ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris Yilmaz, 2 Baran Kömür, 3 Serhat Mutlu, 4 Harun Mutlu, 5 Korhan Özkan, 6 Abdullah Eren 7
|
|
|
- Andrea Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 393 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures operated in first 24 hours with limited medial approach Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris Yilmaz, 2 Baran Kömür, 3 Serhat Mutlu, 4 Harun Mutlu, 5 Korhan Özkan, 6 Abdullah Eren 7 Abstract Objective: To investigate the middle- and long-term radiological and functional results of children with type III supracondylar humerus fractures treated with a limited medial approach and internal fixation. Methods: The retrospective study was conducted at Department of Orthopaedics in Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey, and comprised data of children who underwent surgery between April 1991 and June Patients in group I underwent surgery within the first 8 hours after admission, and those in group II did so 8-24 hours after admission. Patients were evaluated according to the Flynn scoring system. Results: Of the 79 patients, 52(65.8%) were male and 27(34.2%) were female. Fractures involved the left side in 49(62%) patients. Group I had 39(49.4%) patients and group II 40(50.6%). The overall mean age was 6.2±2.95 years (range: 2-13 years), and the mean follow-up was 53.2±14.9 months (range: months). Functional scores were satisfactory (excellent, good and fair results) in all cases in both groups (100%), and the cosmetic results were satisfactory in 37(95%) in group I, and 39(97.5%) in group II (p>0.05). Conclusion: Limited medial approach to the treatment of supracondylar humerus fractures yielded successful functional and cosmetic results. Keywords: Medial approach, Paediatric fractures, Supracondylar humeral fractures. (JPMA 66: 393; 2016) Introduction Supracondylar humerus fractures account for 60-75% of all fractures of the elbow in children. 1 Boys usually have a higher incidence of this type of fracture, but some recent reports in literature have described increasing rates in girls. Most patients are 5-7 years of age. 2 The fracture typically occurs due to a fall on to an outstretched hand with hyperextension of the elbow joint. 3 The distal fragment displaces posteriorly in more than 95% fractures. 2,3 Various methods have been described for treating paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. 1,2 It has been reported that conservative treatment is mainly preferred for undisplaced fractures, whereas closed reduction and percutaneous pinning are chosen for displaced fractures. 3 Open reduction may be considered when an acceptable reduction cannot be achieved via the closed technique, a fluoroscopy device is not available, or the surgeon has insufficient experience in close reduction and percutaneous pinning. 4 Approaches from four 1Year Goverment Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics, Adiyaman, 2 Fatih Sultan Mehmet Training and Research Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics, Istanbul, 3,4Kanuni Sultan Süleyman Training and Research Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics, Istanbul, 5 Taksim Training and Research Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics, Istanbul, 6 Medeniyet University Medical School, Department of Orthopaedics, Istanbul, 7 Sisli Florence Nightingale Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics, Istanbul, Turkey. Correspondence: Serhat Mutlu. serhatmutlu@hotmail.com different anatomical regions to the elbow region have been discussed in the literature. However, there has been no adequate study of these approaches to indicate the superiority of one over another. 5 In our study, if we were unable to apply closed reduction, and instead performed open reduction in a number of cases, regardless of whether the fracture occured under flexion or extension. To avoid damaging the vessel and nerve systems, we considered the limited medial approach to be the safest and best method. Using this method, fractures carrying a high risk of serious vascular complication can be safely managed. Removing the fracture haematoma and maintaining reduction relieves the circulation. If necessary, such an incision makes it possible to visualise and explore the neurovascular structure. The current study was planned to investigate the midand long-term results of open reduction using a limited medial approach and internal fixation in paediatric extension and flexion type III supracondylar humerus fractures. Materials and Methods The retrospective study was conducted at Department of Orthopaedics in Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey, and comprised data of children who underwent paediatric supracondylar humerus fracture Vol. 66, No. 4, April 2016
