CLASS VII SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 NUTRITION IN PLANTS
|
|
|
- Hector Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLASS VII SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTIONS Q1. What is food and nutrition? Ans. Food provides us energy to grow. It gives us resistance against discase. Q2. What is the mode of nutrition in plants? Ans. Autotrophic mode of nutrition. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis process. 2. VERY SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS 1. Autotrophs : The organisms that make their food by using photosynthesis from simple inorganic substances are called autotrophs. 2. Insectivorous : Some green plants meet their nitrogen requirement by feeding on insects. They are known as carnivorous or more appropriately insectivorous. 3. Symbiotic relationship : When two organisms live together and share shelter and nutrients, their association is called symbiosis or symbiotic relationship,and the organisms are called symbionts. 4. Host : The organism which provides food and shelter to the parasite in parasitic association is called host. 5. Nutrients : The components of food that are necessary for our body are called nutrients. 6. Nutrition : The process of taking food by an organism and its utilization by the body. 7. Chlorophyll : Green pigment, present in the chloroplast, that is essential for photosynthesis. 3. SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS Q1. Why do organisms need to take food? Ans. All organisms take food and utilize it to get energy for the growth and maintenance of their bodies. Q2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph? Ans.Parasite : Parasite derives nutrients from the living organisms. Parasite mostly lives on or in the host.
2 Saprotroph : Saprotroph obtain nutrients from dead and decaying organisms. They live on dead and decaying stuff. Q3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves? Ans. When iodine comes in contact with starch, a dark blue colour appears. By dropping iodine solution on the leaves, we can check the presence of starch. Q4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of the food in green plants? Ans. In plants, the synthesis of food occurs by a process called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll containing cell of the leaves use C02 and water to synthesis carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight. The process can be represented by the equation. CO 2 + H 2 OSunlightcarbohydrate + Oxygen Chlorophyll During this process oxygen is released. The carbohydrates formed ultimately get convertedinto starch. The presence of starch n leaves indicates the occurrence of photosynthesis. The starch is also a carbohydrate. Q5. Show with The help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food? Ans. Food chain Q6. Fill in the blanks a. Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesize their own food. b. The food synthesized by the plants is stored as starch. c. In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called chlorophyll. d. During photosynthesis plants take in carbon di oxide and release oxygen. Q7. Name the following: a. A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and tubular stem: Ans. a.cuscuta b. A plant that has both autotrophic and hetrotrophic mode of nutrition: Ans. b. Pitcher plant
3 Ans. c. The pores through which leaves exchange gases: c. Stomata 08. Tick the correct answer a. Amarbel is an example of Ans. a. Parasite b. The plant which traps and feeds on insects is Ans. b. Pitcher Plants Q9. Match the column COLUMN A COLUMN B 1. Chlorophyll Bacteria (2) 2. Nitrogen Heterotrophs (4) 3. Amarbel Pitcher Plant (5) 4. Animals Leaf (1) 5. Insects Parasite (3) Q10. True or False a. Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. False b. Plants which synthesis their food themselves are called saprotrophs. False c. The products of photosynthesis is not a protein. True d. Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. True Q11. Choose the correct option from the following. a. Which part of the plants takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis? Ans. a. Stomata b. Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their? Ans. b. Leaves ACTIVITY Take a fresh slice of bread and keep it in a glass plate in a warm dark place. Observe it after two or three days. Do you see some fluffy growth on it? Ask your teacher about it. Ans. Yes, we will see fluffy thing over slices because on bread slices fungi grown due to the development of favourable conditions for the growth of fungi, such as Humidity, temp., etc. VALUE BASED QUESTION:- Q1. A farmer, for planting rice one season, planted grandnuts in the next season. Why? Ans. To increase the fertility of soil and to maintain the fertility of soil.
4 HOTS QUESTIONS Q1. Why green leaf is boiled in alcohol before testing it for starch? Ans. Green leaf is boiled in alcohol for contamination free testing for starch and it will make leaf suitable for all testing processes. Q2. If a few leaves of a potted plant are coated with a thin layer of Vaseline or oil, what effect would it have on the leaves? Ans. Rate of transpiration will get slow because the pores or the stomata of leaves will get blocked and exchange of air will not take place. Q3. Why water is required for photosynthesis? Ans. Water is the main constituent of photosynthesis and with CO2 in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll gives glucose and oxygen. CO2+H2O Chlorophyll Sunlight Glucose + oxygen. SMART CLASS:- Yes, we will use smart class for better understanding of nutrition of plants. To show difference b/w Auto tropic and Hetoro tropic mode of nutrition.
