Balneo-Research Journal Vol.2, Nr.3, Therapeutic muds
|
|
|
- Penelope Houston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Therapeutic muds Munteanu Constantin 1, Mioara Dumitrascu 2 1 Institutul Naţional de Recuperare, Medicina Fizica şi Balneoclimatologie 2 S.C. BIOSAFETY SRL-D As defined by the "International Society of Medical Hydrology" muds (peloids) are "substances formed under natural conditions under the influence of geological processes and in a state finely divided and mixed with water, that are used in medical practice in general or local baths. The complex geological structure and geographical location of Earth s crust, Romania has a great wealth of natural factors: mineral waters, muds, moffets, salt lakes - spread over almost the entire surface of the country. Use of mud in therapy began in the second half of the XIX century to Techirghiol (mud) and Vatra Dornei (peat mud from Poiana Stampei and Copaceni), while extending the therapy practiced in various spas on the Black Sea. Initially were used by primitive means, that today offer spa resorts and to be highly diverse for both social and mass tourism, as well as the luxury. Mud is a soil with pasty consistency rocks used as therapeutic remedies of since ancient times. Some beneficial effects of mud are empirically known from ancient times, others have recently been studied and described, some have remained and today the stage brief explanations. Mud treatment is also called peloidotherapy, it should be used only for the indication and under medical supervision. The most common therapeutic mud bank are deposits of salt ponds - sulphurous black mud, which forms the bottom of marine estuaries, bays and lakes of continental salt. After the formation, organic and inorganic materials present in sediments, muds are divided into three groups: 1. sapropelic mud 2. peat mud 3. mineral mud The degree of mineralization of mud solution varies from 0.01 g / l in sapropelic mud and peat, up to 350g / l in the sulfide. Between mud and water solution that permanently covers diffusion processes have I.O.C, whose job is to maintain a balance between them, in terms of salt ions. Gases arefound in muds especially in soluble state; the mainly source of their formation are the biochemical processes in solution from which hydrogen sulphide accumulates mud, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen and methane. 1. Sapropelic mud deposits are represented by black colloidal iron rich hydrosulfuric, they look plastic and greasy, salty water can be found at the bottom of microorganisms with the origin of the flora and fauna of water bodies that are also associated minerals or inorganic the lake basin from the ground. Flora consists of algae and macrophyte type revails microfiche Cladophora vagabunda, Cladophora cristalina, algae that grow in salt water only. Aquatic fauna Artemia salina species is represented of mm red organisms. The bodies of Artemia salina, bacterial decomposition, together with algae Cladophora cristalina form mud. 12
2 Examples: sapropelic muds coasts and lakes (Techirg hiol Agigea, etc.) sapropelic muds of continental lakes (Am ara, background, etc.) sludge fossils (Ocna Sibiu, Sovata, etc.) 2. Peat mud is formed by decomposition of plant debris on the bottom of lakes /wetlands under the action of microorganisms. They are brown and rich in organic matter and humic acids, waxes, pectin, cellulose, etc. In our country can be found in: Vatra Dornei Borsec Mineral mud- are formed by sedimentation of carbonated springs, calcium, ferruginous or sulfur. sulfur springs sulfur springs baths Sângeorz-Săcelu Figura 1. Cladophora vagabunda and Artemia salina. Figura 2. Principalele staţiuni din România cu nămoluri de turbă Figura 3. Principalele staţiuni din România cu nămoluri minerale 13
3 The physico-chemical, the mud is a - well decomposed peat. heterogeneous system physico-chemically Physical properties of muds composed of a liquid phase containing water soluble mineral bath salts in the water, a solid hydropexic capacity - absorption capacity phase containing substances such as minerals and and water retention, practice value-peloids with organic and a gas phase which contains hydrogen low hydropexic capacity (mineral sludge) are sulphide. The ionic balance of a mud is reflected used only for packaging, those with average on the ph. Generally, namolurile are alkaline ph hydropexic capacity (sapropelic mud) and large = Therapeutic effect of the mud is given by (peat sludge) can be used for bathrooms. the combination of physical and chemical properties. solid phase is mostly the domain ultramicroeterogen, colloidal-mixed composition and molecular contaminants liquid phase is represented by the water soluble solution humor and inorganic and organic form of the structural aspect of the solution of solid particles imbibatie interstitiala. the gas phase is the result of processes biochemical and physicochemical conducted during the natural peloidogenezei and consists mainly of his of hydrocarbons, CO2, H2S2, O2, H2. The main quality indicators are: macroscopic properties-in particular