Fracture Management. From RAH & IRH refer emergency cases to the on-call orthopaedic FY2/Reg
|
|
|
- Archibald Preston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fracture Management At the RAH most fractures are followed up at the daily orthopaedics fracture clinic. A similar system exists at IRH. There are daily fracture clinics both at RAH and IRH. From RAH & IRH refer emergency cases to the on-call orthopaedic FY2/Reg Fracture Policy Fractures can be divided into four types 1. Fractures requiring no specialist treatment or follow up Can be discharged from ED but must be given appropriate advice re prognosis and GP letter must be completed. At RAH these include 5 th MC, 5 th MT, lateral malleolus, paediatric clavicle and radial head fractures. Specific discharge leaflets exist for these cases 2. Fractures requiring symptomatic treatment e.g. POP cast. These patients must be followed up at fracture clinic. If followed up by ortho then they are seen the following day at the fracture clinic. 3. Fractures for whom advice is required as to whether or not active treatment is necessary or not (surgical or MUA). Discuss with senior then refer to orthopaedic on-call 4. Those not requiring active treatment but who for any reason outpatient management is unsuitable e.g. greater trochanter or minor pelvic fractures in the elderly rendering them immobile. For all those not being admitted GP letter must be sent The specific treatment e.g. type of cast and position of immobilisation must be prescribed in the ED card Appropriate advice re rest, elevation and mobilisation of adjacent joints must be given to patient or relative Those placed in POP or backslab will be given an appointment for POP check/# clinic the following day.
2 All Fractures Assess distal circulation and sensation and record in notes X-Rays 1. Two views True AP and lateral 2. Two joints Above and below fracture 3. Two sides if in doubt in children 4. Special views are dealt with under specific fractures Compound fractures 1. Distal phalanges of fingers Thorough debridement under ring block Oral Flucloxacillin (only rarely required as no substitute for adequate wound toilet/care) Ensure tetanus status ED returns wound review 2. Distal phalanges of toes as above 3. All Others Betadine soaked pad & refer orthopaedics
3 Overview of fracture management This is a brief description of management of the commoner fractures seen in the Emergency Department. If in doubt discuss with Consultant/middle grade staff. Also refer to textbooks in the department. Adult Fractures Sterno-Clavicular Joint UPPER LIMB Anterior Dislocation Broad arm sling or collar and cuff sling. Fracture clinic Posterior Dislocation Refer orthopaedic Clavicle # Broad arm sling or collar and cuff sling and follow up in fracture clinic Acromio-Clavicular Joint Grade I Grade II Grade III no displacement subluxation dislocation with tearing of AC and coracoclavicular ligaments? Grade IIImay need weight bearing & non-weight bearing views Grades I & II Broad arm sling or collar and cuff sling. Analgesia. Advice on mobilisation. Dispense with sling after 2-3 days. Discharge to GP Grade III Refer to fracture clinic Scapular Fractures Relatively uncommon, but, if present, may indicate significant trauma so look closely for associated injury. Treat in broad arm sling. Ortho fracture clinic follow up
4 Dislocation of Gleno-humeral Joint SHOULDER/HUMERUS a. anterior dislocation test and record axillary nerve function. X-ray pre & post reduction. Reduce in A&E. (if unsuccessful, refer to orthopaedic ) Blue polysling, axillary pad. Fracture clinic follow up. b. posterior dislocation clinical diagnosis arm held fixed in internal rotation. Unable to externally rotate arm AP x-ray may look normal. Be aware of light bulb sign. Discuss with senior/orthopaedics. May require GA for reduction. Fracture-dislocations (associated fracture) Greater tuberosity fracture without displacement Reduce joint and check x-ray, Body bandage, collar & cuff, axillary pad. Fracture clinic follow up. Greater tuberosity fracture with displacement > 1cm Refer orthopaedics Fracture of neck of humerus Refer orthopaedics Fracture Head/Neck of Humerus Two part fractures Humeral neck and undisplaced greater tuberosity fracture Body bandage, collar & cuff, axillary pad or Blue Polysling Fracture clinic follow up Displaced greater tuberosity > 1cm Refer orthopaedics Three or more part fractures Refer orthopaedics Humeral Shaft Test and record radial nerve function Humeral brace Refer orthopaedic
