Neonatal Periventricular Leukomalacia: Real-Time
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Sherman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 383 Neonatal Periventricular Leukomalacia: Real-Time Sonographic Diagnosis with CT Correlation Peter P. Chow 1. 2 J. Gerard Horgan 1, 3 Kenneth J. W. Taylor 1 The utility of real-time sonography in the diagnosis of neonatal periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) has been described only recently, Six cases are reported of PVL diagnosed by serial real-time scanning. The sonographic findings were correlated with the computed tomographic findings and the clinical history, In five of six infants in whom scanning was performed, characteristic multiseptated periventricular cavitations developed 2-3 weeks after birth or later, A transition from normal to increased periventricular echogenicity was often observed before the development of the periventricular cavitations in nonhemorrhagic PVL. The parenchymal abnormality demonstrated by sonography correlated well with an abnormal neurologic outcome. It is suggested that serial real-time scanning be performed in neonates whose history suggests the possibility of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, Nonspecific predictors of PVL include seizures, apnea, disturbed mental status, abnormal muscle tone, and leg weakness, Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) results from an ischemic insult to the neonatal brain with involvement of the peri ventricular white matter adjacent to the external angles of the lateral ventricles [1-5]. It is commonly found at autopsy in the brains of neonates. However, it is rarely diagnosed in living infants. Although real-time sonography has been used widely to diagnose intracranial hemorrhage and other abnormalities of the brains in neonates, the sonographic features of PVL are not well known [6-9]. We report six cases of neonatal PVL diagnosed primarily by real-time sonography. The early sonographic findings and the evolution of PVL on serial sonograms are emphasized. Computed tomographic (CT) scans were obtained to confirm the nature and extent of the parenchymal lesions. Subjects and Methods This article appears in the May/June 1985 issue of AJNR and the July 1985 issue of AJR. Received April 2, 1984; accepted after revision August 28, 1984., Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yale University School of Medicine, 333 Cedar St., New Haven, CT Address reprint requests to K. J. W. Taylor. 2 Present address: Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Health Science Center, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY Present address: Department of Radiology, Meath Hospital, Dublin, Ireland. AJNR 6: , May/June /85/ American Roentgen Ray Society Cranial sonograms were obtained with a real-time sector scanner (ATl 300). A 5 MHz transducer with a 90 field of view was used. Multiple coronal and parasagittal images were obtained through the anterior fontanelle. At least four examinations were performed in all but one of our patients (case 6). The indication for serial sonography was usually an abnormal neurologic examination or persistent seizure activity. Cranial CT scans were obtained on a GE 8800 or 9800 scanner. The patients were scanned at 5 mm intervals with 5-mm-thick slices. A summary of patients and clinical data is shown in table 1. The sonographic and CT findings are shown in table 2. Representative cases are illustrated. Representative Case Reports Case 1 A twin girl was born at 28 weeks gestation with a birth weight of 1025 g. The pregnancy was complicated by premature rupture of membranes (PROM) 6 weeks before delivery. A cesarean section was performed. The Apgar scores were 6 at both 1 and 5 min. The infant received assisted ventilation for 3Y2 weeks because of hyaline membrane disease and
2 384 CHOW ET AL. AJNR:6. May/June 1985 TABLE 1: Summary of Clinical Findings in Infants with Periventricular Leukomalacia Case No. Apgar Neurologic Findings (geslalion Iweeksl. Malernal Scores Cardiac Respiratory CSF birthweighl History at Status Status Examination Neonatal Postneonatal Igramsl) 1.5 min Period Period (28, 1025) PROM, CS 6,6 Pericardial RDS, apnea Normal Seizure Lost to FlU effusion 2 (28, 1200) None 8, 3 PDA, CHF BPD i Pressure Seizure Spastic diplegia at 6 mo; delayed development at 13 mo 3 (32, 1290) PROM 7, - Bradycardia BPD, apnea Normal Seizure, Scissoring of legs at hypertonia 2 mo 4 (32, 1580) Breech, head 3, 5 PDA RDS, apnea Hemorrhagic Seizure, Lost to FlU dystocia hyperreflexia, hypertonia in legs 5 (28, 1000) AP, CS 1, 4 PDA BPD Not performed Hyperreflexia, Spastic diplegia at 8 hypertonia mo in legs 6 (38,3500) AP, CS 2, 3 Hypotension None Normal Seizure, Lost to FlU hyperreflexia, hypertonia in legs Note.-CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; PROM = premature rupture of membrane; CS = cesarean section; RDS = respiratory distress syndrome; FlU = follow up; PDA = patent ductus arteriosus; CHF = congestive heart failure; BPD = bronchopulmonary dysplasia; mo = months; AP = abruption of placenta. TABLE 2: Sonographic and CT Findings in Infants with Periventricular Leukomalacia 1 (10) 2 (14) Case No. (Total No. of Sonograms) 3 (4) (14) 5 (8) (1). Early Sonography «2 weeks) SEH/IVH Grade I Grade II Peri ventricular Echogenicity N I (11d) N N I (8d) I (2d) N I (9d) I (8d) 20d 40d 13d Late Sonography (2:2 weeks) (time of cavitations) 17d 38d Not performed Note.