Name: BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS. Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 59
|
|
|
- Thomasina Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGY B2 TISSUES AND ORGANS Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 59
2 In a living organism, the cells are organised into organs, systems and tissues. (a) Use words from the box to complete the list of these structures in order of size. organs systems tissues The smallest structure is at the top of the list and the largest is at the bottom. cells organism () (b) List A gives three tissues found in the human body. List B gives four functions of tissues. Draw a straight line from each tissue in List A to its correct function in List B. List A Tissue List B Function Covers many parts of the body Muscular tissue Contracts to cause movement Glandular tissue Divides by meiosis Epithelial tissue Releases hormones or enzymes (3) (Total 4 marks) Page 2 of 59
3 2 The image below shows some cells in the lining of the stomach. (a) (i) Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane chloroplast cytoplasm vacuole A... B... (2) What is the function of the nucleus? Tick ( ) one box. To control the activities of the cell To control movement of substances into and out of the cell To release energy in respiration () Page 3 of 59
4 (b) Draw one line from each part of the human body to its correct scientific name. Part of human body Scientific name Layer of cells lining the stomach Stomach Mouth, stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas An organ An organism An organ system A tissue (3) (Total 6 marks) Page 4 of 59
5 3 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ, an organ system or a tissue. For each structure, tick ( ) one box. Structure Organ Organ system Tissue Stomach Cells lining the stomach Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestine (2) (b) (i) The blood going to the stomach has a high concentration of oxygen. The cells lining the stomach have a low concentration of oxygen. Complete the following sentence. Oxygen moves from the blood to the cells lining the stomach by the process of.... () Page 5 of 59
6 What other substance must move from the blood to the cells lining the stomach so that respiration can take place? Draw a ring around the correct answer. glucose protein starch () (iii) In which part of a cell does aerobic respiration take place? Draw a ring around the correct answer. cell membrane mitochondria nucleus () (Total 5 marks) 4 Villi are found in some parts of the digestive system. Diagram shows two villi. Diagram (a) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. muscle. (i) Structure A is a nerve. capillary. () Page 6 of 59
7 dialysis. The villi absorb the products of digestion by diffusion. osmosis. () (b) Diagram 2 shows the digestive system. Diagram 2 (i) In which part of the digestive system, X, Y or Z, are most villi found? There are about 2000 villi in each cm 2 of this part of the digestive system. Why is it helpful to have lots of villi? () () (Total 4 marks) Page 7 of 59
8 5 The diagram shows the human digestive system. (a) Heartburn is a burning feeling caused when acid enters the oesophagus. The acid comes from the stomach. (i) Which letter on the diagram shows the stomach? () Name the acid the stomach produces.... () (iii) Medicines taken to treat heartburn contain chemicals that neutralise excess stomach acid. What type of chemical will neutralise stomach acid?... () Page 8 of 59
9 (b) Use words from the box and your own knowledge to describe how carbohydrates are digested. amylase starch sugars (5) (c) Where in the body are the products of digestion absorbed?... () (Total 9 marks) Page 9 of 59
10 6 The diagram in Figure shows a section through the human heart, seen from the front. Figure (a) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. epithelial (i) The wall of the heart is made mostly of glandular tissue. muscular () The resting heart rate is controlled by the pacemaker. The pacemaker is located at position () (iii) If a person s heart rate is irregular, the person may be fitted with an artificial pacemaker. The artificial pacemaker is an electrical device. a pump. a valve. () Page 0 of 59
11 (b) (i) Write a number, 2, 5, 6 or 7, in each of the three boxes to answer this question. Which chamber of the heart: pumps oxygenated blood to the head and body receives deoxygenated blood from the head and body receives oxygenated blood from the lungs? (3) Give the number, 3, 4 or 8, of the valve that closes when the blood pressure in the aorta is greater than the blood pressure in the left ventricle. Write the correct answer in the box. () (c) The diagram in Figure 2 shows one type of artificial heart valve. The plastic ball is in the closed position. Figure 2 This type of artificial valve could be used to replace a faulty valve in the heart. (i) What is the function of valves in the heart? () Page of 59
12 The artificial valve could be used to replace valve 4 shown in Figure. The artificial valve opens to let blood through when the ball is moved towards A. Which end of the valve, A or B, should point towards chamber 5? Explain your answer. (3) (d) (i) The artificial heart valve may cause blood clots to form on its surface. Describe what happens during blood clotting. (2) Read the information in the passage. Replacing a damaged heart valve can dramatically improve the blood circulation and the supply of oxygen to the body s tissues. The operation to replace a heart valve is a long one during which the patient s blood goes through a bypass machine. Sometimes the artificial valve can fail to work. If the surface of the valve becomes rough, small blood clots can form on its surface then break away and be carried around the body by the blood. Page 2 of 59
13 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of artificial heart valves. (4) (Total 7 marks) Page 3 of 59
14 7 Leaves are made from layers of cells. The diagram shows a section through part of a leaf. (a) (i) Which word in the table describes layer A? Tick ( ) one box. Layer A Tick ( ) Tissue Organ Cell () Which word describes a whole leaf? Draw a ring around one answer. organ tissue organism () Page 4 of 59
15 (b) (i) Which two layers of cells, A, B, C and D, can photosynthesise? Use information from the diagram to help you. Tick ( ) two boxes. Layer A Layer B Layer C Layer D (2) Give one reason for your answer. () Page 5 of 59
16 (c) List X gives the names of two parts of a cell. List Y gives information about parts of a cell. Draw one line between each part of the cell in list X and information about it in list Y. List X Part of a cell List Y Information Controls the passage of substances into the cell Vacuole Contains the cell sap Nucleus Controls the activities of the whole cell (2) (Total 7 marks) Page 6 of 59
17 8 The diagram shows a section through a plant leaf. (a) Use words from the box to name two tissues in the leaf that transport substances around the plant. epidermis mesophyll phloem xylem... and... () (b) Gases diffuse between the leaf and the surrounding air. (i) What is diffusion? (2) Name one gas that will diffuse from point A to point B on the diagram on a sunny day. () (Total 4 marks) Page 7 of 59
