MRI of Peripheral Nerves And Entrapment Syndromes
|
|
|
- Martha Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MRI of Peripheral Nerves And Entrapment Syndromes Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Nerve anatomy Basic classification of nerve injury Basic understanding of advantages of MR protocols Nerve disorders Plan of Attack Nerves Enclosed, Cable-like Bundle of Axons Nerve Anatomy Axon (nerve fiber) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell or neuron that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron s cell body Axon is one of 2 types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of the neuron, the other being dendrite Distinguished from dendrites by shape (dendrites taper/ axons maintain constant radius) Length (dendrites are restricted around cell body, axons are much longer) Function (dendrites receive signal, while axons transmit them) Axons make contact with other cells (usually other neurons/ sometimes muscles or glands) at junctions called synapses Individual axons microscopic 1 to 20 microns in diameter but can be several feet in length Axons sheathed in myelin formed by glial cells (Schwann cells in peripheral nervous system/ oligodendrocytes in the CNS) Along the myelinated nerve fibers, gaps in the sheath known as nodes of Ranvier occur at evenly spaced intervals 3 mm External epineurium Internal epineurium Perineurium Endoneurium Axon Myelin μm Nerve Anatomy Nerve Anatomy INTERNAL EPINEURIUM: External epineurium Thick, densely packed collagen fibrils in a lamellar fashion, in longitudinal orientation Internal epineurium 3 mm Perineurium Endoneurium PERINEURIUM: Multiple layers of perineurial cells, basal laminas ( heparan sulfate proteoglycans, fibronectin), interspaced with a lacework of thin collagen fibers. The innermost layer form the BLOOD-NERVE BARRIER 1
2 Standard MR Evaluation External epineurium Internal epineurium Standard High Resolution MR Evaluation Standard High Resolution MR Evaluation Standard High Resolution MR Evaluation 3 mm Perineurium Endoneurium 3T MR Extremity Neurography Protocol High Resolution 3D MRI and Diffusion High resolution imaging (long axis and orthogonal to nerve course) T1w anatomy (fascicular pattern sorrounded by small fat rim) T2w FS pathology (FSE, STIR, SPAIR, 3D T2* ) Abnormalities are recognized by differences in shape, size, and contour of the nerves, as well as by the changes in signal intensity 3T MR Extremity Neurography Protocol High Resolution 3D MRI Technical considerations T2 SPAIR (spectral adiabatic inversion recovery) due to better SNR, better and homogeneous fat suppression, and ability to maintain SAR rate favorability Isotropic submillimeter spin echo type 3D sequences allowing multiplanar isotropic reformats 3T MR Extremity Neurography Protocol Diffusion Fiber Tracking Technical considerations Diffusion-based MRN developed to increase nerve conspicuity by vascular signal suppression and offers potential to quantify SI, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), fractional anisotropy (FA) and fiber tracking Several technical challenges (spatial resolution and adequate SNR, as well as ghosting artifacts) Diffusion-based 3D reversed FISP is hybrid sequence optimized using low diffusion moment, and due to steady state nature enables suppression of vascular signal creating nerve-specific images PSIF Reversed Fast Imaging Steady State Precession 3T MR Extremity Neurography Protocol Diffusion Vascular Suppression Chhabra, et al., Skeletal Radiol :
3 UTE MRI with Variable TI TI 80 ms TI 120 ms TI 160 ms TI 200 ms TI 240 ms UTE MRI with Variable TI Contrast Manipulation (TE 10 microseconds) TI 160 ms TI 280 ms Inversion pulse at 280 ms null the signal of the fascicles (neural tissue + perineurium) TI 280 ms TI 320 ms TI 360 ms TI 400 ms TI 500 ms UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Paolo Felisaz UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Paolo Felisaz Ultra High Field Nerve Evaluation External epineurium Internal epineurium 11.7 T Gradient echo Nerve Imaging Evaluation Features Size Caliber similar to adjacent vascular structures Decreases proximal to distal Signal Normal signal isointense to muscle on T1- and T2-weighted images Fascicular appearance Uniform in size Course No focal deviation, smooth course Enhancement Normal nerves do not enhance due to preserved blood nerve barrier Perineurium Endoneurium Nerve Imaging Evaluation Features Nerve Imaging Evaluation Features Signal Normal signal isointense to muscle on T1- and T2-weighted images (tibial nerve shown here) Fascicular appearance Uniform in size (in this case, slightly increased SI consistent with mild injury) 3
