PENTOUCH TRANSLATION & EDUCATION Utility Vehicles States of Matter
|
|
|
- Patrick Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 States of Matter A. For many years, people did not know what matter was made of. The ancient Greeks tried to figure out what would happen if a rock were broken into smaller and smaller pieces. B. They predicted that you would get to a point where you could not break it down further. You would be left with tiny particles. They would be so small that you would not be able to see them with your eyes. They called these particles "atoms." An atom is the building block of all matter. C. Matter can be classified into three states: solid, liquid, or gas. In the solid state, atoms are tightly packed and move very little; they vibrate but stay in one place. In the liquid state, atoms can move enough to slide past each other. In the gas state, atoms are free from one another and move quickly, so they are farther apart. D. These states of matter can be described by shape. Think of brick, water, and air as examples of matter in the three states. In which state does matter always keep the same shape? In which states can the shape change? E. The states of matter can also be described in terms of volume. Volume is the amount of space an object takes up. Do you think the volume of a solid is constant? (If you move a brick, will its volume change?) How about gas in a balloon after it is heated so the atoms move far apart? Does the volume of gas change? organize it in a table. For example, the table below makes it easy to compare information about utility vehicles. See if you can tell which vehicle costs the most money. Which gets the best gas mileage? Which would be the best choice for a large family? Pickup Truck Utility Vehicles Miles per Gallon (fuel) Number of Passengers Price of Vehicle 17 3 $25,000 Minivan 20 7 $30,000 SUV 12 5 $35,000 G. Tables are very useful for organizing information maybe that's why science textbooks are filled with them! Tables make it easy to learn by comparing. The table below arranges information about solids, liquids, and gases. Look at the table and think about the following questions. Does a solid have a definite shape? Do atoms of gas move slowly or quickly? States of Matter Movement of Atoms Definite Shape? Definite Volume? Solid vibration yes yes Liquid slow no yes Gas quick no no F. To easily understand information, we can
2 1. For each statement, circle T or F for true or false. In each blank, write the number of the SENTENCE that gives the best evidence for your answer. a. All things are made of atoms. b. Metal is one of the three states of matter. c. In a gas, atoms stay together in one place. 4. Use the information in the Utility Best Worst Vehicles table in the lesson to complete the following chart. In each blank cell, write PT (for Pickup Truck), MV (for Minivan), or SUV. (Remember: it is best to have the most room and the least cost!) Utility Vehicles Miles per Gallon (fuel) Number of Passengers Price of Vehicle 2. When ice melts, it changes into water. It goes from a solid state into a liquid state. Describe what happens to the motion of the atoms when ice melts. 5. Complete the table below. Show how the atoms might be spaced apart in a liquid and in a gas (atoms of a solid are drawn for you.) Also, describe the speed of movement of atoms in a solid and in a liquid (the movement of gas is described for you.) Write the numbers of the two sentences that give the best evidence for your answer., 3. What is the most likely meaning of the word "particles," as it is used in sentence 6? a. large pieces b. rocks c. the whole thing d. small pieces State Solid Liquid Gas States of Matter Spacing of atoms ОООО ΟΟΟΟ ΟΟΟΟ Movement of atoms Quick
3 Position, Distance, and Motion A. When you tell someone where an object is, you describe its position. Position is the exact location of an object. Think about lost treasure. A treasure map describes the exact position of a treasure chest. Knowing the object's position helps you find it easily. Finding the Position of an Object B. If the position of an object has changed, the object has moved. Motion describes the movement of an object from one place to another. Therefore, motion is a change of position. C. The measurement of how much an object's position has changed is distance. Distance can also be the measurement from one object to another. Think about the distance from your home to your school or the distance between your knew and your ankle. Long distance are usually measured in kilometers or miles. Short distances are usually measured in centimeters or inches. D. Another measurement that involves distance and motion is speed. We think of speed as how fast an object is moving. If two cars are traveling from Seoul to Busan and one gets there before the other, one changed its position faster. Speed is a measurement of distance traveled during a period of time. Speed is measured in units of distance and time, for example in miles per hour. E. The diagram above shows the position of happy and sad faces. Each face is located at a place where a vertical line and a horizontal line cross each other. A vertical line goes up and down. A horizontal line goes left and right. Look at the happy face wearing a hat. Two lines are passing through it. One line is vertical. The other line is horizontal. F. Find the number of the horizontal line going through the happy face wearing a hat. Find the letter of the vertical line. The position of the happy face wearing a hat is at the point where line B and line 6 cross each other. In other words, the happy face wearing a hat is at B6. What is the position of the sad face wearing a hat? G. A diagram that uses vertical and horizontal lines to show a position is called a grid. Grids can be labeled with letters or numbers or both. The letters and numbers used to tell the exact position of an object on a grid are called the coordinates.
