10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p )
|
|
|
- Jeffry Alexander Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10.2 The Human Digestive System (textbook p ) Learning Goal: Label and explain the anatomy of the Digestive System See text p411 Fig.10.6: Label "Organs of Digestive System": See text p411 Fig.10.6: "Organs that Contain Food" vs "Assist in Breakdown of Food": Accessory Organs (structures that aid digestion) Digestive Tract (organs that contain food) Fact: The digestive tract and associated organs take up a significant portion of the space in the human body. The small intestine is. The large intestine is. 1
2 A) Parts of the Human Digestive System 1. Mouth: See text p411 Fig.10.7: Label "Salivary Glands of Mouth": Read text p411: Describe "Chemical Digestion" vs "Mechanical Digestion" by Explaining Function of Each Part: Part Function/Definition 3 Salivary Glands Teeth 2
3 Video 1: Explanation of Swallowing of the throat and esophagus.html **textbook never mentions 2. Pharynx:? The mouth is equipped with teeth arranged along upper & lower jaws and a tongue to push food back to the pharynx Taste buds (4 main) located on the tongue sweet, salty, sour, or bitter enhance flavour of our food The uvula hangs from the back of the soft palate, a flap that guides food to enter the pharynx as we swallow and then down the esophagus Further down, the epiglottis is another flap that prevents food from entering the larynx (voice box) and trachea where air leads to the lungs If you swallow correctly, solids or liquids will go down your esophagus into your stomach. This is because, when your tongue propels the food into your throat, your voice box elevates to close off your trachea, or breathing pipe. At the same time, the opening of your esophagus opens up (it is usually closed to protect the contents of your stomach from pouring out each time you bend over). Your food really can go down the wrong pipe since your mouth has to do double duty, breathing air in and out and swallowing food, things don t always run smoothly. When somebody feels like something went down the wrong pipe, it usually means that it went into his or her trachea, a process known as aspiration. 3
4 3. Esophagus: Read text p412: Complete Table: Part Function/Definition Bolus Esophagus Esophageal sphincter Q: What does this diagram represent? Q: Briefly explain what happens when you "vomit"? 4
5 4. Stomach: Read text p413: Complete Table: Part Function/Definition Stomach Gastric juices Chyme Pyloric sphincter Stomach's 3 methods of protection See text p413 Fig. 10.9: Label Stomach Diagram Parts of the Stomach 5
6 5. Small Intestine: Read text p : Complete Table: Fact: the intestines contain more than 100 different species of "good" bacteria, with numbers in the billions these bacteria aid in digestion and absorption and also help keep out the "bad" bacteria that make us sick Fact: the small intestine is approximately 6m or 20 ft long Part Function/Definition Small intestine Duodenum Jejunum Ileum See text p413 Fig. 10.9: Label "Lining of Duodenum Diagram": Layers of small intestine 6
7 6. Accessory Organs: Read text p415: Complete Table: Part Function/Definition Pancreas Liver Gall Bladder Q: What is the size and mass of the liver? See text p413 Fig. 10.9: Label Accessory Organs Diagram 7
8 7. Large Intestine (Colon): Read text p418: Complete Table: Part Function/Definition large intestine (ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon) rectum anus Q: Briefly explain why feces is typically a "brown" colour, and briefly explain why feces has an odour? 8
9 ** textbook never mentions all parts of the Large Intestine! (see diagram below) Actual real life pictures text p418 text p426 appendix: an organ that plays no role in digestion, but may help fight infections "Dr. William Parker, (USA) and his team were trying to find out how the immune system interacts with normal bacteria found in the intestines. They found evidence of large populations of good bacteria around the appendix. They think that this little pouch is ideally situated out of the way of intestinal clean outs to provide a place for good bacteria to stay until the bad bacteria have been cleaned out." ** textbook never mentions the cecum (caecum): a short, pouch like region of the large intestine between the ascending colon and appendix "In herbivores, the cecum is used to digest cellulose. This adaptation no longer exists in humans, who cannot digest insoluble plant fibers. Birds and some herbivorous mammals have two cecums, and there is scientific debate as to whether or not the appendix is a remnant of this second cecum. Fish, amphibians and some carnivorous mammals completely lack a cecum." 9
10 You will be expected to label a Digestive System Diagram like this one! mouth (submandibular) common with cystic duct sigmoid colon anus 10
