SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 1, NUTRITION IN PLANTS
|
|
|
- Augusta Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 1, NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. What are the different components of food? Different components of food are Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Vitamins Minerals 2. What is meant by nutrition? Nutrition is the process of taking in food by an organism and its utilization by the body. 3. What are the two main types of nutrition prevalent in living organisms? Two main types of nutrition prevalent in living organisms are: Autotrophic nutrition The mode of nutrition in which organisms prepare their own food from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water by the process of photosynthesis is called autotrophic nutrition. Heterotrophic nutrition The mode of nutrition in which organisms depend directly or indirectly on plants for food is called heterotrophic nutrition. Heterotrophs cannot manufacture their own food. 4. Define photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare their own food. 5. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms? Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms. 6. What indicates the occurrence of photosynthesis? The presence of starch in leaves indicates the occurrence of photosynthesis. 7. Write the raw materials required for photosynthesis. Raw materials required for photosynthesis are Water from soil CO2 from atmosphere Chlorophyll Sunlight
2 8. How do water and minerals present in the soil get absorbed? Water and minerals present in the soil are absorbed by the roots. 9. How do autotrophs differ from heterotrophs? Autotrophs Organisms which can prepare their own food from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water by the process of photosynthesis are called autotrophs. For example: green plants Heterotrophs Organisms which depend directly or indirectly on plants for food are called heterotrophs. They cannot manufacture their own food. For example: Cuscuta 10. What are stomata? What is their role in plants? Draw its diagram. Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves. They help in Exchange of gases Transpiration 11. How are green patches in ponds formed? Green patches in ponds are generally formed by the growth of organisms called algae. 12. Why all the materials of photosynthesis must reach to the leaves? The synthesis of food in plants occur in leaves, therefore, all the raw materials must reach to leaves. 13. What happens when pickles, leather and clothes are left in hot and humid weather for long time? When pickles, leather and clothes are left in hot and humid weather for long time then fungi starts growing on them and they gets spoil. 14. Pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis, then why does it feed on insects? Pitcher plant feeds on insects to fulfill its nitrogen requirements. 15. Do coloured leaves make their own food? Yes, coloured leaves make their own food because they contain chlorophyll.
3 16. Why are manures and fertilizers added to the soil by farmers? Manures and fertilisers are added by farmers to enrich the soil as they contain plant nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, phosphorous. 17. What is so special about the leaves that they can synthesize food? The leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll. It helps the leaves to capture the energy of the sun and synthesize food. 18. Cuscuta is without chlorophyll. How does it obtain food? Cuscuta takes readymade food from the plant on which it climbs. 19. How are water and minerals transported to the leaves? Water and minerals are transported to the leaves by the vessels which run like pipes throughout the roots, the stem, the branches and the leaves. 20. How the process of photosynthesis is carried out in desert plants? The desert plants have spine like leaves to reduce loss of water by transpiration. These plants have green stem which carry out photosynthesis. 21. How fungi appear suddenly during the rainy season? The spores of fungi are generally present in air. When they land on wet things, they germinate and grow. So fungi appear suddenly during the rainy season. 22. What are lichens? When an alga and a fungus live together in symbiotic relationship they are collectively called lichen. 23. What type of relationship is shown by lichen? Explain. Lichen shows symbiotic relationship. In lichen, an alga and a fungus live together. The fungus provides shelter, water and nutrients to the alga and the alga provides food to the fungus. 24. How nutrients are replenished in the soil? By adding fertilizers By adding manure By crop rotation By growing leguminous plants 25. How do plants get nitrogen to make proteins? The soil has certain bacteria which convert nitrogen gas of air into soluble form (nitrates and nitrites) which can be absorbed by the plants. Some plants also obtain nitrogen from insects. Plants also take nitrogen from nitrogenous fertilizers.
