Beuling _SupplFig. 1
|
|
|
- Mitchell Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 euling _SupplFig. 1 Gata6: F: 5 -GGGTGTGG-3 R: 5 -GTGGTTGT-3 hga: F: 5 -GT-3 R: 5 -TTTTTTTT-3 Gcg: F: 5 -TTGGGTGGTTTG-3 R: 5 -TGGGGTGTTGTGGTG-3 Pyy: F: 5 -GGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGGGGGTG-3 Muc2: F: 5 -TTGTGTGTG-3 R: 5 -TGTTGTGGTG-3 Tff3: F: 5 -GTGGTTGG-3 R: 5 -GTGTGGGG-3 Lyz: F: 5 -TTTTGTTTTGT-3 R: 5 -GTGGTGTTGGTT-3 Defa1: F: 5 -GGGGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGTTTTTGGTTT-3 Fzd5: F: 5 -GTGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGTGGTG-3 Β-catenin: F: 5 -TTTGGTGG-3 R: 5 -GTGTGGTTTT-3 c-myc: F: 5 -TTGGTTTTG-3 R: 5 -GGGT-3 d44: F: 5 -TGTTGTTT-3 R: 5 -TTGTGTGTGGTGTG-3 Lgr5: F: 5 -TTTTGTGTT-3 R: 5 -TGGTGTTTGTGT-3 Ephb2: F: 5 -TTGTGTGGTGTTTG-3 R: 5 -GTGTGGTGTGTGTTGTG-3 Ephb3: F: 5 -GGGGTTGG-3 R: 5 -TGTGTGGT-3 Sox9: F: 5 -GGGGTTT -3 R: 5 -GGTTGGGG -3 Gfi1: F: 5 -TGGTGTGTGTTT-3 R: 5 -TGTTTGGTGGTTT-3 Spdef: F: 5 -TGTTGGGT-3 R: 5 -GTTTGTGTT-3 Ngn3: F: 5 -TGGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGGGGTGGGGG-3 Dll1: F: 5 -TTGT-3 R: 5 -GTTTGTGTG-3
2 euling _SupplFig. 1 (cont d) sbt: ar1: poa1: Gata4: Lph: Defa4 Gapdh: F: 5 -TTGTTTGTT-3 R: 5 -GGGGTG-3 F: 5 -GGTGT-3 R: 5 -TTTGG-3 F: 5 -GGTTTGGGTT-3 R: 5 -GTTTGTTTTT-3 F: 5 -TTTGGGGTTGGG-3 R: 5 -GTGGGGTGTG-3 F: 5 -GGTGGGG-3 R: 5 -GGGTTGGGG-3 F: 5 -GGTTTTTTTTTGG-3 R: 3 -GGGGGGTT-3 F: 5 -GTTGTGTTT-3 R: 5 -TGTGTTTT-3 Supplementary Figure 1. Primer sequences used for quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reactions (qrt-pr).
3 euling _SupplFig. 2 D E GT6 / DEF-RS Ki67 GT6 GT6 GT6 HG / GT6 Supplementary Figure 2. GT6 is expressed in all differentiated and proliferating cells in the mature mouse small intestinal epithelium. Immunostaining with rabbit anti-gt6 (1:5, Santa ruz) (-E) revealed that GT6 is expressed in absorptive enterocytes (), goblet cells (), chromogranin (HG)-positive enteroendocrine cells (), alpha-defensin related sequence (DEF-RS)-positive Paneth cells (D) and in Ki67- positive nuclei of proliferating crypt cells as determined on serial sections (E) with the highest staining intensity in the proliferative crypt compartment. iotinylated secondary antibodies were linked to avidin-horseradish peroxidase or avidin-alkaline phosphatase conjugates (Vector Labs), and visualized using 3,3 -diamino benzidine (D) for 2-5 min or 4-nitro blue tetrazolium chloride (NT)/5-bromo-4-chloro-3indolyl-phosphate (IP) for 5-2 min, respectively. Methyl Green was used as a counterstain. rrowheads indicate GT6- positive nuclei.
