Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems
|
|
|
- Malcolm Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /57 Percentage: /00 Page
2 M. (a) to show the experiment was more repeatable (b) (circle) 0.0 at 20 C (c) ignored it / did not use it ignore repeated it (d) increases the rate of reaction up to 30 C (e) 60 C (f) do the experiment at 30 C, 35 C and 40 C (g) Level 2 (3 4 marks): A detailed and coherent plan covering all the major steps is provided. The method is set out logically taking into account control variable and appropriate measurements. The plan could be repeated by another person to determine the effect of ph on breakdown of starch by amylase. Level ( 2 marks): Simple statements relating to relevant apparatus or steps are made but they may not be in a logical order. The plan would not allow another person to determine the effect of ph on breakdown of starch by amylase. 0 marks: No relevant content. Page 2
3 Indicative content range of at least 3 ph values / use of buffer solutions control variables / keep amount or concentration of starch and amylase the same keep temperature the same using water bath / electric heater use iodine test to make qualitative observations observe colour changes at different temperatures do repeats at each ph 4 [0] Page 3
4 M2. (a) (Type 2) diabetes / heart disease / deficiency disease / named allow a relevant health problem ignore obesity or over / under weight / anorexia (b) (i) provides more (energy / sugar) than is used idea of sugar being high in / having a lot of energy eg contains a lot of calories allow it is turned to fat or stored (as fat) fat (c) (i) C no health problems allow as others (may) have (possible) health problems ignore reference to sweetness (iii) idea of informed choice eg in case you have health problems / allergies allow legal requirement ignore diabetes [6] Page 4
5 M3.(a) (i) A = (cell) membrane B = cytoplasm do not accept cytoplast To control the activities of the cell (b) extra lines cancel 3 [6] Page 5
6 M4.(a) extra line from any drug cancels that mark 4 (b) (i) any one from: (live) animals accept named examples, eg mice ignore people / volunteers cells tissues do not allow plants to check that the drug works to find the best dose to use (iii) only scientists at the drug company (c) (i) 420 Page 6
7 statin(s) (iii) any one from: side effects allow cost other medication allow patient choice other (medical) conditions allow family history or age [] Page 7
8 M5.(a) (i) alveoli / alveolus allow air sacs allow phonetic spelling any one from: protection (of lungs / heart) help you breathe / inflate lungs. (b) (i) diffusion capillaries (iii) any two from: (have many) alveoli allow air sacs large surface / area thin (exchange) surface or short diffusion pathway accept only one / two cell(s) thick good blood supply / many capillaries allow (kept) ventilated or maintained concentration gradient. 2 [6] Page 8
9 M6.(a) (i) a catalyst (iii) protein salivary glands (b) extra lines from any enzyme cancels that mark 3 [6] Page 9
10 M7. (a) 300 (b) suitable scale on y-axis label y-axis 4 bars drawn correctly allow mark for 3 correct bars 2 (c) increases from 50 to 500 then decreases from 500 to 0 (d) carbohydrates broken down / digested into sugars broken down by carbohydrase or amylase (e) absorption of glucose into blood Page 0
11 by active transport allow diffusion [2] Page
12 Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 58 minutes Score: /58 Percentage: /00 Page
13 M. (a) 55% 2 marks for correct answer alone accept / 0 00 alone gains mark 2 (b) any three from: amino acids antibodies antitoxins carbon dioxide cholesterol enzymes fatty acid glucose glycerol hormones / named hormones ions / named ions proteins urea vitamins water. ignore blood cells and platelets ignore oxygen max named example of each for ions and hormones allow minerals 3 (c) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Communication (QC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Examiners should also refer to the information in the Marking Guidance and apply a best-fit approach to the marking. 0 marks No relevant content. Level ( 2 marks) There is a description of pathogens with errors or roles confused. or the immune response with errors or roles confused. Level 2 (3 4 marks) There is a description of pathogens and the immune response with some Page 2