those with references to the color and consistency of physics; degree of hydration in the sediment of peloid heterogen according to share of the global composition of moisture: -low-hydrated peloide <37% -hydrated peloide 37-40% -strongly hydrated peloide 40-70% peloidogenetic Stage of evolution as the corresponding degree of therapeutic peloid decomposition of organic substances, depending on the ratio between the quantity of organic substances such as main classes (carbs, protein, humice, organic carbon/organic nitrogen) and biological consumption level oxygen, CBO 5 : - peloids (sapropelic organic, or genetically e volved tendencies mineralization - peat with varying degrees of decomposition of organic matter; - weakly decomposed peat - early decomposed peat; plasticity-the property to change shape under the action of external forces, is given by the solids content, low plasticity (mineral mud), medium (peat) and high (sapropelic). dispersion-date peloid grain size; therapeutic value is directly proportional to grain size. density or specific gravity, is given by its components. Therapeutic value is inversely proportional to the density of the mud. thermopexic capacity -absorb and retain heat. Peloids have a high capacity to retain heat. Chemical properties peloid-water is the most important component, proportional to the amount of colloids minerals depends on the structure-rock and water in the basin. The largest amount of mineral substances have mineral sludge (50-70%), then the sapropelic (20-40%) and peat (below 20%). Pharmaco-dynamic properties As a biological material used in human therapy analysis is carried out according to the methods specified in "Romanian Pharmacopoeia" with some additions made inthe working methods used for soil analysis. The result takes the form of physical- chemical analysis report. In applying of peloids to the skin occurring a series of processes: receiving sensory of the qualities / properties of sludge and their transfer to higher levels of integration and control; exchange of energy and substance with environment of peloid ; fulfillment of adaptive controls: circulatory (peripheral circulation thermoregulation), 14
4 secretory (sweating), protection (keratinization, melanogenesis, lipid film formation); integration skin effects of mud application in general physiology of the body: thermoregulation, vitamin D synthesis, optimization of homeostatic balance: immune, endocrine and neurovegetative body. Mud application on the entire surface of the skin tissue triggers local reactions and general functioning, inhibiting or activating certain enzymes and metabolites intermediate systems. Balneary cure with mud has positive effects persisting for a long time by modifying the adaptive capacity to respond to various stimuli. Peloids act on: the cardiovascular system - stimulate cardiovascular reactions with emphasis on central hemodynamics and peripheral mechanisms. Deposit mobilization occurs immediately blood and their involvement in general circulation, inflammatory processes. nervous system - sedative or stimulating effects on the central nervous system and SNV by sedation of pain receptors. Balneary cure with mud increases the antimicrobial defense capacity by increasing phagocytic power of leucocytes, as evidenced bychanges opsonocitofagic index (I.O.C) immunological systems- control immunoglobulin values, increased non-specific immunity, etc. Enzymatic and metabolic changes occurring in the endocrine glands after peloidotherapy varies by specific secretory gland, after which functional status is related to the type gland andtherapeutic applications. Under the action of mud occurs in all glands harmonic stimulation to increase enzyme activity and synthesis while maintaining the specificity of each. Harmonization activities related to endocrine function is stimulation of hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal translated by optimizing plasma levels: β-endorphin. Endocrine mechanism is involved in induction of anti-inflammatory effects by modulating the activity pelotherapy hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and endocrine balance of general equilibrium effects and postcure persistent. Responsiveness tochemical mediators - acetilcholina and adrenaline ý and the face of ions correlated with autonomic activity, Ca, Mg, K - is increased by external treatment with mud, andautonomic tone has a tendency to control / normalization, which leads to vegetativestigmata remedy. Application methods of peloids: Unction with mud - is the oldest method involves the application of cold mud on the patient's skin (after itwas heated for minutes) in a thin layer on limited areas or the entire body. The patient must then expose to the sun, in an upright position until the mud dries, about30-60 minutes, followed by 10 to 15 in sea water bath or moving to the lakeaccompanied by a brief shower in cold water and rest in bed at least an hour. It is a method of application mechanisms thermoregulation, neuroendocrine stimulation andadaptation processes by alternating hot-cold contrast factors. Mud packs - consist of mud application in 1-2 cm layer heated to ý C limited region or all over your body for minutes. Cataplasms- mud applications at different temperatures on limited regions of the body. Mud baths - in baths with heated lake water plus kg mud, increasing its concentration progressively to 10-25%. The mixture can be heated to 44 ýc. In patients with cardiovascular disease, the temperature should not exceed 37 ý C, and for those withinflammatory rheumatic disease in 36ý C. The bath is minutes. Shower bath should be followed by the ýc and minimum rest hour. A treatement consists of daily baths. Gynecological applications- vaginal swabs as with mud at ýc for 2 hours or vaginal irrigation with mud dissolved in lake water and heated to 37 C. Massage with mud - with mud stretching and massaging. 15
5 Tabel 1. Peloiodoterapia is used for the following diseases: Locomotor System Nervous System Derm Genital System Respiratory System Endocrine System - degenerative rheumatism with different locations: column (spondylosis, discopatii simple chronic low back, etc.), peripheral (coxarthrosis, gonartroze, etc.) - inflammatory rheumatism - rheumatism abarticlar - sequels post tratumatic - SNC and peripheric diseases - psoriazis - chronic Eczema - chronic Rasheed - chronic inflammations - secondary sterility - sfera ORL - TBC sequelae - Hypothyroidism - Obesity - pituitary dwarfism - rickets or debility in children Bibliography 1. Cinteză Delia (coordonator) şi colab. (2011). Ghidul balnear. Institutul Naţional de Recuperare medicină fizică şi Balneoclimtologie. Bucureşti. 2. Aniţei Lidia şi colectivul de autori.(1986). Cura Balneoclimatică- indicaţii şi contraindicaţii. Editura medical. Bucureşti. 3. Olga Surdu. (2007). Studiu histologic comparativ al acţiunii nămolului sapropelic de Techirghiol asupra tegumentului. Teză de doctorat. tratarea-cu-namol-a-bolilor-de-piele.php
Daniela Profir, Viorica Marin, Olga Surdu, Liviu Ion Muja Balneal and Rehabilitation Sanatorium Techirghiol, Romania
 Daniela Profir, Viorica Marin, Olga Surdu, Liviu Ion Muja Balneal and Rehabilitation Sanatorium Techirghiol, Romania Ankylosing spondylitis (AS, from Greek ankylos, bent; spondylos, vertebrae ) is the
Daniela Profir, Viorica Marin, Olga Surdu, Liviu Ion Muja Balneal and Rehabilitation Sanatorium Techirghiol, Romania Ankylosing spondylitis (AS, from Greek ankylos, bent; spondylos, vertebrae ) is the
Testing of Some Enzymatic Levels in Ocna Sibiului Lakes Therapeutic Mud
 Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis Seria F Chemia 9(2006-1):21-28 Testing of Some Enzymatic Levels in Ocna Sibiului Lakes Therapeutic Mud Abstract Neli Darie 1*, Letitia Oprean 1, Claudia Felicia Ognean 1
Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis Seria F Chemia 9(2006-1):21-28 Testing of Some Enzymatic Levels in Ocna Sibiului Lakes Therapeutic Mud Abstract Neli Darie 1*, Letitia Oprean 1, Claudia Felicia Ognean 1
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY
 LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
UNDERSTANDING YOUR WATER PROFILE PRESENTED BY POULTRY PARTNERS AND AHPD
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR WATER PROFILE PRESENTED BY POULTRY PARTNERS AND AHPD WHY DOES IT MATTER? Water intake for commercial poultry breeds is 1.5-2x greater than feed intake Commercial birds drink more now
UNDERSTANDING YOUR WATER PROFILE PRESENTED BY POULTRY PARTNERS AND AHPD WHY DOES IT MATTER? Water intake for commercial poultry breeds is 1.5-2x greater than feed intake Commercial birds drink more now
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Microbial nutrition. Nutrients. Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth. Chapter 7
 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Salts and Chlorides Remediation
 Salts and Chlorides Remediation The remediation of salts and chlorides is not a process of consumption but rather a process of binding, buffering, immobilization, detoxification, filtering, or conversion
Salts and Chlorides Remediation The remediation of salts and chlorides is not a process of consumption but rather a process of binding, buffering, immobilization, detoxification, filtering, or conversion
 anna.ida3@gmail.com/2013 Have you ever heard HUMUS?? A brown to black complex variable of carbon containing compounds as possessing cellular organization in the form of plant and animal bodies Derived
anna.ida3@gmail.com/2013 Have you ever heard HUMUS?? A brown to black complex variable of carbon containing compounds as possessing cellular organization in the form of plant and animal bodies Derived
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter. Build your Own Notes:
 4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes for 4.1 from pages 83 84 Study Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Matter is
4.1 Cycling of Matter Date: Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes for 4.1 from pages 83 84 Study Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Matter is
Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water. It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!!
 Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!! * What is DeepWater (Korean Patent No.: 2003-0078020)? Daehan salty mineral water(deepwater) has 0.9% salinity and
Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!! * What is DeepWater (Korean Patent No.: 2003-0078020)? Daehan salty mineral water(deepwater) has 0.9% salinity and
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 - GRANULE (JAIVIZYME)
 TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
TYPE: ORGANIC NUTRIENTS CODE: BF4 GRANULE (JAIVIZYME) AVAILABLE: BULK, PRIVATE LABEL & BRANDS Composition Ingredient % Potassium Humate 5.00% w/w Min. Carrier Granules 95.00% w/w Max. Advantages Mode of
Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter
 Cycling of Matter Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes from the page given udy Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Organic matter always contains
Cycling of Matter Build your Own Notes: Use these topics as guidelines to create your own notes from the page given udy Notes/Questions Cycling of Organic and Inorganic Matter Organic matter always contains
Chapter 2 pt 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Life. Gregory Ahearn. John Crocker. Including the lecture Materials of
 Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013
 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM
 ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM INTEREST APPROACH Show images of plants suffering from phosphorus and potassium deficiencies. Ask students if they
ANIMAL, PLANT & SOIL SCIENCE D3-6 CHARACTERISTICS AND SOURCES OF PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM INTEREST APPROACH Show images of plants suffering from phosphorus and potassium deficiencies. Ask students if they
IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF LIFE IN CLIMAX WITH KINETOTHERAPY AND NATURAL FACTORS IN VATRA DORNEI RESORT
 IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF LIFE IN CLIMAX WITH KINETOTHERAPY AND NATURAL FACTORS IN VATRA DORNEI RESORT Maria Daniela Crăciun University "Stefan cel Mare" Suceava daniela_mariacr@yahoo.com Abstract Introduction
IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF LIFE IN CLIMAX WITH KINETOTHERAPY AND NATURAL FACTORS IN VATRA DORNEI RESORT Maria Daniela Crăciun University "Stefan cel Mare" Suceava daniela_mariacr@yahoo.com Abstract Introduction
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development. Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization
 Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Unit B: Seed Germination, Growth, and Development Lesson 4: Determining Nutrient Functions and Utilization 1 Terms Denitrification Leach Macronutrient Micronutrient Nitrification Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Effects of Agriculture on Global Population
 Effects of Agriculture on Global Population Remove unwanted plants and animals from a farm area. Plants and animals evolved into a symbiotic relationship. Social organization. Structure. Affluence. Population
Effects of Agriculture on Global Population Remove unwanted plants and animals from a farm area. Plants and animals evolved into a symbiotic relationship. Social organization. Structure. Affluence. Population
INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet. These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements.
 INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet FOOD AND DIET The main elements present in the human body are: Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements. Unlike plants,
INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet FOOD AND DIET The main elements present in the human body are: Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements. Unlike plants,
Essential Elements. Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics
 Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
Essential Elements Original research don by Julius von Sachs 1860 using hydroponics Using various solutions found ones that supported plant life Sachs found several elements that were needed in relatively
The therapeutic benefits of natural therapeutic factors in Baile Tusnad for the rehabilitation of patients with Parkinson s disease
 The therapeutic benefits of natural therapeutic factors in Baile Tusnad for the rehabilitation of patients with Parkinson s disease Gabriela Dogaru¹², Denisa Muresan¹, Ioana Stanescu¹², Marieta Motricala³,
The therapeutic benefits of natural therapeutic factors in Baile Tusnad for the rehabilitation of patients with Parkinson s disease Gabriela Dogaru¹², Denisa Muresan¹, Ioana Stanescu¹², Marieta Motricala³,
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (52) - 2010 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (52) - 2010 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I
 Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I 1. Which image best depicts the hot water, which the cold? 2. What is the relationship between temperature and the speed of molecular motion? 3. If a
Cell Structure and Function Exam Study Guide Part I 1. Which image best depicts the hot water, which the cold? 2. What is the relationship between temperature and the speed of molecular motion? 3. If a
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.37 - SOIL.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
!! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
The role of water in the maintenance of life
 Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Inorganic compounds The role of water in the maintenance of life As mentioned in Table (Reference), up to 65% of our bodies are made up of water. Water is an inorganic compound made up of two hydrogen
Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY
 Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells Elements= Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler form Made up of only one kind of atom Found in the body Carbon
Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells Elements= Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler form Made up of only one kind of atom Found in the body Carbon
Slide 2 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show
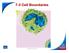 2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization
 Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
Environmental Literacy Project Michigan State University. Lesson 2.3: Materials Plants Are Made Of
 Environmental Literacy Project Michigan State University Lesson 2.3: Materials Plants Are Made Of Benchmark Scale Power of Ten Large Scale: Farm field Decimal Style Large scale Larger 10 5 10 4 10 3 Larger
Environmental Literacy Project Michigan State University Lesson 2.3: Materials Plants Are Made Of Benchmark Scale Power of Ten Large Scale: Farm field Decimal Style Large scale Larger 10 5 10 4 10 3 Larger
Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon
 UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
6 Nutrients Essential for Life
 6 Nutrients Essential for Life Mind Moo-Ver SWBAT identify the 6 essential nutrients for life QOD: What does ph measure Give an example of an acidic substance, a basic substance and a neutral substance
6 Nutrients Essential for Life Mind Moo-Ver SWBAT identify the 6 essential nutrients for life QOD: What does ph measure Give an example of an acidic substance, a basic substance and a neutral substance
PHOTOSYNTHESIS (7.5A)
 PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
Organic compounds. Lipids, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
 Organic compounds Lipids, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Essential for life Organic compounds: Contain carbon Most are covalently bonded Example: C 6 H 12 O 6 (Glucose) Inorganic Compounds:
Organic compounds Lipids, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Essential for life Organic compounds: Contain carbon Most are covalently bonded Example: C 6 H 12 O 6 (Glucose) Inorganic Compounds:
Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
C) amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the animal B) rate of respiration of the animal
 Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Water in the Body. Page Water = ~50 to 70% of body weight, depending on body fat % (higher body fat=lower water content)
 Water in the Body Page 373-375 Water = ~50 to 70% of body weight, depending on body fat % (higher body fat=lower water content) Major fluid compartments: Intracellular fluid: cytoplasm of cells is an aqueous
Water in the Body Page 373-375 Water = ~50 to 70% of body weight, depending on body fat % (higher body fat=lower water content) Major fluid compartments: Intracellular fluid: cytoplasm of cells is an aqueous
