A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
|
|
|
- Annabelle Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1
2 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution on the digestion of triglycerides. The graph below shows their results. The scientists also incubated triglycerides with different concentrations of bile salts. After 30 minutes they measured the diameter of the triglyceride droplets. They used the results to calculate the mean radius of the droplets at each concentration. The table below shows their results. Concentration of bile salts /% Mean radius of triglyceride droplet / μm (a) Describe how you would use a microscope to find the mean diameter of triglyceride droplets on a slide (3) Page 2
3 (i) The ratio of mean radius of triglyceride droplets in bile salts at a concentration of 0% to the mean radius in bile salts at a concentration of 3% is 2 : 1. What is the ratio of their surface areas? Show your working. You can calculate the surface area of a droplet from the formula Where A = surface area r = radius π = 3.14 A = 4πr 2 (2) Use the data in the table to explain the difference between curves Y and Z in the graph. (3) (Total 8 marks) Q2.The diagram represents part of the human digestive system. The organs are labelled A F. Page 3
4 (a) Give the letter of the organ that produces amylase. (1) Give the letter of the organ that produces maltase. (1) (c) Maltose is hydrolysed by the enzyme maltase. Explain why maltase catalyses only this reaction. (3) (Total 5 marks) Q3. (a) Dietary recommendations are that lipid intake should make up 30% of energy intake. The recommended energy intake for most women aged is 8100 kj day 1.The energy content of lipid is 37.8 kj g 1. Calculate the recommended lipid intake per day for these women. Show your working. Answer... g (2) Page 4
5 In humans, triglycerides are the main form of dietary lipids. They are digested in the gut and the products of digestion are absorbed by the small intestine. S Describe a biochemical test that could be performed on a sample of food to determine whether it contained triglycerides. (2) (c) The diagram shows the events that occur in the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids. These molecules enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine by diffusion. Once inside they are reassembled into triglycerides in organelle Q. The triglyceride molecules are formed into chylomicrons in organelle T. Chylomicrons are made from many triglyceride molecules surrounded with protein molecules. The chylomicrons leave the cell and enter vessel S. S (i) Explain the importance of the structures labelled P. (1) Name Page 5
6 R;... S....(2) S (iii) Describe the role played by organelle U in the formation of chylomicrons. (2) S (iv) Suggest how the chylomicrons leave the epithelial cell. Give a reason for your answer....(2) (Total 11 marks) Q4.Biologists divided new-born rats randomly into four groups. They fed the rats in each group on a standard diet which only differed in the carbohydrate content. When these rats were adult, the biologists measured the activity of lactase in the digestive system of the rats. The following table shows the mean results for each group. Diet Mean lactase activity / µ mol of lactose digested per hour (± standard deviation) Low sucrose 57.9 (± 14.5) High sucrose (± 30.8) Low starch 86.9 (± 13.3) High starch (± 25.4) (a) Give one piece of evidence from the table that indicates lactase activity is affected by diet. (1) Some students suggested from these data that increasing starch in the diet was the most effective way to increase lactase activity in lactase deficient people. Is this conclusion valid? Explain your answer. Page 6
7 (2) Q5. Miner s lung is a disease caused by breathing in dust in coal mines. The dust causes the alveolar epithelium to become thicker. People with miner s lung have a lower concentration of oxygen in their blood than healthy people. (a) (i) Describe the path by which oxygen goes from an alveolus to the blood. (Total 3 marks) (2) Explain why people with miner s lung have a lower concentration of oxygen in their blood. (1) In healthy lungs, a gradient is maintained between the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli and the concentration of oxygen in the lung capillaries. (i) Describe how ventilation helps to maintain this difference in oxygen concentration. (2) Give one other way that helps to maintain the difference in oxygen concentration. (1) (c) Scientists investigated the number of cases of miner s lung reported in Britain between 1992 and Page 7
8 Coal mining in Britain had been dramatically reduced by Some scientists concluded that the rise in reported cases of miner s lung after 1992 shows that the disease takes a long time to develop. Evaluate this conclusion. (2) (Total 8 marks) Q6.A scientist used grasshoppers to investigate the effect of composition of air on breathing rate in insects. He changed the composition of air they breathed in by varying the concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The scientist collected 20 mature grasshoppers from a meadow. He placed the grasshoppers in a small chamber where he could adjust and control the composition of air surrounding them. The small chamber restricted the movement of the grasshoppers. His results for three of the grasshoppers are shown in the table below in the form in which he presented them. Percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in different types of air breathed in by grasshoppers A Air from atmosphere B Pure oxygen C Gas mixture 1 D Gas mixture 2 Gas Oxygen Carbon dioxide Page 8
