Chapter 2. Palmyra Fiber Separation Process And Properties Of Fiber And. Polyester Resin
|
|
|
- Marcia Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Palmyra Fiber Separation Process And Properties Of Fiber And Polyester Resin 1.1 Introduction Fibers of lightweight and high strength are embedded in the week matrix to get high strength composites materials. The properties of the composites depend upon the properties of the individual components in the composites. Hence it is essential that the strength of fiber and matrix have to be established. This chapter deals with the fiber separation process and their properties. Moisture absorption of the Palmyra fiber in water and in seawater at room temperature is also studied. The matrix material used is rooflight resin and its mechanical properties are studied and presented here. 2.2 Fiber Separation process The Palmyra tree (Borassus flabellifer) is found in abundance in the southern part of Tamilnadu and in Puthukottai district. This has been the main source of revenue for the people in this area for more than three decades. Loose red soil is best suited to the palmyra and it withstands worst drought condition and high wind force. In Srilanka the Palmyra tree is grown in large numbers and it gives good economic value to the people involved in the Palmyra related cultivation and other related work. Figure 2.1 shows the Palmyra tree and Fig 2.2 shows the leaf stem base and leaf stem of the Palmyra tree. The Palmyra wood has been used as building material for a very long period. The leaf has been used for thatching. Every
2 scrap of the tree can be utilized for some purposes. Rich quantities of fibers are available in leaf stem base and leaf stem. These fibers are separated out from leaf stem base / stem by crushing manually by hand beating and then cleaning manually with the help of a device called comber. This method has been traditionally followed for fiber separation. Also retting followed by hand beating and then washing in water is also used to separate the fibers. These fibers are also separated by mechanical crushing between the rollers and followed by cleaning with motorized combing device fabricated for this purpose. The separated fibers are then dried on open sky. During the separation of leaf stem base fiber, a large quantity of fibrous waste is produced, which has no value and creates environmental problems. Figure 2.3 shows the fiber obtained from leaf stem base, leaf stem and fibrous waste obtained during the separation of fiber from leaf stem base and leaf stem. For the present study the fibers are separated from the leaf stem by a mechanical crushing machine specially, designed for this purpose as shown in Fig 2.4.The fiber thus obtained has lot of spur / pith and these spurs are cleaned by the motorized combing device as shown in Fig 2.5. The fibers and the waste materials are collected separately and both of them are used in the present study. The fibers are subjected to different mechanical test and environmental condition to study their mechanical properties and the environmental effect on mechanical properties.
3 36 AN 4 F1g21. Palmyra tree too Fig. 22 Leaf stem and leaf stem base
4 37 (a) Leaf stem base and stem fiber (b) Fibrous waste Fig-2.3 Leaf stem base, stem fiber and fibrous waste
5 38 S I ptt.i, FV^ W, * I I - L Ei Fig. 24 Mechanical crushing device for fiber separation k -t r - k t1l 1: Fig25. Motorized combing device for cleaning the fibers
6 n 2.3 Fiber properties The leaf stem base fibers are strong stiff and dark brown / black in color. The shape varies from fiber to fiber, and also non uniform. Normally they are circular or elliptical. Fiber diameter is measured by an electron microscope for 50 samples and it is found to be varying between 0.5 mm to 1.5 mm, which depends on the age and area of cultivation of the plant. The density is calculated by Archimedes principle and it is found to be in the range of g/cc The fibers obtained from leaf stem base are wheatish in colour. They can be twisted in to yarns and ropes in wet conditions. Fiber diameter, length, and strength depend upon the age and location of the plant. The length varies from for 1 to 1.5m and diameter is between 0.3 mm mm. The density of the fiber is in the range of g/cc. 2.3.lTensile Strength The cleaned and dried single fiber is mounted along the centerline of a slotted paper window as shown in Fig 2.6. The ends of the paper window are clamped in the grips of the Instron-testing machine with gauge length of 50 mm and its mid section is cut off during loading. The load is applied with the crosshead speed of 1 mm / min till the fiber brakes and the load deflection curve is recorded. At least 25 samples are tested the results are tabulated in table 2.1.
