Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children
|
|
|
- Joshua Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016 Date Accepted:16/2/2016 Address for Correspondence: Dr. Mushtaq Talib Hussein, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Babylon University, Babylon, Iraq. Abstract Background: Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is the second most common fracture in children. Failure to execute a appropriate treatment plan for these fractures may lead tovarus malunion. For that closed reduction and percutaneous pinning is the treatment of choice. Percutaneous K-wire fixation can be inserted either in a cross medial-lateral pattern or through a lateral entry only with each method having its advantage and disadvantage. Aim: Is to evaluate the results of two lateral parallel pin fixation versus cross medial lateral pin fixation in displaced supracondylar humerus fracture in children regarding complications (especially iatrogenic nerve injury, cubitus varus deformity), technique and other concepts. Patients and method: Between March 2010 to May2014, forty _ three (38) patients at Al-Yarmouk Teaching hospital were collected from emergency unite and from orthopedic outpatient to undergo surgery for displaced supracondylar fracture humerus (type B, C) according to gartland classification. it was an urgent operation with less than 24 hours, traumatic posterior supracondylar fracture humerus(type B,C) with no vascular or nerve injury for children aged less than 12 years old. They were divided into two groups [Group I(20 patients) closed reduction and percutaneous two lateral parallel k_wire fixation] and[group II(18 patients) with two cross medial_ lateral k_wire fixation] and we compare the results between the two groups post operatively. Results: There were significant differences(p-value=0.0078)regarding complications postoperatively, there were typical cubitus varus deformity 2{10%} in group I while there were no such complication{0%} in group II, while we report one case {5.55%} with ulnar nerve neuropraxia in group II. Regarding functional results; there were significant differences between the two groups, we reported excellent results 11{55%} in group I, while it was 13{72.22%} in group II, good results were about 5{25%} in group I,while it was 4{27.77%} in group II, fair results 2{10%} in group I, 1{5.55%} in group II. In addition there were significant poor results in group I as we reported 2 cases{10%} in group I, while there were no such results{ 0%} in group II. Conclusion: Closed reduction and medial-lateral percutaneous K-wire fixation is the treatment of choice for displaced pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus with extra precautions during medial wire insertion.. Key words: supracondylar fracture, percutaneous k_wire, ulnar nerve injury. INTRODUCTION Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is the second most common fracture in children and the most common fracture in children under 7 years of age (1), It accounts for 50 70% of all elbow fractures (2). The typical mechanism is a fall on an outstretched hand that puts a hyperextension load on the arm. The distal fragment displaces posteriorly in over 95% of cases (3) As the elbow is forced into hyperextension, the olecranon serves as a fulcrum and focuses the stress on the distal humerus causing fracture. The rare flexiontype supracondylar fracture is often the result of a fall directly onto the flexed elbow.(4)(5) Gartland (22) classified the pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus into three types based on the degree of displacement: Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
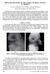
2 Type-A Non displaced Type-B Displaced (with intact posterior cortex) Type-C Displaced (no cortical contact) a. Posteromedial b. Posterolateral The available treatment options range from conservative to closed and/ or open reduction and percutaneous Kirchner wire (K-wire fixation) depending upon treatment modalities available to treat such fractures with different outcomes but closed reduction and percutaneous pinning is the treatment of choice (6). Percutaneous K-wire fixation can be inserted either in a cross medial-lateral pattern or through a lateral entry only with each method having its advantage and disadvantage (7,8). Failure to execute a timely and appropriate treatment plan for these fractures may lead to various complications including, varus malunion, elbow stiffness, Volkmann ischemic syndrome/contracture, neurovascular injury, myositis ossifi cans, etc. (9) There had been continuous debate regarding stability of fracture fixation after different configuration of pinning methods. The stability of crossed pinning method is biomechanically more stable but again carries the risk of ulnar nerve injury. (10,11) Aim of study The aim of this study is to evaluate the results of two lateral parallel pin fixation versus cross medial-lateral pin fixation in displaced supracondylar humerus fracture in children regarding complications (especially