Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
|
|
|
- Francis Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only differ in terms of cell wall. D. A unicellular organism does not need a nucleus to function. Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body. Q2. Which of the following characteristics is true for cell walls? A. They restrict the movement of substances across the cell. B. They support the cellular structure in animal cells from bursting when water enters the cell excessively. C. They are made up of cellulose that cannot be digested by animals easily. D. They are found in some animal cells. Extra: They are the fibres in our diets to help our bowel movement. 1
2 Q3. What is the name of the system that consists of brain and spinal cord in human beings? A. The reproductive system B. The digestive system C. The circulatory system D. The nervous system Nervous system 2
3 Q4. Which of the following organs are parts of the respiratory system? A. heart and blood vessels B. sperm duct and penis C. trachea and bronchi D. mouth and oesophagus Q5. Which of the following organelles are collectively called protoplasm? A. Chloroplast, nucleus, cell wall B. Cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus C. Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm D. Cell wall, cell membrane, Protoplasm is the living contents of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. Cell wall is not part of the protoplasm. Animal has protoplasm but no cell wall. Q6. Which of the following organelles in a cell allows energy transformation from chemical energy to heat energy to take place? A. Nucleus B. Cytoplasm C. Chloroplast D. Cell membrane Cytoplasm is the site where chemical processes in the cell take place. 3
4 Q7. Which of the following terms correctly describes a group of organ systems that performs similar tasks in a systematic and coordinated manner? A. Organs B. Organ systems C. Organism D. Cells Structure Characteristics Examples Tissue A large number of similar cells performing a particular function Plants: Epidermal tissue, photosynthetic tissue, supporting tissue Animals: Epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, nerve tissue Organ System Two or more tissues grouped together, carrying out the same function. Two or more organs working together in the same function Heart (muscle, blood and connective tissues) Brain (nerve and connective tissues) Digestive, circulatory, nervous, respiratory, excretory, reproductive system Q8. Which of the following animals cannot control over their own body temperature? A. Chimpanzees B. Chameleons C. Hummingbirds D. Rodents Cold-blooded animals cannot control their body temperature. Chameleons are reptiles. Fish Amphibians Reptiles They are cold blooded and live in water. Their bodies are covered with slimy scales. They have gills for breathing. They have fins for swimming. They are cold blooded. They have moist skin which is not covered by scales or hair. They live on both land and water but always lay their eggs in water. They have four legs. They are cold blooded. They have leathery skin which is covered with dry scales. They always lay their eggs on land. Their eggs have soft shells 4
5 Birds They are warm blooded. Their bodies are covered with feathers. They have beaks (no teeth) for feeding. They lay eggs with hard shells Mammals They are warm blooded. Their bodies are covered with hair or fur. Mothers produce milk for their babies (suckle their young). Q9. The descriptions of a plant kingdom are as follows: I. Non-flowering II. Reproduce by seed Ill. Growth on land What could be this plant kingdom? A. Ferns B. Conifers C. Mosses D. Hibiscus Conifers reproduce by seeds. 5
6 Mosses Conifers Ferns 6
7 Q10. Which of the following characteristics can be observed in hibiscus and rose? A. Both reproduce by spores. B. Both do not have true roots. C. Both have stems and leaves. D. Both have spores in the capsules. Both are flowering plants. They have true roots, stems and leaves. Q11. Which of the following is one of the characteristics for conifers? A. They have needle-like leaves. B. They have spores under their leaves. C. They are flowering-plants. D. They do not have true roots. They also reproduce by seeds. Conifers leaves Q12. Which of the following organisms does not have true roots but makes its own food? A. Mushroom B. Moss C. Fungi D. Conifer They can carry out photosynthesis. Q13. Which of the following groups of animals are all vertebrates? A. Tiger, starfish, rabbit B. Monkey, rat, roundworm C. Zebra, dolphin, rat D. Ant, crab, starfish 7