14 errors or confusion or a clear description of either pathogens or the immune response with few errors or little confusion. Level 3 (5 6 marks) There is a good description of pathogens and the immune response with very few errors or omissions. Examples of biology points made in the response: bacteria and viruses are pathogens credit any ref to bacteria and viruses they reproduce rapidly inside the body bacteria may produce poisons / toxins (that make us feel ill) viruses live (and reproduce) inside cells (causing damage). white blood cells help to defend against pathogens by: ingesting pathogens / bacteria / (cells containing) viruses credit engulf / digest / phagocytosis to destroy (particular) pathogen / bacteria / viruses producing antibodies to destroy particular / specific pathogens producing antitoxins to counteract toxins (released by pathogens) credit memory cells / correct description this leads to immunity from that pathogen. 6 [] Page 3
15 M2. (a) any three from: parts of organisms have not decayed accept in amber / resin allow bones are preserved conditions needed for decay are absent accept appropriate examples, eg acidic in bogs / lack of oxygen parts of the organism are replaced by other materials as they decay accept mineralised or other preserved traces of organisms, eg footprints, burrows and rootlet traces allow imprint or marking of organism 3 (b) (i) teeth for biting (prey) must give structure + explanation claws to grip (prey) accept sensible uses wing / tail for flight to find (prey) any two from: new predators new diseases better competitors catastrophe eg volcanic eruption, meteor changes to environment over geological time accept climate change allow change in weather prey dies out or lack of food allow hunted to extinction 2 [8] Page 4
16 M3. (a) (i) sucrose fructose is sweeter than sucrose can use less fructose (for same sweetness) cheaper / can use in slimming food allow less calories accept better for diabetics (b) (i) carbohydrases denatured / shape changed ignore inactivated allow enzyme / shape destroyed (iii) faster reaction so more product made / product made in shorter time allow 60 C will kill microorganisms (c) any two from: enzyme can be re-used / not wasted constant-flow system can be automated product (= food) not contaminated by enzyme / enzyme may give allergic reaction / no need to separate P from E allow people do not want to eat enzymes 2 Page 5
17 (d) any three from: volume is smaller so costs less to heat / to maintain temperature / to build temperature is cooler so costs less to heat / to maintain temperature / loses less heat to surroundings reaction time is shorter so reduces running costs (re. heating / stirring) or can make more product in time -stage product refining c.f. 4 stages, leading to reduced labour / time cost need to qualify each point with respect to how it lowers costs 3 (e) (i) 4500 correct answer = 2 marks allow mark for: 500 x 3 2 enzyme used for longer / less enzyme needed less money spent on enzyme [7] Page 6
18 M4. (a) (i) glycerol pancreas / small intestine accept duodenum / ileum ignore intestine unqualified (b) any two from: type of milk volume / amount of milk vol. bile equals vol. water volume of lipase concentration of lipase temperature ignore time interval ignore solution unqualified do not allow ph ignore starting ph ignore volume / amount of bile / water ignore concentration of bile accept amount of lipase if neither volume nor concentration given 2 (c) (i) fatty acid (production) (iii) faster reaction / digestion (with bile) or ph decreases faster (with bile) or takes less time (with bile) or steeper fall / line (with bile) allow use of data ignore easier all fat / milk digested or same amount of fatty acids present or (lower ph) denatures the enzyme / lipase allow all reactants used up ignore reference to neutralisation Page 7
19 allow enzyme won t work at low ph do not allow enzyme killed [7] Page 8
20 M5. (a) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Communication (QC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Examiners should also refer to the information in the Marking guidance and apply a best-fit approach to the marking. 0 marks No relevant content. Level ( 2 marks) The method described is weak and could not be used to collect valid results, however does show some understanding of the sequence of an investigation. Level 2 (3 4 marks) The method described could be followed and would enable some valid results to be collected, but lacks detail. Level 3 (5 6 marks) The method described could be easily followed and would enable valid results to be collected. Examples of the points made in the response: bean seedlings of same age cut material from same part of each organ (for repeats) e.g. top cm of stem / a whole cotyledon / seed equal mass of each organ accept weight for mass grind / homogenise in equal amounts of water / buffer equal volumes of hydrogen peroxide solution equal concentrations of hydrogen peroxide solution same temperature temperature maintained in water bath quantitative measure of gas production eg height of foam in mm / collect gas in graduated syringe in cm 3 for same time period repetitions (3+ times) calculate mean for each. 6 (b) (i) correct answer: 40 mark for 45 as the anomalous result has been included in the calculation or mark for or 2 vertical axis correctly labelled: Enzyme activity in arbitrary units Page 9
