Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet
|
|
|
- Rosemary Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet Joseph A. Baur, Kevin J. Pearson, Nathan. Price, Hamish A. Jamieson, Carles erin, Avash Kalra, Vinayakumar V. Prabhu, Joanne. Allard, Guillermo opez- luch, Kaitlyn ewis, Paul J. Pistell, uresh Poosala, Kevin G. Becker, Olivier Boss, Dana Gwinn, ingyi Wang, haran Ramaswamy, Kenneth W. Fishbein, Richard G. pencer, Edward G. akatta, David e Couteur, Reuben J. haw, Placido Navas, Pere Puigserver, Donald K. Ingram, Rafael de Cabo, and David A. inclair upplementary Figures
2 upplementary Figure 1 a 3 b 12 Food intake (g/week) tandard diet High cal High cal + resv Caloric intake (kcal/week) tandard diet High cal High cal + resv Time (weeks) Time (weeks) c Faecal output (g/mouse/week) D d Faecal lipid content (mg/g) D upplementary Figure 1 Total faecal output and faecal lipid content are not altered by resveratrol. a,b, Food intake by weight (a) or calories (b). c, Total faecal output; n = 3 cages (of 2-3 mice per cage). d, ipid content of faeces. - p < 5 vs. D. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
3 upplementary Figure 2 D F F F 1cm upplementary Figure 2 Fat distribution is not significantly changed by resveratrol as assessed by post-mortem RI. T2-weighted proton spin-echo R images acquired at 7 T showing fat distribution in 1 mm thick axial slices in mice from D,, and groups (n = 3 for each group) through the skeletal muscle of the shoulders (). Images are presented with the anterior (ventral) side of each mouse facing the top of the image. Bright features at the periphery of the each mouse indicate subcutaneous or abdominal fat (F). No pronounced differences were observed in the post-mortem distribution of fat between subcutaneous, abdominal, and epididymal compartments or the distribution of brown fat between the three groups.
4 upplementary Figure 3 a c e APK activity (AU) APK activity (AU) ACC phosphorylation (AU) CHO EtOH AICAR Resv Addition to IP d protein EtOH Resv AP D b d f APK activity (AU) FA expression (AU) APK activity (AU) HEK293 EtOH AICAR Resv DO Addition to recombinant protein Resv D upplementary Figure 3 APK activity is enhanced via an indirect mechanism in cultured cells. a, b, The activity of Flag-tagged human APKα1 (co-transfected with HA-tagged human APKβ, and HA-tagged APKγ at a ratio of 2:1:1) following immunoprecipitation (IP) is enhanced by pre-treatment of CHO (a) or HEK293 (b) cells with 1 µ resveratrol. AICAR (2m) is shown as a positive control, but was not effective in HEK293 cells. c, d, Adding resveratrol directly to the kinase reaction inhibits, rather than activates APK, consistent with its effects on several other kinases. Inhibition was observed with both immunoprecipitated (c) and purified recombinant (d) protein (1 and 2 µ resveratrol, respectively). e,f, Phosphorylation of ACC is increased (e), and expression of fatty acid synthase is decreased (f) in the livers of resveratrol-fed mice, both of which support the conclusion that APK activity is enhanced. n = 5 for all groups. - p < 5. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
5 upplementary Figure 4 a b iver H&E iver weight (g) D D c Heart H&E D Aorta EVG Aorta H&E d upplementary Figure 4 Resveratrol reduces pathological changes in the hearts of high calorie-fed mice. a, Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained slices through the livers of animals from each group. b, Resveratrol prevents the increase in liver weight induced by the diet. c, The histology of hearts is significantly improved, and is more similar to that of the D group than controls, based on the white space and fatty infiltration between the individual cardiac fibers and fiber groups in the samples. The fibers in the group are also are thinner. In contrast, fibers are denser and less dispersed in the D and samples. Blinded pathology ratings are presented in Fig. 3d. d, Representative aortic sections stained with H&E (upper panels) or elastica van Gieson (EVG, lower panels). In mice, the aortic elastic lamina is straighter and less dense compared with D samples. Interestingly, resveratrol preserves, at least in part, the wavy elastic fibers and retards the loss of aortic elastic density. n = 8 for panel b. - media, - lumen.
