CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION
|
|
|
- Nickolas Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION
2
3 More than 20 years ago the founding member of the Wnt gene family, Wnt-1/Int1, was discovered as a proto-oncogene activated in mammary gland tumors by the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) (293;294). Intense investigation by numerous laboratories has since clearly shown that Wnt genes and their downstream effectors play an essential role, not only during carcinogenesis, as was originally assumed, but also in a wide array of developmental processes. The major thrust of this thesis was to examine the function of Wnt signaling during early gut development, as well as intestinal organogenesis and homeostasis. As a functional model to study Wnt signaling in this context we utilized mouse lines deficient for the T cell factors: Tcf4 and Tcf1. Tcf family members are obligatory mediators of Wnt induced transcriptional activation and consequently are considered essential components of the canonical Wnt cascade. In response to Wnt stimulation, Tcfs activate transcription by forming a complex with β-catenin, which in turn serves to further recruit general transcriptional modulators such as Brg1 and CBP (41;43;295). As with many other transcription factors, in the absence of coactivators, Tcfs may recruit general repressors and thereby actively shut off transcription of target genes (50;51). In this thesis we provide genetic evidence that the activator and possibly repressor functions of Tcfs are required for proper patterning and cytodifferentiation of the gastrointestinal tract. In Chapter 2, we characterized the phenotype of compound Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos. These mutants developed major developmental defects consisting of severe posterior truncations and early gastrointestinal malformations. The first abnormality observed was the apparent absence of hindgut, as documented by the complete loss of endodermal markers in the posterior region of Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos. Although this was not addressed in Chapter 2, at least three possible explanations may account for the defects in hindgut formation. Firstly, Wnt/Tcf signals may be stimulating proliferation of posterior endodermal cells, as is known to occur at much later fetal stages in hindgut derivatives such as intestinal epithelial cells (66). Alternatively Tcf1 and Tcf4 may be promoting survival signals within endodermal cells. We believe that this scenario can be ruled out based on our observations that Tcf4/Tcf1 mutants do not show increased numbers of apoptotic cells, as evidenced by whole-mount TUNEL assays (unpublished data). Finally, besides mitotic effects, Tcf4 and Tcf1 may be regulating cell fate decision in early endodermal cells. Indeed in Chapter 2, we speculated that the ectopic neural tissue observed in the caudal regions of Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos may derive from misspecified epiblast cells, which take on a neural fate instead of an endodermal fate. Similar events are thought to occur in Lef-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos, although in this case, presomitic mesoderm is transformed into neural tubes. It should be noted, however, that in Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos the ectopic neural tissue appear as bifurcations of the neural tube and not neural tubes in place of hindgut. Consequently, the bifurcations of the neural tube may simply be a result of hyperproliferating neural cells, rather than cell fate changes in early epiblast cells. To 89
4 resolve this issue it will be necessary to determine at which time-point the ectopic neural tissue is first detected in Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos. Because Tcf4-/-/Tcf1-/- embryos survived until E15.5 we were able to assess the role of Tcf4 and Tcf1 during the patterning phase of the gut tube. As a consequence of the early hindgut defects, Tcf4/Tcf1 mutants displayed severely truncated intestines. Surprisingly in these mutants, we found clear evidence of gastro-intestinal transformations. In particular, the region morphologically appearing as duodenum had taken on a gastric fate. We hypothesized that this anterior transformation reflected a function for Tcfs in impeding the growth of the stomach. Interestingly, in support of this idea we find that Tcf4-/- stomachs display a substantial increase in the number of proliferative epithelial cells, suggesting that Tcf4 represses proliferation in stomach epithelial cells (unpublished observations). Whether this function depends on Tcf4-mediated transcriptional activation or repression remains to be resolved. Moreover if inhibition of Wnt signaling relieves growth constraints imposed upon the stomach during gut patterning, one may consider the possibility that under normal circumstances Wnt activity is effectively blocked in the prospective stomach regions of the gut tube. One possible mechanism to suppress