7 From the load deflection curve the strength and modulus values are calculated. Figure 2.7 a, 2.7 b, 2.7 c and 2.7 d shows the load deflection curves of Palmyra leaf stem fiber. From the above figures it is observed that the strength of the fibers is not uniform and it varies from 70 MPa to 250 MPa. Variation in fiber strength is observed even in the same diameter fiber. The fiber sample 3 with diameter of 0.5 mm has the maximum strength of MPa, where as the fiber sample 1 with diameter of.03 mm has the strength of MPa. From this it is observed that the strength is not proportional to the diameter. The modulus is also in the range of 2.5 GPa tol 0 GPa. The % of elongation varies betweeni.5 and 3. Strength of the fibers depends mainly on the fibrillar structure, micro fibrillar angle and the cellulose content. The relation between the elongation and the fibrillar angle is given by [49] 278±7.28x108+77x10 (2.1) The strength of the fiber is related with micro fibrillar angle and the cellulose content and is given by [49]. a W (2.2) Fig. 2.6 Tensile specimen for single fiber test
8 z -o 30 Co 0 J 20 ber 10 er 0 w Deflection mm 60 Fig 2.7 a. Load deflection curves of leaf stem Palmyra fiber z 0 J ample 13 ample 14 ample 15 ample 19 ample 22 04_ Deflection mm Fig.2.7 b Load deflection curves for the fiber of 0.5 mm diameter
9 z40 -o 0J30 iple 5 iple 8 iple 21 iple Deflection mm Fig.2.7 c Load deflection curves for the fiber of 0.6 mm diameter sample 4 -'i z 0 -J r Deflection mm Fig.2.7 d Load deflection curves for the fiber of 0.4 mm diameter
10 A.-, Table2.1 Tensile Properties of Palmyra leaf stem fiber Sample Fiber Load Deflection Strength No. Dia mm N mm MPa of Modulus Strain n elongation GPa
11 ] J Water absorption kinetics of palmyra fiber Because of their lignocellulosic and organic origin, palmyra fibers exhibit a hydrophilic nature. To achieve the full potential of polymer composites, they must have a good environmental stability. As a raw material for polymer composites, the water-absorption behavior of this fiber has to be comprehensively investigated. Water-diffusion characteristics of palmyra fibers in water and seawater have been investigated and the results are discussed. About 0.5 g of dried and fiber having an approximate length of 5 cm is taken for the water-sorption examination. The samples are immersed in raw water and seawater at room temperature. Increase in weight of the samples is noted at specific time intervals. This process is continued until equilibrium is reached. The molar percentage uptake Q t for water for loog of polymer is plotted against the square root of time. The value is expressed as Q =w2-w1 18W1 2.3
12 45 Where 18 is the relative molecular mass of water. When equilibrium is reached, Q t is taken as the molar percentage uptake at infinite time, Q. [78]. The water sorption of fibers is calculated as the number of moles of water absorbed by bog of the fiber. The major factors that control the interaction between fibers and water are diffusion, permeability, and sorption. Palmyra fiber is lingo cellulose, they contain waxy material and water-soluble substances. The swelling behavior of natural fibers is greatly affected by its morphology as well as physical and chemical structures. The water penetration through the natural fiber can be explained using the diagram given in Fig 2.8 [79]. From the figure it is clear that the water penetration through the microspores of the fiber surface by capillary action is evident from the model. The fibers have a porous internal structure. The penetrating water enters onto the fiber structure and stay in the porous medium. The waxy materials present on the fiber surface help to retain the water molecules in to the fiber. The porous nature of the palmyra fibers accounts for the large initial uptake at the capillary region. Sreekala M.S. et.al [79] reported the water absorption of oil palm fiber. The water entering into the fiber produces an advancing front of water. The portion behind the advancing front is swollen relative to the portion ahead of the front and the outer layer of the fiber continuously changes to accommodate the further sorption. This process stops when the sorption reaches equilibrium.
13 Water Lacuna Micropores Waxy materials Fib iii Is Water penetration Cross section of fiber Fig2.8. Water sorption model The water molecule is small and strongly associated through hydrogenbond formation The initial hydrogen bonds in the water-accessible regions of the fiber are broken to form a sol-like structure that slowly is converted into a gel form with the reformation of inter chain of hydrogen bonds. They can form strong localized interactions with hydroxyl groups available on cellulose and lignin. Water sorption is mainly dependent on the penetrativity of water and radii of the capillaries. The length and radii of the capillaries determine the capillary action. The diffusion of water in water- cellulose system is reported to be non- Fickian or anomalous and two-stage absorption behaviour is reported in natural fibers [79]. In this case only single stage behaviour is observed in both water and seawater, which is shown in Fig 2.9. The initial stage of water penetration is by capillary action, which is shown by the linear portion of the curve, and the second nonlinear portion of the moisture absorption is due to the late filling of micro pores. The equilibrium sorption is higher for seawater, which is due to the presence of Na and Cl -. But in contrast to this Sreekala M.S. et.al [79] observed
