MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
|
|
|
- Elvin Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric patient, please follow adult MSK section protocols unless for unusual indication or questions and then contact MSK radiologist to see if they want pediatric radiology input. *Central Texas Pediatric Orthopedics has a separate PACS that is accessible to our radiologists. It is not necessary to request x-rays from CTPO for comparison. All that is required of the technologist is to state in their tech notes that the patient has comparison films with CTPO. A. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR ALL MR PROTOCOLS BELOW. 1) Use No Phase Wrap / Phase Oversampling whenever possible. 2) T1 is conventional SE T1 unless specifically stated otherwise; T2 s are FSE however. 3) Frequency direction should be perpendicular to plane of growth plate most of interest and please switch phase and frequency if vascular artifacts obscure structures of interest. 4) Most slice thicknesses 3-4 mm with gap of 0,.5, or 1mm unless covering a large area such as axials through pelvis or long bones, then increase slice thickness and gap as needed. 5) Use a TI of 150 for FSE IR. 6) For small joint, for high resolution PD, use 3-4 NEX. 7) Try to keep sequences 7 minutes or less (hopefully less). 8) Need for extra set for whole bone in pedi is because of skip lesions in tumor and marrow diseases. 9) Glucagon is needed for Pediatric Enterography studies. 10) Glucagon is not needed routinely for other Pediatric Abdominal and Pelvic studies but if a Female Pelvis MRI is scheduled on a teenage girl, check with a Radiologist to see if glucagon is needed. B. Pediatric Bone routine, such as tumor, infection must include whole lesion extent, including edema if possible, review with an MSK radiologist to see if IV contrast is needed (some lesions don t, e.g., osteochondroma) and if is small lesion unlikely to be malignant tumor, may not need large FOV s. 1) Coil a) 1 st large FOV whole bone larger or body coil if needed to check for skip lesions in the bone. b) Then place smaller coil to cover area of interest. 2) Sequences Adult Long Bone Protocol C. Pedi non-tumor joint study knee, shoulder, wrist, elbow in teenager, athlete Adult Protocols D. Abbreviated Pediatric specific small joint (e.g., wrist, elbow include for acute or chronic pain, possible bony bridge of growth plate). 1) Put joint as close to center of magnet as possible. 2) Use small surface coil appropriate for size of joint. Adult Protocols
2 E. Pedi Joint for Arthritis, Synovial Derangement Protocol (e.g., Juvenile Chronic (Rheumatoid) Arthritis). 1) Appropriate extremity coil for joint. 2) Base sequences. a) T2 FSE Fat Sat Axial b) T1 FSE Coronal c) T2 FSE Fat Sat Coronal d) T2 FSE Fat Sat Sagittal or STIR 3) Add T1 FSE Fat Sat Coronal to Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist, Hand, Hip, Knee, Ankle exams pre contrast. 4) Add T1 FSE Fat Sat Axial to Feet exams pre contrast. 5) Add T1 FSE Fat Sat Axial and T1 FSE Fat Sat Coronal to Shoulder and Hip exams post contrast. 6) Add T1 FSE Fat Sat Sagittal and T1 FSE Fat Sat Coronal to Elbow, Wrist, Hand, Knee, and Ankle exams post contrast. 7) Add T1 FSE Fat Sat Sagittal and T1 FSE Fat Sat Axial to Feet exams post contrast. F. Cartilage Specific Joint Study- (e.g., congenital and developmental malformations, Blount s disease, post-traumatic or post-infection bony bridges of growth plate). 1) Coil appropriate for specific joint. Adult joint specific protocols G. Pedi Foot Routine (e.g., tumor or infection). 1) Coil smallest that fits foot. Adult foot protocol H. Tarsal Coalition. Place foot in extremity coil, or both feet in head coil. 1) Sequences. Ankle Protocol I. Pedi Shoulder for Dysplasia (e.g., dysplasia due to brachial plexus injury). 1 st Use coil to include both shoulders for 1 st sequence, change to surface coil for rest. 1) Sequences. Adult Protocol J. Unilateral Hip (generally over 5 years) e.g., Legg-Perthes, hip dysplasia check if radiologist wants bilateral or unilateral hip or intravenous contrast. 1) Coil per patient size. Adult Protocol K. Bilateral Hip (generally under 5 years) e.g. AVN, hip dysplasia, SCFE. Adult Protocol L. Pelvic Tumor / Infection / Pain Protocol include whole pelvis, which will include hips. 1) Appropriate coil for age e.g., head coil in very young, torso in larger, etc. center between symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine if area of interest is buttocks, please scan prone. a) T1 Coronal. b) Fast IR Coronal. c) Fast IR Sagittal. d) T2 FSE Fat Sat Sagittal. e) T1 Fat Sat Coronal and T1 Fat Sat Axial post contrast.
