7.4.4 Digestion. 110 minutes. 151 marks. Page 1 of 40
|
|
|
- Marylou Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7.4.4 Digestion 110 minutes 15s Page 1 of 40
2 Q1. The human body has organs and organ systems which have different functions. (a) In which organ does the foetus develop? In which organ is oxygen absorbed into the blood? (b) Complete the table. 2 marks (c) Give one function of the skeleton Maximum 5 marks Q2. (a) The diagram represents the flow of blood to and from a muscle. What type of blood vessel is B?... Page 2 of 40
3 Respiration takes place in the cells of the muscle. In the table, tick one box in each row to compare the concentrations of oxygen, glucose and carbon dioxide in blood vessels A and B. 3 marks (b) Blood flows into and out of all organs. Name the organ represented in the diagram below. Name of organ... A different organ is represented in the diagram below. Name this organ. Name of organ... (c) When a person has an alcoholic drink, the alcohol passes into blood and is circulated throughout the body. Alcohol in the blood causes the blood vessels in the skin to become wider. What effect will this have on the body? Page 3 of 40
4 Alcohol abuse has short-term and long-term effects. Which one of the following is a long-term effect on alcohol abuse? Tick the correct box. shorter reaction time short sightedness damage to liver damage to bones Maximum 8 marks Q3. The drawing shows part of an organ system. (a) Which organ system is it part of? Tick the correct box. circulatory system reproductive system digestive system respiratory system Page 4 of 40
5 (b) Where is this part of the organ system found in the body? Tick one box. Maximum 2 marks Q4. (a) Egg white contains a protein called albumen. A pupil carried out an experiment to investigate the digestion of three identical cubes of cooked egg white using the enzyme pepsin. She set up the experiment as follows. Into beaker A, she put 50 cm 3 pepsin solution and a cube of egg white left whole. Into beaker B, she put 50 cm 3 pepsin solution and a cube of egg white which had been cut into eight small cubes. Into beaker C, she put 50 cm 3 pepsin solution and a cube of egg white which had been cut into sixty four tiny cubes. She added 1 cm 3 hydrochloric acid to each beaker and placed the three beakers in a waterbath at 37 C. The table gives the pupil s observations five hours later. Page 5 of 40
6 Why was the cube of egg white which had been cut into sixty four pieces digested most quickly? When protein is digested it is broken down into smaller molecules. What name is given to these smaller molecules? (b) In another experiment, it was found that pepsin does not digest sucrose (sugar). Explain why sucrose is not digested by pepsin (c) The graph below shows how quickly pepsin digests meat protein at different temperatures. Explain why pepsin does not digest protein at temperatures above 60 C.... (d) Glands in the stomach wall produce mucus, hydrochloric acid and an inactive form of pepsin called pepsinogen. In the stomach hydrochloric acid reacts with the pepsinogen to produce pepsin. Suggest one other purpose of acid in the stomach. Suggest one reason why pepsin is secreted in its inactive form. Page 6 of 40
7 (iii) Suggest one purpose of mucus produced in the wall of the stomach. (iv) Bile from the liver makes the duodenum alkaline. Give one reason why the contents of the duodenum need to be alkaline. Maximum 8 marks Q5. A medical researcher used a tube to remove some of the liquid from a person's stomach. The researcher put the liquid into a flask which had a piece of boiled beef in it. The beef was digested in six hours. The diagrams show the flask at different stages of the experiment. (a) What type of substance in the liquid from the stomach caused the beef to be digested in six hours? The researcher kept the flask at 37 C. Explain why. Page 7 of 40
8 (b) In the human body, the digestion of protein in meat begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. What is digested protein used for in the body? Describe how the products of digestion get from inside the small intestine to the cells in the rest of the body. 2 marks Maximum 5 marks Q6. The diagram below shows a single-cell organism called Chlamydomonas. It lives in pond water. Use the information in the diagram to help you answer the questions below. (a) Give two features of Chlamydomonas which show that it is more like a plant cell than an animal cell marks (b) Chlamydomonas makes a sugar called glucose. Give the name of the process in which Chlamydomonas makes glucose. Page 8 of 40
