Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures
|
|
|
- Alexina Sabrina Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, Available online at ORIGINAL ARTICLE Compared outcomes after percutaneous pinning versus open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures J.B. Yaokreh a,,p. Gicquel b,l. Schneider b, C. Stanchina b, C. Karger b, E. Saliba b, O. Ossenou a, J.-M. Clavert b a Department of Pediatric Surgery, Yopougon Teaching Hospital Center, 21 BP 632, Abidjan 21, Côte d Ivoire b Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics, De Hautepierre Hospital, avenue Molière, Strasbourg cedex, France Accepted: 23 March 2012 KEYWORDS Child elbow fracture; Crossed pinning; Percutaneous pinning; Supracondylar fracture; Surgical treatment Summary Background: Supracondylar fractures of the elbow are common in children. Their treatment is controversial when displacement has occurred, although percutaneous pinning is usually advocated. Hypothesis: In paediatric extension-type supracondylar fractures of the elbow, percutaneous pinning and crossed K-wire fixation after open reduction via the medial approach produce similar functional outcomes and complication rates. Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 58 children aged 2 to 15 years who underwent surgery for extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures between 2004 and Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning was used in 33 patients with a mean age of 7 years and 11 months; open reduction with cross-wiring in 25 patients with a mean age of 7 years. Functional outcomes were assessed using Flynn s criteria. Baumann s angle was determined and postoperative complications and sequelae were recorded. Results: Outcomes were satisfactory in 30 (90.9%) patients treated with percutaneous pinning and in 23 (92%) patients treated with open reduction and cross-wiring. Mean Baumann s angle at last follow-up was 73.9 ± 5.74 after percutaneous pinning and ± 4.07 after open reduction and cross-wiring. Postoperative complications consisted of reoperation in six (10.3%) patients and iatrogenic nerve injury in two (3.4%) patients. Cubitus varus occurred in two (6.06%) patients after closed treatment and in one (4%) patient after open treatment. In each group, three (5.1%) patients had greater than 15 of motion range limitation. Corresponding author. Tel.: / address: enanblaodette@yahoo.fr (J.B. Yaokreh) /$ see front matter 2012 Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. doi: /j.otsr
2 646 J.B. Yaokreh et al. Discussion: In children with extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures, outcomes are similar with percutaneous pinning and with open reduction via the medial approach followed by crosswiring. Level of evidence: Level IV, retrospective study Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. Introduction Supracondylar fractures of the elbow account for 16.6% of all fractures in paediatric patients [1]. The broad range of nonoperative and operative methods developed with the goal of restoring normal elbow anatomy include long-arm plaster cast immobilisation, axial traction applied using tape or a transolecranon pin, Blount s technique, elastic and stable intramedullary nailing, external fixation, percutaneous pinning, and pinning after open reduction [2 5]. Percutaneous pinning is the most widely advocated technique [2 4,6,7]. Open surgery is indicated in patients with irreducible fractures, unstable fractures, vascular complications, or compound fractures [1]. In our department, Blount s technique has been preferred since the study by Clavert et al. [8]. When Blount s technique fails, percutaneous pinning as described by Judet and Judet is performed as the first-line treatment when reduction is satisfactory [9] and open reduction via the medial approach followed by crossed K-wire fixation otherwise. This treatment algorithm is based on the hypothesis that percutaneous pinning and open medial reduction with cross-wiring produce similar functional outcomes and complication rates. We give preference to the less aggressive of these two techniques whenever possible. The objective of this retrospective study of paediatric patients with extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures was to confirm our hypothesis by comparing patients managed with percutaneous pinning and those managed with open reduction and cross-wiring. Materials and method Study population We retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 82 patients younger than 15 years at the time of treatment for extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures. These patients were managed between 2004 and 2008 at the paediatric orthopaedics department of the Hautepierre Hospital, Strasbourg, France. We excluded patients with flexion-type fractures, associated bony injuries in the same limb, and incomplete data. Patients were included if they received regular postoperative follow-up for at least 3 months. Of