21 allow ecf from (b)(i) points plotted correctly ± mm deduct mark for each incorrect plot suitable line of best fit not feathery, not point to point 2 (iii) 6.0 / 6 allow ± 0. if 6.0 not given, allow correct for candidate s graph ± 0. (iv) in range 0 to 4 units allow correct for candidate s graph (v) enzyme denatured / enzyme (active site) shape changed allow substrate no longer fits (active site) ignore reference to temperature do not allow enzyme dies [5] Page 0
22 Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Gold Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 58 minutes Score: /57 Percentage: /00 Page
23 M.(a) stomach and pancreas correctly labelled (b) bacteria not killed (by stomach acid / HCl) and so they damage mucus lining so acid / HCl damages stomach tissue / causes an ulcer allow bacteria infect stomach tissue (c) if the cancer is malignant (cancer) cells can spread to other organs via the blood forming a secondary tumour do not award marking points 2 or 3 without marking point (d) add Biuret reagent to food sample allow sodium / potassium hydroxide (solution) + copper sulfate(solution) mauve / purple colour shows protein present (e) damaged villi reduce surface area for absorption (of food molecules) Page 2
24 (therefore) fewer amino acids and glucose absorbed with less glucose transfer of energy from respiration is reduced and fewer amino acids available to build new proteins [2] M2. (a) any two from: diet ignore exercise Page 3
25 accept any reasonable reference to diet do not accept salt / blood pressure ignore age / gender / HDL / LDL heredity / genes / genetic makeup reference to cholesterol production by liver 2 (b) (i) Blood cholesterol concentration is only one of several factors affecting death from all causes accept [4] \ M3. (a) (substance / chemical) that affects body chemistry / chemical reactions in the body Page 4
26 (b) statin / aspirin / neither recommended no mark, may be implied. If no recommendation or implication, max 4 marks answers should be comparative any five from: argued evaluation in favour of aspirin or statin or neither answers could include reference to accept converse for statins / aspirin but not as advantage of one and disadvantage of other for statins: more people in studies so data / findings more repeatable accept reliable for repeatable ignore accurate / precise reduces cholesterol but aspirin doesn t allow reduces cholesterol but no evidence about aspirin aspirin (may) causes bleeding / poor clotting but statins do not allow aspirin causes bleeding / poor clotting but no evidence about statins smaller (total) percentage suffer side-effects monitored by doctor, aspirins not for aspirin: cheaper can be bought over the counter rather than prescribed statins cause serious damage / muscle damage / kidney failure but aspirins do not similarities: both have similar effect on reducing (non-fatal) heart attacks incidence of side-effects low in both allow (for aspirin) higher reduction of risk of heart attack 5 [6] Page 5
27 M4. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine Page 6
28 concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted into glycogen or allows glucose into liver cells (b) (i) (after 6 hours) most of the glucose has been absorbed from the intestine or from food into the blood because glucagon (made in the pancreas) causes if biological terms incorrectly spelt they must be phonetically accurate do not accept glucagon made / produced by the liver glycogen to be converted into glucose glucose released into blood allow the liver maintains the correct / constant level of glucose in the blood [7] M5.(a) stomach is acidic / has low ph allow any ph below 7 ignore stomach is not alkaline Page 7
29 lactase works best / well in alkali / high ph / neutral / non-acidic conditions allow any ph of 7 and above accept works slowly in acid conditions allow figures from table with a comparison ignore reference to temperature (b) any three from: (below 40( C)) increase in temperature increases rate / speed of reaction reference to molecules moving faster / colliding faster / harder / more collisions enzyme optimum / works best at 40 C allow value(s) in range ignore body temperature unless qualified high temperatures (above 40 C) / 45 C / 50 C enzyme denatured allow synonyms for denaturation, but do not allow killed denaturation at high and low temperature does not gain this mark ignore references to time / ph 3 (c) any two from: acid neutralised or conditions made neutral / alkali accept bile is alkaline (allow) emulsification / greater surface area (of lipid / fat) allow description of emulsification eg fat broken down / broken up into droplets do not accept idea of chemical breakdown lipase / enzymes (in small intestine) work more effectively / better allow better for enzymes ignore reference to other named enzymes 2 [7] Page 8