-SEH = subependymal hemorrhage; IVH = intraventricular hemorrhage; N = nomnal; I = increased; d = days. Ventriculomegaly CT Findings Periventricular and subcortical lucency Periventricular and subcortical lucency Periventricular and subcortical lucency Periventricular hemorrhage Periventricular lucency Periventricular lucency occasional apneic episodes. Myoclonic seizures were noted soon after birth. Several spinal taps showed no evidence of infection. A cranial sonogram on the second day of life was normal (figs. 1A and 1 B). A sonogram on the 11 th day of life showed increased echogenicity of the periventricular areas (figs. 1 C and 1 D). Multiseptated cavitations had developed within the periventricular echogenic areas by 3 weeks of age (figs. 1 E and 1 F). A cranial CT scan on the same day demonstrated prominent bilateral irregular hypodense lesions in the periventricular white matter extending toward the cortex, consistent with PVL (fig. 1 G). Case 2 A 1200 g boy was born at 28 weeks gestation by spontaneous vaginal delivery. Apgar scores were 8 and 3 at 1 and 5 min, respectively. The infant's hospital course was complicated by respiratory distress syndrome, pneumothoraces, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) resulted in congestive heart failure and was treated initially with indomethacin and subsequently by surgical ligation at 3 weeks of age. Several cranial sonograms were normal in the first month of life. A sonogram 6 weeks after birth, however, revealed ventriculomegaly and bilateral, markedly increased echogenicity of the periventricular region with multiseptated cavitations (figs. 2A and 2B). CT on the same day demonstrated periventricular and subcorticallucencies and widening of the interhemispheric fissure, consistent with PVL (fig. 2C). A ventriculoperitoneal shunt was placed because of progressive hydrocephalus. Spastic diplegia was evident at the 6 month neurologic follow-up. At 13 months of age, the patient had delayed developmental age equivalent to 5 3,4 months.
3 AJNR :6. May/June 1985 NEONATAL PERIVENTRICULAR LEUKOMALACIA 385 Fig. 1.-Case 1. Nonhemorrhagic PVL. Coronal (A) and left parasagittal (8) sonograms on day 2. Normal peri ventricular echoes. Coronal (C) and left parasagittal (0) sonograms on day 11. Bilateral increased periventricular echoes extend from mid ventricle to occipital horn. Coronal (E) and left parasagittal (F) sonograms on day 21. Multiple cysts (arrows) developed in previously echogenic areas. G, Unenhanced CT scan on day 21. Bilateral periventricular hypodense areas extend toward cortex (arrowheads). Clearly defined cysts could not be seen. Case 3 A 1290 g boy was born at weeks gestation by vaginal delivery. PROM occurred at 32 hr before delivery. The Apgar score was 7 at 1 min. The infant had respiratory distress syndrome followed by bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Occasional episodes of apnea and bradycardia were noted during the hospitalization. The infant was noted to have alternating states of alertness and occasional seizurelike activity with scissoring of his legs and increased muscle tone. Two electroencephalograms were normal. Cerebrospinal fluid culture was negative. A sonogram at 2 days of age showed a left germinal matrix hemorrhage. A sonogram 8 days after birth revealed ventriculomegaly and increased periventricular echogenicity. Cranial CT at thi s time
4 386 CHOW ET AL. AJNR :6, May/June 1985 A Fig. 2.-Case 2. Nonhemorrhagic PVL. Coronal (A) and right parasagittal (B) sonograms at 40 days of age. Multiple bilateral periventricular cysts in region of trigone of lateral ventricle (arrows). Mild ventriculomegaly. C, Unen- B c hanced CT scan at 40 days of age. Marked bilateral periventricular hypodense areas with subcortical extension (arrows). Widening of interhemispheric fissure indicated cerebral atrophy. A B Fig. 3.-Case 3. Nonhemorrhagic PVL. Initial sonograms showed left germinal matrix hemorrhage at 2 days and ventriculomegaly and increased periventricular echogenicity at 8 days. Coronal (A) and left parasagittal (B) sonograms on day 13. Small cysts (arrowheads) had developed within periventricular echogenic areas. Lateral borders of echogenic areas were irregular but well defined. revealed marked periventricular hypodense areas. A sonogram at 13 days of age showed early cavitations within the echogenic periventricular areas (figs. 3A and 38). showed confluence of the small cysts and communication of these cysts with the ventricles (figs. 4F and 4G). CT showed periventricular and subcortical lucencies but did not reveal definite cysts. Case 4 A 1580 g boy was born at about 32 weeks gestation by breech vaginal delivery. The infant had asphyxia at birth with Apgar scores of 3 and 5 at 1 and 5 min, respectively. Due to hyaline membrane disease and episodes of apnea, assisted ventilation was required for 5 weeks. A POA was treated with indomethacin. Myoclonic