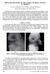
2 394 A.Dost, B. Yilmaz, B. Kömür, et al surgery between April 1991 and June Cases managed with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning and those in whom open reduction was performed through surgical approaches other than the medial were excluded. Surgery was performed on all patients by a single surgeon in cases where closed reduction could not be completed or vessel-nerve damage was present. Consequently, open surgery with a limited medial approach followed by flouroscopy-controlled pinning was preferred. All patients underwent surgery within 24 hours of trauma. Patients in group I underwent surgery within the first 8 hours after admission, and those in group II did so 8-24 hours after admission. The Flynn criteria were used to compare the cosmetic and functional results of both groups. 6 All patients were treated under general anaesthesia by medial minimal open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) after the failure of closed anatomical reduction. Tourniquet use was not required. The skin incision was initiated 3cm proximal to the elbow joint line and extended posteromedially to the distal part of the medial epicondyle. With this approach, the dermis subdermis was dissected until the ulnar nerve and fracture line were exposed through the medial intermuscular aperture. After removal of the fracture haematoma, an indirect reduction was obtained via this aperture by using an index finger (Figure-1). K-wires 1-1.5mm diameter were inserted under flouroscopy from both condyles with a 45 angle to the humerus shaft for fixation. After stability and circulation had been controlled, the tissue layers were closed by atraumatic sutures. The elbow was fixed using a long arm splint at of flexion. Following the operation, radiological control imaging was performed (Figure-2A- D). By the third week post-surgery, the splint was removed and active exercises were started. After the pins were removed at the fourth week, the patient and patient's relatives were provided with information regarding the rehabilitation programme. All patients were followed up at 3-month intervals in the first year and at 6-month intervals in the second year, after which routine follow-up of cases came to an end. In the final visits, physical and neurological surveys and radiological control imaging (Figure-2 E-F) of both upper extremities were performed. Bilateral elbow movements were measured using a goniometre. Carrying angles were measured with the McRae method on both sides. The Baumann angle was considered to be the best indicator of a displacement of the distal humerus. This angle decreased in the medial tilt of the distal fragment and increased the lateral tilt. The correlation with the carrying angle was significant, and every 5º of difference at the Baumann angle created 2º of change at the carrying angle. 7 Data was assessed on Flynn criteria. SPSS 11 was used for statistical analysis. Parametric comparisons were based on means, standard deviations, frequencies and percentages. Student's-t test and chisquare test were used and results were found to have a confidence interval (CI) of 95% with a significance value of p<0.05. Results Data of 576 patients diagnosed with Gartland type III fractures was identified. Among them, limited medial approach was used in 112(19.4%) cases, and complete medical record, including the final follow-up, was available for 79(70%) of them. Of the 79 cases, 52 (65.8%) were male and 27 (34.2%) were female. The mean age was 6.2± 2.95 years (range: 2-13) years. The left side was involved in 49 (62.0%) patients and the right side in 30 (38.0%). Of the total, 39(49.4%) patients in group I underwent surgery in the first 8 hours of admission, and 40(50.6%) in group II 8-24 hours. The mean follow-up was 53.2 ± 14.9 months (range: ). The cause of injury in 42 (53.2%) patients was fall to the ground, 32 (40.5%) fell from a height, and 5 (6.3%) fell off a bicycle. In terms of season, 32 (40.5%) patients suffered injury during the summer, 17 (21.5%) in the spring, 16 (20.3%) in the winter, and 14 (17.7%) were in the autumn. Figure-1: A) Incision line at the elbow. B-C) Indirect reduction of the fracture using a finger. J Pak Med Assoc
