Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants.
|
|
|
- Claire Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ; Sevilla/ES, Cádiz/ES Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal soft tissue, MR, Diagnostic procedure, Image verification DOI: /ecr2014/C-1733 Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service. ECR is not responsible for the content of these pages and does not make any representations regarding the content or accuracy of material in this file. As per copyright regulations, any unauthorised use of the material or parts thereof as well as commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method ist strictly prohibited. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold ECR harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. Page 1 of 48
2 Learning objectives To review the anatomy of the lateral ligaments and anatomic quadrants of the knee through schemes and their correlation with magnetic resonance image (MRI) assessing the main stabilizing structures as well as the more common mechanisms that can injure it. Page 2 of 48
3 Background Anatomical knowledge of the support structures that provide stability to the medial and lateral knee region has gained great interest, especially since the advent of MR imaging, allowing us to give detailed information to specialists in Traumatology and Orthopedics so that, in case of injury to any of them, they can carry out a suitable and satisfactory surgical repair [1]. Page 3 of 48
4 Images for this section: Fig. 1: Support structures of anatomic quadrants. Page 4 of 48
5 Fig. 2: Anatomic quadrants and the main mechanisms of injury. Page 5 of 48
6 Fig. 3: Illustration and axial proton density weighted MR image of anatomic components. Page 6 of 48
7 Findings and procedure details A) LCL and posterolateral corner [1, 2, 3, 5]: They act limiting varus angulation and external rotation of the knee. All are inserted into the fibular head (Fig. 4 on page 12). Display better at: Coronal image: Lateral collateral ligaments, Arcuate ligaments, Popliteofibular ligament, Fabellofibular ligament and Biceps femoris tendon. Axial image: Popliteus muscle and tendon and Oblique popliteal ligament. Sagittal image: Popliteomeniscal fascicles and Lateral gastrocnemius muscle. 1- Lateral collateral ligaments (LCL): it inserts in the proximal femur, posterior to the lateral epicondyle. It extends posterolaterally to insert into the top facet of the fibular head, anterolaterally to the insertion of the Fabellofibular and Arcuate ligaments (Fig. 5 on page 12, Fig. 6 on page 13, Fig. 9 on page 16 ). 2- Popliteus muscle (PM): it inserts into the popliteal sulcus of the lateral femoral condyle, and extends medially through the popliteal hiatus to be inserted into the posteromedial aspect of the tibial metaphysis. PM help in the knee flexion and allows internal rotation. Protects the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus during flexion and rotation and stabilizes the posterolateral angle (Fig. 5 on page 12, Fig. 6 on page 13, Fig. 9 on page 16). 3- Lateral gastrocnemius muscle (LGM): it inserts behind the lateral epicondyle and condyle of the femur (Fig. 5 on page 12). 4- Biceps femoris tendon (BT) (Fig. 6 on page 13, Fig. 7 on page 14, Fig. 9 on page 16): it haves two heads: Long head: the direct arm is inserted into the fibular head. The anterior arm is inserted in front of the direct arm and continues distally as the anterior aponeurosis of the leg. Short head: the direct arm is inserted into the fibular head, medially to the long head. The anterior arm is inserted into the superolateral edge of the lateral tibial condyle, close to Gerdy tubercle. 5- Popliteofibular ligament (PFL): it begins from the confluence of the popliteal meniscal fascicles and is inserted into the fibular head (Fig. 8 on page 15). Page 7 of 48
8 6- Arcuate ligament (AL): It is Y-shaped. Arises from the styloid process of the fibula. The lateral arm runs straight up following the capsule to the lateral femoral condyle. The medial arm inserts into the posterior capsule medially, with the oblique popliteal ligament (Fig. 10 on page 17). 7- Oblique popliteal ligament (OPL): arises from semimembranosus fascicles and the lateral tibial condyle, joining the arcuate ligament at its femoral insertion (Fig. 4 on page 12). 8- Fabellofibular ligament (FFL): originates at fabela and is inserted on the styloid process (Fig. 9 on page 16, Fig. 11 on page 18, Fig. 12 on page 19). 