seizure was noted 2 days after birth. Neurologic examination revealed symmetric, brisk deep tendon reflexes, decreased active tone, and increased passive tone in the legs. A sonogram on the second day of life revealed bilateral subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage (figs. 4A-4C). There were also bilateral intense periventricular echoes that corresponded to periventricular hemorrhage on CT (fig. 40). Multiseptated cavitations were shown by sonography to have developed within the periventricular echogenic areas on the 17th day (fig. 4E). Subsequent sonograms Discussion PVL is a common variety of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [10).' The reported incidence of PVL varies with the selection of case material. The overall autopsy incidence of PVL approximates 20% [1-6]. PVL is observed particularly often in premature infants with postnatal survival of more than 6 days [4]. A significant history of cardiorespiratory disturbances in the neonatal period is especially common among these patients. There are no early neurologic findings specific for PVL. Seizure, apneic spells, disturbance in mental status, abnormal muscle tone, and leg weakness may be found [10]. PVL is not a lethal lesion, but may lead to degeneration of the corticospinal tract, particularly to the legs. The major long-
5 AJNR :6. May/June 1985 NEONATAL PERIVENTRICULAR LEUKOMALACIA 387 Fig. 4.-Case 4. Hemorrhagic PVL. A-C, Sonograms at 2 days of age. A, Anterior coronal sonogram. Bilateral germinal matrix hemorrhage. Posterior coronal (8) and right parasagittal (C) sonograms. Bilateral intense peri ventricular echoes were difficult to distinguish from choroid plexus. D, Unenhanced CT scan at age 5 days. Bilateral germinal matrix/intraventricular hemorrhage and peri ventricular hemorrhage. E, Right parasagittal sonogram on day 17. Multiple cysts within periventricular echogenic areas. Ventriculomegaly. F, Unenhanced CT scan on day 29. No definite cysts discernible within peri ventricular hypodense areas. Coronal (G) and left parasagittal (H) sonograms on day 29. Periventricular cysts enlarged and communicated with ventricles. o E F G H term sequela of PVL is spastic diplegia. Severe lesions may affect the arms as well as visual and intellectual functions. Most authors now believe PVL to be the result of a localized infarctive process in watershed areas between the ventriculopetal and ventriculofugal branches of deep penetrating arteries [2-4]. The two most common sites for PVL are the occipital radiation at the trigone of the lateral ventricles and the white matter around the foramen of Monro. PVL has not been attributed to generalized hypoxia because these lesions are pathologically characteristic of infarction and because areas characteristically damaged by hypoxia (cerebellar cortex and hippocampus) are normal [2, 3]. The evolution of PVL was postulated by OeReuck et al. [2] in an autopsy series of 13 cases. The earliest stage is char-
6 388 CHOW ET AL. AJNR:6, May/June 1985 acterized by foci of coagulation necrosis, Later, there is proliferation of astrocytes and macrophages, followed by phagocytosis of the necrotic tissue, with resulting periventricular cavities of varying size surrounded by gliosis. If the ependyma is destroyed, the cavities may then communicate with the ventricular system. Second '1ry hemorrhage, ranging from microscopic to massive, may occur within these periventricular infarcts, and this feature was demonstrated in 25% of cases studied at postmortem examiration by Armstrong and Norman [3]. Thinning of the white matter can lead to ventriculomegaly in larger infarcts. The progression of the sonographic findings of PVL in our study correlates well with the pathologic evolution. The initial sonogram shortly after birth is often normal. Increased periventricular echogenicity may be demonstrated in the first 2 weeks of life, representing ischemia or hemorrhage [8, 11]. CT at this stage demonstrates peri ventricular lucency unless secondary hemorrhage has occurred. It is not until about 2-3 weeks after birth and sometimes later that the characteristic peri ventricular multiseptated cysts develop and then the diagnosis of PVL becomes certain. Therefore, in neonates with a history of asphyxia and a normal sonogram shortly after birth, follow-up sonograms should be obtained, perhaps on a weekly basis. Our study demonstrated the value of sonography in the diagnosis of neonatal PVL. The location and extent of the parenchymal lesions can be assessed accurately by sonography. Although it is unable to distinguish hemorrhagic from non hemorrhagic infarction, sonography demonstrates periventricular cystic changes not well seen on CT. The fact that neither CT nor sonography detects PVL as often as in autopsy series suggests that both have limited sensitivity. Magnetic resonance imaging may prove to be superior [12, 13]. Subependymaljintraventricular hemorrhage, a more common hemorrhagic lesion of premature infants, may extend into the periventricular white matter and mimic hemorrhagic PVL. The characteristic position for PVL, dorsal and lateral to the germinal matrix layer, helps differentiate these entities. Similarly, focal