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
1.3.1 Function of Food. Why do we need food?
 1.3.1 Function of Food Why do we need food? Need to know The Function of Food Three reasons for requiring food 2 Food is needed for: 1.Energy 2.Growth of new cells and Repair of existing cells, tissues,
1.3.1 Function of Food Why do we need food? Need to know The Function of Food Three reasons for requiring food 2 Food is needed for: 1.Energy 2.Growth of new cells and Repair of existing cells, tissues,
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Back To Your Roots Soil Solutions
 Back To Your Roots Soil Solutions Our mission is to provide producers with access to environmentally friendly products that address soil problems and facilitate sustainable farming practices. We did not
Back To Your Roots Soil Solutions Our mission is to provide producers with access to environmentally friendly products that address soil problems and facilitate sustainable farming practices. We did not
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Prokaryotic Metabolism *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44606 1 Prokaryotic Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m44606 1 Prokaryotic Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
elucidate the role of trace metals in the ecology of the oceans and the
 CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
NUTRITION. Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 NUTRITION Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance What are the essential nutrients for animal production? Good nutrition can increase feed efficiency and the rate of gain for animals. Animals must
NUTRITION Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance What are the essential nutrients for animal production? Good nutrition can increase feed efficiency and the rate of gain for animals. Animals must
Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health
 Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health INTRODUCTION: MicrobeBio Hydro Activator naturally occurring beneficial organisms, 100% organic proteins, and
Microbial Enhanced Fish Fertilizer Supplement with Vitamins and Nutrients for Plant Health INTRODUCTION: MicrobeBio Hydro Activator naturally occurring beneficial organisms, 100% organic proteins, and
Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water.
 Chapter 9 Water Balance Chapter 9 Lesson 9.1 Key Concepts Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water. The concentration of various solute particles
Chapter 9 Water Balance Chapter 9 Lesson 9.1 Key Concepts Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water. The concentration of various solute particles
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS
 FERTILIZER INDUSTRY WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS FERTILIZERS ARE COMPOUNDS GIVEN TO PLANTS WITH THE INTENTION OF PROMOTING GROWTH; THEY ARE USUALLY APPLIED EITHER VIA THE SOIL, FOR UPTAKE BY PLANT ROOTS, OR BY
FERTILIZER INDUSTRY WHAT ARE FERTILIZERS FERTILIZERS ARE COMPOUNDS GIVEN TO PLANTS WITH THE INTENTION OF PROMOTING GROWTH; THEY ARE USUALLY APPLIED EITHER VIA THE SOIL, FOR UPTAKE BY PLANT ROOTS, OR BY
Overview of Physiology. Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology Homeostasis Life s Challenges Nutrients Oxygen Water Temperature regulation Atmospheric pressure Life s Challenges Homeostasis Responding to life s challenges (Maintaining a stable
Overview of Physiology Homeostasis Life s Challenges Nutrients Oxygen Water Temperature regulation Atmospheric pressure Life s Challenges Homeostasis Responding to life s challenges (Maintaining a stable
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
Discuss the importance of healthy soils Soil properties, physical, chemical and biological that one can manage for soil health How organics play a
 Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
FilterSorb SP3 Texture of Water: Part III
 FilterSorb SP3 Texture of Water: Part III By Deepak Chopra Watch Water GmbH Fahrlachstraße 14 68165 Mannheim Germany June 2013 Web: www.watchwater.de email: info@watchwater.de Telefon: +49 (0) 621 87951-0
FilterSorb SP3 Texture of Water: Part III By Deepak Chopra Watch Water GmbH Fahrlachstraße 14 68165 Mannheim Germany June 2013 Web: www.watchwater.de email: info@watchwater.de Telefon: +49 (0) 621 87951-0
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID: GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment
 TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova
 REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
IN VIVO AND IN VITRO COMPARATIVE ASPECTS OF SOME PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM Mytilus galloprovincialis
 IN VIVO AND IN VITRO COMPARATIVE ASPECTS OF SOME PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM Mytilus galloprovincialis Daniela Mariana MIRCEA 1, Natalia ROSOIU 2, Elena DUMITRESCU 1, Andra OROS 1 1 National Institute for
IN VIVO AND IN VITRO COMPARATIVE ASPECTS OF SOME PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM Mytilus galloprovincialis Daniela Mariana MIRCEA 1, Natalia ROSOIU 2, Elena DUMITRESCU 1, Andra OROS 1 1 National Institute for
Semester Assessment. Name. Date
 Lesson 11: Name Date Read each question and circle the letter next to the correct answer. 1. Yucca moths lay eggs in yucca flowers. When the eggs hatch, the larvae eat yucca seeds. The moths help pollinate
Lesson 11: Name Date Read each question and circle the letter next to the correct answer. 1. Yucca moths lay eggs in yucca flowers. When the eggs hatch, the larvae eat yucca seeds. The moths help pollinate
