ENZYME ACTIVITY OF HUMAN MILK DURING THE FIRST MONTH OF LACTATION
|
|
|
- Brandon Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article UDC: : : ENZYME ACTIVITY OF HUMAN MILK DURING THE FIRST MONTH OF LACTATION Gordana Kocić 1, Ljiljana Bjelaković 2, Tatjana Cvetković 1, Zoran Pop-Trajković 3, Marina Jonović 3, Bojko Bjelaković 2, Dušan Sokolović 1, Tatjana Jevtović 1 and Dušica Stojanović 4 The dynamic of enzyme activities in human colostrum and milk changes, depending on the lactation stimulation. The aim of the study was to study the activity of alkaline phosphatase, amylase, transaminases (ALT and AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the samples of human colostrum and mature milk obtained by manual squeezing. The study involved 35 women, years of age, who had given birth at the Clinic for Gynecology and Obstetrics, Faculty of Medicine in Niš, with normal delivery, without any complications reported. The samples of colostrum and milk were collected by mechanical squeezing of milk during three intervals: the first sample of colostrum was obtained immediately after the appearance of the first drops of milk after childbirth; the second sample was obtained after 24 hours, and the third after one month. The samples were collected in the morning, and kept in sterile test tubes in the freezer until the performance of analysis. The activity of these enzymes was reduced (statistically significant for amylase) in the period after one month, which means that it corresponded to the amount of protein. The activity of transaminases (ALT and AST) and alkaline phosphatase activity showed a tendency to fall after a month, but statistically significant difference was obtained with AST. The dynamic of alkaline phosphatase activity showed statistically significant decrease after one month. Enzyme activity in human milk represents an important field of research, from the aspect of functional importance and benefits of human milk compared to the cow s milk, in which enzymes are generally destroyed by pasteurization. On the other hand, increased activity of certain enzymes may be a useful and valid diagnostic marker of mechanical tissue irritation, epithelial desqamation and increase of the concentration of inflammatory cells during mastitis. Acta Medica Medianae 2010;49(2): Key words: human milk, colostrum, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, transaminase, lactate-dehydrogenase Institute of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine in Niš 1 Children's Internal Clinic, Clinical Center Niš 2 Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Faculty of Medicine in Niš 3 Public Health Institute Niš 4 Contact: Gordana Kocić Biohemijski Institut, Medicinski fakultet Niš Bulevar dr Zorana Đinđića 81, Niš, Srbija gkocic@medfak.ni.ac.rs Introduction Milk represents the basis of nutrition, a medium that embodies the perfection of nature reflected in the survival and upbringing of the offspring of mammals. From the chemical point of view, milk represents a stable fat emulsion in colloidal solution of proteins and genuine solution of lactose and mineral matter. The great nutritional and biochemical-metabolic significance of milk in the nourishment of the newborns and infants stems from its richness in vitamins, enzymes, as well as cellular elements that have an active role in protection from infections (1-4). Although at first sight milk appears to be a homogenous liquid, its ultrastructural content reveals the following elements: whey (rich in peptides, minerals and carbohydrates), fat globules which represent lipoprotein complexes, protein micelles primarily casein, and membranous vesicular complex known as the exosomes (1-5). The study of enzyme activity in milk started at the end of the 19 th century. The first findings of enzyme activity in colostrum and milk were followed by a number of clinical and experimental studies which aimed at explaining the reasons, i.e. the sources of enzymes in milk. Enzymes may be present during various milk phases depending on their primary localization, physicalchemical properties and the major reason of their existence in milk. The presence of enzymes in milk is a consequence of spontaneous diffusion of low molecular weight enzymes from plasma, active secretion from apical parts of the mammary gland epithelium or a result of enzymes leaving somatic cells which are present in secreted milk, most often leukocytes or other macrophage cells. At the beginning of the 21 st century it was already known that human colostrum and milk may contain over 70 different enzymes. Even after more than a century of studying milk enzymes, 20
2 Acta Medica Medianae 2010, Vol.49(2) Enzyme activity of human milk during the first month of lactation their exact role and significance in milk cannot be defined with certainty. For some of them, such as xanthine oxidase, lactoperoxidase and lysozyme, the active antimicrobial role in the production of free radicals has been proved. Other enzymes help the digestion of various substances in still undeveloped digestive tract of newborns (pancreatic lipase and amylase). The enzymes from apical parts of epithelial cells increase during inflammatory processes of various etiologies when a greater epithelial desquamation takes place. Another reason for increased activity during inflammatory processes is an extravasation of leukocytes to the area of inflammation. If the inflammation is systemic, the milk enzymes increase due to the transfer from plasma on the basis of concentration gradient. However, the results of some studies showed that the activity of certain enzymes is much greater in milk and cannot be correlated to an increased activity in plasma. One of the reasons for increased enzyme activity in milk is the departure from myoepithelial cells as a consequence of mechanical pressure (milking). The fact that some enzymes are present in milk due to the separation of apical part of epithelial cells is confirmed by the findings that their substrates are often absent from milk, as well as that for a certain number of enzymes the ph balance of milk is far from optimal. Many milk enzymes have some useful effects on the digestive tract of a newborn and this confirms the advantage of breastfeeding over artificial nutrition (4-6). The dynamics of enzyme activity in human colostrum and milk changes depending on the lactation stimulation, mechanical pressure upon squeezing, as well as in relation to the amount of proteins and cells present in milk. Having this in mind, this study aims at examining the activity of alkaline phosphatase, amylase, transaminases (ALT and AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the samples of human colostrum and milk obtained by manual