Index. Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2015 T.J. Boffeli (ed.), Osteomyelitis of the Foot and Ankle, DOI /
|
|
|
- Felicity Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO) conventional radiography, 70 foot, laboratory aides, 69 magnetic resonance imaging, 70, 71 microbiology, 69 pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, 68 skeletal scintigraphy, 70 treatment, X-rays, 70 Acute osteomyelitis, 16, 308 empirical therapy, 57 immunosuppressive medications, 15 oral therapy, 58 targeted therapy, Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO), 253, 304, 313, 317, 326, 328, 329 Antibiotic beads, 131, 133, 162, 185, 188, 189, , 246, 247, 250, 303 ABLC beads, 115 plantar ulcer, 161 polymethylmethacrylate (see Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)) side effects, 114 soft tissue void/bone defect, 114 vs. spacer, 120 Antibiotic spacers, 63, 108, 109 antibiotic-loaded bone cement (ABLC) diabetic foot, high-dose ABLC, 120 postoperative infection/septic joint, removal and wound closure, 120, 122 technique, 120 trauma, ulcer excision and MTP joint resection, 122, 123 vs. beads, 120 Antibiotic therapy, 82, 83, 108, 148, 159, 161, 187, 204, 223, 228, 248, 288, 313, 314, 331 advantages and disadvantages, 7 elusion properties, 114 empirical therapy, MRSA, 56 parenteral and oral antibiotics, 56 targeted therapy, 56, B Baseball flap midfoot amputation technique bone resection, 279 clinical and radiographic follow-up of, 280 complete open fifth ray amputation, 278 DPAA and MPAA flap, 268, 279 gangrene/frostbite, 268, 278 medial and lateral soft tissue necrosis, 268, 278 rotated and sutured, year clinical and radiographic results of, 281 Below knee prosthetics, 283 Bone biopsy, 159 amputation, 41 antibiotic exposure, 41 calcaneal osteomyelitis cortical window with internal medullary debridement technique, 302 wound excision with cortical debridement, 307 Charcot arthropathy, 159 distal fibular osteomyelitis, lateral ankle decubitus ulceration, 328 distal Symes amputation, tip-of-toe ulcers, 210 fl uoroscopy, 40 "gold standard" status, 40 histopathologic evaluation and microbiologic culture, 41 incision and drainage procedure, 41 joint arthroplasty, 42, 44 open corticotomy, partial first ray amputation, 188 percutaneous trephine technique, 41 selection, 39 trephine bone biopsy, 41, 42, 44, 46 calcaneus, 46 hallux, 43 large bones of rearfoot/ankle, 44, 46 small bones of forefoot, 42 WBC count, 40 wound excision, C Calcaneal osteomyelitis, 46, 106 clinical and radiographic workup CT and bone scan, 298, 300 MRI, , 300 X-rays, 297, 300 cortical window with internal medullary debridement technique bone biopsy, 302 bone grafting, incision approach, 302 patient selection, 301 postoperative care, 302, 303 preoperative radiographs, 301 stage 2 procedure, 301, 303 isolated medical management, 298 leg amputation, partial calcanectomy (see Partial calcanectomy) Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2015 T.J. Boffeli (ed.), Osteomyelitis of the Foot and Ankle, DOI /
2 340 Calcaneal osteomyelitis (cont.) treatment pathways, wound excision with cortical debridement biopsy results, 308 bone biopsy, 307 decubitus, traumatic/surgical wound, 302 distal healing, 310 distal wound, partial closure of, 310 exposed and necrotic Achilles tendon, 308 exposed hardware and concern for osteomyelitis, 306 hardware removal and cortical debridement, 307 healing of incision, 305 infected sinus tract, 306 initial postoperative lateral radiograph, 305 nonhealing surgical wound, 304 patient selection, posterior calcaneus, cortical debridement of, 310 postoperative care, 304 preoperative and postoperative X-rays, 309 single-staged debridement, 309 surgical technique, wound closure options, 304 Central metatarsal osteomyelitis partial central ray amputation acute soft tissue infection, 222 extension of incision, 223 intramedullary canal, 223 margin pathology specimen, 223 metatarsal fragment, 222 periosteum, 222 6week post-operative clinical appearance, 223 prevention, 217 proximal metatarsal amputation accessory incision, 224, 225 dead space management, 226 heterotopic ossification, 224 metatarsal base amputation, 224, 225 metatarsal head resection, 227 mid-shaft metatarsal amputation, 224, 225 panmetatarsal head resection, 225, 227 plantar flap closure, 227 plantar rotational flap, 227 soft tissue disruption, 226 transmetatarsal amputation, 228 staged surgical approach, 228 surgical management anesthesia care, 219 dorsal metatarsal head resection, 222 indications, 219 isolated metatarsal head resection, 219 MRI, 219 plantar ulcer excision, 222 two-week post-operative radiographic appearance, 222 surgical modalities nonhealing and recurrent forefoot ulcers, 220 open gastrocnemius recession, 220 pre and 2-week post-postoperative clinical appearance, 220 structural deformities, 219 tendo-achilles lengthening (TAL), 218 Central toe osteomyelitis complete toe amputation, MPJ disarticulation, 211, 214, 215 diagnosis of, digital gangrene, 197, 198, distal Symes amputation, tip-of-toe ulcers, 205 advancement flap closure, 209 bone biopsy technique, 210 clinical results, 212 dorsal and plantar incision, 207 hemostasis with, incision technique, 208 instrumentation, 206 operative room setup, 206 postoperative results, 210 stage 2 distal Symes amputation, 211, 212 elective hammertoe surgery, 200, 202 fl