Digestive Physiology. For: ADVS 1110 Introduction to Animal Science
|
|
|
- Gyles Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digestive Physiology For: ADVS 1110 Introduction to Animal Science
2
3 Digestion Digestive Systems Simple Monogastric Systems: Animal Humans Monkey Pig Dog Poultry Food Class Omnivore Omnivore Omnivore Carnivore Omnivore
4 Digestion Digestive Systems Polygastric Systems: Animal Cow Sheep Goat Food Class Herbivore Herbivore Herbivore
5 Digestion Digestive Systems Monogastric Functional Cecal Systems: Animal Horse Rabbit Guinea Pig Hamster Rat Mouse Food Class Herbivore Herbivore Herbivore Omnivore Omnivore Omnivore
6 Digestion GI Tract FUNCTIONS OF THE GI TRACT: Movement of food. Secretion of digestive juices. Absorption of the digested food, water and electrolytes. Esophagus allows for the simple passage of food from one point to another. Storage of food in the body of the stomach, or fecal matter in the descending colon. Digestion of food in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Absorption of the digestive-end-products (deps) in the entire small intestine and proximal half of the colon (large).
7 Digestion GI Tract Amount of ingested food determined by: 1. Hunger the intrinsic desire for food, regardless of food type or preference. 2. Appetite the specific type of food that is preferentially sought.
8 Digestion GI Tract The mechanical aspects of food ingestion: Mastication includes chewing as well as ingestion. Incisors cutting and food intake 55 psi. Molars grinding 200 psi. Swallowing also referred to as deglutition.
9 Digestion GI Tract DENTITION: Temporary & Permanent Dentition: Horses Cattle Sheep Pig Dog Cat
10 Digestion GI Tract DENTITION/TEETH: (front to back) Incisors = I* Canines = C* Premolars = P Molars = M * Usually absent in the mare.
11 Digestion GI Tract DENTITION SECTION THROUGH A MOLAR TOOTH:
12 Digestion GI Tract TWO TYPES OF MOVEMENT IN THE GI TRACT: 1. Mixing Movements which keep the intestinal contents thoroughly mixed at all times. 2. Propulsive Movements which cause the food to move forward along the tract at an appropriate rate for digestion and absorption.
13 Digestion GI Tract OTHER TYPES OF MOVEMENTS: Peristalsis basic propulsive movement. Peristalsis is the rhythmic contractions and movements by which the GI tract propels it s contents. Distension is the usual stimulus for peristalsis. Analward Peristaltic Movements peristalsis can occur in either direction, from a stimulated point, but normally dies out rapidly in the oral direction. Gradient Theory is that there are more frequent neural impluses (peristaltic) analward than in the oral direction. Example: 11 contractions/minute vs 6-7 contractions/minute.
14 Digestion GI Tract THE HERBIVORE GI TRACT DESCENDING ORDER: 1. Oral Cavity 8. Abomasum (True Stomach) 2. Incisors 9. Small Intestine: a. Duodenum; b. Jejunum; c. Illeum 3. Molars 10. Cecum 4. Esophagus 11. Large Intestine (Colon): a. Ascending, b. Descending 5. Rumen (Paunch) 12. Rectum 6. Reticulum (Hardware Stomach; Honeycomb; Tripe) 7. Omasum (Manyplies) 13. Anus
15 Beef Cattle GI Tract
16 Digestion GI Tract Terminology: Food As It Moves Through The Digestive System 1. Feed or Feedstuff. 2. Ingesta after swallowing. 3. Cud after leaving rumen. 4. Chyme after leaving the true stomach or only stomach. 5. Digestive End Products (DEPs) those nutrient ingredients absorbed after digestion. 6. Fecal Material or Non-Digested End Products lower end of large intestine or large colon. 7. Feces waste matter removed from the rectum after all digestive processes, and deposited outside the body.
17 Digestion GI Tract The ruminant system is large in relation to the size of the animal. It s four (4) compartments are bunched and joined together to form a compact structure.
18 Digestion The most important products of the rumen fermentation vat process as illustrated in a diagrammatic form, are the Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA s) VFA s represent the major source of energy derived from the feed in a usable form.