14 Time (mm) Fig. 2.9.Moisture absorption curves lower equilibrium of sorption in sea water than distilled water at room temperature and higher equilibrium sorption than distilled water at high temperature for OPEFB fibers Matrix properties The physical properties of roof light resin as specified by the supplier is given in table 2.2 To find the mechanical properties a plate is cast with neat resin mixed with accelerator and catalyst in a mould of 150mm X 150mm X 3mm. Tensile samples of 150mm X 10mm are cut from plate and tested
15 48 INSTRON testing machine. Four specimens are tested and the average strength is estimated as 33MPa and the tensile modulus is 1000MPa. Impact samples of size 12.7mm X 65mm are tested by impact testing machine and the impact strength is observed as 0.4 J/cm 2. Bending samples of size 10mm X 80mm are tested by three-point loading and bending strength of 40MPa is observed. Shear specimens with length equal to 6 times of its thickness is tested by three points loading and shear strength is calculated as 4MPa. Table 2.2 properties of the Rooflight resin. Appearance Clear liquid Viscosity 270cps Acid value 23.68mg koh/gm Volatile content 40.59% Gel 14'20" Shelf life 3 months Specific gravity Conclusion The fiber separation process and its physical and mechanical properties are studied. From the test it is observed that the fiber size and the strength are not uniform. Variation in fiber strength is observed even in the same diameter fiber. The moisture absorption characteristic of the fiber is also studied. The mechanical properties of the matrix material are studied and presented in this chapter
CHAPTER 3 PROPERTIES OF ROSELLE FIBER, SISAL FIBER AND POLYESTER RESIN
 37 CHAPTER 3 PROPERTIES OF ROSELLE FIBER, SISAL FIBER AND POLYESTER RESIN 3.1 INTRODUCTION The plant fiber composites have been used by the human race ever since the onset of civilization as a source of
37 CHAPTER 3 PROPERTIES OF ROSELLE FIBER, SISAL FIBER AND POLYESTER RESIN 3.1 INTRODUCTION The plant fiber composites have been used by the human race ever since the onset of civilization as a source of
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 4, Issue 3, April 2016
 UTILIZATION OF COCONUT LEAF SHEATH FIBER AND ITS PROPERTIES DIVYA.G* Dr. C.KRISHNAVENI** *M.Phil, Scholar, Dept. of Botany, PSGR Krishnammal College for Women, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India **Associate
UTILIZATION OF COCONUT LEAF SHEATH FIBER AND ITS PROPERTIES DIVYA.G* Dr. C.KRISHNAVENI** *M.Phil, Scholar, Dept. of Botany, PSGR Krishnammal College for Women, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India **Associate
BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS
 BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS 55 Rahul Sen*, N.C.Upadhayay**, Upender Pandel*** *Research Scholar **Associate Professor
BIO- DEGRADABLE COMPOSITE MADE FROM STARCH AND COCONUT FIBER : MECHANICAL STRENGTH AND BIODEGRATION CHRACTERSTICS 55 Rahul Sen*, N.C.Upadhayay**, Upender Pandel*** *Research Scholar **Associate Professor
POLYMER REINFORCEMENT
 POLYMER REINFORCEMENT CG2 NanoCoatings Inc. 2007 CG 2 NanoCoatings Inc. 21 Pine Needles Court, Suite 200, Ottawa, ON K2S 1G5 CANADA T 613.435.7747 F 413.638.3933 W www.cg2nanocoatings.com POLYMER REINFORCEMENT
POLYMER REINFORCEMENT CG2 NanoCoatings Inc. 2007 CG 2 NanoCoatings Inc. 21 Pine Needles Court, Suite 200, Ottawa, ON K2S 1G5 CANADA T 613.435.7747 F 413.638.3933 W www.cg2nanocoatings.com POLYMER REINFORCEMENT
Section I : Fibers Outline
 Section I : Fibers Outline Introduction o Generic and trade names o Classification o Staple and filament fibers Understanding Fiber Structure and Properties Fiber Terminology o Fiber Structure Length;
Section I : Fibers Outline Introduction o Generic and trade names o Classification o Staple and filament fibers Understanding Fiber Structure and Properties Fiber Terminology o Fiber Structure Length;
Name GLOSSARY. Carrier protein a molecule in the cell membrane that allows materials to pass through it
 2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
2 GLOSSARY Active transport movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
FIBERBOARDS MADE FROM ACETYLATED BAGASSE FIBER. Roger M. Rowell
 FIBERBOARDS MADE FROM ACETYLATED BAGASSE FIBER Roger M. Rowell Chemist USDA Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory 1 One Gifford Pinchot Drive Madison, WI 53705-2398 and Francis M. Keany Consultant
FIBERBOARDS MADE FROM ACETYLATED BAGASSE FIBER Roger M. Rowell Chemist USDA Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory 1 One Gifford Pinchot Drive Madison, WI 53705-2398 and Francis M. Keany Consultant
ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP
 ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP S. J. Yeoh 1, W.Y. Hamad 2, F.K. Ko 1 1 University of British Columbia 2355, East Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T1Z4 2 FPInnovations 3800, Wesbrook
ELECTROSPUN CELLULOSE ULTRA-FINE FIBERS FROM KRAFT PULP S. J. Yeoh 1, W.Y. Hamad 2, F.K. Ko 1 1 University of British Columbia 2355, East Mall, Vancouver, BC, Canada V6T1Z4 2 FPInnovations 3800, Wesbrook
TEST. Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F").
 TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
Evaluating Plasticizer Loss In PVC Membranes
 Evaluating Plasticizer Loss In PVC Membranes Plasticizer loss is shown to be minimal in either moist or exposed environments. Membrane usefulness is not affected by the loss that does occur. By Doug Burwell,
Evaluating Plasticizer Loss In PVC Membranes Plasticizer loss is shown to be minimal in either moist or exposed environments. Membrane usefulness is not affected by the loss that does occur. By Doug Burwell,
Dynamics and Structure Development for Biaxial Stretching PA6 Films
 Dynamics and Structure Development for Biaxial Stretching PA6 Films Toshitaka Kanai 1,a)*, Yoshimune Okuyama 2), Masao Takashige 3) * 1 KT Poymer, 5-7-14 Kuranamidai, Sodegaura, Chiba, 299-0245, Japan
Dynamics and Structure Development for Biaxial Stretching PA6 Films Toshitaka Kanai 1,a)*, Yoshimune Okuyama 2), Masao Takashige 3) * 1 KT Poymer, 5-7-14 Kuranamidai, Sodegaura, Chiba, 299-0245, Japan
Soft tissue biomechanics
 Soft tissue biomechanics Caroline Öhman Pula, 22/06-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to soft tissues Tendon and ligaments Introduction Composition Function and structure In vitro testing Stress-strain
Soft tissue biomechanics Caroline Öhman Pula, 22/06-08 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to soft tissues Tendon and ligaments Introduction Composition Function and structure In vitro testing Stress-strain
EFFECT OF DENSITY AND POLYMER CONTENT ON THE HYGROSCOPIC THICKNESS SWELLING RATE OF COMPRESSION MOLDED WOOD FIBER/POLYMER COMPOSITES. Sheldon Q.
 EFFECT OF DENSITY AND POLYMER CONTENT ON THE HYGROSCOPIC THICKNESS SWELLING RATE OF COMPRESSION MOLDED WOOD FIBER/POLYMER COMPOSITES Sheldon Q. Shi * Assistant Professor Forest Products Department Mississippi
EFFECT OF DENSITY AND POLYMER CONTENT ON THE HYGROSCOPIC THICKNESS SWELLING RATE OF COMPRESSION MOLDED WOOD FIBER/POLYMER COMPOSITES Sheldon Q. Shi * Assistant Professor Forest Products Department Mississippi
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
PROPERTIES OF LAMINATED PLASTICS MADE FROM LIGNIN AND LIGNIN-PHENOLIC RESIN-IMPREGNATED PAPERS
 PROPERTIES OF LAMINATED PLASTICS MADE FROM LIGNIN AND LIGNIN-PHENOLIC RESIN-IMPREGNATED PAPERS August 1944 This Report is One of a Series Issued In Cooperation with the ARMY-NAVY-CIVILCOMMITTEE on AIRCRAFT
PROPERTIES OF LAMINATED PLASTICS MADE FROM LIGNIN AND LIGNIN-PHENOLIC RESIN-IMPREGNATED PAPERS August 1944 This Report is One of a Series Issued In Cooperation with the ARMY-NAVY-CIVILCOMMITTEE on AIRCRAFT
The Effect of Chemical Treatment on Tensile Strength and Weight of Banana Stem Fiber after Treating with Various Chemicals
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. IV (July. 2017), PP 66-70 www.iosrjournals.org The Effect of Chemical Treatment on Tensile
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. IV (July. 2017), PP 66-70 www.iosrjournals.org The Effect of Chemical Treatment on Tensile
3. Describe the study in mimicry, using king snakes and coral snakes. Identify the control in the experiment.
 Biology Semester 1 Exam Review Guide Chapter 1 Biology in the 21 st Century 1. Distinguish between the following key terms: Biology Name : Pd: Hypothesis Variable Controlled experiment Theory Model Technology
Biology Semester 1 Exam Review Guide Chapter 1 Biology in the 21 st Century 1. Distinguish between the following key terms: Biology Name : Pd: Hypothesis Variable Controlled experiment Theory Model Technology
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology
 Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology Essential idea: The structure of biological membranes makes them fluid and dynamic http://www.flickr.com/photos/edsweeney/6346198056/ 1.3.1 Phospholipids
Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology Essential idea: The structure of biological membranes makes them fluid and dynamic http://www.flickr.com/photos/edsweeney/6346198056/ 1.3.1 Phospholipids
What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity?
 Avijit Baidya 12.11.2016 What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity? Introduction : Hydrophobic and amphiphobic surfaces have been studied in great depth over the past couple
Avijit Baidya 12.11.2016 What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity? Introduction : Hydrophobic and amphiphobic surfaces have been studied in great depth over the past couple
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
AvaDent Bonding Procedure Results: The AvaDent bond exceeds ADA requirements.