5 ELBOW Dislocated Elbow Check distal neurovascular status Reduce-longitudinal traction with slight flexion of elbow if needed. Check x-ray. Record reduction, medial epicondyle position, radial head/neck #, coronoid # Assess and record medial nerve stability Long arm back slab Discuss with orthopaedics. May need admission for elevation Fracture-Dislocation Elbow Refer orthopaedics Distal Humerus Classification Supracondylar Intra-articular Transcondylar/intercondylar Olecranon Undisplaced -long arm backslab Any displacement-refer to orthopaedics Radial Head Classification Mason Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 undisplaced marginal with displacement comminuted involving the whole of head associated with dislocation of elbow. Minor radial head involving less than 1/3 rd of the articular surface can be discharged with a collar & cuff and advice leaflet (RAH) no follow up required. At IRH refer # clinic
6 All other radial head fractures refer to orthopaedic fracture clinic. If complicated refer to on-call orthopaedics Radial Neck Undisplaced padded crepe and broad arm sling Fracture clinic Displaced > 15 0 refer orthopaedics Post traumatic effusion/no obvious fracture Treat symptomatically with collar & cuff sling and discharge with radial head # advice sheet. FOREARM FRACTURES Ring structure, so will disrupt in two places in indirect damage. Isolated fracture only with direct below. Fracture dislocations Galeazzi Fractured radius with dislocation of radio-ulnar joint. Monteggia Fractured ulna with dislocation of radial head. Fracture of Radius and Ulna Isolated ulna shaft nightstick fracture WRIST
7 Fracture Dislocation Transcaphoid/perilunate dislocation Obtain true lateral x-ray High energy injury Think if swollen painful wrist and apparently normal x-ray Colles Fracture Fracture distal radius with dorsal displacement of distal fragment. Smith s Fracture (volar displacement) and Barton s Fracture (volar intraarticular#) Scaphoid Definite Scaphoid Fracture Scaphoid cast Fracture clinic follow up Clinical Scaphoid Typical history of fall on outstretched hand FOOSH Scaphoid is located in anatomical snuffbox at base of thumb between tendons of extensor pollicus longus and abductor pollicus longus/extensor pollicus brevis. Always examine for and document presence/absence of ASB tenderness on wrist examination. Consider if history and 1. tender on pressure over anatomical snuff box 2. swelling over anatomical snuff box 3. pain on axial pressure of thumb 4. tenderness over dorsal and palmer aspect of scaphoid. Ask for specific scaphoid views. If no fracture then treat as clinical scaphoid Place in scaphoid crepe or Futuro with thumb extension and refer to fracture clinic in 2 weeks time. There is no evidence to support immobilization of clinical scaphoids in casts until check x-ray at days. Only immobilise if absolutely necessary HAND
8 If immobilising hand, use volar slab in position of function or use padded crepe Instruct on mobilisation SOFT TISSUE INJURY Ulnar collateral ligament of 1 st MCP joint Clinical diagnosis of rupture. x-ray to exclude fracture on call for obvious laxity operative repair always needed. Consider reviewing other patients at next STC who are too sore to assess laxity, tender and swollen over UCL & who have no # on initial xray. Closed Mallet Injury Mallet splint ED clinic in 2 weeks for wound check Advise about use of splint. Give advice card Patient will wear splint for at least 6 Weeks. Traumatic Boutonniere Splint with PIP joint extended Refer to fracture clinic Ruptured Tendons Open & Closed. Limited hand surgery at the RAH. These patients may require referral to the Plastic surgeons at GRI WOUNDS Any doubt, Discuss with Senior Definite tendon division or digital nerve injury, INFECTION Suspected flexor sheath infection or deep palmar space infection Paronychia Drain under local anaesthetic. If pus tracks under the nail-remove it. Most can be followed up at GP If pus drained then usually do not require antibiotics Cellulitis Oral Flucloxacillin Review at hours. If no improvement. Admit under medicine for IV antibiotics (if hand then refer ortho) High Pressure Injection Injury
9 Human Bites See under bites guidelines DISLOCATION Metacarpo-phalangeal Joint Interphalangeal Joint X-ray prior to reduction Reduce by traction (under ring block) Check x-ray Assess stability to hyperextension & lateral stability Neighbour strapping # clinic follow up Carpo-metacarpal dislocation FRACTURES Carpo-metacarpal fracture dislocation Bennet s 1 st CMC joint Intra-articular fracture of base of 1 st MC 2 nd to 5 th Metacarpal Fractures Assess rotation in flexion If any rotation then refer to orthopaedics First Uncomplicated/non-Bennet's Scaphoid type cast Fracture clinic Second to Fourth Volar slab
