, Tossounian J. The hydrodynamically balanced system, a novel drug delivery system for oral use. Drug Dev Ind Pharm., 1984; 10: Hwang SJ, Park H, Park K. Gastroretentive delivery systems. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst., 1998; 15(3): Reddy LH, Murthy RS. Floating dosage system in drug delivery. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst., 2002; 19(6): Kawashima Y, Niwa T, Takenchi H, Hino T, Itoh Y. Hollow microspheres for use as a floating controlled drug delivery system in the stomach. J Pharm Sci 1992; 81: Whiteland L, Fell JT, Collett JH. Development of gastroretentive dosage form. Eur J Pharm Sci., 1996; 4: S Harrigan RM. Drug delivery device for preventing contact of undissolved drug with the stomach lining. US Patent ; October 25, Moes A. Gastroretentive dosage forms. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst., 1993; 10: Faivre V. Aspects theoriques de la bioadhesion. In: Falson- Rieg V, Faivre V, Pirot F. ed. Nonvelles formes medicamenteuses, Editions Medicales Internationales, Editions TEC and DOC, Cachan., 2004; Huang Y, Leobandung W, Foss A, Peppas NA. Molecular aspects of muco- and bioadhesion: tethered structures and site-specific surfaces. J Control Release., 2000; 65(1-2): Klusner EA, Lavy E, Friedman M, Hoffman A. Expandable gasrtroretentive dosage forms. J Control Release., 2003; 90(2): Klusner EA, Lavy E, Stepensley D, Friedman M, Hoffman A. Novel gasrtroretentive dosage form: evaluation of gastroretentivity and its effect on riboflavin absorption in dogs. Pharm Res., 2002; 19: Chen J, Blevins WE, Park H, Park K. Gastric retention of superporous hydrogel composites. J Control Release., 2000; 64(1-3): Robinson, J.R.; Lee, V.H.L. Controlled drug delivery: fundamentals and applications, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker, Inc., NY Mayavanshi, A.V.; Gajjar, S.S. Floating drug delivery systems to increase gastric retention of drugs: A Review, J. Pharm. Tech., 2008; 1(14): Laila H Emara, Aya R. Abdou, Ahmed A. EL-Ashmawy, Nadia M. Mursi, preparation and evaluation of metronidazole sustained release floating tablets, Int J Pham and Pharm Sci., 2014; 6(9): Vol 4, Issue 11,
20 39. Jain, N.K. Progresses in controlled and novel drug delivery system, CBS Publishers, Pande, S.D.; Vaidya, V. floating drug delivery system (fdds): A new way for oral drug delivery system. International journal of pharmaceutical and clinical science, Kawashima, Y.; Niwa, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Hino, T. Ito, Y. Preparation of multiple unit microspheres (microballons) with acrylic resin containing tranilastand their drug release characteristics and floating behaviour. J. Control release, 1991; 16: Vol 4, Issue 11,
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS. Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P.
 Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
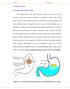 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE
 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE
 METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
EUDRATEC GRS. Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach.
 EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
Patel Tejas B et al / Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 5(5), Sep - Oct Research Article.
 Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
 PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Large scale production
 Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
Biopharmaceutics. Lec: 4
 64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Determination of bioavailability
 Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Review Article. Buccal adhesive tablet
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(8):77-81 Review Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Buccal adhesive tablet Vikesh Kumar Shukla and Tarunendra
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(8):77-81 Review Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Buccal adhesive tablet Vikesh Kumar Shukla and Tarunendra
Studies of Floating Dosage Forms of Furosemide: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations of Bilayer Tablet Formulations
 Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 26(8), 857 866 (2000) RESEARCH PAPER Studies of Floating Dosage Forms of Furosemide: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations of Bilayer Tablet Formulations Nurten Özdemir,
Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 26(8), 857 866 (2000) RESEARCH PAPER Studies of Floating Dosage Forms of Furosemide: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations of Bilayer Tablet Formulations Nurten Özdemir,
M. Chandira etal Der Pharmacia Lettre; 2009, 1 (1): Formulation and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive oral tablet of clarithromycin
 Formulation and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive oral tablet of clarithromycin Margret Chandira*, Sachin, B. S. Venkateshwarlu, Debjit Bhowmik, B. Jayakar Vinayaka Missions College of Pharmacy
Formulation and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive oral tablet of clarithromycin Margret Chandira*, Sachin, B. S. Venkateshwarlu, Debjit Bhowmik, B. Jayakar Vinayaka Missions College of Pharmacy
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems
 Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.4 (2), April-June, 2014 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
Floating Drug Delivery System to Increase Gastric Retention of Drug: A Review
 Review Article Floating Drug Delivery System to Increase Gastric Retention of Drug: A Review Malipeddi Venkata Ramana, Vibhute Abhijeet Arjun*, Mehetre Chandrakant Raosaheb and Awad Supriya Balasaheb Arvind
Review Article Floating Drug Delivery System to Increase Gastric Retention of Drug: A Review Malipeddi Venkata Ramana, Vibhute Abhijeet Arjun*, Mehetre Chandrakant Raosaheb and Awad Supriya Balasaheb Arvind
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF THEOPHYLLINE BILAYERED TABLETS USING HPC AS MATRIX MATERIAL
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF THEOPHYLLINE BILAYERED TABLETS USING HPC AS MATRIX MATERIAL
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF THEOPHYLLINE BILAYERED TABLETS USING HPC AS MATRIX MATERIAL