6 upplementary Figure 5 Gene symbol Hsd3b5 Cycles Z ratio () lco1a aa up1 6.8 CD yd Cidea Gsta1/a / β-actin n.s. GAPDH n.s. upplementary Figure 5 Validation of microarray results by RT-PCR. RNA from all animals in each group was pooled and amplified using primers specific for the indicated targets. For purposes of comparison, the Z scores obtained by microarray analysis are provided. Note that these numbers reflect statistical confidence and do not relate directly to fold-change. For yd6, the arrow indicates the size of the predicted product, while the upper band corresponds to the size predicted to result from amplification of genomic DNA (containing an additional 192 bp intron). A slight decrease in GAPDH mrna in relative to was consistently noted, while amplification of β-actin mrna was indistinguishable in all cases. n.s. - not significant.
7 upplementary Figure 6 Pathway mitochondrial genes 1 mitochondrial genes 2 glutathione metabolism mitochondrial genes 3 val leu ile degradation pepsinogen C related genes Krebs TCA cycle electron transport chain butanoate metabolism upregulated by insulin oxidative phosphorylation propanoate metabolism small leu-rich proteoglycans tat3 pathway erythropoietin pathway extrinsic clotting pathway acute inflammatory response HOX genes/hematopoiesis classic complement pathway lechtin pathway fibrinolysis pathway GPCRs - class A sterol biosynthesis alternative complement pathway upplementary Figure 6 Comparison of the 12 pathways (gene sets) most highly up- (red) or down-regulated (blue) by resveratrol treatment. ome of the pathways have been given more descriptive names for the sake of clarity. Original names, as well as the complete list of significant changes can be found in figure 7a. The acute inflammatory response pathway appears to have been increased due to complement-related genes in the gene set and we did not observe evidence of a widespread inflammatory response.
8 upplementary Figure 7a mitochondr human-mitodb-6-22 AP48-Glutathione-metabolism GO-5739 IG- InsulinReceptorPathwayInCardiacy ocytes CR-PROTEIN-OD drug-resistance-and-metabolism RAP-DOWN p53-signalling etcpathway RO AP38-Tryptophan-metabolism GUCOE-DOWN AP632-Benzoate-degradation IG-PIP3-signaling-in-B-lymphocytes hivnefpathway IG-PIP3IGINCARDIACYOCTE Glycogen-etabolism Fatty-Acid-Degradation feederpathway RAR-UP betaoxidationpathway T-Integrin-ignaling-Pathway GYCOGEN EU-DOWN CR-CE-CYCE glycolysispathway AP24-Pyrimidine-metabolism eif4pathway KET AP33-Arginine-and-prolinemetabolism cell-cycle-arrest Proteasome-Degradation IG-BCR-ignaling-Pathway AP63-Globoside-metabolism mtorpathway T-Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase- Pathway krebpathway electron-transporter-activity cdc42racpathway deathpathway AP6-phingoglycolipidmetabolism AP19-Oxidativephosphorylation AP23-Purine-metabolism AP72-Reductive-carboxylatecycle-CO2-fixation GUT-UP electron-transport G13-ignaling-Pathway atmpathway AP43-Taurine-and-hypotaurinemetabolism raspathway actinypathway CR-ANGIOG BRCA-UP pdgfpathway cell-cycle-checkpoint rnapathway eif2pathway UPREG-BY-HOXA9 AP272-Cysteine-metabolism salmonellapathway tumor-supressor caspasepathway AP71-Carbon-fixation AP32-RNA-polymerase CR-REPAIR IG-CHEOTAXI ghpathway mitochondriapathway mrna-processing hifpathway CR-TRANPORT insulinpathway HUAN-CD34-ENRICHED-TF-JP tollpathway gcrpathway ptenpathway d4gdipathway AP46-Cyanoamino-acidmetabolism ureacyclepathway ifnapathway igf1mtorpathway ecmpathway T-Type-I-Interferon-Pathway