Bioscience Research Print ISSN: Online ISSN:
|
|
|
- Merry O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online freely at Bioscience Research Print ISSN: Online ISSN: Journal by Innovative Scientific Information & Services Network RESEARCH ARTICLE BIOSCIENCE RESEARCH,201815(2): OPEN ACCESS Crossed pinning versus two lateral wires for fixation of displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children Muhammed Mahmoud Naeem 1, Alaa Ahmed Mostafa El Ngehy 2, Amr Mohamed El Adawy 3 and Walid Faisel El Sharkawi 4 1 Resident of orthopedic surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt 2 Professor of orthopedic surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt 3 Assistant Professor of orthopedic surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt 4 Lecturer of orthopedic surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt *Correspondence: naeemmuhammed316@gmail.com Accepted: 02 June.2018 Published online: 27 June The most known pediatric fractures are supracondylar humerus fractures are nearby the elbow and have a peak incidence in the first decade of life. There is no consensus between the orthopedic surgeons as regarding the best treatment for supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Closed reduction and percutaneous pin fixation using Kirschner wires are still the current treatment of choice of the displaced supracondylar fractures. This study was performed prospectively which included 30 pediatric patients who undergone for closed reduction and percutaneous pinning for management of supracondylar humeral fractures age group ranged from 2 to 9 years old. Out of the 30 patients, 17 (65.6%) were preserved by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning with the overlapped pinning technique (medial and lateral wires) and 13 (34.4%) with 2-lateral pin fixation.26 (86.7%) patients had Gartland type III and 4(13.4%). patients had Gartland type II fractures. Four patients from the lateral group (30.8%) had unstable fixation 3 of them (75%) were rotated and only one case (25%) was displaced, and ulnar nerve neuropraxia occurred in one patient from the crossed group (5.80%) and improved by physiotherapy. The crossed pin configuration method provides more stability than the lateral pin configuration method in management of the humerus supracondylar fracture in children. Keywords: Displaced supracondylar fracture humerus, percutaneous pinning, crossed pin, lateral pin. INTRODUCTION Supracondylar humerus fractures are commonplace wound in young age's individuals and constitute the greatest recurrent fractures concerning the elbow (Babal et al., 2010 and Koval et al., 2006). The males are more affected with such fractures than females and happen generally following an extension mechanism (Barron et al., 2015). This mechanism is generally because of a droponextended hand with the elbow in slightly flexion (97 99% of cases), the olecranon occupies the olecranon fossa and works as a fulcrum and at the same time, the anterior side of the capsule offers a stretch ablevigor at the distal portion of the humerus proximal to its insertion (Omid et al., 2008). The present management of displaced supracondylar fractures including secure reduction and percutaneous pinning through applying of Kirschner wires, even as some debates are found about the place of the pins (Dua et al., 2011)..The method of percutaneous pinning has established as the less aggressive and most secure tool for healing of fractured
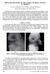
2 bones.the complications of this technique is normally low and it represent about 2% 8% of the cases and comprise principally ulnar nerve injury, pin movement under the skin, infections at the site of pin insertion and lack of fracture healing (Mangwani et al., 2006 and Murnaghan et al., 2010) The optimal configuration of pin fixation is still debated in the literature. Recent textbooks of pediatric orthopedics describe the crossed pin configuration as the desired treatment, except when the medial epicondyle or the ulnar nerve cannot be palpated. Several researches document that lateral pin fixation performed correctly is effective in maintaining reduction (Koval et al., 2006). The technique of crossed-pin versus lateral pin alone is believed to be mechanically more stable in spite of the fact that during the crossed-pin technique, an injury to ulnar nerve can occur (Mommsen et al., 2010). MATERIALS AND METHODS In between April 2017 and March 2018, this prospective randomized-controlled trial blanketed 30 children with Gartland types II and III supracondylar humeral fractures. They had been all handled by means of closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. The inclusion criteria concerned patients below 10 years, early fractures within first four days, no previous fracture in the same elbow, and children with complete data and follow-up more than 6 weeks treated with pin fixation for type II and III fractures according to Wilkins modification of the Gartland classification. The exclusion criteria concerned open fractures of the distal humerus, fractures with vascular injury, fractures with compartmental syndrome, fractures with pre-operative ulnar nerve injury, and patients with multiple bone injuries that required multidisciplinary treatment and/or admission to intensive care. Age at time of surgical treatment, gender, side injured, mechanism of injury, and type of fracture consistent with Gartland classification had been noted. The direction of fracture displacement, time among injury and surgical treatment, time from injury to admission, and the onset of important complications had been amassed using medical and radiographic facts and parental information on the lesion dynamics. Patients underwent clinical examination and conventional radiography of the anteroposterior and lateral side of the affected limb. All patients had been surgically treated, using a closed reduction and fixation with k-wires. Two different pin configurations, cross (group 1) and lateral (group 2). Figure. (1): Intraoperative radiographs, AP and lateral views by the image intensifier during crossed pinning of a 2 years old male child (Group 1). Figure. (2): Intraoperative radiographs, AP and lateral views by the image intensifier during lateral pinning of a 6 years old male child (Group 2). Bioscience Research, 2018 volume 15(2):