iatrogenic nerve injury, cubitus varus deformity), technique and other concepts. Fig.1 Posterior extension type PATIENTS AND METHODS Between March 2010 to May2014, thirty- eight (38) patients at Al-Yarmouk Teaching hospital were collected from emergency unite and from orthopedic outpatient to undergo surgery for displaced supracondylar fracture humerus (type 2, 3) according to gartland classification. There were 28 male and 15 female patients. Mean age of the patients was 6.8 years (range 3-12 years), it was an urgent operation, traumatic posterior supracondylar fracture humerus(type B,C) with no vascular or nerve injury for children aged less than 12 years old. In this study, open fractures, suspicion of compartment syndrome complication, neurovascular injury and children older than 12 years were excluded from our research. In addition any patient with fracture delayed more than 72 hours was excluded; as there will be huge swelling and this will cause close reduction and percutaneous pinning dangerous and difficult. After taking detailed history, thorough clinical examination with meticulous concern on neurovascular component was done for all the patients, followed by plain radiological examination of the injured elbow including anteroposterior (AP) and lateral views. All cases with supracondylar extension type 2, 3 were managed with back slab above elbow at causality and then immediately within hours planning to do surgery (closed reduction and percutaneous pinning by k _ wire) at the surgical orthopedic operative room, they were divided into two groups, group I twenty( 20) child ( closed reduction and parallel 2 lateral percutaneous k _ wire fixation) and group II eighteen (18) child (closed reduction and cross medial_ lateral k_ wire fixation, written patient's consents are adopted. Surgical procedure Either under regional or general anesthesia (depending upon anesthetist s choice and medical fitness of the child), without tourniquet, in lateral position, the surgery was done orthopedic operation table. By applying the traction on the forearm and counter traction of humerus with elbow being in mild flexion(20 degree), the fracture was reduced under image intensifier (gradual correction of rotation and mediolateral shift and then flexing elbow with pressure on olecranon to correct posterior shift, Pronation of forearm and hyperflexion done). Strapping of forearm with arm done in the same position with cotton bandage. Fig. 2 Rare anterior flexion type Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
3 If reduction is acceptable Two K- wires were then inserted under image intensifier from lateral epicondyle towards medial cortex of the proximal fragment with the attempt to put the pins in maximal separation at fracture site and divergent direction. K-wires were bent outside the skin and cut and above elbow back slab applied.(this technique for group I). For group II, after a satisfactory reduction a1.6-2 mm wire was passed percutaneously through lateral epicondyle across the fracture and taking hold into the opposite cortex of the proximal fragment under image intensifier. Before inserting the medial wire through medial epicondyle, important precautions should be followed to minimize the risk of iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury as:(small stab incision was made just behind the medial epicondyle to identify and secure ulnar nerve in few selected cases,skin over the medial epicondyle was stretched posteriorly with the help of overlying fingers. The final position of fracture reduction and K-wires was confirmed by image intensifier. The extra length of K-wires was cut and tip of the remaining wires was bent outside the skin. a posterior slab above elbow,after a week a plaster of Paris (POP) splint was applied for 3 weeks in all the patients followed by a check X-ray immediately after the surgery. Post-operatively Immediately, intravenous antibiotics(second generation cephalosporin),analgesia, with checking of neurovascular bundles especially radial pulse and concentration on ulnar nerve by asking the child to move his or her fingers especially 4 th and 5 th, fingers and if there is any numbness or parasthesia especially in group II Patients(with cross pinning). Next day we sent for x_ray (AP and Lat. Views) elbow joint and discharge the patient on oral antibiotics and ask the family to come weekly for follow up and to confirm clinical and radiological union Clinically, union of the fracture was defined as the absence of tenderness at the fracture site and painless elbow motion while; Radiological union was defined as the presence of bridging callus at the fracture site in both AP and lateral radiographs After 3 weeks POP splint was removed in all the patients and elbow range motion were started. Removal of K- wires was done after confirmation of clinicoradiological union at the fracture site between 4 th and 5 th weeks postoperatively. All patients were followed at the end of 2 months, 4 months,6months & 1 year Fig.3 percutaneous 2 parallel lateral k- wires Fig.4 x-ray postoperative Fig.5 postoperative x-ray cross medial-lateral k- wires Table 1. Flynn s criteria result Satisfactory Unsatisfactory Rating Excellent Good Fair Poor Functional outcome Motion loss (0) >15 Cosmetic factor loss of carrying angle (0) >15 Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