19 Digestion GI Tract In the digestive process most feed materials follow pathways indicated by arrows. The rumen, consisting of several different regions, is much larger than the three (3) other compartments combined.
20 Digestion GI Tract The possible routes of feed in ruminants:
21 Digestion GI Tract The stomach of a monogastric animal is much smaller than that of the ruminant stomach in relation to the size of the animal and other parts of the digestive tract:
22 Digestion GI Tract Approximate relative capacity of ruminant stomach compartments: Compartment At Birth At 4 Months (%) At Maturity (%) (%) Rumen Reticulum Omasum Abomasum Total
23 Digestion GI Tract In contrast with the ruminant system, the stomach of monogastric animals has only one principal digestive cavity, including one (1) non-glandular and three (3) glandular regions:
24 Digestion GI Tract Digestive System of the Horse:
25 Digestion - Avian Digestive Tract of the Chicken:
26 Digestion GI Tract The Cecum in Various Animal Species:
27 Digestion GI Tract Digestive tract sizes and capacities of mature ruminant animals: Species Part of Digestive Tract Stomach Cow Ewe Rumen 40 gal 5 gal Reticulum 2 gal 2 qt Omasum 4 gal 1 qt Abomasum 4 gal 3 qt Small Intestine 15 gal (130 ft) 2 gal (80 ft) Large Intestine 10 gal 6 qt
28 Digestion GI Tract Comparative capacities of monogastric (simple stomach) animals: Part of Digestive Tract Horse Pig Man Stomach 20 qts 8 qts 1 qt Small Intestine 48 qts 8 qts 2 qts Large Intestine 120 qts (cecum also) 8 qts 2 qts
29 Digestion GI Tract - Summary The Digestive Pathway in Monogastrics: Mouth Esophagus Simple Stomach Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) Cecum Large Intestine Rectum Anus
30 Digestion GI Tract - Summary The Digestive Pathway in Poultry: Mouth Esophagus Crop Esophagus (stomach) Proventriculus Gizzard Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) Ceca Large Intestine Cloaca Vent
31 Digestion GI Tract - Summary The Digestive Pathway in Ruminants: Mouth Esophagus Reticulo-rumen Regurgitated, Rechewed, reinsalivated, reswallowed Reticulo-rumen Omasum Abomasum Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) Cecum Large Intestine Rectum Anus
32 Digestion Circulation of Blood in Mammals:
33 Annual Manure Production of Animals: Species Animal Weight (lb.) Total Manure Production (tons/yr) Dairy Cattle 1, Beef Cow 1, Beef Feeder Swine Sheep , Poultry Broiler Horses
34 Digestion - GI Tract The Human Alimentary Canal (GI Tract):
35 Digestion - Avian
36 Digestion - Avian Mouth no teeth; therefore coarse feed must move to gizzard. Fowl break their feed into a size that can be swallowed by pecking with their beaks or by scratching with their feet. Crop is an esophageal diverticulum and serves as a storage area for recently digested food. Proventriculus is similar to the stomach in carnivorous animals. Gizzard primary function is the reduction of the size of food particles by a grinding action. Pepsin is present, an acid-base activity takes place, along with meager proteolysis.
37 Digestion - Avian Small Intestine digestive activity here is similar as in mammals. Enzymes of the pancreas and the brush border aid in digestive activity. Monosaccharides and amino acids are carried by active transport through the gut wall. Fat absorption takes place in lower half of small intestine and enhanced by the presence of bile. Ceca most of the fiber digestion takes place here via fermentation. Large Intestine concerned with water absorption. Cloaca chamber into which the urinary and genital tracts also open into.