vegfpathway eponfkbpathway igf1rpathway KRA-TOP1-CONTRO vitcbpathway relapathway msppathway AP62-Fatty-acid-biosynthesispath-2 AP5-tarch-and-sucrosemetabolism AP71-Fatty-acid-metabolism AP2-Citrate-cycle-TCA-cycle AP251-Glutamate-metabolism FA AP62-Pyruvate-metabolism fatty-acid-metabolism PYR ketonebodiespathway GUT-DOWN AP1-Glycolysis- Gluconeogenesis AP41-beta-Alanine-metabolism TCA pparapathway AP28-Valine-leucine-andisoleucine-degradation PGC Krebs-TCA-Cycle Electron-Transport-Chain AP65-Butanoate-metabolism INUIN-2F-UP VOXPHO AP64-Propanoate-metabolism AP31-ysine-degradation slrppathway T-TAT3-Pathway erythpathway extrinsicpathway lairpathway HOX-IT-JP classicpathway lechtinpathway fibrinolysispathway GPCRs-Class-A-Rhodopsin-like AP1-terol-biosynthesis alternativepathway upplementary Figure 7 Complete listing of pathways significantly altered by high calorie diet and resveratrol treatment. a, Pathways significantly altered by the as compared to controls. In Fig. 4 and 6, more descriptive names were given to some of the gene sets whose original names were esoteric, for the sake of clarity. This figure uses gene set names originally provided by the Broad Institute at gsea/msigdb/msigdb_inde x.html. b, Complete list of pathways significantly changed by either diet vs. D or vs. diet alone. n = 5 for D and, n = 4 for.
9 upplementary Figure 7b malatepathway cdc42racpathway eponfkbpathway AP251-Glutamate-metabolism cell-cycle-checkpoint cd4pathway ifnapathway RAP-DOWN GUT-UP gcrpathway AP272-Cysteine-metabolism CR-CE-CYCE vitcbpathway Proteasome-Degradation vippathway IG-CHEOTAXI tumor-supressor T-Integrin-ignaling-Pathway actinypathway feederpathway T-Type-I-Interferon-Pathway AP24-Pyrimidine-metabolism d4gdipathway GUCOE-DOWN AP63-Glyoxylate-and-dicarboxylate-metabolism AP71-Carbon-fixation mtorpathway salmonellapathway glycolysispathway eif4pathway CR-ANGIOG AP1-terol-biosynthesis CR-REPAIR raspathway mitochondriapathway relapathway AP23-Purine-metabolism aifpathway deathpathway AP19-Oxidative-phosphorylation ghpathway Glycogen-etabolism GYCOGEN igf1rpathway igf1mtorpathway mrna-processing AP32-RNA-polymerase ptenpathway EU-DOWN insulinpathway ecmpathway HUAN-CD34-ENRICHED-TF-JP vegfpathway ureacyclepathway slrppathway AP43-Taurine-and-hypotaurine-metabolism KRA-TOP1-CONTRO fibrinolysispathway AP562-Inositol-phosphate-metabolism AP-kinase-kinase-activity erythpathway asbcellpathway AP46-Cyanoamino-acid-metabolism il4pathway GPCRs-Class-A-Rhodopsin-like akap13pathway shh-lisa extrinsicpathway classicpathway lairpathway AP15-Androgen-and-estrogen-metabolism T-TAT3-Pathway GUCOE-UP HOX-IT-JP muscle-myosin alternativepathway lechtinpathway mitochondr AP28-Valine-leucine-and-isoleucine-degradation AP65-Butanoate-metabolism human-mitodb-6-22 GO-5739 AP64-Propanoate-metabolism AP71-Fatty-acid-metabolism INUIN-2F-UP AP41-beta-Alanine-metabolism AP31-ysine-degradation Krebs-TCA-Cycle AP1-Glycolysis-Gluconeogenesis FA NFKB-INDUCED AP62-Fatty-acid-biosynthesis-path-2 ketonebodiespathway AP62-Pyruvate-metabolism AP2-Citrate-cycle-TCA-cycle AP632-Benzoate-degradation PGC fatty-acid-metabolism AP48-Glutathione-metabolism drug-resistance-and-metabolism Fatty-Acid-Degradation betaoxidationpathway RO pparapathway TCA AP38-Tryptophan-metabolism IG-InsulinReceptorPathwayInCardiacyocytes AP6-phingoglycolipid-metabolism HTERT-DOWN KET T-Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase-Pathway AP63-Globoside-metabolism PYR Electron-Transport-Chain electron-transport VOXPHO cptpathway