How often absence of palmaris longus and functional deficiency of flexor digitorum superficialis occurs?
|
|
|
- Valentine Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, ORIGINAL STUDY How often absence of palmaris longus and functional deficiency of flexor digitorum superficialis occurs? Nikola Vučinić, Mirela Erić, Mirjana Savić From the Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Novi Sad, Serbia This study was designed to find a possible correlation between the presence of the palmaris longus and function of the fifth flexor digitorum superficialis. We examined 300 participants to assess the absence of palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis function by several clinical tests. Overall absence of palmaris longus, was seen in 157 participants (52.3%). Overall deficiency of flexor digitorum superficialis was noted in 100 participants (33.3%). In 15 participants (5%) we noted bilateral absence of palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis deficiency. Five participants (1.7%) had unilateral absence of palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis deficiency on the same, left or right hand. Bilaterally presence of these muscles we noted in 95 participants (31.7%). We believe that there is no connection between absent palmaris longus and absent function of flexor digitorum superficialis. We found a much higher prevalence of muscles absence individually and jointly than in other studies. Keywords : forearm ; muscles, skeletal ; palmaris longus muscle ; flexor digitorum superficialis ; absence. INTRODUCTION Palmaris longus (PL) is a slender, fusiform muscle medial to flexor carpi radialis (7). PL is one of the most variable and most superficial flexor muscles of the forearm. It is well known that there is a wide variation in the reported prevalence of PL absence in different ethnic groups (2,4,8,13). Many authors have reported the incidence of agenesis to be higher on the left side (8,9,16,18). There are controversial findings in the literature regarding the symmetry of muscle absence and distribution of agenesis between genders. Some authors have reported the incidence of agenesis to be higher in females (2,8,21), while others have reported higher incidence of agenesis in males (1,6,23). Understanding of its variations is useful as it is often used as tendon graft and for tendon transfer as well as in other reconstructive procedures. It is a weak flexor of the wrist. It is believed that the muscle once existed as a flexor of proximal phalanges with its tendon lying in the palm superficial to the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and splitting around to be attached to the proximal phalanges. Studies have attempted to n Nikola Vučinić 1, MD. n Mirela Erić 1. n Mirjana Savić 2. 1 Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Serbia. 2 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, University of Novi Sad, Clinical Center of Vojvodina, Novi Sad, Serbia. Correspondence : Nikola Vučinić, Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Novi Sad, Hajduk Veljkova 3, Novi Sad, Serbia. nikolavucinic87@gmail.com 2016, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study. The authors report no conflict of interests. vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
2 414 n. vučinić, m. erić, m. savić correlate absence of palmaris longus with other anatomical anomalies (1,21). Flexor digitorum superficialis is located medial and deep to the PL and flexor carpi ulnaris. FDS is one of the largest superficialis flexor muscles of the forearm. FDS is an extrinsic muscle that flexes the proximal interphalangeal joints (PIPJ) and indirectly flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hand. There is variation in the flexor digitorum superficialis to the fifth digit. The absence of the FDS may influence clinical examination in injured hands (10). Considering that PL and FDS have the same embryological origin, the same innervation, similar functions, belong to the same muscle lodge and that are highly variable in existence and function, there is the possibility that their absence is associated. We examined our population to assess FDS function to the little finger and the incidence of palmaris longus absence. MATERIALS AND METHODS The presence or absence of the PL and FDS tendons was clinically determined in 300 participants (150 males and 150 females), in Caucasian population, using several tests. Individuals with the history of injury, disease or abnormality of the upper limb, which would preclude examination for the presence of the PL tendon and the FDS to the little finger, were excluded from the study. The participants age ranged from 18 to 66, mean age 19.6 years. The examination was carried out in two parts. The first part of the examination assessed the presence of the PL. The presence or absence of the PL tendon was