squeezing. Examinees and methods The study included 35 women, aged who had given birth at the Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics in Niš, with normal delivery without complications such as diabetes, hypertension or eclampsia. The women did not suffer from acute or chronic diseases and had a common, non-vegetarian diet. The colostrum and milk samples were collected by mechanical squeezing in three intervals: the first colostrum sample was obtained immediately after the appearance of the first milk drops upon delivery; the second sample was collected after 24 hours and the third was collected after one month. The samples were collected in the morning before breastfeeding and kept in sterile test tubes in a freezer until the analysis was performed. The activity of alkaline phosphatase, amylase, transaminases (ALT and AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LHD) was determined using readymade tests by Bio Systems on an A25 biochemical analyzer. The total amounts of proteins and albumin were determined in the same way. Statistical analysis included determining the mean value and standard deviation and was performed using the Anova test. Statistical significance appeared in the samples with t>0.05. Results The results of the research are shown in Graphs 1, 2, and 3. Graph 1 displays the total amount of proteins and albumin in milk including the described dynamics. In the first sample, the colostrum is yellowish in color and has a high viscosity. The concentration of proteins in it is usually the highest. Our research had the same results, with the total amount of proteins and albumin significantly different on the second day and after one month, as compared to the first sample. Graph 1. Dynamics of the total amount of proteins and albumin in colostrum and mature milk 21
3 Enzyme activity of human milk during the first month of lactation Gordana Kocić et al. Graph 2. Dynamics of the activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and amylase in colostrum and mature milk Graph 3. Dynamics of the activity of transaminases (ALT and AST) and alkaline phosphatase in colostrum and mature milk 22 Discussion Colostrum, the first milk, is secreted during the first two to seven days after delivery and it provides the newly born child with all the necessary nutrients. Transitional milk is secreted during the next two weeks and is followed by mature milk which appears in the third week after delivery. The average content of human milk is around 86-87% water and 13-14% dry matter. Dry matter is composed of the following substances: organic matter which is mostly formed of proteins (about 2.5%) in colostrum and up to 1.5% in mature milk. The proteins for the most part include casein, lactalbumin and lactoglobulin. Casein is the major milk protein, present in at least four forms; it represents a complete protein, rich in all essential amino acids. The nutritive value of milk and dairy products is the result of the presence of essential amino acids. Recently, data have shed light on the significance of breastfeeding from the aspect of harmful effects of cow s casein. This particularly refers to β- casein type A. This type of casein is also responsible for immunogenic effects of cow s milk and the development of type 1 diabetes, as well as neuropsychiatric defects mostly in children who had been fed by cow s milk. Therefore, human milk represents
4 Acta Medica Medianae 2010, Vol.49(2) Enzyme activity of human milk during the first month of lactation the most natural way of nutrition of newborns and infants and should be valued as much as possible. Albumin is mostly obtained from serum, so it can be taken as a marker of the plasma-milk barrier (5, 6). The amount of proteins in colostrum is greater because an infant develops quickly but does not possess enough strength to suckle actively for a long time. Therefore, a small amount of milk should satisfy all the needs of a newborn. The results of this study (Graph 1) confirmed the dynamics described in literature. Lactate-dehydrogenase is an NAD-dependent enzyme included in the metabolism of glucose in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Therefore, the distribution of isoenzyme forms changes depending on the supply of oxygen to tissues and metabolic activity of tissues. The major source of enzymes in milk is the epithelium of the mammary gland. Some studies have shown that LDH activity is correlated to active milk secretion so that it represents a constitutive component. Increased activity in the first colostrum may be a consequence of an overall increase in the amount of proteins, as well as of proteins leaving myoepithelial and muscle cells caused by mechanical milk squeezing (1,2,4). As for specific enzyme activity in relation to the total amount of proteins, it may be concluded that an enzyme maintains high concentrations even after a period of one month (Graph 2). Amylase is an enzyme that belongs to the class of hydrolytic enzymes included in the digestion of starch. It was the first enzyme isolated in milk at the end of the 19 th century. It was shown later that the main component is α- amylase and it is interesting that amylase activity in human milk is more than times higher than in cow s milk. This enzyme is homologous to the salivary amylase and is times more active than in plasma. These findings show that the presence of enzymes in milk is the result of neither the passive diffusion from plasma nor their presence in the apical part of outlet ducts but that they are products of active secretion. Considering that milk does not contain starch, one of the assumptions is that amylase is necessary for breaking down the oligosaccharide units which are present in milk (5, 7, 8). But milk oligosaccharides contain fucose and N-acetylneuraminic acid, types of monosaccharides which cannot be broken down by α-amylase, the same way it cannot break down lactose, the main disaccharide. One of the hypotheses is that amylase is also produced as a compensatory component in the undeveloped digestive enzymatic system of a newborn child who possesses only % of the total amylase activity that takes place in adults. This enzyme is capable of breaking down the polysaccharide bacteria capsules, so its antimicrobial effect is undeniable. The decrease in activity during lactation after a period of one month is in accordance with the decrease in proteins as well as with the development of the digestive system of infants who do not need this enzyme anymore. The richness of mother s milk in amylase explains why children feeding on human milk are able to digest carbohydrate meals earlier and much better than children taking artificial food (9, 10). Alkaline phosphatase in human milk