Magnetic resonance imaging in adolescent symptomatic navicular tuberosity
|
|
|
- Lenard Watts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 22 ORIGINAL Magnetic resonance imaging in adolescent symptomatic navicular tuberosity Mitsuhiko Takahashi 1, Toshinori Sakai 1, Koichi Sairyo 1, Shoichiro Takao 2, Seiichi Mima 3, and Natsuo Yasui 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics and 2 Department of Radiologic Science, the Institute of Health Biosciences, the University of Tokushima, Tokushima, Japan and 3 Suihou-Daiichi Hospital, Minami- Awaji, Japan Abstract : Background The accessory navicular bone is one of the most common accessory ossicles, which sometimes become symptomatic. Abnormalities in magnetic resonance (MR) image, e.g. edema-like bone marrow pattern, have been reported for symptomatic accessory navicular. However, it has not been completely understood the edema-like bone marrow pattern correlates to the symptom of navicular tuberosity. Methods We investigated the edema-like bone marrow pattern in correlation with alleviation of the symptom and the presence of accessory navicular bone. Ten adolescents with pain localized to the navicular tuberosity were recruited and seven cases were further examined with consecutive MR images. Results Edema-like bone marrow pattern was found in all symptomatic navicular but not in asymptomatic navicular. Intensity of the pattern diminished with alleviation of the symptom. Moreover, this correlation was recognized even in the patients who had no accessory navicular bones. Conclusions MR images could be used not only for diagnosis but for monitor of healing in adolescent symptomatic navicular. There may be different pathologic mechanism for adolescent symptomatic navicular tuberosity, such as an osteitis, in adolescents. J. Med. Invest. 61 : 22-27, February, 2014 Keywords : accessory navicular, magnetic resonance image, edema-like bone marrow pattern, adolescents INTRODUCTION The accessory navicular bone, which is also termed os tibiale externum, is one of the most common accessory ossicles, with a reported incidence of 10-26% (1-3). As most accessory navicular bones are asymptomatic, they are often erroneously considered as normal anatomic and roentgenographic variants. However, they can become Received for publication June 24, 2013 ; accepted August 8, Address correspondence and reprint requests to Mitsuhiko Takahashi, MD, PhD, Department of Orthopaedics, the Institute of Health Biosciences, the University of Tokushima, Kuramoto, Tokushima , Japan and Fax : symptomatic when trauma affects the synchondrosis of the accessory navicular. The symptomatic condition is mainly associated with type II accessory navicular bone, in which there is a large, triangular ossification center adjacent to the navicular tuberosity that is connected by a synchondrosis measuring 1-3 mm (4, 5). This type of accessory navicular bone can be easily distinguished from type I accessory navicular bone which is a sesamoid imbedded in the tibialis posterior tendon and separated from the navicular tuberosity by at least 3 mm (5-7). The cause of symptom is thought to be repetitive tension and shear stress across the synchondrosis as a result of the pull of the posterior tibial tendon (8). Recently, it has been reported that magnetic The Journal of Medical Investigation Vol
2 The Journal of Medical Investigation Vol. 61 February resonance (MR) images of symptomatic type II (synchondrosis type) accessory navicular bone showed an edema-like bone marrow pattern (9-11). Edema-like MR abnormality was also reported in the posterior tibial tendon in adults with flatfoot (12, 13). However, these MR abnormalities have been described mostly in the symptomatic adults, but not in the adolescents with symptomatic navicular tuberosity, nor in correlation with the alleviation of symptom or the presence of accessory navicular. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of edema-like bone marrow pattern of adolescent symptomatic navicular tuberosity in correlation with the course of symptom and the presence of accessory navicular bone. We hypothesized that edema-like bone marrow pattern could tell the symptom of navicular tuberosity and the intensity of the pattern could tell the intensity of symptom. MATERIALS AND METHODS The investigation was performed in accordance with the institutional review board and ethics committee of the University of Tokushima. The subjects of this investigation were ten consecutive adolescent patients (5 males and 5 females) with a mean ageof11.5years(range9to14years)presenting with pain localized to the navicular tuberosity (Table 1). Two patients complained of bilateral symptoms and the others had unilateral symptom (5 on the right and 3 on the left) ; all symptoms were aggravated by physical activity. No patients complained of pain or tenderness on another part of the foot. Either acute injury or chronic overuse preceded the onset of symptoms in all cases with continuous participation in athletic activities. The average duration of symptom before presentation was 1.8 months. Physical examination revealed that all except one patient (case 6, see Table 1) had flexible flatfoot. Static footprints were recorded on a Harris-Beath mat in the half body weight-bearing position (14). The arch index described by Staheli et al. (15) was used to confirm the presence of flexible flatfoot. The symptom was managed non-operatively with suspension of athletic activities in all cases and by wearing a medial longitudinal arch support in all patients with flexible flatfoot until relief of symptom. In more advanced cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications were used. The symptom was successfully healed in all cases and no patients required surgical intervention to alleviate symptom. The mean period until alleviation of symptom was 3.7 months (range 1.0 to 8.0 months, Table 1). All patients underwent bilateral radiographic assessments at the initial presentation to determine the type of accessory navicular bone, followed by MR examination within two weeks after the initial presentation. MR examinations were performed on a Signa Profile 0.2-T whole-body MR imaging system (GE Medical System, Milwaukee, WI) using a standard extremity coil. Pulse sequences comprised spin-echo (SE) T1-weighted (repetition time/echo time (TR/TE), /16-20, 4.0 mm slice thickness ; 22 cm field of view, matrix) and SE T2-weighted fat saturated (TR/effective TE, 4,200-4,500/30-38, 4.0 mm slice thickness ; cm field of view, matrix) images obtained in the horizontal and axial planes. MR abnormality was Table 1. Case Clinical manifestations of the cases in this study Age (years) Gender1 Symptomatic side Type 2 Presence of flatfeet Athletic activity Duration of symptom (months) Period for alleviation (months) Abnormality at the initial MR examination Number of MR studies Diminution of MR abnormality 1 14 F Right II + Athletics ND 2 13 F Bilateral II + Swimming M Left II + Baseball M Right - + Tennis M Left - + Soccer M Right II - Basketball ND 7 11 F Right II + Baseball ND 8 11 M Right - + Soccer F Bilateral II + Volleyball F Left II + Baseball ; Female (F) or male (M), 2 ; type of accessory navicular if present and (-) is used in case of absence, ND ; not determined, + ; present, -;absent.
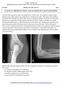
3 24 M. Takahashi, et al. Imaging for symptomatic navicular edema-like bone marrow pattern, whichwasdepicted as an area of low signal intensity on T1- weighted images with high signal intensity on T2- weighted fat-saturated images (9, 16, 17). Neither conventional T2-weighted image nor contrast enhancement using an infusion of gadolinium was applied in this study. Seven patients (cases 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9 and 10) were willing to be further examined with consecutive MR imaging until heal of the symptom (an average of 2.7 times per patient in this group). We investigated the relationships of the symptom alleviation with type of accessory navicular bone on radiograph and edema-like bone marrow pattern on MRI. on the symptomatic side (Fig. 3). This pattern again diminished with the alleviation of symptom. There were no MR abnormalities of the insertion of the posterior tibial tendon, such as signal change of the tendon substance and surrounding fluid throughout this study. We were unable to find any correlation between presence of flatfeet and specific MR findings. RESULTS On radiographic examination, accessory navicular bones were found in 7 cases, all of which were bilateral and were classified into type II. In the remaining three patients (cases 4, 5 and 8), no accessory navicular bones were detected on either side. No tarsal coalition or other abnormality was detected. All symptomatic naviculars presented an edemalike bone marrow pattern (Fig. 1-3) irrespective of whether an accessory navicular bone was present or not. In those patients who took bilateral feet MR examinations, this pattern was observed only on the symptomatic side (Fig. 1). For the seven patients with consecutive MR examinations, the intensity of edema-like bone marrow pattern diminished with alleviation of symptom (Fig. 2 and 3). Surprisingly in the 3 patients without accessory navicular on either side (cases 4, 5 and 8), the navicular tuberosity only presented edema-like bone marrow pattern Fig. 1. Bilateral type II accessory navicular bones in case 1. Anteroposterior radiograph (A) of the symptomatic (right) side shows a type II accessory navicular bone (arrow). The ipsilateral T1-weighted (B ) and T2-weighted fat saturated (C ) horizontal MR images demonstrate edema- like bone marrow pattern on the both the accessory navicular bone and the navicular tuberosity facing to the synchondrosis (arrows), which might be described as kissing edema pattern. In contrast, despite the presence of accessory navicular bone (D ), asymptomatic navicular bone (in the left foot) does not show edema-like bone marrow pattern on either T1- weighted (E ) or T2- weighted fat saturated (F ) MR image (arrows). Fig. 2. For case 3, type II accessory navicular bone on radiograph (A). T2-weighted fat saturated MR image demonstrates the same pattern as the case 1 at the first examination (B ). The edema-like bone marrow pattern gradually diminishes with alleviation of the symptom a month (C ) and three months (D ) after the first presentation.
4 The Journal of Medical Investigation Vol. 61 February Fig. 3. For case 4, no accessory navicular bone is detected on the radiograph (A). T1-weighted (B, C and D ) and T2-weighted fat saturated (E, F and G ) horizontal MR images at the initial (B and E ), after 2 months (C and F )andafter8months(d and G )demonstrate the gradual diminution in the edema-like bone marrow pattern with alleviation of the symptom. DISCUSSION Symptomatic accessory navicular bones are very common conditions and have been reported to occur commonly in adolescence (18, 19). The results of this study indicate that symptomatic navicular in adolescence is described by an edema-like bone marrow pattern on MR image regardless of whether an accessory navicular is present or not, and that alleviation of the symptom is proportional to the diminish of the edema-like bone marrow pattern. The edema-like bone marrow pattern has been typically shown for symptomatic type II accessory navicular bones, in which the both sides of the synchondrosis present this pattern (9-11). In the present study, there were three patients who did not have accessory navicular bones (cases 4, 5 and 8) but still showed an edema-like bone marrow pattern on the navicular tuberosity. Wong et al. suggested the other pathologic mechanism for symptomatic navicular tuberosity in their study of 18 adolescents who had flexible flatfoot with pain of the navicular tuberosity and completed MR examination (20). They concluded that the symptom was not confined to the accessory navicular synchondrosis, and that an enthesopathy like process occurred at the insertion of posterior tibial tendon to the navicular in some cases (20). In the present study, three patients who did not have accessory navicular bone obviously showed bone marrow abnormality, although no patients showed MR abnormality of posterior tibial tendon. In addition to the mechanisms described by Wong et al., we speculate another pathologic mechanism in adolescents, such as an osteitis or osteochondrosis. Thus, we have to manage carefully the adolescent patients with symptomatic navicular tuberosity even without an accessory bone. The edema-like bone marrow pattern in the navicular tuberosity diminished with the alleviation of symptom managed non-operatively in this study. The intensity of edema-like bone marrow pattern, especially the signal intensity on T2-weighted fat saturated images, may indicate pain intensity, despite the small number of patients in the current study and no quantifications of the intensity. To our knowledge, among previous studies of symptomatic foot conditions, only one tried to demonstrate a relationship between MR parameters and pain (16). There was, however, no correlation between bone marrow edema volume and peak pain intensity among patients with various ages. They did not investigate any relationships between bone marrow edema intensity and peak pain intensity. Our study might have several limitations related to study design. First, the sample number was small and any statistical analyses were not performed in this study. Second, we did not have surgical or histologic correction of samples. The edema-like bone marrow pattern have been reported to reflect several different pathologic conditions except for true edema, such as bone marrow necrosis and fibrosis (21), fibrovascular tissue ingrowth and increased blood flow to the area (22), and reactive new bone formation (9). The background of conditions such as age of the patient, the cause of trauma, and anatomic location should be taken into account. Because we did not examine sagittal MR images in this study,