18 9 The diagram below shows a cross-section of a plant root. The transport tissues are labelled. (a) (i) What is tissue A? Draw a ring around the correct answer. cuticle epidermis xylem () Name two substances transported by tissue A (2) (b) Phloem is involved in a process called translocation. (i) What is translocation? () Explain why translocation is important to plants. (2) Page 8 of 59
19 (c) Plants must use active transport to move some substances from the soil into root hair cells. (i) Active transport needs energy. Which part of the cell releases most of this energy? Tick ( ) one box. mitochondria nucleus ribosome () Explain why active transport is necessary in root hair cells. (2) (Total 9 marks) 0 (a) The diagrams show apparatus you could use to mount a piece of leaf epidermis for examination under a microscope. Page 9 of 59
20 (i) Name the pieces of apparatus labelled A, B, C and D on the diagram. A... B... C... D... (4) Describe how you would use A, B, C and D to mount a piece of leaf epidermis for examination under a microscope. (3) Page 20 of 59
21 (b) A student used a grid on a microscope to estimate the number of stomata in some leaf epidermis. The drawings show four of the grid squares the student observed. Each grid has an area of mm 2. (i) Calculate the mean number of stomata per grid square. Mean number of stomata per grid square... (2) Calculate the mean number of stomata per mm 2 of leaf epidermis. Mean number of stomata per mm 2... (2) Page 2 of 59
22 (iii) Each side of a grid square has a length of approximately mm. Use this information to estimate the length of a guard cell. Estimated length of guard cell... mm (2) (c) A group of students looked at stomata on four different species of plant, W, X, Y and Z. The students estimated the number of stomata per cm 2 on the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves of the four species. The results are shown in the table. Plant species Estimated number of stomata per cm 2 of leaf surface Upper surface of leaf Lower surface of leaf W X Y Z (i) Which plant species, W, X, Y or Z, probably lives in a dry region? Explain why you have chosen this species. (3) Page 22 of 59
23 All four species have more stomata on the lower surface of their leaves than on the upper surface. Suggest how this feature could improve the chances of the survival for the plants. (2) (Total 8 marks) The image below shows an epithelial cell from the lining of the small intestine. (a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes. What is the name of part A? () How are most soluble food molecules absorbed into the epithelial cells of the small intestine? Draw a ring around the correct answer. diffusion osmosis respiration () Page 23 of 59
24 (b) Suggest how the highly folded cell surface helps the epithelial cell to absorb soluble food () (c) Epithelial cells also carry out active transport. (i) Name one food molecule absorbed into epithelial cells by active transport. () Why is it necessary to absorb some food molecules by active transport? () Suggest why epithelial cells have many mitochondria. (2) (d) Some plants also carry out active transport. Give one substance that plants absorb by active transport.... () (Total 8 marks) 2 The diagram below shows a single-celled alga which lives in fresh water. Page 24 of 59
25 (a) Which part of the cell labelled above: (i) traps light for photosynthesis () is made of cellulose? () (b) In the freshwater environment water enters the algal cell. (i) What is the name of the process by which water moves into cells? () Give the reason why the algal cell does not burst. () (c) (i) The alga can photosynthesise. Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. water oxygen (2) The flagellum helps the cell to move through water. Scientists think that the flagellum and the light-sensitive spot work together to increase photosynthesis. Suggest how this might happen. (2) Page 25 of 59
26 (d) Multicellular organisms often have complex structures, such as lungs, for gas exchange. Explain why single-celled organisms, like algae, do not need complex structures for gas exchange (3) (Total marks) 3 Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise to fatally high levels. Insulin controls the concentration of glucose in the blood. (a) Where is insulin produced? Draw a ring around one answer. gall bladder liver pancreas () (b) People with diabetes may control their blood glucose by injecting insulin. (i) If insulin is taken by mouth, it is digested in the stomach. What type of substance is insulin? Draw a ring around one answer. carbohydrate fat protein () Apart from using insulin, give one other way people with diabetes may reduce their blood glucose. () Page 26 of 59
27 (c) The bar chart shows the number of people with diabetes in different age groups in the UK. Age in years (i) Describe how the number of males with diabetes changes between the ages of 0 44 years and 75 years and over. (3) Page 27 of 59
28 Compare the number of males and females with diabetes: between the ages of 0 and 64 years over the age of 65 years. (2) (Total 8 marks) 4 Some students investigated the effect of ph on the digestion of boiled egg white by an enzyme called pepsin. Egg white contains protein. The students: put a glass tube containing boiled egg white into a test tube added a solution containing pepsin at ph 7 set up six more tubes with solutions of pepsin at different ph values left the test tubes for 24 hours at room temperature. The image below shows one of the test tubes, at the start and at the end of the 24 hours. At start 24 hours later (a) (i) Name the product of protein digestion. () Page 28 of 59
29 What type of enzyme digests protein? Tick ( ) one box. amylase lipase protease () (b) The egg white in each tube was 50 mm long at the start of the investigation. The table below shows the students results. ph Length in mm of boiled egg white after 24 hours (i) At which ph did the pepsin work best? ph... () The answer you gave in part (b)(i) may not be the exact ph at which pepsin works best. What could the students do to find a more accurate value for this ph? (2) Page 29 of 59
30 (iii) There was no change in the length of the egg white from ph 5 to ph 7. Explain why. (2) (c) Pepsin is made by the stomach. Name the acid made by the stomach which allows pepsin to work well.... () (Total 8 marks) Page 30 of 59
31 5 Fresh milk is a mixture of compounds including lipid, protein and about 5% lactose sugar. Lactose must be digested by the enzyme lactase, before the products can be absorbed. Lactase can be added to fresh milk to pre-digest the lactose. This makes lactose-free milk, which is suitable for people who do not produce enough lactase of their own. A student investigated the effect of changing ph and temperature on the digestion of lactose in milk. The results are shown in Tables and 2. Table Effect of ph Table 2 Effect of temperature ph Time taken to digest lactose in minutes Temperature in C Time taken to digest lactose in minutes No digestion (a) The label on a carton of lactose-free milk states: Lactase is normally produced in the stomach of mammals. The results in Table suggest that this statement is not true. Explain how (2) Page 3 of 59