5 Chapter 2, Nutrition In Animals 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTIONS/ANSWERS:- Q1. How does a unicellular organism life amoeba derive its nutrition? Ans. Through its Pseudopodal action. Q2. Draw a well labeled diagram of amoeba. Ans. 2. FILL IN THE BLANKS a. The main steps of nutrition in human are ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion. b. The largest gland in human body is liver. c. The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and gastric juices which act on food. d. The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger like outgrowths called villi. e. Amoeba digests its food in the food vacuole. 3. STATE TRUE OR FALSE a. Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. False b. The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. True c. The gall bladder temporarily store bile. True d. The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. True 4. TICK FOR THE CORRECT ANSWER a. Fat is completely digested in the Ans. a. Small intestine b. Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the Ans. b. Large intestine 5. MATCH THE FOLLOWING COLUMN A Food components carbohydrates COLUMN B Product (s) of digestion 1. Carbohydrates Fatty acids and glycerol (3) 2. Proteins Sugar (1) 3. Fats Amino acids (2)
6 6. SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS Ques.1Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it help to digest? Ans. Bile is produced by liver and is stored in gall bladder. Bile juice digests fat. Ques.2 Which part of the digestive canal is involved in? a. Absorption of food Small intestine b. Chewing of food Buccal cavity c. Killing of bacteria Stomach d. Complete digestion of food Small intestine Formation of faeces Large intestine 7. SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS Ques.1 What are Villi? What is their location and function? Ans. The inner wall of the small intestine has thousands of fingers like outgrowths. These are called villi. Villi are located in the small intestine. The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials. Ques.2 Name the type of carbohydrates that can be digested by ruminants but notby humans. Give the reason also? Ans.Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Ruminants have a large sac- like structure called rumen which is present in between the small intestine and large intestine. The cellulose is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans. Ques.3 Why do we get instant energy from glucose? Ans. Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrates which can be broken down easily to give energy. So, glucose is called instant energizer. Ques.4 Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings. Ans. Similarity : Both amoeba and human use digestive juices to digest food. Difference : Human needs to chew food, whereas in amoeba, there is no chewing. Ques.5 Matching: COLUMN A COLUMN B 1 Salivary gland Bile Juice secretion (3) 2. Stomach Storage of undigested food (4) 3. Liver Saliva secretion (1) 4. Rectum Acid release (2) 5. Small intestine Digestion is completed (5) 6. Large intestine Absorption of water (6) Release of faeces (4) Ques.6 Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss. Ans. No, because to live a healthy life, we need a complete balance of all nutrients. Raw green
7 vegetables may have cellulose which leafy vegetables will not solve the purpose. cannot be digested by us. So, only green Ques.7 Label the given figure of the digestive system 7. LONG ANSWER Ques.1 Explain the digestion in Ruminants? Ans. They quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. But later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it. This process is called rumination and these animals are called ruminants. The grass is rich in cellulose, a type of carbohydrate. Many animals including humans cannot digest cellulose except reminants. 8. HOTS QUESTION SOLVED Q1. The organ which stores bile? Ans. Liver is largest gland of our body and it stores two types of bile pigments, bilirubin and billverdin. Q2. The part which feels the taste of different food items? Ans. Tongue (taste buds) our toungue has different taste birds for such as salty, sweet, sour, bitter. 9. VALUE BASED QUESTION:- Ques.1 Raman s mother does not allow him to talk while eating. She also does not allow him to eat food while lying down. What could be the reas for it? Ans. The food will get stuck in food pipe or may be enters in air or voice box will get sudden hicwps or some respiratory problems.
