BIRTH DEFECTS AND GENETIC DISEASES BRANCH 6-DIGIT CODE. For Reportable Congenital Anomalies
|
|
|
- Jane Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATTACHMENT 1 BIRTH DEFECTS AND GENETIC DISEASES BRANCH 6-DIGIT CODE For Reportable Congenital Anomalies Based on the 1979 British Pediatric Association (BPA) Classification of Diseases and the World Health Organization's 1979 International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Code modifications developed by Division of Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta, Georgia Doc. No. 6digit88 Version 06/07 Replaces Versions 06/04 and 05/07 A - 32
2 Explanation of 6-Digit Code 6th Digit Code - Master.000 Blank.001 Left Only.002 Right Only.003 Unilateral Unspecified.004 Bilateral Possible, Probable, Borderline, or Rule Out; Defects only diagnosed prenatally should be coded with the last digit 8 when the prenatal diagnosis is not definitive..009 Not Otherwise Specified (NOS) Notes: An asterisk (*) beside a disease code indicates that the code was created by CDC. A pound symbol (#) beside a disease code indicates that the condition or defect is listed on the MACDP Exclusion List. A check (Τ) beside a disease code indicates that an addition/revision was made since the last printing of the Procedure Manual. Use of the code should be according to the exclusion list criteria. The abbreviations NEC and NOS used in this code are defined as not elsewhere classified and as not otherwise specified, respectively. A - 33
3 CONGENITAL ANOMALIES Anencephalus and Similar Anomalies Anencephalus Absence of brain Acrania Anencephaly Hemianencephaly, hemicephaly Other Craniorachischisis Craniorachischisis Iniencephaly Closed iniencephaly Open iniencephaly Unspecified iniencephaly 741 Spina Bifida Includes: Spina bifida aperta (open lesions) myelocele rachischisis Spina bifida cystica (closed lesions) meningocele meningomyelocele myelomeningocele Excludes: Spina bifida occulta (see ) craniorachischisis (see ) Spina Bifida with Hydrocephalus Spina bifida aperta, any site, with hydrocephalus Spina bifida cystica, any site, with hydrocephalus and Arnold-Chiari malformation Arnold-Chiari malformation, NOS Spina bifida cystica, any site, with stenosed aqueduct of Sylvius Spina bifida cystica, cervical, with unspecified hydrocephalus Spina bifida cystica, cervical, with hydrocephalus but without mention of Arnold-Chiari malformation or aqueduct stenosis Spina bifida cystica, thoracic, with unspecified hydrocephalus, no mention of Arnold-Chiari Spina bifida cystica, lumbar, with unspecified hydrocephalus, no mention of Arnold-Chiari Spina bifida cystica, sacral, with unspecified hydrocephalus, no mention of Arnold-Chiari Spina bifida of any site with hydrocephalus of late onset A - 34
4 Other spina bifida, meningocele of specified site with hydrocephalus Spina bifida, meningocele, cervicothoracic, with hydrocephalus Spina bifida, meningocele thoracolumbar, with hydrocephalus Spina bifida, meningocele, lumbosacral with hydrocephalus Spina bifida of any unspecified type with hydrocephalus Spina bifida without mention of hydrocephalus Spina bifida (aperta), without hydrocephalus Spina bifida (cystica), cervical, without hydrocephalus Spina bifida (cystica), thoracic, without hydrocephalus Spina bifida (cystica), lumbar, without hydrocephalus Spina bifida (cystica), sacral, without hydrocephalus Spina bifida, other specified site, without hydrocephalus Includes: cervicothoracic, thoracolumbar, lumbosacral Lipomyelomeningocele Spina bifida, site unspecified, without hydrocephalus (myelocoele, myelomeningocele, meningomyelocele) 742 Other Congenital Anomalies of Nervous System Encephalocele Occipital encephalocele Other encephalocele of specified site (includes midline defects) Frontal encephalocele Parietal encephalocele Unspecified encephalocele Microcephalus Microcephalus Reduction deformities of brain Anomalies of cerebrum Anomalies of corpus callosum Anomalies of hypothalamus Anomalies of cerebellum Agyria and lissencephaly Microgyria, polymicrogyria Holoprosencephaly Arrhinencephaly Other specified reduction defect of brain Unspecified reduction defect of brain Congenital hydrocephalus Excludes:hydrocephalus with any condition in (use 741.0) Anomalies of aqueduct of Sylvius Atresia of foramina of Magendie and Luschka A - 35
5 Dandy-Walker syndrome Hydranencephaly Other specified hydrocephaly Includes: communicating hydrocephaly # Hydrocephalus secondary to intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) or CNS bleed Unspecified hydrocephaly, NOS Other specified anomalies of brain Enlarged brain and/or head megalencephaly macrocephaly Porencephaly Includes: porencephalic cysts Cerebral cysts Other specified anomalies of brain Includes: cortical atrophy cranial nerve defects Ventricular cysts Excludes: arachnoid cysts Small brain Other specified anomalies of spinal cord Amyelia Hypoplasia and dysplasia of spinal cord atelomyelia myelodysplasia Diastematomyelia Other cauda equina anomalies Hydromyelia Hydrorachis Other specified anomalies of spinal cord and membranes Includes: congenital tethered cord Other specified anomalies of nervous system Excludes: congenital oculofacial paralysis Moebius syndrome (use ) Jaw-winking syndrome Marcus Gunn syndrome Familial dysautonomia Riley-Day syndrome Other specified anomalies of nervous system Unspecified anomalies of brain, spinal cord and nervous systems Brain, unspecified anomalies Spinal cord, unspecified anomalies Nervous system, unspecified anomalies A - 36
6 743 Congenital Anomalies of Eye Anophthalmos agenesis of eye cryptophthalmos Microphthalmos, small eyes aplasia of eye hypoplasia of eye dysplasia of eye rudimentary eye Buphthalmos Buphthalmos congenital glaucoma hydrophthalmos Enlarged eye, NOS Enlarged cornea keratoglobus congenital megalocornea Congenital cataract and lens anomalies Absence of lens congenital aphakia Spherical lens Spherophakia Cataract, NOS Cataract, anterior polar Cataract, other specified Displaced lens Coloboma of lens Other specified lens anomalies Unspecified lens anomalies Coloboma and other anomalies of anterior segments Corneal opacity Other corneal anomalies Excludes: megalocornea (use ) Absence of iris aniridia Coloboma of iris Other anomalies of iris polycoria ectopic pupil Peter's anomaly # Excludes: brushfield spots (use ) Blue sclera # If <36 weeks gestation, code only if another reportable defect is present. Always code if 36 weeks gestation Other specified colobomas and anomalies of anterior segments Rieger's anomaly Unspecified colobomas and anomalies of anterior eye segments A - 37