11 Most of us are guilty of eating too fast (inhaling our food) let's try and slow down and enjoy the flavour first! text p418 Gross things you do not want to happen to you! 11
12 B) Chemical Digestion and Absorption Learning Goal: Explain enzymatic digestion of macromolecules text p416 Q: What do bile and pancreatic fluid do? Enzyme Digests what? carbohydrases lipases proteases nucleases p416 Fig Q: What enzymes are where? "Flowchart of Chemical Digestion": complex carbohydrates proteins fats nucleic acids Mouth Stomach Small Intestine 12
13 text p417 Q: Briefly explain the "2 factors" that affect the rate at which enzymes function: Q: Briefly summarize "Absorption in the Small Intestine": 1. monosaccharides: 2. amino acids: 3. glycerol & fatty acids: 13
14 Nerves and hormones regulate secretion of digestive enzymes There are three major hormones involved in digestion: gastrin stimulates the release of digestive juices from the stomach Q: Find the 3 hormones (gastrin, secretin, CCK) in the diagram below and highlight them! secretin stimulates the release of pancreatic juice from the pancreas cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates the release of bile from the gall bladder, into the duodenum Video 1: Hank overviews Digestive System Video 2: Hank tells Alexis St Martin Story "whole in stomach" and Digestive System to the Stomach Video 3: Hank finishes Digestive System YOU ARE FINISHED! 14
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! )
 POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration?
 BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion
 NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells.
 Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
Chapter 11 The Digestive System. Biology 2201
 Chapter 11 The Digestive System Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that provide the energy
Chapter 11 The Digestive System Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that provide the energy
Step 1: Salivary Structures
 (Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
(Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Mar 27 9:53 AM. Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
11/1/2008. The Digestive System. April 2008
 Chapter 11 The Digestive System Biology 2201 April 2008 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that provide
Chapter 11 The Digestive System Biology 2201 April 2008 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that provide
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM THE FOUR STEPS OF DIGESTION
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: 1 2 Digestion Video Questions 1. How many permanent teeth does a human adult have? 2. What does your digestive system do for you? 3. Where does digestion begin? 4. What
The Human Digestive System Name: 1 2 Digestion Video Questions 1. How many permanent teeth does a human adult have? 2. What does your digestive system do for you? 3. Where does digestion begin? 4. What
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Chapter 9 Digestive System. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
Chapter 9 Digestive System Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Points to ponder What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy
 The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Full file at
 An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10
 HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10 The remaining semester The remaining semester June 25 th, Final Exam Day (Thursday) What we will cover Food/Nutrition:
HEALTHY AND ACTIVE LIVING (FOOD/NUTRITION COMPONENT) Date: April 30 th, 2015 Course: PPL10 The remaining semester The remaining semester June 25 th, Final Exam Day (Thursday) What we will cover Food/Nutrition:
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
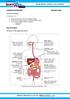 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
The Digestive System: Basics. WedNesday October 24th All organisms need energy to survive. > Use energy to reproduce, grow, and repair
 WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
Digestion, Absorption, and Transport
 Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
Digestion Digestion, Absorption, and Transport Chapter 3 Breaking down foods into nutrients Prepare for absorption Challenges of digestion Accessing Nutrients digestion Getting nutrients through the body
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Jargon. Chapter. Processing Food and Nutrition. Chapter 21
 One ATP Sandwich With extra phosphate Comin up Chapter Processing Food and Nutrition Chapter 21 Processing Food and Nutrition Objectives: 1. Understand the concepts of 2. Identify the anatomical parts
One ATP Sandwich With extra phosphate Comin up Chapter Processing Food and Nutrition Chapter 21 Processing Food and Nutrition Objectives: 1. Understand the concepts of 2. Identify the anatomical parts
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