9 Breathing rate of grasshopper in different types of air / breaths per minute Grasshopper 1 Grasshopper 2 Grasshopper (a) The percentages of oxygen and carbon dioxide in Column A do not add up to 100% but in columns C and D they do. Suggest two reasons for this difference (2) Use all the data to describe the effect of concentration of carbon dioxide on the breathing rate of grasshoppers. (3) (c) One of the different types of air was similar to the air in the meadow where the grasshoppers were collected. It provides data that might be used to calculate a mean breathing rate for grasshoppers in the meadow. (i) Use the data to estimate the mean breathing rate of the three grasshoppers in the meadow. Show your working. Mean breathing rate =... breaths per minute (2) The estimate does not provide a reliable value for the mean breathing rate of all insect species in the meadow. Other than being an estimate, suggest and explain three reasons why this value would not be reliable Page 9
10 (3) (Total 10 marks) Q7. (a) Describe the part played by the diaphragm in causing air to enter the lungs during breathing. (3) Seals are mammals. They have lungs and must breathe air. They can dive and remain under water for a long time. The table shows the flow of blood to the lungs and to the diaphragm in a seal when it is on land and when it is under water. Organ Blood flow / cm 3 min 1 g 1 On land Under water Lungs Diaphragm Explain why the figures in the table are given per gram of tissue. (2) (c) Calculate the percentage by which blood flow to the lungs is reduced when a Page 10
11 seal is swimming under water. Show your working. Answer...(2) (d) There is a greater percentage reduction in blood flow to the diaphragm than to the lungs during a dive. Explain the advantage to a diving seal of (i) blood continuing to flow to the lungs; (1) a large reduction in blood flow to the diaphragm. (2) (Total 10 marks) Q8.A biologist investigated the effect of water temperature on the rate of ventilation of gills in a species of fish. She kept four fish in a thermostatically controlled aquarium and measured the mean ventilation rate by counting movements of their gill covers. Her results are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 In this investigation, the biologist also monitored the concentration of oxygen in the water in the aquarium. The concentration of oxygen in Page 11water changes with temperature of the
12 water. Figure 2 shows how it changes. Figure 2 (a) Suggest a difficulty of counting movements of gill covers as a method of measuring rate of ventilation in fish. (1) The biologist concluded that there was a correlation between rate of ventilation of the gills and temperature of the water. A scatter diagram can be used to look for a correlation but, in this investigation, it was not the appropriate graph for her data. Explain why. (1) (c) (i) Describe the relationship between temperature of water, oxygen in water and rate of ventilation. (1) Use Figure 1 and Figure 2 to explain the advantage to the fish of the change in its rate of ventilation. Page 12
13 (3) (Total 6 marks) Q9.(a) Describe how oxygen in the air reaches capillaries surrounding alveoli in the lungs. Details of breathing are not required. (4) Forced expiratory volume (FEV) is the greatest volume of air a person can breathe out in 1 second. Forced vital capacity (FVC) is the greatest volume of air a person can breathe out in a single breath. The figure below shows results for the volume of air breathed out by three groups of people, A, B and C. Group A had healthy lungs. Groups B and C had different lung conditions that affect breathing. Time breathing out / s Calculate the percentage drop in FEV for group C compared with the healthy people. Page 13
14 Answer =...(1) (c) Asthma affects bronchioles and reduces flow of air in and out of the lungs. Fibrosis does not affect bronchioles; it reduces the volume of the lungs. Which group, B or C, was the one containing people with fibrosis of their lungs? Use the information provided and evidence from the figure above to explain your answer. (3) (Total 8 marks) Q10.(a) What is the function of the coronary arteries?...(2) Figure 1 shows some of the large blood vessels in a mammal. Figure 1 Page 14
15 (i) Which of the blood vessels A to H is the vena cava? (1) Which of the blood vessels A to H is the renal artery? (1) (c) Figure 2 shows how the blood pressure changes as blood travels from the aorta to the capillaries. Figure 2 The rise and fall in blood pressure in the aorta is greater than in the small arteries. Suggest why. Page 15