8 Ques.2 Rishi is a 1 year old boy, his mother use to give him goat s milk inspite of cow s milk? Ans. Because fays in goat s milk are much simpler than those in cow s milk. Therefore, the goat s milk is much easier to digest than the cow s milk. 10. ACTIVITY / PROJECT: - Collect data from your friends, neighbours and classmates to know more about milk teeth. Tabulate your data. One way of doing it is given below. Ans. S.NO Age at which first tooth full Age at which last tooth fell No. of teeth lost No. of teeth replaced 1 4 yrs 7 yrs yrs 7.2 yrs yrs 7.5 yrs yrs 8 yrs yrs 8 yrs 9 9
9 CHAPTER 3 FIBER TO FABRIC 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTIONS Q1. Feel the hair on your body and arms and those on your head. Do you find any difference? Which one seems coarse and which one is soft? Ans. Like us, the hairy skin of the sheep has two types of fibres that forms the fleece: 1. The coarse beard hair, 2. The fine soft under hair close to the skin. The fine hair provide the fibres for making wool. Q2. We wear sweaters in winters, do you know from where we get that fibre. Ans. From the fine hairs of sheep use to make wool. 2. VERY SHORT QUESTION/ANSWER Ques.1 You must be familiar with the following nursery rhymes. (a) Baa baa black sheep, have you any wool (b) Marry had a little lamb, whose fleece was white as snow Answer the following a. Which parts of the black sheep have wool? Ans. a. Wool is obtained from the fine, soft under hair close to the black sheep s skin. b. What is meant by the white fleece of the lamb? Ans. b. White face means the white hair of lambs which is used for making wool. Ques.2 The silk worm is (a) caterpillar, (b) a larva. Choose the correct option a. i b. ii c. both (a) (b) d. neither a nor b Ans. Both a and b Ques.3 Which of the following does not yield wool? a. Yak b. Camel c. Goat d. Woolly dog Ans.Woolly dog. Ques.4 Given below is a sequence of steps in the processing of wool. Which are the missing steps? Add them. Ans. Shearing scouring, sorting dyeing and rolling into yarn.
10 Ques.5 Make sketches of the two stages in the life history of the silk month which are directly related to the production of silk. Ans. Ques.6 Out of the following, which are the two terms related to silk production? Sericulture, Floriculture Moriculture Apiculture Silviculture Ans. Sericulture and mariculture. Ques.7 Match the words of column A with those given in column B COLUMN A COLUMN B 1. Scouring Yields silk fibers 2. Mulberry leaves Wool yielding animal 3. Yak Food of silk worm reeling 4. Cocoon Cleaning sheared skin 3. SHORT QUESTION/ANSWER Ques.1 What is meant by the following terms? Ans. a. Rearing : Raising the sheep and taking its care is called rearing. b. Shearing : For obtaining wool, the fleece of the sheep together with a thin layer of skin is taken off its body. This process is known as shearing. c. Sericulture : By sericulture we mean the rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk.
11 Ques.2 Give below is a crossword puzzle based on this lesson. Use hints to fill the blank spaces with letters that complete the words. Ans. DOWN ACROSS 1. Through washing 1. Keep Warm 2. Animal fiber 2. Its leaves are eaten by silkworms 3. Long thread like structure Hatches from egg to moth 4. LONG QUESTION/ANSWER Ques.1 Discuss in detail the rearing and breeding of sheep. Ans. Sheeps are reared in many parts of our country for producing wool. The quality and texture of the fibres obtained from them is good. Certain breeds of sheep have thick coat of hair on their body which yields good quality wool in large quantities. These shop are selectively bred with one parent being a sheep of good breed. 5. HOTS QUESTIONS SOLVED Ques.1 Why we wear woolen clothes in winters. Ans. Because the fine fibers of wool keep us warm. It maintains the body temperature as much balance with the outside environment during winters. Ques.2 Does shearing hurt sheep. Ans. No, because shearing is removal of upper layes of hairs from sheep s skin and while shearing only dead cells of the body removed not the living tissues connected to the body metabolic system.