7 743.5 Congenital anomalies of posterior segment Specified anomalies of vitreous humour Specified anomalies of retina congenital retinal aneurysm Excludes: Stickler syndrome (use ) Specified anomalies of optic disc hypoplastic optic nerve coloboma of the optic disc Specified anomalies of choroid Coloboma of choroid Other specified anomalies of posterior segment of eye Unspecified anomalies of posterior segment of eye Congenital anomalies of eyelids, lacrimal system, and orbit Blepharoptosis congenital ptosis Ectropion Entropion # Other anomalies of eyelids absence of eyelashes long eyelashes weakness of eyelids Τ # fused eyelids (exclude if <25 weeks gestation unless another reportable defect is present) Blepharophimosis small or narrow palpebral fissures Coloboma of the eyelids Absence or agenesis of lacrimal apparatus absence of punctum lacrimale # Stenosis or stricture of lacrimal duct Other anomalies of lacrimal apparatus (e.g., cyst) Anomalies of orbit Other specified anomalies of eye # Other specified anomalies of eye Includes: exophthalmos epicanthal folds antimongoloid slant upward eye slant Brushfield spots Excludes: congenital nystagmus (use ) retinitis pigmentosa (use ) ocular albinism (use ) wide spaced eyes, hypertelorism (use ) * Epibulbar dermoid cyst Unspecified anomalies of eye Unspecified anomalies of eye congenital: of eye (any part) anomaly, NOS deformity, NOS A - 38
8 744 Congenital Anomalies of Ear, Face, and Neck Anomalies of ear causing impairment of hearing Absence or stricture of auditory canal Absence of auricle (pinna) absence of ear, NOS Anomaly of middle ear fusion of ossicles Anomaly of inner ear Includes: congenital anomaly of membranous labyrinth organ of Corti Unspecified anomalies of ear with hearing impairment Includes: congenital deafness, NOS Accessory auricle # Accessory auricle Polyotia # Preauricular appendage, tag, or lobule (in front of ear canal) # Other appendage, tag, or lobule include papillomas, ear tags Other specified anomalies of ear Τ Macrotia (enlarged pinna) Microtia (hypoplastic pinna and absence or stricture of external auditory meatus) Bat ear # Other misshapen ear pointed ear elfin pixie-like lop ear cauliflower ear cleft in ear malformed ear absent or decreased cartilage Misplaced ears # Low set ears # Posteriorly rotated ears Absence or anomaly of eustachian tube Other specified anomalies of ear (see also ) # Excludes: Darwin's tubercle Unspecified anomalies of ear Unspecified anomalies of ear Congenital: ear (any part) anomaly, deformity, NOS Branchial cleft, cyst, or fistula; preauricular sinus Branchial cleft, sinus, fistula cyst, or pit # Preauricular sinus, cyst, or pit A - 39
9 Other branchial cleft anomalies Includes: dermal sinus of head # Webbing of neck Includes: pterygium colli, redundant neck skin folds Other unspecified anomalies of face and neck Macrostomia (large mouth) Microstomia (small mouth) # Macrocheilia (large lips) # Microcheilia (small lips) Other specified anomalies of face/neck Unspecified anomalies of face and neck # Congenital anomaly of neck, NOS Includes: short neck Congenital anomaly of face, NOS Abnormal facies A - 40
10 745 Bulbus Cordis Anomalies and Anomalies of Cardiac Septal Closure Common truncus (see for pseudotruncus) Persistent truncus arteriosus absent septum between aorta and pulmonary artery Aortic septal defect Includes: aortopulmonary window Excludes: atrial septal defect (use ) Transposition of great vessels N N N N Transposition of great vessels, complete (no VSD) Transposition of great vessels, incomplete (w/ VSD) Taussig-Bing syndrome Corrected transposition of great vessels, L-transposition, ventri in version Excludes: dextrocardia (use ) Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) with normally related great vessels Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) with transposed great vessels Double outlet right ventricle (DORV), relationship of great vessels not specified Other specified transposition of great vessels, no mention of double outlet right ventricle (DORV) Unspecified transposition of great vessels Tetralogy of Fallot Fallot's tetralogy Fallot's pentalogy Fallot's tetralogy plus ASD Single ventricle Single ventricle Common ventricle Cor triloculare biatriatum Ventricular septal defect N Roger's disease Note: This is an oudated term and the code is no longer used. If this diagnostic term is encountered in the medical record, code it as a ventricular septal defect Eisenmenger's syndrome Gerbode defect Τ Other specified ventricular septal defect Includes: cystalline sub-cystalline subarterial conoventricular N Perimembranous VSD Includes: membranous VSD A - 41
11 N Muscular VSD Includes: mid-muscular and apical VSDs N Inlet VSD Includes: common atrioventricular (AV) canal type VSD Note: Code common atrioventricular (AV) canal as Code common atrioventricular (AV) canal with muscular VSD as Ventricular septal defect, NOS Excludes: common atrioventricular canal type (use ) Probable VSD Ostium secundum type atrial septal defect Ν # Nonclosure of foramen ovale, NOS Patent foramen ovale (PFO) 1)Always code if 36 weeks of gestation at birth and defect last noted at 6 weeks of age. 2)If 36 weeks gestation at birth and defect last noted <6 weeks of age, code only if another reportable heart defect is present. 3)Never code if <36 weeks gestation at birth regardless of presence of other defects Ostium (septum) secundum defect N Lutembacher's syndrome Note: This is an outdated term and the code is no longer used. If this diagnostic term is encountered in the medical record, code the individual components, not the syndrome Other specified atrial septal defect ASD (atrial septal defect), NOS Auricular septal defect, NOS Partial foramen ovale PFO vs. ASD Endocardial cushion defects N Ostium primum defects Single common atrium, cor triloculare biventriculare Common atrioventricular canal with ventricular septal defect (VSD) Includes: Common AV canal with muscular VSD Excludes: Inlet VSD or common AV canal type VSD (code as Common atrioventricular canal Other specified cushion defect Endocardial cushion defect, NOS Cor biloculare Cor biloculare Other specified defects of septal closure Other specified defects of septal closure A - 42