16 .(3) (Total 7 marks) Q11. This diagram shows a human heart seen from the front. (a) (i) Which one or more of vessels A to D contains oxygenated blood? (1) During a cardiac cycle, the pressure of the blood in vessel C is higher than the pressure of the blood in vessel B. Explain what causes this difference in pressure. (1) What does the diagram suggest about the pressure in the atria compared to the pressure in the ventricles at the stage in the cardiac cycle represented in the diagram? Explain your answer. (2) (c) The wave of electrical activity which coordinates the heart beat is delayed slightly at part X. It then passes along part Y to the base of the ventricles. Page 16
17 Explain the importance of (i) the slight delay at part X; (2) the electrical activity being passed to the base of the ventricles. (2) (Total 8 marks) Q12.The mean internal diameter and the mean speed of blood flow for different human blood vessels are shown below in the table. Blood vessel Mean internal diameter / mm Mean speed of blood flow / mm s 1 Aorta Coronary artery Arteriole Capillary Vena cava (a) Although the speed of blood flow in an arteriole is greater than speed of blood flow in a capillary, blood does not accumulate in the arterioles. Explain why. (1) Other than causing slow blood flow, explain one advantage of capillaries being narrow. Page 17
18 (2) (c) What factor limits the minimum internal diameter of the lumen of a capillary? (1) (d) The volume of blood leaving the capillary network into the veins is less than the volume of blood entering from the arteries. Explain why. (1) (Total 5 marks) Q13.(a) The table shows three statements about some biological molecules. Complete the table with a tick in each box if the statement is true for haemoglobin, cellulose or starch. Statement Haemoglobin Cellulose Starch Has a quaternary structure Formed by condensation reactions Contains nitrogen (3) The graph shows oxygen dissociation curves for the haemoglobin of a mother and her fetus. Page 18
19 Partial pressure of oxygen (po 2 ) / kpa What is the difference in percentage saturation between the haemoglobin of the mother and her fetus at a partial pressure of oxygen (po 2 ) of 4 kpa? (1) (c) The oxygen dissociation curve of the fetus is to the left of that for its mother. Explain the advantage of this for the fetus. (2) (d) After birth, fetal haemoglobin is replaced with adult haemoglobin. Use the graph to suggest the advantage of this to the baby. Page 19
20 (2) (e) Hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin (HPFH) is a condition in which production of fetal haemoglobin continues into adulthood. Adult haemoglobin is also produced. People with HPFH do not usually show symptoms. Suggest why. (1) (Total 9 marks) Q14.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female volunteers. They measured the resting heart rate of each volunteer before the exercise programme. Both groups took part in the same exercise programme. The scientists measured the resting heart rate of each volunteer after the exercise programme. The scientists determined the mean resting heart rate and the range of resting heart rates for each group before and after the exercise programme. The graph shows their results. (a) What was the range of the resting heart rates in males after the exercise programme? (1) Calculate the percentage decrease in the mean resting heart rate of females after the exercise programme. Show your working. Page 20
21 Answer =... % (2) (c) The scientists used the percentage change in the mean resting heart rate after the exercise programme to compare the results for males and females. Explain why they used percentage change in the resting heart rate. (2) (d) The scientists calculated the cardiac output of the volunteers before and after the exercise programme. In some volunteers, their cardiac output stayed the same, even though their resting heart rate decreased. Explain how their cardiac output could stay the same even when their resting heart rate had decreased. (2) (Total 7 marks) Q15.(a) (i) The human heart has four chambers. In which one of the four chambers of the human heart does pressure reach the highest value? (1) Explain how the structure of this chamber causes this high pressure. (1) The table shows the volume of blood in a man's right ventricle at different times during one cardiac cycle. Page 21
22 Time / s Volume of blood / cm (i) Use the data in the table to calculate the man s heart rate. Heart rate =... beats per minute Use the data in the table and your answer to part (i) to calculate the man s cardiac output. Show your working. Cardiac output =... cm 3 per minute (3) (c) Use information from the table to complete the table below to show whether the valves are open or closed at each of the times shown. Write open or closed in the appropriate boxes. Time / s Valve between right atrium and right ventricle Valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery (2) Q16.The figure below represents a capillary surrounded by tissue fluid. The values of the hydrostatic pressure are shown. Page 22
23 Arteriole end direction of blood flow Venule end Hydrostatic pressure = 4.3 kpa Hydrostatic pressure = 1.6 kpa Tissue fluid Hydrostatic pressure = 1.1 kpa (a) Use the information in the figure above to explain how tissue fluid is formed. (2) The hydrostatic pressure falls from the arteriole end of the capillary to the venule end of the capillary. Explain why. (1) (c) High blood pressure leads to an accumulation of tissue fluid. Explain how. (3) (d) The water potential of the blood plasma is more negative at the venule end of the capillary than at the arteriole end of the capillary. Explain why. (3) (Total 9 marks) Q17. Erythropoietin (EPO) is a substance produced in the body. It increases the Page 23