4 RESULT According to this table (2) there is common age group(3-7 years) in which is more susceptible to sustained traumatic supracondylar fracture humerus. According to sex distribution, the boy is more susceptible than girl to be exposed to supracondylar fracture humerus as he is usually more active than the girl. There is iatrogenic nerve injury(ulnar nerve) in group II, and typical cubitus varus deformity in group II. There is excellent results 72.22% in group II, While it is 55% in group I; again poor results 10% in group I while we have not such results in group II. (Table 3,4,5) Table 2: Age distribution Age of patients (yrs.) Table 3: sex distribution Sex Male Female Group I (No.){%} 12{60%} 5{25%} 3{15%} Group I 14{70%} 6{30%} Table 4: Post-operative complications complication Pin tract infection Iatrogenic nerve injury Vascular injury Compartment syndrome Elbow stiffness Heterotopic ossification Cubitus varus deformity Group I(No.){%} 2 {10%} 1{5%} 2{10%} Group II (No.){%} 11{61.11%} 5{27.77%} 2{11.11%} Group II 15{83.33%} 3{16.66%} Group II(No.){%} 1{5.55%} 1{5.55%} ulnar nerve neuropraxia 1{5.55%} Table 5: Functional results according to Flynn s criteria Criteria Excellent Good Fair Poor Total Group I No. {%} 11 {55%} 5 {25%} 2{10%} 2{10%} 20 DISCUSSION Group II No.{%} 13 {72.22%} 4 {27.77%} 1 {5.55%} This is comparative study between two techniques of closed reduction and percutaneous k- wire fixation in displaced supracondylar fracture humerus in children as 18 this fracture is the commonest( second) in the pediatric age group. As study done by M Julfiqar, Ajay Pant. et al (13). In our results, most of our patients were under 7 years (3-7), about 23 patients{ 61%}, and this is true to that the peak age group with supracondylar fracture humerus in children is between(3-5). (14) Again, there was significant male predominance in our study, as there were 29 male patient {76.5%}and this is logic in our population as the male child is more active, bicycle rider and football player as falling on outstretched hand is the commonest mechanism of injury in this fracture, in opposite to female child. This is comparable to study done by Yadagiri, Sureder et al. (15) Closed reduction and k wire fixation of supra condylar fracture in children is a sound and effective technique especially for type 2 and type 3 fractures, but with sure some complications we encounter in this study. There were 3 cases of superficial pin tract infection, two {10%} cases in Group I, and one {5.55%} in Group II, and every case treated successfully by daily dressing and sterilization and oral antibiotic for one week without hospital admission or intravenous antibiotics. This is again good results in comparism to other studies M Julfiqar, Ajay Pant et al (13) ( superficial pin tract infection {14.3%}.) The major complication of cross K-wire configuration(group II) is the risk of iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury however, it is said to be biomechanically the stronger construct.(lewis, Zneist et al ) (16). The major advantage of lateral K-wire placement(group I) is that it is free from the risk of an iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury (17). In our study only one (5.55. %) patient had an iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury, fortunately it was neuropraxia and there was just parasthesia and numbness for 3 weeks without clawed hand and immediately cured after we remove the medial k- wire. The use of ultrasound to minimize the risk of ulnar nerve injury during insertion of medial pin may be helpful however, it is technically demanding, and the expertise may not be available easily (18), so better to follow instructions intra-operative as mentioned above in inserting medial k- wire to minimize ulnar nerve injury. Although the risk of iatrogenic peripheral nerve injuries following supracondylar fracture of the humerus has been reported ranging from 2% to 6% in various studies (19,20), in our study we observed this complication Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