4 MRN Interpretation Pitfalls MRN Interpretation Pitfalls 0 degrees 55 degrees Subject to magic angle phenomenon Kastel, et al., AJNR : Suboptimal fat suppression and image blurring 1.5T STIR MRN Interpretation Pitfalls MR Characterization of Peripheral Nerve Injury Suboptimal fat suppression and image blurring 1.5T STIR compared with 3T 3D STIR SPACE MIP reconstruction Chhabra, et al., AJR : MR Characterization of Peripheral Nerve Injury: Signal Changes Increased in signal Depends on endoneurial fluid and background fat suppression Causes of increased signal Vascular congestion Block of axoplasmic flow, leading to proximal accumulation of endoneurial fluid Wallerian degeneration Traditional Classification of Nerve Injury Neurapraxia Preserved fasciculation, subtle SI change Axonotmesis Absent fasciculation, clear SI change Neurotmesis Nerve transection Chhabra, et al., AJR :
5 Sunderland Classification Neurapraxia Preserved Fasciculation- Subtle SI Change I and II degree injuries correspond to neurapraxia and axonotmesis III degree injury involves endoneurium IV degree injury involves perineurium MRI appearance typically shows neuroma in contintuity Regenerating nerve sprouts unable to grow down disrupted fascicles tangle in conjunction with perifascicular and intrafascicular fibrosis to form neuroma (seen in continuity with proximal and distal uninvolved nerve segments) V degree injury involves epineurium MRI appearance of complete nerve discontinuity Injury involves only the myelin sheath around the axon with resultant transient functional loss and associated with excellent prognosis MRI shows abnormal T2 hyperintensity and mild enlargement of the nerve Milder MR appearance seen in stretch injury, nerve entrapment (tunnel syndromes), compression from space-occupying lesions T2 hyperintensity of peroneal nerve at fibular tunnel Chhabra, et al., Skeletal Radiol : Neurapraxia Preserved Fasciculation- Subtle SI Change PD FS FSE TE=41 3D CUBE TE=92 3D CUBE TE=92 Preservation of fasciculation, increased SI on CUBE EMG shows slowed conduction of CPN at fibular head Axonotmesis Absent Fasciculation Clear SI Change Axon suffers complete rupture resulting in wallerian degeneration of distal segment, however supporting structures including perineurium and epineurium remain intact Prognosis good, but axonal regeneration is 1mm per day MRI findings include effacement, enlargement or disruption of individual fascicles Similar appearance with moderate to severe nerve entrapment Fascicular appearance of tibial nerve preserved, though mildly increased SI (small arrow) Fascicular appearance of common peroneal obliterated (large arrows) Chhabra, et al., Skeletal Radiol : Neurotmesis Nerve Transection Most severe type of injury and refers to complete severance of the nerve Functional loss complete and without surgical intervention no recovery anticipated MRI appearance acutely shows nerve discontinuity with fluid filled gap and granulation tissue Fibrosis at injury site typically seen in subacute and chronic stages as strandy hypointense soft tissue within the nerve gap on T2-weighted images Transection right femoral nerve with end bulb neuroma Neuroma Any nerve lacerated, avulsed or traumatized may form a neuroma Classified into 2 basic types: NIC Neuroma in Continuity Involves all degrees of nerve injury, from normal to neurotmesis, coexisting within scarred nerve Proximal injured nerve fascicles sprout in attempt to unite Due to lattice disruption, disorganization, regeneration, hypertrophy of nerve fascicles, and associated fibrosis, proximal and distal nerve fibers at site of injury may fail to appose End-bulb neuroma Occur anywhere a nerve is completely divided and unopposed by another neural tissue Chhabra, et al., AJNR :