recorded on both sides. The participant was initially asked to do the Standard test (Schaeffer s test) for the assessment of the PL tendon (Fig. 1). If the tendon was not visualised or palpable, four additional tests were done to confirm the absence. A single examiner checked all participants. The following tests were used : Standard test (Schaeffer s test) : the participant was made to steady their forearm at 90 degrees and asked to oppose the thumb to the little finger with the wrist partially flexed (18). Thompson s test : the participant is asked to make a fist, then flex the wrist and finally the thumb is opposed and flexed over the fingers (22). Mishra s test I : the metacarpophalangeal joints of all fingers are passively hyperextended by the examiner Fig. 1. Standard test (Schaeffer s test) : PL on the right hand. and the participant is asked to actively flex the wrist (11). Mishra s test II : the participant is asked to abduct the thumb against resistance with the wrist in slight palmar flexion (11). Pushpakumar s two-finger sign method : the participant is asked to fully extend the index and middle fingers, the wrist and other fingers are flexed, and finally the thumb is fully opposed and flexed (15). Finally, the wrists of every participant were examined by using the palpation during each of five previous tests, to insure the reliability of obtained results. The results acquired through the palpation were considered as the results of maximal accuracy. The second part of the examination assessed the functional ability of the superficialis tendon to flex the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ) of little finger. FDS function in the little finger was assessed by Standard test and divided into independent (Fig. 2) or absent function (Fig. 3). Independent function was defined as the ability to flex the PIPJ of the little finger > 90 degrees with the PIPJ of the other fingers of the same hand extended by covered with the fingers of the other hand. Absent function was the inability to flex the PIPJ > 90 degrees with the PIPJ of the other fingers of the same hand extended by covered with the fingers of the other hand. When it was unable for sure to determine FDS function, after Standard test were applied Present test and test by blocking the finger metacarpophalangeal joint (MCPJ). In Present test, the participant is asked to press the finger tip pulp of all the fingers together against the proximal part of the palm. If the FDS is acting, the distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) remains in a position of extension to hyperextension while the MCPJ and PIPJ are fully flexed. Flexion of DIPJ is taken as absence of FDS action (12). In vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
3 flexor digitorum superficialis 415 Fig. 2. Standard test : independent function of FDS on the right hand. Fig. 3. Standard test : absent function of FDS on the left hand. test by blocking the MCPJ, participant was also asked to flex the PIPJ. To block the MCPJ, hold the proximal phalanx in extension just distal to the MCPJ, so that the MCPJ is unable to bend when the patient tries to flex the finger (19). We used only three tests for examination of flexor digitorum superficialis functional deficiency. If the FDS function was demonstrated using any of the tests, the subject was deemed to have FDS function. Absence of FDS function on all the tests was required to declare the subject FDS functional deficient. This study was approved by Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine in Novi Sad. RESULTS In general population, unilateral absence of the palmaris longus muscle was recorded in 69 (23%) and bilateral absence in 88 (29.3%) participants. It was absent on the right side in 32 (10.7%) and on the left side in 37 (12.3%) participants. The overall absence of palmaris longus (unilateral and bilateral) was 52.3%. These results are shown in Table I. If PL was absent in one hand, the probability of absence in the opposite hand was If PL was present, the probability of absence in the other hand was In the same population, unilateral deficiency of FDS to the little finger was seen in 48 (16%) and bilateral deficiency in 52 (17.3%) participants. It was absent on the right side in 21 (7%) and on the left side in 27 (9%) participants. The overall absence of flexor digitorum superficialis (unilateral and bilateral) was 33.3%. The absence of the FDS is presented in Table II. If FDS function was absent in one little finger, the probability of absence in the opposite hand was If superficial function was present, the probability of absence in the other little finger was From the obtained data it was found that PL was more frequent absent (unilaterally and bilaterally) in men than women, 92 (61.3%) vs. 65 (43.3%) participants. Regarding to the absence of flexor digitorum superficialis function to the