4 1. For each statement, circle T or F for true or false. In the blanks, write the number(s) of the SENTENCE(s) that give the best evidence for your answer. a. Time is a part of speed. T F, b. Things can change position without moving. T F, c. Scientists use the word "distance" to mean movement from one place to another. T F, 2. Look at the grid in the lesson. Write the coordinates of each object next to its description. The first one is done for you. a. Sad face with no hat G 5 b. Happy face with no hat c. Face with no expression d. Sad face with a hat 3. What is the most likely meaning of the word "location," as it is used in sentence 2? a. motion b. objects c. certain place d. passage of time Heredity A. Which rabbit is most likely to survive is snowy Alaska? One that is white or one that is brown? White, of course. Where do you think the color of a rabbit's fur comes from? It comes from the rabbit's parents. This lesson is about the passing of characteristics like fur color from parent to offspring. B. Offspring are the children of people or the young of animals. Pups are the offspring of dogs. Cubs are the offspring of bears or lions. Can you think of other types of offspring? C. Characteristics are a category used to describe how an object looks. For example, fur color is a characteristic of rabbits. Speed shape is a characteristic of pea plants. D. However, when describing specific characteristics of organisms, scientists use a different term. A trait is an exact characteristic of an organism. For example, white fur and brown fur are traits of a rabbit. Smooth or wrinkled seeds are traits of a pea plant. Can you name three traits of a person you know? 4. Look at the grid in the lesson. Find a point exactly between the two happy faces. What are the coordinates of that point?
5 Animal Needs and Animal Behavior A. Animal use energy to do work. For example, a lion uses energy to hunt, get shelter, and communicate. Like other mammals, a lion also uses energy to keep a constant body temperature, digest food, keep its heart beating, and breathe. B. In order to survive, animals must use energy to get what they need from their environment. For example, if a lion is hungry, it must tract its prey and then run fast to catch it. If there is a storm, a lion must use energy to find shelter. An animal uses energy to move so it can get what it needs. C. When an organism reacts to something, it responds. For example, a lion responds to thirst by drinking. How would you respond to a cold day? Would you add more clothing or take it off? D. Anything that makes you use energy is called a stimulus. Rain is a stimulus. It makes you go inside. Thirst is a stimulus as well. It makes you get a drink. Moving inside and drinking are responses. Each of these stimuli causes a response. Ducking a snowball, laughing at a joke, and coming in out of the cold are responses. Responses use up energy. Animals need energy to respond to stimuli in their environment. Therefore, animals need energy to survive. E. The response of an animal to a stimulus is called a behavior. For example, animals respond to thirst by drinking water. Drinking is a behavior. Animals respond to fear by running away. Running away is a behavior, too. What behavior do people show when they are happy? When they are sad? F. Some behaviors are responses to stimuli in the environment. A typical response to cold weather is to look for shelter. Other behaviors are responses to stimuli that happen inside the animal. For example, thirst is an inside stimulus. Can you think of another example of an inside stimulus? G. Some responses are automatic. When you feel cold, you shiver. What happens when you touch something very hot? You jerk your fingers back without thinking about it. When a behavior is automatic, it is called a reflex. When a dog scratches an itch, the scratching is a reflex. H. Look at the Animal Behavior chart below. It contains a list of stimulus/response pairs. ANIMAL BEHAVIORS Stimulus Internal External Response Hunger Flood X X Get food, eat Find high ground Getting tired X Sleep Thirst X Find water, drink Forest fire X Fun away I. What do you think is meant by the words "Internal" and "External" as they are used on the chart above?