38 Digestion A diagram of a cross-section of the intestinal tract showing it s tissue layers:
39 Digestion - Ruminant
40 Digestion of Feed Nutrients - Ruminants
41 Digestion - Ruminant Routes of carbohydrate utilization in ruminants:
42 Digestion - Non-Ruminant
43 Digestion of Feed Nutrients Non- Ruminants
44 Digestion Non-Ruminant Routes of carbohydrate utilization in nonruminants:
45 Digestion Chemistry Location Digestive Juice Enzyme Kind of Food Acted Upon Mouth Saliva Ptyalin Starch > Maltose Stomach Gastric Pepsin Proteins > Peptones > Proteoses Stomach Gastric Rennin Casein > Paracasein Stomach Gastric Lipase Fats > Higher Fatty Acids, Glycerol
46 Digestion Chemistry Location Digestive Juice Enzyme Kind of Food Acted Upon Pancreas Pancreatic Trypsin Proteins > Proteoses & Peptones, Peptides > Amino Acids Pancreas Pancreatic Amylase Starch > Maltose > Glucose Pancreas Pancreatic Steapsin (Lipase) Fats > Higher Fatty Acids & Glycerol
47 Digestion Chemistry Location Digestive Juice Enzyme Kind of Food Acted Upon Liver Bile Bile Emulsification of fats (Liquid) Small Intestine Intestinal Juices Erepsin Peptides > Amino Acids Small Intestine Intestinal Juices Invertases (Sugar Enzymes)
48 Digestion Chemistry Location Digestive Juice Enzyme Kind of Food Acted Upon Small Intestine Intestinal Juices Invertases (Sugar Enzymes) Maltase Maltose > 2 Glucose Sucrase Sucrose > Glucose & Fructose Lactase Lactose > Glucose & Galactose
49 Digestion - Monosaccharides The more common carbohydrates, sources and functions: This is an abbreviated table and provides only a partial list of the carbohydrates (CHO s); but includes the important animal science ones. Name Sources Functions Pentoses (5-carbon) Monosaccharides Not as common Hexoses (6-carbon ) Glucose Corn syrup, fruit Principal blood sugar Fructose Fruit, honey Converted to glucose Galactose One of the two molecules in milk Converted to glucose
50 Digestion - Disaccharides The more common carbohydrates, sources and functions: Name Sources Functions Disaccharides Lactose Milk Yields glucose and galactose in digestion Maltose Germinating seeds Yields two (2) units of glucose in digestion Sucrose Cane & Sugar Beets Yields glucose and fructose in digestion
51 Digestion - Polysaccharides The more common carbohydrates, sources and functions: Name Sources Functions Pentosans Polysaccharides Hexosans Starch Seeds, tubers Principal energy source for monogastrics Cellulose Glycogen Plant leaves & stems (cell walls) Limited supply in animal tissues Major source of energy for ruminants; requires microbial enzyme cellulase Reserve form of glucose in muscles and liver
52 Digestion The Liver is vital to digestion, filtering and absorption of nutrients Liver Function: Produces exocrine secretion named bile. Bile is stored in the gall bladder until it is required for digestive purposes. Synthetic Reactions: Synthesis of certain amino acids, plasma proteins, prothrombin, antibodies, urea, creatine, cholesterol. Glycogen and glucose (gluconeogenesis). Phospholipids ( for cell membranes). Fatty acids. Ketone bodies.
53 Digestion Liver Function: (continued) Metabolic Reactions: Breakdown of glucose, glycogen, fatty acids, glycerol, amino acids Metabolism of hormones (insulin, aldosterone, testerone, estrogens, and thyroid hormone). Inter-conversion of certain amino acids to simple sugars and vice-versa. Adenine Tri-Phosphate formation. (ATP) Embryonic formation of blood cells. Destruction of aged blood cells.
54 Digestion Liver Function: (continued) Storage: Glycogen Amino acids Fats Vitamins (A, B complex, D and E) Iron and Copper. Detoxification Conversion of toxic substances to harmless compounds.