3 M. Dermatomyositis evaluation Image bilateral pelvis through thighs. 1) Body coil for larger children, head coil or torso coil for smaller scan large FOV, are mapping edema, not looking for fine detail. Do not scan these sequences in segments. In order to obtain accurate measurements, the FOV of the Coronal sequences must include the entire area of interest. Do not split the Coronal sequences into an upper and lower section and then combine them. The Axial sequence needs to be scanned in a single sequence also. Depending on the size of the child, they may not be able to have this exam performed on an Espree. a) T1 Coronal. b) Fast IR Coronal. c) T2 FSE Fat Sat Axial (Increase slice thickness and spacing as needed). N. Vascular mass / birthmark 1) Coil depends on extent of lesion. a) T1 Axial b) GRE Axial c) T1 Coronal (if pathology is medial or lateral) d) T1 Sagittal (if pathology is anterior or posterior) e) T2 Fat Sat Axial (change to STIR if fat sat is poor) f) T2 Fat Sat Coronal (change to STIR if fat sat is poor) g) T2 Fat Sat Sagittal (change to STIR if fat sat is poor) h) T1 Fat Sat Axial i) MR Contrast Angiogram if first study or if AVM (1 arterial and 3 venous phases) j) T1 Fat Sat Axial post contrast k) T1 Fat Sat Coronal post contrast l) T1 Fat Sat Sagittal post contrast O. MSK Pelvis (Includes for diagnosis of imperforate anus). 1) Head coil for infant, torso coil for older if for anorectal musculature, delete Fast IR Coronal, center at anorectal area and use 3mm slices with 0mm gap check with pediatric radiologist. a) Fast IR Coronal. b) T1 Coronal. c) T1 Axial. d) T2 FSE Fat Sat Axial. e) T2 FSE Coronal no fat sat. f) T2 FSE Sagittal no fat sat. O2. Female Pelvis for Primary Amenorrhea & other gynecologic symptoms. 1) Adult Mullerian Duct protocol. 2) With exception of ovarian or pelvic tumor, a female pelvis for gynecologic symptoms are always a mullerian duct protocol. 3) For case by case clarification contact appropriate pediatric radiologist.
4 P. Pediatric Body Tumor. 1) Coil per patient size infant head or extremity, child torso coil. a) Fast IR Coronal. b) Fast IR Sagittal. c) T1 Coronal. d) T2 FSE Fat Sat Axial. e) T1 GRE Axial (out of phase). f) T1 Fat Sat Coronal Post Contrast. g) T1 Fat Sat Axial Post Contrast. Q. Pediatric Renal Study. 1) Torso coil if small infant, can use head coil. a) T1 Axial no fat sat. b) T2 FSE Fat Sat Axial. c) Fast IR Coronal. d) Post Contrast. i) If for pyelo: (1) Coronal post contrast FSE T2 Fat Sat. (2) Coronal Fast IR (TE 20). (3) Axial T1 Fat Sat. ii) If for tumor, nephroblastomatosis: (1) T1 Fat Sat Axial. (2) T1 Fat Sat Coronal. e) MR Urogram post contrast. i) 3D T1 weighted SPGR (70 degree flip angle, 2-2.5mm thick, overlap 1mm, in coronal plane, with fat sat, kidneys to bladder, with large FOV). ii) Recon as MIP parallel to long axis of body and display in 15 degree increments sent to PACS. R. Pediatric Liver 1) Perform exam with patient holding their breath if possible. If not, use free breathing sequences. a) T1 Coronal. b) T2 Fat Sat Coronal. c) T1 Axial (In and Out of Phase). d) T2 Fat Sat Axial. e) Heavy T2 Axial. f) T1 Fat Sat 3D Axial (vibe or lava) Pre Contrast. g) T1 Fat Sat 3D Axial (vibe or lava) Post Contrast. i) Immediate post contrast. ii) 2 minute delay post contrast. iii) 5 minute delay post contrast. iv) 10 minute delay post contrast. S. Routine Abdomen 1) T1 Coronal. 2) T2 Fat Sat Coronal (HASTE / SSFSE if needed). 3) T1 Axial. 4) T2 Fat Sat Axial (HASTE / SSFSE if needed). 5) T1 Fat Sat Axial post contrast. 6) T1 Fat Sat Coronal post contrast.