6 1. For each statement, circle T or F for true or false. In each blank, write the number of the SENTENCE that gives the best evidence for your answer. a. To keep a constant body temperature, humans need food. b. A stimulus causes a response. c. Doing homework is a reflex. d. A stimulus can come only from outside an organism. 5. Are the following statements examples of reflexes? Circle the correct answer. a. A doctor hits your knee with a rubber hammer and your leg jerks up. b. Dark clouds roll in, and it begins to thunder. You run inside your house. c. You accidentally touch a hot stove. Your hand jerks away. d. You put on the brakes of your bicycle to slow down. 2. What is the most likely meaning of track as it is used in sentence 5? a. footprint b. stay away from c. follow d. eat 3. Internal and External, used in sentence 43, probably mean stimuli that are the animal. a. automatic and reflexive b. above and below c. inside and outside d. hot and cold 4. Explain how an animal responds to a forest fire. Write a complete sentence. 6. Complete the chart below. Put an X in the correct column to show whether each stimulus is internal or external. State the correct response to each stimulus. SCHOOL BEHAVIORS Stimulus Internal External Response Hunger Fire alarm Homework Thirst Test
Reflecting on Reflexes
 Reflecting on Reflexes Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What happens when you accidentally touch a hot plate? 2. Name two human reflexes and state how they work. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What happens when you accidentally
Reflecting on Reflexes Pre-Lesson Quiz 1. What happens when you accidentally touch a hot plate? 2. Name two human reflexes and state how they work. 2 Pre-Lesson Quiz Answers 1. What happens when you accidentally
Characteristics of Life (Living Things)
 Unit 2: Biochemistry & the Cell Name: Date: Aim #11 Life Functions: What are the characteristics off living things? What are the main life processes? I. What makes something LIVING? 1. structures made
Unit 2: Biochemistry & the Cell Name: Date: Aim #11 Life Functions: What are the characteristics off living things? What are the main life processes? I. What makes something LIVING? 1. structures made
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Observing Nervous Responses
 Lab #15H Observing Nervous Responses Introduction The nervous system is a series of conducting tissues that carries impulses to all parts of the body. Your nervous system initiates many types of reflex
Lab #15H Observing Nervous Responses Introduction The nervous system is a series of conducting tissues that carries impulses to all parts of the body. Your nervous system initiates many types of reflex
Our Sense Organs Ears
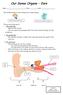 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Chapter 10 Human Nervous System
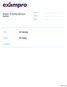 Chapter 0 Human Nervous System Name: Class: Date: Time: 07 minutes Marks: 07 marks Comments: Page of 35 (a) List A gives the names of four stimuli. List B gives four parts of the human body. Draw a straight
Chapter 0 Human Nervous System Name: Class: Date: Time: 07 minutes Marks: 07 marks Comments: Page of 35 (a) List A gives the names of four stimuli. List B gives four parts of the human body. Draw a straight
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2
 IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
Producing and Detecting Sound
 Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Grade Level Expectations for the Sunshine State Standards
 for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The kindergarten student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects have many different observable properties:
for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The kindergarten student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects have many different observable properties:
We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text.