9 Chlamydomonas produces starch grains from glucose. Suggest what will happen to the number of starch grains in the cell if Chlamydomonas is kept in the dark. (c) The diagram below shows another single-cell organism called Amoeba. It also lives in pond water. Amoeba traps a Chlamydomonas and digests it. not to scale Starch is a carbohydrate. Amoeba's digestive enzymes break down the starch in the Chlamydomonas. Suggest what substance is produced from the starch and what it is used for marks Maximum 6 marks Page 9 of 40
10 ## The diagram below shows a villus. There are several thousand villi in every square centimetre of the lining of the small intestine. The cells in the lining of each villus have folds called microvilli on their outer surfaces. One of these cells is shown magnified in the diagram. (a) Explain two ways in which the structure of the villus enables the products of digestion to be absorbed efficiently marks (b) Mucus is produced by some cells in the lining of the small intestine. One function of mucus is to protect the lining of the small intestine against the action of certain chemicals. Give the name of one type of chemical present in the small intestine which would otherwise damage the lining.... Suggest one other function of mucus produced in the small intestine. Page 10 of 40
11 (c) Bile, produced by the liver, enters the small intestine through the bile duct. Describe the effect which bile has on fats in the small intestine Maximum 5 marks Q8. Drawings A, B, C, D and E show the positions of five organ systems in the human body. (a) The names of the five organ systems are given in the table. By each name, write the letter of the drawing which shows the organ system. 5 marks Page 11 of 40
12 (b) Which one of these organ systems is completely different in a man and a woman?... Maximum 6 marks Q9. Sadie and Tom carried out an experiment to investigate the digestion of starch using an enzyme called amylase. (a) Why was the mixture of enzyme and starch kept in a water bath?... Sadie and Tom placed drops of iodine solution on a white tile. They know that starch will turn the iodine solution from brown to dark blue. Every 30 seconds they added a drop of the mixture of enzyme and starch to a drop of iodine solution on the tile. At first the drops turned blue, but after 240 s they stayed brown. (b) Why did the mixture stop turning the drops of iodine solution blue after 240 s? (c) They then carried out the experiment with the water bath at 35 C. This time, the drops stopped turning blue after 120 s. How does raising the temperature from 25 C to 35 C affect the digestion of starch? (d) Sadie and Tom want to compare the experiment at 35 C with the results from the experiment at 25 C. Describe what they need to do to make this a fair comparison Page 12 of 40
13 (e) A balanced diet includes all of the substances in the following list. Starch fat fibre minerals protein vitamins Give the names of the two substances in the list which are absorbed into the blood without being digested Which substance in the list passes through the body without being digested?.... Maximum 6 marks ## The following are important parts of a balanced diet. carbohydrates proteins fats vitamins water A pupil has a sweet, juicy orange to eat. (a) Complete the following sentences using words from the list above. An orange is a good source of... and marks An orange is a poor source of... and marks (b) Give the names of two parts of a balanced diet which are not shown in the list above marks Page 13 of 40
14 (c) In order to obtain the nutrients, food must be chewed Give two reasons why it is important to chew food marks Maximum 8 marks Q11. The diagrams below represent what happens to the energy in the food eaten by a herbivore and a carnivore. The width of each pathway indicates the amount of energy gained or used in a particular way. (a) What percentage of the total energy, taken in by a herbivore, is stored in its tissues? Use the diagram to help you answer.... % The energy stored in an animal s tissues is passed on to the next animal in the food chain. Use information in the diagrams above to explain why there are usually no more than four or five stages in a food chain. Page 14 of 40
15 (b) Respiration takes place in cells, in structures called mitochondria. Why do muscle cells contain large numbers of mitochondria? (c) Cows eat plants, but cannot digest the cellulose cell walls. Micro-organisms in the cow s stomach are able to digest the plant cell walls. Suggest why cows cannot digest the cell walls but micro-organisms can (d) The diagram below shows cells from the inner lining of a mammal s intestine. The cell membranes in contact with the food are folded. Explain why it is an advantage that these cells are adapted in this way marks Maximum 6 marks Q12. New-born mammals produce an enzyme called rennin which clots the protein in milk. Newborn mammals can only digest the protein after it clots. (a) Pat investigated how ph affects the time for rennin to clot the protein in milk. She put 2 cm 3 of milk into each of four test-tubes, A, B, C and D. She put these test-tubes and a test-tube of rennin into a water-bath at 35 C. After a few minutes, Pat transferred 4 drops of the rennin into test-tubes A, B and C. She varied the ph by adding the chemicals shown in the table. To test-tube D she added 2 drops of hydrochloric acid only. Page 15 of 40