4 26. What is a cell? Explain its structure with a diagram. The fundamental unit of all living being is known as cell. It can be seen under microscope. The cell is enclosed by a thin outer boundary, called the cell membrane. Most cells have a distinct, centrally located spherical structure called the nucleus. The nucleus is surrounded by a jelly like structure called cytoplasm. 27. How does a pitcher plant trap insects? The leaf of pitcher plant is modified into pitcher like structure. The apex of the leaf forms a lid. Inside the pitcher, there is hair. When an insect lands on the pitcher, the lid closes and the trapped insect gets entangled into the hair. The insect is then digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher. 28. Explain how rhizobium bacterium and roots of leguminous plants share a symbiotic relationship? Rhizobium bacterium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into soluble form that the plant can take. In return, the plant provides food and shelter to the bacterium. This is how rhizobium bacterium and roots of leguminous plants share a symbiotic relationship.
5 SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 2, NUTRITION IN ANIMALS 1. Which part of stomach in ruminants temporarily stores partially chewed food? Rumen temporarily stores partially chewed food in ruminants. 2. What is cud? Partially digested food in ruminants is known as cud. 3. What is the other name of digestive canal? Alimentary canal is the other name of digestive canal. 4. Name the widest part of the alimentary canal. The widest part of alimentary canal is stomach. 5. What is tooth decay? Damage in teeth caused by acids secreted by bacteria present in buccal cavity is called tooth decay. 6. What is diarrhoea? Diarrhoea is a condition in which a person passes watery stool frequently. 7. How many sets of teeth do humans have in their lifetime? The two sets of teeth humans have in their lifetime are: Milk teeth Permanent teeth 8. What is oesophagus? The oesophagus is a long tube that connects buccal cavity to stomach. It is also known as food pipe. 9. Why do we vomit? When the food is not accepted by our stomach due to indigestion or poisoning, the food is vomited out. 10. What is ORS? When it is given? ORS stands for Oral Rehydration Solution. It is boiled and cooled water with a pinch of salt and sugar dissolved in it. ORS is given to treat dehydration caused due to diarrhoea. 11. What is the main function of the large intestine? The function of large intestine is to absorb water and some salts from the undigested food material.
6 12. What is rumination? The process in which semi digested food (cud) returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it is known as rumination. Such animals are called ruminants. 13. What are pseudopodia? Finger like projections of amoeba that are used for movement and for capturing food are called pseudopodia. 14. Describe the role of saliva, bile juice and pancreatic juice in digestion. Saliva breaks down the starch into sugar. Bile juice plays an important role in digestion of fats. Pancreatic juice act on carbohydrates, fats and proteins and changes them into simpler forms. 15. What are the different ways by which different animals obtain their food? Bees and humming birds suck the nectar of plants. Infants of human and many other animals feed on mother s milk. Snakes like the python swallow the animals they prey upon. Some aquatic animals filter tiny food particles floating nearby and feed upon them. 16. How starfish obtain its food? Starfish feed on animals covered by hard shells of calcium carbonate. After opening the shell, the starfish pops out its stomach through its mouth to eat the soft animal inside the shell. The stomach then goes back into the body and the food is slowly digested. 17. How many types of teeth are present in the buccal cavity of human being? Four types of teeth are present in buccal cavity of human being. They are Incisors - 8 in total, used for cutting and biting Canines - 4 in total, used for tearing Premolars - 8 in total, used for chewing and grinding Molars- 12 in total, used for chewing and grinding 18. What are the functions of tongue? Tongue helps in talking. Tongue helps in mixing saliva with the food. Tongue helps in swallowing food. Tongue has taste buds that detect different tastes of food.
7 19. Why should we rinse the mouth after every meal? We should rinse the mouth after every meal because many harmful bacteria begin to grow on the leftover food. These bacteria break down the sugars present in the leftover food and release acids which gradually damage the teeth. 20. Write the secretions of the stomach along with their functions. The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. Mucous protects the lining of the stomach from the acid. Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria and makes the medium in the stomach acidic so that digestive juices can act. Digestive juice breaks down the proteins into simpler substances. 21. What is the function of small intestine? Small intestine receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas. The wall of small intestine secretes intestinal juices which completes the digestion of all the components of the food. Inner walls of the small intestine have villi which increases the surface area for absorption of digested food. 22. How does amoeba capture food? Amoeba captures its food with the help of pseudopodia (false feet). When amoeba senses food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it. The food becomes trapped in a food vacuole. Digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole which act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. 23. What are the simpler form of carbohydrates, fats and proteins? S. No. Component of food Simpler form 1. Carbohydrates Sugars (glucose) 2. Fats Fatty acids and glycerol 3. Proteins Amino acids 24. List and explain the steps involved in the process of nutrition in animals. Steps involved in the process of nutrition in animals are Ingestion - The process of taking food into the body is called ingestion.