3 Surgical Technique The surgery was performed after general anaethesia was administered; the patient was positioned in a supine position with the injured upper limb on the aspect of the table. Image intensifier was placed alongside the table from caudal end of the patient. The injured elbow became positioned at the plate of the image intensifier. If the anaethesia crew and the image intensifier had been ready, the surgeon could scrub up, clean, and drape the injured arm to the axilla. The fracture could be reduced with the aid of the surgeon and the assistant. The surgeon selected the pin size to be used according to the age of the patient and the size of the arm (commonly 1.6 mm for more youthful children and mm for older children). The fracture was fixed either by the crossed or the lateral technique according to the randomization. The k-wires have been bent outside the skin and sterile dressings were placed around the wires then above elbow slab was carried out. After the procedure, the neurovascular status would be reviewed again in the ward. Reduction and fixation of the fracture would be confirmed by radiography. All patients were discharged 24 hours after surgery with a follow-up card. lateral views. If it was acceptable, the child was seen again three weeks postoperatively. The slab was removed; the elbow was inspected for pin tract infection. The child was seen again five weeks postoperatively, elbow x-ray was obtained and the k-wires were removed. The average follow-up period was 2.1 (2 3) months. Cases with complications would undergo a different follow-up protocol depending on the nature of the complication. RESULTS In the present study 30 children complaining from supracondylar fractures in the humerus were treated along the study period. The ages of children participating in this study were averaged 5.65±1.5 years (range: 2 9 years). Regarding sex there were 9 girls (30.0%) and 21 boys (70.0%). The fractures were associated with a trauma during an extension due to a fall on outstretched hand. This occurred in 19 patients (63.3%) following fall to the ground, 7 patients (23.3%) fall downstairs, and 4 patients (13.4%) fall from height. In 18 patients (60%) the involved limb was on the right side and in 12 patients (40%) on the left side. There were 26 patients Gartland type III (86.7%) and 4 patients Gartland type II (13.4%). Postoperative care The child was seen one week postoperatively in the outpatient clinic for follow up x-rays AP and Table 1: Complications distribution of the study group Stability Crossed Lateral Total X 2 Fisher P Stable % % 26 Unstable 0 0% % 3 (Rotated) 75% 1(Displaced) 25% * Ulnar nerve Injury Yes % 0 0% 1 3.3% No % % % overall complications Crossed Lateral Total X2 P Complicated % % % Not % % % Total % % % ** The children of this research, were classified randomly to two different wires methods: 17 Bioscience Research, 2018 volume 15(2):
4 subjects representing about 65.6% were managed by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning using the crossed pinning method (medial and lateral wires) (Figure 1), whereas thirteen subjects representing about 34.4% were treated with two-lateral pin fixation as seen in Figure(2). The interval passed from exposure to injury until admitted to the hospital was averaged 14.55±19.5 hours and ranged from 2 to 72 hours. All cases were observed post operation for the following, injury in the ulnar nerve, range of motions and infection in the pin tract and postoperative stability. There are a significant variations (p=0.031*) between the two performed methods. Regarding postoperative stability 4 patients from the lateral group (30.8%) had unstable fixation 3 of them (75%) were rotated and only one case (25%) was displaced. With respect to the percentage of cases showed nerve injury, only one case was suffering from ulnar nerve neuropraxia (5.80%) from the crossed group, and was responded for the treatment with physiotherapy, while no ulnar nerve injury occurred in the lateral pinning group. The range of motion was restored after removal of the wires except in five children (16.7%) who needed an additional time of severe physiotherapy due to the persistent of stiffness in the elbow joint ; one of them (6.2%) with crossed and four (30.8%) with lateral pin configuration. Three cases (10%) had local infection two of them (11.7%) with crossed and one (7.6%) with lateral pin configuration treated with antibiotic therapy. DISCUSSION Children are commonly exposed to fractures in the elbow joints particularly supracondylar fracture of the humerus (Cheng et al., 1995 and Attenborough 19539). Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning is considered the appropriate management for fractures of the humerus in the children especially in type III of absolutely displaced extension supracondylar fractures (Prashant et al., 2016). The achievement of the treatment is determined by good reduction, conservation of the reduction without occurrence of complications until complete healing of the fracture and with a good motion and flexibility and cosmetic outcomes. (Zionts et al., 1994). Consistent with previous studies, it was found that one of the advantages of medial-lateral pin fixation is the increase in biomechanical stability of joint after medial lateral entry pin fixation [(Zionts et al., 1994 and Lee et al., 2002),, even though iatrogenic injury in the ulnar nerve can too end result from placement of the medial pin (Brauer et al., 2007). On the contrary, to avoid the injury to the ulnar nerve it is beneficially to approach through lateral entrance pin fixation as a tool for escaping of iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury, even though the concept may be less constant biomechanically (Omid et al., 2008; Skaggs et al., 2004 and Sibinski et al., 2006) and failure to provide torsional stability (Topping et al., 1995 and Zenios et al., 2007). In a study carried by Zionts et al. (1994) for exploring the biomechanical mechanism following different tools for fixing elbow joint, they reported that crossed pinning is more stable than lateral pinning in rotational testing as well as varus and valgus stacking. Conversely, another work which done by Skaggs et al. (2004), reported that no clinical differences in stability between the two techniques crossed and lateral pins entrance. We will compare our results to other series using the same treatment as well as other methods of treatment available in the literature. We followed up all the patients for ulnar nerve injuries to the ulnar nerve, stability of the joint after the surgical operation, range of rotations and presence or absence of infection in the pin tract. Compared to Devkota et al. (2008), their study illustrated that loss of reduction was seen in two patients (1.96%) of the lateral pinning group which was not significant and did not require rereduction or re-pinning. In seven patients of the 79 patients in the crossed pinning group (6.86%) ulnar nerve injury occurred, while no ulnar nerve injury occurred to all the 23 patients of the lateral pinning group. Three patients of the 79 patients in the crossed pinning group (3.79%) and one patient of the 23 patients in the lateral pinning group (4.34%) got poor range of motion. Eight patients from a total of 102 patients (7.84%) were complain from superficial infection in the pin tract, and can be treated after pins removal in addition to administration of systemic antibiotics. Accordingly Zamzam et al., (2009) study, their consequences confirmed that tremendous instability because of insufficient securing of bones, and early shortage of reduction of various grades and indifferent levels, were recorded in nine children (24.3%) of them (eight had type III fractures and one had a type II fracture) who carried fixation via lateral pins and this defaults were observed after the operations by using radiographs. Two patients of the seventy one patients in the crossed pinning group (2.82%) got ulnar nerve injury. They recovered spontaneously all through the follow up duration, while no ulnar Bioscience Research, 2018 volume 15(2):
5 nerve harm occurred to all the 37 patients of the lateral pinning group. All patients recovered from fracture complication and gained full range of motion, with the exception of one child who misplaced about 20 0 of elbow flexion and had an extension lag of <10 0, and one girl who additionally had an extension lag of <10 0. Only one child (0.93%) from a total of 108 patients established a pin-track infection which recovered completely after local application of antiseptics and dressing of the wound. In this study, postoperative instability of the fracture occurred in 4 cases (30.8%) from the 13 cases of the lateral pin configuration group; rotation occurred in 3 cases and posterior displacement in one case, while the fixation was stable in all the 17 cases of the crossed pin configuration subjects. There are a significant variations (p=0.031) between the two treated groups. In the present work, no ulnar nerve injury occurred to all the 13 patients of the lateral pinning group, while one child (5.80%) only from the crossed group was complain from neuropraxia in the ulnar nerve and it improved by physiotherapy in the 4 th month. No significant differences (p=0.89) was recorded between the two studied groups.the range of motions was restored in 2 months after removal of the wires except 5 children (16.7%) who needed an additional regimen of condensed physiotherapy due to the continuation of stiffness in the elbow joint; one of them (6.2%) with crossed and four (30.8%) with lateral pin configuration. All accepted full range of movement after physiotherapy,excluding one child from the lateral group(7.7%) who lost approximately 10 and 20 degrees of elbow flexion and extension, respectively, without a significant variations (p =0.069) among the two studied groups.pin tract infection was noticed in three patients(10%) on the third week ;two of them(11.7%) with crossed and one(7.6%) with lateral pin configuration. All were resolved by dressing, without a significant differences (p=0.71) between the two groups were observed. CONCLUSION In children, the crossed pin configuration method provides more stability than the lateral pin configuration method in the control of supracondylar fracture of the humerus, and the risk of ulnar nerve injury can be avoided if adequate care is given during inserting the medial pin by palpating the ulnar nerve at the time of pinning or making a small opening above the medial epicondyle for engagement of the medial pin in case of severe elbow inflammation CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declared that present study was performed in absence of any conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEGEMENT The authors would thank all participants and their parents. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Naeem M. designed and performed the research and also wrote the manuscript. El Ngehy A., El Adawy A. and El Sharkawi W. performed continuous guidance and suggestions during the performance of the research, data analysis and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version. Copyrights: author (s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. REFERENCES Attenborough, C.G., Remodeling of the humerus after supracondylar fractures in childhood. J Bone Joint Surg Br, B (3): p Babal, J.C., C.T. Mehlman, and G. Klein, Nerve injuries associated with pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a metaanalysis. J PediatrOrthop, (3): p Barron-Torres, E.A., J.F. Sanchez-Cruz, and J.R. Cruz-Melendez, [Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of humeral supracondylar fractures in pediatric patients in a Regional General Hospital]. Cir Cir, (1): p Brauer, C.A., Lee, B. M., Bae, D. S., Waters, P. M.Kocher, M. S., A systematic review of medial and lateral entry pinning versus lateral entry pinning for supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J PediatrOrthop, (2): p Cheng, J.C., T.P. Lam, and W.Y. Shen, Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning for type Bioscience Research, 2018 volume 15(2):
6 III displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Orthop Trauma, (6): p Devkota, P., Khan, J. A., Acharya, B. M., Mainali, L. P.,Pradhan, N. M., Singh, M., Shrestha, S. K.,and Rajbhandari, A. P,Outcome of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children treated by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc, (170): p Dua, A., Eachempati, K. K., Malhotra, R., Sharma, L., Gidaganti, M., Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children with delayed presentation. Chin J Traumatol, (1): p Koval, K.J. and J.D. Zuckerman, Handbook of fractures. 3rd ed. 2006, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Xiii, 685 p. Lee, S.S., Mahar, A. T., Miesen, D., and Newton, P.O. Displaced pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: biomechanical analysis of percutaneous pinning techniques. J Pediatr Orthop, (4): p Mangwani, J., R. Nadarajah, and J.M. Paterson, Supracondylar humeral fractures in children: ten years' experience in a teaching hospital. J Bone Joint Surg Br, (3): p Mommsen, P., Zeckey, C., Hildebrand, F., Frink, M., Khaladj, N., Lange, N., Krettek, C. and Probst, C., Traumatic extremity arterial injury in children: epidemiology, diagnostics, treatment and prognostic value of Mangled Extremity Severity Score. J Orthop Surg Res, : p. 25. Murnaghan, M.L., Slobogean, B. L., Byrne, A., Tredwell, S. J., and Mulpuri, K., The effect of surgical timing on operative duration and quality of reduction in Type III supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Child Orthop, (2): p Omid, R., P.D. Choi, and D.L. Skaggs, Supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am, (5): p Prashant, K., Lakhotia, D. Bhattacharyya, T. D. Mahanta, A. K., and Ravoof, A. A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial-lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric supracondylar fracture of the humerus. J Orthop Traumatol, (3): p Sibinski, M., H. Sharma, and D.A. Sherlock, Lateral versus crossed wire fixation for displaced extension supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Injury, (10): p Skaggs, D.L., Cluck, M. W., Mostofi, A., Flynn, J. M., and Kay, R. M., Lateral-entry pin fixation in the management of supracondylar fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am, A (4): p Topping, R.E., J.S. Blanco, and T.J. Davis, Clinical evaluation of crossed-pin versus lateral-pin fixation in displaced supracondylar humerus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop, (4): p Zamzam, M.M. and K.A. Bakarman, Treatment of displaced supracondylar humeral fractures among children: crossed versus lateral pinning. Injury, (6): p Zenios, M., Ramachandran, M., Milne, B., Little, D., and Smith, N. Intraoperative stability testing of lateral-entry pin fixation of pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures. J Pediatr Orthop, (6): p Zionts, L.E., H.A. McKellop, and R. Hathaway, Torsional strength of pin configurations used to fix supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am, (2): p Bioscience Research, 2018 volume 15(2):
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Introduction. Kumar Prashant 1 Devendra Lakhotia. Anil Kumar Mahanta 3 Aakhil Ravoof
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type III supracondylar fracture: a retrospective analysis
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
--Manuscript Draft-- the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees. Walid A Elnahal, M.Sc Tr & Orth
 Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus Cross Pinning
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
A clinical study of closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
Analysis of displaced supracondylar fractures in children treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and anatomical study
 J Child Orthop (2015) 9:295 302 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0674-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and
J Child Orthop (2015) 9:295 302 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0674-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and
Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury?