12 745.9 Unspecified defect of septal closure Unspecified defect of septal closure 746 Other Congenital Anomalies of Heart Anomalies of pulmonary valve N N Ν Atresia, hypoplasia of pulmonary valve Note: Code pulmonary artery atresia as Code pulmonary artery hypoplasia as Code pulmonic or pulmonary atresia or hypoplasia, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) as Stenosis of pulmonary valve # Excludes: pulmonary infundibular stenosis (use ) Note: Code pulmonary artery stenosis as Code pulmonic or pulmonary stenosis, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) as # Pulmonary valve insufficiency or regurgitation, congenital Never code cases designated as 'mild', minimal', 'trivial', or 'physiologic'. Code cases designated as moderate or severe and those where the degree is not specified (NOS) only if another reportable heart defect is present Other specified anomalies of pulmonary valve # Excludes: pulmonary infundibular stenosis (use ) Unspecified anomaly of pulmonary valve Tricuspid atresia and stenosis N Tricuspid atresia only Excludes: tricuspid stenosis and hypoplasia Ν # Tricuspid valve insufficiency or regurgitation, congenital Never code cases designated as 'mild', minimal', 'trivial', or 'physiologic'. Code cases designated as moderate or severe and those where the degree is not specified (NOS) only if another reportable heart defect is present. N Tricuspid stenosis or hypoplasia Ebstein's anomaly Ebstein's anomaly Congenital stenosis of aortic valve Congenital stenosis of aortic valve Includes: congenital aortic stenosis subvalvular aortic stenosis Excludes: supravalvular aortic stenosis ( ) A - 43
13 746.4 Congenital insufficiency of aortic valve Ν N # Aortic valve insufficiency or regurgitation, congenital Excludes: bicuspid aortic valve. Never code cases designated as 'mild', minimal', 'trivial', or 'physiologic'. Code cases designated as moderate or severe and those where the degree is not specified (NOS) only if another reportable heart defect is present Bicuspid aortic valve * Other specified anomalies of the aortic valves Includes: aortic valve atresia Excludes: supravalvular aortic stenosis ( ) * Unspecified anomalies of the aortic valves Congenital mitral stenosis Congenital mitral stenosis Absence, atresia, or hypoplasia of mitral valve Mitral valve insufficiency or regurgitation, congenital Ν # Mitral valve insufficiency or regurgitation, congenital Never code cases designated as 'mild', minimal', 'trivial', or 'physiologic'. Code cases designated as moderate or severe and those where the degree is not specified (NOS) only if another reportable heart defect is present Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Atresia, or marked hypoplasia of the ascending aorta and defective development of left ventricle (with mitral valve atresia) Other specified anomalies of the heart N N Dextrocardia without situs inversus (situs solitus) Dextrocardia with no mention of situs inversus Excludes: dextrocardia with situs inversus use ) Levocardia Note: This condition has been moved to the never code list Cor triatriatum Pulmonary infundibular (subvalvular) stenosis Trilogy of Fallot Anomalies of pericardium # Anomalies of myocardium cardiomegaly, congenital, NOS cardiomyopathy, congenital cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic Note: Do not code cardiomyopathy of any type in a newborn of a diabetic mother (either gestational or preexisting diabetes). A - 44
14 Congenital heart block N Other specified anomalies of heart Includes: ectopia (ectopic) cordis (mesocardia), conduction defects, NOS Hypoplastic left ventricle Excludes: hypoplastic left heart syndrome ( ) Hypoplastic right heart (ventricle) Uhl's disease * Hypoplastic ventricle, NOS Anomalies of coronary artery or sinus Ventricular hypertrophy (right or left) Note: Do not code ventricular hypertrophy of any type in a newborn of a diabetic mother (either gestational or pre-existing diabetes) Other defects of the atria Excludes: congenital Wolfe-Parkinson-White (use ) rhythm anomalies (use 426.-, 427.-) Unspecified anomalies of heart N Unspecified anomalies of heart valves Anomalous bands of heart Acyanotic congenital heart disease, NOS Cyanotic congenital heart disease, NOS Blue baby Unspecified anomaly of heart: Includes: congenital heart disease (CHD) "Pulmonic" or "pulmonary" atresia, stenosis, or hypoplasia, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) Note: Code pulmonary valve atresia or hypoplasia as Code pulmonary valve stenosis as Code pulmonary artery atresia as Code pulmonary artery stenosis as Code pulmonary artery hypoplasia as Other Congenital Anomalies of Circulatory System Ν # Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Note: 1)Always code if 36 weeks of gestation at birth and defect last noted at 6 weeks of age. 2)If 36 weeks gestation at birth and defect last noted <6 weeks of age, code only if the PDA was treated (e.g. by ligation or indomethicin) or if another reportable heart defect is present. 3)Never code if <36 weeks gestation at birth or if treated with prostaglandins regardless of gestational age. (See PDA Tree Appendix) Probable PDA Coarctation of aorta Preductal (proximal) coarctation of aorta Postductal (distal) coarctation of aorta Unspecified coarctation of aorta A - 45
15 747.2 Other anomalies of aorta N N N N Atresia of aorta absence of aorta pseudotruncus arteriosus Hypoplasia of aorta tubular hypoplasia of aorta Interrupted aortic arch, Type A Interrupted aortic arch, Type B Interrupted aortic arch, Type C Supra-aortic stenosis (supravalvular) Excludes: aortic stenosis, congenital (see ) Persistent right aortic arch Aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva Vascular ring (aorta) double aortic arch Includes: vascular ring compression of trachea Overriding aorta dextroposition of aorta Congenital aneurysm of aorta congenital dilatation of aorta Other specified anomalies of aorta Interrupted aortic arch, NOS, type not specified Unspecified anomalies of aorta Anomalies of pulmonary artery N N N Pulmonary artery atresia, absence or agenesis Note: Code pulmonary valve atresia as Code pulmonic or pulmonary atresia, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) as Pulmonary artery atresia with septal defect Pulmonary artery stenosis Includes: Stenosis of the main pulmonary artery or of the right or left main branches Note: Code pulmonary valve stenosis as Code pulmonic or pulmonary stenosis, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) as Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis Includes: Stenosis of a pulmonary artery peripheral to the main right or left main branches Peripheral pulmonic stenosis (PPS), NOS, documented by echocardiogram # Excludes: Peripheral pulmonic stenosis (PPS) murmur only (not documented by echocardiogram) Note: 1)Always code if 36 weeks of gestation at birth and defect last noted at 6 weeks of age. 2)If 36 weeks gestation at birth and defect last noted <6 weeks of age, code only if another reportable heart defect is present. 3)Never code if <36 weeks gestation at birth. (See PPS Tree Appendix) Aneurysm of pulmonary artery dilatation of pulmonary artery Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation or aneurysm A - 46