16 The table below shows the results of Pat s experiment. Use the results of test-tubes C and D to state the function of the enzyme in the clotting process. Use Pat s results to explain why rennin clots milk quickly in the stomach. (iii) Suggest what happens to the activity of rennin as it passes from the stomach into the small intestine. Explain your answer. 2 marks Page 16 of 40
17 (b) Pat then investigated how temperature affects the time for rennin to clot milk. She prepared four water-baths, at 0 C, 25 C, 35 C and 60 C. Into each water-bath she put a test-tube containing 2 cm 3 of milk and a test-tube containing rennin plus a chemical to give the correct ph. In each water-bath, she transferred four drops of the rennin into the test-tube of milk and timed how long it took for the milk to clot. The table shows her results. temperature of water-bath, in C time for milk to clot, in seconds 0 no clotting no clotting Explain why no clotting occurred in the test-tube at 60 C. Pat took the test-tube out of the water-bath at 0 C and put it into the water-bath at 35 C. The milk clotted. Why was clotting still possible in this test-tube? (iii) Raising the temperature from 25 C to 35 C made the milk clot more quickly. How could Pat change her experiment to show more precisely how temperature affects the time it takes for milk to clot? (c) After rennin clots milk protein, a different enzyme helps to digest the protein. What are the products of protein digestion?... Maximum 8 marks Page 17 of 40
18 Q13. The diagram shows some of the organs of the human body. (a) Give the names of two labelled parts where food is digested.... and... (b) Why do we need to chew our food and mix it with saliva? marks Page 18 of 40
19 (c) Draw one line from each bad habit to the organ it harms. 3 marks Which organ in the list below can be harmed if we eat too much fat? Tick the correct box. brain heart lung ribs Maximum 7 marks Page 19 of 40
20 Q14. The drawings show Sofia taking part in four different sports. The table below shows the average energy needed for each sport for one hour. sport average energy need for one hour (kj) bowling 1030 tennis 1760 football 2260 running 3700 (a) Sofia plays football for two hours each week. She also goes bowling for two hours each week. Explain why Sofia uses up her food reserves more quickly when playing football than when bowling. Page 20 of 40
21 Athletes should not drink alcohol before taking part in sport. Give two effects of alcohol which would affect an athlete s performance (b) Some athletes take glucose tablets before a 100 metre race. They can also obtain glucose from starch in their diet. A starch molecule is made up of many glucose molecules joined together as shown below. In the digestive system, starch is broken down into glucose: An athlete can obtain energy more quickly by eating glucose rather than starch. Explain why maximum 4 marks Q15. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid. (a) Winston used universal indicator solution to find the ph of some hydrochloric acid. Suggest the colour of the mixture of universal indicator solution and the hydrochloric acid.... Suggest the ph of the hydrochloric acid.... Page 21 of 40
22 (b) Indigestion can be caused when too much hydrochloric acid is produced in the stomach. Magnesium carbonate can be used to treat indigestion. Winston crushed some indigestion tablets containing magnesium carbonate. He added them to hydrochloric acid in a test-tube. The mixture fizzed. The word equation for the reaction is shown below. magnesium + hydrochloric magnesium + carbon + water carbonate acid chloride dioxide Use the word equation to explain why the mixture fizzed when the reaction took place. Winston continued to add crushed tablets to the acid until the mixture stopped fizzing. Why did the fizzing stop? (c) When magnesium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, magnesium chloride is formed. Which two words describe magnesium chloride? Tick the two correct boxes. a compound a mixture an element a salt a metal a solvent 2 marks Page 22 of 40