8 Q14. Which of the following characteristics cannot be used to describe millipedes? A. Have no backbones B. Have more than three pairs of legs C. Have jointed legs D. Have soft and moist exoskeleton Millipedes have hard and dry exoskeleton Q15. An organism has the following characteristics. I. Breathe through lung II. Have hair III. Give birth to young Which of the following organisms fits the above characteristics? A. Crocodiles B. Salamanders C. Stingrays D. Giraffe Salamanders 8
9 Stingrays Q16. The diagram below shows an apparatus used to investigate osmosis. After a few hours, which changes in levels will occur and which substances will move across the membrane? Level M Level N Substance A. Fall Rise Starch B. Fall Rise Water C. Rise Fall Starch D. Rise Fall Water 9
10 Starch solution has a lower concentration of water, water will move across the Visking tubing into the starch solution. Q17. Which statement best explains why gases move across the stomata of green leaves during warm and sunny day? A. The gases gain energy which cause them to move more randomly and vigorously. B. The gases expand. As a result, they move out from the stomata to occupy more spaces. C. The gases are warmed. As a result, their densities decrease and they rise up D. The gases have different concentrations inside and outside of the leaves. Questions 18 and 19 refer to the diagram below. It shows a typical plant cell after being placed in a beaker of salt solution for 10 minutes. Q18. What could be the concentration of the salt solution in the beaker? A. 5% salt solution B. 15% salt solution C. 20% salt solution D. 25% salt solution The concentration of salt solution must be higher in the beaker than in the cell, so that water molecules move out from the cell. The diagram shows a plasmolysed plant cell. Q19. Which process is involved to cause this observation of the cell? A. Osmosis B. Diffusion C. Expansion D. Active transport 10
11 Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from the region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a partially permeable membrane. Diffusion is the spreading out of one substance through another due to the random motion of particles. Q20. Which of the following is one of the functions of blood capillaries? A. Allow osmosis of oxygen B. Allow diffusion of glucose C Transport oxygen gas D. Transport plasma Blood capillaries allow exchange of substances between bloodstream and the living cells. Oxygen and useful nutrients move out from the bloodstream into the living cells. Waste products such carbon dioxide leave the living cells and enter the bloodstream. 11
12 Q21. Which statement best explains why red blood cells have biconcave shape? A. To transport more carbon dioxide B. To contain more cytoplasm C. To decrease its density D. To increase the rate of oxygen exchange Red blood cell has a biconcave disc shape to increase surface area to volume ratio for efficient transportation of oxygen. Q22. The diagram below shows part of a root hair cell. Which of the following will take place? A. Salt will move into the root hair cell from the soil through active transport. B. Osmosis of water will not take place. C. Cytoplasm of the cell will change in its volume. D. No passive movement of substances will take place between the soil and the root hair cell. Cytoplasm will decrease in its volume because water molecules move out from the cell into the surrounding by osmosis. Q23. Which of the following substances is not transported by plasma? A. Carbon dioxide B. Glucose C. Heat D. Oxygen Oxygen is transported by red hood cells. 12
13 Q24. The diagram below shows a simplified diagram of blood circulation in a mammal. Which blood vessels transports blood with the highest oxygen content? A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 4 C. 1 and 3 D. 3 and 4 Q25. Which statement about the movement of substances across the living cells is not correct? A. The direction of the movement of one substance depends on the concentration of the other substance. B. No energy is required when a substance moves down its concentration gradient C. Active transport will take place when mineral salts become scarce in soil. D. Osmosis can only take place if cell membrane is present in the living cells The movement of one substance from one region to another depends on its own concentration gradient iii different regions. Q26. The diagram below shows a typical root hair cell. 13
14 Which substance does not moves across the cell membrane by simple diffusion during respiration? A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Glucose D. Excess water This movement of water across the cell membrane is known as osmosis. Q27. An onion layer loses its mass after placing in a beaker of solution for a period of time. Which of the following is not possible to be the solution in the beaker? A. Pure distilled water B. Pure starch solution C. Pure glucose solution D. Pure mineral salt solution Pure distilled water has the highest concentration of water molecules, therefore, there will he net movement of water molecules into the onion cells to cause them to gain mass. Q28. The diagram below shows an experiment to investigate the movement of substances. Which of the following most likely will not happen to the respective regions 1, 2 and 3 at the end of the experiment? 14