 Learning Objective Name We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text. CFU What are we going to do? What does describe mean? Describe means. Activate Prior Knowledge Bethany did not go to school
Learning Objective Name We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text. CFU What are we going to do? What does describe mean? Describe means. Activate Prior Knowledge Bethany did not go to school
Grade 3. Practice Test. Plight of the Polar Bear Giant Pandas
 Name Date Grade 3 Plight of the Polar Bear Giant Pandas Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from Plight
Name Date Grade 3 Plight of the Polar Bear Giant Pandas Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from Plight
Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers
 Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers Please note: Pennsylvania & Next Generation Science Standards as well as Instructional Resources are found on the SDP Curriculum Engine Prepared by:
Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers Please note: Pennsylvania & Next Generation Science Standards as well as Instructional Resources are found on the SDP Curriculum Engine Prepared by:
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Lesson 1 Characteristics of Life
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Describe fully how the structures shown in the diagram bring about this reflex action (6)
 Q. A person accidentally touches a hot pan. Her hand automatically moves away from the pan. The diagram shows the structures involved in this action. (a) Describe fully how the structures shown in the
Q. A person accidentally touches a hot pan. Her hand automatically moves away from the pan. The diagram shows the structures involved in this action. (a) Describe fully how the structures shown in the
ESL Health Unit Unit Four Healthy Aging Lesson Two Exercise
 ESL Health Unit Unit Four Healthy Aging Lesson Two Exercise Reading and Writing Practice Advanced Beginning Checklist for Learning: Below are some of the goals of this lesson. Which ones are your goals
ESL Health Unit Unit Four Healthy Aging Lesson Two Exercise Reading and Writing Practice Advanced Beginning Checklist for Learning: Below are some of the goals of this lesson. Which ones are your goals
Name Date Class. How the Nervous System Works (pages ) 2. Is the following sentence true or false? You can move without your
 CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
Introduction to Body Systems
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
SUN SAFETY SUN USE A LAYERED APPROACH FOR SUN PROTECTION MY GOAL: SUNLIGHT IS THINGS TO LOOK FOR IN A SUNSCREEN. Be Safe in the Sun ENJOY THE OUTDOORS
 SUN SAFETY Be Safe in the Sun SUN SAFETY IS IMPORTANT because it protects us from... USE A LAYERED APPROACH FOR SUN PROTECTION Skin Damage Skin Cancer Heat Stroke Heat Exhaustion SUNLIGHT IS Sunscreen
SUN SAFETY Be Safe in the Sun SUN SAFETY IS IMPORTANT because it protects us from... USE A LAYERED APPROACH FOR SUN PROTECTION Skin Damage Skin Cancer Heat Stroke Heat Exhaustion SUNLIGHT IS Sunscreen
Hand on a Hot Stove. A Neurobiology Activity
 Hand on a Hot Stove A Neurobiology Activity Please complete the Participant Card 2 Put your student hat on Experience the kit Put your teacher hat on Envision classroom use Curriculum integration Support
Hand on a Hot Stove A Neurobiology Activity Please complete the Participant Card 2 Put your student hat on Experience the kit Put your teacher hat on Envision classroom use Curriculum integration Support
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma
 Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma Lesson 2: What causes asthma? Identifying Asthma Triggers Teacher Instructions, Introduction, and Student Worksheets Objectives for Lesson 2: After completing
Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma Lesson 2: What causes asthma? Identifying Asthma Triggers Teacher Instructions, Introduction, and Student Worksheets Objectives for Lesson 2: After completing
Topics Review Questions. 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us.
 Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information
 STO-135 Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information Summary Kit contains Students model the neuron pathways involved in reflex actions, conscious sensations, voluntary movements, and memories. They apply their
STO-135 Hand on a Hot Stove Teacher Information Summary Kit contains Students model the neuron pathways involved in reflex actions, conscious sensations, voluntary movements, and memories. They apply their
Thales Foundation Cyprus P.O. Box 28959, CY2084 Acropolis, Nicosia, Cyprus. Level 3 4
 Thales Foundation Cyprus P.O. Box 28959, CY2084 Acropolis, Nicosia, Cyprus Kangourou Linguistics English Competition 2017 Level 3 4 Date: 4 February 2017 Time: 10:00 11:15 Questions 1 10 = 3 points Questions
Thales Foundation Cyprus P.O. Box 28959, CY2084 Acropolis, Nicosia, Cyprus Kangourou Linguistics English Competition 2017 Level 3 4 Date: 4 February 2017 Time: 10:00 11:15 Questions 1 10 = 3 points Questions
UNIT. Experiments and the Common Cold. Biology. Unit Description. Unit Requirements
 UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
UNIT Biology Experiments and the Common Cold Unit Description Content: This course is designed to familiarize the student with concepts in biology and biological research. Skills: Main Ideas and Supporting
Do Now: Write a detailed account of what happened in the cartoon.