5 26 M. Takahashi, et al. Imaging for symptomatic navicular it is possible that we failed to detect pathologic conditions of the posterior tibial tendon, which were presented in previous studies (10, 20). Bone marrow signal changes were definitely detected on both the horizontal and axial MR images of all the symptomatic navicular in our study. Finally, the low-magnetic field MR used in this study might influence the results. There were several studies that compared the low-field and high-field MR images in musculoskeletal system. Kersting-Sommerhoff et al. reported 92% accordance of MR diagnoses between the low- and high-field for knee lesion and superior ability of the high-field to detect cartilage lesion (23). Taouli et al. concluded that high-field MRI and low-field dedicated MRI showed similar results in terms of cross-sectional grading of bone erosions, joint-space narrowing, and synovitis in the hands and wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (24). Meanwhile, fat saturation might result in incomplete fat suppression in several conditions under lowfield MR (25). Thus, the influences by low-field MR would be small. In summary, symptomatic navicular in adolescents showed an edema-like bone marrow pattern on MR image. This pattern diminished with the alleviation of symptom managed non-operatively. Thus, MR images could be used for the diagnosis of symptomatic navicular and its intensity could monitor of the healing process, although MR would not be necessary for complete healing. Symptom occurred even at the navicular tuberosity without accessory navicular bone, which indicates different pathologic mechanism in adolescents is working, such as an osteitis or osteochondrosis. CONFLICT OF INTEREST No benefit or fund was received in support of this study. REFERENCES 1. Grogan DP, Gasser SI, Ogden JA : The painful accessory navicular : a clinical and histopathological study. Foot Ankle 10(3) : , Kruse RW, Chen J : Accessory bones of the foot : clinical significance. Mil Med 160(9) : , Shands AR, Jr., Wentz IJ : Congenital anomalies, accessory bones, and osteochondritis in the feet of 850 children. Surg Clin North Am : , Lawson JP, Ogden JA, Sella E, Barwick KW : The painful accessory navicular. Skeletal Radiol 12(4) : , Sella EJ, Lawson JP, Ogden JA : The accessory navicular synchondrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res Aug(209) : , Ray S, Goldberg VM : Surgical treatment of the accessory navicular. Clin Orthop Relat Res (177) : 61-66, Bareither DJ, Muehleman CM, Feldman NJ : Os tibiale externum or sesamoid in the tendon of tibialis posterior. J Foot Ankle Surg 34(5) : , Sella EJ, Lawson JP : Biomechanics of the accessory navicular synchondrosis. Foot Ankle 8(3) : , Miller TT, Staron RB, Feldman F, Parisien M, Glucksman WJ, Gandolfo LH : The symptomatic accessory tarsal navicular bone : assessment with MR imaging. Radiology 195(3) : , ChoiYS,LeeKT,KangHS,KimEK:MRimaging findings of painful type II accessory navicular bone : correlation with surgical and pathologic studies. Korean J Radiol 5(4) : , Mosel LD, Kat E, Voyvodic F : Imaging of the symptomatic type II accessory navicular bone. Australas Radiol 48(2) : , Schweitzer ME, Karasick D : MR imaging of disorders of the posterior tibialis tendon. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175(3) : , Khoury NJ, el-khoury GY, Saltzman CL, Brandser EA : MR imaging of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167 (3) : , Kanatli U, Yetkin H, Cila E : Footprint and radiographic analysis of the feet. J Pediatr Orthop 21(2) : , Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M : The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(3) : , Zanetti M, Steiner CL, Seifert B, Hodler J : Clinical outcome of edema-like bone marrow abnormalities of the foot. Radiology 222(1) : , Hayes CW, Conway WF, Daniel WW : MR imaging of bone marrow edema pattern : transient osteoporosis, transient bone marrow edema