32 (b) Explain, as fully as you can, the results shown in Table (3) (c) Bile is produced in the liver and is released into the small intestine. Bile helps the digestion of lipid in the milk. Describe how (2) (Total 7 marks) Page 32 of 59
33 6 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest one has been done for you. (2) (b) The stomach is made of different types of tissue. Draw one line from each type of stomach tissue to the correct description. (3) Page 33 of 59
34 (c) Animals can react to their surroundings because they have nervous systems. A student investigated the behaviour of small animals called woodlice. The student set up the investigation as shown in Figure 2. The student covered one half of a Petri dish with black paper to make that side of the Petri dish dark. The other side had no cover. The student put five woodlice into each side of the dish and then put the clear Petri dish lid back on the dish. Figure 2 After 30 minutes, all the woodlice had moved to the dark side of the Petri dish. Page 34 of 59
35 (i) In this investigation, what is the stimulus that the woodlice responded to? () In this investigation, what is the response that the woodlice made? () (iii) The student concluded that woodlice prefer dark conditions. Give two ways in which the student could improve the investigation to be sure that his conclusion was correct (2) (Total 9 marks) 7 The photograph shows a fossil of a prehistoric bird called Archaeopteryx. By Ghedoghedo (own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 ( or GFDL ( /fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons; By Steenbergs from Ripon, United Kingdom (Small Fishing Boat In North Sea) [CC-BY-2.0 ( via Wikimedia Commons. Page 35 of 59
36 (a) Describe three ways fossils can be made (3) (b) The drawing shows what an Archaeopteryx might have looked like when it was alive. Scientists think that Archaeopteryx was a predator. Page 36 of 59
37 (i) Look at the drawing. Write down three adaptations that might have helped Archaeopteryx to catch prey. How would each adaptation have helped Archaeopteryx to catch prey? Adaptation... How it helps... Adaptation 2... How it helps... Adaptation 3... How it helps... (3) Archaeopteryx is now extinct. Give two reasons why animals may become extinct (2) (Total 8 marks) Page 37 of 59
38 Mark schemes (a) in sequence: 2 = tissue(s) 3 = organ(s) 4 = system(s) (b) mark for each correct line extra line(s) from one tissue cancel 3 [4] 2 (a) (i) A = (cell) membrane B = cytoplasm do not accept cytoplast To control the activities of the cell Page 38 of 59
39 (b) extra lines cancel 3 [6] 3 (a) Structure Organ Organ system Tissue Stomach Cells lining the stomach Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestine all 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = mark or 0 correct = 0 marks (b) (i) diffusion allow phonetic spelling 2 glucose (iii) mitochondria [5] 4 (a) (i) capillary Page 39 of 59
40 diffusion (b) (i) Z ignore any names large / increased surface / area allow all food absorbed or to absorb more food or improved diffusion [4] 5 (a) (i) A (iii) hydrochloric (acid) / HCl alkali / suitable named example accept sodium hydrogen carbonate / sodium bicarbonate / milk of magnesia / other brand names allow bile (salts) ignore antacid (b) amylase breaks down starch (broken down) into sugars / glucose digestion of starch in the mouth (also) starch broken down in small intestine amylase produced in salivary glands / small intestine / pancreas (c) small intestine allow ileum / duodenum do not accept large intestine [9] 6 (a) (i) muscular Page 40 of 59
41 7 (iii) an electrical device (b) (i) in sequence: (c) (i) prevent backflow (of blood) / allow flow in only one direction / in the correct direction A no mark, but max 2 marks if incorrect 2 / atrium contracts / pressure in 2 increases blood pushes ball (down / towards ventricle / towards 5 ) allow this point even if valve in wrong part of heart (opens valve which) allows blood into 5 / ventricle or converse points re closing the valve (d) (i) involvement of platelets / eg platelets trigger clotting process / release enzyme(s) / release clotting factors fibrinogen to fibrin or meshwork formed (which traps blood cells) Page 4 of 59
42 any four from: to gain 4 marks candidates should include at least: one advantage and one disadvantage Advantages (improved circulation / O 2 supply) provides: more cell respiration more energy released (more) active life / not so tired / more physical activity Disadvantages danger of surgery / operation infection from surgery / operation valve may need replacing clots may form and block blood vessels may need to take anti-coagulants eg warfarin clots may cause heart attacks / strokes 4 [7] 7 (a) (i) tissue extra box ticked cancels the mark organ extra ring drawn cancels the mark (b) (i) Layer B Layer C each extra box ticked cancels mark (contain) chloroplasts / chlorophyll other parts disqualify Page 42 of 59
43 (c) two correct = 2 marks one correct = mark extra line from a part of a cell cancels the mark 2 [7] 8 (a) xylem and phloem either order allow words ringed in box allow mis-spelling if unambiguous (b) (i) movement / spreading out of particles / molecules / ions / atoms ignore names of substances / gases from high to low concentration accept down concentration gradient ignore along / across gradient ignore with gradient oxygen / water (vapour) allow O 2 / O2 ignore O 2 / O allow H 2 O / H2O ignore H 2 O [4] Page 43 of 59
44 9 (a) (i) xylem water minerals / ions / named example(s) ignore nutrients (b) (i) movement of (dissolved) sugar allow additional substances, eg amino acids / correct named sugar (allow sucrose / glucose) allow nutrients / substances / food molecules if sufficiently qualified ignore food alone sugars are made in the leaves so they need to be moved to other parts of the plant for respiration / growth / storage (c) (i) mitochondria for movement of minerals / ions Do not accept water against their concentration gradient [9] 0 (a) (i) A slide B coverslip C (teat / bulb) pipette D (mounted) needle place epidermis on (centre of) slide use pipette to add drop of liquid/ water / stain to epidermis use needle to lower coverslip onto liquid Page 44 of 59
45 (b) (i) 8 4 = 4.5 correct answer with or without working gains 2 marks ( 0.000) 4.5 = correct answer with or without working gains 2 marks allow ecf from part (b)(i) (iii) (eg 4 / 5 / 6) (c) (i) X correct answer with or without working gains 2 marks allow answers in range inclusive because it has the low(est) number of stomata or no stomata on upper surface or only 800 (on lower surface) which means there will be less transpiration / evaporation / water loss via stomata it reduces amount of water (vapour) or reduces transpiration (from upper surface) because lower surface is cooler or in the shade or covered by (folded) wilted leaf [8] (a) (i) nucleus diffusion Page 45 of 59