exor and extensor tenotomy, 200, 201 hallux valgus deformity, 200, 202 ideal level of amputation, 204, 205 interdigital ulceration, 200, 202 intravenous antibiotics, 204 isolated medical management, 204 late stage onset of, 197 neuropathic ulcers, partial toe amputation, proximal phalanx, 204, 206, 213 PIPJ arthroplasty, 206, 213, 214 postoperative care, 211 prophylactic treatment, 199 second digital amputation, 200, 202 staged surgery, 204 surgical goals, 204 wound care challenges for, Chainsaw injury, Charcot arthropathy, 109, 158, 244, 264, 273 bone and joint imaging, 160 bone biopsy, 159 bone cultures, 159, 160 clinical evaluation, diagnosis, 157, 160 laboratory evaluation, 159 preoperative evaluation, probe to bone test, 158 treatment antibiotic cement beads/spacers, 161 arthrodesis, 162 culture and sensitivity-based antibiotics, 161 internal and external fixation, 162 intraoperative cultures, 161 medial column screw, 163 negative pressure therapy, 162 non-weight bearing, 162 single-stage procedure, 163, 164 weight bearing, 161 ulceration, 158 Chopart s amputation technique cuboid osteomyelitis, MPAA rotational flap (see Cuboid osteomyelitis) navicular preservation, 286, 287 partial foot prosthesis, 283, 296 patient selection criteria for, plantar space infections, 287 healing, 295 navicular preservation, 295 open TMA, postoperative X-rays, 292 stage 1 guillotine type forefoot amputation, 293 V to T rotational flap, 294 postoperative care, 296 rehabilitation, 283 staged surgical approach, 284 tendon balancing procedures, , 295 traditional approach active ankle dorsiflexion, 284, 285 anterior calcaneal remodeling, 284, 286
3 341 dorsal and plantar fish mouth incision design, 284, 285 full depth incision, 284, 285 healing, 286 midtarsal joint disarticulation, 284, 285 no-touch suture technique, 284 talus head, weight bearing, 286, 287 tibialis anterior tendon (TA), loss of, 284, 285 wound closure, 284, 286 Chronic osteomyelitis, 7, 13, 16, 51, 52, 56, 58, 108, 113, 161, 163, 219, 288, 305 empirical therapy, 58 oral therapy, targeted therapy, 58 Complete blood count (CBC), 69, 141 Crush injury, Cuboid osteomyelitis late stage pan metatarsal head resection, 288 MPAA rotational flap, Chopart s amputation forefoot disarticulation, 290 incision design, 289 partial foot prosthesis, 292 plantar flap remodeling, 290 postoperative weight bearing radiographs, 291 preoperative weight bearing radiographs, 291 raising of flap, 290 wound closure, 291 residual clubfoot deformity, 288 D Degloving injury, 148, 149, Diabetic foot osteomyelitis (DFO), 99, 116 adjuvant agents, bone eradication and soft tissue infection bone margin culture, 102 hybrid external fixation, 100 intraoperative specimens, 102 reconstruction considerations, 100 resection and reconstruction, 100 single-stage procedure, 100 surgical intervention, 100 tissue reconstruction advanced moist wound therapy, 103 angiosomes, 105 calcaneal osteomyelitis, 106 free muscle flaps, 105 limb function, 102 metatarsal phalangeal joint, 104 negative-pressure wound therapy, 102, 103 single-stage resection approach, 104 split-thickness skin graft (STSG) wound, 107 surgical debridement, 102 Distal fibular osteomyelitis, lateral ankle decubitus ulceration AFO bracing, 325, 326, 328 conservative surgical intervention, 326 diagnosis of bone biopsy, 328 bone scan and CT, 328 MRI, 327, 328 X-rays, 327 distal fibulectomy, 326, 331, hematogenous osteomyelitis, 325 late-stage development, musculocutaneous flaps, 326, neuromuscular contracture Achilles tendon lengthening, 329 posterior tibial tendon, Z-lengthening of, 328 soft tissue release, 329 neuropathic ulcers, 325 postoperative care, 331, 337 residual wound defect, 325 secondary osteomyelitis corticotomy, 333 recurrent soft tissue infection, 333 small lateral malleolar pressure sore, surgical treatment, 333 unilobed flap, rotation and closure of, 334 wound margins, undermining of, 333 small lateral malleolar pressure sore, wheelchair-related foot and ankle pressure sores, 325, 326 wound excision and lateral cortical debridement interval healing, 332 near-complete wound healing, 332 NPWT, 330 preoperative and postoperative radiographs, 331 progressive healing, 332 secondary osteomyelitis, 331 soft tissue undermining, 330 Distal Symes amputation, 200, 205 advancement flap closure, 209 bone biopsy technique, 210 clinical results, 212 dorsal and plantar incision, 207 hemostasis with, incision technique, 208 instrumentation, 206 operative room setup, 206 postoperative results, 210 stage 2 distal Symes amputation, 211, 212 Dorsalis pedis artery angiosome (DPAA), 268, 279 E Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), Extensor hallucis longus (EHL), 169 F Fifth metatarsal phalangeal joint (MPJ) osteomyelitis fi fth metatarsal head resection, 233, 236 partial fifth ray amputation with digital fillet flap, plantar ulceration, rotational flap for, 233, tennis racket incision, 233, 237 Fifth ray osteomyelitis complete fifth ray amputation antibiotic bead placement, 245, 247 antibiotic bead removal, 246, 247 cuboid remodeling, 245, 246, 248 fi fth metatarsal dissection, 246 fi fth metatarsal removal, 245, 246 healed incision, 250 incision planning, 245 indications, 244 peroneal tendon transfer, , 248, 249 plantar ulceration, preoperative appearance of, 245, 250 postoperative X-rays, 244, 249 preoperative X-rays, 244 soft tissue balancing procedures, 250, 251 tennis-racquet incision, 245 wound closure, 245, 249 fi fth MPJ ulceration and osteomyelitis ( see Fifth metatarsal phalangeal joint (MPJ) osteomyelitis) fi fth toe amputation