5. Groups A and B in the table below contain molecular formulas of compounds.
 1. Which group consists entirely of organic molecules? A) protein, oxygen, fat B) protein, starch, fat C) water, carbon dioxide, oxygen D) water, starch, protein 2. Which statement describes starches,
1. Which group consists entirely of organic molecules? A) protein, oxygen, fat B) protein, starch, fat C) water, carbon dioxide, oxygen D) water, starch, protein 2. Which statement describes starches,
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
HUMIC SOLUTIONS THE NEXT GENERATION OF SOIL HEALTH DISPERSIBLE SOLUBLE SPREADABLE BLENDABLE
 HUMIC SOLUTIONS UltraMate 12 SG THE NEXT GENERATION OF SOIL HEALTH DISPERSIBLE SOLUBLE SPREADABLE BLENDABLE DISPERSING GRANULE TECHNOLOGY 0 minutes 3 minutes 5 minutes Enhanced particle distribution results
HUMIC SOLUTIONS UltraMate 12 SG THE NEXT GENERATION OF SOIL HEALTH DISPERSIBLE SOLUBLE SPREADABLE BLENDABLE DISPERSING GRANULE TECHNOLOGY 0 minutes 3 minutes 5 minutes Enhanced particle distribution results
In USA, NASA have chosen to use it for astronauts food in space, and even plan to grow and harvest it in space stations in the near future.
 What is Spirulina? Spirulina is 100% natural and a highly nutritious micro salt water plant. It was discovered in South American and Africa in natural alkaline lakes. This spiral shaped algae is a rich
What is Spirulina? Spirulina is 100% natural and a highly nutritious micro salt water plant. It was discovered in South American and Africa in natural alkaline lakes. This spiral shaped algae is a rich
Unit C: Poultry Management. Lesson 1: Nutrients for Maintenance, Growth and Reproduction
 Unit C: Poultry Management Lesson 1: Nutrients for Maintenance, Growth and Reproduction 1 1 Carbohydrates Fats Minerals Nutrients Proteins Vitamins Water Terms 2 2 I. Nutrients are the chemical substances
Unit C: Poultry Management Lesson 1: Nutrients for Maintenance, Growth and Reproduction 1 1 Carbohydrates Fats Minerals Nutrients Proteins Vitamins Water Terms 2 2 I. Nutrients are the chemical substances
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
... THE MAINTENANCE OF STATIC OR CONSTANT CONDITIONS IN THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT...
 Homeostasis... THE MAINTENANCE OF STATIC OR CONSTANT CONDITIONS IN THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT... External Environment External Environment Internal Environment External Environment External Environment Homeostasis
Homeostasis... THE MAINTENANCE OF STATIC OR CONSTANT CONDITIONS IN THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT... External Environment External Environment Internal Environment External Environment External Environment Homeostasis
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K
 PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM
 DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56799 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective by OpenStax Mitch Singer This work
OpenStax-CNX module: m56799 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 08.0 Metabolism from a microbes perspective by OpenStax Mitch Singer This work
A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. Carbon atoms can form long chains, leading to a huge number of possible
 Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013
 PHYSIOLOGY & METABOLISMS of Microorganisms By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013 What is metabolisms? Can you explain it? Overall biochemical reaction within cells of
PHYSIOLOGY & METABOLISMS of Microorganisms By: Mochamad Nurcholis Food Science Department Brawijaya University 2013 What is metabolisms? Can you explain it? Overall biochemical reaction within cells of
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System
 To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
Cardiovascular System Module 1: An Overview of Blood *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49668 1 Cardiovascular System Module 1: An Overview of Blood * Donna Browne Based on An Overview of Blood by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
OpenStax-CNX module: m49668 1 Cardiovascular System Module 1: An Overview of Blood * Donna Browne Based on An Overview of Blood by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
Lecture 5: Chapter 7 Nutrition and Growth. Microbial Nutrition
 Lecture 5: Chapter 7 Nutrition and Growth Topics Microbial Nutrition (Amended by Chapter 24, EM) 1 Microbial Nutrition Nutritional requirements Sources of nutrients Ways to get nutrients (Transport mechanisms)
Lecture 5: Chapter 7 Nutrition and Growth Topics Microbial Nutrition (Amended by Chapter 24, EM) 1 Microbial Nutrition Nutritional requirements Sources of nutrients Ways to get nutrients (Transport mechanisms)