6 Neuroma in Continuity Distinguished from neurogenic tumors by presence of surrounding scarring, lack of a split fat or target sign and absence of abnormal enhancement Neuroma in continuity CPN (large arrow), normal tibial nerve (medium arrow), cutaneous nerves (small arrows) Secondary Findings Nerve Injury Muscle signal changes Shown to represent shift between intra- and extracompartmental fluid components and do not reflect real edema Edema-like SI may manifest as early as 24 hours after onset of neuropathy Subacute changes, edemalike SI and minimal fatty replacement, weeks to months Chronic changes, fatty replacement and atrophy months to years after injury Chhabra, et al., AJNR : Bendszus, et al., AJNR : Peripheral Nerve Disorders Injury or entrapment Suprascapular and Axillary nerves Compressive Suprascapular and Axillary nerves Intraneural ganglion Inflammatory/dysmyelinating Radiation Superior Inferior Pop v Fib Tib Theories of Pathogenesis Degenerative Mucoid degeneration of the epineurium leads to cyst formation Articular Fluid dissects through the epineurium from the joint Tumoral Tumor within the epineurium involutes with cystic degeneration Spinner RJ, Scheithauer BW, Amrami KK, et al. Neurosurg 2009;65:A115-A124 Synovial Theory of Pathogenesis Cyst fluid dissects from a degenerative synovial joint along an articular nerve branch Fluid follows path of least resistance Pressure fluxes further alter cyst dimensions, configurations, and directionality >> waxingwaning clinical symptoms guide.com 6
7 Synovial Theory of Pathogenesis Imaging Findings Popliteus Denervation Popliteus changes Edema (denervation change) Tibial nerve Articular branch Spinner RJ, Herbert-Blouin MN, Maniker AH, et al. Skeletal Radiol 2009;38: Imaging Findings J Sign Tibial nerve Posterior to anterior hook of articular branch Imaging Findings Signet Ring Eccentric displacement of nerve fascicles by cyst Spinner RJ, Herbert-Blouin MN, Maniker AH, et al. Skeletal Radiol 2009;38: Spinner RJ, Herbert-Blouin MN, Maniker AH, et al. Skeletal Radiol 2009;38: Imaging Findings Clock Face Pathology Tibial nerve articular branch 9 o clock Signet ring sign 4-5 o clock Transverse limb sign 12-2 o clock Spinner RJ, Herbert-Blouin MN, Maniker AH, et al. Skeletal Radiol 2009;38: Entrapment Syndromes Upper Extremity Brachial Plexus at the Thoracic Outlet Entrapment at the Shoulder Musculocutaneous Nerve Axillary Nerve Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment at the Arm and Elbow Radial Nerve (Arm) Ulnar Nerve (Elbow) Radial Nerve and Posterior Interosseous Nerve (Elbow) Median Nerve and Anterior Interosseous Nerve (Elbow) Entrapment at the Wrist Ulnar nerve Median Nerve Palmar Cutaneous Branch of the Median Nerve Superficial Branch of the Radial Nerve 7
8 Entrapment Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve C5 root C6 root Ant scalene m. C C7 root C8 root T1 root From upper trunk of brachial plexus, C5 and C6 nerve roots Motor fibers to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles Sensory fibers to the glenohumeral and A-C joints Entrapment Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve H Suprascapular a. Transverse ligament H S Suprascapular n. Suprascapular n. S UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Niyata Chitrapazt Spinoglenoid notch perilabral cyst with secondary findings of infraspinatus edema Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Thickened Transverse Scapular Ligament Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Post-Traumatic Scar Transverse scapular ligament Spinoglenoid ligament Coracoclavicular ligament injury with fibrous scar and tethered suprascapular nerve 8
9 Shoulder: Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Post-Traumatic Scar Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Axillary a. Coracoid Subscapularis m. Terminal branch of posterior cord of brachial plexus, contributions from C5 and C6 Courses along anterior surface of subscapularis muscle, then sharp turn posteriorly to travel along the inferior glenohumeral joint and then enters the quadrilateral space Axillary nerve can be injured by trauma following anterior shoulder dislocation Axillary nerve can be compressed in the quadrilateral space Coracoclavicular ligament injury with fibrous scar and tethered suprascapular nerve Axillary n. UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Niyata Chitrapazt Axillary Nerve Anterior Dislocation Traction Phenomenon Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Deltoid H H G G Teres Minor Axillary n. Axillary n. Edema deltoid and teres minor post reduction follow-up UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Niyata Chitrapazt Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Quadilateral Space H Axillary n. Long head of triceps m. Teres minor m. Teres major m. Superior: Teres Minor Inferior: Teres Major Medial: Long head triceps Lateral: Humerus UCSD MSK Imaging Research Group Niyata Chitrapazt Axillary Nerve Quadilateral Space Syndrome (Entrapment) Fibrous Band 9