4 342 Fifth ray osteomyelitis (cont.) fifth metatarsal head removal, 233, 234 primary wound closure, 233, 234 proximal and middle phalanges, 232, 234 tennis racket incision, 234 trap door digital fillet flap technique, infected gangrene, internal pedal amputations, 230 lateral column decubitus ulcers, 229 location of, 229, 230 neuropathic ulcers, PIPJ arthroplasty and partial syndactylization, procedure selection for, 230 structural deformities, 230, 231 surgical goals, 229 traditional podiatric reconstructive procedures, 230 First ray osteomyelitis, complete first ray amputation antibiotic bead implantation, 193 bead removal, clinical appearance after, 195 extensive osteomyelitis, 192, 194 first metatarsal cuneiform joint, disarticulation, 196 first metatarsal head resection and biopsy, 194 heterotopic ossification, 192 midshaft plantar ulcer, 192 peroneus longus, preservation of, recurrence of HO, 193 recurrent plantar ulceration, 192 stage 2 and 3 procedures, 195 tibialis anterior, preservation of, 185 complete hallux amputation, 174, , 185 complications, 187 elective procedure pathways, 169, 170 foot and ankle deformities, 167 hallux distal Symes amputation ( see Hallux distal Symes amputation) hallux hammertoe deformity EHL lengthening, 169 elective hammertoe surgery, 169 hallux IPJ fusion/arthroplasty, 169, 173 tip-of-toe ulcers, FHL tenotomy ( see Tip-of-toe hallux ulceration) hematogenous osteomyelitis, 167, 168 infected gangrene, 167, 168 IPJ plantar ulcer, hallux IPJ arthroplasty benefits of, 170 bone resection, intraoperative imaging, 176 dorsal incision, 169 functional hallux limitus, 173 incision plan, 174 IPJ sesamoid bone, removal of, 177 patients, clinical exam of, 170 patient selection, 170 postoperative results, 178 preoperative imaging, 174 raising of unilobe flap, 175 rotation of unilobed flap, 177 secondary dorsal incision, 176 staged surgery, 171 valgus deformity of toe, 173 wound closure, 178 wound excision technique, 175 location of, 169, 170 medial column, 167 nail bed wounds, 167, 168 neuropathic ulcers, 167, 168 open fractures, 167, 168 partial first ray amputation ( see Partial first ray amputation) partial hallux amputation, , 185 plantar MPJ ulcers ( see Plantar first metatarsophalangeal joint (MPJ) ulceration) postoperative management, procedure selection flowchart, 169, 170 puncture wound, 167, 168 reconstructive podiatric procedures, 169 surgical treatment pathways, 169, 170 toenail-related infections, 167, 168 ulcerated tophaceous gout, 167, 168 Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) tenotomy, 169, 171, 172, 304 G Gustilo Anderson classification, 139, 140 H Hallux distal Symes amputation, disarticulation, hallux interphalangeal joint, 175, 183 incision and drainage of infection, 175, 182 incision plan, 175, 183 intraoperative radiographs, 175, 184 neuropathic and ischemic ulcers, 175, 181 patient selection for, 175, 181 proximal phalanx head, remodeling, 175, 183, 184 vascular intervention, clinical appearance after, 175, 182 wound closure, 175, 184 wound excision, 175, 182 wound healing, 175, 184 Hallux interphalangeal joint (IPJ) arthroplasty benefits of, 170 bone resection, intraoperative imaging, 176 dorsal incision, 169 functional hallux limitus, 173 incision plan, 174 IPJ sesamoid bone, removal of, 177 patients, clinical exam of, 170 patient selection, 170 postoperative results, 178 preoperative imaging, 174 raising of unilobe flap, 175 rotation of unilobed flap, 177 secondary dorsal incision, 176 staged surgery, 171 valgus deformity of toe, 173 wound closure, 178 wound excision technique, 175 Hallux valgus deformity, 43, 179, 200, 202 Heterotopic ossification (HO), 192, 254 clinical presentation, 129 etiology of, incidence of, 127 metatarsal amputation sites, 128 pharmacological prophylaxis, radiation therapy prophylaxis, 133, 135 surgical prophylaxis, antibiotic-impregnated beads, 134 histologic features, 133 osteoprogenitor cells, 133 soft tissue closure, 131 techniques, 134
5 343 treatment and prophylactic measures antibiotic beads, 131 bone growth, 131 intraoperative findings, 131 metatarsal resection site, 131 radiographs, 131 Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy, 7, 63 I Infected implants, 117 and epidemiology, pathogenesis, surgery, protocols, removal of 1-stage approach, stage approach, salvage strategies, treatment debridement, 79 exogenous and hematogenous colonization, 78 preclinical research, 80 stabilization, Staphylococcus aureus, J Joint arthroplasty, 40, 42 44, 171, 233 Joint sepsis, 143, 144, 168, 179 clinical presentation and diagnosis, of foot, medical and surgical treatment ankle portals, 94 anterolateral ankle portals, 93 antiseptics, 93 arthroscopic debridement, 95 doppler ultrasound, 94 insufficient response, 96 intraoperative fluoroscopy, 93 intraoperative staging, 95 open arthrotomy, 95 standard anteromedial portals, 93 Staphylococcus aureus, 92 2 weeks postoperatively arthroscopy portals, 96 L Lateral ankle decubitus ulceration. See Distal fibular osteomyelitis, lateral ankle decubitus ulceration Lateral plantar artery angiosome (LPAA) rotational flap, 261, 287 dorsal soft tissue defects, 262 forefoot