 Tests Summary: AvaDent Bonding Procedure Results: The AvaDent bond exceeds ADA requirements. AvaDent Color Stability Results: AvaDent is more color stable than conventional dentures. AvaDent Acrylic Porosity
Tests Summary: AvaDent Bonding Procedure Results: The AvaDent bond exceeds ADA requirements. AvaDent Color Stability Results: AvaDent is more color stable than conventional dentures. AvaDent Acrylic Porosity
Chicken Feather Fiber as an Additive in MDF Composites
 Chicken Feather Fiber as an Additive in MDF Composites Jerrold E. Winandy James H. Muehl Jessie A. Glaeser Walter Schmidt ABSTRACT. Medium density fiberboard (MDF) panels were made with aspen fiber and
Chicken Feather Fiber as an Additive in MDF Composites Jerrold E. Winandy James H. Muehl Jessie A. Glaeser Walter Schmidt ABSTRACT. Medium density fiberboard (MDF) panels were made with aspen fiber and
PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH MODIFIED BY PECTIN
 E_E0026 1 PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH MODIFIED BY PECTIN Worawan Pattanasin, Jutarat Prachayawarakorn* Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
E_E0026 1 PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH MODIFIED BY PECTIN Worawan Pattanasin, Jutarat Prachayawarakorn* Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
LIQUID (DYE) PENETRANT INSPECTION (LPI)
 LIQUID (DYE) PENETRANT INSPECTION (LPI) Introduction This module is intended to provide an introduction to the NDT method of penetrant testing. Liquid penetrant inspection (LPI) or Penetrant Testing (PT),
LIQUID (DYE) PENETRANT INSPECTION (LPI) Introduction This module is intended to provide an introduction to the NDT method of penetrant testing. Liquid penetrant inspection (LPI) or Penetrant Testing (PT),
Effects of the modification of fiber surface on the mechanical properties of cotton fabric
 KEER2014, LINKÖPING JUNE 11-13 2014 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON KANSEI ENGINEERING AND EMOTION RESEARCH Effects of the modification of fiber surface on the mechanical properties of cotton fabric Sawako
KEER2014, LINKÖPING JUNE 11-13 2014 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON KANSEI ENGINEERING AND EMOTION RESEARCH Effects of the modification of fiber surface on the mechanical properties of cotton fabric Sawako
Preparation and Properties of Cornstarch Adhesives
 Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 5(8): 168-172, 213 ISSN: 242-4868; e-issn: 242-4876 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 213 Submitted: April 16, 213 Accepted: May 14, 213 Published: August
Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 5(8): 168-172, 213 ISSN: 242-4868; e-issn: 242-4876 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 213 Submitted: April 16, 213 Accepted: May 14, 213 Published: August
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY
 LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH/LOW-DENSITY POLYETHYLENE BLEND MODIFIED BY CARRAGEENAN
 E_E0027 1 PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH/LOW-DENSITY POLYETHYLENE BLEND MODIFIED BY CARRAGEENAN Wanida Pomdage, Jutarat Prachayawarakorn,* Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King
E_E0027 1 PROPERTIES OF THERMOPLASTIC CASSAVA STARCH/LOW-DENSITY POLYETHYLENE BLEND MODIFIED BY CARRAGEENAN Wanida Pomdage, Jutarat Prachayawarakorn,* Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
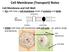 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT OSMOSIS, DIFFUSION AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT CLASS 9 Name :... Date:... d) Movement of substances into and
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
HSC Biology. Year 2016 Mark Pages 46 Published Jan 18, Biology Notes. By James (99.05 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
BEHAVIOUR OF LONG-LASTING STRESS RELAXATION OF VARIOUS TYPES OF YARNS
 BEHAVIOUR OF LONG-LASTING STRESS RELAXATION OF VARIOUS TYPES OF YARNS Ginta Laureckienė*, Rimvydas Milašius Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Design, Kaunas University
BEHAVIOUR OF LONG-LASTING STRESS RELAXATION OF VARIOUS TYPES OF YARNS Ginta Laureckienė*, Rimvydas Milašius Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Design, Kaunas University
5.1 STANDARD CURVES OF DRUGS USED
 223 Glipizide and Glimepiride matrix tablets were prepared by using Aloe barbadensis miller leaves mucilage, Guar gum, Povidone and were evaluated. Similarly Glipizide and Glimepiride transdermal patches
223 Glipizide and Glimepiride matrix tablets were prepared by using Aloe barbadensis miller leaves mucilage, Guar gum, Povidone and were evaluated. Similarly Glipizide and Glimepiride transdermal patches
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Lab #6: Cellular Transport Mechanisms Lab
 Lab #6: Cellular Transport Mechanisms Lab OVERVIEW One of the major functions of the plasma membrane is to regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell. This process is essential in maintaining
Lab #6: Cellular Transport Mechanisms Lab OVERVIEW One of the major functions of the plasma membrane is to regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell. This process is essential in maintaining
BYA1. BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 1 Molecules, Cells and Systems
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 01, October 2015, Pages 17-25
 Original article: A Comparative evaluation of shear bond strengths of denture base to cross linked acrylic resin maxillary anterior teeth with and without retentive grooves - An invitro study Dr.D.Sudha
Original article: A Comparative evaluation of shear bond strengths of denture base to cross linked acrylic resin maxillary anterior teeth with and without retentive grooves - An invitro study Dr.D.Sudha
> What are chemicals of life made from?