the 82 patients, 58 met these criteria and were included in the study. There were 31 (53.4%) boys and 27 (46.6%) girls with a mean age of 7 years and 6 months and an age range of 2 to 15 years. The fractures were classified according to Lagrange and Rigault [10] (Table 1). Operative treatment Surgery was performed under general anaesthesia by a senior surgeon in all 58 patients. Time to treatment was defined as the time from emergency department admission to arrival in the operating room. When Blount s technique failed and closed reduction of the fracture was satisfactory, percutaneous pinning was performed. When closed reduction was not satisfactory, open reduction was performed via the medial approach then stabilised using crossed K-wire fixation. Patients with recurrent displacement after percutaneous pinning were also managed using cross-wiring. For percutaneous pinning, the surgeon gradually applied traction to the limb with the elbow extended while the assistant applied counter-traction at the axilla. Fluoroscopy was used to determine whether translation of the distal humerus occurred. While gradually flexing the elbow to about 120, the surgeon applied direct pressure to the olecranon with the thumb to correct any residual posterior tilting. With the elbow flexed, anteroposterior and lateral radiographs were obtained to evaluate the quality of the reduction. An Esmarch s bandage was placed to maintain the position. After sterile preparation of the elbow, two identical wires 1.6 to 2 mm in diameter were inserted from lateral to medial, using a slow-rotation power drill (Fig. 1). For cross-wiring (Fig. 2), a medial incision centred on the medial epicondyle was performed and the ulnar nerve was isolated and placed in a noose. The fracture site was then approached via the intermuscular interstice. Reduction was achieved and a wire 1.6 to 2 mm in diameter was then inserted from medial to lateral using a slow-rotation power drill. A lateral wire of the same diameter was inserted percutaneously under fluoroscopic guidance starting at the lateral epicondyle. The wound was closed in two planes with a continuous intradermal suture. In all patients, the wires were bent back and buried under the skin. A long arm plaster cast with the elbow flexed at 90 was used in all patients for 45 days, after which the wires were removed under general anaesthesia. Comparison of the two operative techniques To compare the two operative techniques, we retrospectively allocated the patients into two groups based on the surgical technique used. Although treatment allocation was not randomised, provided the two groups were homogeneous, this method allowed comparisons of treatment outcomes. The percutaneous pinning (PP) group included 33 patients (20 boys and 13 girls) with a mean age of 7 years and 11 months and the open reduction/crossed pinning (OR/CP) group included 25 patients (11 boys and 14 girls) with a mean age of 7 years. Table 1 reports the main epidemiological, diagnostic, and therapeutic features in the study patients. Associated injuries were present in 24 (41.3%) patients and consisted of vascular abnormalities in nine (14.5%), nerve injuries in 10 (16.1%), and breaks in the skin in five (8%). Of the nine vascular abnormalities, seven were arterial spasms
3 Percutaneous pinning vs. open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures 647 Table 1 Main epidemiological, diagnostic, and therapeutic features in the groups managed with percutaneous pinning and open reduction followed by crossed K-wire fixation. Percutaneous pinning (n = 33) Open reduction + cross-wires (n = 25) Age, years [range] 7.95 [2 15] 7 [2 14] Sex Male Female Associated injuries Vascular 5 4 Skin break 4 1 Nerve injuries M 3 M 1 U 1 R 0 M + R 2 U + M 1 NR 1 NR 1 Classification according to Lagrange et Rigault Stage III 9 5 Stage IV Time to treatment, hours [range] 1.67 [0.45 4] 1.74 [ ] U: ulnar nerve; M: median nerve; R: radial nerve; NR: not reported. that resolved after reduction and pinning and two were vascular injuries that required patch reconstruction. A pressure sensor was placed in the anterior forearm compartment to allow postoperative monitoring. The nerve injuries consisted in neurapraxia secondary to contusion, stretching, or entrapment. Open surgery was performed when closed reduction failed, the fracture was unstable, vascular abnormalities persisted despite reduction and the application of Blount s technique, or secondary displacement occurred after Blount s technique (which was the first-line treatment). Evaluation of outcomes Mean time to fracture healing was 45 days in both groups. Postoperative functional outcomes were assessed using Flynn s criteria (Table 2) [6]. We recorded hospital stay length (mean ± SD), Baumann s angle (mean ± SD) at the fractured elbow, postoperative complications (iatrogenic nerve injury, re-operation, infection, and compartment syndrome), and sequelae (elbow axis deviation, motion range limitation, and neurological