9- Popliteomeniscal fascicles (PMF): extends from the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus to the popliteal tendon (Fig. 10 on page 17). Mechanisms of injury: It is less common than the injury of medial structures. The mechanisms are: Violent external rotation of the tibia with the knee extended. Impact at the medial portion of the proximal tibia towards posterolateral (Fig. 13 on page 20). Hyperextension (Fig. 14 on page 21). It is frequently associated with cruciate ligaments injury. The clinic is pain in the posterolateral aspect of the knee and feeling unsteady to extension. The most frequently injured structures are LCL, Joint capsule, BT, PT, AL and PFL. The popliteus muscle is the main lateral stabilizer of the knee. The ligament rupture could be complete or incomplete (Fig. 15 on page 22). If the rupture is complete all the fiber are disrupted while in the partial rupture only a portion has presence of fluid signal (Fig. 16 on page 23, Fig. 17 on page 24). The tendons tend to break in the myotendinous junction. If there is complete rupture of the tendon, the fibers retraction simulates a mass (Fig. 18 on page 25, Fig. 19 on page 26). Page 8 of 48
9 At radiography the only sign could be a subtle avulsion fracture of the upper portion of the fibular head (arcuate sign) (Fig. 20 on page 27, Fig. 21 on page 28). B) Anterolateral corner [1, 2, 4]: Is best assessed on coronal plane. 1- Knee Joint capsule (JC) 2- Iliotibial tract (ITT): formed by the fusion of the aponeurosis of tensor fascia lata, gluteus maximus and minimus. It origins on lateral supracondylar tubercle of the femur and inserts on Gerdy s tubercle of tibia, patella and patellar ligament (Fig. 22 on page 29, Fig. 23 on page 30). 3- Anterior oblique band (AOB): It joins the iliotibial tract and lateral collateral ligament. It inserts on the lateral tibia (Fig. 22 on page 29). Mechanisms of injury: It is most frequently than the injury of lateral structures. The mechanism is a combination of varus force and internal rotation of the knee (Fig. 24 on page 31). It is frequently associated with anterior cruciate ligament and medial meniscus injury. The most frequently injured structures are ITT and AOB (Fig. 25 on page 32). It may be associated with Segond fracture (a tibial avulsion fracture secondary to the abnormal tension) (Fig. 26 on page 33). C) Posteromedial corner [1, 5]: Is best assessed on coronal and axial plane. 1- Medial collateral ligament (MCL): It originates on medial femoral epycondile and extends anteriorly and inferiorly till its insertion on proximal tibia. It has been described in three layers based on the depth of the structure. The most superficial, composed of the deep fascia, invests the sartorius muscle posteriorly and extends in an anterior direction. Along the anterior margin of the knee it forms the superficial fascia of the vastus medialis and inserts onto the patella as the superficial fibers of the medial retinaculum. The most deep comprises the medial joint line capsule and joins the medial meniscus (Fig. 27 on page 34, Fig. 28 on page 35, Fig. 29 on page 36) Page 9 of 48
10 2- Semimembranosus tendon (SMT): It is primarily inserted into the posteromedial tibial plateau. It has other insertions on popliteal fascia, medial collateral ligament and oblique popliteal ligament (Fig. 27 on page 34, Fig. 29 on page 36). 3- Oblique popliteal ligament (OPL): It originates on medial condyle of tibia and the tendon of the Semimembranosus. Extends superiorly and medially till its insertion on lateral condyle of the femur (Fig. 29 on page 36). 4- Posterior oblique ligament (POL): thickening of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) attached proximally to adductor tubercle of femur and distally to tibia and posterior aspect of the capsule, next to the internal meniscus. Is best assessed on coronal oblique plane (Fig. 30 on page 37). 5- Medial gastrocnemius muscle (MGM): it originates from the medial condyle of the femur and area just above condyle. Its end forms a common tendon with the soleus and lateral gastrocnemius muscle: Achilles tendon. Inserts onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus. Mechanisms of injury: They are: Valgus force applied to the flexed knee Direct blow to the lateral aspect of the knee (Fig. 31 on page 38). Torque injury The most frequently injured structures are MCL (Fig. 32 on page 39, Fig. 33 on page 40) and POL. D) Anteromedial corner [1, 2, 4]: Is best assessed on coronal and axial plane. - Medial retinacular complex (MR) (Fig. 34 on page 41, Fig. 35 on page 42): It is formed by several components: Medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL): it is the cephalad edge of the complex. Originates at the level of the adductor tubercle and runs in a slight rostral direction to insert on the patella (Fig. 35 on page 42). Patellotibial ligament (PTL): originates on the tibia at the level of the insertion of the semitendinosus muscle and insert on the inferior aspect of the patella and on the patellar tendon (Fig. 35 on page 42). Page 10 of 48