Wnt signaling in the stomach has recently been proposed. Shivdasani and colleagues have shown that loss of the stomach specific transcription factor Barx1 prevents stomach epithelial differentiation (296). These authors went on to show that Barx1 specifies gastric fate through its ability to promote the transient expression of secreted Wnt antagonists sfrp1 and sfrp2 in the stomach mesenchyme. In Chapter 3, we moved beyond gut development to study the localization of Wnt signaling components in the mature adult intestine. Despite the wealth of genetic evidence supporting a role for Wnt signaling in the adult intestine, very little was known regarding the expression pattern of individual Wnts and their downstream signaling components in the intestine. Previously several authors hypothesized that the Wnt ligands driving proliferation of crypt epithelial cells would be expressed in surrounding mesenchymal cells (87;88). Although we found several Wnts expressed in the villus mesenchyme none were detected in crypt regions, implying that proliferation of epithelial cells may solely be driven by autocrine Wnt signals. Otherwise, we can only conclude that crypt mesenchyhmal Wnts are expressed below the detection levels of our in situ hybridization protocol. The expression of Wnts and Fzs in the differentiated compartments of the crypt/villus axis, including Wnt4, Wnt5a, Wnt2b, Fz4, Fz6 implicated a role for non-canonical Wnt signaling in the intestine. As an attempt to uncover what this function might be we have since examined intestines derived from single Wnt5a and Wnt4 mutant mice. Histological analysis, however, revealed no obvious abnormalities (data not shown). Unlike the classical Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which has one major endpoint, non-canonical Wnts induce pleiotropic cellular responses. These are often categorized into two branches, including the so-called planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway and the Wnt-Ca ++ pathway. The former stimulates cytoskeletal rearrangements through activation of the small GTPases Rho and Rac, whereas the Wnt- Ca ++ pathway relies on the following effectors phospholipase C (PLC), calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase 2 (CamK2) and protein kinase C (PKC) (297). Complicating matters further is the fact that 90
5 these non-canonical signaling components are also regulated by numerous other extracellular stimuli besides Wnts. Consequently a clear picture of the role for this pathway has yet to emerge. Besides evidence for non-canonical signaling, our screen revealed a putative role for secreted Wnt antagonists, including Wif, Dkk2, Dkk3, sfrp1 and sfrp5. The most intriguing of these factors appears to be sfrp5, based on its restricted expression immediately above the Paneth cells. The precise localization of intestinal stem cells is subject to much debate. The classical view based on radiolabeling experiments suggests that in the small intestine stem cells reside on average around the fourth cell position from the crypt bottom (298). However other reports have proposed that proliferative columnar cells (in-between Paneth cells) at the crypt bases represent the bone fide stem cell compartment (299;300). Assuming sfrp5 is uniquely expressed in stem cells, we may ask what role a Wnt antagonist may play in regulating intestinal stem cells. One of the hallmarks of stem cells is their reduced mitotic rate when compared to other crypt progenitor cells (301). Therfore sfrp5 may be required to maintain stem cells in a relative quiescent state by locally blocking the stimulatory effect of Wnts on proliferation. Another important issue, assuming again this model to be correct, is how sfrp5 expression is activated specifically in stem cells. Based on the absence of sfrp5 in adenomas and most crypt progenitor cells it is unlikely that sfrp5 is regulated by Wnt signaling. In the future it will be of interest to investigate whether other signaling pathways known to affect stem cell proliferation (eg. Notch and BMP signaling) regulate sfrp5 expression. Recent work has highlighted a putative role for sfrp5 and other sfrps in human colon cacerogenesis. The vast majority of human colon cancer cells appear to silence sfrp5 expression through methylation. Consistent with the above-mentioned model, these latest findings suggest that downregulation of sfrp5 may provide cells with a growth advantage. In Chapter 4 and 5, we identified Wnt/Tcf4 responsive genes during fetal intestinal development. In our initial microarray experiments, we noticed that the products of Paneth cells including cryptdins were amongst the most strongly downregulated genes in Tcf4-/- intestines. Paneth cells are differentiated intestinal epithelial cells which unlike other differentiated lineages reside at the very bottom of the crypts of Lieberkühn, express high levels of nuclear β-catenin and secrete at least two Wnt ligands (Wnt3 and Wnt9b). To demonstrate that Paneth cells depend on Wnt signaling to drive part of