4 euling _SupplFig. 3 Gata6 loxp Gata6 del VillinreER T2 1 3 Small intestine Prox Mid Dist Gata6 Gapdh Gata6 Gapdh mrn abundance (relative to ) Gata *** Supplementary Figure 3. onditional, inducible deletion of Gata6 in adult mouse intestine. () Schematic representation of the Gata6 loxp and Gata6 del alleles (Sodhi P, et al, M Dev iol 26;6:19) used in this study. VillinreER T2 -mediated recombination of the inserted loxp sites results in the deletion of exon 2 of the Gata6 allele. oxes with numbers indicate exons. Red arrowheads indicate loxp sites. () Semi-quantitative RT-PR revealed that Gata6 mrn is expressed normally in mice (Gata6 loxp/loxp, VillinreER T2 negative) and is specifically deleted in the intestine of mice (Gata6 loxp/loxp, VillinreER T2 positive). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) mrn was used as a positive control. () Quantitative RT-PR showed a >9% decrease in Gata6 mrn abundance in as compared to ileum (***P<.1, as compared to, n=5 in each group). Primer sequences used: F:5 - GGGTGTGG-3, R:5 -GTGGTTGT-3.
5 euling _SupplFig. 4 Process Lipid metabolic process ellular lipid metabolic process Organic acid metabolic process Steroid metabolic process arboxylic acid metabolic process Lipid biosynthetic process ellular alcohol metabolic process Oxidative reduction Monocarboxylic acid metabolic process Steroid biosynthetic process -log(p-value) Supplemental Figure 4. Intestinal Gata6 deletion results in aberrant cellular differentiation. Microarray analyses on (1-3) and (KO1-3) ileum (n=3 in each group) revealed transcript-level changes after Gata6 deletion. Significantly differentially expressed transcripts were determined at the 5% FDR level using Significance nalysis of Microarrays (SM) and then visualized using Gene luster and Treeview. () Goblet cell markers were increased, Paneth and enteroendocrine cell markers were decreased, and secretory lineage regulators showed a mixed response. () Markers for the top 15 up- and down-regulated absorptive enterocyte genes. Green, down-regulated; red, up-regulated; level of color saturation = magnitude of regulation compared to. () Gene Ontology data showing the processes most likely to be affected by conditional Gata6 deletion.
6 euling _SupplFig. 5 Lyz mrn abundance (relative to ) weeks wks 2wks 3wks 4wks Supplementary Figure 5. Intestinal Gata6 deletion results in a gradual disappearance of Paneth cells. () Quantitative RT-PR showed a gradual decrease in Lyz mrn abundance beginning after two weeks, and reaching the lowest level at four weeks after the 5-day tamoxifen treatment (n=1 in each group). () Structural analysis by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on sections harvested, 2, 3 and 4 weeks after the 5-day tamoxifen treatment revealed that Paneth cells disappear, while goblet-like cells accumulate gradually over 4 weeks after tamoxifen treatment in the crypts of ileum.
7 euling _SupplFig. 6 mrn abundance (relative to ) Lyz Defa4 *** LYZ Supplemental Figure 6. Intestinal Gata6 deletion results in an increase in Paneth cells markers in the duodenum. () qrt-pr showed increases in lysozyme (Lyz) and alpha-defensin 4 (Defa4) mrn abundance after Gata6 deletion. ***P<.1, as compared to. () Immunohistochemistry revealed an increased intensity and a more widespread pattern of LYZ staining in duodenal crypts after Gata6 deletion.
8 euling _Suppl Fig. 7 G6G4del Ki67 mrn abundance (relative to ) Ngn3 ** G6G4del mrn abundance (relative to ) Lyz G6G4del D mrn abundance (relative to ) ar1 * G6G4del Supplemental Figure 7. GT4 is redundant for most GT6 functions in the mature duodenum. () Sections stained for Ki67 revealed a decrease in the number of Ki67-positive cells per crypt in G6G4del as compared to duodenum. qrt-pr showed decreases in () neurogenin 3 (Ngn3) and () lysozyme (Lyz) mrn abundances, and (D) an increase in carbonic anhydrase (ar1) mrn abundance in G6G4del as compared to duodenum. *P<.5, **P<.1, as compared to.
Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by
 Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification
 icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of phospho-sik3 in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage in the knee. (a) Semiserial histological sections
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of phospho-sik3 in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage in the knee. (a) Semiserial histological sections of normal cartilage were stained with safranin O-fast
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of phospho-sik3 in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage in the knee. (a) Semiserial histological sections of normal cartilage were stained with safranin O-fast
Summary and Concluding Remarks
 Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION
 CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION More than 20 years ago the founding member of the Wnt gene family, Wnt-1/Int1, was discovered as a proto-oncogene activated in mammary gland tumors by the mouse mammary
CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION More than 20 years ago the founding member of the Wnt gene family, Wnt-1/Int1, was discovered as a proto-oncogene activated in mammary gland tumors by the mouse mammary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis
 Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Sarah F. Andres, 1 M. Agostina Santoro, 1 Amanda T. Mah, 2 J. Adeola Keku, 1 Amy E. Bortvedt, 1 R. Eric Blue, 1 and P.
 m J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 38: G1 G111, 215. First published November 13, 214; doi:1.1152ajpgi.287.214. Deletion of intestinal epithelial insulin receptor attenuates high-fat diet-induced elevations
m J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 38: G1 G111, 215. First published November 13, 214; doi:1.1152ajpgi.287.214. Deletion of intestinal epithelial insulin receptor attenuates high-fat diet-induced elevations
Expanded View Figures
 Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
Shao-Ming Shen et al Role of I in MT of cancers MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. nalysis of the expression of I isoforms in cancer cells and their interaction with PTN. RT PR detection of Ish and
F-box and WD Repeat Domain-Containing 7 Regulates Intestinal Cell Lineage Commitment and Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2010;139:929 941 F-box and WD Repeat Domain-Containing 7 Regulates Intestinal Cell Lineage Commitment and Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor ROCIO SANCHO,* ANETT JANDKE,* HAYLEY DAVIS,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2010;139:929 941 F-box and WD Repeat Domain-Containing 7 Regulates Intestinal Cell Lineage Commitment and Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor ROCIO SANCHO,* ANETT JANDKE,* HAYLEY DAVIS,
Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TCAGCCGATTTGCTATCTCAT A
 Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Imtiyaz et al., Fig. S1
 . Imtiyaz et al., Fig. S1 1. 1.1 1% O.1.5 Lin/Sca-1/IL-7Rα GMPs.17 MPs.3 Days 3% O.1 MEPs.35 D3 Days 1, N, N, H, H 1 1 Days Supplemental Figure S1. Macrophage maturation, proliferation and survival are
. Imtiyaz et al., Fig. S1 1. 1.1 1% O.1.5 Lin/Sca-1/IL-7Rα GMPs.17 MPs.3 Days 3% O.1 MEPs.35 D3 Days 1, N, N, H, H 1 1 Days Supplemental Figure S1. Macrophage maturation, proliferation and survival are
Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:887 896 Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage BENOIT A. AUCLAIR,* YANNICK D. BENOIT,* NATHALIE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2007;133:887 896 Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Is Essential for Terminal Differentiation of the Intestinal Secretory Cell Lineage BENOIT A. AUCLAIR,* YANNICK D. BENOIT,* NATHALIE
CHAPTER 3. Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. Gastroenterology 23: (2005)
 CHAPTER 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Gastroenterology 23:1825-1833 (2005) Chapter 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Alex
CHAPTER 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Gastroenterology 23:1825-1833 (2005) Chapter 3 Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine Alex
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Figure 1. Dnmt3b expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. (A) Representative images
 Figure Legends Figure. expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. () Representative images showing that Dnmta is not expressed in chondrocytes from mo W articular cartilage [Dnmta expression