little finger (unilaterally and bilaterally) it was more frequent in women than men, 60 (40%) vs. 40 (26.7%) participants. The results are presented in Table I and Table II. We compared the deficiency of the FDS in the little finger with the absence of the PL tendon, and we found that difference was statistically significant in general population (X 2 = 22.11, p < 0.001), while gender distribution of the FDS deficiency with PL absence was statistically significant in males (X 2 = 57.74, p < 0.001) and statistically was not significant in females (X 2 = 0.34, p > 0.05). In relation to the hand dominance, we found 23 left-handed individuals (7.7%). Differences between the left and right-handed individuals as for the absence or presence of these two muscles were not significant. We did not encounter any other congenital anomalies in the study group. vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
4 416 n. vučinić, m. erić, m. savić Palmaris longus tendon Table I. Palmaris longus absence according to gender and limb laterality No. of examined individuals % Men % Women Bilateral present Right absence Left absence Bilateral absence Total % DISCUSSION Muscular variations of the flexor compartment of forearm are usual and could result in multiple clinical conditions limiting the functions of forearm and hand. Palmaris longus is one of the most variable muscles in the body. It may be agenetic, double, tendinous, split, incomplete, digastric or exhibit anomalous insertions. It has been suggested that palmaris longus is a phylogenetically degenerate metacarpophalangeal joint flexor (8,9,20,26). One advantage of the PL tendon is that it protects the median nerve which passes deep into in. In the absence of the PL tendon, the most superficial structure in the wrist is median nerve, which is at risk of injury during trauma and surgical incisions (1). PL muscle is very useful for its role in orthopedic and plastic surgeries. Its presence in 70-85% population and its superficial location makes it the most common donor material for tendon and joint reconstructive surgeries. PL is completely developed at birth while fascia lata, which is also used for reconstructive surgeries, is not so well developed at that age. Surgeons should acquaint themselves with prevalence in their areas of practice (1). The palmaris longus agenesis among various races and ethnic groups is variable (13), from 0.6% in the Korean population to 63.9% in the Turkish population (2,4). The absence of palmaris longus muscle is strictly hereditary characteristic. Palmaris longus muscle is an inherited autosomal dominant trait. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is probably connected with a single dominant gene (which shows incomplete penetration and variable expressivity), and/or absence is due to the effects of mutations (27). Erić et al in study which includes 800 participants, were found that unilateral absence of the palmaris longus was record in 173 (21.6%) and bilateral in 127 (15.9%) study participants. According to body side, right-sided absence of palmaris longus was found in 69 (8.6%) and left-sided in 104 (13%) participants. It has been suggested that this tendon is rapidly disappearing in humans (8). Absence of flexor digitorum superficialis function in the little finger is a relatively common congenital anomaly that can complicate assessment of little finger injuries. Townley et al reviewed the prevalence of flexor digitorum superficialis absence of superficialis function, unilateral and bilateral, in Table II. Flexor digitorum superficialis functional deficiency according to gender and limb laterality Flexor digitorum superficialis No. of examined % Men % Women % individuals Bilateral present Right absence Left absence Bilateral absence Total vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
5 flexor digitorum superficialis 417 Table III. Published series documenting absence of PL and FDS Authors Year Participants Ages (years) Overall absence PL % Overall deficiency FDS % Our study Agarwal (1) Sandeep et al (18) Thompson et al (24) the published literature. In appropriate studies (cadaveric studies were excluded) gathering 1352 people, the anomaly was unilateral in 92 individuals (6.8%) and bilateral in 81 (6.0%). Also, they were founded that absence of little finger superficialis function in one hand is therefore not a reliable indicator of this function in the opposite hand (25). A separate flexor digitorum superficialis tendon for the index finger has been identified (5). Some studies mention that if a patient has a PL tendon, then there is the high chance of Dupuytren s disease developing in that hand (1,14). Also, some other studies recommended that the presence of the PL tendon should potentially increase the pressure within the carpal tunnel it can be suspected that the presence of this tendon versus its absence can be