 Do Now: Write a detailed account of what happened in the cartoon. Tracking Our Mastery We will be tracking how much we learn throughout the year, so we can create goals. 1. Complete the mastery worksheet
Do Now: Write a detailed account of what happened in the cartoon. Tracking Our Mastery We will be tracking how much we learn throughout the year, so we can create goals. 1. Complete the mastery worksheet
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Unit 2P 1: Forces. By the end of this unit you should be able to: Identify the effects of forces, such as squashing, twisting and stretching.
 Unit 2P 1: Pushes and Pulls Changing shape Speeding up and slowing down Science skills: Classifying Predicting Measuring By the end of this unit you should be able to: Identify the effects of forces, such
Unit 2P 1: Pushes and Pulls Changing shape Speeding up and slowing down Science skills: Classifying Predicting Measuring By the end of this unit you should be able to: Identify the effects of forces, such
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System
 To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
To Produce and To Consume Food: Photosynthesis and the Digestive System Living Things Living Things need To Produce (verb) = To Make Producer (noun) = uses energy to make its own food To consume (verb)
1. 1. When you exercise, your body uses the fuel to keep you going strong. a) deep b) general c) extra d) hard
 Pre- university book Lesson one --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- I. choose the correct answer : 1. 1. When you exercise, your
Pre- university book Lesson one --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- I. choose the correct answer : 1. 1. When you exercise, your
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Digestive System: Where does food go? Student Version
 Digestive System: Where does food go? Student Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
Digestive System: Where does food go? Student Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy.
 Contraceptives are used to prevent pregnancy. (a) Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy. Contraceptive device Method of preventing pregnancy Contains hormones to stop
Contraceptives are used to prevent pregnancy. (a) Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy. Contraceptive device Method of preventing pregnancy Contains hormones to stop
Character and Life Skills: Self-Control Lesson Title: Red Light, Green Light Grade Level: 3-5
 Lesson Title: Red Light, Green Light Project and Purpose Students discuss various strategies to show self-control and use a red light, yellow light, green light model to represent how they choose to show
Lesson Title: Red Light, Green Light Project and Purpose Students discuss various strategies to show self-control and use a red light, yellow light, green light model to represent how they choose to show
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story
 Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
Welcome to the Animal Ambassador Program From IFAW!
 Welcome to the Animal Ambassador Program From IFAW! This month s featured animals: ELEPHANTS Female elephants and their female offspring spend their entire lives together. If danger is near, the adult
Welcome to the Animal Ambassador Program From IFAW! This month s featured animals: ELEPHANTS Female elephants and their female offspring spend their entire lives together. If danger is near, the adult
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults
 Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
Name Date Class. To complete the following sentences, choose the correct term from each pair of terms listed, and write the term in the blank.
 CHAPTER 2 IT S ALIVE!! OR, IS IT? Chapter 2 Test USING VOCABULARY To complete the following sentences, choose the correct term from each pair of terms listed, and write the term in the blank. 1. In the
CHAPTER 2 IT S ALIVE!! OR, IS IT? Chapter 2 Test USING VOCABULARY To complete the following sentences, choose the correct term from each pair of terms listed, and write the term in the blank. 1. In the
Winter Worries and Health Hazards
 Non-fiction: Winter Worries and Health Hazards Winter Worries and Health Hazards Sir Ranulph Fiennes, the man the Guinness Book of World Records named "The World's Greatest Living Explorer" in 1984, is
Non-fiction: Winter Worries and Health Hazards Winter Worries and Health Hazards Sir Ranulph Fiennes, the man the Guinness Book of World Records named "The World's Greatest Living Explorer" in 1984, is
1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms may be used more than once.
 THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
Introduction to the Human Body
 Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
c. Construct a boxplot for the data. Write a one sentence interpretation of your graph.
 STAT 280 Sample Test Problems Page 1 of 1 1. An English survey of 3000 medical records showed that smokers are more inclined to get depressed than non-smokers. Does this imply that smoking causes depression?
STAT 280 Sample Test Problems Page 1 of 1 1. An English survey of 3000 medical records showed that smokers are more inclined to get depressed than non-smokers. Does this imply that smoking causes depression?