10 Fracture clinic Fifth Shaft undisplaced Displaced volar slab & fracture clinic follow up Neck assess for rotation of little finger If no rotational deformity. Buddy strap/padded crepe and discharge with advice leaflet (RAH), at IRH refer to # clinic If rotational deformity or angulation > 30 o then refer to orthopaedics. Phalangeal Fractures Assess stability by clinical examination Assess rotation in flexion Angulated or rotated unstable fractures refer to orthopaedics Displaced condylar, neck or basal fractures Minor Phalangeal fractures buddy strap & review in # clinic Major Injuries PELVIS The pelvis is a ring structure so indirect violence will disrupt the pelvis in two places
11 Anatomy Pelvic ring stability is provided by the ligaments shown below: Fractures of the Pelvic Ring Tiles Classification (Tile,M: Pelvic ring fractures. Should they be fixed? J. Bone and joint surgery. 70B: ) Type A Stable A1-Fractures of the pelvis not involving the ring. A2-Stable, minimally displaced fractures of the ring. Type B Rotationally unstable, vertically stable. Open book/lateral compression B1-Open book B2-Lateral compression: ipsilateral B3-Lateral compression: contralateral(bucket handle) Type C Rotationally unstable, vertically unstable, ipsilateral SI joint and rami C1-Rotationally and vertically unstable C2-Bilateral C3-Associated with acetabular fracture. Young & Burgess Classification (J.Trauma 30: )
12 Stability can be judged by fracture pattern, direction of force of the injury and by knowledge of the pelvic ligamentous anatomy. See overleaf. Young and Burgess Classification Type Description Mechanism Un/Stable Picture Lateral Compression Unilateral pubic rami fractures, with or without symphysis injury, and bilateral rami fractures with or without pubic symphysis injury LC1 Unilateral ramii (Transverse) & ipsilateral sacral compression Lateral force compressing sacrum Usually stable
13 LC2 Unilateral ramii & ipsilateral post. Iliac# Lateral force compressiong ilium Usually stable LC3 LC I&II & contralateral APC Trapped between unyielding object/rollover Unstable AP Compression APC AP1 Symphysis <2cm or ramii (vertical) & ant.si ligament stretched Low to moderate energy forces (sports) Direct Anterior Force Stable
14 AP2 AP3 Symphysis >2cm or ramii & ant SI ligt torn (+ the ligaments of the floor of the pelvis) Symphysis or ramii & ant & post SI ligament torn High energy- open book High energypelvis rotates externally until the post iliac wing contacts the posterior sacrum Unstable Very unstable Vertical Shear (VS) Ant & post vertical displacement Fall from a height with vertical forces Unstable
15 Combined Mechanical (CM) Combination of other injuries combination Unstable Please note that springing the pelvis is not a reliable sign of pelvic fracture, except where there is gross disruption of the pelvic ring (where it is, therefore, unnecessary) Massive blood loss can occur with pelvic fractures Pelvic binder should be applied (if not already done so prehospital) to all suspected significant pelvic #s Refer all pelvic fractures to orthopaedics. Only exception to this is undisplaced pubic rami fractures. If patient able to mobilise and has adequate home support then discharge with analgesia/advice. Obviously, an elderly patient must never be sent home from the Emergency department when unable to weight bear, irrespective of apparently normal x-rays. He/she should be referred to the on call orthopaedic on-call for admission. Not infrequently, further x-ray studies reveal pathology not seen on the initial films ACETABULUM HIP
16 Dislocation of hip Leg held shortened and internally rotated Examine for sciatic nerve integrity Generally reduced under general anaesthetic Fractures Femoral Head Fractures Femoral Neck Fractures Classification Intracapsular Subcapital Transcervical Extracapsular Basal Intertrochanteric Subtrochanteric There is a system of fast tracking fractured neck of femur patients at RAH 1. Diagnosis suggested by history of fall, leg lying shortened and externally rotated 2. Ensure adequate history and examination 3. If suspected, obtain IV access and provide analgesia, intravenous morphine. Remember patient has to get moved for x-ray 4. When putting in venflon take off bloods including group and save 5. Identify patient to nurses as? NOF. Send to x-ray. 6. Once returned from x-ray- if diagnosed as #NOF then inform nursing staff and they will contact orthopaedic page holder to arrange a bed in orthopaedic unit. 7. If time permits and history suggests collapse then organise ECG in department, otherwise this can be done in the ward. 8. Refer patient to orthopaedics, giving the ward that patient is going to. 9. Orthopaedic on-call will review patient in ward, not in ED Classification of hip fractures:
17 Garden s Classification of neck of femur fractures NB: 1. A flexion contracture of the hip may result from psoas spasm secondary to pelvic pathology e.g. appendicitis etc.