6 The Journal of Medical Investigation Vol. 61 February syndrome, or osteonecrosis. Radiographics 13(5) : , Macnicol MF, Voutsinas S : Surgical treatment of the symptomatic accessory navicular. J Bone Joint Surg Br 66(2) : , Chen YJ, Hsu RW, Liang SC : Degeneration of the accessory navicular synchondrosis presenting as rupture of the posterior tibial tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79(12) : , Wong MW, Griffith JF : Magnetic resonance imaging in adolescent painful flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int 30(4) : , Zanetti M, Bruder E, Romero J, Hodler J : Bone marrow edema pattern in osteoarthritic knees : correlation between MR imaging and histologic findings. Radiology 215(3) : , Saadat E, Jobke B, Chu B, Lu Y, Cheng J, Li X, Ries MD, Majumdar S, Lnk TH : Diagnostic performance of in vivo 3-T MRI for articular cartilage abnormalities in human osteoarthritic knees using histology as standard of reference. Eur Radiol 18(10) : , Kersting-Sommerhoff B, Hof N, Lenz M, Gerhardt P : MRI of peripheral joints with a low-field dedicated system : a reliable and costeffective alternative to high-field units? Eur Radiol 6(4) : , Taouli B, Zaim S, Peterfy CG, Lynch JA, Stork A, Guermazi A, Fan B, Fye KH, Cenant HK : Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand and wrist : comparison of three imaging techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182(4) : , Delfaut EM, Beltran J, Johnson G, Rousseau J, Marchandise X, Cotten A : Fat suppression in MR imaging : techniques and pitfalls. Radiographics 19(2) : , 1999
The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes
 The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Young Uk Park, M.D. *, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Young Tae Rho, M.D. KT Lee s Orthopedic
The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Young Uk Park, M.D. *, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Young Tae Rho, M.D. KT Lee s Orthopedic
MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies
 MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies Yun Sun Choi, MD 1 Kyung Tai Lee, MD 2 Heung Sik Kang, MD 3 Eun Kyung Kim, MD 4 Index terms:
MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies Yun Sun Choi, MD 1 Kyung Tai Lee, MD 2 Heung Sik Kang, MD 3 Eun Kyung Kim, MD 4 Index terms:
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot
 Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot Poster No.: C-2598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Á. Gómez Trujillo; Madrid/ES Keywords: Education and training, Education, MR, Digital radiography,
Accessory ossicles of the ankle and foot Poster No.: C-2598 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Á. Gómez Trujillo; Madrid/ES Keywords: Education and training, Education, MR, Digital radiography,
Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries
 369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle
 Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle Poster No.: C-0978 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Kesimal, M. OYNAK, C. Cevikol; Antalya/TR Keywords: Anatomy, Musculoskeletal bone, Musculoskeletal
Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle Poster No.: C-0978 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Kesimal, M. OYNAK, C. Cevikol; Antalya/TR Keywords: Anatomy, Musculoskeletal bone, Musculoskeletal
Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging Studies
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Case Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case.
 Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot.
 It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot. Poster No.: P-0120 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. C. Vieira, A. Vieira, R. Cunha; Porto/PT
It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot. Poster No.: P-0120 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. C. Vieira, A. Vieira, R. Cunha; Porto/PT
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
(July, 0) Conflicts of interest All the authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest with people or organizations that could bias the natur
 (July, 0) Bony Healing of Discontinuous Laminar Stress Fractures due to Contralateral Pars Defect or Spina Bifida Occulta Toshinori Sakai, Tsuyoshi Goto, Kosuke Sugiura, Hiroaki Manabe, FumitakeTezuka,
(July, 0) Bony Healing of Discontinuous Laminar Stress Fractures due to Contralateral Pars Defect or Spina Bifida Occulta Toshinori Sakai, Tsuyoshi Goto, Kosuke Sugiura, Hiroaki Manabe, FumitakeTezuka,
Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition:
 Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition: Radiological Features 1 Yun Sun Choi, M.D., Sung Moon Kim, M.D. 2, Kyung Tae Lee, M.D. 3, Ki Won Young, M.D. 3, Sang Jin Bae, M.D. 2, Joong Mo Ahn, M.D. 4, Myung Jin
Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition: Radiological Features 1 Yun Sun Choi, M.D., Sung Moon Kim, M.D. 2, Kyung Tae Lee, M.D. 3, Ki Won Young, M.D. 3, Sang Jin Bae, M.D. 2, Joong Mo Ahn, M.D. 4, Myung Jin
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Case Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer.