 Carbon Compounds > What are chemicals of life made from? ) What is the role of carbohydrates in cells? :> What do lipids do? ) What detennines the functions of proteins? carbohydrate lipid protein amino
Carbon Compounds > What are chemicals of life made from? ) What is the role of carbohydrates in cells? :> What do lipids do? ) What detennines the functions of proteins? carbohydrate lipid protein amino
Engineering Materials
 Engineering Materials PREPARED BY Academic Services August 2011 Applied Technology High Schools, 2011 Module Objectives After the completion of this module, the student will be able to: Explain the basic
Engineering Materials PREPARED BY Academic Services August 2011 Applied Technology High Schools, 2011 Module Objectives After the completion of this module, the student will be able to: Explain the basic
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules The Chemistry of Life : Learning Outcomes 2.4) Describe the significance of carbon in forming the basis of the four classes of biological
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules The Chemistry of Life : Learning Outcomes 2.4) Describe the significance of carbon in forming the basis of the four classes of biological
PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF TAPIOCA STARCH / SUGARCANE FIBER CELLULOSE COMPOSITE
 PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF TAPIOCA STARCH / SUGARCANE FIBER CELLULOSE COMPOSITE A. R. Jeefferie 1, O. Nurul Fariha 1, A. R. Mohd Warikh 1, M. Y. Yuhazri 1, Haeryip Sihombing
PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF TAPIOCA STARCH / SUGARCANE FIBER CELLULOSE COMPOSITE A. R. Jeefferie 1, O. Nurul Fariha 1, A. R. Mohd Warikh 1, M. Y. Yuhazri 1, Haeryip Sihombing
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
INVISTA TERRIN Polyols
 Technical Data Sheet INVISTA TERRIN Polyols Cost-Effective Alternative to Conventional Polyether and Polyester Polyols Introduction TERRIN polyols can be used in lieu of or in combination with conventional
Technical Data Sheet INVISTA TERRIN Polyols Cost-Effective Alternative to Conventional Polyether and Polyester Polyols Introduction TERRIN polyols can be used in lieu of or in combination with conventional
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. 2. In plants, which characteristic or behavior is typically independent of the plant's environment?
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Living System and Free Energy Blizzard Bag 2014 2015 1. How is cellular respiration useful to the cell? A. producing ATP, which provides the nucleotides
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Living System and Free Energy Blizzard Bag 2014 2015 1. How is cellular respiration useful to the cell? A. producing ATP, which provides the nucleotides
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
CPGAN #002. FTIR Quantification of Absorbed Radiation Dose in Polyethylene
 1.1 Introduction Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is the current material of choice for bearing surface applications in total joint arthroplasty. In an effort to enhance the wear properties
1.1 Introduction Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is the current material of choice for bearing surface applications in total joint arthroplasty. In an effort to enhance the wear properties
Transdermal Delivery of Newer Atypical Antipsychotics ABSTRACT
 Transdermal Delivery of Newer Atypical Antipsychotics ABSTRACT Abstract Risperidone and olanzapine, newer atypical antipsychotics are highly effective and safer in the treatment of psychosis. A low dose
Transdermal Delivery of Newer Atypical Antipsychotics ABSTRACT Abstract Risperidone and olanzapine, newer atypical antipsychotics are highly effective and safer in the treatment of psychosis. A low dose
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 2, 2013 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 2, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Analyzing Performance of Esterified Starch against Thin Boiling Starch for Warp Sizing
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 2, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Analyzing Performance of Esterified Starch against Thin Boiling Starch for Warp Sizing
Membranes for Textile and Garment Applications
 Membranes for Textile and Garment Applications Dr Mark Whiskens PIL Membranes Ltd Stand number: A 39 Why use Membranes Membranes are used inside a garments Typically they are laminated to the outer fabric
Membranes for Textile and Garment Applications Dr Mark Whiskens PIL Membranes Ltd Stand number: A 39 Why use Membranes Membranes are used inside a garments Typically they are laminated to the outer fabric
Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis
 STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
STO-112 Cell Membranes: Diffusion and Osmosis Part 1: Diffusion Diffusion is a process by which molecules move into or out of cells. To diffuse into or out of a cell, molecules must pass through the cell
Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1)
 14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins.
 Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Hydrolysis of Semi-finished Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Fiber
 Hydrolysis of Semi-finished Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Fiber Juan Xu & Shulin An School of Materials Science and Engineering Tianjin Polytechnic University Tianjin 0160, China E-mail: xujuan060608@163.com
Hydrolysis of Semi-finished Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Fiber Juan Xu & Shulin An School of Materials Science and Engineering Tianjin Polytechnic University Tianjin 0160, China E-mail: xujuan060608@163.com
What is the difference between cellulose and cellulose?
 Specialty Papers Conference 2010 schnell flexibel innovativ What is the difference between cellulose and cellulose? Walter Roggenstein, ead of R&D What is the difference between cellulose and cellulose?
Specialty Papers Conference 2010 schnell flexibel innovativ What is the difference between cellulose and cellulose? Walter Roggenstein, ead of R&D What is the difference between cellulose and cellulose?