23 (d) It is important that the hydrochloric acid in the stomach is not completely neutralised by indigestion tablets. Why is hydrochloric acid needed in the stomach? maximum 7 marks Q16. (a) The graph below shows how the concentration of alcohol in a person s blood changed after drinking alcoholic drinks. It is illegal to drive if the concentration of alcohol in the blood is higher than 80 mg/100 cm 3. Use the graph to find out how long the concentration of alcohol in this person s blood was higher than 80 mg/100 cm hours (b) Why does alcohol in the blood increase the chance of having an accident? Tick the correct box. It causes slurred speech. It increases the size of the pupil in the eye. It dulls the senses of taste and smell. It increases the time taken to react. Page 23 of 40
24 (c) Alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream from the stomach. Digested food is absorbed into the blood from a different part of the digestive system. Give the name of this part.... (d) Give the name of one organ that is damaged by drinking a lot of alcohol over a long period of time.... (e) The drawing below shows a foetus in its mother s uterus. If a pregnant woman drinks large quantities of alcohol, the blood vessels in the umbilical cord may get very narrow for a while. Give one way this could affect the foetus maximum 5 marks Page 24 of 40
25 Q17. The diagram shows some of the organs of the human body. (a) The heart pumps blood around the body. What useful gas does the blood take in from the air in the lungs?... What useful substance does the blood take in from the intestine?... Page 25 of 40
26 (b) Blood vessels carry blood to organs of the body. Sometimes a blood clot forms in a blood vessel as shown below. a blood vessel not to scale A blood clot may stop an organ working properly. Give one reason for this (c) Rahma cut his foot on a piece of glass. A scab formed over the cut. Give one way a scab protects the body maximum 4 marks Q18. Andy investigated the digestion of a protein called gelatin. He used an enzyme called pepsin from the human stomach, and three cubes of gelatin each 1 cm 3. He set up the experiment shown below and put the test-tubes in a water-bath at 37 C. He measured the time for the digestion of the gelatin. Page 26 of 40
27 (a) Why did Andy choose a temperature of 37 C for the water-bath? (b) In test-tube C, the cube of gelatin that had been cut into pieces was digested more quickly than the whole cube in test-tube A. Give the reason for this (c) The boiled pepsin in test-tube B did not digest the gelatin. Why did boiling this enzyme stop it working? (d) Protein is needed for growth and repair. The digestion of protein begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. What are the products of the digestion of protein? Tick the correct box. amino acids energy sugars vitamins Why is it necessary to digest protein before it can be used for growth and repair? maximum 5 marks Page 27 of 40
28 Q19. (a) The diagram shows a group of cells from the lining of the mouth. Give the name and function of part P. name of part P function of part P Which word describes this group of cells? Tick the correct box. compound organism organ tissue (b) The diagram below shows muscle cells from the wall of the human intestine. Muscle cells can contract. Give one reason why muscles are needed in the intestine. Page 28 of 40
29 Other cells in the intestine produce enzymes. What effect do enzymes in the intestine have on nutrients such as protein? (iii) Which of the following is required in the diet to keep food moving through the intestine? Tick the correct box. fat fibre protein starch maximum 6 marks Q20. The diagram below shows the digestive system. (a) Give the letter which labels the stomach.... Page 29 of 40
30 Give the letter which labels the small intestine.... (iii) Glucose is absorbed in the small intestine. What carries glucose from the intestine to other parts of the body? (b) Some athletes take glucose tablets before a race. Why do they take glucose? Tick the correct box. for growth for healthy bones and teeth to prevent disease to provide energy (c) The table below shows what four people ate for lunch. name Jon Nadia Clare Zak lunch chicken and salad cheeseburger and chips lemonade and a jam doughnut mushroom soup and an orange Whose lunch had the most sugar in it?... Whose lunch had the most fat in it?... (iii) Eating too much fat is bad for you. Give one reason for this. maximum 7 marks Page 30 of 40
31 Q21. (a) The diagram shows a sperm cell. Sperm cells are adapted for fertilisation. Sperm cells use their tails to swim towards an ovum (egg). Give one other way the sperm cell is adapted for fertilisation (b) The diagrams below show two other cells. not to scale Look at the diagrams above. What is the difference between the location of the genetic material in the bacterium and in the cell from the lining of the intestine? What is the function of the genetic material in a cell?.... Page 31 of 40