 Case 13609 Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer. Joris De Win 1, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 4, Els Goossens3 1: Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation; University Ghent (UGent), Belgium; Email:de_win_joris@hotmail.com
Case 13609 Iselin's disease in a Thai boxer. Joris De Win 1, 3, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 4, Els Goossens3 1: Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation; University Ghent (UGent), Belgium; Email:de_win_joris@hotmail.com
MR Imaging of the Distribution and Location of Acute Hamstring Injuries in Athletes
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.197.176 on 2/4/18 from IP address 46.3.197.176. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Arthur A. De Smet 1 Thomas M. Best 2 Received May 3,
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.197.176 on 2/4/18 from IP address 46.3.197.176. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Arthur A. De Smet 1 Thomas M. Best 2 Received May 3,
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Personal use only. MRI of the extensor mechanism of the knee. 5 th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting. Falkowski, MD, MHBA
 MRI of the extensor mechanism of the knee 5 th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting Falkowski, MD, MHBA Outline extensor mechanism - anatomy - pathology - controversies anterior knee pain biomechanics 05.05.2018
MRI of the extensor mechanism of the knee 5 th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting Falkowski, MD, MHBA Outline extensor mechanism - anatomy - pathology - controversies anterior knee pain biomechanics 05.05.2018
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
«Foot & Ankle Surgery» 04. Sept THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT. Norman Espinosa, MD
 THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
Who, What, Where, When & Why s of The Pediatric Forefoot
 Essential Pediatric Biomechanics Who, What, Where, When & Why s of The Pediatric Forefoot Louis J. DeCaro, DPM President, ACFAP APMA 2018 drlouisjames@aol.com The APMA's only recognized clinical interest
Essential Pediatric Biomechanics Who, What, Where, When & Why s of The Pediatric Forefoot Louis J. DeCaro, DPM President, ACFAP APMA 2018 drlouisjames@aol.com The APMA's only recognized clinical interest
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs)
 Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Emilie Williamson, BS; Jeremy Chan, MD; Jayme C Burket, PhD; Jonathan T Deland, MD; Scott Ellis, MD
New Radiographic Parameter Assessing Hindfoot Alignment in Stage II Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Emilie Williamson, BS; Jeremy Chan, MD; Jayme C Burket, PhD; Jonathan T Deland, MD; Scott Ellis, MD
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Focal Periphyseal Edema (FOPE) Zone on MRI of the Adolescent Knee: A Potentially Painful Manifestation of Physiologic Physeal Fusion?