10 Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Quadilateral Space Syndrome (Compression) Osteophyte Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Posterior Instability with Traction Phenomenon Prominent osteophytes can compress axillary nerve POLPSA with edema teres minor Shoulder: Axillary Nerve Posterior Instability with Traction Phenomenon 3% incidence of isolated teres minor atrophy Associated findings Rotator cuff 47/61 Posterior labral tear 31/61 GHJ OA 29/61 Possible relationship to traction or rotator cuff injury during translational episode Sofka,, et al., Skeletal Radiol 2004,33(9): Ulnar Nerve At the midhumerus level, it pierces the intermuscular septum and enters the posterior compartment. The ulnar nerve may pass under the arcade of Struthers and follows a groove in the medial head of the triceps muscle, arriving at the cubital tunnel. Cubital tunnel is formed by Anterior: medial epicondyle Lateral: olecranon Roof: arcuate ligament Travels between the humeral and ulnar heads of FCU muscle and enters the anterior compartment of forearm after piercing flexor pronator aponeurosis Ulnar Nerve Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Thickened Osborne s Ligament (Arcuate Ligament) Posterior humerus, groove of triceps, proximal to cubital tunnel Abnormal caliber, SI and loss of fasciculation 10
11 Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Mass Effect from Anconeus Epitrochlearis/ Hypertrophied Medial Head Triceps Valgus Extension Overload With existing valgus instability, elbow slightly subluxed in valgus position as flexion occurs Valgus Extension Overload and Posteromedial Impingement Distal to elbow bifurcates to Posterior Interosseous Nerve (PIN) and Superficial Radial Nerve (SRN) Ulnar Nerve Injury Common Flexor Tendon Injury Terminal branch posterior cord brachial plexus SRN superficial to supinator PIN courses between heads of supinator 5 potential sites of compression of PIN: Proximal edge of superficial portion of supinator arcade of Fröhse (1) Fibrous bands of tissue anterior to radiocapitellar joint between brachialis and brachioradialis (2) Recurrent radial vessels aka leash of Henry (3) Edge of extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) (4) Distal edge of supinator muscle (5) 11
12 ECRB Ext. Dig Brachioradialis /ECRL ECU Supinator Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor digitorum communis Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digiti minimi Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis, Extensor indicis proprius Ganglion at level of Arcade of Frohse T1 PIN T1 FS Post Gado Thickened ECRB Tendon Lipoma Edema ECRB, ED and Supinator ECRB Ext. Dig Supinator ECRB Ext. Dig Supinator ECU Resistant Tennis elbow Motor neuropathy Deep forearm pain Weakness /loss extension of all digits and decreased wrist extension Median Nerve Crosses elbow, passes deep to bicipital aponeurosis Dives into antecubital fossa, medial to both biceps tendon and brachial artery, volar to the brachialis Then passes between 2 heads of pronator teres, deep to the humeral head and superficial to the ulnar head Median Nerve After this, nerve travels deep to the proximal fibrous arch of the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) Continues through forearm between the FDS and FDP Continues distally through carpal tunnel 12
13 Median and Anterior Interosseous Nerve AIN courses off main trunk of the median nerve approximately 4 cm distal to medial epicondyle Supply: deep muscles of the forearm (flexor pollicis longus (FPL), FDP to the index and middle fingers, and the pronator quadratus) Median and Anterior Interosseous Nerve FCR FDS FDP Median AIN FPL FDP Median and Anterior Interosseous Nerve Kiloh Nevin Syndrome R Compression of anterior interosseous nerve in proximal forearm, purely motor Motor weakness of FPL, FDP of index and middle finger and Pronator Quadratus Unable to form a O with thumb and index finger Imaging of elbow and forearm: courses over FDP and interosseous membrane Causes: Direct trauma (most common), surgery, cast pressure, bulky tendinous origin of ulnar head of pronator teres, mass, accessory muscle FPL R Pronator Quadratus Upper Extremity Nerve Entrapment Take Home Points Nerve structure MR appearance Site specific anatomy Manifestations and Distribution of Findings H Suprascapular n. S 13
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound
 Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Elbow Elbow Anatomy. Flexion extension. Pronation Supination. Anatomy. Anatomy. Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT
 Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla.