arenrf2pathway msppathway RAR-UP IG-PIP3IGINCARDIACYOCTE electron-transporter-activity AP5-tarch-and-sucrose-metabolism atmpathway p53-signalling AP72-Reductive-carboxylate-cycle-CO2-fixation CR-PROTEIN-OD krebpathway cell-cycle-arrest G13-ignaling-Pathway chemicalpathway UPREG-BY-HOXA9 pdgfpathway torpathway tollpathway BRCA-UP bcrpathway gleevecpathway IG-BCR-ignaling-Pathway AP33-Arginine-and-proline-metabolism rnapathway GUT-DOWN GO-RO hifpathway CR-TRANPORT A-B-CE-RECEPTOR-COPEXE caspasepathway etcpathway IG-PIP3-signaling-in-B-lymphocytes AP79-Folate-biosynthesis hivnefpathway eif2pathway YC-UT :D :D
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as. TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we
 Supplemental Results K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we performed a similar GE analysis
Supplemental Results K-means Clustering of a subset of five datasets that were identified as TNBC by IHC. Since TNBCs are not identified by GE in the clinical setting, we performed a similar GE analysis
Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR
 Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR Name: guest623839008349489450 February 7, 2018 1 Background Understanding the functional importance of metabolites in untargeted metabolomics is limited due
Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR Name: guest623839008349489450 February 7, 2018 1 Background Understanding the functional importance of metabolites in untargeted metabolomics is limited due
Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease
 Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease Craig E. Wheelock 1,2*, Åsa M. Wheelock 2,3,4, Shuichi Kawashima 5, Diego Diez 2, Minoru Kanehisa 2,5, Marjan van Erk
Systems biology approaches and pathway tools for investigating cardiovascular disease Craig E. Wheelock 1,2*, Åsa M. Wheelock 2,3,4, Shuichi Kawashima 5, Diego Diez 2, Minoru Kanehisa 2,5, Marjan van Erk
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
 Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
THE IMPACT OF THE RESVERATROL ON THE BODY MASS INDEX IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE
 2014 THE IMPACT OF THE RESVERATROL ON THE BODY MASS INDEX IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Annamaria* * Oradea University, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, 23 N. Jiga St., Oradea, Romania, e-mail: katifodor@yahoo.com
2014 THE IMPACT OF THE RESVERATROL ON THE BODY MASS INDEX IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Annamaria* * Oradea University, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, 23 N. Jiga St., Oradea, Romania, e-mail: katifodor@yahoo.com
Sustainable Fish Diets for the 21st Century using Soybean Protein. Paul B. Brown, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
 Sustainable Fish Diets for the 21st Century using Soybean Protein Paul B. Brown, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA pb@purdue.edu *Introduction *If you want to grow an animal, you must provide
Sustainable Fish Diets for the 21st Century using Soybean Protein Paul B. Brown, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA pb@purdue.edu *Introduction *If you want to grow an animal, you must provide
E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core
 1 E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Each student should be able to: Describe the glycolysis pathway in the core model. Describe the TCA cycle in the core model. Explain gluconeogenesis.