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Zbojniewicz and Laor MRI of the Adolescent Knee Pediatric Imaging Original Research Andrew M. Zbojniewicz 1 Tal Laor Zbojniewicz AM, Laor T Keywords: children, knee,
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Zbojniewicz and Laor MRI of the Adolescent Knee Pediatric Imaging Original Research Andrew M. Zbojniewicz 1 Tal Laor Zbojniewicz AM, Laor T Keywords: children, knee,
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month a
 Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Tibial stress injury: MRI findings
 Tibial stress injury: MRI findings Poster No.: P-0047 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Castrillo 1, J. J. Fondevila 2, B. Canteli 3, A. Urresola Olabarrieta 1, A. I. Ezquerro 2,
Tibial stress injury: MRI findings Poster No.: P-0047 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Castrillo 1, J. J. Fondevila 2, B. Canteli 3, A. Urresola Olabarrieta 1, A. I. Ezquerro 2,
The Clinical Importance of the Os Peroneum: A Dissection of 156 Limbs Comparing the Incidence Rates in Cadavers versus Chronological Roentgenograms
 Open Access Publishing The Clinical Importance of the Os Peroneum: A Dissection of 156 Limbs Comparing the Incidence Rates in Cadavers versus Chronological Roentgenograms by Brion Benninger, MD 1, Jessica
Open Access Publishing The Clinical Importance of the Os Peroneum: A Dissection of 156 Limbs Comparing the Incidence Rates in Cadavers versus Chronological Roentgenograms by Brion Benninger, MD 1, Jessica
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients. Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015
 Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle
 Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle Poster No.: P-0013 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Kobashi 1, T. Mogami 1, S. Yamazoe 1, A. Baba 2, S. Ogiwara 1 ; 1 2 Chiba/JP, Tokyo/JP
Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle Poster No.: P-0013 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Kobashi 1, T. Mogami 1, S. Yamazoe 1, A. Baba 2, S. Ogiwara 1 ; 1 2 Chiba/JP, Tokyo/JP
17/10/2017. Foot and Ankle
 17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Frequency of Baker s Cysts in Cases of Meniscal Injury
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology. Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Pseudotumor Deltoideus in the Left Humerus of a Young Adult Female Patient with Acute Lateral Shoulder Pain: A Case Report
 of a Young Adult Female Patient with Acute Lateral Shoulder Pain: A Gulsen Aykol 1, Senol Fatih Elbir 2 1 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Private Sevgi Medical Centre, Malatya, Turkey 2 Radiology
of a Young Adult Female Patient with Acute Lateral Shoulder Pain: A Gulsen Aykol 1, Senol Fatih Elbir 2 1 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Private Sevgi Medical Centre, Malatya, Turkey 2 Radiology
Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients
 Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING
 Case Report CR_018_2016 renanrochadanobrega@gmail.com CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING Nóbrega RR; Duarte ML; Prado JLMA; Scoppetta LCD SÃO PAULO - BRASIL The authors declare that they have no
Case Report CR_018_2016 renanrochadanobrega@gmail.com CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING Nóbrega RR; Duarte ML; Prado JLMA; Scoppetta LCD SÃO PAULO - BRASIL The authors declare that they have no
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot
 Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot Ozgur Basal, Halil Burc, Tolga Atay Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty
Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot Ozgur Basal, Halil Burc, Tolga Atay Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
MRI IN NONOSSEOUS ABNORMALITIES OF THE FOREFOOT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW I Delgado, P Melloni, M Veintemillas, R Valls, M Vilagran, A Valera UDIAT. Sabadell (Barcelona). Spain. PURPOSE To catalog the wide spectrum
분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT
 분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT CASE M/12 CC Insidous onset of heel pain 축구를좋아해서많이했다. 걷거나뛰면더아프다. PE pes planus heelcord tightness Tenderness over the posterior calcaneus Sqeeze
분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT CASE M/12 CC Insidous onset of heel pain 축구를좋아해서많이했다. 걷거나뛰면더아프다. PE pes planus heelcord tightness Tenderness over the posterior calcaneus Sqeeze
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction?
 AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 196~200, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.196 Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report Risa Utsunomiya,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 196~200, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.196 Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report Risa Utsunomiya,
Imaging of the Elbow. Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich
 Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever s Disease) a Poorly Identified Pathology: Easy Radiological Evaluation.
 Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever s Disease) a Poorly Identified Pathology: Easy Radiological Evaluation. Poster No.: C-3133 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. M. Dautt Medina, M. D. R.
Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever s Disease) a Poorly Identified Pathology: Easy Radiological Evaluation. Poster No.: C-3133 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. M. Dautt Medina, M. D. R.
Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee in children
 Pediatr Radiol (2005) 35: 880 886 DOI 10.1007/s00247-005-1507-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kathleen Gebarski Ramiro J. Hernandez Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee
Pediatr Radiol (2005) 35: 880 886 DOI 10.1007/s00247-005-1507-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kathleen Gebarski Ramiro J. Hernandez Stage-I osteochondritis dissecans versus normal variants of ossification in the knee
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know
 Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical spine bilateral facet dislocations
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 2005 Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 2005 Posterior longitudinal ligament status in cervical
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
The magic angle phenomenon in tendons: effect of varying the MR echo time
 T he British Journal of Radiology, 7 (998), 3 36 998 The British Institute of Radiology The magic angle phenomenon in tendons: effect of varying the MR echo time W C G PEH, FRCR and J H M CHAN, MSc Department
T he British Journal of Radiology, 7 (998), 3 36 998 The British Institute of Radiology The magic angle phenomenon in tendons: effect of varying the MR echo time W C G PEH, FRCR and J H M CHAN, MSc Department
Apophysis. Apophyseal Avulsion. Apophyseal avulsion injuries 3/2/2017
 Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Avulsion Fracture of the Calcaneal Tuberosity: Classification and Its Characteristics
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:134-138 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.2.134 Avulsion Fracture of the Calcaneal Tuberosity: Classification and Its Characteristics Sang-Myung
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:134-138 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.2.134 Avulsion Fracture of the Calcaneal Tuberosity: Classification and Its Characteristics Sang-Myung
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Case Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent
 Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Case 14039 Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle in an adolescent Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1, Kris Van Crombrugge 2, Lieven Tack 2, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Unilateral osteonecrosis. imaging findings
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES. Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium
 PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
) Flexible Flatfoot Prevalence Correlating Factor Foot Pressure Physical Performance and Gait Analysis (Year III) NSC B
 ( ) Flexible FlatfootPrevalenceCorrelating FactorFoot Pressure Physical Performance and Gait Analysis (Year III) NSC91-2314-B-006-062 89 08 01 92 07 31 or severe FF noted among 377 preschool children after
( ) Flexible FlatfootPrevalenceCorrelating FactorFoot Pressure Physical Performance and Gait Analysis (Year III) NSC91-2314-B-006-062 89 08 01 92 07 31 or severe FF noted among 377 preschool children after
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle
 Мобильный портал WAP версия: wap.altmaster.ru Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle Dec 26, 2017. The extensor retinaculum describes the set of. Interactive Anatomical Interface and also the extensor
Мобильный портал WAP версия: wap.altmaster.ru Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle Dec 26, 2017. The extensor retinaculum describes the set of. Interactive Anatomical Interface and also the extensor
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses. Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital
 Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
A Patient s Guide to Accessory Navicular Problems. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Accessory Navicular Problems Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written
A Patient s Guide to Accessory Navicular Problems Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability.
 Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
Congenital absence of lumbosacral articular facet joint associated with conjoined nerve root: a case report
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2010) 11:183 187 DOI 10.1007/s10195-010-0100-4 CASE REPORT Congenital absence of lumbosacral articular facet joint associated with conjoined nerve root: a case report Shinji Yoshioka
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2010) 11:183 187 DOI 10.1007/s10195-010-0100-4 CASE REPORT Congenital absence of lumbosacral articular facet joint associated with conjoined nerve root: a case report Shinji Yoshioka
Case report. Your Diagnosis?
 Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
European Journal of Radiology
 European Journal of Radiology 84 (2015) 1777 1781 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Imaging of posterior tibial tendon
European Journal of Radiology 84 (2015) 1777 1781 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Imaging of posterior tibial tendon
MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation. Bone Marrow
 MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation Bone Marrow Thomas M. Link, MD Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California, San Francisco (i) Introduction Bone marrow consists of trabecular
MSK Tumors and Marrow Evaluation Bone Marrow Thomas M. Link, MD Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California, San Francisco (i) Introduction Bone marrow consists of trabecular
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Soft Tissue Imaging in. Total Hip Arthroplasty
 FDA Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Devices Panel Medical Devices Advisory Committee Meeting Thursday June 28th 2012 Soft Tissue Imaging in Metal-on on-metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Young-Min Kwon MD, PhD, FRCS,
FDA Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Devices Panel Medical Devices Advisory Committee Meeting Thursday June 28th 2012 Soft Tissue Imaging in Metal-on on-metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Young-Min Kwon MD, PhD, FRCS,