and multifocal ischemic brain necrosis is associated with cavity formation, tending to follow the distribution of the major cerebral vessels. Multiple cystic encephalomalacia results from a variety of insults [14, 15], producing cysts of relatively large size and not necessarily located in the periventricular white matter. Recognition of PVL is of considerable clinical significance as it implies significant brain damage and a less favorable neurologic developmental outcome. Prompt diagnosis with real-time sonography may affect family counseling and further management. Vigorous supportive care, particularly maintenance of ventilation and perfusion, and control of seizure can be instituted to prevent accentuation of the existing injury [10]. In neonates at risk for the development of PVL, the peri ventricular echogenicity should be evaluated carefully. Appreciation of the abnormal, increased echogenicity equal to or greater than that of the choroid plexus and in the characteristic anatomic location should raise suspicion of PVL. The predictable evolution of the sonographic appearances on sequential scans will establish the diagnosis of this distinct entity. REFERENCES 1. Banker BO, Larroche JC. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. Arch Neural 1962;7: OeReuck J, Chattha AS, Richardson EP. Pathogenesis and evolution of periventricular leukomalacia in infancy. Arch Neural 1972;27: Armstrong 0, Norman MG. Peri ventricular leucomalacia in neonates: complications and sequelae. Arch Dis Child 1974;49 : Shuman RM, Selednik LJ. Periventricular leukomalacia. Arch Neural 1980;37: Leech RW, Alvord EC. Morphologic variations in periventricular leukomalacia. Am J Patho/1974;74 : Hill A, Melson GL, Clark HB, Volpe JJ. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia: diagnosis by real-time ultrasound and correlation with autopsy finding. Pediatrics 1982;69 : Levene MI, Wigglesworth JS, Oubowitz V. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia in the neonate: a real-time ultrasound study. Pediatrics 1983;71 : Martin OJ, Hill A, Fitz CR, Oaneman A, Havill OA, Becker LE. Hypoxic/ischaemic cerebral injury in the neonatal brain: a report of sonographic features with computed tomographic correlation. Pediatr Radio/1983;13 : Manger MN, Feldman RC, Brown WJ, Mitchell LS, Wattarn KF, Shields WO. Intracranial ultrasound diagnosis of neonatal periventricular leukomalacia. J Ultrasound Med 1984;3 : Volpe JJ. Neurology of the newborn. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1981 : Hill A, Martin OJ, Oaneman A, Fitz CR. Focal ischemic cerebral injury in the newborn: diagnosis by ultrasound and correlation with computed tomographic scan. Pediatrics 1983;71 : Johnson MA, Pennock JM, Bydder GM, et al. Clinical NMR imaging of the brain in children: normal and neurologic disease. AJNR 1983;4: , AJR 1983;141 : Levene MI, Whitelaw KA, Oubowitz V, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in children. Br Med J [Clin Res] 1982;285 : Chutorian AM, Michener RC, Oefendini R, Hilal SK, Gamboa ET. Neonatal polycystic encephalomalacia: four new cases and review of the literature. J Neural Neurasurg Psychiatry 1979; 42 : Stannard MW, Jimenez JF. Sonographic recognition of multiple cystic encephalomalacia. AJNR 1983;4: , AJR 1983;141:
Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia: Sonographic
 439 Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia: Sonographic and CT Findings Dieter Schellinger 1 Edward G. Grant James D. Richardson Periventricular leukoencephalopathy (PVL) is a pathologic process that has
439 Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia: Sonographic and CT Findings Dieter Schellinger 1 Edward G. Grant James D. Richardson Periventricular leukoencephalopathy (PVL) is a pathologic process that has
Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Periventricular Cavitations in the First Week of Life
 291 Periventricular Cavitations in the First Week of Life Marc S. Keller 1 Michael A. DiPietro 2 Rita L. T eele 3 Susan J. White 2 Harbhajan S. Chawla 4 Marjorie Curtis-Cohen4 Caroline E. Blane 2 Eleven
291 Periventricular Cavitations in the First Week of Life Marc S. Keller 1 Michael A. DiPietro 2 Rita L. T eele 3 Susan J. White 2 Harbhajan S. Chawla 4 Marjorie Curtis-Cohen4 Caroline E. Blane 2 Eleven
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
Prevalence of "Compressed" and Asymmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic
 Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
MR Imaging of Periventricular Leukomalacia in Childhood
 111 MR Imaging of Periventricular Leukomalacia in Childhood Olof Flodmark 1 Brian Lupton 2 David Li 1 Gary K. Stimac 3 Elke H. Roland 2 Alan HiII2 Michael F. Whitfield 2 Margaret G. Norman 4 Eight children
111 MR Imaging of Periventricular Leukomalacia in Childhood Olof Flodmark 1 Brian Lupton 2 David Li 1 Gary K. Stimac 3 Elke H. Roland 2 Alan HiII2 Michael F. Whitfield 2 Margaret G. Norman 4 Eight children
neurodevelopmental outcome in