11 Anterior portion of medial collateral ligament (APMCL): its anterior fibers extends above the vastus medialis. Mechanisms of injury: They are the same that injure posteromedial corner: Valgus force applied to the flexed knee Direct blow to the lateral aspect of the knee (Fig. 31 on page 38). The most frequently injured structures are MCL, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and internal meniscus (IM). The medial patellofemoral ligament or medial retinaculum injury may be associated with lateral patellar dislocation (Fig. 36 on page 43, Fig. 37 on page 44, Fig. 38 on page 45). Page 11 of 48
12 Images for this section: Fig. 4: Posterolateral corner anatomy. Posterior illustration of knee. Page 12 of 48
13 Fig. 5: Oblique sagittal view of the outside of the knee. Page 13 of 48
14 Fig. 6: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Lateral collateral ligament (LCL), Biceps femoris tendon (BT) and popliteus tendon (PT), Page 14 of 48
15 Fig. 7: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Biceps femoris tendon (BT). Page 15 of 48
16 Fig. 8: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Popliteofibular ligament (PFL) Page 16 of 48
17 Fig. 9: Oblique sagittal view of the outside of the knee. LCL: lateral collateral ligament. FFL: Fabellofibular ligament. BT: Biceps femoris tendon. ITT: Iliotibial tract. PT: Popliteus tendon. Page 17 of 48
18 Fig. 10: Sagital T2 GE weighted MR image: Superior popliteomeniscal fascicle (SPMF), inferior popliteomeniscal fascicle (IPMF) and Arcuate ligament (AL) Page 18 of 48
19 Fig. 11: Sagital T1 TSE weighted MR image: Fabellofibular ligament (FFL) Page 19 of 48
20 Fig. 12: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Fabellofibular ligament. Page 20 of 48
21 Fig. 13: Impact at the medial portion of the proximal tibia towards posterolateral. Jose A. Recondo et al (2000). Lateral Stabilizing Structures of the Knee: Functional Anatomy and Injuries Assessed with MR Imaging. Radiographics 20:S91-S102 Page 21 of 48
22 Fig. 14: Hyperextension Jose A. Recondo et al (2000). Lateral Stabilizing Structures of the Knee: Functional Anatomy and Injuries Assessed with MR Imaging. Radiographics 20:S91-S102 Page 22 of 48
23 Fig. 15: Coronal view of the knee: a) Complete tear of Lateral collateral ligament. b) Partial tear of Lateral collateral ligament. Page 23 of 48
24 Fig. 16: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: LCL partial tear on its femoral insertion, with bone cysts and soft tissue edema. Page 24 of 48
25 Fig. 17: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: LCL partial tear on its femoral insertion, with bone cysts and soft tissue edema. Page 25 of 48
26 Fig. 18: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: BT partial tear Page 26 of 48
27 Fig. 19: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: BT partial tear Page 27 of 48
28 Fig. 20: Coronal view of the knee. Avulsion fracture of the styloid process of the fibula, with lateral collateral ligament (LCL), biceps tendon (BT) and popliteomeniscal fascicle (PMF) tear, and tibia fracture. MCL: Medial collateral ligament. EM: External meniscus. Page 28 of 48
29 Fig. 21: Anteroposterior radiograph of the knee: Avulsion fracture above the head of the fibula in relation to the "arcuate sign". Page 29 of 48
30 Fig. 22: Lateral view of the knee: Anterior oblique band (AOB) extends anteriorly and inferiorly to the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). ITT: Iliotibial tract. Page 30 of 48
31 Fig. 23: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Iliotibial tract (ITT) Page 31 of 48
32 Fig. 24: Mechanism of injury to the anterolateral corner: combination of varus force and internal rotation of the knee. Jose A. Recondo et al (2000). Lateral Stabilizing Structures of the Knee: Functional Anatomy and Injuries Assessed with MR Imaging. Radiographics 20:S91-S102 Page 32 of 48
33 Fig. 25: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Iliotibial tract (ITT) complete tear. Page 33 of 48
34 Fig. 26: Anteroposterior radiograph of the knee: Avulsion fracture of the lateral tibial condyle (Segond fracture) Page 34 of 48
35 Fig. 27: Oblique sagittal view of the medial side of the knee: ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament. LCL: Lateral collateral ligament. MCL: Medial collateral ligament. PCL: Posterior cruciate ligament. PT: Patellar tendon. QT: Quadriceps tendon. Page 35 of 48