12 6. VALUE BASED QUESTION: Q1. Boojho is wondering why it hurts when someone pulls his hair but not when he goes for a hair cut? Ans. Because when someone pulls his hair it also pulls his skin and muscles in which hairs are fixed but during hair cut only upper part of hair cuts. Q2. Paheli wants to know why a cotton garment cannot keep us as warm in winter as a woolen sweater does. Ans. because cotton fibres are very thin and it allows air to pass through but woollen clothes have thick fibres and act as. Insulators as it dose not allows air to pass. 7. Activity: - Classroom Activity Collect pieces of silk cloth of various types and paste them in your scrap book. You can find them in a tailors shop among the heap of waste cut pieces
13 Chapter 4 Heat 1. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE QUESTION Q1. We wear woolen clothes in winters and light coloured cotton clothes when it is hot? Why? Ans. Because woolen clothes keep us warm and light coloured cotton clothes give us a feeling of coolness. Q2. How do we know whether an object is hot or cold? Ans. By measuring its temperature and by feeling its coldness and hotness. 2. VERY SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS Ques.1 One liter of water at 30 c is mixed with one liter of water at 50 C. The temperature of the mixture will be? Ans.Between 30 C and 50 C Ques.2 An iron ball at 400G is dropped in a mug containing water at 40 C. The heat will Ans. Not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball. Ques.3 A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream its other end. Ans. Does not become cold. Ques.4 Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that. Ans. Copper is a superior conductor of heat to the stainless steel. 3. SHORT QUESTION ANSWERS Ques.1 State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer. Ans LABORATORY THERMOMETER CLINICAL THERMOMETER Similarities a. In this thermometer, mercury is used. a. In this too, mercury is used. b. In this thermometer, the scale is b. In this also, the scale is denoted in Celsius. denoted in Celsius. Differences a. Besides body temperature, it is used for a. This is used only formeasuring
14 measuring the temperatures of other objects. human bodythermometer. b. Its temperature measuring capacity ranges b. Its temperature measuring from 10 o c to 100 o c capacity ranges from 35 c to42 c only. Ques.2 Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat? Ans. Conductors :Aluminum and copper Insulators :Plastic and wood Ques.3 Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing? Ans. During winter, when we have so many layers of clothing on our body, the air trapped in between two layers of cloth acts as an insulator. This is the reason why wearing more layers of clothing keep our body warm in winter. Ques.4 In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain. Ans. In hot season, the outer walls of houses should be painted white, because white colour reflects back the heat radiation which falls upon it. That is why the rooms remain cool they do not warm up in summer. Ques.5 Look at figure. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation? Ans.
15 4. LONG QUESTION ANSWERS Ques.1 Give reasons for the following. a. Cooking utensils are made of metals are good conductor of heat and electricity. b. Pressure cooker is provided with Bakelite handle. c. We wear woolen clothes in winter. Ans. a. Because all metals are good conductor of heat and electricity. b. Bakelite is insulator hence heat is not passing them. c. Wool is poor conductor of heat. Air is trapped in between wool fibres and prevents the flow of heat from our body. 4. FILL IN THE BLANKS Ans. a. The hotness of an object is determined by its temperature. b. Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a clinical thermometer. c. Temperature is measured in degree Celsius. d. No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of radiation. e. A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of conduction. f. Clothes of dark colours absorb heat better than clothes of light colours. 5. MATCH THE FOLLOWING: COLUMN A COLUMN B 1. Land breeze blows during Summer 2. Sea breeze blows during winter 3. Dark coloured clothes are preferred during Day 4. Light coloured clothes are preferred during Night 6. EXTRA QUESTIONS Q1. What is the significance of kinkin a clinical thermometer? Ans.The kink (bend) does not allow the mercury to fall as soon as the thermometer is taken out of the mouth Q2. What object are the best absorbers of the radiant energy? Ans. Black object
16 Q3. Do all substances conduct heat easily? Ans. No. Q4. Can you lift a hot pan by holding it from the handle without getting hurl? Ans. Yes, if the handle is covered with the help of an insulated material. Q5. How does the heat from the sun reach us? Ans.By radiation. 7. HOTS QUESTIONS SOLVED Ques.1 Which material has the highest melting pointing? Ans. Mercury is semi liquid and has very high melting point and it melts at near about c. Ques.2 Why does a clinical thermometer have such a narrow range? Ans. It is because the temperature of a human body cannot fall below 35 o C or go above 42 o C. It is use to measure only human body temperature not in laboratory. 8. VALUE BASED QUESTION Q1. Rohit says, My left hand tells me that the water in a mug is hot and the right hand tells me that the same water is cold, what should I conclude? Ans. Rohit s confusion shows that we cannot always rely on our sense of touch to decide whether an object is hot or cold. A reliable measure of the hotness of an object is its temperature. Q2. Seema gets a naughty idea. He wanted to measure the temperature of hot milk using a clinical thermometer. Paheli stooped him doing so. Ans. Because it may break, clinical thermometer is only for measuring human body temperature. 9. ACTIVITY Take two identical tin cans. Paint the outer surface of one black and of the other white. Pour equal amount of water in each and leave them in the mid day sun for about an hair. Measure the temperature of water in both the cans. You can feel the differences even by touching water in the two cans.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect
 Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect manuscripts in the past? 4. List some of the technological
Holiday Homework SST.-7 th Class 1. Who is a cartographer? 2. Who was considered a foreigner in the past? 3. What are archives? Who used to collect manuscripts in the past? 4. List some of the technological
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 1, NUTRITION IN PLANTS
 SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 1, NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. What are the different components of food? Different components of food are Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Vitamins Minerals 2. What is meant by
SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 1, NUTRITION IN PLANTS 1. What are the different components of food? Different components of food are Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Vitamins Minerals 2. What is meant by
Downloaded from INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH
 1 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH Academic Year 2011-2012 VII Science Chapter 1 : Nutrition in Plants 1. The components of food which are necessary for our body are called 2. Green plants synthesise
1 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH Academic Year 2011-2012 VII Science Chapter 1 : Nutrition in Plants 1. The components of food which are necessary for our body are called 2. Green plants synthesise
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs
 INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR Summative Assessment I, 2014 Class: VII SCIENCE M.M: 60 17/09/14 Time: 3 hrs General Instructions: (i) The question paper comprises of three sections A, B and C. (ii) All
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
2.1 DIFFERENT WAYS OF TAKING FOOD
 2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
You have learnt in Chapter 1 that
 2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
2 Nutrition in Animals You have learnt in Chapter 1 that plants can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis but animals cannot. Animals get their food from plants, either directly by eating
Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food
 Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food 1. Why do we need food? Explain briefly. Ans. We need food for following reasons : (i) To produce energy that is used to perform various metabolic activities in
Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food 1. Why do we need food? Explain briefly. Ans. We need food for following reasons : (i) To produce energy that is used to perform various metabolic activities in
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System
 To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
Digestion is a process in which the complex food we eat is broken down in to simple, soluble, substances which our body is able to use.
 KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
Human Digestion. Junior Science
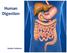 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Digestion of the Bison
 Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
The function of the digestive system is to break down
 Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY)
 GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-A HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-A HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
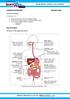 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY)
 GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-B HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
GURU NANAK INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC SCHOOL (SENIOR SECONDARY) Hindi CLASS: X-B HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK English 1. Revise the whole syllabus. 2. Do unseen passages (1 to 5) of BBC in book only. 3. Write letter on
MAHESH TUTORIALS SECTION - A
 S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
S.S.C. MAHESH TUTORIALS Test - I Batch : SB Marks : 0 Date : SCIENCE Chapter :,, 4, 6, 0, Time : hr. SECTION - A Q.I (A) Rewrite the following statements by choosing the correct option : (i) The centre
( 1 mark questions) (2 mark questions) ( 3mark questions) ( 5 mark questions) (1mark questions) (2 mark questions) (3 mark questions)
 NUTRITION IN PLANTS ( 1 mark questions) 1. Define nutrition. 2. Define Photosynthesis. 3. Write equation for photosynthesis. 4. What are the raw materials needed for photosynthesis? 5. Name the cells that
NUTRITION IN PLANTS ( 1 mark questions) 1. Define nutrition. 2. Define Photosynthesis. 3. Write equation for photosynthesis. 4. What are the raw materials needed for photosynthesis? 5. Name the cells that
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Topic: Food And Digestion Q1. MCQs. A. Which juice is rich in iron? (a) Orange (b) Carrot (c) Apple (d) Mango B. Vitamin E is found in (a) Egg yolk
Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Topic: Food And Digestion Q1. MCQs. A. Which juice is rich in iron? (a) Orange (b) Carrot (c) Apple (d) Mango B. Vitamin E is found in (a) Egg yolk
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad , A.P.
 THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
THE HYDERABAD PUBLIC SCHOOL Begumpet, Hyderabad 500 016, A.P. Work Sheet for the Academic Year 2014-15 CLASS VII SECOND TERM SYLLABUS BIOLOGY ===============================================================
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings. 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being
 1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution
 Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution I. 1. (a) Hydrogen peroxide has the molecular formula H 2 O 2. This means that there are two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms in one
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution I. 1. (a) Hydrogen peroxide has the molecular formula H 2 O 2. This means that there are two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms in one
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3
 Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2
 1 Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2 Question 1 How are autotrophs classified? Autotrophs are classified based on their source of energy. If they use the light energy of the sun, they are called
1 Class 10 Nutrition Important questions-2 Question 1 How are autotrophs classified? Autotrophs are classified based on their source of energy. If they use the light energy of the sun, they are called
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
EDULABZ INTERNATIONAL 7 LIFE PROCESSES
 7 LIFE PROCESSES I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Which one is an insectivorous plant? (a) Lichens (b) Venus fly-trap (c) Mushrooms (d) Yeast Ans. (b) 2. Two different organisms
7 LIFE PROCESSES I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Which one is an insectivorous plant? (a) Lichens (b) Venus fly-trap (c) Mushrooms (d) Yeast Ans. (b) 2. Two different organisms
Body Systems. Unit. Key Words. In this unit you will learn to: cell. function. system. convert. circulate
 Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
PHOTOSYNTHESIS (7.5A)
 PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2
 Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
 ALL living things are Building from smallest to LARGEST: Organelles- Cells- Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes The basic unit of structure
ALL living things are Building from smallest to LARGEST: Organelles- Cells- Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes The basic unit of structure
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals. Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Warm-Up. Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element. Compound
 Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes:
 Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL
 WARNING: This Question Paper MUST be returned with your answer book(s) at the end of the examination: otherwise marks will be lost. STUDENT NAME SCHOOL L.37 For Examiner s use only Sect. Q. Mark Sect.
WARNING: This Question Paper MUST be returned with your answer book(s) at the end of the examination: otherwise marks will be lost. STUDENT NAME SCHOOL L.37 For Examiner s use only Sect. Q. Mark Sect.
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3759785418* BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core) October/November 2018 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3759785418* BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core) October/November 2018 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Chemical Compounds in Cells
 Cell Processes and Energy Guided Reading and Study Chemical Compounds in Cells This section identifies the basic building blocks of cells. It also explains the importance of water to cells. Use Target
Cell Processes and Energy Guided Reading and Study Chemical Compounds in Cells This section identifies the basic building blocks of cells. It also explains the importance of water to cells. Use Target
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
1.0 Learning Intentions
 Subject: Junior Certificate Science Teacher: Mrs Welby Week: Week 1 Lesson: Living Things, Cell and Microscope and Food 1.0 Learning Intentions At the end of the lesson, tick of each of the learning intentions
Subject: Junior Certificate Science Teacher: Mrs Welby Week: Week 1 Lesson: Living Things, Cell and Microscope and Food 1.0 Learning Intentions At the end of the lesson, tick of each of the learning intentions
Year 8 Assessment. Autumn Term Remember!
 Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System
 Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System According to the new frame of the question paper, it is proposed that textual questions shall not be asked and other thing is that, a question once asked
Tenth Biology Nutrition - Food Supplying System According to the new frame of the question paper, it is proposed that textual questions shall not be asked and other thing is that, a question once asked
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8954733823* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8954733823* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient.
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
ITL Public School Half Yearly ( )
 ITL Public School Half Yearly (017-18) Science(SET A)ANSWER KEY Date: 1.09.17 Class: VII Time: hrs M.M : 80 Q.1 Which gas present in air is essential for aerobic respiration? CO Q. Name the carbohydrate
ITL Public School Half Yearly (017-18) Science(SET A)ANSWER KEY Date: 1.09.17 Class: VII Time: hrs M.M : 80 Q.1 Which gas present in air is essential for aerobic respiration? CO Q. Name the carbohydrate