15 A. Region 1 increases in volume. B. There are same numbers of glucose molecules in these three regions. C. Regions 2 and 3 have equal volume. D. Blue-black observed in region 3 when two drops of iodine is added to it. Starch cannot move across the partially permeable membrane. Q29. Which statement best explains why the muscular walls of veins is thinner than that of arteries? A. They carry deoxygenated blood. B. They carry smaller volume of blood. C. They carry less substance in blood. D. They carry blood that flows slower in the vessels. Blood flows with a lesser pressure in the veins, so the speed of the blood is slower. Therefore, it does not require a thicker wall to withstand the low pressure. Q30. The diagram below shows the effect of solution Y on a red blood cell after half an hour. Which statement is not correct from this observation? A. Solution Y contains a higher concentration of solute than in the red blood cell B. The cell membrane of this red blood cell eventually will break apart. C. The red blood cell is said to be dehydrated. D. The red blood decreases in its volume and becomes soft. 15
16 The red blood cell shrinks. The appearance of thin red blood cell indicates that it loses water by osmosis. Therefore, the cell membrane will not burst. Hypotonic solution means dilute solution or less concentrated solution Hypertonic solution means concentrated solution or solution with little water. 16
17 Q31. Which of the following is not one of the differences between a red blood cell and a white blood cell? A. Presence of haemoglobin B. Presence of nucleus C. Presence of cytoplasm D. Presence of chromosomes White blood cells and red blood cells both have cytoplasm. 17
18 Q32. The diagram below shows the structure found in a typical human cheek cell. Which statement about this structure is correct? A. They restrict the movement of any substances across it by their masses. B. Water is the only substance that its direction of movement depends on the presence of this structure. C. It only allows the substances to move from its region of higher concentration to its region of lower concentration. D. It is present in a typical plant cell but is made of cellulose Osmosis takes place. A partially permeable membrane does not prevent active transport of a substance. Q33. Which of the following movements of substances is not an example of diffusion in plants? A. Oxygen is given out to the surroundings through the stomata after photosynthesis. B. Mineral salts are taken in by root hair cells when they have a lower concentration in soil. C. Water vapour is lost from the leaves through stomata during a warm and sunny day. D. Food is transferred from the leaves to the various parts of the plant after photosynthesis. Active transport is a process when a substance moves from its region of low concentration to its region of high concentration against a concentration gradient. Energy is involved. 18
19 Q34. Which of the following components transport substances in the circulatory system? I. Plasma II. White blood cells Ill. Red blood cells A. I only B. Ill only C. I, II and Ill D. I and Ill White blood cells do not transport substances. They only fight against infections. Q35. Which of the following is not one of the differences between an artery and a vein? A. Compositions of blood B. The size of lumen C. Thickness of muscular wall D. Blood flow pressure Blood flow in both vessels contains the same compositions, i.e. plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Q36. The diagram below shows a section from the plant root after taken out from a red dye solution. Which structure most likely transports substance made in the green leaves? 19
20 D. This diagram shows the section from the root. The structure which is stained red is a xylem vessel because xylem vessels transport water containing the red dyes. Option D is phloem. Q37. The diagram below shows part of the human circulatory system. Which substance occurs at a higher concentration in the blood flow 1 than in the blood flow 2? A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Nitrogen D. Glucose Blood floss from the lungs to the heart has the highest oxygen concentration after picking up fresh oxygen front the atmosphere. Q38. Which of the following blood vessels most likely contains the highest concentration of dissolved oxygen in the blood vessels? A. Pulmonary artery B. Pulmonary vein C. Aorta D. Renal artery Pulmonary vein receives fresh oxygen from the lungs. 20