deficits). Comparisons were Table 2 Flynn s criteria [6]. Results Cosmetic factor: loss of carrying angle (in degrees) Satisfactory Excellent Good Fair Unsatisfactory Poor > 15 > 15 Functional factor: loss of motion (in degrees) with the Chi 2 and t tests, with P values smaller than 0.05 being considered significant. Results Satisfactory outcomes were noted in 30 (90.9%) patients in the PP group, 23 (92%) patients in the OR/CP group, and 53 (91%) patients overall (Table 3). The difference between the two groups was not significant (P = , Chi 2 test). Mean hospital stay length was 3.03 ± 1.45 days (range, 2 7 days) in the PP group and 4.08 ± 1.82 days (range, 2 7) in the OR/CP group; again, the difference was not significant (P = , Chi 2 test). Mean Baumann s angle immediately after surgery was ± 7.31 (range, ) in the PP group and ± 5.96 (range, ) in the OR/CP group; the difference was not significant (P = , t test). At last follow-up, mean Baumann s angle was 73.9 ± 5.75 (range, ) in the PP group and ± 4.08 (range, ) in the OR/CP group (non-significant: P = , t test). Postoperative complications occurred in eight (13.8%) patients. They consisted in re-operation in six (10.3%) patients and iatrogenic nerve injuries in two (3.4%) patients. The reasons for re-operation were inadequate reduction or secondary displacement detected on the postoperative radiograph. Re-operation was required in five patients in the PP group and one in the OR/CP group (non-significant difference, P = , Chi 2 test). Both cases of iatrogenic nerve injury occurred in the PP group. The median nerve was involved in one patient and the radial nerve in the other. The outcome was favourable within 4 to 5 months in six (75%) of the eight patients with trauma-related nerve injuries and in both patients with iatrogenic nerve injuries. The two patients with persistent trauma-related nerve dysfunction required electrophysiological studies. No cases of infection or compartment syndrome were recorded.
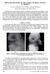
4 648 J.B. Yaokreh et al. Figure 1 Stage IV supracondylar fracture managed with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning: a: preoperative appearance (anteroposterior view); b: preoperative appearance (lateral view); c: postoperative appearance (anteroposterior view); d: postoperative appearance (lateral view). Table 3 Outcomes according to Flynn s criteria [6] in the groups managed with percutaneous pinning and open reduction followed by crossed K-wire fixation. Percutaneous pinning (n = 33) Open reduction + cross-wires (n = 25) Follow-up, months [range] 9.7 [3 46] 14.2 [3 55] Satisfactory results Excellent (%) 17 (51.5) 14 (56) Good (%) 8 (24.1) 5 (20) Fair (%) 5 (15.2) 4 (16) Poor results (%) 3 (9.1) 2 (8)
5 Percutaneous pinning vs. open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures 649 Figure 2 Stage IV supracondylar fracture managed with open reduction and crossed K-wire fixation: a: preoperative appearance (anteroposterior view); b: preoperative appearance (lateral view); c: postoperative appearance (anteroposterior and lateral views). Cubitus varus was noted in three (5.1%) patients; the angles were 10, 15, and 25, respectively. Of these three patients, two (6.06%) had had PP and one (4%) OR/CP. The patients with 15 and 25 of angulation were managed by lateral closed wedge osteotomy of the humerus. Another patient in the OR/CP group had 10 of cubitus valgus. In each group, three patients had greater than 15 of motion range limitation. In two patients managed with PP, the cause was a bone spur arising from the anterior metaphysis (Fig. 3). Two patients in the OR/CP group reported pain at the site of the medial scar. Discussion Limitations of our study are the retrospective design, small sample size, and absence of randomisation, with the surgical strategy being dependent on the usual practice of a single centre. Thus, open reduction was performed when inadequate closed reduction precluded percutaneous pinning or secondary displacement occurred after percutaneous pinning. The diverse range of treatment methods attests to the challenges raised by extension-type supracondylar fractures of the elbow. The management of severely displaced forms is controversial and has given rise to various schools of thought. Advantages of percutaneous pinning include rapidity and absence of periosteal separation and dissection, which result in a minimal risk of infection. Disadvantages are the higher risk of secondary displacement and the risk of iatrogenic nerve injury. The open technique allows fracture reduction under visual guidance, which limits the risk of ulnar nerve injury, but is associated with higher risks of infection and motion