3 Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures Figure-2: 11-year-old male operated upon 8-24 hours (Group II) after admission to hospital. A) Preoperative antereoposterior (AP) X-ray. B) Preoperative lateral X- ray. C) Early postoperative AP X-ray. D) Early postoperative lateral X-ray. E) Postoperative 100. month AP X-ray. F) Postoperative 100-month lateral X-ray. Radial nerve palsy was diagnosed in 8(10.1%) cases, median and isolated anterior interosseous nerve palsy was in 5(6.3%) cases, and ulnar nerve palsy in 1(1.2%) case. Two (2.4%) patients suffered from pulselessnes of the radial artery and distal circulatory system complications. All neurovascular complications healed without additional treatment during the first 3 months. According to last follow-up, Flynn's Scoring Criteria the functional scores in all patients in both groups (100%) were satisfactory (excellent, good and fair results), while cosmetic results were satisfactory in 37(95%) in group I, and 39(97.5%) in group II (p>0.05). Overall functional results were 100% satisfactory, while cosmetic results were satisfactory in 76(96.2%) patients (Table). The mean carrying angle of the normal elbow was 10.08±3.21 and that of the fractured arm was 7.66±5.63 (p=0.186). In females, the corresponding values were 10.93±3.56 and 8.26±5.71, while in n males they were Table: Flynn criteria according to operation time. Flynn Outcome Criteria Operation Time 0-8 Hour 8-24 Hour n % n % Chi-square Test p Cosmetic Excellent Good Fair Poor Functional Excellent Good Fair Poor Vol. 66, No. 4, April 2016
4 396 A.Dost, B. Yilmaz, B. Kömür, et al 9.63±2.94 and 7.35±5.62 (p=0.498 for the fractured arm; and p=0.090 for the normal arm). Baumann angles of both elbows were compared, and there was an average change in angle for the normal elbow of ± 4.59 and an average change in angle for the fractured elbow of ± 6.84 (p=0.409). Cubitus varus deformity developed in 5(6.3%) cases. No iatrogenic ulnar nerve damage was found in any patient. During followups, no complications, such as myositis ossificans, compartment syndrome, fracture non-union or infection, were observed. No patient required a second operation due to a reduction loss or any other reason. Discussion There are several studies on paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. In the case series of Flynn, 84% paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures were seen in children under the age The mean age of occurence was reported as 6.0 years by Khoshbin, 6.3 years by Cheng, and 6.2 years by Nikolic The mean age of our patient group was 6.2 years. In addition, paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures are more common among boys and occur most frequently on the left side. 11 Wilkins reported rates of 62% in boys, 38% in girls, 60.8% on the left side, and 39.2% on the right side. 8 Cheng reported a rate of 1:1.5 on the dominant side. 9 This rate was explained by the fact that the reflex protective mechanism of the patient uses the non-dominant left side during falling. 12 In our study, 52 (65.8%) patients were male, and 27 (34.2%) were female; the fracture occurred on the left side in 49 (62.0%) and on the right side in 30 (38.0%). These results are in accordance with the literature. According to studies, 6,13-15 paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures are more often seen during the spring and the summer. This prevalence can be explained by the start of the school holidays and the greater amount of time spent outdoors in increasingly ambient temperatures as well as by boys' preference for more boisterous games. Most of our patients visited the emergency room during the summer time. From an aetioligical perspective, Farnswort reported that falling from high places accounted for 70% of supracondylar fractures. Falling from a bed was also common among children of approximately 3 years of age, whereas falls in play areas were common among children of around 4 years of age and older. 14 Of our patients, 42 (53.2%) experienced a fall to the floor, 32 (40.5%) fell from a height, and 5 (6.3%) fell from a bed. There have been conflicting reports in the literature on the neurological and vascular damage that can develop after such fractures. Dormans found the rate of peripheral nerve injury to be 9.5% in 200 children. 16 This rate has also been presented as 10-15% in various texts. 12 In our study, 8(10.1%) patients had a radial nerve lesion, 5(6.3%) had median and isolated anterior interosseous nerve lesions, and 1(1.2%) had an ulnar nerve lesion. The complaints of all patients were resolved during follow-up. Only 2(2.5%) patients had circulatory problems and radial pulselessness. Following ORIF, the pulse and circulation recovered. Promising results have recently been reported for the treatment of these fractures by closed reduction and percutaneous fixation. 