was discovered at the beginning of the 20 th century. It is a membranous enzyme particularly present in lipoprotein structures of the Golgi complex. Therefore, it is not surprising that it is secreted in milk in high concentrations. Considering the structural homology, alkaline phosphatase from milk is very homologous to the enzyme in liver and placenta because, besides structural homology, it also has a similar bond with phosphatidylinositol in the lipoprotein complex of the membrane. These kinds of membranous fat globules are actively secreted in milk. More complex researches of the structure and origin have shown that milk contains two forms of enzymes, one from myoepithelial cells and the other from cytoplasm (11,12). The richness of canaliculi epithelium in this enzyme points to the reason why it can be taken as a marker of mastitis. Our research also had samples of milk with very high alkaline phosphatase activity which is the result of mastitis developed as a consequence of mechanical irritation due to milking and milk retention (Graph 3). Alanine transferase (ALT-GPT) and aspartatetrasferase (AST-GOT) are transaminases which transfer amino groups from amino acids to α- Ketoglutaric acid, although this reaction is also reversible. The origin of ALT is strictly cytosolar whereas AST is localized in cytoplasm and mitochondria. During mastitis, the activity of these enzymes increases. AST may also be increased as a consequence of irritation of the surrounding muscle tissue and myoepithelial cells. After a period of one month, the activity of milk enzymes decreases but the AST/ALT activity ratio is lower than 1, which means that it does not completely imitate the relation in the cytoplasm (1, 2, 13). It may be concluded that enzyme activity in human milk represents a significant field of research from the point of view of functional significance and advantages of human milk over cow s milk in which enzymes are mostly destroyed by pasteurization. On the other hand, increased activity of some enzymes may be a useful and valid diagnostic marker of mechanical tissue irritation, epithelial desquamation and increase of the concentration of inflammatory cells during mastitis. 23
5 Enzyme activity of human milk during the first month of lactation Gordana Kocić et al. References 1. Fox PF, Kelly AL. Indigenous enzymes in milk: Overview and historical aspects Part 1. Int Dairy J 2006; 16: Kelly AL, O Flaherty FO, Fox PF. Indigenous proteolytic enzymes in milk: A brief overview of the present state of knowledge. Int Dairy J2006; Kitchen BJ. Review of the Progress of Dairy Science, bovine mastitis: Compositional changes and related diagnostic tests. J Dairy Res 1981; 48: Velonà T, Abbiati L, Beretta B, Gaiaschi A, Flaùto U, Tagliabue P, Galli CL, Restani P. Protein profiles in breast milk from mothers delivering term and preterm babies. Pediatr Res 1999;45: Heyndrickx GV. Further investigations on the enzymes in human milk. Paediatrics 1963;31: Zimecki M, Kruzel ML. Milk-derived proteins and peptides of potential therapeutic and nutritive value. J Exp Ther Oncol 2007; 6(2): Kunz GMJ, C., Kinne-Saffran E, Rudloff S. Human milk oligosaccharides are minimally digested in vitro. Journal of Nutrition 2002; 130: Miller JB, McVeigh P. Human milk oligosaccharides, 130 reasons to breast feed. Br J Nutr 1999; 82: Lindberg T, Skude G. Amylase in human milk. Pediatrics 1982; 70: Heitlinger LA, Lle PC, Dillon WP, Labenthal F. Mammary amylase, a possible alternative pathway of carbohydrate digestion in infancy. Pediatric Res 1983; 17: Bingham EW, Garver K, Powlem D. Purification and properties of alkaline phosphatase in the lactating bovine mammary gland. J Dairy Sci 1992; 75: Bingham EW, Malin EL. Alkaline phosphatase in the lactating bovine mammary gland and the milk fat globule membrane. Release by phosphatidylinositolspecific phospholipase C. Comp Biochem Physiol 1992; 102: Qin YD, Luo X, Huang DL, Xu CZ. Dynamic changes of enzymes activities and growth factors contents in human colostrum. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2004; 39(7): AKTIVNOSTI ENZIMA U HUMANOM MLEKU U TOKU PRVOG MESECA LAKTACIJE Gordana Kocić, Ljiljana Bjelaković, Tatjana Cvetković, Zoran Pop-Trajković, Marina Jonović, Bojko Bjelaković, Dušan Sokolović, Tatjana Jevtović i Dušica Stojanović Dinamika aktivnosti enzima u humanom kolostrumu i mleku menja se u zavisnosti od stimulacije laktacije. Za cilj studije bilo je postavljeno izučavanje aktivnosti alkalne fosfataze, amilaze, transaminaza (ALT i AST) i laktat dehidrogenaze (LDH) u uzorcima humanog kolostruma i zrelog mleka dobijenog manuelnim istiskivanjem u prvom mesecu laktacije. U studiju je bilo uključeno 45 žena, dobne starosti godina, koje su se porodile na Klinici za ginekologiju i akušerstvo Kliničkog centra u Nišu, normalnim porođajem, bez postojanja komplikacija. Uzorci kolostruma i mleka skupljani su mehaničkim istiskivanjem mleka u tri intervala: prvi uzorak kolostruma je dobijen odmah nakon pojave prvih kapi mleka nakon porođaja; drugi uzorak je dobijen nakon 24 časa i treći nakon mesec dana. Uzorci su skupljani u jutarnjim časovima, pre podoja deteta i čuvani u sterilnim epruvetama u zamrzivaču do izvođenja analiza. Aktivnost pomenutih enzima se smanjuje (statistički značajno kod amilaze) u periodu nakon mesec dana, što znači da prati količinu proteina. Aktivnost transaminaza (ALT i AST) i alkalne fosfataze pokazuje tendenciju pada aktivnosti nakon mesec dana, ali je statistički značajna razlika dobijena kod AST. Aktivnost alkalne fosfataze pokazuje dinamiku koja upućuje na visoko statistički značajan pad nakon mesec dana. Aktivnost enzima u humanom mleku predstavlja značajno polje istraživanja, jer se potenciraju značaj i prednosti humanog mleka nad kravljim, u kome su enzimi pasterizacijom uglavnom uništeni. Povećana aktivnost određenih enzima može biti koristan i validan dijagnostički marker mehaničke iritacije tkiva, deskvamacije epitela i porasta koncentracije inflamatornih ćelija u toku mastitisa. Acta Medica Medianae 2010;49(2): Ključne reči: humano mleko, kolostrum, alkalna fosfataza, amilaza, transaminaze, laktat-dehidrogenaza 24
Selecting Beneficial Protein Components From all Dairy Animals for Manufacturing Next Generation Infant Formulas FOOD AND NUTRITION
 Selecting Beneficial Protein Components From all Dairy Animals for Manufacturing Next Generation Infant Formulas FOOD AND NUTRITION Jared Raynes 14 th September 2017 What is the Problem? Breast milk is
Selecting Beneficial Protein Components From all Dairy Animals for Manufacturing Next Generation Infant Formulas FOOD AND NUTRITION Jared Raynes 14 th September 2017 What is the Problem? Breast milk is
WHY STUDY THE MAMMARY GLAND AND MILK SECRETION?