32 (c) Cells in the lining of the intestine are adapted to absorb digested food. How does the folded membrane of these cells enable them to absorb the maximum amount of digested food? (d) A group of cells in the lining of the intestine is a tissue. Why is a number of sperm cells not a tissue? maximum 5 marks Q22. The drawing below shows the human rib cage. (a) The rib cage protects organs in the chest. Give the names of two organs in the chest marks (b) The ribs are attached to the breast bone by cartilage which bends easily. This lets the space in the chest get bigger. Why is it important that the space can get bigger? Page 32 of 40
33 (c) The drawings below show parts of three different organ systems. Draw a line from each organ system to its function. Draw only three lines. 3 marks maximum 6 marks Page 33 of 40
34 Q23. (a) Green beans contain vitamin C. Which other food is a good source of vitamin C? Tick the correct box. cheese chicken eggs oranges (b) The amount of vitamin C changes in the beans and in the water as the beans are cooked. The shading shows how it changes. Use the diagram. How does the amount of vitamin C in the beans and in the water change as the beans are cooked? Tick one box in each row. amount of vitamin C increases decreases stays the same in the beans in the water Page 34 of 40
35 (c) Cheese is a source of calcium. Why do we need calcium?... (d) Draw a line from each nutrient to a good source of that nutrient in our diet. 2 marks (e) The diagram shows part of the human digestive system. Write the letter which labels the small intestine.... Write the letter which labels the stomach.... maximum 7 marks Page 35 of 40
36 Q24. (a) Pineapple juice contains a substance that speeds up the digestion of protein. What is the name for substances that speed up digestion?... What happens to a molecule of protein during digestion?.... (b) Asim did an experiment to investigate the digestion of gelatin. Gelatin is the protein in jelly. In test tubes A and B he used one cube of jelly in each. In test tube C he used one cube of jelly that he had chopped up. A B C 5 g jelly cube 5 g jelly cube 5 g jelly cube + + chopped into 15 cm 3 15 cm 3 fresh pieces cold water pineapple + juice 15 cm 3 fresh pineapple juice He recorded how long it took for the jelly to be digested in each test tube. The table below shows his results. test tube A B C result not digested after 2 hours jelly digested in 2 hours jelly digested in 1 hour What was the purpose of test tube A?.... Page 36 of 40
37 It is helpful to chew your food. How do the results in test tube C show this?.... (c) The substances that speed up digestion stop working when they have been boiled. What does Asim need to put in a fourth test tube to test this in his experiment? Label test tube D. Test tubes A, B and C contain the same as in the first experiment. A B C D 5 g jelly 5 g jelly cube 5 g jelly cube... cube + chopped into + 15 cm 3 fresh pieces cm 3 pineapple + + cold water juice 15 cm 3 fresh pineapple marks Predict what Asim would observe in test tube D after 2 hours... maximum 7 marks Page 37 of 40
38 Q25. Sally investigated how the human body digests and absorbs starch. She used saliva to digest the starch. To model digestion she used special bags made from a semi-permeable membrane. These bags have lots of very small holes. Sally sets up the equipment as shown below. There is one special bag in each beaker. She keeps the water in the beakers at 37ºC. After 20 minutes, Sally tested the contents of each beaker and bag for starch and sugar. The table below shows Sally s results. Was starch found in the bag? Was sugar found in the bag? Was starch found in the water? Was sugar found in the water? beaker A beaker B beaker C (a) Suggest why Sally kept the water at 37ºC.... (b) Explain why sugar was found in the bag in beaker A. Starch was not found in the water outside the bag in any beaker. Suggest why. Page 38 of 40
39 (c) Why did Sally set up beaker C? Tick the correct box. for a fair test for accuracy for reliability for a control (d) Sally used diagrams to show what happened in her investigation. Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions. Which diagram shows the results of beaker B? Write the letter.... Which diagram shows the results of beaker A? Write the letter.... (e) What does saliva contain that causes starch to change in beaker A?... (f) Sally chewed a piece of bread for 5 minutes without swallowing. What would she notice about the taste of the bread after chewing for 5 minutes? Use Sally s results to help you.... maximum 8 marks Page 39 of 40
40 Page 40 of 40
7.4.1 Healthy Human Diet
 7.4.1 Healthy Human Diet 112 minutes 16s Page 1 of 39 Q1. Carbohydrate, fat and protein are three types of nutrient. (a) Give the names of two other types of nutrient needed for a balanced diet. 1....