6,17 The advantages of this method include short hospitalisation, minimal surgery, and lower rates of infection and myositis ossificans. On the other hand, the disadvantages include the risk of ulnar nerve injury during K-wire insertion and the increased use of flouroscopy and X-ray exposure. In addition, repeated manoeuvers during closed reduction may lead to neurovascular injury. 18,19 Indeed, open reduction has been a recommended form of treatment for this fracture from the beginning. However, open reduction has also been considered for open fracture cases in situations with neurovascular injury, in the absence of a fluoroscopy device, or when the surgeon has insufficient experience in percutaneous detection. 8,20,21 Anterior, lateral, medial, and posterior approaches are preferred when open reduction is necessary. However, a common surgical approach has not yet been determined. The advantages and disadvantages of all surgical approaches have been presented in the literature, and satisfactory results have been achieved with all. It is well known that such favourable results are in direct correlation to the surgeon's experience. Surgeons usually prefer the approach with which they have the most experience. The aim of surgical treatment is to gain the best functional results with minimal cosmetic problems. With this in mind, we performed a modified version of the medial approach recommended by Danielson-Peterson in all patients. 21 The surrounding tissues were protected by minimal dissection and surgical trauma. Sufficient anatomical reduction of the medial and lateral columns was possible by palpation and under direct vision when necessary. In addition, we observed that rotations in the coronal, saggital, and axial planes could be retracted during open reduction. We achieved maximal stabilisation by medial and lateral cross-pins following localisation of the ulnar nerve. The current literature also recommends cross-pins for maximal stabilisation. 22 As the incision is medial, it allows the ulnar nerve to be located and prevents iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury. We found that J Pak Med Assoc
5 Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures this approach yielded very good cosmetic results in all patients except 3(3.79%), and all patients were satisfied with the results. To evaluate a surgical approach favourably, we must determine that the long-term results are as satisfactory as the short-term results. Our evaluation of the long-term outcomes of our patients based on Flynn's criteria revealed 97.5% excellent, good, and fair results according to the functional assessment and 96.2% excellent, good, and fair results according to the cosmetic assessment. Some authors have suggested that a carrying-angle loss greater than 10 is not acceptable and that the ideal difference should be less than 5, 6,8 because the most important late complication after paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures is the development of cubitus varus or cubitus valgus deformity. Varus deformity is more apparent cosmetically and is the source of more patient complaints than cubitus valgus deformity. 12,23,24 We observed cubitus varus deformity in 5(6.3%) patients, which is in accordance with the literature. During followup, 2 of the 5 patients showed a varus deformity less than 10, and the remaining 3 patients showed a varus deformity greater than 10. All of these patients complained of curvature, but none had functional complaints. Finally, according to radiological examinations performed during follow-up visits, none of the patients showed neurovascular complications or myositis ossificans during the postoperative period. It has been reported that repeated and forcing manoeuvers during closed reduction in patients who are treated with repetitive manipulations may lead to myositis ossificans. 25 We suggest that our approach may reduce the risk of myositis ossificans. The limitations of our study are its retrospective design, small sample size, and absence of randomisation, with the surgical strategy being dependent on the usual practice of a single centre. In light of these results, we suggest that our treatment approach is a safe and convenient method to restoring the humerus supracondylar region anatomy, because ORIF can be performed by the medial approach without risk of injury to the surrounding tissues of the elbow. In addition, this method proves advantageous postoperationally. Conclusion Limited medial approach to paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures is a safe and successful method in terms of the functional and cosmetic results. The approach may be preferred in patients with type 3 paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures in whom closed reduction may have failed