30 M6. (a) (i) mitochondrion / mitochondria must be phonetically correct carbon dioxide / CO 2 Page 9
31 water / H 2O in either order accept CO2 but not CO 2 accept H2O or HOH but not H 2 O (iii) diffusion high to low concentration allow down a concentration gradient through (cell) membrane or through cytoplasm do not accept cell wall (b) ribosomes make proteins / enzymes using amino acids part A / mitochondria provide the energy for the process allow ATP do not accept produce or make energy [9] M7.A + B most effective (treatment) ignore descriptions of LDL levels Page 0
32 D is (the most) effective (treatment) D is the best single (treatment) neither A nor B (alone) are effective allow increase risk of heart disease instead of not effective can t tell if C is effectiveora + C is not effective [4] M8. (a) (i) diaphragm accept phonetic spelling (because) the volume (inside the jar) increases maximum two marks if no reference to correct part of model Page
33 (causing) the pressure to decrease (and) air enters the balloon allow oxygen (b) (i) (so it moves by) diffusion do not allow osmosis or active transport from a high concentration (of oxygen) to a low concentration allow down its / oxygen concentration gradient from the air or to the blood or (because) there is a high(er) concentration (of oxygen) in the air or there is a low(er) concentration of oxygen in the blood ignore reference to amount of oxygen many gill filaments must be in the correct pairs to gain 2 marks (give a) large surface / area do not allow surface area to volume ratio or thin (so) short diffusion pathway or good blood supply (to) maintain the concentration gradient or water continually flows over them / continually ventilated (to) maintain the concentration gradient [8] Page 2
34 Plant tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Plant tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 56 minutes Score: /56 Percentage: /00 Page
35 M. (a) (i) wind temperature answers in either order ignore weather different plants have different sizes / different numbers of leaves / different sizes of leaves / different plants take up different amounts of water ignore reference to validity allow different plants need different amounts of water (b) in table, in sequence: C all 3 correct = 2 marks B A all 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = mark 0 or correct = 0 mark 2 (c) transpiration [6] Page 2
36 M2. (a) (i) root hairs if clear which word then allow xylem if clear which word then allow (iii) stomata if clear which word then allow (iv) storage organs in this order phloem (b) (i) 23.2 loss of water (from flask with plant) from leaves / plant via transpiration / via evaporation if no other marks allow used in photosynthesis for one mark [8] Page 3
37 M3. (a) transpiration (b) increase then decrease maximum rate at ( C ) / (grams per day) any figure in these ranges (c) (i) reduce water loss / prevent wilting allow stops water loss C [5] Page 4
38 M4. (a) transpiration (b) (i) 200 correct answer with or without working if answer incorrect: allow mark for 8 25 or allow mark for answer from candidate s count 25 2 R allow P or Q if candidate s answer to (b)(i) nearer to value for one of those do not allow R if the answer to (b)(i) would give an answer of P or Q allow R if (b)(i) is blank (iii) few stomat allow no stomata on upper surface / all stomata on lower surface little / less transpiration or little / less water (vapour) loss / enable water to be retained allow no water loss from upper surface [6] Page 5
39 M5. (a) (i) water / H 2O accept oxygen allow H 2O do not allow H 2 O or H2O (iii) the mineral ions are absorbed by active transport the absorption of mineral ions needs energy have (many root) hairs (which) give a large surface area (for absorption) (b) carbon dioxide in or oxygen out or control water loss accept gas exchange ignore gases in and out ignore gain / lose water (c) (i) guard cells (stomata are) closed allow there is no gap / space (iii) plant will wilt / droop ignore die [9] Page 6
40 M6. (a) xylem and phloem either order allow words ringed in box allow mis-spelling if unambiguous (b) (i) movement / spreading out of particles / molecules / ions / atoms ignore names of substances / gases from high to low concentration accept down concentration gradient ignore along / across gradient ignore with gradient oxygen / water (vapour) allow O 2 / O2 ignore O 2 / O allow H 2O / H2O ignore H 2 O [4] Page 7