16 Other specified anomaly of pulmonary artery Includes: pulmonary artery hypoplasia Note: Code pulmonary valve hypoplasia as Code pulmonic or pulmonary hypoplasia, NOS (no mention of valve or artery) as Unspecified anomaly of pulmonary artery Anomalies of great veins Stenosis of vena cava (inferior or superior) Persistent left superior vena cava (TAPVR) Total anomalous pulmonary venous return Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return Anomalous portal vein termination Portal vein - hepatic artery fistula Other specified anomalies of great veins Unspecified anomalies of great veins Absence or hypoplasia of umbilical artery # Single umbilical artery Other anomalies of peripheral vascular system Stenosis of renal artery Other anomalies of renal artery Arteriovenous malformation (peripheral) Excludes: pulmonary ( ) cerebral ( ) retinal ( ) Congenital phlebectasia congenital varix Other anomalies of peripheral arteries Includes: aberrant subclavian artery Other anomalies of peripheral veins Excludes: Budd-Chiari - occlusion of hepatic vein (use ) Ν Other anomalies of peripheral vascular system # Includes: primary pulmonary artery hypertension ONLY if it is present in an infant at >7 days of age Unspecified anomalies of peripheral vascular system Other specified anomalies of circulatory system Arteriovenous (malformation) aneurysm of brain Other anomalies of cerebral vessels Includes: vein of Galen Other specified anomalies of circulatory system Excludes: congenital aneurysm: coronary ( ) peripheral ( ) pulmonary ( ) retinal ( ) ruptured cerebral arteriovenous aneurysm ( ) A - 47
17 ruptured cerebral aneurysm Unspecified anomalies of circulatory system ( ) Unspecified anomalies of circulatory system A - 48
18 748 Congenital Anomalies of Respiratory System Choanal atresia Choanal atresia atresia of nares, anterior or posterior congenital stenosis Other anomalies of nose Agenesis or underdevelopment of nose Accessory nose Fissured, notched, or cleft nose Sinus wall anomalies Perforated nasal septum # Other specified anomalies of nose flat bridge of nose wide nasal bridge small nose and nostril absent nasal septum Tubular nose, single nostril, proboscis Unspecified anomalies of nose Excludes: congenital deviation of the nasal septum (use ) Web of larynx Web of larynx-glottic Web of larynx-subglottic Web of larynx-nos Other anomalies of larynx, trachea, and bronchus Anomalies of larynx and supporting cartilage Τ Congenital subglottic stenosis Never code if chart states the condition was acquired or secondary to endotracheal (ET) intubation or ventilation Other anomalies of trachea # Excludes: vascular ring compression of the trachea (use ) Stenosis of bronchus Other anomalies of bronchus Congenital laryngeal stridor, NOS Other specified anomalies of larynx and bronchus Cleft larynx, laryngotracheoesophageal cleft Unspecified anomalies of larynx, trachea, and bronchus Congenital cystic lung Single cyst, lung or lung cyst Multiple cysts, lung Polycystic lung Honeycomb lung Other specified congenital cystic lung A - 49
19 748.5 Agenesis or aplasia of lung Τ Agenesis or aplasia of lung Hypoplasia of lung; Pulmonary hypoplasia # Exclude if isolated defect in infants <36 weeks gestation Sequestration of lung Other specified dysplasia of lung Fusion of lobes of lung * Unspecified dysplasia of lung Other anomalies of lung Ectopic tissues in lung Bronchiectasis Accessory lobe of lung Bilobar right lung or right lung with left lung bronchial pattern Other and unspecified anomalies of lung Other specified anomalies of respiratory system Anomaly of pleura Congenital cyst of mediastinum Other specified respiratory system anomalies Includes: congenital lobar emphysema lymphangiectasia of lungs Unspecified anomalies of respiratory system Unspecified anomalies of respiratory system Absence of respiratory organ, NOS Anomaly of respiratory system, NOS A - 50
20 749 Cleft Palate and Cleft Lip Cleft palate alone (If description of condition includes Pierre Robin sequence, use additional code, ) Cleft hard palate, unilateral Cleft hard palate, bilateral Cleft hard palate, central Cleft hard palate, NOS Cleft soft palate, alone unilateral Cleft soft palate, alone bilateral Cleft soft palate, alone central Cleft soft palate, alone, NOS Cleft uvula Cleft palate, NOS palatoschisis Cleft lip alone Includes: alveolar ridge cleft cleft gum harelip Cleft lip, unilateral Cleft lip, bilateral Cleft lip, central Cleft lip, NOS (fused lip) cleft gum Cleft lip with cleft palate Cleft lip, unilateral, with any cleft palate Cleft lip, bilateral, with any cleft palate Cleft lip, central, with any cleft palate Cleft lip, NOS, with any cleft palate A - 51
21 750 Other Congenital Anomalies of Upper Alimentary Tract # Tongue tie Ankyloglossia Other anomalies of tongue Excludes: protruding tongue (never a defect) Aglossia Absence of tongue Hypoglossia (small tongue) Microglossia Macroglossia (large tongue) Dislocation or displacement of tongue Glossoptosis Cleft tongue or split tongue Other specified anomalies of tongue Unspecified anomalies of tongue Other specified anomalies of mouth and pharynx Pharyngeal pouch Other pharyngeal anomalies Other anomalies of salivary glands or ducts # High arched palate Other anomalies of palate Lip fistulae or pits Other lip anomalies Includes: notched lip, prominent philtrum, long philtrum Excludes: cleft lip (see 749) Other specified anomalies of mouth and pharynx Excludes: receding jaw (see 524.0) large and small mouth (see 744.8) Tracheoesophageal (T-E) fistula, esophageal atresia and stenosis Esophageal atresia without mention of T-E fistula Esophageal atresia with mention of T-E fistula Tracheoesophageal fistula without mention of esophageal atresia Tracheoesophageal fistula - "H" type Bronchoesophageal fistula with or without mention of esophageal atresia Stenosis or stricture of esophagus Esophageal web Other tracheoesophageal anomalies Other specified anomalies of esophagus Congenital dilatation of esophagus giant esophagus Displacement of esophagus Diverticulum of esophagus esophageal pouch Duplication of esophagus Other specified anomalies of esophagus A - 52
22 750.5 Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis # Pylorospasm Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Other congenital pyloric obstruction Congenital hiatus hernia Congenital hiatus hernia Cardia displacement through esophageal hiatus Partial thoracic stomach Excludes: congenital diaphragmatic hernia ( ) Other specified anomalies of stomach Microgastria Megalogastria Cardiospasm achalasia of cardia, congenital Displacement or transposition of stomach Diverticulum of stomach Duplication of stomach Other specified anomalies of stomach Other specified anomalies of upper alimentary tract Other specified anomalies of upper alimentary tract Unspecified anomalies of upper alimentary tract Unspecified anomalies of mouth and pharynx Unspecified anomalies of esophagus Unspecified anomalies of stomach Unspecified anomalies of upper alimentary tract A - 53