 WHY STUDY THE MAMMARY GLAND AND MILK SECRETION? 1. Greater knowledge allows us to alter environment, nutrition, milking procedures, or general management to maximize production WHY STUDY THE MAMMARY GLAND
WHY STUDY THE MAMMARY GLAND AND MILK SECRETION? 1. Greater knowledge allows us to alter environment, nutrition, milking procedures, or general management to maximize production WHY STUDY THE MAMMARY GLAND
Dairy Technology-Multiple Choice Questions
 Dairy Technology-Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the principal carbohydrate in the milks of all mammals? a. Lactose b. Glucose c. Sucrose d. Fructose 2. Percentage of water in buffalo milk is:- a.
Dairy Technology-Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the principal carbohydrate in the milks of all mammals? a. Lactose b. Glucose c. Sucrose d. Fructose 2. Percentage of water in buffalo milk is:- a.
Do Now Makeups. 4. In which organelle would water and dissolved materials be stored? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5. A. mitochondria B.
 Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
For Adults and Children
 Goat's Milk: Why it's a Better Choice For Adults and Children What does goat's milk give you that cow's milk doesn't? In many parts of the world, goat s milk is preferred to cow's milk. Even in the United
Goat's Milk: Why it's a Better Choice For Adults and Children What does goat's milk give you that cow's milk doesn't? In many parts of the world, goat s milk is preferred to cow's milk. Even in the United
Lactose Lab: Some Don't Like it Sweet
 Lactose Lab: Some Don't Like it Sweet Grade Level(s) 9-12 Estimated Time 60 minutes Purpose In this lesson students will learn the chemistry and composition of milk, identify the difference between a monosaccharide
Lactose Lab: Some Don't Like it Sweet Grade Level(s) 9-12 Estimated Time 60 minutes Purpose In this lesson students will learn the chemistry and composition of milk, identify the difference between a monosaccharide
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
, CCNE: What s the difference between cow s milk, goat s milk, formula, and breast milk?
 00-000-00, CCNE: What s the difference between cow s milk, goat s milk, formula, and breast milk? Client-centered nutrition education uses methods like group discussions and hands-on activities to engage
00-000-00, CCNE: What s the difference between cow s milk, goat s milk, formula, and breast milk? Client-centered nutrition education uses methods like group discussions and hands-on activities to engage
Calf Notes.com. happens to the rest of the protein? It s an interesting observation and may provide some insights into the newborn calf s metabolism.
 Calf Notes.com Calf Note 168 Where does the protein go? Introduction Colostrum is special stuff. The composition of maternal colostrum (MC) is profoundly different from that of milk; it s so different
Calf Notes.com Calf Note 168 Where does the protein go? Introduction Colostrum is special stuff. The composition of maternal colostrum (MC) is profoundly different from that of milk; it s so different
Human milk. The Gold Standard. Human milk. Human milk. Human milk. Human milk. 3 Types of Human Milk 4/23/2015
 The Gold Standard Defining characteristic of the class Mammalian Ability to produce designed specifically to nourish the young It is a unique complex fluid with a species specific composition It is the
The Gold Standard Defining characteristic of the class Mammalian Ability to produce designed specifically to nourish the young It is a unique complex fluid with a species specific composition It is the
Study Exercises: 1. What special dietary needs do children <1 yr of age have and why?