Lesson 2.7: Diagnosing Elisa
 Lesson 2.7: Diagnosing Elisa Today, you will finally diagnose Elisa! You ll share your expertise with your group, explaining the condition you investigated and how it could affect Elisa s body systems.
Lesson 2.7: Diagnosing Elisa Today, you will finally diagnose Elisa! You ll share your expertise with your group, explaining the condition you investigated and how it could affect Elisa s body systems.
Be Physically Active. Key #7. It s Never Too Late to Start! Why Should You Be Active? Exercise Safely
 Key #7 Be Physically Active It s Never Too Late to Start! Regular physical activity is an important component in healthy aging. It has been proven that regular activity is very beneficial to our health
Key #7 Be Physically Active It s Never Too Late to Start! Regular physical activity is an important component in healthy aging. It has been proven that regular activity is very beneficial to our health
Materials: Activity: Explanation:
 Children will model how fat can be digested by bile. Materials: Whole milk Water Shallow dish or pie pan Food coloring Liquid dish or hand soap Cotton swabs Activity: 1) Pour about ½ inch of milk into
Children will model how fat can be digested by bile. Materials: Whole milk Water Shallow dish or pie pan Food coloring Liquid dish or hand soap Cotton swabs Activity: 1) Pour about ½ inch of milk into
I am sad. It is big. I set it on the pot. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. Mom will help. It is lost. It is red. My Cap. Name:
 My Cap It is red. It is big. I set it on the pot. It is lost. I am sad. Mom will help. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. 2 5 8 14 17 20 23 28 32 Day 1: What color is my cap? Day 2: What happened to my
My Cap It is red. It is big. I set it on the pot. It is lost. I am sad. Mom will help. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. 2 5 8 14 17 20 23 28 32 Day 1: What color is my cap? Day 2: What happened to my
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Kings Ely Senior 13+ Entry Exam. Specimen Paper SCIENCE
 Name. Kings Ely Senior 13+ Entry Exam Specimen Paper SCIENCE 60 minutes Answer all questions in the spaces provided. There are 7s available. Write your name in the space provided at the top of this page
Name. Kings Ely Senior 13+ Entry Exam Specimen Paper SCIENCE 60 minutes Answer all questions in the spaces provided. There are 7s available. Write your name in the space provided at the top of this page
The story of Snow White is a beautiful fairytale with princesses, princes and
 The story of Snow White is a beautiful fairytale with princesses, princes and dwarfs. The fairytale is about a queen who has a very pretty daughter with black hair, snow-white face and red lips. 1. What
The story of Snow White is a beautiful fairytale with princesses, princes and dwarfs. The fairytale is about a queen who has a very pretty daughter with black hair, snow-white face and red lips. 1. What
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA:
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
2 ND FORM REVISION EXERCISE
 1 2 ND FORM REVISION EXERCISE Name: Form: 1. The human eye focuses on different objects at different distances by changing:- a. the position of the eye lens b. the position of the cornea c. the shape of
1 2 ND FORM REVISION EXERCISE Name: Form: 1. The human eye focuses on different objects at different distances by changing:- a. the position of the eye lens b. the position of the cornea c. the shape of
Pennies for Patients cutting-edge work
 This is a sample lesson plan from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society STEM Curriculum for grades 1-8. The sample is a 3 rd grade lesson on the circulatory system. The lesson includes background information
This is a sample lesson plan from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society STEM Curriculum for grades 1-8. The sample is a 3 rd grade lesson on the circulatory system. The lesson includes background information
Multicellular. Organisms
 Multicellular Organisms Part 4 Maintaining Stable Body Conditions 1 Maintaining Stable Body Conditions LI To identify the parts of the Nervous System and their function LI To understand the mechanisms
Multicellular Organisms Part 4 Maintaining Stable Body Conditions 1 Maintaining Stable Body Conditions LI To identify the parts of the Nervous System and their function LI To understand the mechanisms
Science - Year 4. Sound Block 4S. Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack
 Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1
 Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
Please copy into your agenda:
 Monday, September 19 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Advanced only-project part 2 (due Fri) Tuesday: Vocab bonds (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Human inheritance (due Thur)
Monday, September 19 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Advanced only-project part 2 (due Fri) Tuesday: Vocab bonds (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Human inheritance (due Thur)
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY
 Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Human nervous system
 Human nervous system Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Human nervous system Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
Human nervous system Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Human nervous system Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
9.3 Sound The frequency of sound Frequency and pitch pitch Most sound has more than one frequency The frequency spectrum
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
(adaptations) Today s Vocabulary: Behavior- Migration- Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- WARM UP. 1. What is an adaptation?