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 50/ June 22, 2015 Page 8632
 MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN
 1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin configuration
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Late Presentation in Children: A Preliminary Report
 Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Percutaneous pinning after closed reduction of supracondylar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures
 TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
(Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children
 519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Original Research Article. ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) DOI: /sajb
 DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
Surgical Complications
 Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial Head with Both-Bone Forearm Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique AJO DO NOT COPY
 An Original Study Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique Andrew G. Georgiadis, MD, and Jeffrey J. Settecerri, MD Abstract The
An Original Study Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique Andrew G. Georgiadis, MD, and Jeffrey J. Settecerri, MD Abstract The
Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children treated by closed reduction with percutaneous crossed pin fixation
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient Fishtail Deformity after Surgery
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
We report the results of 116 consecutive displaced
 Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction
 Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Elbow fractures account for approximately 5% to
 Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Tuomilehto, N
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children
 Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children
 Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography
 108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE
 Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of a new surgical technique
 SICOT J 2016, 2, 15 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2016010 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of
SICOT J 2016, 2, 15 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2016010 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Unstable elbow dislocations: a case report of
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture. of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child
 Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Pediatric Elbow Radiology. Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar
 Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE CHILDREN
 DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
Outcome of surgically treated displaced medial epicondyle fracture of humerus in children: A prospective study
 2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
 Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Biomechanical analysis between Orthofix external fixator and different K-wire configurations for pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:188 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0893-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Biomechanical analysis between Orthofix external fixator and different K-wire
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:188 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0893-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Biomechanical analysis between Orthofix external fixator and different K-wire
Delayed traumatic dislocation of the radial head
 Delayed traumatic dislocation of the radial head Dr.S.P.Gupta (1), Dr. Anil Agarwal (2) (1) Associate Professor in Orthopaedics, Medical College, Kota, Rajasthan, India (2) Consultant in Orthopaedics,
Delayed traumatic dislocation of the radial head Dr.S.P.Gupta (1), Dr. Anil Agarwal (2) (1) Associate Professor in Orthopaedics, Medical College, Kota, Rajasthan, India (2) Consultant in Orthopaedics,
The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning
 WELCOME The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning Vũ Công Tầm Nguyễn Bá Minh Phước Phạm Anh Tuấn
WELCOME The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning Vũ Công Tầm Nguyễn Bá Minh Phước Phạm Anh Tuấn
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V?
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. No disclosures for this presentation 10/29/18. Agenda
 Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN
 THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department. October 2012
 Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures.
 Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures. Surgical Technique MR Safe Radiolucent Table of Contents System Description 3 Indications and Contraindications 4 Fixation Components
Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures. Surgical Technique MR Safe Radiolucent Table of Contents System Description 3 Indications and Contraindications 4 Fixation Components
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review
 Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.11, No.3, July, 1998
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol11, No3, July, 1998 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Gyeong-Sang National Univeristy, Chinju, Korea Post-traumatic elbow stiffness
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol11, No3, July, 1998 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Gyeong-Sang National Univeristy, Chinju, Korea Post-traumatic elbow stiffness
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
 original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
CiSE. New Fixation Method Using Two Crossing Screws and Locking Plate for Cubitus Varus Deformity in Young Adult Elbow: Case Report CASE REPORT
 SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Anterior Elbow Capsulodesis
 7(1):72 76, 2006 m R E V I E W m Anterior Elbow Capsulodesis Donald H. Lee, MD, Douglas R. Weikert, and Jeffry T. Watson Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Nashville, TN
7(1):72 76, 2006 m R E V I E W m Anterior Elbow Capsulodesis Donald H. Lee, MD, Douglas R. Weikert, and Jeffry T. Watson Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Nashville, TN
NEW MANAGEMENT IN POST TRAUMATIC STIFFNESS OF THE ELBOW AND OLD UNREDUCED DISLOCATION OF THE ELBOW JOINT
 Vol. 5, No. 4. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 220 December, 1964. NEW MANAGEMENT IN POST TRAUMATIC STIFFNESS OF THE ELBOW AND OLD UNREDUCED DISLOCATION OF THE ELBOW JOINT By Sailendra Bhattacharyya, M.B.B.S.
Vol. 5, No. 4. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 220 December, 1964. NEW MANAGEMENT IN POST TRAUMATIC STIFFNESS OF THE ELBOW AND OLD UNREDUCED DISLOCATION OF THE ELBOW JOINT By Sailendra Bhattacharyya, M.B.B.S.