 Exam 3 Review: Lectures 21+ Nutrition 150 Winter 2007 Exam: Monday, March 19, 8-10am in regular classroom Strategies for Studying: 1) Go over all lectures including those given by fellow students 2) Read
Exam 3 Review: Lectures 21+ Nutrition 150 Winter 2007 Exam: Monday, March 19, 8-10am in regular classroom Strategies for Studying: 1) Go over all lectures including those given by fellow students 2) Read
Learning from nature for a healthier start Staged infant formulas with Lacprodan mimic the changing protein profile of breast milk
 Learning from nature for a healthier start Staged infant formulas with Lacprodan mimic the changing protein profile of breast milk By Lotte Neergaard Jacobsen Arla Foods Ingredients. May 013 1 3 4 www.arlafoodsingredients.com
Learning from nature for a healthier start Staged infant formulas with Lacprodan mimic the changing protein profile of breast milk By Lotte Neergaard Jacobsen Arla Foods Ingredients. May 013 1 3 4 www.arlafoodsingredients.com
IMPORTANCE OF ALPHA-LACTALBUMIN IN INFANT NUTRITION
 IMPORTANCE OF ALPHA-LACTALBUMIN IN INFANT NUTRITION By Dr Dan Alaro Learning Objective Describe the roles of α-lactalbumin as an important nutrients for infants. Protein Composition : Human milk The whey-to
IMPORTANCE OF ALPHA-LACTALBUMIN IN INFANT NUTRITION By Dr Dan Alaro Learning Objective Describe the roles of α-lactalbumin as an important nutrients for infants. Protein Composition : Human milk The whey-to
Objective Students will learn what causes lactose intolerance and carry out a laboratory activity to test a treatment for lactose intolerance.
 Oklahoma Ag in the Classroom Making the Most of Milk Understanding Lactose Intolerance Objective Students will learn what causes lactose intolerance and carry out a laboratory activity to test a treatment
Oklahoma Ag in the Classroom Making the Most of Milk Understanding Lactose Intolerance Objective Students will learn what causes lactose intolerance and carry out a laboratory activity to test a treatment
Digestive System Processes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Breast Milk. Composition of Breast Milk
 Breast Milk Composition of Breast Milk Knowledge of the biological composition and constituents of breast milk are critical to the dietitian, because they form the rationale for effective practice in both
Breast Milk Composition of Breast Milk Knowledge of the biological composition and constituents of breast milk are critical to the dietitian, because they form the rationale for effective practice in both
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
Introduction to Carbohydrate metabolism
 Introduction to Carbohydrate metabolism Some metabolic pathways of carbohydrates 1- Glycolysis 2- Krebs cycle 3- Glycogenesis 4- Glycogenolysis 5- Glyconeogenesis - Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) - Curi
Introduction to Carbohydrate metabolism Some metabolic pathways of carbohydrates 1- Glycolysis 2- Krebs cycle 3- Glycogenesis 4- Glycogenolysis 5- Glyconeogenesis - Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) - Curi
Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion
 M57_MARI0000_00_SE_EX08.qxd 8/22/11 3:08 PM Page 394 8 E X E R C I S E Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Suggest to the students that they become familiar with
M57_MARI0000_00_SE_EX08.qxd 8/22/11 3:08 PM Page 394 8 E X E R C I S E Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Suggest to the students that they become familiar with
1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Untitled Document EOC Macromolecules 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell membrane D. nuclear membrane 4. Plants and animals are composed of organic
Untitled Document EOC Macromolecules 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell membrane D. nuclear membrane 4. Plants and animals are composed of organic
MATERI 10 LAKTASI DAN PUERPUREUM
 MATERI 10 LAKTASI DAN PUERPUREUM MK. ILMU REPRODUKSI Lab. Reproduksi Ternak Fapet UB 1 SUB POKOK BAHASAN Proses laktasi (Mekanisme Let down susu) Peranan Laktasi bagi Reproduksi Proses Pengembalian organ
MATERI 10 LAKTASI DAN PUERPUREUM MK. ILMU REPRODUKSI Lab. Reproduksi Ternak Fapet UB 1 SUB POKOK BAHASAN Proses laktasi (Mekanisme Let down susu) Peranan Laktasi bagi Reproduksi Proses Pengembalian organ
Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each.
 2007 Junior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 03 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
2007 Junior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 03 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (52) - 2010 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 3 (52) - 2010 Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering RESEARCH ON THE INFLUENCE OF MICROWAVE TREATMENT ON MILK COMPOSITION
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AcuDairy Mid-Range Infrared instrument, 211 263 Adiponectin, 151 164 Advocacy, for lactation maintenance, 3 Alanine, 151 164 Albuminuria,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AcuDairy Mid-Range Infrared instrument, 211 263 Adiponectin, 151 164 Advocacy, for lactation maintenance, 3 Alanine, 151 164 Albuminuria,
LAB 3: Biomolecules and Digestion
 Page 3.1 LAB 3: Biomolecules and Digestion Food taken into our bodies must first be broken down by mechanical and chemical digestion before it can be absorbed and used as an energy source. The chemical
Page 3.1 LAB 3: Biomolecules and Digestion Food taken into our bodies must first be broken down by mechanical and chemical digestion before it can be absorbed and used as an energy source. The chemical
Digestive System. Part 3
 Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration =
 1 AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration = Day 1 p. I. Overview A. Cellular Respiration 1. Respiration breathing, exchange of O 2 for CO 2 2. Cellular respiration aerobic harvesting of energy from food
1 AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration = Day 1 p. I. Overview A. Cellular Respiration 1. Respiration breathing, exchange of O 2 for CO 2 2. Cellular respiration aerobic harvesting of energy from food
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
Unit 1: Biochemistry
 Name: Date: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and enzymes 1. All living things contain which element? A. helium B. sodium C. copper D. carbon 4. Which of the following elements is best able to combine with
Name: Date: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and enzymes 1. All living things contain which element? A. helium B. sodium C. copper D. carbon 4. Which of the following elements is best able to combine with
9. At about 0 C., most enzymes are (1.) inactive (2.) active (3.) destroyed (4.) replicated
 Study Guide 1. Which of the following enzymes would digest a fat? (1.) sucrase (2.) fatase (3.) protease (4.) lipase 2. At high temperatures, the rate of enzyme action decreases because the increased heat
Study Guide 1. Which of the following enzymes would digest a fat? (1.) sucrase (2.) fatase (3.) protease (4.) lipase 2. At high temperatures, the rate of enzyme action decreases because the increased heat
The bovine milk proteome: what s in it and how can it be manipulated?