23 751 Other Congenital Anomalies of Digestive System Meckel's diverticulum Persistent omphalomesenteric duct persistent vitelline duct # Meckel's diverticulum Atresia and stenosis of small intestine Stenosis, atresia or absence of duodenum Stenosis, atresia or absence of jejunum Stenosis, atresia or absence of ileum Stenosis, atresia or absence of small intestine Stenosis, atresia or absence of small intestine with fistula Atresia and stenosis of large intestine, rectum and anal canal Stenosis, atresia or absence of large intestine Stenosis, atresia or absence of appendix Stenosis, atresia or absence of rectum with fistula Stenosis, atresia or absence of rectum without mention of fistula Stenosis, atresia or absence of anus with fistula Includes: imperforate anus with fistula Stenosis, atresia or absence of anus without mention of fistula Includes: imperforate anus without fistula Hirschsprung's disease and other congenital functional disorders of the colon Total intestinal aganglionosis Long-segment Hirschsprung's disease; aganglionosis beyond the rectum Short-segment Hirschsprung's disease; aganglionosis involving no more than the anal sphincter and the rectum Hirschsprung's disease, NOS Congenital megacolon congenital macrocolon, not aganglionic Anomalies of intestinal fixation Malrotation of cecum and/or colon Anomalies of mesentery Congenital adhesions or bands of omentum and peritoneum; Ladd's bands Other specified and unspecified malrotation Malrotation of small intestine alone Other anomalies of intestine Duplication of anus, appendix, cecum, or intestine enterogenous cyst Transposition of appendix, colon, or intestine Microcolon A - 54
24 R Ectopic (displaced) anus Congenital anal fistula Persistent cloaca Exstrophy of cloaca Excludes exstrophy of urinary bladder not associated with imperforate anus (use ) * Duodenal web # Other specified anomalies of intestine Includes: rectal fissures Unspecified anomalies of intestine Anomalies of gallbladder, bile ducts, and liver Absence or agenesis of liver, total or partial Cystic or fibrocystic disease of liver # Other anomalies of liver hepatomegaly hepatosplenomegaly (also use code ) Excludes: Budd-Chiari (use ) Agenesis or hypoplasia of gallbladder Other anomalies of gallbladder duplication of gallbladder Agenesis or atresia of hepatic or bile ducts Includes: Excludes: biliary atresia congenital or neonatal hepatitis (use or ) Choledochal cysts Other anomalies of hepatic or bile ducts Anomalies of biliary tract, NEC Anomalies of pancreas Excludes: fibrocystic disease of pancreas ( ) diabetes mellitus, congenital neonatal Absence, agenesis or hypoplasia of pancreas Accessory pancreas Annular pancreas Ectopic pancreas Pancreatic cyst Other specified anomalies of pancreas Unspecified anomalies of pancreas Other specified anomalies of digestive system Absence of alimentary tract, NOS (complete or partial) Duplication of alimentary tract Ectopic digestive organs, NOS Other specified anomalies of digestive system A - 55
25 751.9 Unspecified anomalies of digestive system Unspecified anomalies of digestive system congenital of digestive system, NOS anomaly, NOS deformity, NOS obstruction, NOS A - 56
26 752 Congenital Anomalies of Genital Organs Excludes: congenital hydrocele ( ) testicular feminization syndrome ( ) syndromes associated with anomalies in number and form of chromosomes (758) Anomalies of ovaries Absence or agenesis of ovaries Streak ovary Accessory ovary Other specified anomalies of ovaries Multiple ovarian cysts Unspecified anomalies of ovaries Anomalies of fallopian tubes and broad ligaments Absence of fallopian tube or broad ligament Cyst of mesenteric remnant epoophoron cyst cyst of Gartner's duct Fimbrial cyst parovarian cyst Other and unspecified anomalies of fallopian tube and broad ligaments Doubling of uterus Doubling of uterus doubling of uterus (any degree) or associated with doubling of cervix and vagina Other anomalies of uterus Absence or agenesis of uterus Displaced uterus Fistulae involving uterus with digestive or urinary tract Includes: uterointestinal fistula uterovesical fistula Other anomalies of uterus bicornuate uterus unicornis uterus Unspecified anomalies of uterus Anomalies of cervix, vagina, and external female genitalia Absence, atresia or agenesis of cervix Absence or atresia of vagina, complete or partial Congenital rectovaginal fistula # Imperforate hymen # Absence or other anomaly of vulva fusion of vulva hypoplastic labia majora Always code if 36weeks gestation. If <36 weeks gestation, code only if another reportable defect is present. A - 57
27 # Absence or other anomaly of clitoris Includes: clitoromegaly enlarged clitoris clitoral hypertrophy prominent clitoris # Embryonal cyst of vagina Other cyst of vagina, vulva, or canal of Nuck # Other specified anomalies of cervix, vagina, or external female genitalia Includes: vaginal tags hymenal tags Unspecified anomalies of cervix, vagina, or external female genitalia Undescended testicle # 1)If < 36 weeks gestation, code only if there is a medical/surgical intervention for this problem; 2)If 36 weeks gestation and defect last noted at <1 year of age, code only if there was a medical/surgical intervention for this problem or if another reportable defect is present 3)Always code if 36 weeks gestation and defect first noted at 1 of age. # Undescended testicle, unilateral undescended, unpalpable # Left undescended testicle # Right undescended testicle # Undescended testicle, bilateral # Undescended testicle, NOS (Cryptorchidism) Ectopic testis, unilateral and bilateral Hypospadias and epispadias Hypospadias (alone), NOS o, glandular,coronal o, penile o, perineal, scrotal Epispadias Congenital chordee (with hypospadias), NOS Congenital chordee alone (chordee w/o hypospadias) Cong. chordee with 1 o, coronal hypospadias Cong. chordee with 2 o, penile hypospadias Cong. chordee with 3 o, perineal, scrotal hypospadias Indeterminate sex and pseudohermaphroditism Excludes: pseudohermaphroditism: female, with adrenocortical disorder (see ) male, with gonadal disorder with specified chromosomal anomaly (see 758) True hermaphroditism ovotestis A - 58
28 Pseudohermaphroditism, male Pseudohermaphroditism, female pure gonadal dysgenesis Excludes: gonadal agenesis ( ) Pseudohermaphrodite, NOS Indeterminate sex, NOS ambiguous genitalia Other specified anomalies of male genital organs Absence of testis monorchidism, NOS # Aplasia or hypoplasia of testis and scrotum Other anomalies of testis and scrotum polyorchidism bifid scrotum Excludes: torsion of the testes or spermatic cord (use # ) Atresia of vas deferens Other anomalies of vas deferens and prostate Absence or aplasia of penis # Other anomalies of penis absent or hooded foreskin # redundant foreskin (never a defect) Small penis, hypoplastic penis, or micropenis Cysts of embryonic remnants cyst: hydatid of Morgagni Wolffian duct appendix testis Other specified anomalies of genital organs microgenitalia macrogenitalia Unspecified anomalies of genital organs Unspecified anomalies of genital organs Congenital: of genital organ, NEC anomaly, NOS or deformity, NOS A - 59