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987, 62, 3-36 Periventricular leucomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome in C L FAWER, P DIEBOLD, AND A CALAME preterm infants Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987, 62, 3-36 Periventricular leucomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome in C L FAWER, P DIEBOLD, AND A CALAME preterm infants Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois,
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound
 Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review
 Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1
 P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1 Bokyung Kim Han, M.D., Mu n hyang Lee, M.D. 2, Hye - Kyung Yoon, M.D., Kyung-Jae
P rominent Extraaxial CSF Space on Cranial Ultra s o u n d in Infants: C o r relation with Neuro d evelopmental Outc o m e 1 Bokyung Kim Han, M.D., Mu n hyang Lee, M.D. 2, Hye - Kyung Yoon, M.D., Kyung-Jae
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1203-1207 Intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation J Q TROUNCE, D FAGAN, AND M I LEVENE Department of
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1203-1207 Intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation J Q TROUNCE, D FAGAN, AND M I LEVENE Department of
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
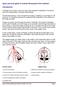 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review
 Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia Intraventricular Hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is bleeding inside the lateral ventricles. Bleeding frequently occurs in areas
Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia Intraventricular Hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is bleeding inside the lateral ventricles. Bleeding frequently occurs in areas
Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants
 253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
Periventricular/Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Newborn
 Khalid N. Haque, FRCP(Ed), FRCP(I), FAAP, FICP, DCH, DTM&H; Omar B. A. Basit, MRCP(UK), DCH; Meeralebbae M. Shaheed, MD, MRCP(UK), DCH From the Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, College
Khalid N. Haque, FRCP(Ed), FRCP(I), FAAP, FICP, DCH, DTM&H; Omar B. A. Basit, MRCP(UK), DCH; Meeralebbae M. Shaheed, MD, MRCP(UK), DCH From the Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, College
Cribside Neurosonography:
 501 Cribside Neurosonography: Real-Time Sonography for Intracranial Investigation of the Neonate Mary K. Edwards 1 David L. Brown 1 Jans Muller Charles B. Grossman 1 Gonzalo T. Chua 1 prospective study
501 Cribside Neurosonography: Real-Time Sonography for Intracranial Investigation of the Neonate Mary K. Edwards 1 David L. Brown 1 Jans Muller Charles B. Grossman 1 Gonzalo T. Chua 1 prospective study
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development
 Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1196-1202 Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate J Q TROUNCE, N RUTTER, AND M LEVENE Department of Child Health,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1196-1202 Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate J Q TROUNCE, N RUTTER, AND M LEVENE Department of Child Health,
Cerebrovascular Accidents in Neonates Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation
 355 Cerebrovascular Accidents in Neonates Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation George A. Taylor1 "3 Charles R. Fitz 1-2 Sudesh Kapur2 ' 4 Billie L. Short2-5
355 Cerebrovascular Accidents in Neonates Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation George A. Taylor1 "3 Charles R. Fitz 1-2 Sudesh Kapur2 ' 4 Billie L. Short2-5
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes
 Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1
 9 The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1 periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). These lesions are more common in the smallest and most
9 The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1 periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). These lesions are more common in the smallest and most
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
Neuro. Development. Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC. ! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation. ! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months!
 Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation
 Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation Benedetta Pettorini Consultant Paediatric Neurosurgeon Alder Hey Childrens Hospital Liverpool, UK Risk Factors for IVH 1. Prematurity: Occurs
Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation Benedetta Pettorini Consultant Paediatric Neurosurgeon Alder Hey Childrens Hospital Liverpool, UK Risk Factors for IVH 1. Prematurity: Occurs
I t is increasingly recognised that arterial cerebral infarction
 F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33: Underlying causal pathways. Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum. Acute near total asphyxia
 Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI
 Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease
 Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation.
 Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation. Ricardo Faingold,MD Montreal Children s Hospital Medical
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation. Ricardo Faingold,MD Montreal Children s Hospital Medical
I mprovements in perinatal and neonatal care have contributed
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posthaemorrhagic ventricular in the premature infant: natural history and predictors of outcome B P Murphy, T E Inder, V Rooks, G A Taylor, N J Anderson, N Mogridge, L J Horwood, J J Volpe...
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posthaemorrhagic ventricular in the premature infant: natural history and predictors of outcome B P Murphy, T E Inder, V Rooks, G A Taylor, N J Anderson, N Mogridge, L J Horwood, J J Volpe...
Intracranial Serratia Infection in Preterm Newborn Infants
 447 Intracranial Serratia Infection in Preterm Newborn Infants A. H. Lam' A. Berrl M. desilva' G. Williams 2 Four cases of cerebral Serratia infection in preterm infants were diagnosed with the aid of
447 Intracranial Serratia Infection in Preterm Newborn Infants A. H. Lam' A. Berrl M. desilva' G. Williams 2 Four cases of cerebral Serratia infection in preterm infants were diagnosed with the aid of
Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review
 Review Article Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review Shahina Bano, Vikas Chaudhary 1, Umesh Chandra Garga Department of Radiodiagnosis, PGIMER, Dr. RML Hospital, 1 Department
Review Article Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review Shahina Bano, Vikas Chaudhary 1, Umesh Chandra Garga Department of Radiodiagnosis, PGIMER, Dr. RML Hospital, 1 Department
Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
ultrasonography in preterm infants: association with outcome
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
Insults to the Term Brain
 Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Periventricular white matter injury, that is, periventricular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography
 Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Guidelines for the Procedure and Atlas of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy With 121 Figures and
Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Guidelines for the Procedure and Atlas of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy With 121 Figures and
Intracranial Abnormalities in Infants Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Update on Sonographic and CT Findings
 Intracranial Abnormalities in Infants Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Update on Sonographic and CT Findings Dorothy I. Bulas, George A. Taylor, Regina M. O Donnell, Billie Lou Short,
Intracranial Abnormalities in Infants Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Update on Sonographic and CT Findings Dorothy I. Bulas, George A. Taylor, Regina M. O Donnell, Billie Lou Short,
The clinical presentation of preterm cerebellar haemorrhage
 Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:1249 1253 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1217-4 ORIGINAL PAPER The clinical presentation of preterm cerebellar haemorrhage Ginette M. Ecury-Goossen & Jeroen Dudink & Maarten Lequin & Monique
Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:1249 1253 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1217-4 ORIGINAL PAPER The clinical presentation of preterm cerebellar haemorrhage Ginette M. Ecury-Goossen & Jeroen Dudink & Maarten Lequin & Monique
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge
 Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
P eriventricular leucomalacia (PVL), which is characterised
 F275 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitations of ultrasonography for diagnosing white matter damage in preterm infants T Debillon, S N Guyen, A Muet, M P Quere, F Moussaly, J C Roze... See end of article for authors
F275 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitations of ultrasonography for diagnosing white matter damage in preterm infants T Debillon, S N Guyen, A Muet, M P Quere, F Moussaly, J C Roze... See end of article for authors
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Transcranial Perinatal Neurosonogram for Intracranial Pathology: Study of 165 Cases
 Transcranial Perinatal Neurosonogram for Intracranial Pathology: Study of 165 Cases K Humsene 1, N Krishnaveni 2, B Sarada 3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Background: The presence of open fontanelle in infants
Transcranial Perinatal Neurosonogram for Intracranial Pathology: Study of 165 Cases K Humsene 1, N Krishnaveni 2, B Sarada 3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Background: The presence of open fontanelle in infants
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara
 Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Superficial Echogenic Lesions Detected on Neonatal Cranial Sonography
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Superficial Echogenic Lesions Detected on Neonatal Cranial Sonography Possible Indicators of Severe Birth Injury Byoung Hee Han, MD, Mi Jin Song, MD, Kyung Sang Lee, MD, Young-Hwa Kim,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Superficial Echogenic Lesions Detected on Neonatal Cranial Sonography Possible Indicators of Severe Birth Injury Byoung Hee Han, MD, Mi Jin Song, MD, Kyung Sang Lee, MD, Young-Hwa Kim,
Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Neonatal Brain in Cases of Birth Asphyxia
 Original Article Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Neonatal Brain in Cases of Birth Asphyxia DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/16149:2106 Radiology Section Susmita Giri, Tapan Kumar Jana, Arunabha Tapadar ABSTRACT
Original Article Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Neonatal Brain in Cases of Birth Asphyxia DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/16149:2106 Radiology Section Susmita Giri, Tapan Kumar Jana, Arunabha Tapadar ABSTRACT
State-of-the-Art Cranial Sonography: Part 1, Modern Techniques and Image Interpretation
 Pediatric Imaging Review Lowe and ailey Cranial Sonography Pediatric Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.98 on 02/10/18 from IP address 37.44.206.98. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pediatric Imaging Review Lowe and ailey Cranial Sonography Pediatric Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.206.98 on 02/10/18 from IP address 37.44.206.98. Copyright RRS. For personal
Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection
 Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection Abhik Das, RTI International John Barks, University of Michigan Subrata Sarkar, University of Michigan
Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection Abhik Das, RTI International John Barks, University of Michigan Subrata Sarkar, University of Michigan
Quantitative Sonographic Feature Analysis of Clinical Infant Hypoxia: A Pilot Study
 Quantitative Sonographic Feature Analysis of Clinical Infant Hypoxia: A Pilot Study Lori L. Barr, Patrick J. McCullough, William S. Ball, Jr, Brian H. Krasner, Brian S. Garra, and James A. Deddens PURPOSE:
Quantitative Sonographic Feature Analysis of Clinical Infant Hypoxia: A Pilot Study Lori L. Barr, Patrick J. McCullough, William S. Ball, Jr, Brian H. Krasner, Brian S. Garra, and James A. Deddens PURPOSE:
Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
 Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Department of Neurosurgery, Emory University; and 2 Pediatric Neurosurgery Associates at Children s Healthcare of Atlanta, Georgia
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:184 189, 2014 AANS, 2014 Poor correlation between head circumference and cranial ultrasound findings in premature infants with intraventricular hemorrhage Clinical article Martha-Conley
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:184 189, 2014 AANS, 2014 Poor correlation between head circumference and cranial ultrasound findings in premature infants with intraventricular hemorrhage Clinical article Martha-Conley
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Pediatr Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 October 30.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Pediatr Neurol. 2008 May ; 38(5): 329 334. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.12.012. Very Early Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Premature
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Pediatr Neurol. 2008 May ; 38(5): 329 334. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.12.012. Very Early Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Premature
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant April 2009 2 Mészàros A, el Helou S, Zimmermann U, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant April 2009 2 Mészàros A, el Helou S, Zimmermann U, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital
 Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital Please complete in black ballpoint pen Hospital name: Form 6: Baby Outcomes Please complete this form when a Baby-OSCAR participant is transferred to another
Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital Please complete in black ballpoint pen Hospital name: Form 6: Baby Outcomes Please complete this form when a Baby-OSCAR participant is transferred to another
NORMAL PARAMETERS OF VENTRICULAR SYSTEM IN HEALTHY INFANTS
 NORMAL PARAMETERS OF VENTRICULAR SYSTEM IN HEALTHY INFANTS J.P. Soni B.D. Gupta M. Soni R.N. Singh N.N. Purohit M. Gupta D.R. Dabi K.R. Nemal ABSTRACT Six hundred healthy inborn newborns and infants upto
NORMAL PARAMETERS OF VENTRICULAR SYSTEM IN HEALTHY INFANTS J.P. Soni B.D. Gupta M. Soni R.N. Singh N.N. Purohit M. Gupta D.R. Dabi K.R. Nemal ABSTRACT Six hundred healthy inborn newborns and infants upto
The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique
 The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique A. James Barkovich, University of California, San Francisco The central nervous system (CNS) of the neonate may be injured by a number
The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique A. James Barkovich, University of California, San Francisco The central nervous system (CNS) of the neonate may be injured by a number
Incidence and diagnosis of unilateral arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants *
 J. Perinat. Med. 33 (2005) 170 175 Copyright by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/JPM.2005.032 Short communication Incidence and diagnosis of unilateral arterial cerebral infarction in newborn