8 Digestion The process of breakdown of complex components of food into simpler substances is called digestion. Absorption The process by which digested nutrients are taken in (absorbed) from the intestine by the blood vessels is called absorption. Assimilation The process of utilizing absorbed food materials for energy, growth and development is called assimilation. Egestion The process of removing undigested food materials (waste materials) from the body through the anus is called egestion. 25. Draw diagram of human digestive system.
9 SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 3, FIBRE TO FABRIC 1. From which animal, angora wool is obtained? Angora wool is obtained from angora goats. 2. Which type of wool is common in Tibet and Ladakh? Yak wool is common in Tibet and Ladakh. 3. Shearing does not hurt sheep. Give reason for it. Shearing does not hurt sheep because the uppermost layer of the skin is dead. 4. Why is scouring essential? Scouring is essential to remove grease, dust and dirt from the sheared skin. 5. What is meant by reeling the silk? The process of taking out the threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk. 6. To which class of organic substance does silk fibre belong to? Silk fibre is a natural protein. 7. Name two animal fibres and their sources. S.No. Animal Fibre Source 1. Silk Cocoons of silk moth 2. Wool Fleece of sheep, yak, goat or camel 8. Why wool on burning gives smell similar to smell produced on burning natural silk? Wool on burning gives smell similar to smell produced on burning natural silk because they both are animal products and contain protein. 9. Why do animals like sheep, goat and yak have a thick coat of hair on their body? Animals like sheep, goat and yak have a thick coat of hair to keep them warm as hair trap a lot of air and air is a bad conductor of heat. So it does not allow their body heat to escape. 10. What is meant by selective breeding? The process of selecting parents for obtaining desirable characters in their offspring is called selective breeding.
10 11. What is sorter s disease? Sorter s disease is a fatal blood disease caused by bacterium anthrax. People working in sorting department of wool industry generally develop this disease. 12. Name four breeds of sheep in India and the quality of wool they yield. S.No. Name of breed Quality of wool 1. Lohi Good quality wool 2. Rampur bushair Brown fleece 3. Nali Carpet wool 4. Marwari Coarse wool 13. Why is shearing done in hot weather? Shearing is done in hot weather because sheep can survive without their protective coat of hair in summer season. If shearing is done in winter season then the sheep would die due to severe cold. 14. What does caterpillar secrete? Caterpillar secretes fibre made up of a protein which hardens on exposure to air and becomes silk fibre. 15. Name four varieties of silk. Four varieties of silk are: Tassar silk Moonga silk Kosa silk Mulberry silk 16. List any three characteristic properties of silk fibre. Silk fibres are: Soft Lustrous Elastic 17. Why a cotton garment cannot keep us as warm in winter as a woollen sweater does? Woollen fibres trap air and air is a bad conductor of heat, so it does not allow our body heat to escape and keep us warm during winter while cotton fibres do not trap air, so they cannot keep us warm during winter.
11 18. What is the scientific name of mulberry leaves? The scientific name of mulberry leaves is Morus alba. 19. What are occupational hazards? The problems or diseases faced by workers working in any industry are called occupational hazards. Example sorter s disease 20. List and explain the steps involved in processing fibres into wool. Steps involved in processing fibres into wool are: a) Shearing The fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body. This process is called shearing. b) Scouring The sheared skin with hair is thoroughly washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This is called scouring. c) Sorting After scouring, sorting is done. The hairy skin is sent to a factory where hair of different textures are separated or sorted. d) Picking of burrs The small fluffy fibres called burrs are picked out from the hair. The fibres are scoured again and dried. e) The fibres are dyed in various colours. f) The fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn. 21. Explain the life history of silk moth. a) The female silk moth lays eggs. b) From the eggs, larvae hatch out. The larvae of silk moth are called silkworm or caterpillar. c) Caterpillar first weaves a net to hold itself then it swings its head from side to side in the form of figure eight. d) During these movements of the head, the caterpillar secretes silk fibre. e) As the caterpillar completely covers itself by silk fibres, it turns into pupa. This covering is called cocoon. f) The further development of pupa into moth continues inside the cocoon. 22. Explain the process of obtaining silk from silk moth. a) For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. b) A female silk moth lays hundreds of eggs at a time. The eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
12 c) The larvae (silkworm) are kept in clean bamboo trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves. d) The caterpillar or silkworm spins the cocoon inside which develops the silk moth. e) The cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled or exposed to steam. The silk fibres separate out. f) Silk fibres are then spun into silk threads which are woven into silk cloth by weavers.