29 753 Congenital Anomalies of Urinary System Renal agenesis and dysgenesis Bilateral absence, agenesis, dysplasia, or hypoplasia of kidneys Potter's syndrome Renal agenesis, NOS Unilateral absence, agenesis, dysplasia or hypoplasia of kidneys Cystic kidney disease Renal cyst (single) Polycystic kidneys, infantile type Polycystic kidneys, adult type Polycystic kidneys, NOS Medullary cystic disease, juvenile type Medullary cystic disease, adult type Medullary sponge kidney Multicystic renal dysplasia Multicystic kidney Other specified cystic disease Includes: cystic kidneys, NOS Obstructive defects of renal pelvis and ureter Congenital hydronephrosis Atresia, stricture, or stenosis of ureter Includes: ureteropelvic junction obstruction/stenosis ureterovesical junction obstruction/stenosis hypoplastic ureter Megaloureter, NOS Includes: hydroureter Other and unspecified obstructive defects of renal pelvis and ureter Other specified anomalies of kidney Accessory kidney Double or triple kidney and pelvis pyelon duplex or triplex Lobulated, fused, or horseshoe kidney Ectopic kidney Enlarged, hyperplastic or giant kidney Congenital renal calculi Other specified anomalies of kidney Other specified anomalies of ureter Absence of ureter Accessory ureter double ureter, duplex collecting system Ectopic ureter Other specified anomalies of ureter Includes: ureterocele A - 60
30 Variations of vesicoureteral reflux Exstrophy of urinary bladder Exstrophy of urinary bladder ectopia vesicae extroversion of bladder Atresia and stenosis of urethra and bladder neck Congenital posterior urethral valves or posterior urethral obstruction Other atresia, or stenosis of bladder neck Obstruction, atresia or stenosis of anterior urethra Obstruction, atresia or stenosis of urinary meatus Includes: meatal stenosis Other and unspecified atresia and stenosis of urethra and bladder neck Anomalies of urachus Τ # Patent urachus Cyst of urachus Other and unspecified anomaly of urachus Other specified anomalies of bladder and urethra Absence of bladder or urethra Ectopic bladder Congenital diverticulum or hernia of bladder Congenital prolapse of bladder (mucosa) Double urethra or urinary meatus Ectopic urethra or urethral orifice Congenital digestive-urinary tract fistulae rectovesical fistula Urethral fistula, NOS Other specified anomalies of bladder and urethra Unspecified anomalies of urinary system Unspecified anomaly of kidney Unspecified anomaly of ureter Unspecified anomaly of bladder Unspecified anomaly of urethra Unspecified anomaly of urinary system, NOS A - 61
31 754 Certain Congenital Musculoskeletal Anomalies Of skull, face, and jaw Excludes: dentofacial anomalies (524.0) Pierre Robin sequence ( ) syphilitic saddle nose ( ) Asymmetry of face Compression (Potter's) facies # Congenital deviation of nasal septum bent nose Τ Dolichocephaly Always code if 36 weeks gestation # If <36 weeks gestation, code only if another reportable defect is present # Depressions in skull Includes: large fontanelle small fontanelle Plagiocephaly Asymmetric head Τ # * Scaphocephaly, no mention of craniosynostosis * Trigonocephaly, no mention of craniosynostosis Always code if 36 weeks gestation # If <36 weeks gestation, code only if another reportable defect is present * Other specified skull deformity, no mention of craniosynostosis Includes:brachycephaly acrocephaly turricephaly oxycephaly * Deformity of skull, NOS Anomalies of sternocleidomastoid muscle Anomalies of sternocleidomastoid muscle * Includes: absent or hypoplastic sternocleidomastoid contracture of sternocleidomastoid muscle sternomastoid tumor Excludes: congenital sternocleidomastoid torticollis (use ) Certain congenital musculoskeletal deformities of spine Congenital postural scoliosis Congenital postural lordosis Congenital postural curvature of spine, NOS Congenital dislocation of hip Congenital dislocation of hip Unstable hip preluxation of hip subluxation of hip predislocation status of hip at birth A - 62
32 754.4 Congenital genu recurvatum and bowing of long bones of leg Bowing, femur Bowing, tibia and/or fibula Bow legs, NOS Genu recurvatum Dislocation of knee, congenital Deformity of leg, NOS Varus (inward) deformities of feet Talipes equinovarus Talipes calcaneovarus # Metatarsus varus or metatarsus adductus Complex varus deformities Unspecified varus deformities of feet Valgus (outward) deformities of feet Talipes calcaneovalgus Congenital pes planus Pes valgus Other specified valgus deformities of foot Unspecified valgus deformities of foot Other deformities of feet Pes cavus Claw foot (use for claw foot) Short Achilles tendon Clubfoot, NOS talipes, NOS Congenital deformities of foot, NOS Other specified deformities of ankle and/or toes Includes: dorsiflexion of foot Excludes: widely spaced 1st and 2nd toes (use ) Other specified congenital musculoskeletal deformities Pigeon chest (pectus carinatum) Funnel chest (pectus excavatum) Other anomalies of chest wall Includes: deformed chest, barrel chest Shield chest Dislocation of elbow Club hand or fingers Spade-like hand Other specified deformity of hands (see for specified anomalies of fingers) A - 63
33 755 Other Congenital Anomalies of Limbs Polydactyly Accessory fingers (postaxial polydactyly, Type A) # Skin tag (postaxial polydactyly, Type B) Exclude: Do not code in black infants Unspecified finger or skin tag (postaxial polydactyly, NOS) Accessory thumbs (preaxial polydactyly) Accessory toes (postaxial) Accessory big toe (preaxial) Accessory digits, NOS (hand/foot not specified) Accessory digits hand, NOS (preaxial, postaxial not specified) Accessory digits foot, NOS (preaxial, postaxial not specified) Syndactyly Τ Fused fingers Webbed fingers Fused toes # Webbed toes Code webbing of the second and third toes only if another reportable defect is present. Always code webbing of other toes regardless of whether another reportable defect is present Unspecified syndactyly (see below for specified site) Unspecified syndactyly thumb and/or fingers, unilateral Unspecified syndactyly thumb and/or fingers, bilateral Unspecified (webbed vs. fused) syndactyly thumb and/or fingers, NOS Unspecified syndactyly toes unilateral Unspecified syndactyly toes bilateral Unspecified syndactyly toes, NOS Unspecified syndactyly (i.e., webbed vs. fused) digits not known Reduction defects of upper limb Τ If description of the condition includes amniotic or constricting bands use additional code, (Only use if another reportable defect is present) Excludes shortening of upper limb (use ) or hypoplasia of upper limb (use ) Absence of upper limb Absent: humerus (total or partial), radius,ulna and hand Includes: amelia of upper limb, NOS infants with rudimentary or nubbin fingers attached to stump of humerus or shoulder girdle Absence of upper arm and forearm Absent: humerus (total or partial), radius and ulna (total or partial) Present: hand (total or partial) Includes: phocomelia of upper limb, NOS; intercalary reduction defect of upper limb, NOS A - 64