18 2. Other causes of hip joint pain include: Reiter s Syndrome Rheumatoid Arthritis Ankylosing Spondylitis Bony Metastases (thyroid, kidney, lung, breast, prostate) Femoral Shaft Fractures Manage patient in resus/ensure senior staff involved Patients can lose 1-2 litres of blood around fracture Resus as per A, B, C IV access, fluids, analgesia, Femoral nerve block with 0.5% bupivocaine ( Marcain) is helpful in pain control. If no pelvis fracture, place in Thomas splint. The ED/Fracture clinic nurses will assist you in applying this. Soft Tissue Injury Careful history and assessment 1. Unstable 2. Locked knee KNEE
19 3. Tense effusion 4. Small effusion Padded crepe & crutches. Review in ED ST clinic at 2 weeks Dislocated Patella Usually dislocates laterally Reduce by extension of knee. Use entonox For first dislocation place in pipestem cast For recurrent dislocation- padded crepe crutches. Ortho fracture clinic follow up. Fractures Distal Femur Patella Tibial plateau Tibial Fractures All tibial shaft fractures should be referred to orthopaedics Fibular Neck Fractures Assess knee stability Check ankle Check function of common peroneal nerve- dorsiflexion, eversion of ankle. Sensation lateral border of foot If any of above impaired- refer to orthopaedics Fibular Shaft Fracture Padded crepe and ortho fracture clinic follow up ANKLE Soft Tissue Injury Obtain history Document if patient can weight bear Examine and document tenderness at fibular neck, Achilles, Os Calcus, malleoli, 5th MT
20 Use Ottawa ankle injury rules to determine need for x-ray. If in doubt err on side of caution. If no fracture then treat with RICE R I C E rest for hours ice 10 minutes every 1-2 hours for first 2 days. No direct skin contact compression. Tubigrip or padded crepe elevation. Ankle needs to be higher than knee Ensure adequate analgesia Advise that will settle but can take 8-12 weeks to heal If unable to weight bear then provide crutches and review in ED soft tissue clinic in 2 weeks Ruptured tendo-achilles Simmond s calf squeeze test. Document whether palpable gap present. Refer to orthopaedics to allow discussion re operative vs conservative Rx Fractures Distal Tibia Including medial malleolus. Ankle Classification Type A Type B Type C X-ray Clinical Weber Fibula # below syndesmosis Fibula # above syndesmosis +/- medial injury High fibula # + medial injury-diastasis of tibia and fibula careful assessment of talus within ankle mortice record medial joint findings bruising/swelling/pain
21 Management Type A BKPOP or BREG boot, # clinic follow up Type B No Talar shift BKPOP #clinic follow up Talar shift Type C Bimalleolar fractures Isolated medial malleolus fracture Unless small avulsion. All ankle fractures, unless very small avulsion fractures from the tips of the malleoli, should be followed up at orthopaedic fracture clinic. Minor avulsions treat symptomatically & discharge with advice leaflet (RAH) Fractures FOOT Talus Os Calcus Ask for specific calcaneal view Measure bohler's angle. Normally about 40 0
22 Metatarsals 5 th Metatarsal Base Note in children that the epiphysis is vertical and fractures are transverse Treat in padded crepe/crutches Discharge with advice leaflet (RAH) Beware Jones fracture - fracture distal to intertarsal joint. This must be immobilized in a Breg boot or POP Shaft of Metatarsal BKPOP. Ortho fracture clinic Multiple fractures Fracture Dislocation True lateral x-ray of foot for all swollen feet or if run over Phalanges Great toe Treat with Toe spika. Plaster slipper if in great pain 2 nd -5 th toes we generally do not x-ray these unless dislocation suspected. Treat with buddy strapping. PAEDIATRIC FRACTURES There are some types of fractures, which are unique to children 1. Greenstick fracture break in one cortex only 2. Torus fracture bend in bone without cortical breech 3. Plastic bowing fracture 4. Salter & Harris epiphyseal fracture. Type I-V Undisplaced/greenstick # distal radius or ulna Treat in colles POP Undisplaced torus fracture: RAH: place in splint and discharge with advice leaflet
23 At IRH these injuries are still followed up in # clinic Displaced Supracondylar Assess distal CSM Undisplaced Supracondylar Above elbow backslab Ortho fracture clinic follow up Clavicle Ensure assess and document distal CSM Undisplaced Broad arm sling discharge with advice leaflet (RAH) Displaced Broad arm sling ortho fracture clinic Lateral Malleolus BKPOP ortho fracture clinic follow up Tibia Discuss with orthopaedics May require admission for elevation to reduce risk of compartment syndrome Metatarsal BKPOP ortho fracture clinic follow up Non Accidental Injury X-ray signs Certain x-ray findings are highly suggestive of physical abuse. These include rib and skull fractures. Other x-ray features, which may indicate abuse, include: 1. Multiple fractures in different stages of healing 2. Multiple metaphyseal/epiphyseal injuries 3. A single fracture with multiple bruises. 4. Subperiosteal new bone formation. Occurs after few days of trauma. If present on day of injury it can be concluded that some time has elapsed between injury and presentation. 5. Corner fracture. Small fracture at the corner of metaphysis of long bones
24 Iain Young October 16
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Fracture Guideline
 Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures. Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England
 Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England Objectives Types Fracture Patterns Fracture Healing Assessing
Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England Objectives Types Fracture Patterns Fracture Healing Assessing
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities
 Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center
 Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Goals. Initial management skeletal trauma. Physical Exam ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT 12/4/2010
 ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack
 1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES
 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care. David W. Gray, M.D.
 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures. Rena Heathcote
 Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN
 - 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
- 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
Trauma Films for Upper Body. LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC
 Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB.
 ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries. J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics
 Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002
 Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Common Limb Fractures. Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009
 Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
Common Limb Fractures Mr Sheraz Malik MB BS MRCS Instructor Mr Paul Ofori-Atta Mb ChB FRCS President Motc Life UK April 2009 Objectives To be able to describe all characteristics of a fracture Describe
PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP
 PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP TOPICS (1) Fracture types ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding CPT procedure coding Fracture care treatments: Manipulated
PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP TOPICS (1) Fracture types ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding CPT procedure coding Fracture care treatments: Manipulated
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss!
 Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss! 2018 Primary Care Approach to Treating the Injured Athlete May 4, 2018 John H. Wilckens, MD Associate Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss! 2018 Primary Care Approach to Treating the Injured Athlete May 4, 2018 John H. Wilckens, MD Associate Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
What can a redesigned facture pathway look like?
 GRI FRACTURE CLINIC MODERNISATION What can a redesigned facture pathway look like? Lech Rymaszewski Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon DETROIT BAILOUT TRADITIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC FRACTURE (#) CLINIC All non operated
GRI FRACTURE CLINIC MODERNISATION What can a redesigned facture pathway look like? Lech Rymaszewski Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon DETROIT BAILOUT TRADITIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC FRACTURE (#) CLINIC All non operated
Title Protocol for the Management of Shoulder Injuries in MIUs and WICs
 Document Control Title in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate, Logistics and Resilience Department Emergency Department Version Date Issued Status
Document Control Title in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate, Logistics and Resilience Department Emergency Department Version Date Issued Status
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
11/5/14. I will try to make this painless. Great, a Fracture, Now What? Objectives. Basics for Fracture Workup. Basics for Fracture Workup
 Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Appendicular Skeletal Trauma
 Appendicular Skeletal Trauma Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Types of cognitive error Satisfaction of search; Once
Appendicular Skeletal Trauma Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Types of cognitive error Satisfaction of search; Once
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference. Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014
 St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA. Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009
 EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
Orthopedic X-Rays most commonly missed
 Orthopedic X-Rays most commonly missed Vukiet Tran, MD, MHSc, MBA University Health Network Toronto, Canada 1 COI Disclosure I am the current Medical Director for Best Doctors Canada. Presenter: Dr. Vu
Orthopedic X-Rays most commonly missed Vukiet Tran, MD, MHSc, MBA University Health Network Toronto, Canada 1 COI Disclosure I am the current Medical Director for Best Doctors Canada. Presenter: Dr. Vu
CASE ONE CASE ONE. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mason Classification. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mechanism of Injury. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Imaging
 CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
Orthopedics - Dr. Ahmad - Lecture 2 - Injuries of the Upper Limb
 The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
Elbow Problems.
 Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs
 Document Control Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Emergency Services, Logistics and
Document Control Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Emergency Services, Logistics and
Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb AP; Lat. PA. PA; Lat.: Obls.; Elongated PA with ulnar deviation
 Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
COURSE TITLE: Skeletal Anatomy and Fractures of the Lower Arm, Wrist, and Hand
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
SNAP, CRACKLE, POP. Randy L Aldret, EdD, ATC, LAT Stephanie Aldret, DO, CAQSM OOA Winter CME Seminar January 26, 2018
 SNAP, CRACKLE, POP Randy L Aldret, EdD, ATC, LAT Stephanie Aldret, DO, CAQSM OOA Winter CME Seminar January 26, 2018 1 OBJECTIVES Review terms to describe fractures Identify fractures that can be treated
SNAP, CRACKLE, POP Randy L Aldret, EdD, ATC, LAT Stephanie Aldret, DO, CAQSM OOA Winter CME Seminar January 26, 2018 1 OBJECTIVES Review terms to describe fractures Identify fractures that can be treated
Release Notes and Installation Instructions. Medtech32. ACC Subsidy Updates
 Release Notes and Installation Instructions Medtech32 ACC Subsidy Updates General Practitioners, Medical Specialists, Nurses, Podiatrists and Specified Treatment Providers (April 2014) These Release Notes
Release Notes and Installation Instructions Medtech32 ACC Subsidy Updates General Practitioners, Medical Specialists, Nurses, Podiatrists and Specified Treatment Providers (April 2014) These Release Notes
QUEST.6. This patient fell from a tree a. What is the diagnosis? (2) b. What would be your management for this injury in casualty?
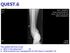 QUEST.6 This patient fell from a tree a. What is the diagnosis? (2) b. What would be your management for this injury in casualty? (3) P381 A. Right sided fractures of medial and lateral malleoli with a
QUEST.6 This patient fell from a tree a. What is the diagnosis? (2) b. What would be your management for this injury in casualty? (3) P381 A. Right sided fractures of medial and lateral malleoli with a
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013
 Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38
 Fractures (non-complex): assessment and management NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Fractures (non-complex): assessment and management NICE guideline Published: 17 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng38 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries
 Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Orthopedic Emergencies. Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta
 Orthopedic Emergencies Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose I do not intend to discuss unapproved
Orthopedic Emergencies Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose I do not intend to discuss unapproved
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Introduction to Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3
 Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE IN FEMUR
 Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
LRI Emergency Department
 LRI Emergency Department Guideline for the management of: Finger Tip Injuries in Children In the Paediatric Emergency Department (UHL Category C Guidance) Staff relevant to: ED Medical and Nursing staff
LRI Emergency Department Guideline for the management of: Finger Tip Injuries in Children In the Paediatric Emergency Department (UHL Category C Guidance) Staff relevant to: ED Medical and Nursing staff
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators
 Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators Mark Halstead, MD Dr. Mark Halstead is the Associate Professor of the Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics at Washington University School of Medicine; Director of
Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators Mark Halstead, MD Dr. Mark Halstead is the Associate Professor of the Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics at Washington University School of Medicine; Director of
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department. October 2012
 Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
THE Salter-Harris classification is a radiologic
 Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Activity: Synopsis of Fractures and Dislocations. Approval Date: 3/1/2018. Termination Date: 2/29/2021
 Activity: Synopsis of Fractures and Dislocations Approval Date: 3/1/2018 Termination Date: 2/29/2021 Target Audience: All local physicians working in the fields of primary care, physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Activity: Synopsis of Fractures and Dislocations Approval Date: 3/1/2018 Termination Date: 2/29/2021 Target Audience: All local physicians working in the fields of primary care, physical medicine and rehabilitation,
Common Elbow Problems
 Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Case. Case 8/29/ yo man with fever, cough. Vitals: Temp 102, HR 130, RR 20, bp 120/80. Ill appearing, crackles R side chest. Now what?
 Kate Aberger, MD August 28, 2016 Help from : Raphael Brancato DO, and Jordan Jeong DO Case 56 yo man with fever, cough Vitals: Temp 102, HR 130, RR 20, bp 120/80 Ill appearing, crackles R side chest Now
Kate Aberger, MD August 28, 2016 Help from : Raphael Brancato DO, and Jordan Jeong DO Case 56 yo man with fever, cough Vitals: Temp 102, HR 130, RR 20, bp 120/80 Ill appearing, crackles R side chest Now
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