5 S2. ABDOMEN HEMACHROMATOSIS WITHOUT CONTRAST See ACC Axial: (1) Out: GRE 120 / 2 / 20 (1) In: GRE 120 / 4 / 20 (2) In: GRE 120 / 9 / 20 (T2) (3) In: GRE 120 / 14 / 20 (T2*) (4) In: GRE 120 / 19 / 20 (T2**) Coronal: (5) Out: GRE 120 / 2 / 20 (5) In: GRE 120 / 4 / 20 (6) T2 TRUFI Axial: if time permits (7) In: GRE 120/ 4 / 90 NOTE: Coil: Body, auto-selection off Sequence: GRE Options: No fat saturation Bandwidth: Adapt it to get the correct TEs N excitations: 1 Thickness: 7 or 8 mm Gap: Could be large (10 mm) if you have a small number of slice matrix, asymmetric to reduce acquisition time, ex: 128 x 116 Phase: A>P FOV (cm): 40, may adjust base on patient's size, but make sure the TR/TE are adjusted Acquisition time: approx. 15 sec. NOTE: Example ACC
6 S3. UROGRAM 1) Pre Scan a) Patient arrives 1 hour prior to table time. IV and catheter placed. b) Ringer Lactate IV, total dose 10ml/Kg at approximately 1 liter/hour rate, minutes prior to imaging. c) PT positioned on table, immediately inject Lasix 1mg/Kg, max dose 20mg over 2 minutes, approximately 15 minutes before contrast injection. Include upper pole of kidneys to the perineum. 2) Localizer & Free breathing localizer 3) T2 Trufi Axial 4) T2 FS Trufi Axial 5) T2 Haste Axial 6) T2 Trufi Coronal (5x1.5mm, angle along aorta/ureters for true coronal) 7) T2 Haste Coronal 8) T1 Vibe Cor (2.5mm) 9) T2 Space Coronal trigger 10) T1 FS Vibe Coronal (dynamic, 25 measurements, inject contrast after 1 st measurement at.5ml/sec) 11) T1 FS Vibe Axial Post 12) T1 FS Vibe Coronal Post (dynamic, 6 measurements, free breathing) 13) T1 FS Vibe Axial Post Delay 14) T1 FS Vibe Coronal Post Delay 15) T1 FS Vibe Axial Post Delay 16) T1 FS Vibe Sagittal Post Delay NOTE: Example ACC Create RT Lateral, LT Lateral MPRs & Bilateral Lateral MIP from T2 Space Coronal. T. TMJ for Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis 1) Do Routine adult protocol. 2) Add Bilateral T1 Fat Sat Sagittal post contrast (closed mouth). 3) Add Bilateral T1 Fat Sat Coronal post contrast (closed mouth). 4) Add Bilateral Straight On T1 Fat Sat Coronal post contrast (closed mouth).