 Bovine milk protein The bovine milk proteome: what s in it and how can it be manipulated? Sabrina Greenwood Bovine Milk Proteins (30 35g/L) 80% Casein Casein composition αs1 Casein 32% αs2 Casein 8% Κ
Bovine milk protein The bovine milk proteome: what s in it and how can it be manipulated? Sabrina Greenwood Bovine Milk Proteins (30 35g/L) 80% Casein Casein composition αs1 Casein 32% αs2 Casein 8% Κ
LIFIB. Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board. LIFIB Briefing Paper: Lactose Intolerance in Infants
 LIFIB Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board Briefing Paper 2 January 2015 LIFIB Briefing Paper: in Infants The purpose of this Briefing Paper is to equip Midwives, Health Visitors and partners (including
LIFIB Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board Briefing Paper 2 January 2015 LIFIB Briefing Paper: in Infants The purpose of this Briefing Paper is to equip Midwives, Health Visitors and partners (including
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Bio Metabolism. Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry. Chloroplasts and mitochondria. What is food?
 Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
New Studies Continue to Reveal the Health Benefits of Colostrum
 New Studies Continue to Reveal the Health Benefits of Colostrum by Barbara L. Minton (see all articles by this author) (NaturalNews) Colostrum is the thin yellowish fluid produced during the first few
New Studies Continue to Reveal the Health Benefits of Colostrum by Barbara L. Minton (see all articles by this author) (NaturalNews) Colostrum is the thin yellowish fluid produced during the first few
Name: Period: Date: Testing for Biological Macromolecules Lab
 Testing for Biological Macromolecules Lab Introduction: All living organisms are composed of various types of organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, starches, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. These
Testing for Biological Macromolecules Lab Introduction: All living organisms are composed of various types of organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, starches, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. These
Comparison of cow-milk, breast milk and formula: nutritional, immunologic and developmental considerations
 Comparison of cow-milk, breast milk and formula: nutritional, immunologic and developmental considerations Eugene Dinkevich, MD Downstate Healthy Lifestyles Program Department of Pediatrics SUNY-Downstate
Comparison of cow-milk, breast milk and formula: nutritional, immunologic and developmental considerations Eugene Dinkevich, MD Downstate Healthy Lifestyles Program Department of Pediatrics SUNY-Downstate
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION.
 PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION. 1. STAGES IN LACTATION PERIOD IN DAIRY COWS The lactation period is divided into four phases based on the cow s physiological cycle and
PIONEER FEEDS DAIRY CATTLE AND CALF FEEDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION. 1. STAGES IN LACTATION PERIOD IN DAIRY COWS The lactation period is divided into four phases based on the cow s physiological cycle and
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Biochemistry Name: Practice Questions
 Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
#9 - Digestion. Objectives: Prelab Activity. I Digestive System
 #9 - Objectives: Observe and understand the process of emulsification Understand the digestion of fats by pancreatic lipase and the purpose of bile Understand the digestion of protein by pepsin and the
#9 - Objectives: Observe and understand the process of emulsification Understand the digestion of fats by pancreatic lipase and the purpose of bile Understand the digestion of protein by pepsin and the
Liposomal Delivery: the LD Advantage
 Liposomal Delivery: the LD Advantage Why this is so important for colostrum effectiveness When a baby is born, the mother s breast does not immediately begin producing milk. Instead it produces a yellowish
Liposomal Delivery: the LD Advantage Why this is so important for colostrum effectiveness When a baby is born, the mother s breast does not immediately begin producing milk. Instead it produces a yellowish
Lab Activity 30. Digestive Enzymes. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 30 Digestive Enzymes Portland Community College BI 233 Cellular Reactions All molecular bonds have energy barriers that prevent spontaneous breakdown Enzymes lowering these activation energy
Lab Activity 30 Digestive Enzymes Portland Community College BI 233 Cellular Reactions All molecular bonds have energy barriers that prevent spontaneous breakdown Enzymes lowering these activation energy
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Easy to digest. Kabrita protein digestibility (1)
 Easy to digest Kabrita protein digestibility (1) In vitro analyses of human milk, Kabrita goat milk infant formula (IF) and cow s milk IF in the gastrointestinal model Tiny-TIM agc 90 80 Cum. nitrogen
Easy to digest Kabrita protein digestibility (1) In vitro analyses of human milk, Kabrita goat milk infant formula (IF) and cow s milk IF in the gastrointestinal model Tiny-TIM agc 90 80 Cum. nitrogen
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Human Complex Milk Lipids: Concentrations, benefits and the implications for Paediatric Nutrition
 Human Complex Milk Lipids: Concentrations, benefits and the implications for Paediatric Nutrition Alastair MacGibbon, Bertram Fong, Angela Rowan and Paul McJarrow Fonterra Research and Development Centre,
Human Complex Milk Lipids: Concentrations, benefits and the implications for Paediatric Nutrition Alastair MacGibbon, Bertram Fong, Angela Rowan and Paul McJarrow Fonterra Research and Development Centre,
Mare s milk. Mare s milk, in chemical composition and particularly in the protein content, it is one of the most similar milks of human milk.