and vascular intervention, demarcation of, 264 forefoot, medial necrosis of, 263 forefoot resection, 264, 265 intraoperative assessment of, 266 metatarsal resection, 262, 264 necrotic tissue resection, 262, 264 pivot point of, 262 postoperative radiographs, 267 postoperative results, 267 raising of flap, 262, 265 rotated and sutured, Lawn mower injury, Lisfranc tarsometatarsal amputation Achilles tendon lengthening, 258 dorsal and plantar fish mouth incision design, 258, 262 extensive tissue necrosis, frostbite, 257, 261 forefoot disarticulation, 258, 260, 262 forefoot gangrene, 257, incision technique, 258 lateral column breakdown, 253 level of, 253, 254 medial cuneiform, TA and PL insertions, 258, 263 midfoot ulceration, 257, 261 MPAA rotational flap (see Medial plantar artery angiosome (MPAA) rotational flap) musculotendinous structures, loss of, 253 peroneus brevis function, loss of, 257 peroneus longus function, loss of, 257 postoperative care, 270 postoperative radiographs, 263 PT tendon open Z-lengthening, 258, 262 tarsal bone remodeling, 258, 263 tendon balancing procedures, need for, 253 tibialis anterior function, loss of, 257 wound closure, 260 M Medial plantar artery angiosome (MPAA) rotational flap, 261 baseball flap midfoot amputation, 268, 279 choke vessels, 266 cuboid osteomyelitis, Chopart s amputation forefoot disarticulation, 290 healing, 292 incision design, 289 partial foot prosthesis, 292 plantar flap remodeling, 290 postoperative weight bearing radiographs, 291 preoperative weight bearing radiographs, 291 raising of flap, 290 wound closure, 291 Lisfranc amputation Charcot related plantar lateral midfoot wound, 273 healing of, 275 incision plan, 273 intraoperative imaging in, 274 postoperative radiographs of, 275 tarsal bone remodeling, 273 wound closure, 274 pivot point approach, 265 transmetatarsal amputation incision planning, 270 intraoperative flap creation, 271 metatarsal resection, 269 necrotic tissue resection, 269 plantar lateral forefoot gas gangrene, 268 postoperative radiographs of, 272 rotated and sutured, 272 Medical management adjunctive therapies, 63 anaerobes, 61 antibiotic therapy empirical therapy, MRSA, 56 parenteral and oral antibiotics, 56 targeted therapy, 56, coagulase-negative staphylococci, 60 duration of therapy, enterococci and vancomycin-resistant enterococci, 60 gram-negative organisms, 60 61
6 344 Medical management (cont.) indications, local antibiotic therapy, 63 oral antibiotics, organisms, 59, 60 polymicrobial infections, 61 prosthesis infections, 61 Staphylococcus Aureus and MRSA, Streptococcus spp., 60 Metatarsophalangeal joint (MPJ), 87, 97, , , 173, 176, , 185, 190, 201, 202, , 214, 215, 233, 256 partial fifth ray amputation ( see Partial fifth ray amputation, MPJ osteomyelitis) plantar first MPJ ulceration ( see Plantar first metatarsophalangeal joint (MPJ) ulceration) Methacillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), 4, Midfoot amputation, 163, 167, 220, 253, 258, baseball flap technique, 268, Lisfranc amputation (see Lisfranc tarsometatarsal amputation) transmetatarsal (see Transmetatarsal amputation (TMA)) Motor vehicle collision (MVC), N Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), 141, 330 O Open fractures, 1, 2, 67, 77, 82, 116 fi rst ray osteomyelitis, 167, 168 traumatic injuries antibiotics, 148 chainsaw injury, definition, 148 degloving injury, industrial crush injury, lawn mower injury, motor vehicle collision, road rash injury, Osteomyelitis acute phase reactants C-reactive protein, 22 erythrocyte sedimentation rate, procalcitonin, blood cultures, 21 bone biopsy, 20 calcaneal (see Calcaneal osteomyelitis) central metatarsal osteomyelitis ( see Central metatarsal osteomyelitis) of central toe ( see Central toe osteomyelitis) charcot arthropathy (see Charcot arthropathy) classifications, clinical findings and laboratory markers, 23 clinical signs and symptoms, computed tomography, diagnosis, 5 6 epidemiological data, 1 etiology and classification, 2 3 fifth ray ( see Fifth ray osteomyelitis) of first ray ( see First ray osteomyelitis) laboratory evaluation, leukocytosis, 21 limb salvage, 1 magnetic resonance imaging abscesses, 33 bone marrow, 30, 31 callus formation, 30 gadolinium contrast enhanced imaging, 33 marrow edema, 32 meta-analysis, 34 soft tissue structures, 30 STIR imaging, 30 tendon involvement, 34 T1 weighted imaging, 31 T2 weighted imaging, 32 ulcerations, 30, 31 management, 6 8 neuroarthropathy, nuclear medicine scans labeled white blood cell scans, technetium 99m phosphate bone scans, 28 pathologic diagnosis acute osteomyelitis, 50, 51 bone culture, 49 chronic osteomyelitis, 52 cortex subperiosteal scalloping, 50 histologic features, 51 osteoclasts, 49 osteocytes, 49 postsurgical changes, 51, 52 septic arthritis, 52 sequestrum, 51 pathophysiology and microbiology, 3 4 populations at risk, 4 5 positron emission tomography imaging, probe-to-bone (PTB), radiography, 27 risk factor bacteremia, in adults, 14 circulation disorders, 15 comorbidities, 14 environmental settings, 15 exposures, 13 illicit drug abusers, 15 patient s age and gender, prescription medications, 15 trauma/osseous surgery, 15 traumatic injuries (see Traumatic injuries) vital signs, wound characteristics depth, 18 duration, 17 size, 18 O-to-Z flap technique fl ap closure, 173, 180 incision design, 173, 179 sesamoidectomy surgical technique, 173, 180 P Partial calcanectomy fl ap design and wound closure options decubitus ulcer, zones of, 307, 309, 311 fl ap planning, 309, 312 wheelchair-bound patients, 309, 311 goal of, 314 junctional heel ulceration, 314, 319, 320 patient selection, , 311 plantar heel decubitus ulceration, 314, posterior heel decubitus ulceration, 313 contralateral leg amputation, 317 fl ap creation and closure, 318 stage 1 surgery, 318