6 650 J.B. Yaokreh et al. Figure 3 Bone spur on the anterior metaphysis. range limitation and may result in unsightly or painful scars. Our assessment of outcomes using Flynn s criteria showed no significant difference between percutaneous pinning and open reduction with crossed K-wire fixation (90.9% versus 92% of satisfactory outcomes; P = ). Percutaneous pinning has produced satisfactory outcomes in 95% to 100% of cases in earlier studies [2,4,11] and is consequently the most widely advocated first-line treatment [2 7,12,13]. The postoperative complication rates were 8.6 and 22% in case-series of cross-wire fixation [2,13] and 13.8% in our study. Of eight postoperative complications, six (10.4%) consisted in secondary displacement, of which five cases occurred after percutaneous pinning and a single case after open reduction and cross-wiring (non-significant difference, P = ). Secondary displacement was chiefly ascribable to technical shortcomings. Crossing of the pins in the fracture site is associated with secondary displacement, as occurred in 21% of cases in the case-series by Damsin et al. [14]. Therefore, keeping the pins parallel and at least 10 mm apart has been advocated [15]. To avoid secondary displacement, Judet and Judet [9] used either a lateral pin or a thoracobrachial plaster cast to prevent shoulder rotation or a second lateral pin inserted through the olecranon and condyle into the diaphysis. More recently, Skaggs et al. [16] recommended using three diverging lateral epicondylar pins when concern arose about the stability of the fixation. Using three pins provides the same degree of biomechanical stability as the cross-pinning technique described in 1948 by Swenson [17] and demonstrated in experimental studies by Zionts et al. [18]. Although the multiple drill homes in the distal humeral physis might in theory impair epiphyseal growth, this complication did not occur in any of the patients studied by Skaggs et al. [16]. Iatrogenic nerve injuries are seen in about 6% of patients with supracondylar fractures [19] and consist chiefly in damage to the ulnar nerve during percutaneous pinning, which has been reported in 11% of patients [20]. Gurkan et al. [19] reported iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury in 4.5% of cases after reduction via the medial approach. The cause was probably stretching of the nerve during reduction manoeuvres. In contrast, we found no cases of iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury after open reduction. Electrostimulation to identify the ulnar nerve during pinning has been advocated [7,20]. The favourable outcome of nerve injuries in our study is consistent with earlier reports [20,21]. Cubitus varus is the most common residual abnormality after extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures in children [6,14,21]. Cubitus varus is a cosmetic rather than a functional disability and is due to persistent distal fragment rotation after reduction. Baumann s angle should be measured to minimise the risk of cubitus varus, [14,22]. In our study, the cubitus varus rate was 6.06% after percutaneous pinning and 4% after open reduction with cross-wiring. El-Adl et al. [2] reported a rate of 8.6% after percutaneous pinning and Shakir et al. [13] a rate of 6% after reduction via the medial approach. Cubitus varus can occur after all types of treatment and remains stable over time [22]. Kohler et al. [22] suggested that correction might be best-performed 18 to 24 months after the initial injury. Correction of cubitus varus relies on hemi-epiphysiodesis or humeral osteotomy [20,22]. In our case-series, we performed lateral closed wedge osteotomy of the humerus. The limited growth potential of the distal humeral growth plate does not allow full correction of architectural deformities, and anatomic reduction must therefore be performed. Motion range limitation of the elbow is common after supracondylar fractures, with a rate of 15% in the study by Damsin and Langlais [14]. The causes include soft tissue injuries, posttraumatic remodelling, fibrous surgical scars, and malunion. In our study, a bone spur on the anterior metaphysis caused motion range limitation in two patients, who were managed with surgical release of the elbow. The appropriateness of physical therapy in patients with restricted elbow motion remains controversial. Long-term follow-up is in order, as the physical activities to which children are naturally inclined result in some degree of self-rehabilitation. Conclusion Blount s technique remains the preferred treatment of extension-type supracondylar elbow fractures at our surgical centre. When this technique fails or is contraindicated, percutaneous pinning is the first-line alternative, with open reduction via the medial approach as the second-line strategy. In our study, no significant differences were found between percutaneous pinning and open reduction with cross-wiring in terms of postoperative stability, functional outcomes, and complications. We believe these results support the fist-line use of percutaneous pinning, which is simpler and less aggressive than open reduction and crosswiring. Disclosure of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