34 Absence of forearm only or upper arm only Absent: radius and ulna Present: humerus, hand (total or partial) or Absent: humerus Present: radius, ulna, and hand Absence of forearm and hand Absent: radius and ulna (total or partial) and hand Includes: infants with rudimentary or nubbin fingers attached to stump of forearm or elbow Absence of hand or fingers Absent: hand or fingers (total or partial) not in conjunction with ray or long bone reduction Includes: rudimentary or nubbin fingers; absent individual phalanges; absent or missing fingers, NOS Excludes: isolated absent or hypoplastic thumb (use ) Split-hand malformation Absent: central fingers (third with or without second, fourth) and metacarpals (total or partial) Includes: monodactyly; lobster-claw hand Excludes: isolated absent central fingers without metacarpal defects (use ) Preaxial longitudinal reduction defect of upper limb Absent: radius (total or partial) and/or thumb with or without second finger (total or partial) Includes: isolated absent or hypoplastic thumb; radial ray defect, NOS Longitudinal reduction defect of upper limb, NOS Includes: absent forearm long bone with absent fingers, NOS Postaxial longitudinal reduction defect of upper limb Includes: isolated absent ulna (total or partial); absent fifth with or without fourth finger (total or partial) only if ulna or fifth ± fourth metacarpal also totally or partially absent; ulnar ray defect, NOS Other specified reduction defect of upper limb Transverse reduction defect of upper limb, NOS Includes: congenital amputation of upper limb, NOS Unspecified reduction defect of upper limb Reduction defects of lower limb Τ If description of condition includes amniotic or constricting bands use additional code, (Only use this code if another reportable defect is present) Excludes shortening of lower limb (use ) and hypoplasia of lower limb (use ) A - 65
35 Absence of lower limb Absent: femur (total or partial), tibia, fibula, and foot Includes: amelia of lower limb, NOS infants with rudimentary or nubbin toes attached to stump of femur or pelvic girdle Absence of thigh and lower leg Absent: femur (total or partial), tibia and fibula (total or partial) Present: foot (total or partial) Includes: phocomelia of lower limb, NOS; intercalary reduction defect of lower limb, NOS Absence of lower leg only or femur only Absent: tibia and fibula Present: femur, foot (total or partial) or Absent: femur Present: tibia, fibula, and foot Absence of lower leg and foot Absent: tibia and fibula (total or partial), foot Includes: infants with rudimentary or nubbin toes attached to stump of leg or knee Absence of foot or toes Absent: foot or toes (total or partial) not in conjunction with ray or long bone reduction Includes: rudimentary or nubbin toes; absent individual phalanges; absent or missing toes, NOS Excludes: isolated absent or hypoplastic great toe (use ) Split-foot malformation Absent: central toes (third with or without second, fourth) and metatarsals (total or partial) Includes: monodactyly; lobster claw foot Excludes: isolated absent central toes without metatarsal defects (use ) Note: preaxial lower limb reductions can occur with split-hand malformations of the upper limb and these lower limb defects should be coded Longitudinal reduction defect of lower limb, NOS Includes: absent long bone of leg with absent toes, NOS Preaxial longitudinal reduction defect of lower limb Absent: tibia (total or partial) and/or great toe with or without second toe (total or partial) Includes: isolated absent or hypoplastic great toe; tibial ray defect, NOS Postaxial longitudinal reduction defect of lower limb Includes: isolated absent fibula (total or partial); absent fifth with or without fourth toe (total or partial) only if fibula or fifth ± fourth metatarsal also totally or partially absent; fibular ray defect, NOS Other specified reduction defect of lower limb Transverse reduction defect of lower limb, NOS Includes: congenital amputation of lower limb, NOS Unspecified reduction defect of lower limb A - 66
Congenital Anomalies
 Congenital Anomalies Down Syndrome 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q900 Q90.0 : Trisomy 21, meiotic nondisjunction 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q901 Q90.1 : Trisomy 21, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction) 7580
Congenital Anomalies Down Syndrome 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q900 Q90.0 : Trisomy 21, meiotic nondisjunction 7580 7580 DOWN''S SYNDROME Q901 Q90.1 : Trisomy 21, mosaicism (mitotic nondisjunction) 7580
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester
 Supplementary material Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester Medication Count Overall 1152 Atorvastatin 538 Cerivastatin * Fluvastatin 47 Lovastatin 132 Pravastatin
Supplementary material Table S1. Number of patients dispensed a statin, by drug, during the 1 st trimester Medication Count Overall 1152 Atorvastatin 538 Cerivastatin * Fluvastatin 47 Lovastatin 132 Pravastatin
List by Region - Visceral Anomalies
 1 List by Region - Visceral Anomalies General Terms 10127 Situs inversus 80,00 10125 Aneurysm 68,42 10126Fluid-filled abdomen -35,00 Brain 10131 Hydrocephaly 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 20,00 10132
1 List by Region - Visceral Anomalies General Terms 10127 Situs inversus 80,00 10125 Aneurysm 68,42 10126Fluid-filled abdomen -35,00 Brain 10131 Hydrocephaly 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 20,00 10132
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
List by Terms Visceral anomalies
 1 List by Terms Visceral anomalies Dilated 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 11 7 2 0 20,00 10201 Dilated aorta 9 8 2 1 5,26 10207 Dilated aortic arch 9 8 3 0 5,00 10213 Dilated carotid 3 12 4 1-47,37 10218
1 List by Terms Visceral anomalies Dilated 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 11 7 2 0 20,00 10201 Dilated aorta 9 8 2 1 5,26 10207 Dilated aortic arch 9 8 3 0 5,00 10213 Dilated carotid 3 12 4 1-47,37 10218
Table P-l. Summary of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects
 Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