Properties of Binderless Particleboard and Particleboard with Addition of Urea Formaldehyde Made from Oil Palm Trunk Waste
 Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(3), 151 159, 2017 Properties of Binderless Particleboard and Particleboard with Addition of Urea Formaldehyde Made from Oil Palm Trunk Waste Mohana Baskaran, Nur Adilah
Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(3), 151 159, 2017 Properties of Binderless Particleboard and Particleboard with Addition of Urea Formaldehyde Made from Oil Palm Trunk Waste Mohana Baskaran, Nur Adilah
Failure criteria for Adhesives. Sainath Kadam, 3mE 19 oktober 2014
 Failure criteria for Adhesives Sainath Kadam, 3mE 19 oktober 2014 () Failure criteria for Adhesives 1 / 59 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Testing 3 Data analysis 4 FEM 5 Results and Conclusions () Failure criteria
Failure criteria for Adhesives Sainath Kadam, 3mE 19 oktober 2014 () Failure criteria for Adhesives 1 / 59 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Testing 3 Data analysis 4 FEM 5 Results and Conclusions () Failure criteria
Welcome! Training Module - Light. Part of Qualification as a Continence Advisor
 Welcome! Training Module - Light Part of Qualification as a Continence Advisor Need Criteria for all Incontinence Products 1. Safe and leak-proof 2. Odour-proof / Anti-Odour 3. Discreet and quiet 4. Convenient
Welcome! Training Module - Light Part of Qualification as a Continence Advisor Need Criteria for all Incontinence Products 1. Safe and leak-proof 2. Odour-proof / Anti-Odour 3. Discreet and quiet 4. Convenient
Orthodontic Screw System
 1 st Pride ental Group Orthodontic Screw System HEA OFFICE 8th F. WorldMeridian Venture CenterⅡ, 426-5, Gasan-dong, Geumcheon-gu, Seoul, Korea tel_ 82 2 2016 7000, fax_ 82 2 2016 7001 homepage_ http://www.osstem.com
1 st Pride ental Group Orthodontic Screw System HEA OFFICE 8th F. WorldMeridian Venture CenterⅡ, 426-5, Gasan-dong, Geumcheon-gu, Seoul, Korea tel_ 82 2 2016 7000, fax_ 82 2 2016 7001 homepage_ http://www.osstem.com
Experiment 4: Synthesis of hydrogels of acrylamide and bisacrylamide in water.
 Experiment 4: Synthesis of hydrogels of acrylamide and bisacrylamide in water. Aim: (a) To synthesize polyacrylamide electrophoresis hydrogels by copolymerization of acrylamide and bisacrylamide in water
Experiment 4: Synthesis of hydrogels of acrylamide and bisacrylamide in water. Aim: (a) To synthesize polyacrylamide electrophoresis hydrogels by copolymerization of acrylamide and bisacrylamide in water
SKF bearings with Solid Oil the third lubrication choice
 SKF bearings with Solid Oil the third lubrication choice SKF bearings with Solid Oil the third lubrication choice Millions of micro-pores retain the oil in Solid Oil. There are three ways to ensure good
SKF bearings with Solid Oil the third lubrication choice SKF bearings with Solid Oil the third lubrication choice Millions of micro-pores retain the oil in Solid Oil. There are three ways to ensure good
Chapter MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Managing Aerial Spray Drift. by Paul E. Sumner Extension Engineer
 Managing Aerial Spray Drift by Paul E. Sumner Extension Engineer 2 This guide discusses the conditions that cause particle drift and the methods aerial applicators may employ to reduced the drift potential
Managing Aerial Spray Drift by Paul E. Sumner Extension Engineer 2 This guide discusses the conditions that cause particle drift and the methods aerial applicators may employ to reduced the drift potential
Development and Characterization of Biodegradable Film Using Corn Starch
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 6 (2016) pp. 1033-1040 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.506.110
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 6 (2016) pp. 1033-1040 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.506.110
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE
 METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics
 Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Centre of Mechanics of Biological Materials - CMBM
 Centre of Mechanics of Biological Materials - CMBM MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF THE DEEP FASCIAE Head of the Centre Prof. Arturo N. Natali Collaborator Prof. Piero G. Pavan From the basic researches to the clinical
Centre of Mechanics of Biological Materials - CMBM MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF THE DEEP FASCIAE Head of the Centre Prof. Arturo N. Natali Collaborator Prof. Piero G. Pavan From the basic researches to the clinical
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
4. Monitoring of dissolution induced changes in film coat
 4. Monitoring of dissolution induced changes in film coat composition 4.1 Introduction As membrane controlled drug delivery coatings are subjected to changes in coating composition, it is necessary to
4. Monitoring of dissolution induced changes in film coat composition 4.1 Introduction As membrane controlled drug delivery coatings are subjected to changes in coating composition, it is necessary to
Utilizing Biosolids As Packaging or Building Material
 Utilizing Biosolids As Packaging or Building Material Methods and equipment necessary to produce value added products from biosolids for packaging and building material applications. John F. Hunt, P.E.
Utilizing Biosolids As Packaging or Building Material Methods and equipment necessary to produce value added products from biosolids for packaging and building material applications. John F. Hunt, P.E.
KURARAY POVAL & EXCEVAL
 Characteristics Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) having varying degree of polymerization and. Recommended Uses Ranging from emulsion polymerization aid to binder for pigments in paper applications. Form supplied
Characteristics Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) having varying degree of polymerization and. Recommended Uses Ranging from emulsion polymerization aid to binder for pigments in paper applications. Form supplied
CALCIUM CASEINATE. What Is Casein?
 CALCIUM CASEINATE A high quality milk protein that is Calcium Rich, manufactured from fresh pasteurized skimmed milk through precipitation of casein followed by neutralization and natural drying, which
CALCIUM CASEINATE A high quality milk protein that is Calcium Rich, manufactured from fresh pasteurized skimmed milk through precipitation of casein followed by neutralization and natural drying, which
The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance.