their genetic program we utilized Fz5 conditional mutant mice. As a result of defective expression of the Tcf target gene, EphB3, Fz5 deficient Paneth cells did not home the bottom of the crypts but rather scattered throughout the epithelial lining. In these mis-positioned Paneth cells cryptdin expression was abrogated. This result indicated that Wnt signaling controls proliferation of progenitors but also drives maturation of epithelial cells by regulating a post-mitotic genetic program. In Chapter 5, a more exhaustive analysis of Tcf4 responsive genes allowed us to further propose that Wnt/Tcf4 signals are involved in commitment of progenitor cells towards secretory lineages and that Tcf4 negatively regulates enterocyte differentiation. Indeed in 91
6 Tcf4-/- intestines we found a reduction in secretory cell fate determinants such as Math1 as well as Ngn3, NeuroD, Pax4 etc. and upregulation of enterocyte markers. Importantly these Tcf4-mediated effects were independent of Hes1, the well established Math1 repressor and early enterocyte determinant. A number of questions arise from these observations. Firstly, how does Tcf4 regulate Math1 expression? To answer this question we are now looking at the possibility that Tcf4 directly activates transcription of the Math1 gene. Obviously we must also consider the possibility that Tcf4 regulates Math1 via an indirect route. Regardless of the mechanism it is clear that Math1 expression is not entirely blocked following loss of Tcf4. Math1 positive cells were frequently detected near the gastro-duodenal junction and the very distal portion of Tcf4-/- intestines, albeit at reduced levels when compared to wild-type intestines (data not shown). These positional effects suggest that other factors can compensate for or take over Tcf4 function, depending on the compartment of the intestinal tract one is examining. Further supporting this view is our observation that at E18.5 in the proximal portion of the colon, loss of Tcf4 does not result in any changes in goblet cells numbers, despite the absence of proliferative cells (data not shown). It is unclear from the current reading of the literature whether these positional effects also occur in other mouse models displaying defective Wnt signaling in the intestine (ie β-catenin-/- and DkkTg mice) (65;68). On a related issue we may also question how Tcf4 negatively regulates the expression of enterocyte markers.. In Chapter 4, we demonstrated that Tcf4 promotes Paneth cell differentiation by directly activating cryptdin gene expression. In a similar manner we may propose that Tcf4 inhibits enterocyte maturation by directly repressing markers such as Fabp1, Creb3l3 and Nr1h4 etc. As with Math1, chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments will need to be performed to verify this hypothesis. As an alternative explanation, in Chapter 5 we discussed an attractive model initially proposed by van de Wetering et al. (69), whereby Tcf4 indirectly regulates enterocyte differentiation by controlling c-myc, and in turn, p21waf/cip1 levels. Loss and gain of function experiments suggest that in progenitor cells p21 is repressed by c-myc, and as c-myc levels drop, p21 is derepressed and can stimulate differentiation of progenitors. To test this hypothesis we are now examining whether expression of p21 precedes or coincides with the increase in expression of enterocyte markers seen in Tcf4-/- intestines. If so, this observation would provide indirect evidence supporting the above model. In this context it would also be interesting to verify whether the ectopic increase of enterocytic markers as a result of the inactivation of Tcf4 is blocked in a p21 deficient background. Besides p21 we shall also examine other cell cycle inhibitors, such as p27kip1 and p57kip2, both of which have been linked to differentiation processes in intestinal epithelial cells (302;303). 92
CHAPTER 3. Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. Gastroenterology 23: (2005)
 CHAPTER 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Gastroenterology 23:1825-1833 (2005) Chapter 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Alex
CHAPTER 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Gastroenterology 23:1825-1833 (2005) Chapter 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Alex
Summary and Concluding Remarks
 Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer
 19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0321-05 ( 510405) Wnt Notch BMP R735.35; R730.21 A From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer WEN Bin*, CHEN Weiwen
19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0321-05 ( 510405) Wnt Notch BMP R735.35; R730.21 A From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer WEN Bin*, CHEN Weiwen
The Evolution and Development of the Gut. Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department
 The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
C. elegans Embryonic Development
 Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5.