7.4.1 Healthy Human Diet 112 minutes 16s Page 1 of 39 Q1. Carbohydrate, fat and protein are three types of nutrient. (a) Give the names of two other types of nutrient needed for a balanced diet. 1....
Food and digestion/respiration
 Medway LEA Advisory Service Food and digestion/respiration 8A & 8B 36 min 38 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L4, Q4-L5, Q5-L5, Q6-L6 Medway LEA Advisory Service 1 1. The card shows the amounts of fat and fibre
Medway LEA Advisory Service Food and digestion/respiration 8A & 8B 36 min 38 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L4, Q4-L5, Q5-L5, Q6-L6 Medway LEA Advisory Service 1 1. The card shows the amounts of fat and fibre
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes:
 Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Body Systems. S2 Science. Homework. Holy Cross High School Page 1
 Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet. These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements.
 INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet FOOD AND DIET The main elements present in the human body are: Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements. Unlike plants,
INTERMEDIATE 1 1 Food and Diet FOOD AND DIET The main elements present in the human body are: Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon These elements are present in compounds - not as free elements. Unlike plants,
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
PAST PAPERS PRACTICE PACK
 PAST PAPERS PRACTICE PACK PROTEINS AND ENZYMES Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 65 The table shows the amounts of carbohydrate, fat and protein in 00 g portions of five foods, A - E. MASS IN
PAST PAPERS PRACTICE PACK PROTEINS AND ENZYMES Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 65 The table shows the amounts of carbohydrate, fat and protein in 00 g portions of five foods, A - E. MASS IN
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Digestive Enzyme Lab
 Digestive Enzyme Lab Objectives 1. To describe the function of enzymes 2. To define: reactants, products, activation energy 3. To describe the enzymatic digestion of carbohydrates by salivary amylase 4.
Digestive Enzyme Lab Objectives 1. To describe the function of enzymes 2. To define: reactants, products, activation energy 3. To describe the enzymatic digestion of carbohydrates by salivary amylase 4.
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
Nutrition, part 2. Because 1 part isn t enough!
 Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Year 8 Assessment. Autumn Term Remember!
 Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2
 Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Medway LEA Advisory Service. Cells/reproduction 7A & 7B. 35 min 35 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L5, Q4-L5, Q5-L6, Q6-L
 Medway LEA Advisory Service Cells/reproduction 7A & 7B 1. Andrew put his rabbit s cage on the grass. 35 min 35 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L5, Q4-L5, Q5-L6, Q6-L6 A week later, the grass under the cage had
Medway LEA Advisory Service Cells/reproduction 7A & 7B 1. Andrew put his rabbit s cage on the grass. 35 min 35 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L5, Q4-L5, Q5-L6, Q6-L6 A week later, the grass under the cage had
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Inheritance and selection/fit and healthy
 Medway LEA Advisory Service Inheritance and selection/fit and healthy 9A & 9B 31 min 3s Q1-L4, Q2-L4, Q3-L5, Q4-L5, Q5-L7, Q6-L7 1. The table shows the mass of water, fat, fibre and vitamin C in 100 g
Medway LEA Advisory Service Inheritance and selection/fit and healthy 9A & 9B 31 min 3s Q1-L4, Q2-L4, Q3-L5, Q4-L5, Q5-L7, Q6-L7 1. The table shows the mass of water, fat, fibre and vitamin C in 100 g
Body Systems. Unit. Key Words. In this unit you will learn to: cell. function. system. convert. circulate
 Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
Unit 1 Body Systems Key Words cell chest function system convert circulate In this unit you will learn to: describe the levels of biological organization. identify the basic structures and functions of
Digestion: An Absorbing Tale
 8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
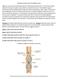 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Understanding Food and Nutrition
 Understanding Food and Nutrition Dr Joan Webster-Gandy Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Food and Nutrition Dr Joan Webster-Gandy Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS. PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient.
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? A
 1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
The teacher places a microphone near the pupil as she plays her flute. The diagram below shows the pattern on an oscilloscope screen.