to provide sufficient anatomical reduction. References 1. Eren A, Ozkut AT, Altinta? F, Güven M. Comparison between the lateral and medial approaches in terms of functional and cosmetic results in the surgical treatment of type III supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Act Orth Trau Turc. 2005; 39: Keskin D, Sen H. The comparative evaluation of treatment outcomes in pediatric displaced supracondylar humerus fractures managed with either open or closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Act Chir Orth Trau Cech. 2014; 81: Abzug JM, Herman MJ. Management of supracondylar humerus fractures in children: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012; 20: Yaokreh JB, Gicquel P, Schneider L, Stanchina C, Karger C, Saliba E, et al. Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98: Pretell Mazzini J, Rodriguez Martin J, Andres Esteban EM. Surgical approaches for open reduction and pinning in severely displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children: a systematic review. J Child Orthop. 2010; 4: Flynn JC, Matthews JG, Benoit RL. Blind pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Sixteen years' experience with long term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974; 56: Kasser JR, Beaty JH. Supracondylar humerus fractures. In: James H. Beaty, eds. Rocwood and Wilkins' Fractures in Children. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001; pp Khoshbin A, Leroux T, Wasserstein D, Wolfstadt J, Law PW, Mahomed N, et al. The epidemiology of paediatric supracondylar fracture fixation: a population-based study. Injury. 2014; 45: Cheng JC, Lam TP, Maffulli N. Epidemiological features of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in Chinese children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2001; 10: Nikolic H, Bukvic N, Tomasic Z, Bosak A, Cicvaric T. Bone remodeling after supracondylar humeral fracture in children. Coll Antropol. 2014; 38: Harris IE. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Orthopedics. 1992; 15: Kasser JR, Beaty JH. Supracondylar fractures of the elbow region. In: Beaty JH, Kasser JR, eds. Rockwood and Wilkin's fractures in children. Vol III, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2001; pp Kurer MH, Regan MW. Completely displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. A review of 1708 comparable cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;256: Farnsworth CL, Silva PD, Mubarak SJ. Etiology of supracondylar humerus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998; 18: Khoshbin A, Leroux T, Wasserstein D, Wolfstadt J, Law PW, Mahomed N, et al. The epidemiology of paediatric supracondylar fracture fixation: a population-based study. Injury. 2014; 45: Dormans JP, Squillante R, Sharf H Acute neurovascular complications with supracondylar humerus fractures in children. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20: de las Heras J, Durán D, de la Cerda J, Romanillos O, Martínez- Miranda J, Rodríguez-Merchán EC. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 432: Vol. 66, No. 4, April 2016
6 398 A.Dost, B. Yilmaz, B. Kömür, et al 18. Skaggs DL, Hale JM, Bassett J, Kaminsky C, Kay RM, Tolo VT.. Operative treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. The consequences of pin placement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83: Lyons ST, Quinn M, Stanitski CL. Neurovascular injuries in type III humeral supracondylar fractures in children. Clin Orthop. 2000; 376: Beck JD, Riehl JT, Moore BE, Deegan JH, Sartorius J, Graham J, et al. Risk factors for failed closed reduction of pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:e Danielson L, Petterson H. Open reduction and pin fixation of severely displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980; 51: Mohammed R, Bhogadi P, Metikala S. A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylarhumeral fractures. J Child Orthop. 2014; 8: Bhende HS. Bhende. Clinical measurement of varus-valgus deformity after supracondylar fracture of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994; 76: Eren A, Güven M, Erol B, Akman B, Ozkan K. Correlation between posteromedial or posterolateral displacement and cubitus varus deformity in supracondylar humerus fractures in children. J Child Orthop. 2008; 2: Prietto CA. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus. A comparative study of Dunlop's traction versus percutaneous pinning. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61: J Pak Med Assoc
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type III supracondylar fracture: a retrospective analysis
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury?