46 (b) increases / larger surface area (for diffusion) ignore large surface area to volume ratio (c) (i) sugar / glucose accept amino acids / other named monosaccharides (iii) against a concentration gradient or from low to high concentration (active transport requires) energy (from) respiration (d) minerals / ions accept named ion ignore nutrients do not accept water [8] 2 (a) (i) chloroplast cell wall (b) (i) osmosis accept diffusion cell wall (prevents bursting) (c) (i) carbon dioxide allow correct formula glucose allow sugar / starch any two from: (d) light sensitive spot detects light tells flagellum to move towards light more light = more photosynthesis (cell has) larger SA:volume ratio 2 Page 46 of 59
47 short (diffusion) distance allow correct description (diffusion) via cell membrane is sufficient / good enough or flow of water maintains concentration gradient [] 3 (a) pancreas apply list principle (b) (i) protein apply list principle any one from: (controlling / changing) diet accept sugar(y foods) / named eg ignore references to starch / fat / protein / fibre exercise accept example, eg go for a run (c) (i) increase pancreas transplant then fall accept named drug eg metformin ignore reference to women relevant data quote (for male) eg max at ages or starts at 0 (per thousand) or max at 30 (per thousand) or ends at 20 (per thousand) accept a difference between any pairs of numbers in data set accept quotes from scale eg 30 or 30 per thousand but not 30 thousand ; to within accuracy of +/- 2 (per thousand) (between 0 and 64) more females (than males) or less males (than females) ignore numbers allow eg females more diabetic than males Page 47 of 59
48 do not allow incorrect formula e.g. H 2 Cl / HCl 2 (over 65) more males (than females) or less females (than males) allow eg males more diabetic than females [8] 4 (a) (i) amino acid(s) accept peptide(s) do not allow polypeptide(s) protease (b) (i) 2 (iii) repeat do not allow other enzyme / substrate using smaller ph intervals between ph and ph3 allow smaller intervals on both sides of / around ph2 allow smaller intervals on both sides of / around answer to (b)(i) enzyme / pepsin denatured / shape changed do not allow enzyme killed allow enzyme destroyed enzyme / pepsin no longer fits (substrate) allow enzyme / pepsin does not work (c) hydrochloric (acid) allow phonetic spelling accept HCl allow HCL ignore hcl [8] 5 (a) stomach is acidic / has low ph allow any ph below 7 ignore stomach is not alkaline Page 48 of 59
49 lactase works best / well in alkali / high ph / neutral / non-acidic conditions allow any ph of 7 and above accept works slowly in acid conditions allow figures from table with a comparison ignore reference to temperature (b) any three from: (below 40( C)) increase in temperature increases rate / speed of reaction reference to molecules moving faster / colliding faster / harder / more collisions enzyme optimum / works best at 40 C allow value(s) in range ignore body temperature unless qualified high temperatures (above 40 C) / 45 C / 50 C enzyme denatured allow synonyms for denaturation, but do not allow killed denaturation at high and low temperature does not gain this mark ignore references to time / ph 3 (c) any two from: acid neutralised or conditions made neutral / alkali accept bile is alkaline (allow) emulsification / greater surface area (of lipid / fat) allow description of emulsification eg fat broken down / broken up into droplets do not accept idea of chemical breakdown lipase / enzymes (in small intestine) work more effectively / better allow better for enzymes ignore reference to other named enzymes 2 [7] 6 (a) tissue organ organ system one right for mark three right for 2 marks 2 Page 49 of 59
50 (b) Epithelial tissue covers the outside and the inside of the stomach more than one line from a tissue = no mark Glandular tissue produces digestive juices Muscular tissue allows food to be churned around the stomach (c) (i) light ignore dark (iii) moving (to the dark) any two from: use more woodlice repeat the experiment run for a longer time 2 [9] 7 (a) any three from: parts of organisms have not decayed accept in amber / resin allow bones are preserved conditions needed for decay are absent accept appropriate examples, eg acidic in bogs / lack of oxygen parts of the organism are replaced by other materials as they decay accept mineralised or other preserved traces of organisms, eg footprints, burrows and rootlet traces allow imprint or marking of organism 3 (b) (i) teeth for biting (prey) must give structure + explanation claws to grip (prey) accept sensible uses wing / tail for flight to find (prey) Page 50 of 59
51 any two from: new predators new diseases better competitors catastrophe eg volcanic eruption, meteor changes to environment over geological time accept climate change allow change in weather prey dies out or lack of food allow hunted to extinction 2 [8] Page 5 of 59
52 Examiner reports (a) (b) Almost half of the students were able to list tissues-organs-systems in the correct size order. The distracters in this section proved very distracting and less than half the students could assign the correct function to all three types of tissue muscular, glandular and epithelial. 2 This question was well answered by most students. (a) (i) Most knew that structure A in the diagram of cells from the stomach lining was the cell membrane and that B was the cytoplasm, although a few got these the wrong way round. Nearly all students knew that the function of the nucleus was to control the activities of the cell. 3 (b) (a) Over three quarters of students were able to assign the three parts of the body to their scientific name. Over three quarters of students knew that the stomach was an organ, that the cells lining it made up a tissue, and that the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestine constituted an organ system. (b) (i) Just over half the students recognised that the process of diffusion had been defined in the question as the process by which oxygen moves from the blood to the cells lining the stomach, although some suggested respiration and others photosynthesis. (iii) The vast majority selected glucose as the other substance that would also need to be supplied for use in respiration. Most students knew that the mitochondria were used for aerobic respiration, although the cell membrane and the nucleus distracted a few in equal proportion. 4 This question was well answered by most students. (a) Most knew that structure A in the diagram of the villus was a capillary and that the villi absorbed the products of digestion by diffusion. (b) Similarly, most were able to identify region Z (the small intestine) on the diagram of the digestive system as the part where most villi were found. Just under half of the students knew that the purpose of having large numbers of villi was to increase the surface area or to allow more food to be absorbed. Some clearly confused the situation with gas exchange and wrote about the absorption of oxygen. Page 52 of 59