1 E.coli Core Model: Metabolic Core 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Each student should be able to: Describe the glycolysis pathway in the core model. Describe the TCA cycle in the core model. Explain gluconeogenesis.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Proteins and Amino Acids. Benjamin Caballero, MD, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Protein Class/Name KEGG Pathways
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
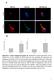 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
CHEM/MBIO 2370 Biochemistry 2: Catabolism, Synthesis and Information Pathways--Syllabus
 An introductory course dealing with the basic metabolic processes that occur in living cells including the production and use of metabolic energy, the breakdown and synthesis of biomolecules, the synthesis
An introductory course dealing with the basic metabolic processes that occur in living cells including the production and use of metabolic energy, the breakdown and synthesis of biomolecules, the synthesis
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver
 Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver Objective Use microarray results as input to the virtual liver model for prediction of toxicity Combine multiple experimental information for toxicity
Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver Objective Use microarray results as input to the virtual liver model for prediction of toxicity Combine multiple experimental information for toxicity
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus 1 Course title Biochemistry for Medical students 2 Course number 0501213 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 3 Contact hours
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus 1 Course title Biochemistry for Medical students 2 Course number 0501213 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 3 Contact hours
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Control. csarnt -/- Cre, f/f
 ody weight (g) A re,f/f re x f/f f/+ re, f/+ re,f/+ f/f x f/f f/+ cs -/- re, f/f re f/f re, f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen Tamoxifen Tamoxifen W 4W re f/f re, re/ff f/f re f/f re, re/ff f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen
ody weight (g) A re,f/f re x f/f f/+ re, f/+ re,f/+ f/f x f/f f/+ cs -/- re, f/f re f/f re, f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen Tamoxifen Tamoxifen W 4W re f/f re, re/ff f/f re f/f re, re/ff f/f Normal chow Tamoxifen
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Glycolysis. Cellular Respiration
 Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Disaccharides. Compound dehydration synthesis puts sugars together Hydrolysis (hydro-water, lysisbreakdown)
 Carbohydrate Carbo-hydrate -carbon, water Cn(H2O) n Monosaccharides Hexose hex = 6 [carbons], "-ose" means sugar Glucose monosaccaccharide usually assume a ring structure Disaccharides Compound dehydration
Carbohydrate Carbo-hydrate -carbon, water Cn(H2O) n Monosaccharides Hexose hex = 6 [carbons], "-ose" means sugar Glucose monosaccaccharide usually assume a ring structure Disaccharides Compound dehydration
Protein Class/Name. Pathways. bat00250, bat00280, bat00410, bat00640, bat bat00270, bat00330, bat00410, bat00480
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 1. Proteins Increased in Either Soil or Laboratory media Table 1A. Proteins Increased
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 1. Proteins Increased in Either Soil or Laboratory media Table 1A. Proteins Increased
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM LAB SECTION
 BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
Cornstarch
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary data : Supplementary Table 1: Diet composition (g/kg) on the basis of the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary data : Supplementary Table 1: Diet composition (g/kg) on the basis of the
Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
 Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle Amino Acids: Final class of biomolecules whose oxidation contributes significantly to the generation of energy Undergo oxidation in three metabolic circumstances
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at
 Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Fuel the Failing Heart: glucose or fatty acids? Rong Tian, MD, PhD Mitochondria and Metabolism Center University of Washington, Seattle
 Fuel the Failing Heart: glucose or fatty acids? Rong Tian, MD, PhD Mitochondria and Metabolism Center University of Washington, Seattle Metabolic Remodeling: Fatty Acids Carbohydrates PCr/ATP Glucose vs.
Fuel the Failing Heart: glucose or fatty acids? Rong Tian, MD, PhD Mitochondria and Metabolism Center University of Washington, Seattle Metabolic Remodeling: Fatty Acids Carbohydrates PCr/ATP Glucose vs.
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
So where were we? But what does the order mean? OK, so what's a protein? 4/1/11
 So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Spring 2011 BIBC 102 final Hampton 6:30 T, Th
 Enzymes and Energetics (10 pts) 1) Enzymes alter A) The equilbirum constant of a reaction B) The rate of a reaction C) The free energy of a reaction D) All of the above 2) The kcat for an enzyme A) changes
Enzymes and Energetics (10 pts) 1) Enzymes alter A) The equilbirum constant of a reaction B) The rate of a reaction C) The free energy of a reaction D) All of the above 2) The kcat for an enzyme A) changes
Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004
 Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
Metabolism. Metabolic pathways. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
Role of the Pyruvate
 Role of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex in the Regulation of Blood Glucose Robert A. Harris Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, Indiana Kyungpook National University School of Medicine
Role of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex in the Regulation of Blood Glucose Robert A. Harris Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, Indiana Kyungpook National University School of Medicine
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer
 Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine
 Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Chem 280 Final Exam. Here is the summary of the total 150 points plus 6 points bonus. Carefully read the questions. Good luck!
 May 2 nd, 2012 Name: CLID: Score: Chem 280 Final Exam There are 32 multiple choices that are worth 3 points each. There are 5 problems and one bonus problem. Try to answer the questions, which you know
May 2 nd, 2012 Name: CLID: Score: Chem 280 Final Exam There are 32 multiple choices that are worth 3 points each. There are 5 problems and one bonus problem. Try to answer the questions, which you know
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Supplementary Figure 1
 VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy. Examples:
 Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Multiple choice: Circle the best answer on this exam. There are 12 multiple choice questions, each question is worth 3 points.
 CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe
 number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer)
 Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions - 2006 ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer) 1. Essential fatty acids are: A. precursors of biotin B. precursors of tyrosine C.
Dental Students Biochemistry Exam V Questions - 2006 ( Note: In all cases, the only correct answer is the best answer) 1. Essential fatty acids are: A. precursors of biotin B. precursors of tyrosine C.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln
 The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Expanded View Figures
 Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Unit 2 Biology Course Outline Winter BIOC 305 Molecular Biochemistry (3) TTh 8 a.m.- 9:20 a.m. Art 376
 Unit 2 Biology Course Outline 2013 Winter BIOC 305 Molecular Biochemistry (3) TTh 8 a.m.- 9:20 a.m. Art 376 Instructor: Dr. Joyce Boon Office: Science 316 Phone: (250-807- 9545) Email: Joyce.Boon@ubc.ca
Unit 2 Biology Course Outline 2013 Winter BIOC 305 Molecular Biochemistry (3) TTh 8 a.m.- 9:20 a.m. Art 376 Instructor: Dr. Joyce Boon Office: Science 316 Phone: (250-807- 9545) Email: Joyce.Boon@ubc.ca
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Supplementary Materials: Global Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanism of Phelipanche Aegyptiaca Seed Germination
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1139; doi:.3390/ijms17071139 S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Global Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanism of Phelipanche Aegyptiaca Seed Germination Zhaoqun Yao, Fang
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1139; doi:.3390/ijms17071139 S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Global Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Mechanism of Phelipanche Aegyptiaca Seed Germination Zhaoqun Yao, Fang
Metabolism. Chapter 5. Catabolism Drives Anabolism 8/29/11. Complete Catabolism of Glucose
 8/29/11 Metabolism Chapter 5 All of the reactions in the body that require energy transfer. Can be divided into: Cell Respiration and Metabolism Anabolism: requires the input of energy to synthesize large
8/29/11 Metabolism Chapter 5 All of the reactions in the body that require energy transfer. Can be divided into: Cell Respiration and Metabolism Anabolism: requires the input of energy to synthesize large
CITRIC ACID CYCLE ERT106 BIOCHEMISTRY SEM /19 BY: MOHAMAD FAHRURRAZI TOMPANG
 CITRIC ACID CYCLE ERT106 BIOCHEMISTRY SEM 1 2018/19 BY: MOHAMAD FAHRURRAZI TOMPANG Chapter Outline (19-1) The central role of the citric acid cycle in metabolism (19-2) The overall pathway of the citric
CITRIC ACID CYCLE ERT106 BIOCHEMISTRY SEM 1 2018/19 BY: MOHAMAD FAHRURRAZI TOMPANG Chapter Outline (19-1) The central role of the citric acid cycle in metabolism (19-2) The overall pathway of the citric
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics
 Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
How Cells Release Chemical Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4171
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1 a b c PF %Change - -4-6 Body weight Lean mass Body fat Tissue weight (g).4.3.2.1. PF GC iwat awat BAT PF d e f g week 2 week 3 NEFA (mmol/l) 1..5. PF phsl (Ser565)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1 a b c PF %Change - -4-6 Body weight Lean mass Body fat Tissue weight (g).4.3.2.1. PF GC iwat awat BAT PF d e f g week 2 week 3 NEFA (mmol/l) 1..5. PF phsl (Ser565)
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
Name: Chem 351 Exam 3
 Multiple hoice: Pick the BEST answer and write it in the box at the end of the section. 1) The TA (Krebs) ycle depends on oxygen availability, though it does not directly use it. How can you best explain
Multiple hoice: Pick the BEST answer and write it in the box at the end of the section. 1) The TA (Krebs) ycle depends on oxygen availability, though it does not directly use it. How can you best explain
1.4. Lipids - Advanced
 1.4. Lipids - Advanced www.ck12.org In humans, triglycerides are a mechanism for storing unused calories, and their high concentration in blood correlates with the consumption of excess starches and other
1.4. Lipids - Advanced www.ck12.org In humans, triglycerides are a mechanism for storing unused calories, and their high concentration in blood correlates with the consumption of excess starches and other