associated factor in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Theoretically the presence and function of FDS tendon, as well, should increase pressure on the median nerve (17). However, Saied and Karamoozian found that the absence of a functional fifth FDS and a PL tendon are risk factors for developing CTS (17). This study showed that the absence of the PL tendon and fifth FDS function, independently and in combination, is more frequent in patients with CTS. In the group with CTS, 16/60 hands (26.7%) did not have a PL tendon and 18/60 hands (30%) were lacking fifth FDS function. Eight hands had neither of these (12.3%) and 34 hands had both (56.7%). In the group without CTS, 27/180 hands (15%) lacked the PL and 25/180 (13.9%) lacked a functional fifth FDS. Eight hands had neither of these (4.5%) and 136 hands had both (75.6%). In their study of 300 patients, Thompson et al (24) found 10 (3%) participants with absolute superficialis deficiency to the little finger (unilaterally and bilaterally). The overall absence of PL (unilaterally and bilaterally) was seen in 71 participants (25%). In this study, only two patients had concomitant absence of the PL and the FDS to the little finger. In the sample of 385 Indian men and women, the overall unilateral absence of the PL tendon was 16.9% and the bilateral absence was in 3.3%. The overall prevalence of the weak FDS in the little finger irrespective of the presence or absence of the PL tendon in this study was 16.1% (1). The overall prevalence of absence of the PL, in the Chinese population study that included 329 Chinese men and women, was 4.6%. Also, deficiency of FDS to the little finger was seen in 6.4% (18). In our study, overall prevalence of absent PL (unilateral and bilateral) was 52.3%. The overall prevalence of weak FDS in the little finger in our study was 33.3%. The prevalence of the unilateral and bilateral absence of the PL tendon and prevalence of weak FDS in the little finger in our population is much higher than the others studies. This high prevalence of lack function of the fifth finger flexion may indicate a gradual regression fifth tendon of FDS, due to insufficient amounts of the fifth finger during flexion of the fingers. That shows four studies with approximately same number of subjects (Table III). In the present study, we further confirmed earlier claims that PL tendon is rapidly disappearing in humans (8). On the other side, the overall prevalence of associated absent FDS function unilateral or bilateral with absent PL unilateral or bilateral on the same, left or right hands, in our study was 6.7%. As well, 31.7% had bilaterally presence both of these muscles. Lack of association between these two muscles is also the highest in our study. vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
6 418 n. vučinić, m. erić, m. savić Statistically difference between FDS deficiency in the little finger and PL tendon absence in general population was significant (p < 0.001), while gender distribution of the FDS deficiency and PL absence was statistically significant in males (p < 0.001), on the other hand statistically was not significant in females. Validation of used clinical tests, in the examination of PL presence in our study, was performed in comparing to palpation. Effectiveness of different tests were : Thompson s test- 83.5%, Standard test (Schaeffer s test)- 81%, Pushpakumar s two-finger sign method- 91%, Mishra s test I- 78% and Mishra s test II- 87.5%. Borkach and Rákoczi in study of PL in 1839 Hungarians, showed these results of effectiveness : Thompson s test- 83.5%, Standard test (Schaeffer s test)- 88.7%, Pushpakumar s two-finger sign method- 84.6%, Mishra s test I- 96.3% and Mishra s test II- 86.7% (3). According to the results of our study, the most reliable is the Pushpakumar s two-finger sign method and in Hungarian study the Mishra s test I showed the highest efficiency. Although there is no congruency in the previous order, the most reliable test between these studies, it is interesting that effectiveness of Thompson s test was identical between the two studies. We consider that there is no connection between absent function of flexor digitorum superficialis to the little finger and absent palmaris longus as well as present function of FDS to the little finger and present PL. In this conclusion we cite the fact that less than half (38.4%) of the participants had associated the absence or presence of these two muscles in both forearms. But, we have established that association with the absence or presence of these two muscles in both forearms, are much more frequent than in other studies. It has been postulated that an absence of the plantaris may be associated with the agenesis of the PL tendon, but we did not examine that possible association. Possible limitation of these clinical studies is the difficulty in assessment