24 production of red blood cells. Synthetic EPO is made artificially. It is used to treat patients who have a form of anaemia in which there is a reduced number of red blood cells. Scientists investigated the effect of synthetic EPO on volunteers with this form of anaemia. The scientists injected synthetic EPO in a salt solution into patients in the experimental groups. They also set up control groups. They gave the different experimental groups different doses of synthetic EPO and different lengths of treatment. At the beginning and end of the treatment, the scientists measured each patient s haemoglobin concentration. From these measurements, they calculated the mean increase in haemoglobin concentration. Some of the results are shown in the table. Number of volunteers Length of treatment / weeks Dose of synthetic EPO / units per kilogram per week Mean increase in haemoglobin concentration / arbitrary units (a) Explain why treatment with synthetic EPO affects the haemoglobin concentration in these volunteers. (2) Suggest how the control groups should have been treated in this investigation. (2) Page 24
25 (c) The scientists measured the dose of synthetic EPO per kilogram per week. Explain why they measured the dose per unit mass and per unit time. (2) (d) Explain how the information that the scientists collected might be useful in treating patients with anaemia. (2) (e) Some athletes have used synthetic EPO as a performance enhancer. Explain how synthetic EPO may improve performance in long-distance events. (4) (f) Athletes may be tested to see if the concentration of EPO in their blood is above normal. Suggest how scientists determine the normal concentration of EPO in blood....(2) Page 25
26 (g) Synthetic EPO can increase blood pressure. Suggest why. (1) (Total 15 marks) Q18.Students investigated the effect of removing leaves from a plant shoot on the rate of water uptake. Each student set up a potometer with a shoot that had eight leaves. All the shoots came from the same plant. The potometer they used is shown in the diagram. (a) Describe how the students would have returned the air bubble to the start of the capillary tube in this investigation. (1) Give two precautions the students should have taken when setting up the potometer to obtain reliable measurements of water uptake by the plant shoot. 1 2(2) (c) A potometer measures the rate of water uptake rather than the rate of transpiration. Give two reasons why the potometer does not truly measure the rate of transpiration. 1 2 (2) Page 26
27 (d) The students results are shown in the table. Number of leaves removed from the plant shoot Mean rate of water uptake / cm 3 per minute Explain the relationship between the number of leaves removed from the plant shoot and the mean rate of water uptake. (3) (Total 8 marks) Q19. (a) Explain how each of the following is related to the function of xylem tissue. (i) Xylem tissue contains hollow tubes. Lignin is present in xylem cell walls. (2) Page 27
28 In an investigation the total area of the stomatal openings and the rate of flow of water through xylem were measured in a plant over a period of 24 hours. The results are shown in the graph. (i) Describe the relationship between the rate of flow of water and the total area of the stomatal openings for the period of time between midday and midnight. (1) Between 8 am and midday the rate of flow of water continues to rise although the total area of the stomatal openings remains constant. Explain why the rate of flow of water rises. (1) (iii) How would the curve showing the total area of the stomatal openings differ if the investigation was repeated on a dull day? (1) (c) Some xerophytic plants have sunken stomata. Explain the advantage of this adaptation. (2) (Total 7 marks) Page 28
29 Q20.Scientists studied three species of plant. They selected fully grown leaves from five different plants of each species. For each leaf they measured: leaf surface area leaf thickness the number of stomata per mm 2. The scientists results are shown in the table below. Plant species Mean leaf surface area Mean leaf thickness / mm 2 / µm Mean number of stomata per mm 2 A B C (a) How did the scientists ensure they could make a valid comparison between leaves from different species? (1) Describe a method you could use to find the surface area of a leaf. (3) (c) (i) Which species, A or B, would you predict grew in a drier environment? Explain one feature that caused you to choose this species. Species... Explanation... (1) Page 29
30 Other than the features of leaves in the table above, give two features of leaves of xerophytes. For each feature explain how it reduces water loss. Feature 1... Explanation... Feature 2... Explanation... (2) (d) Species C has a high number of stomata per mm 2. Despite this it loses a small amount of water. Use the data to explain why. (1) (Total 8 marks) Q21. (a) Scientists measured the rate of water flow and the pressure in the xylem in a small branch. Their results are shown in the graph. (i) Use your knowledge of transpiration to explain the changes in the rate of flow in the xylem shown in the graph. Page 30