41 M7. (a) (i) wind answers in either order temperature ignore weather different plants have different sizes ignore reference to validity / different numbers of leaves / different sizes of leaves / different plants take up different amounts of water / different number of stomata / different surface area allow different plants need different amounts of water (b) in table, in sequence: C B A all 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = mark 0 or correct = 0 marks max 2 (c) transpiration [6] Page 8
42 M8. (a) (i) xylem phloem (iii) transpiration (iv) stomata (b) (i) any one from: reduce / prevent evaporation of water from flask holds plant shoot in place prevent damage to the plant same surface area or number of leaves (because if they used larger / smaller size shoots) there would be a larger / smaller surface area or a larger/ smaller number of leaves allow same number of stomata from which (the same amount of) water evaporates (and therefore) more / less water would escape allow from which water escapes (iii) 4.5 look for answer written in table (iv) increasing temperature / heat increases (rate of) water loss / evaporation Page 9
43 (v) having moving air / a fan increases (rate of) water loss / evaporation (c) (i) 0.3 g plastic bag reduces air flow across leaves or air is humid around the leaves allow plastic bag stops water (vapour) leaving allow air (in plastic bag) becomes saturated (with water) [2] Page 0
44 Plant tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Plant tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 52 minutes Score: /5 Percentage: /00 Page
45 M. (a) active transport (b) by transpiration stream / pull in xylem (c) any three in the correct order from: mount epidermis on a slide count stomata in one area repeat in four more areas repeat method on other surface of leaf calculate mean allow nail varnish film 3 (d) allow numbers written out in a line with middle number circled (e) ( ) / 5 = allow 4 with no working shown for 2 marks allow 4.2 for mark (f) less water lost Page 2
46 so it does not wilt [] Page 3
47 M2. (a) guard cells (b) (i) any one from: species / plant length of time ignore temperature and size of leaves 20 correct answer = 2 marks accept or for mark 2 (c) less water loss / transpiration / evaporation (d) hot ignore bright / sunny conditions dry / low humidity wind(y) [8] Page 4
48 M3.(a) A - atrium ignore references to right / left B - ventricle (b) (i) muscular push blood accept pump / force (c) arrows approx as indicated arrow(s) showing flow from A to B from B out / up / to artery (d) (i) male 65 and over fatty deposits / material in (coronary) arteries allow correct points made about heart attacks Page 5
49 narrows / blocks / reduces flow decreases oxygen supply (to heart muscle) [] Page 6
50 M4. (a) to kill virus or to prevent virus spreading (b) take (stem) cells from meristem or tissue culture allow take cuttings (c) use Benedict s solution glucoses turns solution blue to orange (d) Level 2 (3 4 marks): A detailed and coherent explanation is provided. The student makes logical links between clearly identified, relevant points that explain why plants with TMV have stunted growth. Level ( 2 marks): Simple statements are made, but not precisely. The logic is unclear. 0 marks: No relevant content. Indicative content less photosynthesis because of lack of chlorophyll therefore less glucose made so less energy released for growth because glucose is needed for respiration and / or therefore less amino acids / proteins / cellulose for growth because glucose is needed for making amino acids / proteins / cellulose 4 [8] Page 7
51 M5. (a) (i) 5.0 (5 0.8) or 4 allow ecf from distance 0.4 allow ecf from 0-min volume increased (rate of uptake) more transpiration / evaporation (b) correct scales allow reversed axes correctly labelled axes with units correct points one plot error = max mark curved line of best fit allow correct straight line 2 (c) leaves wilt because plants lose too much water (by evaporation) through the stomata or because cells become plamolysed or stomata close controlled by guard cells to prevent wilting [3] Page 8
52 Plant tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Plant tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Gold Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 30 minutes Score: /30 Percentage: /00 Page
53 M. (a) (i) guard (cells) allow phonetic spelling any one from: ignore reference to cells allow carbon dioxide to enter allow control loss / evaporation of water or control transpiration rate allow oxygen to leave. allow gaseous exchange (b) (i) 200 correct answer gains 2 marks with or without working allow mark for = 0.0 (mm 2 ) 2 more / a lot of / increased water loss allow plant more likely to wilt (in hot / dry conditions) (c) (i) 0.2 the lower surface has most stomata stomata are now covered / blocked (by grease) so water cannot escape / evaporate from the stomata ignore waterproof to gain credit stomata must be mentioned at least once [9] Page 2