Figure Legends Figure. expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. () Representative images showing that Dnmta is not expressed in chondrocytes from mo W articular cartilage [Dnmta expression
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice
 Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Supplementary Figure 1: Co-localization of reconstituted L-PTC and dendritic cells
 a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
Spdef deletion rescues the crypt cell proliferation defect in conditional Gata6 null mouse small intestine
 Spdef deletion rescues the crypt cell proliferation defect in conditional Gata6 null mouse small intestine The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Spdef deletion rescues the crypt cell proliferation defect in conditional Gata6 null mouse small intestine The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22
 Supplementary Information High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22 Max Gulhane 1, Lydia Murray 1, Rohan Lourie 1, Hui Tong 1, Yong H. Sheng 1, Ran
Supplementary Information High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22 Max Gulhane 1, Lydia Murray 1, Rohan Lourie 1, Hui Tong 1, Yong H. Sheng 1, Ran
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from
 Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
PepT1 Expression Helps Maintain Intestinal Homeostasis by Mediating the Differential. Expression of mirnas along the Crypt-Villus Axis
 PepT Expression Helps Maintain Intestinal Homeostasis by Mediating the Differential Expression of mirnas along the Crypt-Villus Axis Yuchen Zhang,*, Emilie Viennois, Mingzhen Zhang, Bo Xiao, 3, Moon Kwon
PepT Expression Helps Maintain Intestinal Homeostasis by Mediating the Differential Expression of mirnas along the Crypt-Villus Axis Yuchen Zhang,*, Emilie Viennois, Mingzhen Zhang, Bo Xiao, 3, Moon Kwon
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis
 High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure S1. Representative CRBP-1 immunostaining of non-neoplastic
High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure S1. Representative CRBP-1 immunostaining of non-neoplastic
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Fig. S1. Gpa33 -/- mice do not express Gpa33 mrna or GPA33 protein. (A) The Gpa33 null allele contains a premature translational stop codon (STOP) in exon 2, and almost all of the
Supplementary Material Fig. S1. Gpa33 -/- mice do not express Gpa33 mrna or GPA33 protein. (A) The Gpa33 null allele contains a premature translational stop codon (STOP) in exon 2, and almost all of the
Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium
 Article Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium Katja Horvay 1, Thierry Jardé 1, Franca Casagranda 2, Victoria M Perreau 2, Katharina Haigh
Article Snai1 regulates cell lineage allocation and stem cell maintenance in the mouse intestinal epithelium Katja Horvay 1, Thierry Jardé 1, Franca Casagranda 2, Victoria M Perreau 2, Katharina Haigh
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Dll1- and Dll4-Mediated Notch Signaling Are Required for Homeostasis of Intestinal Stem Cells
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1230 1240 Dll1- and Dll4-Mediated Notch Signaling Are Required for Homeostasis of Intestinal Stem Cells LUCA PELLEGRINET,* VERONICA RODILLA, ZHENYI LIU, SHUANG CHEN, UTE KOCH,*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1230 1240 Dll1- and Dll4-Mediated Notch Signaling Are Required for Homeostasis of Intestinal Stem Cells LUCA PELLEGRINET,* VERONICA RODILLA, ZHENYI LIU, SHUANG CHEN, UTE KOCH,*
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
AdPLA ablation increases lipolysis and prevents obesity induced by high fat feeding or leptin deficiency
 AdPLA AdPLA ablation increases lipolysis and prevents obesity induced by high fat feeding or leptin deficiency Kathy Jaworski, Maryam Ahmadian, Robin E. Duncan, Eszter Sarkadi-Nagy, Krista A. Va rady,
AdPLA AdPLA ablation increases lipolysis and prevents obesity induced by high fat feeding or leptin deficiency Kathy Jaworski, Maryam Ahmadian, Robin E. Duncan, Eszter Sarkadi-Nagy, Krista A. Va rady,
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis
 Downloaded from http:// on July 11, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395 Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim
Downloaded from http:// on July 11, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395 Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5.