31 (3) Explain why the values for the pressure in the xylem are negative. (1) Doctors measured the thickness of the walls of three blood vessels in a large group of people. Their results are given in the table. Name of vessel Mean wall thickness /mm (± standard deviation) Aorta 5.7 ± 1.2 Pulmonary artery 1.0 ± 0.2 Pulmonary vein 0.5 ± 0.2 (i) Explain the difference in thickness between the pulmonary artery and the pulmonary vein. (1) The thickness of the aorta wall changes all the time during each cardiac cycle. Explain why (3) Page 31
32 (iii) Which of the three blood vessels shows the greatest variation in wall thickness? Explain your answer. (1) (c) Describe how tissue fluid is formed and how it is returned to the circulatory system. (6) (Total 15 marks) Q22.(a) (i) Give two ways in which the structure of starch is similar to cellulose (2) Give two ways in which the structure of starch is different from cellulose (2) Page 32
33 In plants, mass transport of sugars takes place through columns of sieve cells in the phloem. Other cells, called companion cells, transport sugars into, and out of, the sieve cells. The diagram shows the structure of phloem. Structures I and J allow the transport of sugars between cells. (i) Using the diagram, suggest and explain one other way in which sieve cells are adapted for mass transport (2) Using the diagram, suggest and explain one other way in which companion cells are adapted for the transport of sugars between cells (2) (Total 8 marks) Page 33
What was the range of the resting heart rates in males after the exercise programme?
 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Answers. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Answers Name: Total Marks: Page 1 M1.(a) Measure with eyepiece graticule / scale; Calibrate with stage micrometer
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Answers Name: Total Marks: Page 1 M1.(a) Measure with eyepiece graticule / scale; Calibrate with stage micrometer
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Putting bee honey on a cut kills bacteria. Honey contains a high concentration of sugar
 Q1.(a) Give two ways in which pathogens can cause disease. 1... 2... (b) Putting bee honey on a cut kills bacteria. Honey contains a high concentration of sugar. Use your knowledge of water potential to
Q1.(a) Give two ways in which pathogens can cause disease. 1... 2... (b) Putting bee honey on a cut kills bacteria. Honey contains a high concentration of sugar. Use your knowledge of water potential to
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
PMT. What evidence in the paragraph suggests that galactose is a monosaccharide? (1)
 1. Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. In the small intestine, it is digested into glucose and galactose by the enzyme lactase. Molecules of lactase are located in the plasma membranes of cells lining
1. Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. In the small intestine, it is digested into glucose and galactose by the enzyme lactase. Molecules of lactase are located in the plasma membranes of cells lining
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
A Level. A Level Biology. Biological Molecules and Enzyme Questions. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Biological Molecules and Enzyme Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram represents part of the human digestive system. The organs are labelled A F.
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Biological Molecules and Enzyme Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram represents part of the human digestive system. The organs are labelled A F.
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
A level Biology Preparation Work
 A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
BYA1. BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 1 Molecules, Cells and Systems
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and the Environment
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Page 2. The pie charts show the results. What conclusions can you make from the data? [Extra space]
![Page 2. The pie charts show the results. What conclusions can you make from the data? [Extra space] Page 2. The pie charts show the results. What conclusions can you make from the data? [Extra space]](/thumbs/80/80973572.jpg) Q1.Nutritionists investigated the relationship between eating oily and non-oily fish and the incidence of asthma. They analysed the diets of children with asthma and the diets of children without asthma.
Q1.Nutritionists investigated the relationship between eating oily and non-oily fish and the incidence of asthma. They analysed the diets of children with asthma and the diets of children without asthma.
Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice
 AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
AS Level Biology Summer Work Separate Science Revision & Exam Practice The booklet needs to be completed and handed in as part of the enrolment process on Thursday 20 th August 2015 Please ensure your
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
9 Transport in animals
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2.