21 Q39. The diagrams show three types of blood vessels, 1, 2 and 3. Which of the following describes the characteristics for each type of vessel? Blood flow under high pressure Location of exchange of substances Blood flow controlled by valves A B C D Arteries Veins Capillaries Function carry blood away from the heart Structure Thick, elastic and muscular wall carry blood towards the heart Thin, less elastic and less muscular wall 21 allow exchange of substances between blood and the body cells One-cell thick to allow substances can diffuse to and from the cells Valves Absent Present Absent Blood flow Very fast as blood is under high pressure In spurts Slow as under low pressure Smooth flow Slow as under low pressure
22 Size of lumen Small Large Very narrow Q40. Which of the following is the correct pathway for blood circulation in human? A. Right atrium left atrium left ventricle lungs right ventricle B. Lungs left atrium left ventricle right ventricle right atrium C. Left ventricle right atrium right ventricle lungs left atrium D. Lungs left ventricle left atrium right ventricle right atrium 22
23 Q41. A plant was placed in jar as shown below. The condition was suitable for the plant to make food, as there was sunlight and the soil was moist. The air inside the jar contained carbon dioxide gas which is made up of radioactive carbon element. The carbon from the gas was incorporated into food during photosynthesis. After two hours, the plant was removed from the jar. The stem was cut crosssectional. It was then placed on photographic film which became black when exposed to radioactivity. Which diagram shows the correct positions of the black spots found on the film? A. The black spots should only be observed in phloem tissues as they transport food substances. 23
24 Q42. The diagram below shows a human heart and its attached vessels. Which of the following correctly describes the conditions of the blood in the different vessels? A B C D P Q R S Oxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure Deoxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, high pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Oxygenated, high pressure Deoxygenated, low pressure 24
25 25
26 Q43. The diagram below shows part of the human alimentary canal What is the function of X? A. To remove solid waste from the body B. To absorb water into body C. To take in mineral salts into the body D. To store solid waste temporarily It is a rectum. Q44. Which of the following is not one of the end products of digestion in the small intestine? A. Fatty acids B. Short protein chains C. Glycerol D. Glucose Proteins are broken down into short protein chains in the stomach. In the small intestine, they are further digested into amino acids. Q45. Which of the substances is taken into the bloodstream when it reaches the large intestine? A. Vitamins B. Glucose C. Amino acids D. Fatty acids and glycerol Large intestine absorbs mineral salts, vitamins and water. Note that no chemical digestion takes place in large intestine. 26
27 Q46. The diagram below shows part of the human alimentary canal. What would happen when part P is removed? A. Digestion of fats becomes slower B. No production of bile in the digestive system C. No secretion of lipase D. No secretion of hydrochloric acid Bile breaks up fats into droplets to increase its total surface area so that lipase can digest them at a faster rate. Bile is produced by the liver. Structure P is bile duct. The bile secreted by the liver passes through a Y-shaped duct, as shown in Figure. The bile travels down one branch of the Y shaped duct and then up the other branch to the gallbladder, a saclike organ that stores and concentrates bile. 27
28 Q47. Which chemical digestion takes places in the beginning of the human alimentary canal? A. Complex protein molecules are broken down into smaller protein molecules. B. Large and complex food is broken into smaller pieces by the action of chewing. C. Food is pushed down into the stomach by a long muscular tube. D. Large and complex starch in food is broken down into maltose. Starch is digested first in the mouth by salivary amylase. Salivary amylase is released by the salivary glands. Q48. Which of the following statements about starch and glucose is correct? A. They both contain the constituent elements of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only. B. Starch can provide twice the amount of energy than glucose in a same amount of mass. C. Starch gives blue--black colour with iodine after mixed with salivary amylase. D. Glucose is the first carbohydrate that is broken down in the mouth of the human alimentary canal. Glucose and starch are carbohydrates. Fats are also made up of elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only. 28