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 50/ June 22, 2015 Page 8632
 MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
A clinical study of closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction
 Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
We report the results of 116 consecutive displaced
 Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Surgical Complications
 Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture. of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child
 Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Analysis of displaced supracondylar fractures in children treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE
 Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Original Research Article. ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) DOI: /sajb
 DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children
 Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Late Presentation in Children: A Preliminary Report
 Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children treated by closed reduction with percutaneous crossed pin fixation
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures
 TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Introduction. Kumar Prashant 1 Devendra Lakhotia. Anil Kumar Mahanta 3 Aakhil Ravoof
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children
 Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Outcome of surgically treated displaced medial epicondyle fracture of humerus in children: A prospective study
 2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic review
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
Pediatric Elbow Radiology. Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar
 Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography
 108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus Cross Pinning
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Elbow fractures account for approximately 5% to
 Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN
 THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient Fishtail Deformity after Surgery
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 645 651 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 645 651 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric
Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
International Journal of Research and Review www.gkpublication.in E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Prospective Observational Study of Management of Supracondylar Fracture
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department. October 2012
 Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Prospective study of cubitus varus deformity, its etiopathology, clinical study and treatment
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dudhekar U. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):201-205 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164549
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dudhekar U. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):201-205 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164549
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE CHILDREN
 DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
 original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
Follow-up and evaluation
 Original Article Comparison of Medial and Posterior Surgical Approaches in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures E Şahin, S Zehir 1, S Sipahioglu 2 Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Faculty
Original Article Comparison of Medial and Posterior Surgical Approaches in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures E Şahin, S Zehir 1, S Sipahioglu 2 Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Faculty
Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin configuration
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:473 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin
DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
Tuomilehto, N
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
(Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Common Limb Fractures. Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009
 Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
--Manuscript Draft-- the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees. Walid A Elnahal, M.Sc Tr & Orth
 Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN
 1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children
 Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018
 PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. No disclosures for this presentation 10/29/18. Agenda
 Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
CiSE. New Fixation Method Using Two Crossing Screws and Locking Plate for Cubitus Varus Deformity in Young Adult Elbow: Case Report CASE REPORT
 SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES.
 PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review
 Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with Triceps Sparing Method in Paediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2016), PP 41-45 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2016), PP 41-45 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with
Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
DOI 10.1007/s00402-013-1820-8 TRAUMA SURGERY Proximal radioulnar translocation associated with elbow dislocation and radial neck fracture in child: a case report and review of literature Hong Kee Yoon
---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity Fractures---
 Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 212;4:91-97 http://dx.doi.org/1.455/cios.212.4.1.91 Consensus and Different Perspectives on Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children
Triceps-sparing approach for open reduction and internal fixation of neglected displaced supracondylar and distal humeral fractures in children
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2015) 16:105 116 DOI 10.1007/s10195-015-0334-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Triceps-sparing approach for open reduction and internal fixation of neglected displaced supracondylar and distal
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2015) 16:105 116 DOI 10.1007/s10195-015-0334-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Triceps-sparing approach for open reduction and internal fixation of neglected displaced supracondylar and distal
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
A new surgical technique for the treatment of supracondylar humerus fracture malunions in children
 J Child Orthop (2011) 5:305 312 DOI 10.1007/s11832-011-0349-z TECHNICAL NOTE A new surgical technique for the treatment of supracondylar humerus fracture malunions in children David L. Skaggs David Glassman
J Child Orthop (2011) 5:305 312 DOI 10.1007/s11832-011-0349-z TECHNICAL NOTE A new surgical technique for the treatment of supracondylar humerus fracture malunions in children David L. Skaggs David Glassman
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent
 Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
Elbow, forearm injuries. K. Fekete
 Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Percutaneous pinning after closed reduction of supracondylar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN. Dr.K.
 STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY Dr.K.SARAVANAN A Dissertation submitted to the BOOLEAN EDUCATION In partial
STUDY OF RESULTS OF PERCUTANEOUS PARALLEL LATERAL AND CROSS PINNING IN TYPE III SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY Dr.K.SARAVANAN A Dissertation submitted to the BOOLEAN EDUCATION In partial
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index
 Gorelick et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index Lauren Gorelick
Gorelick et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index Lauren Gorelick
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.16, No.1, January, 2003
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