54 M2. (a) guard cell ignore stoma / stomata (b) Species A : allow converse points for species B stomata open in dark / at night or close in light / in day stomata closed during warm(est) period or open when cool(er) heat (energy) /warmth increases evaporation / transpiration must give explicit link between heat and transpiration reduces water loss / evaporation / transpiration ignore photosynthesis [5] Page 3
55 M3. (a) guard (cell) ignore stoma / stomata (b) Species A: stomata open in dark / at night or close in light / in day stomata closed during warm(est) period or open when cool(er) heat (energy) / warmth increases evaporation / transpiration must give explicit link between heat and transpiration reduces water loss / evaporation / transpiration ignore photosynthesis allow converse points for species B [5] Page 4
56 M4. (a) solution in soil is more dilute (than in root cells) concentration of water higher in the soil (than in root cells) so water moves from the dilute to the more concentrated region so water moves down (its) concentration gradient or water moves from a high concentration of water to a lower concentration concentration of ions in soil less (than that in root cells) so energy needed to move ions or ions are moved against concentration gradient the direction of the concentration gradient must be expressed clearly accept correct reference to water potential or to concentrations of water (b) any three from: movement of water from roots / root hairs (up stem) via xylem to the leaves (water) evaporates via stomata 3 (c) (i) 0.67/0.7 accept 0.66, or ⅔ or 0.6 Page 5
57 correct answer gains 2 marks with or without working if answer incorrect allow evidence of do not accept 0.6 or 0.70 for mark 2 during the first 30 minutes any one from: it was warmer it was windier it was less humid there was more water (vapour) in the leaves so there was more evaporation ignore water loss or stomata open during first 30 minutes or closed after 30 minutes () so faster (rate of) evaporation in first 30 min or reducing (rate of) evaporation after 30 min () [] Page 6
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Q1.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction.
 ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical that can be used to preserve milk.
 Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
2 Organisation higher (import)
 2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Name: Paper 1 exp skills. Class: Date: 128 minutes. Time: 126 marks. Marks: Comments:
 Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
remove solution / liquid (on outside of worm) allow water variable amounts removed from each worm ignore reference to length of timing 1
 M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Gold Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Gold Level Mark Scheme
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
PMT SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BIOLOGY PAPER 1F. Mark scheme. Specimen Version 1.0
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BIOLOGY PAPER F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 MARK SCHEME GCSE BIOLOGY PAPER F SPECIMEN MATERIAL Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BIOLOGY PAPER F Mark scheme Specimen 208 Version.0 MARK SCHEME GCSE BIOLOGY PAPER F SPECIMEN MATERIAL Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
 3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED
 Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
Year 10 Biology Revision List - COMBINED This is a summary of everything you need to know for the Biology part of your Combined science GCSE for your exam on 8 th March 2019. 9 Cells and Simple Cell Transport
Name: B2 Organisation. Class: 35 Questions. Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Brookvale Groby Learning Trust
 B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
M1. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine 1
 M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
1 Living organisms: variety and common features
 Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
Name: BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS. Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 59
 BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 59 In a living organism, the cells are organised into organs, systems and tissues. (a) Use words from the box to complete the list
BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 59 In a living organism, the cells are organised into organs, systems and tissues. (a) Use words from the box to complete the list
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Mark Scheme (Results) March GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Where in the cell are proteins made? Which part of a cell controls its activities? ribosomes. nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur?
 Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
GCSE BIOLOGY. Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a scientific calculator. Please write clearly in block capitals. Surname.
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Mark Scheme (Results) January Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2B
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper B Pearson Edexcel Certificate in Biology (KBI0) Paper B Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Mark Scheme (Results) January 016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper B Pearson Edexcel Certificate in Biology (KBI0) Paper B Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
BL3FP. (Jun14BL3FP01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June Unit Biology B3 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Biology Unit Biology B3 Tuesday 13 May 2014 For this paper you must have: a ruler.
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Biology Unit Biology B3 Tuesday 13 May 2014 For this paper you must have: a ruler.
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
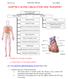 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
UR Revision Guide. igcse Biology. Page 1
 UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice
 AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
17. What are lipids made from? Fatty acids and glycerol 18. What are proteins used in the body for? (What is their function?) Growth and repair 19.
 100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Homeostasis. Mark Scheme 1. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Level GCSE (9-1) Exam Board 4.5 Homeostasis and Response. Booklet Mark Scheme 1
 Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes:
 Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules.
 The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Carbohydrates. Mark Scheme. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Exam Board 3.1 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates. Page 1.
 Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
B2 Cells and simple transport
 B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
Mark Scheme. Additional Science 4463 / Biology General Certificate of Secondary Education. BLY2F Unit Biology examination June series
 Version: 04/08/20 General Certificate of Secondary Education Additional Science 4463 / Biology 44 Unit Biology 2 Mark Scheme 20 examination June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version: 04/08/20 General Certificate of Secondary Education Additional Science 4463 / Biology 44 Unit Biology 2 Mark Scheme 20 examination June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Theory (Core) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:80 Published This mark scheme is published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/31 Paper 3 Theory (Core) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:80 Published This mark scheme is published
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist
 Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
B3 Essential Questions - Answers
 B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Do Now Makeups. 4. In which organelle would water and dissolved materials be stored? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5. A. mitochondria B.
 Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Movement of substances
 1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
COMBINED SCIENCE GCSE. Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier. Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes. Materials. For this paper you must have: Instructions all
 GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
Surname. Other Names. Candidate Signature
 A Surname Other Names Centre Number For Examiner s Use Candidate Number Candidate Signature Additional Science Unit Biology B2 Biology Unit Biology B2 BL2FP General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation
A Surname Other Names Centre Number For Examiner s Use Candidate Number Candidate Signature Additional Science Unit Biology B2 Biology Unit Biology B2 BL2FP General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation
FOOD. Why do we need food? What's in our food? There are 3 trace elements, Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) and Zinc (Zn).
 Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY
 GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY BL2HP Report on the Examination 4408 / 4401 June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA and its licensors. All
GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY BL2HP Report on the Examination 4408 / 4401 June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA and its licensors. All
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION TRANSPORT REGULATION SYNTHESIS EXCRETION GROWTH REPRODUCTION RESPIRATION
 8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
Cambridge O Level Biology Syllabus code 5090 All candidates enter for three papers Papers 1 and 2 and Paper 6. PAPER 1 Multiple Choice
 1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Movement of substances across the cell membrane
 Ch 4 Movement of substances across the cell membrane Think about (Ch 4, p.2) 1. The structure of the cell membrane can be explained by the fluid mosaic model. It describes that the cell membrane is mainly
Ch 4 Movement of substances across the cell membrane Think about (Ch 4, p.2) 1. The structure of the cell membrane can be explained by the fluid mosaic model. It describes that the cell membrane is mainly
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/23 Paper 2 (Core Theory),
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
6 The chemistry of living organisms
 Living organisms are composed of about 22 different chemical elements. These are combined to form a great variety of compounds. Six major elements make up almost 99% of the mass of the human body, as shown
Living organisms are composed of about 22 different chemical elements. These are combined to form a great variety of compounds. Six major elements make up almost 99% of the mass of the human body, as shown
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/21
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/21
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