7 Percutaneous pinning vs. open reduction in paediatric supracondylar elbow fractures 651 References [1] Naji UK, Zahid A, Faheem U. Type III supracondylar fracture humerus: results of open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction. Rawal Med J 2010;35: [2] El-Adl WA, El-Said MA, Boghdady GW, Ali AS. Results of treatment of displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children by percutaneous lateral cross-wiring technique. Strat Traum Limb Recon 2008;3:1 7. [3] De Buys Roessingh AS, Reinberg O. Open or closed pinning for distal humerus fractures in children? Swiss Surg 2003;9: [4] Mazda K, Boggione C, Fitoussi F, Penneçot GF. Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001;83-B: [5] Oh CW, Park BC, Kim PT, Park IH, Kyung HS, Ihn JC. Completely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children: results of open reduction versus closed reduction. J Orthop Sci 2003;8: [6] Flynn JC, Matthews JG, Benoit RL. Blind pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: sixteen years experience in long term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1974;56: [7] Sibinski M, Sharma H, Sherlock DA. Lateral versus crossed wire fixation for displaced extension supracondylar humeral fracture in children. Inj Int J Care Inj 2006;37: [8] Clavert JM, Lecerf C, Mathieu JL, Buck P. Retention in flexion of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children. Comments about of the treatment of 120 displaced fractures. Rev Chir Orthop 1984;70: [9] Judet J, Judet H. Fracture supracondylienne transversale de l humérus. In: Fractures et orthopédie de, l enfant. Indications-techniques-voies d abord. Membre supérieur, tronc et thorax. Tome 1, Volume A3. Paris: Maloine SA; p [10] Lagrange J, Rigault P. Supracondylar fractures. Rev Chir Orthop 1962;48: [11] Kazimoglu C, Cetin M, Sener M, Agus H, Kalanderer O. Operative management of type III extension supracondylar fractures in children. Intern Orthop 2009;33: [12] Ababneh M, Shannak A, Agabi S, Hadidi S. The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Intern Orthop (Sicot) 1998;22: [13] Shakir H, Malik FA, Khalid W. Displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children treated with open reduction and cross K-wire fixation. JPMI 2010;24: [14] Damsin JP, Langlais J. Fractures supra-condyliennes. Symposium sur les fractures du coude chez l enfant sous la direction de Pouliquen JC. Rev Chir Orthop 1987;73: [15] Skaggs DL, Hale JM, Bassett J, Kaminsky C, Kay RM, Tolo VT. Operative treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. The consequences of pin placement. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2001;83: [16] Skaggs DL, Cluck MW, Mostofi A, Flynn JM, Kay RM. Lateral entry pin fixation in the management of supracondylar fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86: [17] Swenson AL. The treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus by Kirschner-wire transfixion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1948;30: [18] Zionts LE, McKellop HA, Hathaway R. Torsional strength of pin configurations used to fix supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994;76: [19] Gurkan O, Ugur G, Asim K, Kursat T, Turlay TP. Displaced supracondylar humeral fracture in children: open reduction vs. closed reduction and pinning. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2004;124: [20] Kasser JR, Beaty JH. Supracondylar fractures of the distal humerus. In: Rockwood and Wilkins fractures in children. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p [21] Barlas K, George B, Hashmi F, Bagga T. Open medial placement of Kirschner wires for supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Orthop Surg 2006;14:53 7. [22] Kohler R, Ducret H, Willemen L. Cubitus varus posttraumatique. In: Damsin JP, Langlais J, editors. Traumatologie du coude de l enfant. Cahier d enseignement de la SOF- COT n o 72. Paris: Expansion Scientifique Française; p
We report the results of 116 consecutive displaced
 Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Systematic pinning of displaced extension-type supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 116 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS K. Mazda, C. Boggione, F. Fitoussi, G. F. Penneçot From
Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 808 812 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Delayed treatment of supracondylar elbow fractures in children J.B. Yaokreh,
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type III supracondylar fracture: a retrospective analysis
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162619 Cross pinning versus lateral pinning in type
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/409 Comparative Evaluation of Results of Cross Pin Fixation by Conventional Method with Dorgan s Method in Displaced Supracondylar Fracture in Children Prasanta
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 50/ June 22, 2015 Page 8632
 MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury?