 (adaptations) 1. What is an adaptation? WARM UP 2. How do you think adaptations are related to variations and environments? Behavior- Migration- Today s Vocabulary: Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- 1 Part
(adaptations) 1. What is an adaptation? WARM UP 2. How do you think adaptations are related to variations and environments? Behavior- Migration- Today s Vocabulary: Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- 1 Part
Adaptation 22 Reproduction 24 Cloning and genetic engineering 26 Extinction and evolution 28 Natural selection 30 Pollution 32 Global warming 34
 Contents Exam board specification map iv Introduction vi Topic checker * Topic checker answers * Biology Unit B1a Human Biology The nervous system 2 Hormones 4 Controlling reproduction 6 Diet and exercise
Contents Exam board specification map iv Introduction vi Topic checker * Topic checker answers * Biology Unit B1a Human Biology The nervous system 2 Hormones 4 Controlling reproduction 6 Diet and exercise
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Warmer
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Warmer
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 14 - Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Most drivers with permanent disabilities understand their
Chapter 14 - Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Most drivers with permanent disabilities understand their
Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3. Introduction...6 Lessons...7. Introduction...12 Lessons Introduction...19 Lessons...
 ARISE Life-Skills for Middle School - Volume 4 Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3 SECTION ONE: Health care is self-care Introduction...6 Lessons...7
ARISE Life-Skills for Middle School - Volume 4 Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3 SECTION ONE: Health care is self-care Introduction...6 Lessons...7
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
Exercises for Chronic Pain
 Exercises for Chronic Pain Many research studies show aerobic and strengthening exercises can lessen chronic pain and improve a person s ability to do daily activities. What is Exercise? It is any activity
Exercises for Chronic Pain Many research studies show aerobic and strengthening exercises can lessen chronic pain and improve a person s ability to do daily activities. What is Exercise? It is any activity
What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Nervous System. Dentalelle Tutoring. 1
 Nervous System Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com 1 Basics The nervous system along with the endocrine (hormonal) system works to control all activities within the human body. It does this by communicating
Nervous System Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com 1 Basics The nervous system along with the endocrine (hormonal) system works to control all activities within the human body. It does this by communicating
LESSON 2. Section I. GENERAL INFORMATION 2-1. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KNOW THE PATIENT'S TEMPERATURE?
 LESSON 2 Section I. GENERAL INFORMATION 2-1. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KNOW THE PATIENT'S TEMPERATURE? a. To Determine the Cause of the Patient's Condition. When a person becomes ill, one of the first things
LESSON 2 Section I. GENERAL INFORMATION 2-1. WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO KNOW THE PATIENT'S TEMPERATURE? a. To Determine the Cause of the Patient's Condition. When a person becomes ill, one of the first things
A Kazoo For You. Science Activity.
 A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
Photosynthesis and Respiration. The BIG Idea All cells need energy and materials for life processes.
 Photosynthesis and Respiration Objectives Explain why cells need energy. Summarize how energy is captured and stored. Describe how plants and animals get energy. The BIG Idea All cells need energy and
Photosynthesis and Respiration Objectives Explain why cells need energy. Summarize how energy is captured and stored. Describe how plants and animals get energy. The BIG Idea All cells need energy and
How the Nervous System Works (pp )
 How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Summary The Work of Gregor Mendel Probability and Punnett Squares. Oass
 --------------------------- Oass ---------------- Date Chapter 11 Summary Introduction to Genetics 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Gregor Mendel used
--------------------------- Oass ---------------- Date Chapter 11 Summary Introduction to Genetics 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Gregor Mendel used
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
AIM: To improve the fitness levels of participants and their enjoyment and understanding of being active.