 Mare s milk The mare s milk is produced for the mare (the female of horse) Mares, like all the mammal females, have mammary glands that secrete what it have to the unique food for their children during
Mare s milk The mare s milk is produced for the mare (the female of horse) Mares, like all the mammal females, have mammary glands that secrete what it have to the unique food for their children during
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
Ingredients for the next generation
 Arla Foods Ingredients Ingredients for the next generation Using infant formulas is second to breastfeeding, a fact supported by WHO. This information is for professional use only. 002 003 Infant nutrition
Arla Foods Ingredients Ingredients for the next generation Using infant formulas is second to breastfeeding, a fact supported by WHO. This information is for professional use only. 002 003 Infant nutrition
220 SUBJECT INDEX. D Diarrhea and sodium balance, 74 weanling, 161,179,208,212; see also Infection
 Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each.
 2006 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 07 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
2006 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 07 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport. Lecture 2. Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients
 BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
D. glycerol and fatty acids 4. Which is an example of an inorganic compound?
 Name: ate: 1. Glucose and maltose are classified as organic compounds because they are both 3. Which process is most directly responsible for the production of O 2 in these sugar solutions?. carbon-containing
Name: ate: 1. Glucose and maltose are classified as organic compounds because they are both 3. Which process is most directly responsible for the production of O 2 in these sugar solutions?. carbon-containing
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION Chemical Reactions The cells of organisms, from bacteria to plants to animals, carry out hundreds to thousands of chemical reactions that must be properly coordinated
LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION Chemical Reactions The cells of organisms, from bacteria to plants to animals, carry out hundreds to thousands of chemical reactions that must be properly coordinated
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each.
 2007 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 01 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
2007 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 01 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
Mozzarella Cheese Making
 Mozzarella Cheese Making Ricki s 30 Minute Mozzarella from New England CheeseMaking Supply Company http://www.cheesemaking.com/ Kathryn McCarthy, Professor Emerita Erin DiCaprio, Food Safety Extension
Mozzarella Cheese Making Ricki s 30 Minute Mozzarella from New England CheeseMaking Supply Company http://www.cheesemaking.com/ Kathryn McCarthy, Professor Emerita Erin DiCaprio, Food Safety Extension
CHEM121. Unit 6: Enzymes. Lecture 10. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to:
 CHEM121 Unit 6: Enzymes Lecture 10 At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term enzyme Name and classify enzymes according to the: type of reaction catalyzed type of specificity
CHEM121 Unit 6: Enzymes Lecture 10 At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term enzyme Name and classify enzymes according to the: type of reaction catalyzed type of specificity
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion
 Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Global Market for Clinical Nutrition and Dairy Ingredients
 Global Market for Clinical Nutrition and Dairy Ingredients 2015-2020 Published in September 2016 1 Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Global market overview 3. Clinical nutrition ingredients 4. Conclusions 5. Appendix
Global Market for Clinical Nutrition and Dairy Ingredients 2015-2020 Published in September 2016 1 Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Global market overview 3. Clinical nutrition ingredients 4. Conclusions 5. Appendix
Objectives. Objectives. Essentials of Breastfeeding. E Course on Programming for IYCF. UNICEF and Cornell University
 Objectives To review the physiology of and the important aspects of milk composition Essentials of Breastfeeding Kathleen M. Rasmussen, ScD To describe 3 major recommended practices To describe potential
Objectives To review the physiology of and the important aspects of milk composition Essentials of Breastfeeding Kathleen M. Rasmussen, ScD To describe 3 major recommended practices To describe potential
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Calf Notes.com. Calf Note #155 Day 2. Introduction
 Calf Notes.com Calf Note #155 Day 2 Introduction Calf nutrition and management seems to be divided into two distinct periods namely, the first day of life and everything after. We all know of the importance
Calf Notes.com Calf Note #155 Day 2 Introduction Calf nutrition and management seems to be divided into two distinct periods namely, the first day of life and everything after. We all know of the importance
Digestion and Absorption
 Digestion and Absorption General Considerations - No absorption in esophagus, little in the stomach and vast majority of absorption occurs in small intestine. - The small intestine has specialized structures
Digestion and Absorption General Considerations - No absorption in esophagus, little in the stomach and vast majority of absorption occurs in small intestine. - The small intestine has specialized structures
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: Compounds composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen arranged as monosaccharides or multiples of monosaccharides. Most,
BCH 445 Biochemistry of nutrition Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 1 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: Compounds composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen arranged as monosaccharides or multiples of monosaccharides. Most,
Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry
 Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry 6. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below. A. utilize energy B. detect changes in the environment C. rearrange and synthesize
Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry 6. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below. A. utilize energy B. detect changes in the environment C. rearrange and synthesize
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Energy & Reactions Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400
Jeopardy Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Energy & Reactions Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity.
 1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
Colostrum Don t be born without it!
 Colostrum Don t be born without it! Gerald R. Bertoldo, DVM Extension Dairy Specialist Cornell Cooperative Extension A Foundation for Health and Growth colostrum Passive immunity Superior nutrition Growth
Colostrum Don t be born without it! Gerald R. Bertoldo, DVM Extension Dairy Specialist Cornell Cooperative Extension A Foundation for Health and Growth colostrum Passive immunity Superior nutrition Growth
Where are we heading?