13
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Downloaded from INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH
 1 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH Academic Year 2011-2012 VII Science Chapter 1 : Nutrition in Plants 1. The components of food which are necessary for our body are called 2. Green plants synthesise
1 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH Academic Year 2011-2012 VII Science Chapter 1 : Nutrition in Plants 1. The components of food which are necessary for our body are called 2. Green plants synthesise
Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect
 Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect manuscripts in the past? 4. List some of the technological
Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect manuscripts in the past? 4. List some of the technological
2.1 DIFFERENT WAYS OF TAKING FOOD
 2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
You have learnt in Chapter 1 that
 2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System
 To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
CLASS VII SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 NUTRITION IN PLANTS
 CLASS VII SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTIONS Q1. What is food and nutrition? Ans. Food provides us energy to grow. It gives us resistance against discase. Q2. What is
CLASS VII SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTIONS Q1. What is food and nutrition? Ans. Food provides us energy to grow. It gives us resistance against discase. Q2. What is
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad , A.P.
 THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Digestion is a process in which the complex food we eat is broken down in to simple, soluble, substances which our body is able to use.
 KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment.
 HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment. 1 Heterotrophic organisms are most bacteria, some protists, and ALL fungi
HETEROTROPHS cannot make their own food like Autotrophs(Plants). They must get their nutrition from their surrounding environment. 1 Heterotrophic organisms are most bacteria, some protists, and ALL fungi
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The function of the digestive system is to break down
 Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2
 Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Human Digestion. Junior Science
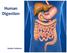 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Digestion: An Absorbing Tale
 8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
4 th primary. 2 nd term 1 Science
 2 nd term 1 Science A-Choose: Model Answer (work sheet) 1-16 2-pharynx 3-stomach 4-seven meters 5-stomach. 6-digestive system. 7-lung 8-respiration 9-nose 10-hair and mucus. 11-organs 12-cell 13-chloroplast
2 nd term 1 Science A-Choose: Model Answer (work sheet) 1-16 2-pharynx 3-stomach 4-seven meters 5-stomach. 6-digestive system. 7-lung 8-respiration 9-nose 10-hair and mucus. 11-organs 12-cell 13-chloroplast
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
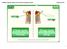 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
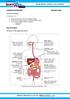 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
B17 instructions for 227. April 15, 2011
 Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals,
Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals,
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs
 INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2
 1 Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2 Question 1 How are autotrophs classified? Autotrophs are classified based on their source of energy. If they use the light energy of the sun, they are called
1 Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2 Question 1 How are autotrophs classified? Autotrophs are classified based on their source of energy. If they use the light energy of the sun, they are called
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
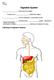 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Digestive System Exam Questions
 The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical
 15 Digestion: An Absorbing Tale r e a d i n g Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical breakdown. Everything you eat and drink, including medicines, enters your body through
15 Digestion: An Absorbing Tale r e a d i n g Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical breakdown. Everything you eat and drink, including medicines, enters your body through
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System
 Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System According to the new frame of the question paper, it is proposed that textual questions shall not be asked and other thing is that, a question once asked
Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System According to the new frame of the question paper, it is proposed that textual questions shall not be asked and other thing is that, a question once asked
How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness?
 3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
Page 1. Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Page 1. Electrolytes. Required to maintain certain functions. Imbalance causes death. Muscles, neurons, etc.
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