 (c) The teacher places a microphone near the pupil as she plays her flute. The diagram below shows the pattern on an oscilloscope screen. The pupil then plays her flute at a higher pitch and more quietly.
(c) The teacher places a microphone near the pupil as she plays her flute. The diagram below shows the pattern on an oscilloscope screen. The pupil then plays her flute at a higher pitch and more quietly.
LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: UNIT 1.3 Nutrition and Health
 Name 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 1.3.1-1.3.10 UNIT 1.3 Nutrition and Health LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Requires Pupils should be able to: Good Average Attention 1.3.1 Understand
Name 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 1.3.1-1.3.10 UNIT 1.3 Nutrition and Health LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Requires Pupils should be able to: Good Average Attention 1.3.1 Understand
The function of the digestive system is to break down
 Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness?
 3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical
 15 Digestion: An Absorbing Tale r e a d i n g Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical breakdown. Everything you eat and drink, including medicines, enters your body through
15 Digestion: An Absorbing Tale r e a d i n g Your digestive system is responsible for both mechanical and chemical breakdown. Everything you eat and drink, including medicines, enters your body through
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
CONCEPTS: OBJECTIVES: MATERIALS:
 CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TEACHER COPY THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM There are three primary functions for the digestive system 1. Break down food into molecules the body can use 2. The molecules are absorbed into the
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Using particle models to understand digestion and absorption
 Using particle models to understand digestion and absorption 1 During Key Stage 3 pupils will learn about the structure and function of the digestive system, the names of organs and their function. This
Using particle models to understand digestion and absorption 1 During Key Stage 3 pupils will learn about the structure and function of the digestive system, the names of organs and their function. This
09 Enzymes. December 04, Chapter 9 Enzymes. Mr. C Biology 1
 Chapter 9 Enzymes Mr. C Biology 1 Chapter 9 Enzymes Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body. Your metabolism is controlled by enzymes. Enzymes are proteins made in the ribosome from
Chapter 9 Enzymes Mr. C Biology 1 Chapter 9 Enzymes Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body. Your metabolism is controlled by enzymes. Enzymes are proteins made in the ribosome from
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
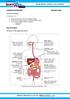 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
1. The diagram shows two families. Some of the people in the diagram have freckles. and. and
 1. The diagram shows two families. Some of the people in the diagram have freckles. family A family B grandparents Bob married to Emily John married to Mary parents Rachel married to Bill Pam married to
1. The diagram shows two families. Some of the people in the diagram have freckles. family A family B grandparents Bob married to Emily John married to Mary parents Rachel married to Bill Pam married to
Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Topic: Food And Digestion Q1. MCQs. A. Which juice is rich in iron? (a) Orange (b) Carrot (c) Apple (d) Mango B. Vitamin E is found in (a) Egg yolk
Science Class 8 Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Topic: Food And Digestion Q1. MCQs. A. Which juice is rich in iron? (a) Orange (b) Carrot (c) Apple (d) Mango B. Vitamin E is found in (a) Egg yolk
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
Digestion of the Bison
 Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 26 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Textbook pages 64 81 Before You Read Section 2.2 Summary Many structures and organs work together to digest food. What parts
Digestion and Excretion
 Digestion and Excretion The Digestive System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Digestion and Excretion The Digestive System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Structure and Function of Cells, Organs and Organ Systems 1
 I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Attaching lactase to the beads is a more efficient use of lactase than adding the lactase directly to cow s milk
 Q1.Cow s milk contains the sugar lactose. Many cats are unable to digest cow s milk because they are lactose intolerant. Cow s milk can be made suitable for these cats by treating it with the enzyme lactase
Q1.Cow s milk contains the sugar lactose. Many cats are unable to digest cow s milk because they are lactose intolerant. Cow s milk can be made suitable for these cats by treating it with the enzyme lactase
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Video Quiz
 1 Video Quiz At the conclusion of the videotape, there will be a short quiz with these questions. Write your answers in the space provided. Use the back of this sheet if necessary. Question 1: What is
1 Video Quiz At the conclusion of the videotape, there will be a short quiz with these questions. Write your answers in the space provided. Use the back of this sheet if necessary. Question 1: What is
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