7 345 postoperative care heel off-loading posterior splint, 313, 316 pillow dressing, 313, 315 rigid ankle-foot orthoses, 313, 317 surgical technique bone resection, extent of, 311, 313 Eschar excision, 312 flap closure, 311, 313 guide pin technique, 311, 313 no-touch technique, patient positioning, 309 preoperative antibiotics, 309 Partial fifth ray amputation, MPJ osteomyelitis digital fillet flap, plantar ulceration, rotational flap for, 233 bone exposure, 238 flap closure, 240 flap design, 238 metatarsal head resection, 239 predisposing factors, 238 raising of flap, 238 tissue, marking of, 238 tennis racket incision, 233, 237 Partial first ray amputation plantar MPJ ulcer, rotational flap for incision planning, 181, 190 intraoperative imaging, 181, 191 metatarsal resection, 181, 190 raising of flap, 181, 190 wound closure, 184, 191 traditional technique bone biopsy, 188 dorsal and plantar flap incision design, 179, 187 hallux, infection and necrosis of, incision technique, 179 metatarsal head resection, , 189 MPJ disarticulation, 179, 188 no-touch technique, 179, 187 plantar tissue necrosis, 186 proximal medullary canal, 180, 189 raising of flap, 188 serial X-rays, 186 tennis racquet-type incision, 179 wound closure, 180, 189 Partial foot prosthetics, 283, 292, 296 Partial hallux amputation, 167, , 185 Partial syndactylization technique, Patzaki classification system, 142 Pedal puncture wounds, 141, 142 Peripheral vascular disease (PVD), 5 Plantar first metatarsophalangeal joint (MPJ) ulceration bilobed rotational flap, 173, 181 diabetic patients, peripheral neuropathy, 171 metatarsal/proximal phalanx, 173, 179 O-to-Z flap closure of, 173, 180 incision design, 173, 179 sesamoidectomy surgical technique, 173, 180 partial first ray amputation ( see Partial first ray amputation) related deformities, 173 sesamoid bone, osteomyelitis of, 173, 179 Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), 108, 121 antibiotic selection, 114 cardiopulmonary complications, 114 methyl methacrylate, 113 Postamputation heterotopic ossification. See Heterotopic ossification (HO) Posterior tibial (PT) tendon, 258, 262 Probe-to-bone (PTB), Proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ) arthroplasty dorsal ulceration, hammertoe deformity, 206, 213, 214 fi fth toe osteomyelitis, Pseudomonas, 143, 148 P. aeruginosa, 4 Puncture wounds antibiotics, foreign body, removal of, imaging technique, 142, 143 Patzaki classification system, 142 pedal, 141, 142 surgical treatment, R Radionuclide imaging, 160 Rigid ankle-foot orthoses, 317 Road rash injury, S Skeletal reconstruction, 121 Small lateral malleolar pressure sore, Staphylococcus aureus, 3, 69, 92, , 148 T Tendo-Achilles lengthening (TAL), 250, 255, 287, 295 Tetanus prophylaxis, 139, 140 Tip-of-toe hallux ulceration FHL tenotomy clinical appearance after, 169, 172 percutaneous plantar incision, 169, 171 preoperative and postoperative radiographs, 169, 172 hallux distal Symes amputation, 169 with hammertoe contracture, 169, 171 Transmetatarsal amputation (TMA), 241. See also Lisfranc tarsometatarsal amputation ankle tourniquet, 256 atraumatic surgical technique, 256 biomechanical consequence, 254 cross-contamination, risk of, delayed posterior lengthening, 256 dorsal and plantar fish mouth incision design, forefoot disarticulation, 256, 259 gangrene-related TMA, 255 gastrocnemius recession, 255 heterotopic ossification, 254 interrupted skin sutures, 257, 260 level of, 253, 254 LPAA rotational flap dorsal soft tissue defects, 262 forefoot and vascular intervention, demarcation of, 264 forefoot, medial necrosis of, 263 forefoot resection, 264, 265 intraoperative assessment of, 266 metatarsal resection, 262, 264 necrotic tissue resection, 262, 264 pivot point of, 262 postoperative radiographs of, 267 postoperative results, 267 raising of flap, 262, 265 rotated and sutured, margin biopsy, 257, 260 metatarsal osteomyelitis, 254
8 346 Transmetatarsal amputation (TMA) (cont.) metatarsal preservation approach, 254 metatarsal resection, 256, 259 MPAA rotational flap (see Medial plantar artery angiosome (MPAA) rotational flap) pathologic mechanics, 254 patient selection criteria, 256, plunge-cut technique, 256, 258 postoperative care, 268, 270 postoperative imaging, 257, 261 profound equinus contracture, 256 TAL procedures, 255 V to T flap technique, 268 incisions, 276, 277 intraoperative imaging, 278 larger central plantar soft tissue defects., 268, 277 plantar forefoot wound, 276 postoperative radiographic imaging, 276, 278 second metatarsal head, resection of, 276 wound closure, 278 zone of resection, 254 Trap door digital fillet flap technique, Traumatic injuries antibiotic and bacteria concern, 139, 140 Gustilo-Anderson classification, 139, 140 irrigation and debridement, 141 lower extremity, 139 open fractures antibiotics, 148 chainsaw injury, definition, 148 degloving injury, industrial crush injury, lawn mower injury, motor vehicle collision, road rash injury, puncture wounds antibiotics, foreign body, removal of, imaging technique, 142, 143 Patzaki classification system, 142 pedal, 141, 142 surgical treatment, radiographs, 141 tetanus prophylaxis, 139, 140 Trephine bone biopsy calcaneus, 46 hallux, 43 large bones of rearfoot/ankle, 44, 46 small bones of forefoot, 42 V V to T flap technique, 268 incisions, 276, 277 intraoperative imaging, 278 larger central plantar soft tissue defects., 268, 277 plantar forefoot wound, 276 postoperative radiographic imaging, 276, 278 second metatarsal head, resection of, 276 wound closure, 278 W Waldvogel classification, 2