of all variations of PL muscle depending solely on a physical examination. Although rarely seen, these variations may lead to misinterpretation of an existing muscle as absent. Ultrasonography or MRI would confirm these variations precisely, but it is neither cost-effective nor time sparing (8). Muscle ultrasonography is a convenient technique to visualize muscle tissue as it is non-invasive and real-time. The use of ultrasonography is recommended in certain pathological conditions, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or other neuromuscular disorders (muscle atrophy and intramuscular fibrosis and fatty infiltration can be visualized with ultrasonography). Usually, ultrasonography has not found the routine use of either a reconstructive surgeons in preoperative preparation of palmaris longus tendon as well as in routine examination of intact structure and function (7). Most surgeons determine the existence of the palmaris longus simply by performing previously described clinical tests. The function of the hand is a very complex and human hand is in the center of daily life activities. Because of those injuries of hand and flexor tendons are very common. PL muscle is very useful for its role in orthopedic and plastic surgeries and it protects the median nerve which passes deep into it. Its superficial location makes it the most common donor material (tendon graft) for flexor tendon and joint reconstructive surgeries. The absence of the FDS may influence clinical examination of injured hands in the first order it complicates assessment of little finger injuries. In some musicians absence or functional deficiency of this muscle may limit movements of the little finger. REFERENCES 1. Agarwal P. Absence of the palmaris longus tendon in Indian population. Indian J Orthop 2010 ; 44 : Ahn DS, Yoon ES, Koo SH, Park SH. A prospective study of the anatomic variations of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel in Asians. Ann Plast Surg 2000 ; 44 : Borkach NE, Rákoczi F. Efficiency of different tests in reviling the palmaris longus muscle during the study of its agenesis. GISAP : Medical Science, Pharmacology 2013 ; 1 : Ceyhan O, Mavt A. Distribution of agenesis of palmaris longus muscle in years old age groups. Indian J Med Sci 1997 ; 51 : Çiftçioğlu E, Kopuz C, Çorumlu U, Demir M. Accessory muscle in the forearm : a clinical and embryological approach. Anat Cell Biol 2011 ; 44 : vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
7 flexor digitorum superficialis Dong-Soo K, Jae-Ho L, In-Jang C, Dae-Kwang K. Different frequency of the absence of the palmaris longus according to assessment methods in a Korean population. Anat Cell Biol 2012 ; 45 : Enhesari A, Saied A, Mohammadpoor L, Mousavi Ayatollahi A, Arabnejhad F. Presence or absence of palmaris longus anf fifth superficial flexor digitorum ; Is there any effect on median nerve surface area in wrist sonography. Iran J Radiol 2014 ; 11 : e Erić M, Krivokuća D, Savović S, Lekšan I, Vučinić N. Prevalence of the palmaris longus through clinical evaluation. Surg Radiol Anat 2010 ; 32 : Kapoor SK, Tiwari A, Kumar A, Bhatia R, Tantuway V, Kapoor S. Clinical relevance of palmaris longus agenesis : common anatomical aberration. Anat Sci Int 2008 ; 83 : Kigera JWM, Katusiime A. Prevalence of agenesis of flexor digitorum superficialis of the fifth digit in East Africa through clinical examination. SA Orthop J 2011 ; 10 : Mishra S. Alternative tests in demonstrating the presence of Palmaris longus. Indian J Plast Surg 2001 ; 34 : Mishra S. A new test for demonstrating the action of flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) tendon. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2006 ; 59 : Natsis K, Levva S, Totlis T, Anastasopoulos N, Paraskevas G. Three-headed reversed palmaris longus muscle and its clinical significance. Ann Anat 2007 ; 189 : Powell BW, McLean NR, Jeffs JV. The incidence of a palmaris longus tendon in patients with Dupuytren s disease. J Hand Surg Br 1986 ; 11 : Pushpakumar SB, Hanson RP, Carroll S. The two finger sign. Clinical examination of palmaris longus (PL) tendon. Br J Plast Surg 2004 ; 57 : Reimann AF, Daseler EH, Anson BJ, Beaton LE. The palmaris longus muscle, tendon. A study on 1600 extremities. Anat Rec 1944, 89 : Saied A, Karamoozian S. The relationship of presence or absence of palmaris longus and fifth flexor digitorum superficialis with carpal tunnel syndrome. Eur J Neurol 2009 ; 16 : Sandeep JS, Aymeric YTL, Hwee-Bee W. Clinical assessment of absence of the palmaris longus and its association with other anatomical anomalies-a Chinese population study. Ann Acad Med Singap 2006 ; 35 : Semer NB. The normal hand exam. In : Semer NB (ed). Practical Plastic Surgery for Nonsurgeons. Hanley and Belfus inc, Philadelphia, 2001, p Standring S. Gray s anatomy. 