 The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5. Submitted for publication: Irma M. Oving *, Marielle E. van Gijn *, Johan H. van Es, Marc
The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5. Submitted for publication: Irma M. Oving *, Marielle E. van Gijn *, Johan H. van Es, Marc
Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by
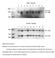 Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer
 WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer Jamie N. Anastas 1,2,3,4 and Randall T. Moon 1,2,4 Abstract Since the initial discovery of the oncogenic activity of WNT1 in mouse mammary glands,
WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer Jamie N. Anastas 1,2,3,4 and Randall T. Moon 1,2,4 Abstract Since the initial discovery of the oncogenic activity of WNT1 in mouse mammary glands,
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines
 Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4
 Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs)
 GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification
 icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 19: ,
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 19: 197-201, 2007 197 WNT antagonist, DKK2, is a Notch signaling target in intestinal stem cells: Augmentation of a negative regulation system for canonical
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 19: 197-201, 2007 197 WNT antagonist, DKK2, is a Notch signaling target in intestinal stem cells: Augmentation of a negative regulation system for canonical
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Wnt1 is epistatic to Id2 in modeling mammary gland development and in causing mammary tumors Authors: Susan Marino (smarino@cmgm.stanford.edu) Claire Romelfanger (clairefrog@yahoo.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Wnt1 is epistatic to Id2 in modeling mammary gland development and in causing mammary tumors Authors: Susan Marino (smarino@cmgm.stanford.edu) Claire Romelfanger (clairefrog@yahoo.com)
Molecular Regulation of Intestinal Stem Cells
 Molecular Regulation of Intestinal Stem Cells Review Tulay Bayram Biomedical Sciences University of Utrecht Table of contents Abstract... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Structure of the small intestine and
Molecular Regulation of Intestinal Stem Cells Review Tulay Bayram Biomedical Sciences University of Utrecht Table of contents Abstract... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1 Structure of the small intestine and
Wnt/β-catenin s regulatory role in embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation
 Wnt/β-catenin s regulatory role in embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation Wim de Jonge 3361039 Supervisor: Prof. Dr. S.J.L. van den Heuvel Group: Developmental Biology, Faculty of Science,
Wnt/β-catenin s regulatory role in embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation Wim de Jonge 3361039 Supervisor: Prof. Dr. S.J.L. van den Heuvel Group: Developmental Biology, Faculty of Science,
MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV. Slide 1
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV Slide 1 Pathways that require regulated proteolysis 1. Notch and Delta 2. Wnt/ b-catenin 3. Hedgehog 4. NFk-B Our last topic on cell signaling are pathways that
MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV Slide 1 Pathways that require regulated proteolysis 1. Notch and Delta 2. Wnt/ b-catenin 3. Hedgehog 4. NFk-B Our last topic on cell signaling are pathways that
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Recommended reading: Abbas et al. 5th edition, chapters 7 and 10; Janeway and Travers, 5th edition, chapter 7.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Stem cells in homeostasis and cancer of the gut
 Heijden and Vermeulen Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:66 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0962-x REVIEW Stem cells in homeostasis and cancer of the gut Maartje van der Heijden and Louis Vermeulen * Open Access
Heijden and Vermeulen Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:66 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0962-x REVIEW Stem cells in homeostasis and cancer of the gut Maartje van der Heijden and Louis Vermeulen * Open Access
Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Twists and Turns in the Development and Maintenance of the Mammalian Small Intestine Epithelium
 Birth Defects Research (Part C) 75:58 71 (2005) REVIEW Twists and Turns in the Development and Maintenance of the Mammalian Small Intestine Epithelium Andrew L. Hauck, Kelly S. Swanson, Paul J. A. Kenis,
Birth Defects Research (Part C) 75:58 71 (2005) REVIEW Twists and Turns in the Development and Maintenance of the Mammalian Small Intestine Epithelium Andrew L. Hauck, Kelly S. Swanson, Paul J. A. Kenis,
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Quantification of early stage lesions for loss of p53 should be shown in the main figures.
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors. Implications for adrenal diseases. Gary D.
 Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors Implications for adrenal diseases Gary D. Hammer Condensation of the Ventral Intermediate Mesoderm Forms the
Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors Implications for adrenal diseases Gary D. Hammer Condensation of the Ventral Intermediate Mesoderm Forms the
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
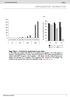 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade)
 HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Cell Type Nervous System I. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation. Human issues.
 7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition
 EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION. Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling.
 EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
The Multiple Phases and Faces of Wnt Signaling During Cardiac Differentiation and Development
 This Review is the introduction of a new thematic series on Wnts in Cardiovascular Development and Disease, which includes the following articles: An Updated Overview on Wnt Signaling Pathways: A Prelude
This Review is the introduction of a new thematic series on Wnts in Cardiovascular Development and Disease, which includes the following articles: An Updated Overview on Wnt Signaling Pathways: A Prelude
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Hematopoiesis. - Process of generation of mature blood cells. - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human)
 Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor
 BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
Meeting Report. From December 8 to 11, 2012 at Atlanta, GA, U.S.A
 Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines
 Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:887 896 Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage BENOIT A. AUCLAIR,* YANNICK D. BENOIT,* NATHALIE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:887 896 Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage BENOIT A. AUCLAIR,* YANNICK D. BENOIT,* NATHALIE
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS
 ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
 p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
CANCER. Inherited Cancer Syndromes. Affects 25% of US population. Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease)
 CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Nutritional Omics Technologies for Elucidating the Role(s) of Bioactive Food Components in Colon Cancer Prevention
 Nutritional Omics Technologies for Elucidating the Role(s) of Bioactive Food Components in Colon Cancer Prevention Dietary Components Modify Gene Expression: Implications for Carcinogenesis 1 Kan Yang,*
Nutritional Omics Technologies for Elucidating the Role(s) of Bioactive Food Components in Colon Cancer Prevention Dietary Components Modify Gene Expression: Implications for Carcinogenesis 1 Kan Yang,*
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
NUMB is a break of WNT - Notch signaling cycle
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 18: 517-521, 2006 517 NUMB is a break of WNT - Notch signaling cycle MASUKO KATOH 1 and MASARU KATOH 2 1 M&M Medical BioInformatics, Hongo 113-0033; 2 Genetics
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 18: 517-521, 2006 517 NUMB is a break of WNT - Notch signaling cycle MASUKO KATOH 1 and MASARU KATOH 2 1 M&M Medical BioInformatics, Hongo 113-0033; 2 Genetics
Supplementary Table S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort. Chr. # of Gene 2. Chr. # of Gene 1
 Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Beuling _SupplFig. 1
 euling _SupplFig. 1 Gata6: F: 5 -GGGTGTGG-3 R: 5 -GTGGTTGT-3 hga: F: 5 -GT-3 R: 5 -TTTTTTTT-3 Gcg: F: 5 -TTGGGTGGTTTG-3 R: 5 -TGGGGTGTTGTGGTG-3 Pyy: F: 5 -GGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGGGGGTG-3 Muc2: F: 5 -TTGTGTGTG-3
euling _SupplFig. 1 Gata6: F: 5 -GGGTGTGG-3 R: 5 -GTGGTTGT-3 hga: F: 5 -GT-3 R: 5 -TTTTTTTT-3 Gcg: F: 5 -TTGGGTGGTTTG-3 R: 5 -TGGGGTGTTGTGGTG-3 Pyy: F: 5 -GGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGGGGGTG-3 Muc2: F: 5 -TTGTGTGTG-3
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Cell Polarity and Cancer
 Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
5-ASA and Carcinogenesis in IBD
 5-ASA and Carcinogenesis in IBD Maikel P. Peppelenbosch Typical lunch table at the Peppelenbosch residence This seminar takes place at a most awkward time: People would rather munch their lunch in peace
5-ASA and Carcinogenesis in IBD Maikel P. Peppelenbosch Typical lunch table at the Peppelenbosch residence This seminar takes place at a most awkward time: People would rather munch their lunch in peace
The Wnt/βcatenin signaling pathway
 Wnt signaling is crucial for functioning of the endometrium The Role of Wnt Signaling in Uterus Development (I) and in Homeostasis (II) and Malignancy (III) of the Uterine Endometrium Leen J Blok Erasmus
Wnt signaling is crucial for functioning of the endometrium The Role of Wnt Signaling in Uterus Development (I) and in Homeostasis (II) and Malignancy (III) of the Uterine Endometrium Leen J Blok Erasmus
T cell development October 28, Dan Stetson
 T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal
 Related Commentary, page 2528 Research article Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal transition Erica L. McCoy,
Related Commentary, page 2528 Research article Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal transition Erica L. McCoy,
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development.
 Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Colonic polyps and colon cancer. Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern
 Colonic polyps and colon cancer Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern Improtance of the problem of colon cancers - Epidemiology Lifetime risk 5% Incidence/10 5 /annum (US Detroit
Colonic polyps and colon cancer Andrew Macpherson Director of Gastroentology University of Bern Improtance of the problem of colon cancers - Epidemiology Lifetime risk 5% Incidence/10 5 /annum (US Detroit
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis
 Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
a) They are the most common cause of pediatric kidney failure. b) They are always symptomatic. c) They can be asymmetric.
 Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance
 Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland 1. Endocrine Glands 2. Exocrine Glands Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
 Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
T Cell Development. Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD. November 3, 2015
 T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium
 Article Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium Katja Horvay 1, Thierry Jardé 1, Franca Casagranda 2, Victoria M Perreau 2, Katharina Haigh
Article Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium Katja Horvay 1, Thierry Jardé 1, Franca Casagranda 2, Victoria M Perreau 2, Katharina Haigh
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