53 5 (a) The vast majority were able to identify structure A on the diagram as the stomach. Less than one-fifth knew that the acid produced by the stomach was hydrochloric acid. (iii) More students knew that some sort of alkali would need to be present in a medicine that would neutralise excess stomach acid. (b) (c) Most answers to this question were very poor, with half of the students scoring no marks at all for their accounts of carbohydrate digestion, despite being given the words amylase, starch and sugars for guidance. Many did not seem to know that starch was a carbohydrate or that starch was made of sugar molecules joined together. The site of amylase production and the site of its action were not always distinguished digestion of starch does not occur in the pancreas or in the salivary glands as some students inferred. Some also wasted time by writing about topics irrelevant to the question, such as absorption and defaecation. Just over one-quarter of students knew that the site of absorption of the products of digestion was the small intestine. Page 53 of 59
54 6 (a) (b) (c) These parts were made up of five multiple-choice questions based upon a diagram of a section through the human heart. Nearly all students knew that the heart wall was composed mainly of muscular tissue, but only half knew the location of the pacemaker, although the fact that the latter was an electrical device (rather than a pump or a valve) was again well known. The majority also knew which chambers of the heart pumped out oxygenated blood and received either deoxygenated blood or oxygenated blood, and which valve would close when the blood pressure in the aorta exceeded that in the left ventricle. These parts were made up of five multiple-choice questions based upon a diagram of a section through the human heart. Nearly all students knew that the heart wall was composed mainly of muscular tissue, but only half knew the location of the pacemaker, although the fact that the latter was an electrical device (rather than a pump or a valve) was again well known. The majority also knew which chambers of the heart pumped out oxygenated blood and received either deoxygenated blood or oxygenated blood, and which valve would close when the blood pressure in the aorta exceeded that in the left ventricle. This section introduced the concept of an artificial replacement valve. Most knew that valves prevent the backflow of blood or ensure that the blood flows in only one direction. Only the more able students were successful in part, being able to work out how the pressure of the blood would alter the position of the ball in the valve and thus allow blood to pass only from the atrium to the ventricle. Very few students mentioned contraction of the atrium as a means of generating pressure. (d) (i) Students had some extraordinary ideas about the nature of blood clotting, many evidently confusing it with the antigen-antibody interaction which was the subject of a question in the January 204 paper. About one-quarter of the students were able to invoke both the involvement of platelets and the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin fibres. This question included some information about the dangers of blood clot formation on an artificial heart valve. Using this information students had to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of such valves. For about one-third of the students, this was an invitation to copy out most of the given passage rather than to use it as a source of information for developing their own argument such students scored zero marks. Given that the replacement valve can dramatically improve the blood circulation and supply of oxygen to the body s tissues, students were expected to point out that this would improve cell respiration, releasing more energy for physical activity (these points alone would have scored three out of the four marks available for this question). And, given that blood clots can form on (the valve s) surface then break away and be carried around the body by the blood, it was hoped that students would realise the consequences of this in terms of blockage of blood vessels followed by perhaps a heart attack or stroke. Very few students were able to make more than one or two valid points. Being an evaluation question, students were expected to include both advantages and disadvantages in their answers. Page 54 of 59
55 7 (a) The concept of organisation, as in part (a), has not been directly examined for several sessions and it was clear that many candidates had not included this in their preparation, as answers here often showed a disappointing lack of understanding. (i) The correct answer, tissue, was selected by only just over half the candidates, with cell coming a very close second. By far the greatest number of candidates chose the incorrect organism. This is particularly surprising for examiners, who expect that the term organism is one that candidates will encounter frequently in their work. (b) (c) However, there were more pleasing attempts in part (b) Many candidates selected the correct two layers, B and C and then went on to explain their selections with appropriate reasons, referring to chloroplasts or chlorophyll. Those who selected A and D in part (b)(i) usually gave a logical, if incorrect reason for their choice, usually that these two layers were on the outside so would be most exposed to light. Despite there being a general improvement in candidates following instructions, in questions such as this, around 6% did not tick just two boxes despite the required number being emboldened twice, along with the mark allocation providing further evidence as to how many boxes should be ticked. Those who gave reasons which did not exclusively refer to chloroplasts / chlorophyll were not credited. Thus answers such as the cells in these layers have chloroplasts and a nucleus provided a list for the examiners to choose from. In such circumstances the examiners are instructed not to make a choice, whichever order the components of the list should be in, and thus not award the mark. A high proportion of candidates scored both marks, with most of the rest gaining one mark, the most common problem for candidates being the decision as to what the nucleus controls. 8 This was the first of three standard demand questions common to both the Foundation and Higher Tier papers. (a) (b) A little less than half of students recognised the terms xylem and phloem as the names of the two tissues in the leaf that are used for transport. Just over a quarter of the students were able to give a satisfactory definition of diffusion. Although many knew that a substance would move from high to low concentration by diffusion, far fewer stressed that it was molecules / particles of the substance that moved. in part, most answers were either oxygen or carbon dioxide, less than half of the students correctly gave the former as the gas that would diffuse out of the leaf on a sunny day. Page 55 of 59