 1 Some students investigated osmosis in raw potato sticks. (a) Define the term osmosis. [3] (b) The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance. Fig. 4.1 shows an
1 Some students investigated osmosis in raw potato sticks. (a) Define the term osmosis. [3] (b) The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance. Fig. 4.1 shows an
How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili. Robert R Smith
 Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Essential Plant Nutrients How to Develop a Balanced Program for Pecan and Chili Robert R Smith Nutrition Management Involves Knowledge of: Site/Soil characteristics and chemistry Plant requirements Cropping
Selection of cassava starch carnauba wax composite edible coating used to preserve fresh-cut apples Marcela Chiumarelli a, Miriam Dupas Hubinger a
 Selection of cassava starch carnauba wax composite edible coating used to preserve fresh-cut apples Marcela Chiumarelli a, Miriam Dupas Hubinger a a Dept. of Food Engineering, School of Food Engineering,
Selection of cassava starch carnauba wax composite edible coating used to preserve fresh-cut apples Marcela Chiumarelli a, Miriam Dupas Hubinger a a Dept. of Food Engineering, School of Food Engineering,
Chapter 2 pt 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Life. Gregory Ahearn. John Crocker. Including the lecture Materials of
 Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
ISO 1567 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Dentistry Denture base polymers. Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires. Third edition
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1567 Third edition 1999-02-15 Dentistry Denture base polymers Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires A Reference number Contents 1 Scope...1 2 Normative references...1
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1567 Third edition 1999-02-15 Dentistry Denture base polymers Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires A Reference number Contents 1 Scope...1 2 Normative references...1
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids
 Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids Mikal E. Saltveit Mann Laboratory, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616-8631 Use of Edible Films and Coatings Reduce water loss
Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids Mikal E. Saltveit Mann Laboratory, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616-8631 Use of Edible Films and Coatings Reduce water loss
Effect of Chemical Treatment on Water Absorption Capability of Polyester Composite Reinforced with Particulate Agro-Fibres
 Effect of Chemical Treatment on Water Absorption Capability of Polyester Composite Reinforced with Particulate Agro-Fibres Aderonke Esther FAOLA 1,2, Isiaka Oluwole Oladele, 1, Bolu Omotayo Adewuyi 1,
Effect of Chemical Treatment on Water Absorption Capability of Polyester Composite Reinforced with Particulate Agro-Fibres Aderonke Esther FAOLA 1,2, Isiaka Oluwole Oladele, 1, Bolu Omotayo Adewuyi 1,
The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers
 The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers Yimin Qin, Huiqun Hu, Aixiang Luo The Biochemical Materials Research and Development Center, Jiaxing College,
The Conversion of Calcium Alginate Fibers into Alginic Acid Fibers and Sodium Alginate Fibers Yimin Qin, Huiqun Hu, Aixiang Luo The Biochemical Materials Research and Development Center, Jiaxing College,
Measuring Osmotic Potential
 Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Research Article The Rheological Property of Potato Starch Adhesives
 Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 6(2): 275-279, 214 DOI:1.1926/ajfst.6.24 ISSN: 242-4868; e-issn: 242-4876 214 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: November 4, 213 Accepted: November
Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 6(2): 275-279, 214 DOI:1.1926/ajfst.6.24 ISSN: 242-4868; e-issn: 242-4876 214 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: November 4, 213 Accepted: November
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL VIA AD SUCCESSORUM LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 11 CONTROL TEST 1-2017 TIME: 1½ hours MARKS: 80 INSTRUCTIONS: Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions. 1.
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL VIA AD SUCCESSORUM LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 11 CONTROL TEST 1-2017 TIME: 1½ hours MARKS: 80 INSTRUCTIONS: Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions. 1.
Step-By-Step Product Selection Guide
 AUTHORIZED DISTRIBUTOR Step-By-Step Product Selection Guide S I L I C O N E M O L D M A K I N G M A T E R I A L S F R O M A M E R D O W I C A S C O R N I N G E D I T I O N quality Create reproductions,
AUTHORIZED DISTRIBUTOR Step-By-Step Product Selection Guide S I L I C O N E M O L D M A K I N G M A T E R I A L S F R O M A M E R D O W I C A S C O R N I N G E D I T I O N quality Create reproductions,
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management
 Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management David E. Kissel University of Georgia Overview Urea Consumption Definitions UAN Solution Reactions Urea Dissolution and Diffusion
Ammonia Volatilization from Urea, Mechanisms, Magnitude, and Management David E. Kissel University of Georgia Overview Urea Consumption Definitions UAN Solution Reactions Urea Dissolution and Diffusion
Effect of Rejection Performance on Hollow Fiber Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Alcohols Additives
 Effect of Rejection Performance on Hollow Fiber Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Alcohols Additives Xinghua Wang & Wei Wang Key Laboratory of Hollow Fiber Membrane Material and Membrane Process Tianjin
Effect of Rejection Performance on Hollow Fiber Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Alcohols Additives Xinghua Wang & Wei Wang Key Laboratory of Hollow Fiber Membrane Material and Membrane Process Tianjin
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