39 th Edn, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Edinburg, 2005, pp Tan J, Oh L, Louis D. Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis As Determined by an Expanded Clinical Examination. J Hand Surg Am 2009 ; 34 : Thompson JW, McBatts J, Danforth CH. Hereditary and racial variations in the musculus palmaris longus. Am J Phys Anthrop 1921 ; 4 : Thompson NW, Mockford BJ, Cran GW. Absence of the palmaris longus muscle : a population study. Ulster Med J 2001 ; 70 : Thompson NW, Mockford BJ, Rasheed T, Herbert KJ. Functional absence of the flexor digitorum superficialis to the little finger and absence of the palmaris longus is there a link? J Hand Surg Br 2002 ; 7 : Townley WA, Swan MC, Dunn RLR. Congenital absence of flexor digitorum superficialis : implications for assessment of little finger lacerations. J Hand Surg Eur 2010 ; 5 : Vanderhooft E. The frequency and relationships between the palmaris longus and plantaris tendon. Am J Orthop 1996 ; 25 : Vučinić N. Testing inheritance of palmaris longus muscle in our population. Medicinski fakultet, Kragujevac, 2011, p vucinic-.indd /06/16 15:13
Clinical Assessment of Absence of the Palmaris Longus and its Association With Other Anatomical Anomalies A Chinese Population Study
 Original Article 249 Clinical Assessment of Absence of the Palmaris Longus and its Association With Other Anatomical Anomalies A Chinese Population Study Sandeep J Sebastin, 1 MCh (Plastic), Aymeric YT
Original Article 249 Clinical Assessment of Absence of the Palmaris Longus and its Association With Other Anatomical Anomalies A Chinese Population Study Sandeep J Sebastin, 1 MCh (Plastic), Aymeric YT
Anatomic variation of palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis of little finger in Indian population
 SICOT J 2015, 1, 5 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2015006 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Anatomic variation of palmaris longus and
SICOT J 2015, 1, 5 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2015006 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Anatomic variation of palmaris longus and
Palmaris Longus Agenesis (PLA) among Dusun & Bajau ethnic groups of Northern Borneo
 386 Palmaris Longus Agenesis (PLA) among Dusun & Bajau ethnic groups of Northern Borneo Aye Mya Thidar 1*, Tin Tin Myint 1, Daw Khin Saw Naing 2, Zainal Ariffin Mustapha 1 1,2&4 Department of Biomedical
386 Palmaris Longus Agenesis (PLA) among Dusun & Bajau ethnic groups of Northern Borneo Aye Mya Thidar 1*, Tin Tin Myint 1, Daw Khin Saw Naing 2, Zainal Ariffin Mustapha 1 1,2&4 Department of Biomedical
Received December 27, 2017; Revised March 2, 2018; Accepted March 11, 2018
 Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of different methods of examination for presence of palmaris longus and examination of fifth superficial flexor
Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of different methods of examination for presence of palmaris longus and examination of fifth superficial flexor
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2012; 3(4): 2597-2602 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Int J Biol Med Res. 2012; 3(4): 2597-2602 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
A study on the absence/presence of the muscle Palmaris Longus in an Indian population
 Original Research: A study on the absence/presence of the muscle Palmaris Longus in an Indian population *Sudhir Saxena *Associate Professor, Dept of Anatomy, GR Medical College, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh,
Original Research: A study on the absence/presence of the muscle Palmaris Longus in an Indian population *Sudhir Saxena *Associate Professor, Dept of Anatomy, GR Medical College, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh,
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Morphological Variations in Lumbricals of Hand A Cadaveric Study
 IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Clinical Study The Variation in the Absence of the Palmaris Longus in a Multiethnic Population of the United States: An Epidemiological Study
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2012, Article ID 282959, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/282959 Clinical Study The Variation in the Absence of the Palmaris Longus in a Multiethnic Population of the United
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2012, Article ID 282959, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/282959 Clinical Study The Variation in the Absence of the Palmaris Longus in a Multiethnic Population of the United
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the Little Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
A STUDY OF PALMARIS LONGUS MUSCLE: ITS ANATOMIC VARIATIONS WITH EMBRYOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE AND CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Sunitha. R 1, Prathap Kumar J * 2.