56 9 (a) (i) Almost all students were able to correctly identify xylem labelled on the diagram. About two-thirds of the students knew that both water and minerals were transported in the xylem. Of those who scored one mark, water was the most common response. Many students incorrectly wrote sugars or nutrients. (b) (i) Just over half of the students could define translocation. Many students mentioned water only being transported in phloem. Very few students gained both marks to explain why translocation is important. The crux of the question lay in recognising that sugars are made in the leaves but need to be moved to other parts of the plant for respiration or growth. (c) (i) Almost all students could identify mitochondria as the cell part releasing energy. This was a high demand item and only about one-third of students scored two marks and one-third one mark only. One mark was awarded if substances or nutrients were mentioned as being moved against the concentration gradient since this term could include minerals or ions. Some students wrote water is moved against the concentration gradient and although the latter part is true for minerals, in the wrong context (water) no marks could be awarded. (a) (i) The majority of students correctly identified the nucleus in the epithelial cell. Nearly all of the students knew that soluble food molecules were absorbed by diffusion. Osmosis was the most common incorrect answer. (b) A highly folded cell surface increases the surface area of a cell. Many students lost a mark in this question for failing to use comparative wording, hence a large surface area did not gain a mark, whereas a larger surface area did. Some students referred to the surface area to volume ratio which was not relevant. (c) (i) Over half of students know one food molecule absorbed by active transport. Glucose and amino acids were the most common answers. Other correctly named monosaccharides were accepted but protein was not allowed. (iii) Just over half the cohort were able to state why some food molecules area absorbed by active transport. Students most commonly said that absorption was against the concentration gradient. Some students elaborated in more detail to state that there was a higher concentration of molecules in the cell or blood compared to the gut. Fewer than half the students correctly described that energy released from respiration is required for active transport. Many students lost at least one mark by saying that respiration produces or makes or creates energy. Energy may only be released or transferred or provided by respiration. (d) Only two thirds of the cohort was able to state one substance that plants absorb by active transport. The most common answer was mineral ions but many also named an ion, most commonly nitrates. The most common incorrect responses were water, nutrients, nitrogen, pollen, oxygen and proteins. Page 56 of 59
57 2 (a) (i) The majority of students were able to correctly identify the chloroplast and cell wall. The majority of students were able to correctly identify the chloroplast and cell wall. (b) (i) Almost all students were able to name osmosis (or diffusion) as the process by which water moves into the cell. About two-thirds of the students answered correctly with explicit reference to how the cell wall prevents the algae from bursting. If an incorrect reason was given, the mark was not awarded, eg the cell wall controls how much water enters and leaves the cell, the cell wall is thin making diffusion easy. Some common incorrect answers included; it is isotonic ; the vacuole ; the cell is turgid ; the cell wall is partially permeable. (c) (i) Almost all students were able to complete the word equation for photosynthesis with correct formulae accepted. The majority of students were awarded the maximum of two marks for this question to suggest how the light-sensitive spot and flagellum could work to increase photosynthesis. In fact, many responses included all of the three available marking points. Credit was given where students had interpreted the information differently to say that the light-sensitive spot detects when the cell is dark and so the flagella move the cell to a lighter position. Some incorrect responses included: light sensitive spot sees the light, flagellum would catch the light, flagellum have a large surface area to catch the light and flagellum detect levels of carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis. (d) Very few students scored full marks in this question. Again, students found it difficult to express their ideas and knowledge in this high demand area of the specification. 3 (a) The most common correct answer was marking point (larger SA:volume ratio), followed by marking point 2 (short diffusion distance). Where students gained two marks, both of the first two marking points were linked. Some students were not awarded marking point because they just wrote large surface area with no reference to volume. Many students missed out on the third marking point because they referred to the cell wall as opposed to the cell membrane. Some other incorrect responses included: gas exchange is easier in water than air single celled organisms use their cell walls for gas exchange diffusion is easy because they are small they don't need a lot of oxygen because they are small not enough space inside their cell for complex structures they don't have a respiratory system because they photosynthesise thin walls so gas can diffuse easily. The pancreas as the site of insulin production was well known by the overwhelming majority of students. However students were not secure in their understanding that proteins are digested in the stomach, thus insulin must be a protein, this piece of deduction requiring two steps. Many students here selected carbohydrate perhaps because of the link between insulin and blood glucose concentrations described in the question stem. Page 57 of 59
58 (b) Exercise, eating less sugar or simply control through the diet were commonly given although a surprisingly high number of students believed that additional dietary sugar would be helpful. (c) (i) Students often appeared to forget which part of the chart they should be describing, as there were many descriptions of the changes in females and comparisons between males and females at the various ages. Some students merely referred to the start and end points, ignoring the reduction after the ages of An appropriate reference to the data was expected for the third mark and students could attain this in a wide variety of ways. Most chose to quote either start or end values, others deduced the change from start to end, or quoted the peak value. All of these were acceptable, however incorrect reading of the scale on the y-axis was not accepted, thus suggestions such as diabetic males at years, rather than 30 per 000, were not credited. Just a few (appropriate) words would have secured the marks for both parts. Students often went into unnecessary detailed descriptions and even explanations. However, the majority of students did identify the relevant differences. 