J. Perinat. Med. 33 (2005) 170 175 Copyright by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/JPM.2005.032 Short communication Incidence and diagnosis of unilateral arterial cerebral infarction in newborn
In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage
 In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage G Dekker, MB ChB, MFam Med H B Louw, S Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rad (SA) M Pienaar, BSc, MB ChB S Hlongwane, MB ChB A Brandt, MB ChB D van der Merwe, MB ChB Department
In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage G Dekker, MB ChB, MFam Med H B Louw, S Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rad (SA) M Pienaar, BSc, MB ChB S Hlongwane, MB ChB A Brandt, MB ChB D van der Merwe, MB ChB Department
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Neurosonography of the Pre-Term Neonate
 Neurosonography of the Pre-Term Neonate Neurosonography of the Pre-Term Neonate Edited by Edward G. Grant With Contributions by James D. Richardson, Dieter Schellinger, Yolande F. Smith, K.N. Siva Subramanian,
Neurosonography of the Pre-Term Neonate Neurosonography of the Pre-Term Neonate Edited by Edward G. Grant With Contributions by James D. Richardson, Dieter Schellinger, Yolande F. Smith, K.N. Siva Subramanian,
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
Cranial ultrasound abnormalities in full term infants in a postnatal ward: outcome at 12 and 18 months
 F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Objectives. Introduction 11/2/2015
 Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Ventricular Septa in the Neonatal Age Group: Diagnosis
 1065 Ventricular Septa in the Neonatal ge Group: Diagnosis and Considerations of Etiology Dieter Schellinger' Edward G. Grant' Herbert J. Manz 2 Nicholas J. Patron as' Ronald H. Uscinski 3 Twenty-four
1065 Ventricular Septa in the Neonatal ge Group: Diagnosis and Considerations of Etiology Dieter Schellinger' Edward G. Grant' Herbert J. Manz 2 Nicholas J. Patron as' Ronald H. Uscinski 3 Twenty-four
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal gastric perforation
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal gastric perforation September 2002 2 Zankl A, Stähelin J, Roth K, Boudny P and Zeilinger G, Children s Hospital of Aarau (ZA, SJ, RK, ZG) and Institute of Pathology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal gastric perforation September 2002 2 Zankl A, Stähelin J, Roth K, Boudny P and Zeilinger G, Children s Hospital of Aarau (ZA, SJ, RK, ZG) and Institute of Pathology
Posterior Fontanelle Sonography: An Acoustic Window into the Neonatal Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1274 1282, August 2004 Posterior Fontanelle Sonography: An Acoustic Window into the Neonatal Brain Flavia Correa, Goya Enríquez, José Rosselló, Javier Lucaya, Joaquim Piqueras,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1274 1282, August 2004 Posterior Fontanelle Sonography: An Acoustic Window into the Neonatal Brain Flavia Correa, Goya Enríquez, José Rosselló, Javier Lucaya, Joaquim Piqueras,
The incidence of cerebral palsy (CP) is
 Paediatrica Indonesiana p-issn 0030-9311; e-issn 2338-476X; Vol.58,.2(2018). p. 95-100; doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14238/pi58.2.2018.95-100 Original Article Risk factors and the occurrence of cerebral palsy
Paediatrica Indonesiana p-issn 0030-9311; e-issn 2338-476X; Vol.58,.2(2018). p. 95-100; doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14238/pi58.2.2018.95-100 Original Article Risk factors and the occurrence of cerebral palsy
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form
 National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
Neonatal Seizure. Dr.Nawar Yahya. Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan. Supervised by:
 Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
The rationale for routine cerebral ultrasound in premature infants
 Pediatr Radiol (2015) 45:646 650 DOI 10.1007/s00247-014-2985-1 RESEARCH FORUM The rationale for routine cerebral ultrasound in premature infants Maria I. Argyropoulou & Corinne Veyrac Received: 4 October
Pediatr Radiol (2015) 45:646 650 DOI 10.1007/s00247-014-2985-1 RESEARCH FORUM The rationale for routine cerebral ultrasound in premature infants Maria I. Argyropoulou & Corinne Veyrac Received: 4 October
Cerebellar Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
RESEARCH ARTICLE EVALUATION OF NEUROIMAGING IN CEREBRAL PALSY. S.H. Hasanpour avanji MD
 RESEARCH ARTICLE EVALUATION OF NEUROIMAGING IN CEREBRAL PALSY S.H. Hasanpour avanji MD Assistant Professor of Child Neurology, Iran University of Medical Sciences Corresponding Author: S.H. Hasanpour avanji
RESEARCH ARTICLE EVALUATION OF NEUROIMAGING IN CEREBRAL PALSY S.H. Hasanpour avanji MD Assistant Professor of Child Neurology, Iran University of Medical Sciences Corresponding Author: S.H. Hasanpour avanji
Neurological and Neuromuscular Disorders. Elizabeth Papp, RN, MSN, CNS
 Neurological and Neuromuscular Disorders Elizabeth Papp, RN, MSN, CNS June, 2018 Neuromuscular Birth Injuries: Overview Nerve damage caused by trauma during delivery Prolonged labor LGA CPD Abnormal presentation
Neurological and Neuromuscular Disorders Elizabeth Papp, RN, MSN, CNS June, 2018 Neuromuscular Birth Injuries: Overview Nerve damage caused by trauma during delivery Prolonged labor LGA CPD Abnormal presentation