7.1 SIX-DIGIT CODES FOR REPORTABLE BIRTH DEFECTS
 7. SIX-DIGIT CODES FOR REPORTABLE BIRTH DEFECTS Based on the British Pediatric Association (BPA) Classification of Diseases (979) and the World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases,
7. SIX-DIGIT CODES FOR REPORTABLE BIRTH DEFECTS Based on the British Pediatric Association (BPA) Classification of Diseases (979) and the World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases,
Auswertung visceraler Anomalien:
 Auswertung visceraler Anomalien: General 10125 Aneurysm 15 2 2 1 20 68,42 10126 Fluid-filled abdomen 4 11 5 0 20-35,00 10127 Situs inversus 18 2 0 0 20 80,00 Brain 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 11 7
Auswertung visceraler Anomalien: General 10125 Aneurysm 15 2 2 1 20 68,42 10126 Fluid-filled abdomen 4 11 5 0 20-35,00 10127 Situs inversus 18 2 0 0 20 80,00 Brain 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 11 7
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June 30, 2009
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ)
 Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
NYEIS Version 4.3 (ICD) ICD - 10 Codes Available in NYEIS at time of version launch (9/23/2015)
 D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE
 PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
Chromosome 13. Introduction
 Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on ICD-10 Coding of Neoplasms Introduction The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10 th Revision (ICD-10)
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on ICD-10 Coding of Neoplasms Introduction The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10 th Revision (ICD-10)
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
LABORATORY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL
 LABORATORY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL JUNE 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL JUNE 2018 LABORATORY SERVICES Table of Contents 25.1 Enrollment......................................................................
LABORATORY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL JUNE 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL JUNE 2018 LABORATORY SERVICES Table of Contents 25.1 Enrollment......................................................................
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Development of the urinary system
 Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Laboratory Services. Chapter
 Laboratory Services Chapter.1 Enrollment..................................................................... -2.1.1 Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988.............. -3.1.1.1 Waiver
Laboratory Services Chapter.1 Enrollment..................................................................... -2.1.1 Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988.............. -3.1.1.1 Waiver
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Name: Fetal Pig Dissection Internal Anatomy
 In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Appendix 3.1 Birth Defects Descriptions for NBDPN Core, Recommended, and Extended Conditions
 Birth Defects s for NBDPN Core, Recommended, and Extended Conditions Updated March 2017 Participating members of the Birth Defects s Group: Lorenzo Botto (UT) John Carey (UT) Cynthia Cassell (CDC) Tiffany
Birth Defects s for NBDPN Core, Recommended, and Extended Conditions Updated March 2017 Participating members of the Birth Defects s Group: Lorenzo Botto (UT) John Carey (UT) Cynthia Cassell (CDC) Tiffany
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
 BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
82330 CALCIUM; IONIZED. ICD-10 Codes that Support Medical Necessity. ICD-10 Code. Description. A15.0 Tuberculosis of lung
 82330 CALCIUM; IONIZED ICD-10 Codes that Support Medical Necessity ICD-10 Code Description A15.0 Tuberculosis of lung A15.4 Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymph nodes A15.5 Tuberculosis of larynx, trachea
82330 CALCIUM; IONIZED ICD-10 Codes that Support Medical Necessity ICD-10 Code Description A15.0 Tuberculosis of lung A15.4 Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymph nodes A15.5 Tuberculosis of larynx, trachea
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
Covered Diagnosis Code Reference Tool for Habilitative Services: Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy
 Covered Diagnosis Code Reference Tool for Habilitative Services: Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy Effective: October 1, 2017 OVERVIEW Habilitative services are provided for a person
Covered Diagnosis Code Reference Tool for Habilitative Services: Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy Effective: October 1, 2017 OVERVIEW Habilitative services are provided for a person
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Papworth Hospital NHS Trust INTRODUCTION. Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan INTRODUCTION
 Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
Slide 1 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Jakub Kadlec/Catherine Sudarshan NHS Trust Slide 2 INTRODUCTION Most common congenital illness in the newborn Affects about 4 9 / 1000 full-term live births in the UK 1.5
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
ICD-10 Common Codes per CMS
 Abdominal Pain (ICD09-CM 789.00 TO 789.09 range) R10.0 Acute abdomen R10.10 Upper abdominal pain, unspecified R10.11 Right upper quadrant pain R10.12 Left upper quadrant pain R10.13 Epigastric pain R10.2
Abdominal Pain (ICD09-CM 789.00 TO 789.09 range) R10.0 Acute abdomen R10.10 Upper abdominal pain, unspecified R10.11 Right upper quadrant pain R10.12 Left upper quadrant pain R10.13 Epigastric pain R10.2
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Page 1 of 16 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Professional Institutional
Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Page 1 of 16 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Professional Institutional
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities. Basic Training
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders
 Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Development of the urogenital system
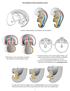 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
Fetal Pig Dissection. preserved fetal pig dissecting tray and paper towels length of string plastic storage bag and twist tie
 Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Professional Institutional
Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Professional Institutional
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Teaching Objectives
 Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