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatry. Procedure List. As Of. 01 April Government of Alberta
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
CLAD Error Key. Error Levels: Definite, Possible. Error Procedure Scope. Validation Scope. Location Scope. Violation/Information Text
 CLAD Key s: Definite, Possible Procedure 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Two or more category 1 procedures Digit Definite 1.6 plus one or more of the following: 2.1.3, 2.1.7, 2.2.2, 2.2.6, and 2.3.4 Side Definite
CLAD Key s: Definite, Possible Procedure 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Two or more category 1 procedures Digit Definite 1.6 plus one or more of the following: 2.1.3, 2.1.7, 2.2.2, 2.2.6, and 2.3.4 Side Definite
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot
 Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence. Watermark. Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas
 Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas J. Randolph Clements, DPM Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics Virginia Tech- Carilion School of Medicine
Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas J. Randolph Clements, DPM Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics Virginia Tech- Carilion School of Medicine
Surgical Off-loading. Reiber et al Goals of Diabetic Foot Surgery 4/28/2012. The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration
 Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Proper Logging of Surgical Procedures (Effective July 1, 2018)
 Proper Logging of Surgical Procedures (Effective July 1, 2018) GENERAL GUIDELINES: 1) For the procedure codes listed below, the program director must review each entry to determine proper usage. The following
Proper Logging of Surgical Procedures (Effective July 1, 2018) GENERAL GUIDELINES: 1) For the procedure codes listed below, the program director must review each entry to determine proper usage. The following
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatric Surgery. Procedure List. As Of.
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2016 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2016/03/22 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2016/04/01 07 PHYSICAL MEDICINE, REHABILITATION,
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2016 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2016/03/22 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2016/04/01 07 PHYSICAL MEDICINE, REHABILITATION,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, with diabetic foot ulcers, 472 Achilles tendon, in calcanectomy, for osteomyelitis, 473, 483 in calcaneus anatomy, 477 478 in Syme
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, with diabetic foot ulcers, 472 Achilles tendon, in calcanectomy, for osteomyelitis, 473, 483 in calcaneus anatomy, 477 478 in Syme
American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery
 American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery Logging Guidelines Revisions ABFAS Task Force Mindy Benton, DPM Randall Dei, DPM Charles Lombardi, DPM John Thomas Marcoux, DPM Roya Mirmiran, DPM Michael Vaardahl,
American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery Logging Guidelines Revisions ABFAS Task Force Mindy Benton, DPM Randall Dei, DPM Charles Lombardi, DPM John Thomas Marcoux, DPM Roya Mirmiran, DPM Michael Vaardahl,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, in puncture wounds, 531 Absorbable fixation, for Lisfranc joint injuries, 556 Advanced glycosylation end products, complications due
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, in puncture wounds, 531 Absorbable fixation, for Lisfranc joint injuries, 556 Advanced glycosylation end products, complications due
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Index. Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscesses, 27 30 Acellular products, for bone healing, 55 56 Acetaminophen, 79 80 Achilles tendon lengthening, for pediatric flatfoot,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscesses, 27 30 Acellular products, for bone healing, 55 56 Acetaminophen, 79 80 Achilles tendon lengthening, for pediatric flatfoot,
Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes
 Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes Surgical approaches are often necessary to off-load excessive pressure. By Derek Ley, DPM, and Barry Rosenblum, DPM Introduction In approaching diabetic
Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes Surgical approaches are often necessary to off-load excessive pressure. By Derek Ley, DPM, and Barry Rosenblum, DPM Introduction In approaching diabetic
Technique Guide. 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot.
 Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
An Independent, Specialized Accrediting Agency
 9312 Old Georgetown Road Bethesda, Mar yland 20814 P 301.581.9200 I F 301.571.4903 www.cpme.org MEMORANDUM March 20, 2018 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Program Directors and Residents Council on Podiatric Medical
9312 Old Georgetown Road Bethesda, Mar yland 20814 P 301.581.9200 I F 301.571.4903 www.cpme.org MEMORANDUM March 20, 2018 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Program Directors and Residents Council on Podiatric Medical
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME
 2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
2017 SAFSA CONGRESS PROGRAMME THURSDAY, MAY 25 07h45 07h55: WELCOME & INTRODUCTIONS Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes (08h00-10h00 Lectures) 08h00 08h30: Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Rippstein,
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne
 What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped
 Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor hallucis (ABH) tendon transfer, for hallux varus, technique for, 458 462 bone tunnels and course diagram in, 458, 460 capsulotomy
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor hallucis (ABH) tendon transfer, for hallux varus, technique for, 458 462 bone tunnels and course diagram in, 458, 460 capsulotomy
*Rippstein, Trnka, Saragas, Hoffman
 THURS 25th MAY 07:00 07:10 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 07:10 09:45 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 40 mins 07:10 07:50 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus 30
THURS 25th MAY 07:00 07:10 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 07:10 09:45 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 40 mins 07:10 07:50 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus 30
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Rippstein, Trnka, Saragas, Narramore
 THURS 25th MAY 07:45 07:55 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 08:00 10:20 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 30 mins 08:00 08:30 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Saragas,
THURS 25th MAY 07:45 07:55 Welcome and Introductions Paulo Ferrao Lecture 1: 08:00 10:20 Forefoot I: Hallux Valgus and Lesser Toes Mark Easley 30 mins 08:00 08:30 Surgical Management of Hallux Valgus Saragas,
6.5 mm midfoot fusion bolt
 6.5 mm midfoot fusion bolt For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot SurgIcal technique Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
6.5 mm midfoot fusion bolt For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot SurgIcal technique Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS DECEMBER 9-11, 2010 Hyatt Regency Hill Country Resort & Spa Resort, San Antonio, TX USA. Program Agenda
 6 th ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL EXTERNAL FIXATION SYMPOSIUM The Diabetic Charcot Foot SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS DECEMBER 9-11, 2010 Hyatt Regency Hill Country Resort & Spa Resort, San Antonio, TX USA Program Agenda
6 th ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL EXTERNAL FIXATION SYMPOSIUM The Diabetic Charcot Foot SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS DECEMBER 9-11, 2010 Hyatt Regency Hill Country Resort & Spa Resort, San Antonio, TX USA Program Agenda
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes), 20 Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease (ADVANCE), 20 Action to Control Cardiovascular
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes), 20 Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease (ADVANCE), 20 Action to Control Cardiovascular
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT
 TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
Transmetatarsal and Midfoot Amputations
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDIGS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 361, pp 85-90 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Transmetatarsal and Midfoot Amputations John S. Early, MD The objective of lower extremity amputation
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDIGS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 361, pp 85-90 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Transmetatarsal and Midfoot Amputations John S. Early, MD The objective of lower extremity amputation
Anthony J. Cavallo, DPM Sentara Podiatry Specialists 4/27/2018. Lose a toe, Save a Limb: The Value of Complex Foot Reconstructions
 Anthony J. Cavallo, DPM Sentara Podiatry Specialists 4/27/2018 Lose a toe, Save a Limb: The Value of Complex Foot Reconstructions Objectives Review the morbidity and mortality associated with amputation
Anthony J. Cavallo, DPM Sentara Podiatry Specialists 4/27/2018 Lose a toe, Save a Limb: The Value of Complex Foot Reconstructions Objectives Review the morbidity and mortality associated with amputation
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Foot and Ankle Systems Coding Reference Guide
 Foot and Ankle Systems Coding Reference Guide Physician Arthrodesis 27870 Arthrodesis, ankle, open 27871 Arthrodesis, tibiofibular joint, proximal or distal 28705 Arthrodesis; pantalar 28715 Arthrodesis;
Foot and Ankle Systems Coding Reference Guide Physician Arthrodesis 27870 Arthrodesis, ankle, open 27871 Arthrodesis, tibiofibular joint, proximal or distal 28705 Arthrodesis; pantalar 28715 Arthrodesis;
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY PODIATRIC SURGERY
 NAME: DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY PODIATRIC SURGERY Applicant: Check the Requested box for each privilege requested. Applicants have the burden of producing information deemed adequate by the hospital for a
NAME: DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY PODIATRIC SURGERY Applicant: Check the Requested box for each privilege requested. Applicants have the burden of producing information deemed adequate by the hospital for a
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Proper Logging of Podiatric Medical / Surgical Residency Experiences
 Proper Logging of Podiatric Medical / Surgical Residency Experiences Revisions effective July 1, 2018 John T. Marcoux, DPM, FACFAS ABFAS Proper Logging Task Force Mindy Benton, DPM Randall Dei, DPM Charles
Proper Logging of Podiatric Medical / Surgical Residency Experiences Revisions effective July 1, 2018 John T. Marcoux, DPM, FACFAS ABFAS Proper Logging Task Force Mindy Benton, DPM Randall Dei, DPM Charles
NORTHERN OHIO FOUNDATION
 NORTHERN OHIO FOOT & ANKLE FOUNDATION! The!Northern!Ohio!Foot!and!Ankle!Journal!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Official!Publication!of!the!NOFA!Foundation!! Partial First Ray Amputations: Success Rates and Biomechanics
NORTHERN OHIO FOOT & ANKLE FOUNDATION! The!Northern!Ohio!Foot!and!Ankle!Journal!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Official!Publication!of!the!NOFA!Foundation!! Partial First Ray Amputations: Success Rates and Biomechanics
ABPS 500. Examination Blueprints (Revised Classification) American Board of Podiatric Surgery 445 Fillmore Street San Francisco, CA
 ABPS 500 Examination Blueprints () American Board of Podiatric Surgery 445 Fillmore Street San Francisco, CA 94117-3404 (415) 553-7800 (415) 553-7801 (FAX) info@abps.org November 2012 Purpose, Test Specification,
ABPS 500 Examination Blueprints () American Board of Podiatric Surgery 445 Fillmore Street San Francisco, CA 94117-3404 (415) 553-7800 (415) 553-7801 (FAX) info@abps.org November 2012 Purpose, Test Specification,
2013/10/18 GANGLION CYSTS ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY ARTHROSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OPEN GANGLIONECTOMY COMPARED TO FOOT AND ANKLE
 GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Foot & Ankle Disorders
 Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Treatment of infection
 Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
17/10/2017. Foot and Ankle
 17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
Index. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
 1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in
 Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene.
Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene.
pedcat Clinical Case Studies
 pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
~, /' ~::'~ EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS. Leg-anterolateral :.:~ / ~\,
 TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendon injury of, pathophysiology of, 10 peritendinitis of, 119 120 rupture of, 32 35, 117 135 anatomy of, 117 118 chronic, 126
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendon injury of, pathophysiology of, 10 peritendinitis of, 119 120 rupture of, 32 35, 117 135 anatomy of, 117 118 chronic, 126
Ankle Tendons in Athletes. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendon, Zadek osteotomy effects on, 430 Adult acquired flatfoot disorder, 387 403 calcaneal Z osteotomy for, 397 399 historical
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendon, Zadek osteotomy effects on, 430 Adult acquired flatfoot disorder, 387 403 calcaneal Z osteotomy for, 397 399 historical
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Surgical Technique. Customer Service:
 Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
Patent and Patent Pending CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Axis Charcot Fixation System in diameters of 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5mm
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve. Lumbar radiculopathy Instability MTPJ joint or inflammatory MPJ
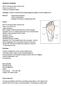 MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
MORTON S NEUROMA 80% III web space (next common is II). Never occurs in III or IV Common in females in fifties Aetiology: Pressure of Distal intermetatarsal ligament against common digital nerve Rule out
Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity
 REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage
 Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
Page 1 of 6. Appendix 1
 Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants
 Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants JOSHUA L. MOORE, DPM FACFAS ASSISTANT DEAN OF EDUCATIONAL AFFAIRS TUSPM CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF SURGERY Definitions Hallux Limitus 1 st MTPJ range of motion
Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants JOSHUA L. MOORE, DPM FACFAS ASSISTANT DEAN OF EDUCATIONAL AFFAIRS TUSPM CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF SURGERY Definitions Hallux Limitus 1 st MTPJ range of motion
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
ABC of Emergency Radiology
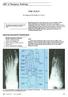 l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction
 Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI. Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY
 CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants Design Rationale Pain of the great toe joint often leads to altered lifestyles. The goal of MPJ implant
CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants Design Rationale Pain of the great toe joint often leads to altered lifestyles. The goal of MPJ implant
High Ankle Sprains: Diagnosis & Treatment
 High Ankle Sprains: Diagnosis & Treatment Mark J. Mendeszoon, DPM, FACFAS, FACFAOM Precision Orthopaedic Specialties University Regional Hospitals Advanced Foot & Ankle Fellowship- Director It Is Only
High Ankle Sprains: Diagnosis & Treatment Mark J. Mendeszoon, DPM, FACFAS, FACFAOM Precision Orthopaedic Specialties University Regional Hospitals Advanced Foot & Ankle Fellowship- Director It Is Only
Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot
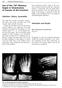 168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Surgical Classification of the Cavus Foot Deformity
 CHAPTER 43 Surgical Classification of the Cavus Foot Deformity Jobn A. Rucb, D.PM. Historically, surgical repair of the cal,us foot deformity has been based on many different complicated and confusing
CHAPTER 43 Surgical Classification of the Cavus Foot Deformity Jobn A. Rucb, D.PM. Historically, surgical repair of the cal,us foot deformity has been based on many different complicated and confusing
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
The American Academy of Foot & Ankle Osteosynthesis. presents
 The American Academy of Foot & Ankle Osteosynthesis presents Comprehensive Course of Internal Fixation for Reconstructive Surgery and Trauma of the Foot & Ankle September 4-6, 2014 Goodlett Farms Innovation
The American Academy of Foot & Ankle Osteosynthesis presents Comprehensive Course of Internal Fixation for Reconstructive Surgery and Trauma of the Foot & Ankle September 4-6, 2014 Goodlett Farms Innovation
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction
 Original Article Plastic and Aesthetic Research Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction Pradeoth Mukundan
Original Article Plastic and Aesthetic Research Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction Pradeoth Mukundan
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