5 in only5.5% patients, and this injury recovered at 3 weeks post-operative. Fortunately, in this study we did not cause vascular injury, and there was no compartment syndrome postoperative as we exclude cases with impending compartment syndrome, in addition we did our study on patients within 72 hours as it is easy to reduce the fracture under fluoroscopy in one or two trials apposite to cases with delayed treatment as it will be difficult to close reduction and it may need more than one manipulation and many cases need open reduction and internal fixation and this is out of our patients. In a study by M Julfiqar, Ajay Pant et al (13), only one case sustained compartment syndrome, and another study done by Yadagiri Sureder et al (15), no case of compartment syndrome was reported as post-operative complication. Another complication we reported which is elbow stiffness, actually there were no difference between the two techniques as we report one case of stiffness in lateral pinning and one case in cross pinning, and both cases there was delay in removal of k- wires and pop because the family delayed to consult outpatient because of national holiday. Within 2 weeks both cases managed successfully with active physiotherapy. In comparism to other studies we report 2 cases 10.55%, while a study by M julficar,ajay Pant, et al (13), elbow stiffness was about 11.5%( 4 patients), actually closed reduction and percutaneous pinning (lateral pinning or cross pinning) had less incidence to cause stiffness of the elbow joint in comparism to open reduction and internal pinning as there will be soft tissue dissection and damage. Regarding heterotopic ossification, there were no such complication in our study post-operatively and this is can be explained as we did closed reduction and percutaneous pinning,in addition we remove k- wires and pop cast in less than 1 month (4weeks) and start early physiotherapy and active exercises., this is again comparable to study done by H.K. Gupta, K.D. Khare, D. Chaurasia, et al (21), in which there were no heterotopic ossification complication reported postoperatively. To evaluate our results, we chosed Flynn s modified over all rating (Table I). This is the most rigorous classification since any cubitus varus deformity is considered to be a poor result, whatever the function of the elbow. According to this, we got excellent results 11 {55%} in group I (lateral pinning) while it was 13{72.22%} in group II(cross pinning), good results were 5{25%} in Group I, and 4{27.77%} in Group II, fair results 2{10%}in group I while it was 1{5.55%}in group II. we got no poor results(no patient) 0% in Group II, while unfortunately we got 2 patients{10%} with poor results (complicated by cubitus varus deformity)in Group I. The 2 patients with cubitus varus deformity in the Group I, were both type 3 Gartland supracondylar fracture, aged 6 years, 6.5 years, in the x- ray fellow up we see there were displacement of the distal fragment (medial tilt and rotation), and actually both cases the 2 lateral wires were close to each other and no enough space (more than 1 cm) between them. The K-wires must be strictly parallel and separated by a distance of more than 10 mm. If the wires are positioned too closely, the mechanical construct is equivalent to a single wire construct and allows rotation of the distal fragment around the axes of the wires In comparism to other study, M julficar,ajay Pant, et al (13), (cross pinning) excellent results 24 {68.6%}, good 6{17%}, poor2{5.8%}, these results is near similar to our study results. Other study by H.K. Gupta, et al (21), (lateral pinning), excellent results 17 { 68%}, good 8{32%}, Poor 0{0%}, again these results are comparable to our study results. Conclusion Closed reduction and medial-lateral percutaneous K- wire fixation is the treatment of choice for displaced pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus with extra precautions during medial wire insertion REFERENCES 1- Ozkoc G, Gonc U, Kayaalp A, Teker K, Peker T Tdisplaced supracondylar humeral fracture in children: open reduction vs. closed reduction and pinning. Arch orthop trauma surg 2004;124: El-Adl WA, EL-Said MA, Boghdady WG, Ali AM Results of treatment of displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children by percutaneous lateral crosswiring technique. Strat Traum Limb Recon 2008; 3: Cekanauskas E, Degliute R, Kalesinskas RJ Treatment of supracondylar humerus fractures in children, according to Gartland classification. Medicina 2003; 39: Leitch KK, Kay RM, Femino JD, Tolo VT, Storer SK, Skaggs DL. Treatment of multidirectionally unstable supracondylar humeral fractures in children. A modified Gartland type-iv fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2006; 88: Carmichael KD, Joyner K. Quality of reduction versus timing of surgical intervention for pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures Orthopedics 2006; 29: Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
6 6- R. omid, P D. Choi, D. L. Skaggs. Supracondylar humeral fracture in children Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery; 2008; 90; (5) V C Arino, E. E. Lluch A.M. Ramirez et al Percutaneous fixation of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997;59; F.J. Shannon. Dor gan,s percutaneous lateral cross wiring of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children J Pediatr Orthop 2004; 24: Ucar BY, Demirtas A, Ucar DE. Treatment approaches and outc omes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmaco l Sci :2012,16: J. P L yons, E Ashley M. M. Hof fer Ulnar nerve palsies after percutaneous cross-pinning of supracondylar fractures in children s elbows Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 1998; 18(1): D. L. Skaggs, J.M. Hale, J. Bassett et al. Operative treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: the consequences of pin placement Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 2001;83(5):735_ J. C. Flynn, J.G Mathews, R.L. Benoit. Blind pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children J Bone Joint Surg Am 1974; 56 : 263_ M Julfiqar, Ajay Pant,Najmul Huda, Mohammed Aslam, Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus International Journal of Scientific Study k asser JR, Beaty JH, editors. Supracondylar fractures of the distal humerus. In: Rockwood and Wilkins Fractures in Children. 