 Unit 2: Where are we heading? Unit 2: Introduction Unit 1: What s in your food? Unit 2: How does your body use food? Unit 3: What is metabolic disease? Unit 4: How do I identify good and bad food? Unit
Unit 2: Where are we heading? Unit 2: Introduction Unit 1: What s in your food? Unit 2: How does your body use food? Unit 3: What is metabolic disease? Unit 4: How do I identify good and bad food? Unit
c. Reaction will drive Reaction in a reaction. d. Which statement (A or B) has more energy in products than reactants?
 Energy and Enzymes (32 questions) 1. Chemical reactions involve a. Formation of chemical bonds b. Breakage of chemical bonds c. Both formation and breakage of chemical bonds d. Neither formation and breakage
Energy and Enzymes (32 questions) 1. Chemical reactions involve a. Formation of chemical bonds b. Breakage of chemical bonds c. Both formation and breakage of chemical bonds d. Neither formation and breakage
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Monosaccharides: Little amounts Don t need any digestion
 Slide 8 Digestion result in mono and disaccharides & alpha-dextrins (oligosaccharides) Alpha1-4 in sequences / alpha1-6 at branches Dietary carbohydrates: Polysaccharides: 1) Containing α(1,4)/ α(1,6)
Slide 8 Digestion result in mono and disaccharides & alpha-dextrins (oligosaccharides) Alpha1-4 in sequences / alpha1-6 at branches Dietary carbohydrates: Polysaccharides: 1) Containing α(1,4)/ α(1,6)
Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each.
 2007 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 05 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
2007 Senior Dairy Quiz Bowl Questions Round 05 Phase B 5 Questions Correct answers are worth 10 points each. Only the team being asked the questions is to be in the room. Each team will be asked these
A Level Bridging Work Biology
 A Level Bridging Work Biology The tasks below are designed to support you as you start A Level Biology. Complete each of the tasks below and bring your work to your first lesson. Task 1 Write an essay
A Level Bridging Work Biology The tasks below are designed to support you as you start A Level Biology. Complete each of the tasks below and bring your work to your first lesson. Task 1 Write an essay
LITTLE TREASURE. Premium Australian Made Powdered Milk Products
 LITTLE TREASURE Premium Australian Made Powdered Milk Products Little Treasure Infant Formula and other Milk Powder products. Made in Australia to the highest possible standard, using milk from Australian
LITTLE TREASURE Premium Australian Made Powdered Milk Products Little Treasure Infant Formula and other Milk Powder products. Made in Australia to the highest possible standard, using milk from Australian
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only CAMPUS GROSSHADERN CAMPUS INNENSTADT BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH Maria Grunewald, Hans Demmelmair, Berthold Koletzko AGENDA Breast Milk
Note: for non-commercial purposes only CAMPUS GROSSHADERN CAMPUS INNENSTADT BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH Maria Grunewald, Hans Demmelmair, Berthold Koletzko AGENDA Breast Milk
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
Protein & Enzyme Lab (BBT 314)
 Protein & Enzyme Lab (BBT 314) Experiment 3 A: Determination of the enzyme ALT or SGPT activity in serum by enzymatic method using Bioanalyzer Background: Alanine aminotransferase (glutamate pyruvate transaminase)
Protein & Enzyme Lab (BBT 314) Experiment 3 A: Determination of the enzyme ALT or SGPT activity in serum by enzymatic method using Bioanalyzer Background: Alanine aminotransferase (glutamate pyruvate transaminase)
PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT WITH LIFELINE. EVERY NEWBORN IS A HIGH-VALUE CALF. WHAT ARE FUNCTIONAL PROTEINS?
 PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT WITH LIFELINE. You have just one chance to start your newborns right. Count on LIFELINE nutrition products for young production animals formulated with the power of functional proteins
PROTECT YOUR INVESTMENT WITH LIFELINE. You have just one chance to start your newborns right. Count on LIFELINE nutrition products for young production animals formulated with the power of functional proteins
WARM-UP. Grab a. Write down anything written in RED. Milk 4/18/2011. Student Learning Objectives. Terms. Student Learning Objectives
 Grab a WARM-UP Sheet Question: Milk Processing Using what we ve talked about in class, along with what you may know outside of class, brainstorm what kinds of processes raw milk goes through before it
Grab a WARM-UP Sheet Question: Milk Processing Using what we ve talked about in class, along with what you may know outside of class, brainstorm what kinds of processes raw milk goes through before it
Animal Survival. Standard Grade Biology
 Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Lec: 21 Biochemistry Dr. Anwar J Almzaiel. Clinical enzymology. Very efficient can increase reaction rates at the order of x 10
 Clinical enzymology Enzymes Biological catalysis Very efficient can increase reaction rates at the order of x 10 All are proteins- so liable to denaturation Specific to substrates Partly specific to tissues
Clinical enzymology Enzymes Biological catalysis Very efficient can increase reaction rates at the order of x 10 All are proteins- so liable to denaturation Specific to substrates Partly specific to tissues
IPH - Internationaler Produkt Handel KG. Baby Milk Powder. Products 2018
 IPH - Internationaler Produkt Handel KG Baby Milk Powder & more Products 2018 Who We Are IPH is an international trading company specializing in the sale of dairy products. The focus here is on the sale
IPH - Internationaler Produkt Handel KG Baby Milk Powder & more Products 2018 Who We Are IPH is an international trading company specializing in the sale of dairy products. The focus here is on the sale
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
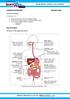 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
BIOMOLECULES. Ms. Bosse Fall 2015
 BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