29 Q49. The diagram below shows the movement of substances in a muscular tube. Which of the following regions in the human alimentary canal can this movement be found? I. Oesophagus II. Mouth III. Large intestine A. I only B. II only C. I and Ill D. II and Ill As you can see in Figure, alternating contractions of these muscle layers push the bolus through the esophagus and into the stomach. This series of rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations is called peristalsis. Peristalsis is so efficient at moving materials down the esophagus that you can drink while standing on your head. The smooth muscles move the water up the esophagus, against the force of gravity. 29
30 Q50. Which of the following does not secrete enzymes in the human alimentary canal? A. The liver B. The small intestine C. The pancreas D. The stomach Liver secretes bile. Q51. The diagram below shows part of the human alimentary canal. Which statement about structure P is not correct? A. It is part of the human alimentary canal which carries out chemical digestion of food B. Digestion of fatty food substances can only be carried out from the secretion of P. C. Protease from structure P digests the smaller protein molecules into amino acids. D. Maltase secreted by structure P completes the digestion of starch into glucose. P is pancreas. It is an organ associated to alimentary canal but it is not part of it. It does not carry out chemical digestion. Chemical digestion is carried out in the small intestine. 30
31 Q52. The diagram below shows part of the human alimentary canal. Which of the following actions does not take place in structure M? A. Killing bacteria in food B. Breaking down proteins chemically C. Absorption of amino acids D. Churning action on the digested food Absorption of simpler food molecules only takes place in the small intestine. Q53. Which statement best explains why fibres are not taken into the bloodstream in the small intestine? A. Fibres are too heavy to move through the wall of the small intestine. B. Fibres do not have any useful functions in our body, so they are not being absorbed. C. Fibres are not able to move across the partially permeable membrane present in the wall of the small intestine. D. Fibres cannot move against its concentration gradient from the lumen of the small intestine into the bloodstream. 31
32 Q54. The diagram below shows the human alimentary canal. Which regions show the enzyme activities? A. 1 and 4 B. 1, 3 and 5 C. 2, 3 and 5 D. 1, 2 and 4 32
33 The Human Digestive System. Food breaks down as it moves through the chambers of the digestive tract. Accessory organs aid in digestion. 33
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
4 Grouping of living things
 4 Grouping of living things 4.1 Characteristics of living things 1 Choose the group which consists of all living things living in garden soil. A Earthworms, millipedes, ants B Cockroaches, snails, centipedes
4 Grouping of living things 4.1 Characteristics of living things 1 Choose the group which consists of all living things living in garden soil. A Earthworms, millipedes, ants B Cockroaches, snails, centipedes
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Body Systems. S2 Science. Homework. Holy Cross High School Page 1
 Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
c Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology Part I D. Amphibians
 c Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology Duration: 03 hours Part I Index No:- 1. Which is not a characteristic of fungi A. Have a nuclei B. Do not have
c Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology Duration: 03 hours Part I Index No:- 1. Which is not a characteristic of fungi A. Have a nuclei B. Do not have
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
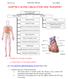 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY
 S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
IGCSE Biology Revision Answers
 IGCSE Biology Revision Answers Test 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms 1. (b), (c) and (e) 2. Nutrition; respiration 3. (b) and (d) 4. T, F, F, F 5. Nutrition; respiration Metabolism; excretion 7. F,
IGCSE Biology Revision Answers Test 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms 1. (b), (c) and (e) 2. Nutrition; respiration 3. (b) and (d) 4. T, F, F, F 5. Nutrition; respiration Metabolism; excretion 7. F,
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes
 Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
HSC Biology. Year 2016 Mark Pages 46 Published Jan 18, Biology Notes. By James (99.05 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
Animal Survival. Standard Grade Biology
 Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? A
 1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular
 transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. Materials: Markers Ruler 1,000 cm string Map Pencils Digestive Organ Mouth 11 Esophagus 25