4 (a) (i) Less than one-third of students knew that amino acids (or, alternatively, peptides) were the product of protein digestion. There was much more success in selecting protease as the name of the proteindigesting enzyme. (b) (i) Almost two-thirds of students were able to select ph 2 from the table of data as the ph at which the enzyme worked best, although a significant minority chose a value between 5 and 7 (the table showed that no reaction had taken place at these values, whereas ph 2 had the greatest decrease in length of the egg white). (iii) Most students appreciated that the experiment would need to be repeated; however, this would not have improved the accuracy, as demanded by the question. Very few students were able to qualify their answer with a suitable ph range around their answer for (i), and at smaller intervals of ph. While a few students knew that denaturation of the enzyme would be the likely reason for it not working at ph 5 to 7, many thought that digestion of the protein was brought about by acid and argued that, since the solution was less acidic, digestion would cease. The most common mark awarded was for the idea that the enzyme did not work at these phs. 5 (c) (a) Just over one-third of students knew that hydrochloric acid was responsible for the low ph in the stomach. Incorrect answers included bile and amino acid. Many students were able to explain that the contents of the stomach are acidic and that the evidence in Table showed lactase was more active in alkaline conditions. Others only got halfway to this, giving either one side or the other of this explanation. However a considerable number of students appeared to have little understanding of the ph scale, suggesting that high ph means acid conditions. These students then struggled to gain any marks here. Page 58 of 59
59 6 (b) (c) (a) (b) Students often failed to refer to the rate of enzyme activity; choosing to describe the results in Table 2, rather than to explain them as demanded by the question. This usually left them with no marks, despite having filled the available space. Those students who did attempt explanations often omitted to refer to temperatures below the optimum, thus limiting their maximum mark to two. Denaturation was a commonly known term, although some believed that this happens at both high and low temperatures. There were very few references to enzymes being killed. Optimum, along with an appropriate temperature was also commonly accepted. Only the neutralising effect of bile is described in the specification. Examiners also accepted emulsification or a description of this process. The advantage of both these processes is the same, intestinal enzymes work better / faster. Students were sometimes confused as to where bile was added to food, often describing neutralisation as being in the stomach, rather than occurring after the food had left the stomach. References to helping lactase work faster may be true, but were not accepted as the question asked about the digestion of lipid. The knowledge of bile, its composition and effects was surprisingly sparse. Many believed that it contains enzymes or is an acid or that it simply breaks down fats and as a result marks for this final part were below what the examiners had hoped. This general marked question was a straightforward start to the paper with nearly all students answering correctly. Students had to complete the order of tissue, organ and organ system. A few students completed the boxes in reverse, which gained one mark since tissue was then still in the correct position. More students than expected did not match all the tissue types to the correct descriptions. (c) (i) Students were asked to state the stimulus in the investigation. Generally this question was well answered with few mistakes. Most students gave "light" as the answer, or acceptable derivatives of thereof. Some incorrect answers included: darkness, colour of paper and black paper. (iii) Students were asked to state the response of the woodlice. Again, a generally well answered question with the majority of students responding correctly. Some common incorrect answers included: muscular contractions, without any reference to movement, attracted to the dark side and phototropism. This question assessed the AO3 skill of method improvement. Around half of students scored the full two marks on this question. The most common correct answers came from the first two marking points in the mark scheme. Almost half of the students gained one mark. Page 59 of 59
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
2 Organisation higher (import)
 2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical that can be used to preserve milk.
 Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems
 Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level
Animal tissues, organs and organ Systems Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.2 Organisation Sub-Topic Animal tissues, organs and organ systems Difficulty Level Bronze Level
(a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes.
 Q1.The image below shows an epithelial cell from the lining of the small intestine. (a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes. What is the name of part A? How are
Q1.The image below shows an epithelial cell from the lining of the small intestine. (a) (i) In the image above, the part of the cell labelled A contains chromosomes. What is the name of part A? How are
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
B2 Cells and simple transport
 B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
remove solution / liquid (on outside of worm) allow water variable amounts removed from each worm ignore reference to length of timing 1
 M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
Name: B2 Organisation. Class: 35 Questions. Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Brookvale Groby Learning Trust
 B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
B2 Organisation 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 2 Figure shows an animal cell. Figure (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock Cell membrane Cell
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes:
 Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
Q1. We use enzymes in industry. These are some of the properties of enzymes: they work at low temperatures and this can save energy they work at atmospheric pressures and therefore use less expensive equipment
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY
 GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY BL2HP Report on the Examination 4408 / 4401 June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA and its licensors. All
GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE / BIOLOGY BL2HP Report on the Examination 4408 / 4401 June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA and its licensors. All
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
CELL STRUCTURE / QUESTIONS. Q1. Figure 1 shows an animal cell. Figure 1. alex-mit/istock/thinkstock. (a) What is structure A? Tick one box.
 CELL STRUCTURE / QUESTIONS Q1. Figure 1 shows an animal cell. Figure 1 alex-mit/istock/thinkstock (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. Cell membrane Cell wall Chromosome Cytoplasm What is structure B?
CELL STRUCTURE / QUESTIONS Q1. Figure 1 shows an animal cell. Figure 1 alex-mit/istock/thinkstock (a) What is structure A? Tick one box. Cell membrane Cell wall Chromosome Cytoplasm What is structure B?
Where in the cell are proteins made? Which part of a cell controls its activities? ribosomes. nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur?
 Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Surname. Other Names. Candidate Signature
 A Surname Other Names Centre Number For Examiner s Use Candidate Number Candidate Signature Additional Science Unit Biology B2 Biology Unit Biology B2 BL2FP General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation
A Surname Other Names Centre Number For Examiner s Use Candidate Number Candidate Signature Additional Science Unit Biology B2 Biology Unit Biology B2 BL2FP General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College
 St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre Course Tasks: BIOLOGY Student Name GCSE science grade Mark /127 Percentage % This booklet contains 15 GCSE examination questions
St Robert of Newminster Catholic School and Sixth Form College Year 12 Pre Course Tasks: BIOLOGY Student Name GCSE science grade Mark /127 Percentage % This booklet contains 15 GCSE examination questions
Cells and Simple Transport Revision 2
 Cells and Simple Transport Revision 2 46 minutes 46 marks Page of 8 Q. The diagram shows a cell from a plant leaf. (a) Name structures A and B. A... B... (2) Structure C is a chloroplast. What is the function
Cells and Simple Transport Revision 2 46 minutes 46 marks Page of 8 Q. The diagram shows a cell from a plant leaf. (a) Name structures A and B. A... B... (2) Structure C is a chloroplast. What is the function
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Year 10A2 10A7. Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59%
 Year 10A2 10A7 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
Year 10A2 10A7 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Q1.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction.
 ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
ENZYMES. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Catalase is an enzyme found in many different tissues in plants and animals.it speeds up the rate of the following reaction. hydrogen peroxide water +
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The image below below shows the separated parts of a 10 cm 3 blood sample. Calculate the percentage of the blood that is made up of plasma
 Q1.The parts of the blood can be separated from each other by spinning the blood in a centrifuge. The image below below shows the separated parts of a 10 cm 3 blood sample. (a) Calculate the percentage
Q1.The parts of the blood can be separated from each other by spinning the blood in a centrifuge. The image below below shows the separated parts of a 10 cm 3 blood sample. (a) Calculate the percentage
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Animal cells: label the main parts. Plant and algal cells: label the parts Cell wall. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. nucleus. mitochondrion.
 B2 Cells and simple transport: Part 1: cell, ribosomes, respiration, chemical reactions, protein, nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplasts, cell wall, mitochondrion, vacuole, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, sap,
B2 Cells and simple transport: Part 1: cell, ribosomes, respiration, chemical reactions, protein, nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplasts, cell wall, mitochondrion, vacuole, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, sap,
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Name: Paper 1 exp skills. Class: Date: 128 minutes. Time: 126 marks. Marks: Comments:
 Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
Paper exp skills Name: Class: Date: Time: 28 minutes Marks: 26 marks Comments: Page of 46 Figure shows a human cheek cell viewed under a light microscope. Figure Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images (a)
chloroplasts cell membrane nucleus nucleus cell wall vacuole cytoplasm Animal cell Plant cell Investigating Cells Summary Booklet page 1
 1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
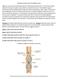 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Mark Scheme (Results) March GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules.
 The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
1 Living organisms: variety and common features
 Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
Living organisms: variety and common features Using and interpreting data a) S = scale linear and uses at least half of the grid L = lines neat, straight and through points A = axes correct way round (Temperature
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
OCR (A) Biology GCSE. Topic 1: Cell Level Systems
 OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Investigating Cells Homework and Question Booklet 1 Investigating Cells (a) Investigating Living Cells... 2 Investigating Cells (b) Investigating Diffusion...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Investigating Cells Homework and Question Booklet 1 Investigating Cells (a) Investigating Living Cells... 2 Investigating Cells (b) Investigating Diffusion...
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION TRANSPORT REGULATION SYNTHESIS EXCRETION GROWTH REPRODUCTION RESPIRATION
 8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
Section A: Organisms and Life Processes
 Section A: Organisms and Life Processes The cells of all living organisms have common features, and the organisms themselves share common processes. In this chapter you will read about these features and
Section A: Organisms and Life Processes The cells of all living organisms have common features, and the organisms themselves share common processes. In this chapter you will read about these features and
Animal Survival. Standard Grade Biology
 Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
A level Biology Preparation Work
 A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
A level Biology Preparation Work Topic Completed Score 1. Cells /26 2. Mammalian circulatory system /16 3. Transport and Exchange /22 4. Genetics /20 5. Evolution /16 6. Enzymes /17 1. Cells Units of measurement
Lady Lumley s School
 Biology @ Lady Lumley s School In order for you to be armed and ready for the Biology course you will be embarking on, we would like you to refresh your knowledge and clear up doubts before you arrive.
Biology @ Lady Lumley s School In order for you to be armed and ready for the Biology course you will be embarking on, we would like you to refresh your knowledge and clear up doubts before you arrive.
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Mark Scheme. Additional Science 4463 / Biology General Certificate of Secondary Education. BLY2F Unit Biology examination June series
 Version: 04/08/20 General Certificate of Secondary Education Additional Science 4463 / Biology 44 Unit Biology 2 Mark Scheme 20 examination June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version: 04/08/20 General Certificate of Secondary Education Additional Science 4463 / Biology 44 Unit Biology 2 Mark Scheme 20 examination June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes
 AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes Page 1 B2.1 Cells and Cell Structures Summary All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions.
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes Page 1 B2.1 Cells and Cell Structures Summary All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
B2.5 Proteins and Enzymes Home Learning Pack. Due for 2 nd September (whether we have a lesson or not!) Name: Target Grade: Grade:
 B2.5 Proteins and Enzymes Home Learning Pack Due for 2 nd September (whether we have a lesson or not!) Name: Target Grade: Grade: Heya, Your task over the summer is to teach this topic to yourself. You
B2.5 Proteins and Enzymes Home Learning Pack Due for 2 nd September (whether we have a lesson or not!) Name: Target Grade: Grade: Heya, Your task over the summer is to teach this topic to yourself. You
Name: ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2. Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 35
 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2 Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 35 The table shows the amounts of energy used in running and in walking at different speeds by people of
ADDITIONAL SCIENCE BIOLOGY EXERCISE AND HEART RATE 2 Name: Class: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 35 The table shows the amounts of energy used in running and in walking at different speeds by people of