36 Fig. 28: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Medial collateral ligament (MCL) Page 36 of 48
37 Fig. 29: Oblique sagittal view of the posteromedial corner of the knee: AL: Arcuate ligament. MCL: Medial collateral ligament. POL: Posterior oblique ligament. PM: Popliteus muscle. SMT: Semimembranosus tendon. Page 37 of 48
38 Fig. 30: Sagital view of the knee: MCL: Medial collateral ligament. POL: Posterior oblique ligament. OPL: Oblique popliteal ligament. SMT: Semimembranosus tendon. Page 38 of 48
39 Fig. 31: Mechanism of injury to the posteromedial corner: Direct blow to the lateral aspect of the knee. Page 39 of 48
40 Fig. 32: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: Grade I medial collateral tear (microscopic, with normal thickness and signal) with surrounding edema. Page 40 of 48
41 Fig. 33: Coronal proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: A) Medial collateral ligament partial tear with surrounding edema. B) Medial collateral ligament complete tear and edema. C) Dislocation of the medial meniscus body with medial collateral ligament partial tear and surrounding edema. Page 41 of 48
42 Fig. 34: Anterior view of the knee: BT: Biceps femoris tendon. ITT: Iliotibial tract. LCL: Lateral collateral ligament. LR: Lateral retinaculum. MCL: Medial collateral ligament. MR: Medial retinaculum. PA: Pes anserinus. PLM: Peroneus longus muscle. PT: Patellar tendon. QT: Quadriceps tendon. VL: Vastus lateralis. VM: Vastus medialis. Page 42 of 48
43 Fig. 35: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: A) MPFL: Medial patellofemoral ligament. B) MR: Medial retinaculum. C) PTL: Patellotibial ligament. Page 43 of 48
44 Fig. 36: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: medial patellofemoral ligament partial tear near its patellar insertion. Page 44 of 48
45 Fig. 37: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: medial patellar retinaculum complete tear. Page 45 of 48
46 Fig. 38: Axial proton density weighted MR image with fat saturation: medial patellofemoral ligament partial tear with lateral patellar dislocation. Page 46 of 48
47 Conclusion Anatomical knowledge of the structures that provide stability to the lateral and medial regions of the knee is of great importance because of its complexity and need be familiar with both the normal anatomy as anatomical variants. The purpose of the assessment by MR imaging after injury is merely identify those anatomical elements or supporting structures that may be injured and to provide adequate information to specialists in trauma and orthopedics for repair. Page 47 of 48
48 References 1.Beall DP, Googe JD, Moss JT et al. Imagen de RM de los ligamentos colaterales y de los cuadrantes anatomicos de la rodilla. Radiol Clin N Am 2007; 45: Recondo JA, Salvador E, Villanúa JA et al. Lateral stabilizing structures of the knee: functiuonal anatomy and injuries assessed with MR imaging. Radiographics 2000; 20:S91-S Hayes CW, Brigido MK, Jamadar DA y Propeck T. Mechanism-based pattern approach to classification of the complex injuries of the knee depicted at MR imaging. Radiographics 2000; 20 S121-S Ostlere S. The extensor mechanism of the knee. Radiol Clin N Am 2013; 51: Geiger D, Chang E, Pathria M y Chung CB. Posterolateral and posteromedial corner injuries of the knee. Radiol Clin N Am 2013; 51: Page 48 of 48
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional
 MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance
 Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings
 The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Knee Ultrasonography step by step
 Knee Ultrasonography step by step Poster No.: C-2809 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Torres de Abreu Macedo, N. Pereira da Silva, A. I. Aguiar, F. Alves, F. Caseiro Alves; Coimbra/PT
Knee Ultrasonography step by step Poster No.: C-2809 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Torres de Abreu Macedo, N. Pereira da Silva, A. I. Aguiar, F. Alves, F. Caseiro Alves; Coimbra/PT
Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis.
 Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis. Poster No.: R-0057 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. George, A. Thomas, R. Dutta, K. Gummalla; Singapore/SG
Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis. Poster No.: R-0057 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. George, A. Thomas, R. Dutta, K. Gummalla; Singapore/SG
Ultrasonographic evaluation of patellar deviation and its influence on knee muscles and tendons
 Ultrasonographic evaluation of patellar deviation and its influence on knee muscles and tendons Poster No.: C-0984 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. A. M. Santos, A.