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Iatrogenic or fracture-related nerve injuries in supracondylar humerus fracture: is treatment necessary for nerve injury? S. GUNER, N. GUVEN, S.
To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Compare the Outcome of Patients with Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus Treated by Cross K-Wires and Lateral Entry K-Wires in Children SHAFI-UR-REHMAN 1, KHIZAR HAYAT 2, ABBAS BAJWA
A clinical study of closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of displaced supracondylar fractures of humerus in children
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Asimuddin M et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):282-286 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170787
Analysis of displaced supracondylar fractures in children treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sakthivel RN et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1590-1596 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161232
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
Outcome of surgically treated displaced medial epicondyle fracture of humerus in children: A prospective study
 2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
2017; 3(3): 287-291 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 287-291 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 08-05-2017 Accepted: 10-06-2017 Sahu RL M.S. Orthopaedics, Professor, Dr. Nadeem Ahmad Outcome of surgically
Introduction. Kumar Prashant 1 Devendra Lakhotia. Anil Kumar Mahanta 3 Aakhil Ravoof
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2016) 17:223 229 DOI 10.1007/s10195-016-0410-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study of two percutaneous pinning techniques (lateral vs medial lateral) for Gartland type III pediatric
Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures
 TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
TRAUMA AND ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 524 528 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2017.0040 Distance of translation as a predictor of failure of fixation in paediatric supracondylar fractures P
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children
 Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
Children s orthopaedics Elevated, straight-arm traction for supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children A. Gadgil, C. Hayhurst, N. Maffulli, J. S. M. Dwyer From University Hospital of North Staffordshire
Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus Cross Pinning
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/190 Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children by Lateral Entry Pinning versus (Maj Gen) V P Pathania 1, Nishant Dubey 2, Sanjay Gupta
Original Research Article. ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) DOI: /sajb
 DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
DOI: 10.21276/sajb.2016.4.10.22 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2016; 4(10B):934-951 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic
DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF HUMERUS IN CHILDREN TREATED WITH OPEN REDUCTION AND CROSS K-WIRE FIXATION Shakir Hussain, Malik Faiz Ahmad, Khalid, Waqas Orthopaedics Unit District
A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:435 441 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0607-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A study of biplanar crossed pin construct in the management of displaced pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures
Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Crossed Versus Lateral Pinning In The Treatment Of Displaced Extension-Type Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus: A Prospective
Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/458 Outcomes of Percutaneous Medial-Lateral Cross Pinning of the Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus M Julfiqar 1, Ajay Pant 2, Najmul Huda 3, Mohammed
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris Yilmaz, 2 Baran Kömür, 3 Serhat Mutlu, 4 Harun Mutlu, 5 Korhan Özkan, 6 Abdullah Eren 7
 393 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures operated in first 24 hours with limited medial approach Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris
393 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Middle and long term radiologic and functional results of childhood supracondylar humeral fractures operated in first 24 hours with limited medial approach Abdulkadir Dost, 1 Baris
Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Treatment approaches and outcomes in childhood supracondylar humerus fractures B.Y. UÇAR, A. DEMIRTAŞ, D.E. UÇAR* 2012; 16: 936-941 Department of
Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children treated by closed reduction with percutaneous crossed pin fixation
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(4):241-247 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Study of type-iii supracondylar humerus fractures in children
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction
 Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Original Article Type-III supracondylar fracture humerus: results 0f open reduction and internal fixation after failed closed reduction ABSTARCT Objective Naji ullah Khan, Zahid Askar, Faheem ullah Department
Surgical Complications
 Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN
 1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
1 PERCUTANEOUS FIXATION OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURE IN CHILDREN COMPARING LATERAL WITH MEDIAL AND LATERAL PIN A THESIS SUBMITTED TO UNIVERSITY OF SEYCHELLES American Institute of medicine In fulfillment
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
Article Treatment of displaced flexion-type pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures in the prone position Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume: 25(1) 1 6 ª Journal of
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Percutaneous pinning after closed reduction of supracondylar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications After Pinning of Supracondylar Distal Humerus Fractures Ravi K. Bashyal, MD,*w z Jennifer Y. Chu, MD,* Perry L. Schoenecker, MD,*w z Matthew B. Dobbs, MD,*w z Scott J. Luhmann,
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic review
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:57 64 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0091-y REVIEW Does open reduction and pinning affect outcome in severely displaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children? A systematic
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of Late Presentation in Children: A Preliminary Report
 Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 9256540, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9256540 Clinical Study Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture. of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child
 Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Posterolateral dislocation of the elbow with concomitant fracture of the lateral humeral condyle in a five year old child H Sharma ( ), L Al-badran, S Bhagat, R Sharma, M Naik Department of Trauma and
Bioscience Research Print ISSN: Online ISSN:
 Available online freely at www.isisn.org Bioscience Research Print ISSN: 1811-9506 Online ISSN: 2218-3973 Journal by Innovative Scientific Information & Services Network RESEARCH ARTICLE BIOSCIENCE RESEARCH,201815(2):1409-1414
Available online freely at www.isisn.org Bioscience Research Print ISSN: 1811-9506 Online ISSN: 2218-3973 Journal by Innovative Scientific Information & Services Network RESEARCH ARTICLE BIOSCIENCE RESEARCH,201815(2):1409-1414
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography
 108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
108472 NV-OA8 pg29-33.qxd 11/05/2007 05:05 PM Page 29 (Black plate) Anterior Displacement of Ulnar Nerve at the Elbow in Children Based on Ultrasonography H Shamsul, MS (Ortho)*, A Saw, FRCS*, G John,
--Manuscript Draft-- the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees. Walid A Elnahal, M.Sc Tr & Orth
 Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma Crossed Wires versus Two Lateral Wires in Management of Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children in the Hands of Junior Trainees --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number:
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN
 THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
THE FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN SIULTANEOUS SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUERUS AND OF THE FOREAR IN THE SAE UPPER LIB PETER A. TEPLETON. H. KERR GRAHA From the Royal Belfast Hospital for Sick Children,
Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
 Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index
 Gorelick et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index Lauren Gorelick
Gorelick et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of the normal and pathological alignment of the elbow in children using the trochleocapitellar index Lauren Gorelick
THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE
 Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
Trauma Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children THE EXPERIENCE OF A SPECIALIST REFERRAL CENTRE M. Ramachandran, R. Birch, D. M. Eastwood From
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE CHILDREN
 DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children
 519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
519/, p. 519 523 Surgical Treatment of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Chirurgická léčba suprakondylických zlomenin humeru u dětí K. REISING, H. SCHMAL, M. KOHR, K. KUMINACK, N. P. SÜDKAMP,
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
Prof. Mohamed M. Zamzam, MD Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon College of Medicine, King Saud University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Accounts for 10-20% of all childhood elbow fractures The diagnosis
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical?