 The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5. Submitted for publication: Irma M. Oving *, Marielle E. van Gijn *, Johan H. van Es, Marc
The Wnt target MASH-2 regulates expression of the putative intestinal specific stemcell markers Sox4 and Sfrp5. Submitted for publication: Irma M. Oving *, Marielle E. van Gijn *, Johan H. van Es, Marc
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplemental Tables and Figures. The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate,
 Supplemental Tables and Figures The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate, tendon-specific protective mechanism against heterotopic ossification Timothy Mead et al Supplemental
Supplemental Tables and Figures The metalloproteinase-proteoglycans ADAMTS7 and ADAMTS12 provide an innate, tendon-specific protective mechanism against heterotopic ossification Timothy Mead et al Supplemental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Development Supplementary information. Supplementary Figures * * +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/-
 Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia/epithelial hyperplasia (AAH/EH),
Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia/epithelial hyperplasia (AAH/EH),
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Atg5 flox/flox ; CAG-Cre, 19M brain heart lung. spleen stomach colon. Takamura_Fig. S1
 Takamura_Fig. S1 brain heart lung spleen stomach colon kidney SM Supplemental Figure 1 Histological findings of tg5 flox/flox ;CG-Cre mouse tissues. H&E staining of the brain, heart, lung, spleen, stomach,
Takamura_Fig. S1 brain heart lung spleen stomach colon kidney SM Supplemental Figure 1 Histological findings of tg5 flox/flox ;CG-Cre mouse tissues. H&E staining of the brain, heart, lung, spleen, stomach,
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Figure 1
 VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
Glutamine supplementation improves intestinal cell proliferation and stem cell differentiation in weanling mice
 food & nutrition research ORIGINAL ARTICLE Glutamine supplementation improves intestinal cell proliferation and stem cell differentiation in weanling mice Siyuan Chen 1, Yaoyao Xia 1, Guoqiang Zhu 2, Jiameng
food & nutrition research ORIGINAL ARTICLE Glutamine supplementation improves intestinal cell proliferation and stem cell differentiation in weanling mice Siyuan Chen 1, Yaoyao Xia 1, Guoqiang Zhu 2, Jiameng
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
2.28E E AKT/CAT P-3-4:
 Supplemental Table 1: IPA network analysis of the microarray data presented in Figure 6 showing the most significant molecular and cellular function classifications along with the respective number of
Supplemental Table 1: IPA network analysis of the microarray data presented in Figure 6 showing the most significant molecular and cellular function classifications along with the respective number of
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Supplementary Figures. T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ
 Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplemental Data. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors. Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte
 Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
Supplemental Data Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Mesenchymal Progenitors Controls Osteoblast and Chondrocyte Differentiation during Vertebrate Skeletogenesis Timothy F. Day, Xizhi Guo, Lisa Garrett-Beal, and
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
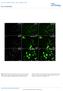
Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W. Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W
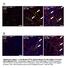 A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overview of the transplant procedure and supplementary data to Figure 1. a. Under isofluorane anesthesia, the lumen of the colon is washed by a gentle PBS enema. b. Using a p200
Supplementary Figure 1 Overview of the transplant procedure and supplementary data to Figure 1. a. Under isofluorane anesthesia, the lumen of the colon is washed by a gentle PBS enema. b. Using a p200
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]
![1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h] 1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]](/thumbs/87/97258189.jpg) 7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Lactase, sucrase-isomaltase, and carbamoyl phosphate synthase I expression in human intestine van Beers, E.H. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 10 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas
 a CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 1 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas.5 1 2 4 6 2 4 6 Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas b Heart Lung Pancreas Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas
a CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 1 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas.5 1 2 4 6 2 4 6 Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas b Heart Lung Pancreas Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas
Supporting Information. Supporting Tables. S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Product size. Gene Primer pairs
 Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
The Role of MicroRNAs in NEC Misty Good, MD
 The Role of MicroRNAs in NEC Misty Good, MD Neonatologist, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Newborn Medicine, Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Department of Pediatrics, University of Pittsburgh
The Role of MicroRNAs in NEC Misty Good, MD Neonatologist, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Newborn Medicine, Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Department of Pediatrics, University of Pittsburgh
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