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = X X= 325 g
 BIOCHEMISTRY ½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = 13 100 X X= 325 g These spinach imposters contain less than 2 percent of
BIOCHEMISTRY ½ cup of CHEX MIX contains 13 g of carbs = 4% daily value. How much more can you have the rest of the day??? _4_ = 13 100 X X= 325 g These spinach imposters contain less than 2 percent of
Animal Form and Function. Exchange surfaces. Animal Form and Function
 Animal Form and Function Surface:Volume ratio decreases with size Today s topics: Review for exam Physical Constraints affect the design of animals Homeostasis Sensors and effectors Exchange surfaces Design
Animal Form and Function Surface:Volume ratio decreases with size Today s topics: Review for exam Physical Constraints affect the design of animals Homeostasis Sensors and effectors Exchange surfaces Design
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Homeostasis * Robert Bear David Rintoul. Based on Homeostasis by OpenStax. 1 Homeostatic Process
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47426 1 Homeostasis * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on Homeostasis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m47426 1 Homeostasis * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on Homeostasis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food
 Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food 1. Why do we need food? Explain briefly. Ans. We need food for following reasons : (i) To produce energy that is used to perform various metabolic activities in
Question Bank Nutrition : Classes of Food 1. Why do we need food? Explain briefly. Ans. We need food for following reasons : (i) To produce energy that is used to perform various metabolic activities in
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
Effects of Micro Nano Bubble
 - 1/9- Effects of Micro Nano Bubble Micro Bubble Generator Y E G A - 2/9- An unimaginable functionality can be found right from micro Nano-sized Micro-fine air bubbles. What are the Micro Nano-sized bubbles?
- 1/9- Effects of Micro Nano Bubble Micro Bubble Generator Y E G A - 2/9- An unimaginable functionality can be found right from micro Nano-sized Micro-fine air bubbles. What are the Micro Nano-sized bubbles?
EconovaPlus Fertiliser
 EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Choosing What You Eat and Why. Chapter 1 BIOL1400 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos
 Choosing What You Eat and Why Chapter 1 BIOL1400 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Objectives Following this lecture, you should be able to describe: - Nutrition definition - Sources of nutrients - Energy sources
Choosing What You Eat and Why Chapter 1 BIOL1400 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Objectives Following this lecture, you should be able to describe: - Nutrition definition - Sources of nutrients - Energy sources
Plants, soil, and nutrients. Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University
 Plants, soil, and nutrients Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University Where do plants get their nutrients? Atmospheric deposition (N, S) Irrigation water Shallow groundwater
Plants, soil, and nutrients Created in partnership with Alex Lindsey, Ph.D., The Ohio State University Where do plants get their nutrients? Atmospheric deposition (N, S) Irrigation water Shallow groundwater
The diagram below represents the root growth of various plants. Use the diagram to answer question 2.
 TEKS 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants 10C analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and
TEKS 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants 10C analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and
Nutrient level (EC) in a pot is like a bank
 Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
of Life Chemical Aspects OBJ ECTIVESshould be able to: ENCOUNTERS WITH LIFE H" ~ ~O N-C-C H R OH After completing this exercise, the student
 ENCOUNTERS WT LFE Chemical Aspects of Life C 20 C--O. /1 '\. O \/ '\./ C C / \. O / -, O \.1 C--C 1 O GLYCEROL After completing this exercise, the student OBJ ECTVESshould be able to: Define organic and
ENCOUNTERS WT LFE Chemical Aspects of Life C 20 C--O. /1 '\. O \/ '\./ C C / \. O / -, O \.1 C--C 1 O GLYCEROL After completing this exercise, the student OBJ ECTVESshould be able to: Define organic and
Lesson: Plankton. We will use each of these three categories in our investigations of plankton.
 Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