 Original Research Article A STUDY OF PALMARIS LONGUS MUSCLE: ITS ANATOMIC VARIATIONS WITH EMBRYOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE AND CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Sunitha. R 1, Prathap Kumar J * 2. India. ABSTRACT Background:
Original Research Article A STUDY OF PALMARIS LONGUS MUSCLE: ITS ANATOMIC VARIATIONS WITH EMBRYOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE AND CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Sunitha. R 1, Prathap Kumar J * 2. India. ABSTRACT Background:
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Absent Palmaris Longus: A Case Report & A Live Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XI (Oct. 2017), PP 65-71 www.iosrjournals.org Absent Palmaris Longus: A Case Report
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XI (Oct. 2017), PP 65-71 www.iosrjournals.org Absent Palmaris Longus: A Case Report
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Department of Community Health, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia INTRODUCTION
 Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences (ISSN 1675-8544); Novel Method Vol. 9 (2) to Estimate June 2013: the 19-24 Length of the Palmaris Longus Tendon 19 Novel Method to Estimate the Length
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences (ISSN 1675-8544); Novel Method Vol. 9 (2) to Estimate June 2013: the 19-24 Length of the Palmaris Longus Tendon 19 Novel Method to Estimate the Length
CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS
 IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
VARIANT ARTERIAL PATTERN IN THE FOREARM WITH ITS EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS. Vaishnavi Joshi and Dr. Shaheen Sajid Rizvi
 Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Management of the injured hand - Principles of assessment K. Karunadasa Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Unit, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama, Sri Lanka Keywords:
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Management of the injured hand - Principles of assessment K. Karunadasa Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Unit, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama, Sri Lanka Keywords:
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Dynamic High Resolution Sonography (d-hrus) of the hand: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic High Resolution Sonography (d-hrus) of the hand: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-1634 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Fabbro, A. Corazza, A. Arcidiacono, F.
Dynamic High Resolution Sonography (d-hrus) of the hand: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-1634 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Fabbro, A. Corazza, A. Arcidiacono, F.
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Interesting Case Series. Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries
 Interesting Case Series Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries Evgenios Evgeniou, MBBS, MRCS, a and Harriet Walker, MBBS, MRCS b a North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol, United Kingdom, b Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust,
Interesting Case Series Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries Evgenios Evgeniou, MBBS, MRCS, a and Harriet Walker, MBBS, MRCS b a North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol, United Kingdom, b Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust,
Palmaris Longus Muscle s Prevalence in Different Nations and Interesting Anatomical Variations: Review of the Literature
 Elmer ress Review J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(11):825-830 Palmaris Longus Muscle s Prevalence in Different Nations and Interesting Anatomical Variations: Review of the Literature Dimitriou Ioannis a, d, Katsourakis
Elmer ress Review J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(11):825-830 Palmaris Longus Muscle s Prevalence in Different Nations and Interesting Anatomical Variations: Review of the Literature Dimitriou Ioannis a, d, Katsourakis
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
The Sonographic Morphology of Musculus Palmaris Longus in Humans
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 The Sonographic Morphology
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 The Sonographic Morphology
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
HAND SURGERY- GUIDELINES for POST-OP TREATMENT and REFERRAL to HAND THERAPY
 HAND SURGERY- GUIDELINES for POST-OP TREATMENT and REFERRAL to HAND THERAPY Please use the specific hand therapy referral form. Always give at least one telephone number for the patient so that there is
HAND SURGERY- GUIDELINES for POST-OP TREATMENT and REFERRAL to HAND THERAPY Please use the specific hand therapy referral form. Always give at least one telephone number for the patient so that there is
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND
 Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Interesting Case Series. Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy
 Interesting Case Series Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy Leyu Chiu, BA, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, a,b and Paul A. Luce, MD, a,b,c a Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids,
Interesting Case Series Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy Leyu Chiu, BA, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, a,b and Paul A. Luce, MD, a,b,c a Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids,
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND. Majoring in Minors Conference th January 2013 Derriford Hospital
 HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND Majoring in Minors Conference 16-17 th January 2013 Derriford Hospital Objectives Anatomy & Terminology History Examination Look Feel Move Investigations
HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND Majoring in Minors Conference 16-17 th January 2013 Derriford Hospital Objectives Anatomy & Terminology History Examination Look Feel Move Investigations
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel
 Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release
 Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome associated with extension of flexor digitorum muscle bellies into the carpal tunnel: A case series
 Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome associated with extension of flexor digitorum muscle bellies into the carpal tunnel: case series Rochelle Castillo 1, Khushboo Sheth 2, lan abigian 3, Christopher Scola
Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome associated with extension of flexor digitorum muscle bellies into the carpal tunnel: case series Rochelle Castillo 1, Khushboo Sheth 2, lan abigian 3, Christopher Scola
Interesting Case Series. Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female
 Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
ANATOMY. Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date :
 ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy
 Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers
 J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
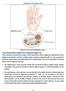 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