7 U. Entire Spine done in 2 sections. 1) Maximum FOV Sagittal localizer with sufficient signal and resolution for counting the Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar spine. If the child is too large to obtain a Sagittal localizer that includes the Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar spine in full, the Entire Spine study must be done in 3 sections, not 2. 2) Upper half of spine as follows: a) T1 Sagittal 250mm FOV. b) T2 Fat Sat Sagittal 250mm FOV. c) T1 Coronal. d) T1 Axial. e) T2 Axial. f) If giving patient contrast. i) T1 Axial post contrast. ii) T1 Fat Sat Sagittal 250mm FOV post contrast. 3) Lower half of spine as follows: a) T1 Sagittal 250mm FOV. b) T2 Fat Sat Sagittal 250mm FOV. c) T1 Coronal. d) T1 Axial. e) T2 Axial. f) If giving patient contrast. i) T1 Axial post contrast. ii) T1 Fat Sat Sagittal 250mm FOV post contrast. V. SI Joints for Rheumatoid Arthritis for Dr. Carrasco. 1) These studies should be scanned as an MSK Pelvis. Do not oblique the Coronal and Axial sequences. 2) T1 Axial. 3) T2 Fat Sat Axial. 4) T1 Coronal. 5) IR Coronal. 6) T1 Sagittal. 7) T1 Fat Sat Axial Pre Contrast. 8) T1 Fat Sat Axial Post Contrast. 9) T1 Fat Sat Coronal Post Contrast X. Orthopedic cases for Dr. Yandow. 1) Dr. Yandow will provide notes detailing how she wants each patient to be scanned. Her notes will request that the patient be scanned with specific parameters including but not limited to: FOV, sequence weighting, scan plane, slice thickness, slice spacing, and matrix. Consult with the Pedi Radiologist on each of these cases in order to determine how to integrate Dr. Yandow s order with our standard protocols. Scan Dr. Yandow s notes into synapse so that the radiologist will have access to them when reading the case. If Dr. Yandow orders a bilateral study (femur, tib-fib, etc.) and the Coronal sequences include both sides, be sure to send the Coronal sequences to both folders in Synapse.
8 Y. Brain Routine Run the Adult Protocol that applies to the patient s diagnosis. 1) Add T1 Axial Pre Contrast (if child is 9 or below or has pathology) 2) Replace T1 Sag with T1 SPGR / MPRAGE Sagittal (for DX of developmental delay) a) Reformat into Axial and Coronal planes. Y2. Brain Non Contrast 1) T1 3D Sagittal (reformat into Axial and Coronal planes with 3mm slices) 2) Diffusion Axial 3) FLAIR Axial 4) T2 Fat Sat Axial 5) T2 Fat Sat Coronal 6) GRE Coronal Y3. Brain Other Run the Adult Protocol that applies to the patient s diagnosis. Z. LUMBAR SPINE for Sacral Dimple 1) T1 Sagittal 2) T2 Fat Sat Sagittal 3) T1 Coronal 4) T1 Axial 5) T2 Axial 6) T1 Axial Post Contrast 7) T1 Fat Sat Sagittal Post Contrast Place one marker at the site of the dimple and another marker at the Superior Gluteal Fold. Scan through both markers on all sequences. It is very important to state in your tech notes which marker is located at the site of the dimple. AA. LUMBAR SPINE 1) T1 Sagittal 2) T2 Sagittal 3) STIR Sagittal 4) T1 Axial 5) T2 Axial AB. SPINE for Scoliosis or Vertebral Anomalies 1) Routine Cervical, Thoracic, or Lumbar Protocol 2) T2 Coronal
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018)
 General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T
 BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations
 MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations Hand: Patient lying in prone position, with affected arm extended above head. Place body off centered in effort to set affected hand in isocenter. Hand
MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations Hand: Patient lying in prone position, with affected arm extended above head. Place body off centered in effort to set affected hand in isocenter. Hand
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
Revised June Body MR Protocols
 Body MR Protocols Abdomen focus protocols A 1: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI A 1L: Abdomen MRI without contrast A 1P: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI (pancreas protocol) A 1R: Pre- and post-contrast
Body MR Protocols Abdomen focus protocols A 1: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI A 1L: Abdomen MRI without contrast A 1P: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI (pancreas protocol) A 1R: Pre- and post-contrast
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018)
 General Guidelines 3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE HASTE TR 1600, no
General Guidelines 3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE HASTE TR 1600, no
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Upper Extremity Page Lower Extremity Special Cases
 MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Page Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol MSK
MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Page Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol MSK
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
UPPER EXTREMITY
 UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis
 ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis Sequence Coverage Slice/Gap Notes COR T2 ssfse 32-40 6/-1 Coverage from all sequences is above the liver dome, through the kidneys.
ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis Sequence Coverage Slice/Gap Notes COR T2 ssfse 32-40 6/-1 Coverage from all sequences is above the liver dome, through the kidneys.
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Upper Extremity Page Lower Extremity Special Cases
 MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol Page MSK
MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol Page MSK
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park):
 Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
W/ (2) (3) (4) (5) (5) (6) (6) CTA
 Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Body MRI General Comments
 Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for oral contrast**
 MRB AB01AMR 01aAbdomen (with dynamics) + Pelvis (pre/post) A74183 A72197 Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for
MRB AB01AMR 01aAbdomen (with dynamics) + Pelvis (pre/post) A74183 A72197 Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for
revised originals as separate pages on I://DX(all folders)/trauma X Manual and project
 06-25-14 revised originals as separate pages on I://DX(all folders)/trauma X Manual and project Procedure for Suspected Child Abuse Imaging Trauma X GUIDELINES: Every effort should be made to request studies
06-25-14 revised originals as separate pages on I://DX(all folders)/trauma X Manual and project Procedure for Suspected Child Abuse Imaging Trauma X GUIDELINES: Every effort should be made to request studies
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS
 BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous)
 CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD
 Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
Musculoskeletal Imaging What to order? Brian Cole, MD my background: 1994 University of Illinois 1998 MD University of Illinois College of Medicine 1999-2003 Diagnostic Radiology Mayo Clinic 2004 Fellowship
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less)
 Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Spine. aus: Möller u.a., Pocket Atlas of Radiographic Positioning (ISBN ) 2009 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
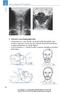 2 Cervical Spine: AP Projection Spine Criteria for a Good Radiographic View Odontoid process, axis and atlas are clearly visible through the open mouth, occiput does not obscure the odontoid, atlantoaxial
2 Cervical Spine: AP Projection Spine Criteria for a Good Radiographic View Odontoid process, axis and atlas are clearly visible through the open mouth, occiput does not obscure the odontoid, atlantoaxial
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
FieldStrength. Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging. SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology. Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
HI-Res Extremity Sensation 16
 Page 1 Routine Extremity - (2/14/2013) CTDI: ~20 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Humerus Forearm Femur Knee Tib/Fib Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without contrast, with contrast,
Page 1 Routine Extremity - (2/14/2013) CTDI: ~20 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Humerus Forearm Femur Knee Tib/Fib Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without contrast, with contrast,
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
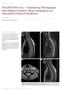 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA
 Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
CPT CODES. Ph: (307) Fax: (307) CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00
 Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Spine. After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial)
 CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
We Accept Care Credit
 We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging
 Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
Non-Contrast MRA. How and When 1996! Why Non-Contrast MRA? Angiography: What are our goals? Inflow Techniques Differences in excitation hx
 A major teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Angiography: What are our goals? Non-Contrast MRA: How and When Neil M. Rofsky, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of MRI &
A major teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Angiography: What are our goals? Non-Contrast MRA: How and When Neil M. Rofsky, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of MRI &
Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide
 Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide PROTEUS XR/F Now a single digital x-ray room accommodates nearly all your radiographic studies. With extended tube coverage and wireless detectors, Proteus XR/f gives
Proteus XR/f Patient positioning guide PROTEUS XR/F Now a single digital x-ray room accommodates nearly all your radiographic studies. With extended tube coverage and wireless detectors, Proteus XR/f gives
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