Ultrasonographic evaluation of patellar deviation and its influence on knee muscles and tendons Poster No.: C-0984 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. A. M. Santos, A.
POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW?
 OTHER KNEE SURGERIES POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW? Written by Jacques Ménétrey, Eric Dromzée and Philippe M. Tscholl, Switzerland Injury of the posterolateral corner (PLC) is relatively
OTHER KNEE SURGERIES POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW? Written by Jacques Ménétrey, Eric Dromzée and Philippe M. Tscholl, Switzerland Injury of the posterolateral corner (PLC) is relatively
CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability
 CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability Poster No.: C-2157 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Ruef, C. Edgar, C. Lebedis, A. Guermazi, A. Kompel, A. Murakami; Boston, MA/US Keywords:
CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability Poster No.: C-2157 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Ruef, C. Edgar, C. Lebedis, A. Guermazi, A. Kompel, A. Murakami; Boston, MA/US Keywords:
Financial Disclosure. Medial Collateral Ligament
 Matthew Murray, M.D. UTHSCSA Sports Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. Matthew Murray has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Medial Collateral Ligament Most commonly
Matthew Murray, M.D. UTHSCSA Sports Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. Matthew Murray has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Medial Collateral Ligament Most commonly
Downloaded from by on 12/22/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
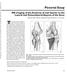 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
Periosteal stripping of the MCL
 Periosteal stripping of the MCL Poster o.: P-0014 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Pedersen; Toensberg/O Keywords: Musculoskeletal soft tissue, Musculoskeletal joint, Anatomy, MR,
Periosteal stripping of the MCL Poster o.: P-0014 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. Pedersen; Toensberg/O Keywords: Musculoskeletal soft tissue, Musculoskeletal joint, Anatomy, MR,
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes
 Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes Poster No.: P-0121 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Chowdhury, G. Rajeswaran, J. Lee, J.
Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes Poster No.: P-0121 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Chowdhury, G. Rajeswaran, J. Lee, J.
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity
 Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children.
 Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children. Poster No.: C-2365 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Yakimov, M. Nikonova, E. Prokhorova, D. Vybornov,
Basic low - field MR imaging of meniscal injuries in children. Poster No.: C-2365 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Yakimov, M. Nikonova, E. Prokhorova, D. Vybornov,
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist
 Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents.
 Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
The radiologist and the raiders of the lost image
 The radiologist and the raiders of the lost image Poster No.: P-0072 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. J. Ereño Ealo, E. Montejo Rodrigo, B. Sancho, E. Pastor; Galdakao/ES Keywords:
The radiologist and the raiders of the lost image Poster No.: P-0072 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. J. Ereño Ealo, E. Montejo Rodrigo, B. Sancho, E. Pastor; Galdakao/ES Keywords:
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when?
 Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies.
 Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies. Poster No.: C-2434 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, M. Inglot,
Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies. Poster No.: C-2434 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, M. Inglot,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Suprapatellar fat-pad impingement:mri findings
 Suprapatellar fat-pad impingement:mri findings Poster No.: C-1672 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Arslan, S. Ulus, S. A. Kara, O. SAYG#L#; istanbul/tr Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic
Suprapatellar fat-pad impingement:mri findings Poster No.: C-1672 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Arslan, S. Ulus, S. A. Kara, O. SAYG#L#; istanbul/tr Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability
 Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability Poster No.: C-1687 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit C. Prieto Santa Cruz 1,
Correlation between findings on stress X-rays (Telos) and MRI in patients with anterior knee instability Poster No.: C-1687 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit C. Prieto Santa Cruz 1,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience
 MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. Schvartzman, A. Fernandez Viña, F. Olmos Cantarero, J. 1 2 1 1
MR findings in patients with athletic pubalgia: our experience Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. Schvartzman, A. Fernandez Viña, F. Olmos Cantarero, J. 1 2 1 1
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be?
 MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be? Poster No.: C-2324 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Pierre-Jerome
MRI assessment of the plantar fascia in diabetic versus nondiabetic patients: How thick should it be? Poster No.: C-2324 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Pierre-Jerome
Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis
 Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. F. de Souza 1, P. P. Collier 1, E. J. M. Bronzatto 1, G. L. P. Keywords: DOI:
Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. F. de Souza 1, P. P. Collier 1, E. J. M. Bronzatto 1, G. L. P. Keywords: DOI:
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region
 MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region Poster No.: C-0151 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Vukojevi#, M. Mustapic, D. Marjan; Zagreb/HR
MRI in Patients with Forefoot Pain Involving the Metatarsal Region Poster No.: C-0151 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Vukojevi#, M. Mustapic, D. Marjan; Zagreb/HR
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging
 When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging Poster No.: C-2444 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Zakhary 1, M. Adix 2, C. Yablon
When Pads of Fat are a Welcome Sight: Fat Pads in Acute Musculoskeletal Imaging Poster No.: C-2444 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Zakhary 1, M. Adix 2, C. Yablon
Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament
 Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, I. Tsifoundoudis,
Mucoid degeneration of the posterior cruciate ligament Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, I. Tsifoundoudis,
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography.
 A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures
 Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine
 Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine Poster No.: C-2125 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit S. patil 1, A. M.
Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine Poster No.: C-2125 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit S. patil 1, A. M.
MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review.
 MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter, L. Dewachter, A. P. Parkar ; Lier/BE, Bergen/ NO Keywords:
MRI of the long head of the biceps tendon: a pictorial review. Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter, L. Dewachter, A. P. Parkar ; Lier/BE, Bergen/ NO Keywords:
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach.
 High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, U. Zaleska-Dorobisz; Wroclaw/PL Keywords:
High-resolution ultrasound of the elbow - didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2358 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, U. Zaleska-Dorobisz; Wroclaw/PL Keywords:
The posterolateral corner (PCL) of the knee: Dynamic evaluation with high-resolution ultrasound (D-HRUS)
 The posterolateral corner (PCL) of the knee: Dynamic evaluation with high-resolution ultrasound (D-HRUS) Poster No.: C-2205 Congress: ECR 200 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: F.
The posterolateral corner (PCL) of the knee: Dynamic evaluation with high-resolution ultrasound (D-HRUS) Poster No.: C-2205 Congress: ECR 200 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: F.
Sonography of Knee and Calf Pain: the differential considerations
 Sonography of Knee and Calf Pain: the differential considerations Dr. Lisa L. S.Wong Consultant Radiologist St Paul s Hospital Outline Ultrasound techniques Common pathologies in calf and posterior knee
Sonography of Knee and Calf Pain: the differential considerations Dr. Lisa L. S.Wong Consultant Radiologist St Paul s Hospital Outline Ultrasound techniques Common pathologies in calf and posterior knee
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective
 On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
Imaging of the Athle/c Knee: injuries associated with ACL disrup/on
 Imaging of the Athle/c Knee: injuries associated with ACL disrup/on Brian Petersen, MD Associate Professor of Radiology and Orthopaedics Chief of MSK Radiology University of Colorado CU Sports Medicine
Imaging of the Athle/c Knee: injuries associated with ACL disrup/on Brian Petersen, MD Associate Professor of Radiology and Orthopaedics Chief of MSK Radiology University of Colorado CU Sports Medicine
Hip and Knee Approaches
 Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study
 Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study Poster No.: R-0016 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Au, A. Webb, G. Buirski, P. Smith, M. Pickering, D.
Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study Poster No.: R-0016 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Au, A. Webb, G. Buirski, P. Smith, M. Pickering, D.
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort.
 Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life
 Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Ultrasound of the Knee Joint. Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine
 Ultrasound of the Knee Joint Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine Clinical History and P/E Chronic or Acute Symptoms Chronic Sx. : possible of systemic articular
Ultrasound of the Knee Joint Jun Sung Park,M.D. Bundang General Hospital Dept. of Rehabilitation Medicine Clinical History and P/E Chronic or Acute Symptoms Chronic Sx. : possible of systemic articular
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
Reliability of the pronator quadratus fat pad sign to predict the severity of distal radius fractures
 Reliability of the pronator quadratus fat pad sign to predict the severity of distal radius fractures Poster No.: C-0669 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Tonak, I. Wobbe, R. L. Duschka,
Reliability of the pronator quadratus fat pad sign to predict the severity of distal radius fractures Poster No.: C-0669 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Tonak, I. Wobbe, R. L. Duschka,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas Poster No.: C-0317 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. P. Sathe, E. Soh, K. Y. Seto, B. Yeh, D. W. Y. chee, R. Quah,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Perianal Fistulas Poster No.: C-0317 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. P. Sathe, E. Soh, K. Y. Seto, B. Yeh, D. W. Y. chee, R. Quah,
MRI evaluation of medial hamstring tendons after harvesting for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 MRI evaluation of medial hamstring tendons after harvesting for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction Poster No.: C-2211 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
MRI evaluation of medial hamstring tendons after harvesting for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction Poster No.: C-2211 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
Radiological evaluation of the causes of patellar instability.