 1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION
 MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민
 Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
The Elbow 3/5/2015. The Elbow Scanning Sequence. * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint
 Scanning Sequence * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint Anterior Elbow Pyramid Courtesy of Jay Smith, MD. Vice chair PMR Mayo Clinic Rochester,
Scanning Sequence * Anterior Joint (The anterior Pyramid ) * Lateral Epicondyle * Medial Epicondyle * Posterior Joint Anterior Elbow Pyramid Courtesy of Jay Smith, MD. Vice chair PMR Mayo Clinic Rochester,
Dr. Mahir Alhadidi Anatomy Lecture #9 Feb,28 th 2012
 Quick Revision: Upper arm is divided into two compartments: 1. Anterior Compartment: Contains three muscles (Biceps brachii, Coracobrachialis, Brachialis). Innervated by Musculocutaneous nerve. 2. Posterior
Quick Revision: Upper arm is divided into two compartments: 1. Anterior Compartment: Contains three muscles (Biceps brachii, Coracobrachialis, Brachialis). Innervated by Musculocutaneous nerve. 2. Posterior
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
The Arm and Cubital Fossa
 The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
The Arm and Cubital Fossa Dr. Andrew Gallagher School of Anatomical Sciences University of the Witwatersrand Introduction The ARM (BRACHIUM) is the most proximal segment of the upper limb musculoskeletal
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Abduction of arm until your hand rich your head. Flexion of forearm at elbow joint. Extension of arm at elbow joint. Flexion of fingers 10.
 Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016
 LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Elbow Pain. Lateral Elbow Pain. Lateral Elbow Pain. tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis extensor tendinopathy
 Elbow Pain Peter Brukner OAM, FACSP Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Health, Exercise and Sports Medicine University of Melbourne Lateral Elbow Pain tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis
Elbow Pain Peter Brukner OAM, FACSP Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Health, Exercise and Sports Medicine University of Melbourne Lateral Elbow Pain tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Systematic Anatomy (For international students)
 Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Lateral Elbow Pathology
 Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
David G. Simpson, Ph.D.
 David G. Simpson, Ph.D. ARM & CUBITAL FOSSA Revised 7/08 Text References Moores 3 rd ed., p402 408, 436 439, 439 443, 478, 481 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the humerus, indicating the sites of muscle
David G. Simpson, Ph.D. ARM & CUBITAL FOSSA Revised 7/08 Text References Moores 3 rd ed., p402 408, 436 439, 439 443, 478, 481 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the humerus, indicating the sites of muscle
Figure 27: The synovial membrane of the shoulder joint (anterior view)
 The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
The coracoacromial ligament; is an accessory ligament that protects the superior aspect of the joint extending from the coracoid process to the acromion over the tendon of supraspinatus. The synovial membrane
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex. The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow.
 Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Joints of the upper limb II
 Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
Joints of the upper limb II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Elbow joint The elbow joint is connecting the upper arm to the forearm. It is classed
CNS & PNS Entrapment. Disclosure - Nothing
 Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles
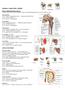 Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles Rotator cuff/scapulohumeral muscles 4 muscles (SITS) form musculotendinous rotator cuff around glenohumeral joint, provide stability of joint Supraspinatus Course: med 2/3 supraspinatous
Anatomy Upper Limb Muscles Rotator cuff/scapulohumeral muscles 4 muscles (SITS) form musculotendinous rotator cuff around glenohumeral joint, provide stability of joint Supraspinatus Course: med 2/3 supraspinatous
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone
 *the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
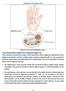 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures
 Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures Poster No.: C-2089 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Castelo, E. Matos, F. C. Pires ; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT,
Ultrasound of the elbow joint - anatomical review of normal structures Poster No.: C-2089 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Castelo, E. Matos, F. C. Pires ; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT,
#12. Joint نبيل خوري
 #12 30 Anatomy Joint هيام الر جال 9/10/2015 نبيل خوري Salam Awn Some notes before starting : ** Not all slides are included, so I recommend having a look at the slides beside this sheet ** If you find
#12 30 Anatomy Joint هيام الر جال 9/10/2015 نبيل خوري Salam Awn Some notes before starting : ** Not all slides are included, so I recommend having a look at the slides beside this sheet ** If you find
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW
 PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Accessory Muscles. Anatomy, Symptomatology, and Imaging. Melanie Chang February 16, 2017
 Accessory Muscles Anatomy, Symptomatology, and Imaging Melanie Chang February 16, 2017 Objectives Review anatomy of common accessory muscles Discuss potential role in symptom causation Describe characteristic
Accessory Muscles Anatomy, Symptomatology, and Imaging Melanie Chang February 16, 2017 Objectives Review anatomy of common accessory muscles Discuss potential role in symptom causation Describe characteristic
Mononeuropathies of the Upper and Lower Extremity
 15 Mononeuropathies of the Upper and Lower Extremity Kevin R. Scott and Milind J. Kothari Summary Nerves of both the upper and lower extremities are frequently injured for a variety of reasons. In the
15 Mononeuropathies of the Upper and Lower Extremity Kevin R. Scott and Milind J. Kothari Summary Nerves of both the upper and lower extremities are frequently injured for a variety of reasons. In the
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb.
 Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Preface The first decade of the twenty-first century has witnessed the continuation of an explosion in our knowledge and understanding of all aspects of disease. Accompanying this has been the increasing
Preface The first decade of the twenty-first century has witnessed the continuation of an explosion in our knowledge and understanding of all aspects of disease. Accompanying this has been the increasing
Practical Reporting of Musculoskeletal Imaging Studies: MRI Elbow
 Practical Reporting of Musculoskeletal Imaging Studies: MRI Elbow James F Griffith History Where is pain located? For how long? Trauma if so, what and when Radiographers can get this info Grade. Don t
Practical Reporting of Musculoskeletal Imaging Studies: MRI Elbow James F Griffith History Where is pain located? For how long? Trauma if so, what and when Radiographers can get this info Grade. Don t
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
Interesting Case Series. Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female
 Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
The Elbow Scanning Protocol
 The Elbow Scanning Protocol Diagnostic Imaging of the Elbow: Introduction The elbow maybe considered as consisting of four quadrants, anterior, medial, lateral and posterior. Ultrasound would normally
The Elbow Scanning Protocol Diagnostic Imaging of the Elbow: Introduction The elbow maybe considered as consisting of four quadrants, anterior, medial, lateral and posterior. Ultrasound would normally
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017
 Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
imaging sequences obtained in brachial plexopathy with/without TOS MR Imaging Sequences Associated Anatomic Structures or Pathologic Conditions
 Brachial plexus imaging sequences obtained in brachial plexopathy with/without TOS MR Imaging Sequences Associated Anatomic Structures or Pathologic Conditions Sagittal TSE T2WI through cervical spine
Brachial plexus imaging sequences obtained in brachial plexopathy with/without TOS MR Imaging Sequences Associated Anatomic Structures or Pathologic Conditions Sagittal TSE T2WI through cervical spine
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow
 Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