 Family Fun Fit Family Fun fit is a school based initiative involving children and parents to improve health, particularly fitness levels, of participants. It has been developed from similar projects such
Family Fun Fit Family Fun fit is a school based initiative involving children and parents to improve health, particularly fitness levels, of participants. It has been developed from similar projects such
SPHE PUPIL WORKSHEETS 7A - 7F
 Worksheet 7A: Fuel For Your Day You need to eat a lot of different foods to stay fit and healthy as food is fuel for your body. The food you eat gives you energy for school and your daily activities but
Worksheet 7A: Fuel For Your Day You need to eat a lot of different foods to stay fit and healthy as food is fuel for your body. The food you eat gives you energy for school and your daily activities but
Posterior Total Hip Replacement
 Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
GCSE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 2 LEARNING REVISION
 GCSE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 2 LEARNING REVISION GCSE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 2 CLASSICAL CONDITIONING LEARNING LEARNING= Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour due to experience Some behaviours are learnt, but
GCSE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 2 LEARNING REVISION GCSE PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 2 CLASSICAL CONDITIONING LEARNING LEARNING= Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour due to experience Some behaviours are learnt, but
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
spinal cord P finger Q What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action?
 1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over!
 Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over! Introduction This is a recent picture, taken when we went on a family picnic. We climbed up this big hill and I
Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Adult Asthma My Days of Living in Tension with Asthma are Over! Introduction This is a recent picture, taken when we went on a family picnic. We climbed up this big hill and I
Module Three: Components of Physical Fitness
 Module Three: Components of Physical Fitness Background Information Physical fitness is defined as the capacity for the human body to function efficiently and effectively in a variety of activities. In
Module Three: Components of Physical Fitness Background Information Physical fitness is defined as the capacity for the human body to function efficiently and effectively in a variety of activities. In
Portfolio Introduction
 0 Portfolio Introduction Fitness is the overall term that we ll be using to describe a journey to optimal health and well-being. Like all great journeys, you ll need a map to guide your way. This personal
0 Portfolio Introduction Fitness is the overall term that we ll be using to describe a journey to optimal health and well-being. Like all great journeys, you ll need a map to guide your way. This personal
Reaction time MATERIALS. - Pencil - Chair - Ruler
 Reaction time NAME DATE A hand accidentally touches the hot plate of an oven and is withdrawn immediately. A young child runs out in front of your car and you hammer on the brakes. A lottery ball falls
Reaction time NAME DATE A hand accidentally touches the hot plate of an oven and is withdrawn immediately. A young child runs out in front of your car and you hammer on the brakes. A lottery ball falls
What You Can Do About a Lung Disease Called COPD
 GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE What You Can Do About a Lung Disease Called COPD Adults may have COPD if they have trouble breathing or a cough that will not go away. BASED ON THE
GLOBAL INITIATIVE FOR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE What You Can Do About a Lung Disease Called COPD Adults may have COPD if they have trouble breathing or a cough that will not go away. BASED ON THE
Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages )
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
SRS Achievement Statements. Science
 SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
Agenda and Objectives
 Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
Take Charge of Your Pain Program: Patient Booklet
 Take Charge of Your Pain Program: Patient Booklet TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS BOOKLET... 3 THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT PAIN... 4 Pain Gate... 6 BECOMING MORE ACTIVE... 7 RELAXATION... 8 DEEP BREATHING... 9 IMAGERY...
Take Charge of Your Pain Program: Patient Booklet TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THIS BOOKLET... 3 THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT PAIN... 4 Pain Gate... 6 BECOMING MORE ACTIVE... 7 RELAXATION... 8 DEEP BREATHING... 9 IMAGERY...
Monday, February 8. Please copy into your agenda:
 Monday, February 8 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Tuesday: Genetics review (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Genetics quiz Thursday-Friday: Collect data (dues Tues) Reminder:
Monday, February 8 Please copy into your agenda: Monday: Finish Snapchat (due Tuesday) Tuesday: Genetics review (due Wednesday) Wednesday: Genetics quiz Thursday-Friday: Collect data (dues Tues) Reminder:
