LYMPHOCYTIC MENINGITIS WITH LUNG INVOLVEMENT OCCURRING IN CHILDHOOD
|
|
|
- Ross Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LYMPHOCYTIC MENINGITIS WITH LUNG INVOLVEMENT OCCURRING IN CHILDHOOD BY JOHN APLEY, M.D., M.R.C.P. Little more than twenty years ago Wallgren (1925) separated from the confused group of the meningitides those with pronounced lymphocytosis in the cerebrospinal fluid yet not due to tuberculosis or to syphilis. Since that time his 'acute aseptic meningitis' has become variously known as lymphocytic meningitis, choriomeningitis, and so on. It is considered that in approximately one-third of the cases a virus is undoubtedly implicated (Baird and Rivers, 1938), and at least three different types of virus have so far been identified. In the past two decades the term 'atypical pneumonia' has come into common use, to cover a clinical group of infectious diseases which are similar in many respects. In a considerable proportion of cases in this group viruses are also considered to be the causative agents, and have in some instances been isolated. Relating these two groups of diseases, both at one time euphemistically labelled ' benign,' some interesting facts have recently come to light. A virus isolated from a case of atypical pneumonia in man gave rise either to pneumonia or to meningitis in mice, according to the site of inoculation (Francis and Magill, 1938). As a corollary, the antigen developed in animals by this so-called ' meningo- (From the Children's Hospital, Bristol) pneumonitis ' was fixed by human serum from many cases of atypical pneumonia (Rake et al., 1941). Moreover, rare cases have now been recorded in which both the nervous system and the lungs were affected by virus disease in the same patient (Scadding, 1937; Reimann, 1938; Smadel et al., 1942; Hein, 1943; Perrone and Wright, 1943). In one case the virus of lymphocytic meningitis was shown to have changed its site of election; at autopsy it was demonstrated that the lungs were affected, while the nervous system remained uninvolved (Smadel et al., 1942). There is, therefore, some relationship, albeit a rare one, between these two disease groups. The apparent rarity of involvement of both systems in a single patient may, however, be fallacious. In part it can be explained by the commonly benign course of the infections, so that revealing autopsies are exceptional; and it may be also, to some extent, an index of incompleteness of investigation. On the one hand, in atypical pneumonia symptoms suggesting the possibility of nervous involvement are notably common. Severe headache, for example, is a prominent symptom; lumbar puncture, however, is rarely performed. It is particularly in childhood that mild nervous manifestations occurring with chest disease tend to be labelled 'meningism,' and may, with improvement, be dismissed without investigation. On the other hand, in lymphocytic meningitis minor abnormal physical signs in the lungs tend to be regarded as of no significance. Atypical pneumonia is notoriously difficult to detect clinically, yet in how many instances of lymphocytic meningitis is the chest radiographed? In this connexion, perusal of eleven consecutive case reports of infants and older children who had suffered from lymphocytic meningitis revealed that abnormal physical signs in the chest had been recorded in four. Lymphocytic meningitis is predominantly a disease of childhood. Atypical pneumonia, on the contrary, commonly affects adults. The remarkably few recorded cases in which both the nervous and respiratory symptoms have been demonstrably involved in the same patient are confined to adults; the following cases suggest a similar combination in children. Case Reports Case 1. D. P., ten months old, was admitted to hospital on March 7, 1946, with a history of four days' anorexia, constipation, and repeated vomiting. On the second day of the illness she had become feverish and drowsy, and a macular rash appeared all over the body, passing off by the next day. On the fourth day she developed a stiff neck; the parents became alarmed, and she was brought to hospital. 18
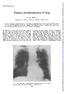
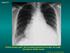
2 LYMPHOCYTIC MENINGITIS WITH LUNG INVOL VEMENT 19 (fig. 2). Three weeks later the lungs were clinically and radiologically clear. A Mantoux test ( 110,000) was negative. The general condition remained poor for two weeks, then quickly improved. Irregular fever persisted for five weeks, after which the patient was sent home. When seen two months later she had remained well, there were no abnormal physical signs on examination, and a radiograph showed that the chest was clear. Sulphadiazine had no appreciable effect on the disease process. The effect of penicillin was extremely doubtful; 360,000 units given during three days at the commencement of the period in hospital produced no evident change, but 960,000 units during eight days about the middle of this period coincided with a fall in temperature almost to the normal level. FIG. I.-CaSe 1: opaque shadow at right lung base. FIG. 2.-Case 1 (after thirteen days): basal shadow resolved, new area of opacity in right upper lobe. EXAMNATION ON ADMISSION. The temperature was 103- F. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Neck rigidity was marked. The spinal fluid contained 17 cells (85 per cent. lymphocytes) per c.mm., 100 mg. protein, and 680 mg. chlorides per 100 c.cm., but no organisms were seen on direct examination and zulture was sterile. Nine days later the cells had increased to 50 per c.mm., almost all lymphocytes. The neck rigidity passed off in about two weeks. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. On admission the respiration rate was per minute, and harsh breath sounds were audible throughout the lungs. Next day a radiograph showed a shadow at the right lung base (fig. 1). At no time was coughing a feature of the illness, and no localizing signs were elicited in the lungs. but thirteen days later a radiograph showed that the original shadow had cleared and a new one had appeared in the right upper zone Case 2. N. B., five years and ten months old, was admitted to hospital on March 11, There was a history of two weeks' cough and cold, with vomiting and fever after the first few days. A few days before admission the fever became more pronounced and was accompanied by thirst and constipation, and photophobia developed. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. When first seen at hospital he was drowsy and extremely irritable. Photophobia was marked, neck rigidity pronounced, and Kernig's sign positive. The spinal fluid FIG. 3.-Case 2: consolidation of right upper lung and left base.
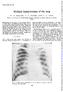
3 20 FIG. 4.--Case 2 (after five days): complete resolution at left base, consolidation and segmental collapse of right upper lung. contained 26 cells per c.mm., predominantly lymphocytes, and 70 mg. protein per 100 c.cm., but no organisms were visible on direct examination, and culture was sterile. A few days later the cells had increased to 51 per c.mm., protein was 45 mg. per cent., and chlorides 720 per cent., and direct examination and culture were again non-productive. After a further eleven days the fluid contained 6 lymphocytes per c.mm., protein and chlorides were respectively 15 and 720 mg. per cent., direct examination and culture were again negative, Lange test showed , and Wassermann reaction was negative. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. On admission to hospital the respiration rate was 40 per minute, and there was clinical evidence of consolidation of the right upper lung, and possibly of the extreme left base. Chest radiograph showed shadows in these regions (fig. 3). After five days the smaller of these shadows, that at the left base, had completely cleared (fig. 4), but in the right upper lung a minor degree of segmental collapse was superimposed. The shadow in the right lung gradually cleared, though even after three months a small thickened area the size of a pea was still visible in the radiograph. One month later the radiograph was completely clear. Mantoux tests to a dilution of 1/100 were negative, and sputum examination revealed no tubercle bacilli. At the height of the illness the blood contained 14,000 cells per c.mm., of which 68 per cent. were polymorphonuclear leucocytes. ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD FIG. 5.-Case 3: enlarged left hilar shadow. For two weeks after admission the temperature was raised four or five degrees; for a further three weeks irregular fluctuation round the 99" F. level was maintained. The respiration rate quickly fell to normal, but a mild cough persisted for several weeks. Photophobia was noted for about a month after admission, and during this period the patient vomited occasionally. There was no evident response to sulphadiazine administered over two separate periods of several days. Case 3. K. F., one year and eight months old, was admitted on March 13, 1946, with a history of irritability and vomiting for one week. CENYRAL NERvous SYSTEM. On admission he was markedly irritable, the anterior fontanelle was patent and bulging, neck rigidity was noted, Kernig's sign was positive, and the left pupil was larger than the right, though both reacted to light and accommodation. The spinal fluid contained 350 cells per c.mm., predominantly lymphocytes, the protein content was considerably higher than 200 mg. per cent., and direct examination and culture were negative for organisms. Two weeks later the number of cells had fallen to 31 lymphocytes per c.mm., protein and chlorides were respectively 80 mg. and 700 mg. per cent., and again direct examination and culture were non-productive. Signs of meningism persisted for two weeks; bulging of the fontanelle was the last abnormal sign to disappear.
4 LYMPHOCYTIC MENINGITIS WITH LUNG INVOLVEMENT RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. The respiration rate on admission was 25 per minute. The patient had no cough, but moist sounds were audible at the left lung mid-zone. These adventitia persisted locally for a week, but repeated chest radiographs showed only enlargement ofthe left hilum (fig. 5). Mantoux tests were negative to a dilution of 1/1,000. After five days in hospital the child's general condition improved, though signs of meningism persisted longer, and the temperature was slightly and irregularly raised for three weeks from the date of admission. There was no evidence of response to sulphadiazie given over two separate periods of several days' duration. Cont It is a striking fact that au three cases were admitted to hospital within the space of one week, two to one hospital and the third to another. The patients were admitted from one large city, but their homes are separated from each other by a mile or more. No epidemic was prevalent at the time, and no connexion between the cases has been suggested. Geneal syjomnatdooy. Persistent vomiting was an unexpected symptom common to all three patients. A macular rash, as in case 1, has been reported in similar cases (Reimann et al, 1942, and Hein, 1943), and occurs in apparently uncomplicated cases of lymphocytic meningitis. Central nervou system. In all cases meningeal involvement was marked. The photophobia in case 2 and the pupillary changes in case 3 suggest in addition some degree of encephalitis. This is consistent with previous findings; in the few cases of lymphocytic meningtis which have come to autopsy there has been no limitation of the infection to the meninges as distinct from the brain tissue (Viets and Warren, 1937). The five weeks duration of the photophobia in case 2 is striking; the symptom itself was noted in five of eight cases reported by Reimann (1938). As compared with the majority of cases of lymphocytic meningitis, the duration of signs of mniingeal involvement was unusually protacted in the the cases reported in this paper. Respimtory systenm In only one instance (case 2) was coughing a symptom. Admittedly, the remaining two patients were infants, in whom the presence or absence of cough is notoriously unreliable as a guide to respiratory infection; nevertheless the observation lends force to the stion that lung involvement may occur more commonly than is suspected in cases of apparently uncomplicated lymphocytic meningtis. The time relationship between the onset ofnervous and respiratory involvement is of interest, but is D 21 dificult of assessment since both systems were manifestly implicated when the patients were first examined. In case 1 both systems were involved by the fourth day of apparent illness, with no clue as to the sequence. In case 2, according to the history, infection of the lungs evidently preceded that of the nervous system. In case 3 the degree of hilar enlargement suggsted pulmonary infection of some considerable duration, probably antedating that of the nervous lesion. From this incomplete evidence the possibility of simultaneous involvement of the two systems concerned cannot be excluded. In case 2 almost certainly, and in case 3 probably, it seems more reasonable to postulate primary infection of the lungs with subsequent involvement of the nervous system. D o The diagnosis of a lymphocytic type of meningitis seems clear. It was based on the clinical evidence of meningeal involvement, on the characteristic findings in the cerebrospinal fluid, on the lack of response to chemotherapy, and on the course of the illness. The diagnosis of atypical pneumonia was made on the clinical and radiological findings, on the lack of response to treatment, and on the course of the diseas. The coincident occurrence of lesions in two systems suggested a common pathogenesis, and tuberculosis was excluded by the repeatedly negative Mantoux responses and by the benign course of the disease. In case 1, as is common in atypical pneumonia, the radiological appearances were out of proportion to the scanty physical signs, and an additional shadow appeared as the first regressed. Characteristically, the shadows were indefinitely outlined, were comparatively lacking in density, and did not extend to the lung periphery. In case 2 the larger of the two areas of consolidation was easily demonstrable clinically in the early stages, but persisted radiologically for many weeks. In atypical pneumonia the persistence of radiographic shadows long after the patient has recovered clinically is not uncommon (Turner, 1945). In case 3 the consistent localization of the physical signs in the lung, over a period of a week of repeated examinations, indicated an inflammatory lesion of the lung parenchyma, and militated against a diagnosis of simple bronchitis. Not infiequently, the earliest radiological evidence of atypical pneumonia is an increase in the hilar shadow (Weber, 1944), and the usual sequence of extension from the hilus into the lung substance may possibly fail to develop. Nevertheless, in this single case doubt remains; but the tentative diagnosis of atypical pneumonia is advanced to emphasiz the possibility of the occurrence of incomplete examples of the syndrome.
5 22 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD REFERN 1. An accoumt is given of viu disease producing Baird, R. D., and Rivers, T. M. (1938). Amn. J. Pad. Ym ocytic m ns and pneumona simulta- H&h, 2, 47. Fracis, T., Jr., and Magill, T. P. (1938). J. exp. Med., 68, It is sgged that the rarity of this coincident Hei, G. E. (1943). Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 36, 387. involvement of two systems is more apparent than Prone, H., and Wright, M. (1943). fi. med. J., 2,63. real Rale, G. et al. (1941). Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. N.Y., 3. The diagnoms of lymphocytic meningitis with 48, 528. Reinann, H. A. (1938). J. Amer. med. Ass., atypical pneumoni, presumably due 111, to virus infection, was made in three cases occurring in children. Sicaddngn J. G. (1937). it. med. J., 2, , et al. (1942). Arch. inter Med, 70, 513. Smadel J. E., et al. (1942). Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Mad. My thanks are due to Dr. L. M. Brierley and to N.Y., 49, 683. Dr. T. Stratton for their unstinting co-operation in Tuenr, R. W. D. (1945). Lmacet, 1, 493. the investigaton of these cases. For permission to Viets, H. R., and Warren, S. (1937). J. Amer. med. Ass., 108,357. publish and for his imulating advice and continued interest I am greatly indebted to Prof. C. Weber, H. M. (1944). Amer. J. med. Sa., 208, 680. Walgren, A. (1925). Acta paediatr. Stockh., 4, 158. Bn Perry. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 March Downloaded from on 2 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN
 THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis
 Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER
 THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER BY JAMES S. ANDERSON, M.A., M.D., D.P.H., Medical Superintendent, Leeds City Hospitals, and Lecturer in Infectious Diseases, University of Leeds. In this country during the
THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER BY JAMES S. ANDERSON, M.A., M.D., D.P.H., Medical Superintendent, Leeds City Hospitals, and Lecturer in Infectious Diseases, University of Leeds. In this country during the
THE DIAGNOSIS OF VIRUS PNEUMONIA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 THE DIAGNOSIS OF VIRUS PNEUMONIA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN 'The diagnosis of primary atypical pneumonia at the present time is in reality a process of excluding the known specific diseases which may present
THE DIAGNOSIS OF VIRUS PNEUMONIA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN 'The diagnosis of primary atypical pneumonia at the present time is in reality a process of excluding the known specific diseases which may present
SUGARS AND GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES OF SPINAL FLUID IN EPIDEMIC CEREBROSPINAL MENINGITIS
 SUGARS AND GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES OF SPINAL FLUID IN EPIDEMIC CEREBROSPINAL MENINGITIS By ROGER S. HUBBARD, NELSON G. RUSSELL, JR., AND NELLIE M. RUSSELL (From the Buffalo General Hospital, Buffalo, New York)
SUGARS AND GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES OF SPINAL FLUID IN EPIDEMIC CEREBROSPINAL MENINGITIS By ROGER S. HUBBARD, NELSON G. RUSSELL, JR., AND NELLIE M. RUSSELL (From the Buffalo General Hospital, Buffalo, New York)
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
General History. 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : ~ Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious 5 minutes in the morning.
 General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
ABERDEEN DURING THE FIFTY YEARS
 MORTALITY IN YOUNG CHILDREN IN THE CITY OF ABERDEEN DURING THE FIFTY YEARS 19-199 BY JOHN CRAIG From the Department of Child Health of the University of Aberdeen Much has been written and spoken concerning
MORTALITY IN YOUNG CHILDREN IN THE CITY OF ABERDEEN DURING THE FIFTY YEARS 19-199 BY JOHN CRAIG From the Department of Child Health of the University of Aberdeen Much has been written and spoken concerning
EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS.
 EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS. BY ERNEST G. STILLMAN, M.D., AND ARNOLD BRANCH, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller
EXPERIMENTAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE FOLLOWING THE INHALATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS H2EMOLYTICUS AND OF FRIEDLANDER'S BACILLUS. BY ERNEST G. STILLMAN, M.D., AND ARNOLD BRANCH, M.D. (From the Hospital of The Rockefeller
Bacterial meningitis
 Bacterial meningitis Children s Ward Parent/Carer Information Leaflet What is meningitis? Meningitis is an infection that causes inflammation (swelling) of the meninges. The meninges are protective membranes
Bacterial meningitis Children s Ward Parent/Carer Information Leaflet What is meningitis? Meningitis is an infection that causes inflammation (swelling) of the meninges. The meninges are protective membranes
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases
 Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MENINGITIS. All children with suspected or confirmed meningitis
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MENINGITIS Reference: Mennigitis Version No: 1 Applicable to All children with suspected or confirmed meningitis Classification of document: Area for Circulation: Author:
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF MENINGITIS Reference: Mennigitis Version No: 1 Applicable to All children with suspected or confirmed meningitis Classification of document: Area for Circulation: Author:
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II
 MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction
 Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
ANTIBODIES TO HERPES-SIMPLEX VIRUS IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF PATIENTS WITH HER- PETIC ENCEPHALITIS
 ANTIBODIES TO HERPES-SIMPLEX VIRUS IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF PATIENTS WITH HER- PETIC ENCEPHALITIS F. 0. MACCALLUM, I. J. CHINN AND J. V. T. GOSTLMG Virology Laboratory, Radclife Infirmary, Oxford
ANTIBODIES TO HERPES-SIMPLEX VIRUS IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF PATIENTS WITH HER- PETIC ENCEPHALITIS F. 0. MACCALLUM, I. J. CHINN AND J. V. T. GOSTLMG Virology Laboratory, Radclife Infirmary, Oxford
RUPTURED AORTIC VALVE WITH MYCOTIC
 RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
 THE NUTRITIONAL STATE OF CHILDREN WITH CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE BY JOSEPH BENN, M.D., M.R.C.P. Tutor in Medicine, University of Bristol Gray Hill (1933) stated that while the child's physical development
THE NUTRITIONAL STATE OF CHILDREN WITH CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE BY JOSEPH BENN, M.D., M.R.C.P. Tutor in Medicine, University of Bristol Gray Hill (1933) stated that while the child's physical development
SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT*
 Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 165. SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT* BY IAN A. KELLOCK Senior Medical Registrar, Manchester Royal Infirmary Late adult bone syphilis, in which the characteristic lesion
Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 165. SKELETAL SYPHILIS IN THE ADULT* BY IAN A. KELLOCK Senior Medical Registrar, Manchester Royal Infirmary Late adult bone syphilis, in which the characteristic lesion
CASE REPORT A CASE SHOWING COMBINED FEATURES OF ACUTE RHEUMATISM AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 CASE REPORT A CASE SHOWING COMBINED FEATURES OF ACUTE RHEUMATISM AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. ELAINE FIELD, M.D., M.R.C.P. (From the Children's Unit, Hempstead House Emergency Hospital) 'There are not
CASE REPORT A CASE SHOWING COMBINED FEATURES OF ACUTE RHEUMATISM AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. ELAINE FIELD, M.D., M.R.C.P. (From the Children's Unit, Hempstead House Emergency Hospital) 'There are not
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE
 THE USE OF THE SKIN TEST WITH THE TYPE SPECIFIC POLY- SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE IN PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA By COLIN M. MAcLEOD, CHARLES L. HOAGLAND, AND PAUL B. BEESON (From the Hospital
THE USE OF THE SKIN TEST WITH THE TYPE SPECIFIC POLY- SACCHARIDES IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM DOSAGE IN PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA By COLIN M. MAcLEOD, CHARLES L. HOAGLAND, AND PAUL B. BEESON (From the Hospital
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS AND
 III PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS AND SYPHILIS By R. R. TRAIL MEDICAL opinion is still strongly divided into two camps on the question of the incidence and extent of pulmonary syphilis. Some writers say that
III PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS AND SYPHILIS By R. R. TRAIL MEDICAL opinion is still strongly divided into two camps on the question of the incidence and extent of pulmonary syphilis. Some writers say that
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children
 Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children This leaflet tells you about the DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB vaccine, also known as 6 in 1 as it protects against six diseases,
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children This leaflet tells you about the DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB vaccine, also known as 6 in 1 as it protects against six diseases,
Index No. All five (05) questions should be answered. All questions carry equal marks.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
Meningitis and Septicaemia
 Meningitis and Septicaemia Name: Who to contact and how: Notes: Diana, Princess of Wales Scartho Road Grimsby DN33 2BA 03033 306999 www.nlg.nhs.uk Scunthorpe General Hospital Cliff Gardens Scunthorpe DN15
Meningitis and Septicaemia Name: Who to contact and how: Notes: Diana, Princess of Wales Scartho Road Grimsby DN33 2BA 03033 306999 www.nlg.nhs.uk Scunthorpe General Hospital Cliff Gardens Scunthorpe DN15
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
How to Detect and Confirm Epidemic Meningococcal Disease
 How to Detect and Confirm Epidemic Meningococcal Disease Men/Detect & Confirm/1 Detection and Confirmation of Epidemic Meningococcal Disease 1. Maintain surveillance Health facilities report suspected
How to Detect and Confirm Epidemic Meningococcal Disease Men/Detect & Confirm/1 Detection and Confirmation of Epidemic Meningococcal Disease 1. Maintain surveillance Health facilities report suspected
A rash case Infection control management of measles
 A rash case Infection control management of measles 23 th June 2013 PanCeltic Meeting Dr Jo Hargreaves Microbiology SpR University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Acknowledgements Dr Harriet Hughes Nicola Bevan,
A rash case Infection control management of measles 23 th June 2013 PanCeltic Meeting Dr Jo Hargreaves Microbiology SpR University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Acknowledgements Dr Harriet Hughes Nicola Bevan,
Student Guide Module 5: Management of Prevalent Infections in Children Following a Disaster
 Student Guide Module 5: Management of Prevalent Infections in Children Following a Disaster Objectives for this session Section I - Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Understand the IMCI
Student Guide Module 5: Management of Prevalent Infections in Children Following a Disaster Objectives for this session Section I - Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Understand the IMCI
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report
 Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
WHAT IS MENINGITIS? Autoras: Irene Laguna Cruañes* Nereida Blanco Rovira* Mª Ángeles Macía Escriche* *Alumnas 2º Curso EUE La Fe
 WHAT IS MENINGITIS? Autoras: Irene Laguna Cruañes* Nereida Blanco Rovira* Mª Ángeles Macía Escriche* *Alumnas 2º Curso EUE La Fe 1 Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord.
WHAT IS MENINGITIS? Autoras: Irene Laguna Cruañes* Nereida Blanco Rovira* Mª Ángeles Macía Escriche* *Alumnas 2º Curso EUE La Fe 1 Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord.
infections, mainly with pneumonia, observed from They comprised two
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 56 (1983), 493-503 M. pneumoniae Respiratory Diseases: Clinical Features -Children YASUTAKA NIITU, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, The Research Institute for Tuberculosis
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 56 (1983), 493-503 M. pneumoniae Respiratory Diseases: Clinical Features -Children YASUTAKA NIITU, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, The Research Institute for Tuberculosis
RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 196-200 RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND BY Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, The Queen's University of Belfast INTRODUCTION A recent survey of
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 196-200 RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND BY Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, The Queen's University of Belfast INTRODUCTION A recent survey of
Khaled Ali Abu Ali. BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. -Nursing. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer
 Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
 COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
H. INFLUENZAE MENINGITIS
 H. INFLUENZAE MENINGITIS BY I. A. B. CATHIE, M.D., and S. D. V. WELLER, M.D., M.R.C.P. (From the Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London) Tie treatment of influenzal meningitis, particularly
H. INFLUENZAE MENINGITIS BY I. A. B. CATHIE, M.D., and S. D. V. WELLER, M.D., M.R.C.P. (From the Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London) Tie treatment of influenzal meningitis, particularly
Aurora Health Care South Region EMS st Quarter CE Packet
 Name: Dept: Date: Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 1 st Quarter CE Packet Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammatory disease of the leptomeninges. Leptomeninges refer to the pia matter and the arachnoid
Name: Dept: Date: Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 1 st Quarter CE Packet Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammatory disease of the leptomeninges. Leptomeninges refer to the pia matter and the arachnoid
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH. Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch
 ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
Laboratory Diagnosis of Endemic
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Endemic Typhus and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever* L. F. BADGER, M.D. P. A. Surgeon, U. S. Public Health Service, Washington, D. C. THERE is widely scattered throughout the world
Laboratory Diagnosis of Endemic Typhus and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever* L. F. BADGER, M.D. P. A. Surgeon, U. S. Public Health Service, Washington, D. C. THERE is widely scattered throughout the world
PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES
 10 BLOOD PHOSPHORUS IN HEALTH AND DISEASE: IV-THE PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES MELLITUS F B BYROM From the Dunn Laboratories, London Hospital Received for publication November 24th, 1928
10 BLOOD PHOSPHORUS IN HEALTH AND DISEASE: IV-THE PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES MELLITUS F B BYROM From the Dunn Laboratories, London Hospital Received for publication November 24th, 1928
Meningitis. Author : - Dr. Edward Tsang (registered Chinese Herbalist & Acupuncturist ) Wu Zhu Metaphysician
 Meningitis Author : - Dr. Edward Tsang (registered Chinese Herbalist & Acupuncturist ) Wu Zhu Metaphysician Definition Meningitis is usually restricted to inflammation due to infective agents. Microorganisms
Meningitis Author : - Dr. Edward Tsang (registered Chinese Herbalist & Acupuncturist ) Wu Zhu Metaphysician Definition Meningitis is usually restricted to inflammation due to infective agents. Microorganisms
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
TUBERCULOSIS. By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi
 TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
Meningitis. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Meningitis This fact sheet provides information on meningitis. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be concise.
A fact sheet for patients and carers Meningitis This fact sheet provides information on meningitis. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be concise.
CASE REPORTS REPORT OF A CASE OF NEURENTERIC CYST WITH ASSOCIATED CHRONIC MENINGITIS AND HYDROCEPHALUS*
 CASE REPORTS NEURENTERIC CYSTS REPORT OF A CASE OF NEURENTERIC CYST WITH ASSOCIATED CHRONIC MENINGITIS AND HYDROCEPHALUS* LCDR. FREDERICK E. JACKSON (MC), U.S.N. Department of Neurological Surgery, U.
CASE REPORTS NEURENTERIC CYSTS REPORT OF A CASE OF NEURENTERIC CYST WITH ASSOCIATED CHRONIC MENINGITIS AND HYDROCEPHALUS* LCDR. FREDERICK E. JACKSON (MC), U.S.N. Department of Neurological Surgery, U.
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Th e material for this note is derived from the experience of
 M O R T A L IT Y IN TU BERCU LIN -PO SITIVE IN FA N T S by M ir i a m B r a i l e y, m.d., dr.p.h.* Th e material for this note is derived from the experience of the special outpatient clinic for childhood
M O R T A L IT Y IN TU BERCU LIN -PO SITIVE IN FA N T S by M ir i a m B r a i l e y, m.d., dr.p.h.* Th e material for this note is derived from the experience of the special outpatient clinic for childhood
of 46 cases were due to the particular pneumococcal types mentioned and in the series 41 out of 64 cases were caused by the same types,
 THE TREATMENT OF LOBAR PNEUMONIA WITH PENICILLIN' By WILLIAM S. TILLETT, JAMES E. McCORMACK, AND MARGARET J. CAMBIER (From the Department of Medicine of New York University College of Medicine and the
THE TREATMENT OF LOBAR PNEUMONIA WITH PENICILLIN' By WILLIAM S. TILLETT, JAMES E. McCORMACK, AND MARGARET J. CAMBIER (From the Department of Medicine of New York University College of Medicine and the
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- VIII Advance Nursing Management Of neurovascular Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- VIII Advance Nursing Management Of neurovascular Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
using this recommended dose of 1 TU PPD, should
 Archives of Disease in Childkood, 1980, 55, 795-799 Unreliability of the Mantoux test using 1 TU PPD in excluding childhood tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea KATHLEEN MURTAGH Department of Clinical Sciences,
Archives of Disease in Childkood, 1980, 55, 795-799 Unreliability of the Mantoux test using 1 TU PPD in excluding childhood tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea KATHLEEN MURTAGH Department of Clinical Sciences,
Your short guide to meningitis
 Your short guide to meningitis Babies and Toddlers What is meningitis? Meningitis can affect anyone, it can strike quickly and kill within hours its impact can last a lifetime. Meningitis is the inflammation
Your short guide to meningitis Babies and Toddlers What is meningitis? Meningitis can affect anyone, it can strike quickly and kill within hours its impact can last a lifetime. Meningitis is the inflammation
Hot Topics in Pediatric Infectious Disease. Roadmap KIDS ARE NOT LITTLE ADULTS
 Hot Topics in Pediatric Infectious Disease PIAA Claims/Risk Management Workshop Wendi K. Drummond DO, MPH November 5, 2012 Roadmap Brief review of Pediatric Medical Professional Liability Review the top
Hot Topics in Pediatric Infectious Disease PIAA Claims/Risk Management Workshop Wendi K. Drummond DO, MPH November 5, 2012 Roadmap Brief review of Pediatric Medical Professional Liability Review the top
Viral Meningitis. 2. Use the information on the Possible Diseases sheet to complete the other four columns in the chart.
 Disease Detectives Part 1: What is wrong with Mike? Yesterday, Mike Wright developed a severe headache, a high fever, and a stiff neck. Then, he became nauseated and began vomiting. He just wanted medicine
Disease Detectives Part 1: What is wrong with Mike? Yesterday, Mike Wright developed a severe headache, a high fever, and a stiff neck. Then, he became nauseated and began vomiting. He just wanted medicine
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA
 ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
IN THE TREATMENT OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 THE ROLE OF ACTH AND CORTISONE IN THE TREATMENT OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS The steroids ACTH and cortisone have now been used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus for over five years.
THE ROLE OF ACTH AND CORTISONE IN THE TREATMENT OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS The steroids ACTH and cortisone have now been used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus for over five years.
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Hths 2231 Laboratory 7 Infection
 Watch Movie: Meningitis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Go to the patho web page and click on activity 1. Click on Tutorials Click on Immunopathology
Watch Movie: Meningitis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Go to the patho web page and click on activity 1. Click on Tutorials Click on Immunopathology
Clinical Features of Mycoplasmal Pneumonia in Adults
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 56 (1983), 505-510 Clinical Features of Mycoplasmal Pneumonia in Adults KINICHI IZUMIKAWA, M.D., AND KOHEI HARA, M.D. Second Department of Internal Medicine, Nagasaki
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 56 (1983), 505-510 Clinical Features of Mycoplasmal Pneumonia in Adults KINICHI IZUMIKAWA, M.D., AND KOHEI HARA, M.D. Second Department of Internal Medicine, Nagasaki
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
THE DIMENSIONS OF THE CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASE PROBLEM
 THE DIMENSIONS OF THE CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASE PROBLEM Harry E. Walkup, M.D., and Eleanor C. Connolly, M.P.H. CHIIONIC disease, with the exception of pulmonary tuberculosis, has until recently been
THE DIMENSIONS OF THE CHRONIC RESPIRATORY DISEASE PROBLEM Harry E. Walkup, M.D., and Eleanor C. Connolly, M.P.H. CHIIONIC disease, with the exception of pulmonary tuberculosis, has until recently been
Radiology of uncomplicated asthma
 Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
FEVER. What is fever?
 FEVER What is fever? Fever is defined as a rectal temperature 38 C (100.4 F), and a value >40 C (104 F) is called hyperpyrexia. Body temperature fluctuates in a defined normal range (36.6-37.9 C [97.9-100.2
FEVER What is fever? Fever is defined as a rectal temperature 38 C (100.4 F), and a value >40 C (104 F) is called hyperpyrexia. Body temperature fluctuates in a defined normal range (36.6-37.9 C [97.9-100.2
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection
 Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Acute neurological syndromes
 Acute neurological syndromes Assoc.Prof. Murat Sayan Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Rutin PCR Lab. Sorumlu Öğt.Üyesi Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi, DESAM Kurucu Öğrt. Üyesi sayanmurat@hotmail.com 0533 6479020 Medical
Acute neurological syndromes Assoc.Prof. Murat Sayan Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Rutin PCR Lab. Sorumlu Öğt.Üyesi Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi, DESAM Kurucu Öğrt. Üyesi sayanmurat@hotmail.com 0533 6479020 Medical
Inspiratory crackles-early and late
 Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
How It Spreads Symptoms Can Include Complications
 OUR BEST SHOT: The Importance of Vaccines for Older Adults VACCINES QUICK GUIDE TO VACCINATION FOR ADULTS AGES 60+ Vaccines are an important step in protecting your health and the health of your family.
OUR BEST SHOT: The Importance of Vaccines for Older Adults VACCINES QUICK GUIDE TO VACCINATION FOR ADULTS AGES 60+ Vaccines are an important step in protecting your health and the health of your family.
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
Help protect your baby against MenB
 Help protect your baby against MenB 2015 New vaccine for babies available from 1 September 2015 1 From 1 September 2015, all babies born on or after 1 July 2015 will be offered the MenB vaccine along with
Help protect your baby against MenB 2015 New vaccine for babies available from 1 September 2015 1 From 1 September 2015, all babies born on or after 1 July 2015 will be offered the MenB vaccine along with
NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN DENGUE PATIENTS
 NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN DENGUE PATIENTS Chitsanu Pancharoen and Usa Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. To determine the
NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN DENGUE PATIENTS Chitsanu Pancharoen and Usa Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. To determine the
Whooping cough-a study of severity in hospital cases
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 687-691 Whooping cough-a study of severity in hospital cases D A ROBINSON, B K MANDAL, A G IRONSIDE, AND E M DUNBAR Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 687-691 Whooping cough-a study of severity in hospital cases D A ROBINSON, B K MANDAL, A G IRONSIDE, AND E M DUNBAR Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre,
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE*
 SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
RESEARCH ARTICLE IS LUMBAR PUNCTURE ALWAYS NECESSARY IN THE FEBRILE CHILD WITH CONVULSION?
 RESEARCH ARTICLE IS LUMBAR PUNCTURE ALWAYS NECESSARY IN THE FEBRILE CHILD WITH CONVULSION? MR. Salehi Omrani MD¹, MR. Edraki MD 2, M. Alizadeh MD 3 Abstract: Objective Febrile convulsion is the most common
RESEARCH ARTICLE IS LUMBAR PUNCTURE ALWAYS NECESSARY IN THE FEBRILE CHILD WITH CONVULSION? MR. Salehi Omrani MD¹, MR. Edraki MD 2, M. Alizadeh MD 3 Abstract: Objective Febrile convulsion is the most common
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Case N 1. Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds. Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania
 Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women
 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Multiple hamartomata of the lung
 ".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health. Learn About Pertussis PERTUSSIS
 CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
through a Seitz filter, 0 5% phenol was added. The concentrated tuberculin solution was then
 B.C.G. TUBERCULIN BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, the University of Sheffield It is well known that after Bacille Calmette-Gue'rin (B.C.G.) vaccination the degree of allergy as shown
B.C.G. TUBERCULIN BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, the University of Sheffield It is well known that after Bacille Calmette-Gue'rin (B.C.G.) vaccination the degree of allergy as shown
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia
 Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Protecting your baby against meningitis and septicaemia caused by meningococcal B bacteria MenB vaccine now available! Information about the MenB vaccine and recommended paracetamol use mmunisation The
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Acute pneumonia Simple complement
 Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
WOMENCARE. Herpes. Source: PDR.net Page 1 of 8. A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407)
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
TUBERCULOUS PERICARDIAL EFFUSION
 BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
Elderly Man with Dyspnoea
 Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