55 Digestion Hormones Other Than Those of the Pituitary: Hormone Source Primary Function Thyroxin Thyroid Growth, metabolic rate Thyrocalcitonin Thyroid Lowers blood calcium and phosphate Parathyroidhormone Parathyroid Elevates blood calcium, lowers blood phosphate Epinephrine Adrenal Medulla Mobilization of glycogen, increased blood flow
56 Digestion Hormones Other Than Those of the Pituitary: Hormone Source Primary Function Insulin Pancreas Lowers blood glucose, increase utilization of glucose, and synthesis of protein and fat, decreases glucogenesis Glucocorticoids (Cortisol, Corticosterone) Mineral Corticoids (Aldosterone) Adrenal Cortex Adrenal Cortex Promotes synthesis of carbohydrates; protein breakdown Sodium retention and potassium loss through kidney
57 Digestion Hormones Important in Gastro-Intestinal Function: Hormone Origin Releasing Mechanism Gastrin Pylorus Distension and movement of stomach Function Stimulation of acid secretion by gastric glands Entero-gastrone Duodenum Fat and fatty acids + bile in duodenum Secretin Duodenum Acids and peptones in duodenum Inhibition of gastric secretion and motility Stimulation of pancreatic secretion (water & electrolytes)
58 Digestion Hormones Important in Gastro-Intestinal Function: Hormone Origin Releasing Mechanism Pancreozymin Duodenum Acids and peptones in duodenum Function Stimulation of pancreas secretion (enzymes) Chole-cystokinin Duodenum Fat in duodenum Contraction of gall bladder and relaxation of the sphincter of oddi Enterocrinin Jejunum Food digestion products Simulation of intestinal secretions: 1) sucrase; 2) maltase; 3) lactase; & 4) Intestinal lipase
59 Digestion - Blood Distribution of total blood volume in different portions of the cardiovascular system: Part of Cardiovascular System Percent of Total (%) Arterioles & Capillaries 7 Heart 9 Arteries 11 Pulmonary Circulation 12 Veins & Venules 61
60 Digestion - Blood Components of blood: Plasma: Liquid portion of blood Straw colored 55-57% of blood volume Water Electrolytes (Na +, K +, Ca ++, Cl -, HCD 3-, PO 4 ) Carbohydrates (Glucose) Lipids Vitamins Urea CO 2 (Gases from lungs or tissue) O 2
61 Digestion - Blood Components of blood: (continued) Proteins (Mostly manufactured from liver, some from cell disintegration) Important All of the prior components, Plasma and Proteins are absorbed from the gut. Formed Elements of blood: Erythrocytes RBC Leukocytes WBC Platelets: Non-nucleated Aids in clotting
62 Digestion - Blood Mammalian Heart in Longitudinal Section:
63 Digestion - Blood
64 Digestion
65 Questions?
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals. Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Monogastric. SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS
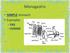 Monogastric SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS Mouth, part of digestive system. The mouth contains the TEETH, TONGUE, and SALIVARY GLAND. Chewing action or MASTICATION. Food is cut and torn in the mouth,
Monogastric SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS Mouth, part of digestive system. The mouth contains the TEETH, TONGUE, and SALIVARY GLAND. Chewing action or MASTICATION. Food is cut and torn in the mouth,
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2. By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP
 Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2 By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Digestive System Ruminant System Rumen Largest compartment Food is soaked, mixed. Microorganisms ferment the feed. Carbohydrates
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2 By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Digestive System Ruminant System Rumen Largest compartment Food is soaked, mixed. Microorganisms ferment the feed. Carbohydrates
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Figure Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore
 Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
AF 1201 Digestive System. Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences
 AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
Unit 2: Animals on the land
 GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Animal Digestion and Nutrition. Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process
 Animal Digestion and Nutrition Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process RUMINANTS Ruminant Animals Animals with complex digestive systems Capable of digesting material with a high fiber concentration
Animal Digestion and Nutrition Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process RUMINANTS Ruminant Animals Animals with complex digestive systems Capable of digesting material with a high fiber concentration
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Unit Title: Digestive Systems. Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson. Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will:
 Course: Livestock Production TEKS: 130.3(c)(5)(a) Unit Title: Digestive Systems Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will: A. Define what a digestive
Course: Livestock Production TEKS: 130.3(c)(5)(a) Unit Title: Digestive Systems Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will: A. Define what a digestive
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
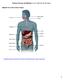 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Types of Digestive Systems. Types of Digestive Systems. Types of Digestive Systems. Types of Digestive Systems. The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Chapter 48 Types of Digestive Systems Heterotrophs are divided into three groups based on their food sources -Herbivores are animals that eat plants exclusively -Carnivores are animals
The Digestive System Chapter 48 Types of Digestive Systems Heterotrophs are divided into three groups based on their food sources -Herbivores are animals that eat plants exclusively -Carnivores are animals
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Monogastric Digestive System
 Monogastric Digestive System Matching Species Cow Pig Kangaroo Sheep Horse Dog Chicken Digestive System Ruminant Monogastric Pre-gastric Fermentation Post-gastric Fermentation Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore
Monogastric Digestive System Matching Species Cow Pig Kangaroo Sheep Horse Dog Chicken Digestive System Ruminant Monogastric Pre-gastric Fermentation Post-gastric Fermentation Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Animal Digestion and Nutrition
 Animal Digestion and Nutrition Competency: Analyze the parts and functions of the digestive system of farm animals By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Ruminants Objective: Describe the function
Animal Digestion and Nutrition Competency: Analyze the parts and functions of the digestive system of farm animals By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Ruminants Objective: Describe the function
Page 1. Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Page 1. Electrolytes. Required to maintain certain functions. Imbalance causes death. Muscles, neurons, etc.