 Radiological evaluation of the causes of patellar instability. Poster No.: C-0054 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. M. Spaccesi Pau, D. Pomato, N. CEDOLA; La Plata/AR
Radiological evaluation of the causes of patellar instability. Poster No.: C-0054 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. M. Spaccesi Pau, D. Pomato, N. CEDOLA; La Plata/AR
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
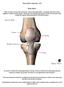 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions
 MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions Poster No.: C-2355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: A. Kassarjian, X. Tomás,
MR imaging of the quadratus femoris: Anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions Poster No.: C-2355 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: A. Kassarjian, X. Tomás,
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging
 Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
MRI of distended bursa around the knee
 MRI of distended bursa around the knee Poster No.: C-2240 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, N. Michailidis, I. Tsifoundoudis,
MRI of distended bursa around the knee Poster No.: C-2240 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: P. Papadopoulou, I. Kalaitzoglou, N. Michailidis, I. Tsifoundoudis,
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution
 MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
11/16/2015. No disclosures or conflicts of interest relevant to the presentation
 Travis C. Burns, MD SAMMC, Ft Sam Houston, Tx Chief, Sports Medicine Advanced Concepts in Sports Medicine Nov 6 8, 2015 Las Vegascourse.com No disclosures or conflicts of interest relevant to the presentation
Travis C. Burns, MD SAMMC, Ft Sam Houston, Tx Chief, Sports Medicine Advanced Concepts in Sports Medicine Nov 6 8, 2015 Las Vegascourse.com No disclosures or conflicts of interest relevant to the presentation
MRI in staging of rectal carcinoma
 MRI in staging of rectal carcinoma Poster No.: C-0152 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. R. Ramos Rodriguez, M. Atencia Ballesteros, M. D. M. Muñoz Ruiz, A. J. Márquez Moreno, M. D.
MRI in staging of rectal carcinoma Poster No.: C-0152 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. R. Ramos Rodriguez, M. Atencia Ballesteros, M. D. M. Muñoz Ruiz, A. J. Márquez Moreno, M. D.
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability
 Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability Poster No.: P-0114 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: S. Dumonteil, M. A. Shah, A. Srikanthan, V. Ejindu, N. Papadakos; London/UK
Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability Poster No.: P-0114 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: S. Dumonteil, M. A. Shah, A. Srikanthan, V. Ejindu, N. Papadakos; London/UK
Learning Objectives. Lecture Outline. Knee Stability. Cruciate Ligaments. Knee Stability. MRI of the Knee: Part 3: ligaments
 Learning Objectives MRI of the Knee: Part 3: ligaments Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the anatomy
Learning Objectives MRI of the Knee: Part 3: ligaments Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the anatomy
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot
 Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot Poster No.: C-2598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Á. Gómez Trujillo; Madrid/ES Keywords: Education and training, Education, MR, Digital radiography,
Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot Poster No.: C-2598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Á. Gómez Trujillo; Madrid/ES Keywords: Education and training, Education, MR, Digital radiography,
Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure
 Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure Poster No.: C-1670 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Erden, E. Peker, Z. B#y#kl# Gençtürk, I. Erden; Ankara/TR
Evaluation of anal canal morphology with MRI in cases with anal fissure Poster No.: C-1670 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Erden, E. Peker, Z. B#y#kl# Gençtürk, I. Erden; Ankara/TR
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Feasibility of magnetic resonance elastography using myofascial phantom model
 Feasibility of magnetic resonance elastography using myofascial phantom model Poster No.: C-0971 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. J. Kang, J.-S. Yoon, S.-J. Hong, C.-H. Oh, S. H.
Feasibility of magnetic resonance elastography using myofascial phantom model Poster No.: C-0971 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. J. Kang, J.-S. Yoon, S.-J. Hong, C.-H. Oh, S. H.