6th ed., Ch. 14 Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p Y adagiri, Surender, Rao Manoj Chakravorthy,Yadagiri, A study of percutaneous K wire fixation in supracondylar fracture of humerus (SCFH) in children, J M e d A l l i e d S c i ; 5 (1) : Zionts LE, McKellop HA, Hathaway R T orsional strength of pin configurations used to fix supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children J Bone Joint Surg[Am] 1994;253: Y Ozturkmen,. Karamehmtoglu, I Azboy Closed reduction and percutaneous lateral pin fixation in the treatment of displaced Supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2005;39(5): Soldado F, Knorr J, Haddad S, Diaz-Gallardo P, Palau-Gonzal ez J, Mascarenhas VV et al Ultrasoundguided percutaneous medial pinning of pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures to avoid ulnar nerve injury. Arch Bone Joint Surg 2015;3: Rasool MN. Ulnar nerve injury after K-wire fi xation of supracondylar humerus fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop 1998;18: Birch R, Achan P. Peripheral nerve repairs and their result s in children Hand Clin 2000;16: H.K. Gupta,K.D. Khare, D. Chaurasia, Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, V ol-8, No-1, Apley s System of Orthopaedics and Fractures 9th ed 2010, Louis Solomon MD FRCS Emeritus Professor of Orthopaedics. Mustansiriya Medical Journal Volume 15 Issue 2 August
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type III supracondylar fracture: a retrospective analysis
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
A clinical study of closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 50/ June 22, 2015 Page 8632
 MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Analysis of displaced supracondylar fractures in children treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus Cross Pinning
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Introduction. Kumar Prashant 1 Devendra Lakhotia. Anil Kumar Mahanta 3 Aakhil Ravoof
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury?
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children treated by closed reduction with percutaneous crossed pin fixation
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Original Research Article. ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) DOI: /sajb
 DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
Surgical Complications
 Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Bioscience Research Print ISSN: Online ISSN:
 Available online freely at www.isisn.org Bioscience Research Print ISSN: 1811-9506 Online ISSN: 2218-3973 Journal by Innovative Scientific Information & Services Network RESEARCH ARTICLE BIOSCIENCE RESEARCH,201815(2):1409-1414
Available online freely at www.isisn.org Bioscience Research Print ISSN: 1811-9506 Online ISSN: 2218-3973 Journal by Innovative Scientific Information & Services Network RESEARCH ARTICLE BIOSCIENCE RESEARCH,201815(2):1409-1414
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department. October 2012
 Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
 Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction
 Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN
 1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography
 108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
We report the results of 116 consecutive displaced
 Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children
 Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Late Presentation in Children: A Preliminary Report
 Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic review
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris Yilmaz, 2 Baran Kömür, 3 Serhat Mutlu, 4 Harun Mutlu, 5 Korhan Özkan, 6 Abdullah Eren 7
 393 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures operated in first 24 hours with limited medial approach Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris
393 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures operated in first 24 hours with limited medial approach Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Elbow fractures account for approximately 5% to
 Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Pediatric Elbow Radiology. Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar
 Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
--Manuscript Draft-- the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees. Walid A Elnahal, M.Sc Tr & Orth
 Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES.
 PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Outcome of surgically treated displaced medial epicondyle fracture of humerus in children: A prospective study
 2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN. Dr.K.
 STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY Dr.K.SARAVANAN A Dissertation submitted to the BOOLEAN EDUCATION In partial
STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY Dr.K.SARAVANAN A Dissertation submitted to the BOOLEAN EDUCATION In partial
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Elbow Problems.
 Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient Fishtail Deformity after Surgery
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture. of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child
 Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review
 Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Common Limb Fractures. Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009
 Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN
 THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE
 Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
Percutaneous pinning after closed reduction of supracondylar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
Tuomilehto, N
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity Fractures---
 Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
 original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE CHILDREN
 DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 645 651 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 645 651 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric
Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children
 Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
The Outcome of Supracondyler Fractures of Elbow Joint Treated during Different Periods of Time by Different Techniques in District Population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Outcome of Supracondyler Fractures of Elbow Joint Treated during Different Periods of Time by Different Techniques in District Population MIAN MUHAMMAD AZHAR ABSTRACT Objective: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Outcome of Supracondyler Fractures of Elbow Joint Treated during Different Periods of Time by Different Techniques in District Population MIAN MUHAMMAD AZHAR ABSTRACT Objective: To
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow
 Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children
 519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
Outcome of Transcapitellar K-wire Fixation for Radial Neck Fractures
 Research Article Outcome of Transcapitellar K-wire Fixation for Radial Neck Fractures Ali A. Ali * (M.B.Ch.B., F..B.M.S(ortho), C.A.B.S(ortho)) Abstract Date Submitted:20/1/2014 Date Accepted: 8/4/2014
Research Article Outcome of Transcapitellar K-wire Fixation for Radial Neck Fractures Ali A. Ali * (M.B.Ch.B., F..B.M.S(ortho), C.A.B.S(ortho)) Abstract Date Submitted:20/1/2014 Date Accepted: 8/4/2014
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent
 Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Elbow injuries.
 Elbow injuries www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Objectives Revise a wee bit anatomy Learn elbow movements Know common injuries Know management of those injuries Anatomy Examination Inspection Palpation Movements
Elbow injuries www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Objectives Revise a wee bit anatomy Learn elbow movements Know common injuries Know management of those injuries Anatomy Examination Inspection Palpation Movements
Outcome of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children treated by closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire fixation
 Original article: Outcome of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children treated by closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire fixation Dr. Prashanth P, Dr. Srinivasan S, Dr. Arunprasath C,
Original article: Outcome of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children treated by closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire fixation Dr. Prashanth P, Dr. Srinivasan S, Dr. Arunprasath C,
Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. No disclosures for this presentation 10/29/18. Agenda
 Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Patient Education. Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
 Patient Education Supracondylar Humerus Fractures This is the most common fracture requiring surgery in children age 3-10. It can happen in younger and older kids as well. *Remember! Fracture, crack, break
Patient Education Supracondylar Humerus Fractures This is the most common fracture requiring surgery in children age 3-10. It can happen in younger and older kids as well. *Remember! Fracture, crack, break
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018
 PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning
 WELCOME The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning Vũ Công Tầm Nguyễn Bá Minh Phước Phạm Anh Tuấn
WELCOME The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children by closed reduc5on under ultrasound guidance and percutaneous pinning Vũ Công Tầm Nguyễn Bá Minh Phước Phạm Anh Tuấn
GALEAZZI FRACTURE. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations can be difficult to recognize and are often not initially appreciated.
 GALEAZZI FRACTURE Introduction In the Galeazzi fracture-dislocation there is a fracture of the distal third of the shaft of the radius in association with a subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulna
GALEAZZI FRACTURE Introduction In the Galeazzi fracture-dislocation there is a fracture of the distal third of the shaft of the radius in association with a subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulna
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1503.010 Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children Shabir AD, MS, Tahir AD, MS, Sharief AW, MS, Imtiyaz HD, MS, Shahid
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1503.010 Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children Shabir AD, MS, Tahir AD, MS, Sharief AW, MS, Imtiyaz HD, MS, Shahid
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