EXAMS_ Page 1/5 SORTED - NUMERIC
 BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers
 P a g e 1 Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without
P a g e 1 Hi RES Extremity - (04/18/2011) CTDI: ~13 mgy per acquisition Used for evaluation of: Ankle Elbow Hand Wrist Foot /Calcaneous Toes Fingers Billing: 1. CT Upper/Lower Extremity of concern without
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Cine loop of tomosynthesis slice images through the chest. 14 Standard PA chest radiograph (left) and single slice from the tomosynthesis image dataset (right) of a patient
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Cine loop of tomosynthesis slice images through the chest. 14 Standard PA chest radiograph (left) and single slice from the tomosynthesis image dataset (right) of a patient
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Pain Management. Medicine. without limits
 Pain Management Medicine without limits Minimally invasive therapies for chronic pain relief Thanks to advances in medicine, you don t have to live with the debilitating effects of chronic pain. The physicians
Pain Management Medicine without limits Minimally invasive therapies for chronic pain relief Thanks to advances in medicine, you don t have to live with the debilitating effects of chronic pain. The physicians
Special Instructions
 FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
RADIOLOGY (Management)
 ULTRASOUND BETA SCAN/ U/S ORBITAL 1600 Daily U/S WHOLE ABDOMEN (Abd + Pelvis) 1200 Daily U/S PELVIS 1200 Daily U/S ABDOMEN 1200 Daily U/S BREAST 1800 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR STUDY 3000 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR
ULTRASOUND BETA SCAN/ U/S ORBITAL 1600 Daily U/S WHOLE ABDOMEN (Abd + Pelvis) 1200 Daily U/S PELVIS 1200 Daily U/S ABDOMEN 1200 Daily U/S BREAST 1800 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR STUDY 3000 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
Radiological / Imaging Services Fee Schedule Provider Specialty 093
 CODE MOD Description 70250 TC RADIOLOGIC EXAM SKULL $18.30 $18.30 7/1/2012 71010 TC RADIOLOGIC EXAM, CHEST $11.41 $11.41 7/1/2012 71020 TC RADILOGICAL EXAM CHEST TWO VIEWS FRONTAL/LATERAL $15.76 $15.76
CODE MOD Description 70250 TC RADIOLOGIC EXAM SKULL $18.30 $18.30 7/1/2012 71010 TC RADIOLOGIC EXAM, CHEST $11.41 $11.41 7/1/2012 71020 TC RADILOGICAL EXAM CHEST TWO VIEWS FRONTAL/LATERAL $15.76 $15.76
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO
 Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Magnetization Preparation Sequences
 Magnetization Preparation Sequences Acquisition method may not give desired contrast Prep block adds contrast (and/or encoding) MP-RAGE = Magnetization prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo (Mugler,
Magnetization Preparation Sequences Acquisition method may not give desired contrast Prep block adds contrast (and/or encoding) MP-RAGE = Magnetization prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo (Mugler,
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest
 (Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Diagnostic Imaging Exams
 Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa
 Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
Imaging of Pediatric MSK Tumors
 Imaging of Pediatric MSK Tumors Kirsten Ecklund, M.D. Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School kirsten.ecklund@childrens.harvard.edu Tumor Imaging Goals Diagnosis Lesion characterization Benign
Imaging of Pediatric MSK Tumors Kirsten Ecklund, M.D. Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School kirsten.ecklund@childrens.harvard.edu Tumor Imaging Goals Diagnosis Lesion characterization Benign
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
For more information call , or visit
 Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
FOLLICULAR / OVULATION STUDY USG HIP JOINT (LEFT) USG HIP JOINT (RIGHT) USG KNEE JOINT (LEFT) USG KNEE JOINT (RIGHT) USG KUB USG MUSKULOSKELETAL USG
 RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
Imaging the musculoskeletal system. An Introduction
 Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula
 Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula No instrumentation With metal or cast KV/ Effective mas/rotation time 140/300/1.0
Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula No instrumentation With metal or cast KV/ Effective mas/rotation time 140/300/1.0
Field Strength. California clinic scrutinizes peripheral nerves role in symptomology
 Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community California clinic scrutinizes peripheral s role in symptomology Oak Tree Medical Center, builds expertise in brachial/sacral plexus MRI This article
Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community California clinic scrutinizes peripheral s role in symptomology Oak Tree Medical Center, builds expertise in brachial/sacral plexus MRI This article
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