 1 (a) Table 5.1 and Table 5.2 list events that occur during the cardiac cycle. Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2. Complete Table 5.1 by inserting
1 (a) Table 5.1 and Table 5.2 list events that occur during the cardiac cycle. Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2. Complete Table 5.1 by inserting
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
sphere A diameter / cm 1 3 (i) The student calculated the surface area: volume ratio of sphere B as 2:1.
 1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport
 THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport *CUP/T52744* Candidates answer on the question paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic calculator
THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport *CUP/T52744* Candidates answer on the question paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic calculator
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
BIO3X. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June AS Externally Marked Practical Assignment.
 Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2010
Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2010
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review
 Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
GraspIT AQA GCSE Organisation Questions
 A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1)
 Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Applied Science SC14 (JUN15SC1401) General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2015 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Applied Science General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Applied Science General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
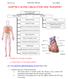 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
Part 2- Biology Paper 1 Organisation Knowledge Questions
 Part 2- Biology Paper 1 Organisation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.2 Organisation Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe the levels of organisation within living organisms
Part 2- Biology Paper 1 Organisation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.2 Organisation Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe the levels of organisation within living organisms
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
For this paper you must have: a ruler with millimetre measurements a calculator, which you are expected to use where appropriate.
 Z Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature AS BIOLOGY PAPER 2 7401/2 Tuesday 7 June 2016 Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes For this paper you must have: a ruler with
Z Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature AS BIOLOGY PAPER 2 7401/2 Tuesday 7 June 2016 Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes For this paper you must have: a ruler with
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION
 Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport
 THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport *OCE/T78243* Candidates answer on the question paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic calculator
THIS IS A LEGACY SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY 2803/01 Transport *OCE/T78243* Candidates answer on the question paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required: Electronic calculator
Attaching lactase to the beads is a more efficient use of lactase than adding the lactase directly to cow s milk
 Q1.Cow s milk contains the sugar lactose. Many cats are unable to digest cow s milk because they are lactose intolerant. Cow s milk can be made suitable for these cats by treating it with the enzyme lactase
Q1.Cow s milk contains the sugar lactose. Many cats are unable to digest cow s milk because they are lactose intolerant. Cow s milk can be made suitable for these cats by treating it with the enzyme lactase
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
BIO3T/P10/test. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June AS Investigative Skills Assignment.
 Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Candidate Number General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2010 For Teacher s Use Stage 1 Skills Stage 2 Skills Section
Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Candidate Number General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2010 For Teacher s Use Stage 1 Skills Stage 2 Skills Section
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
Trial Examination VCE Biology Unit 1. Written Examination. Question and Answer Booklet. Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes
 Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
Trial Examination 2006 VCE Biology Unit 1 Written Examination Question and Answer Booklet Reading time 15 minutes Writing time 1 hour 30 minutes Student s Name: Teacher s Name: Structure of Booklet Section
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
BLY3H. (Jan11BLY3H01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January Unit Biology B3. Written Paper TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January 2011 1 2 Biology
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January 2011 1 2 Biology
This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
BYA6. BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and the Environment. General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2005 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Q1. Lugworms live in mud where the partial pressure of oxygen is low. The graph shows oxygen dissociation curves for a lugworm and for a human.
 Q1. Lugworms live in mud where the partial pressure of oxygen is low. The graph shows oxygen dissociation curves for a lugworm and for a human. (a) Explain the advantage to the lugworm of having haemoglobin
Q1. Lugworms live in mud where the partial pressure of oxygen is low. The graph shows oxygen dissociation curves for a lugworm and for a human. (a) Explain the advantage to the lugworm of having haemoglobin
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION MODIFIED LANGUAGE
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY Cells, Exchange and Transport F211 * OCE / 2 384 9 * Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE BIOLOGY Cells, Exchange and Transport F211 * OCE / 2 384 9 * Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
BIOL1. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit 1 Biology and disease. Monday 14 May am to 10.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Surname. Number OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE F211 BIOLOGY. Cells, Exchange and Transport
 Candidate Forename Centre Number Candidate Surname Candidate Number OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE F211 BIOLOGY Cells, Exchange and Transport TUESDAY 12 JANUARY 2010: Morning
Candidate Forename Centre Number Candidate Surname Candidate Number OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE F211 BIOLOGY Cells, Exchange and Transport TUESDAY 12 JANUARY 2010: Morning