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1707.017 Displaced Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children Are They All Identical? Gera SK, MS Orth, Tan MCH, MBBS, Lim YG, MRCS Ed, Lim KBL, FRCSEd Orth Department
Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient Fishtail Deformity after Surgery
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9053949, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9053949 Case Report Medial Condyle Fracture (Kilfoyle Type III) of the Distal Humerus with Transient
Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1503.010 Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children Shabir AD, MS, Tahir AD, MS, Sharief AW, MS, Imtiyaz HD, MS, Shahid
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1503.010 Delayed Operative Management of Fractures of the Lateral Condyle of the Humerus in Children Shabir AD, MS, Tahir AD, MS, Sharief AW, MS, Imtiyaz HD, MS, Shahid
Prospective study of cubitus varus deformity, its etiopathology, clinical study and treatment
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dudhekar U. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):201-205 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164549
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dudhekar U. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):201-205 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164549
Treatment of Medial Epicondyle Fracture without Associated Elbow Dislocation in Older Children and Adolescents
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1190 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(6):1190-1196, 2012 Treatment of Medial Epicondyle Fracture without Associated Elbow Dislocation
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1190 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(6):1190-1196, 2012 Treatment of Medial Epicondyle Fracture without Associated Elbow Dislocation
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent
 Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
Clinical Results of Surgically Treated Medial Humeral Epicondylar Apophyseal Avulsion Injury in Children and Adolescent Ruban Raj Joshi, a,c Gabriel David Sundararaj b,c Original Research Article ABSTRACT:
Elbow fractures account for approximately 5% to
 Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
CiSE. New Fixation Method Using Two Crossing Screws and Locking Plate for Cubitus Varus Deformity in Young Adult Elbow: Case Report CASE REPORT
 SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
SE REPORT linics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 19, No. 1, March, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2016.19.1.43 ise linics in Shoulder and Elbow New Fixation Method Using Two rossing Screws and Locking
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES.
 PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children
 Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
Research Article Comparative study between two patterns of percutaneous K- wire fixation of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children Mushtaq Talib Hussein F.I.B.M.S,C.A.B.O Date Submitted: 5/1/2016
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Common Limb Fractures. Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009
 Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA
 original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
original article FLOATING ELBOW IN CHILDREN: A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY OF 31 CASES ATTENDED IN A REFERENCE CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC TRAUMA Dorotea Starling Malheiros 1, Gustavo Henrique Silva Bárbara 2, Leandro
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children
 Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Supracondylar Fractures of humerus in Children Introduction By Dr John Ebnezar Children below 10 years, especially boys, are more prone for fall from heights like tree, buildings, bicycle etc. (Fig No
Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique AJO DO NOT COPY
 An Original Study Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique Andrew G. Georgiadis, MD, and Jeffrey J. Settecerri, MD Abstract The
An Original Study Safe Cross-Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures With a Flexion-Extension External Rotation Technique Andrew G. Georgiadis, MD, and Jeffrey J. Settecerri, MD Abstract The
Pediatric Elbow Radiology. Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar
 Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Tuomilehto, N
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
https://helda.helsinki.fi Postponing surgery of paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures to office hours increases consultant attendance in operations and saves operative room time Tuomilehto, N. 2018-06
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with Triceps Sparing Method in Paediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2016), PP 41-45 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2016), PP 41-45 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Outcome of Open Reduction with
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and anatomical study
 J Child Orthop (2015) 9:295 302 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0674-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and
J Child Orthop (2015) 9:295 302 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0674-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Pin tract infection of operatively treated supracondylar fractures in children: long-term functional outcomes and
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018
 PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V?
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
(Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 368-374 ORIGINAL STUDY (Un)importance of physical therapy in treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children Sinisa Ducic, Marko Bumbasirevic, Vladimir
Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion
 Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Case Report Elastic Intramedullary Nailing of a Medial Clavicle Fracture in a Pediatric Patient
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 6354284, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6354284 Case Report Elastic Intramedullary Nailing of a Medial Clavicle Fracture in a Pediatric
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 6354284, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6354284 Case Report Elastic Intramedullary Nailing of a Medial Clavicle Fracture in a Pediatric
Elbow, forearm injuries. K. Fekete
 Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
Extensor Mechanism Sparing Approach to the Elbow for reduction and Internal Fixation of Intercondylar Fracture of the Humerus
 Extensor Mechanism Sparing Approach to the Elbow for reduction and Internal Fixation of Intercondylar Fracture of the Humerus Pages with reference to book, From 164 To 167 A. R. Jamali,Ghulam Mehboob,Saghir
Extensor Mechanism Sparing Approach to the Elbow for reduction and Internal Fixation of Intercondylar Fracture of the Humerus Pages with reference to book, From 164 To 167 A. R. Jamali,Ghulam Mehboob,Saghir