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1
 Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1 Different Digestive Systems The three different types of digestive systems are: Monogastric Modified Monogastric Ruminant 8/7/2014 2 A few animals with ruminant digestive
Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1 Different Digestive Systems The three different types of digestive systems are: Monogastric Modified Monogastric Ruminant 8/7/2014 2 A few animals with ruminant digestive
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
Digestive System Processes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
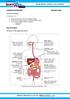 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
3/26/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores eat other
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores eat other
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition. 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations
 Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
1. Overview of Animal Nutrition
 Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition 2. Digestive Organs 3. Digestive Adaptations 1. Overview of Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed Feeding satisfies 3 requirements: 1 chemical energy
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestive Systems of Livestock. A basic Look. To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems.
 Digestive Systems of Livestock A basic Look Goal: To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems. Objectives: To understand methods of prehension. To understand the different types of digestive
Digestive Systems of Livestock A basic Look Goal: To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems. Objectives: To understand methods of prehension. To understand the different types of digestive
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Topic: Human Digestive System Page 1 of 13. The Chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed
 Figure 41.1 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores eat other animals Omnivores regularly consume
Figure 41.1 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition The Need to Feed In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores eat other animals Omnivores regularly consume
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Digestion and Nutrition. Chapter 40
 Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that you wouldn't live more than a few days without it? A) vitamins B) water C) minerals D) protein
 Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms. Mouth
 Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35
 Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE
 2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE EASY 2495 (easy) TH190/HIH705-1 Q: In reference to digestion, describe 2 main functions of the horse's mouth. A: Intake food, chew food, wet food with saliva 2496 (easy) TH93/HIH405-1,2
2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE EASY 2495 (easy) TH190/HIH705-1 Q: In reference to digestion, describe 2 main functions of the horse's mouth. A: Intake food, chew food, wet food with saliva 2496 (easy) TH93/HIH405-1,2
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Nutrition, part 2. Because 1 part isn t enough!
 Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
6) Name the phase of digestion that reduces food into smaller pieces of the same material.
 Class: import Description: Test: Digestive Test Points: 178 Test Number: 16007 Printed: 22-March-10 15:08 1) What serves as a link between the mouth and the stomach? The Larynx The Common Bile Duct The
Class: import Description: Test: Digestive Test Points: 178 Test Number: 16007 Printed: 22-March-10 15:08 1) What serves as a link between the mouth and the stomach? The Larynx The Common Bile Duct The
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Overview. Herbivore Digestive Anatomy. Herbivory. Fraction of Primary Production Consumed By Various Herbivores
 Herbivore Digestive Anatomy Integrated Rangeland Management REM 456 Sergio Arispe, Ph.D. Overview Comparative Digestive Anatomy Herbivory Anatomy Digestive End-Products Foregut Fermenters http://www.lelylife.com
Herbivore Digestive Anatomy Integrated Rangeland Management REM 456 Sergio Arispe, Ph.D. Overview Comparative Digestive Anatomy Herbivory Anatomy Digestive End-Products Foregut Fermenters http://www.lelylife.com
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
