Memory of One s Life
|
|
|
- Samuel Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Memory of One s Life
2 Flashbulb Memories Term coined by Roger Brown and James Kulik Memory of the circumstances where one learned of a major event (personal or public) These memories are usually especially vivid live quality Robert B. Livingston s idea of Now Print mechanism causing a particularly vibrant trace to be left.
3 Accuracy of Flashbulb Memories For many years I have remembered how I heard the news of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, which occurred on the day before my thirteenth birthday. I recall sitting in the living room of our house we only lived in that house for one year, but I remember it will listening to a baseball game on the radio. The game was interrupted by an announcement of the attack, and I rushed upstairs to tell my mother. This memory has been so clear for so long that I never confronted its inherent absurdity until last year: no one broadcasts baseball games in December! (Neisser, 1982, p. 45)
4 Memory Exercise Recall as much as you can about how you heard the news of the attack on the World Trade Center Recall as much as you can about what you did on the morning of September 10, 2001
5 Studies of the Accuracy of Flashbulb Memories Method: After a particularly major public event (Challenger crash, California earthquake), ask people to write down how they heard about the event. Then return as ask them again sometime (6 months, 2 years) later. Frequently many discrepancies between subject s first report and subsequent report Nonetheless, the memories remain very vivid Those who experienced the events first hand (e.g., were in the region of the earthquake and had to take action) generally had much more accurate later recalls.
6 Neisser s Challenger Study
7 Neisser s Challenger Study
8 Memory and Trauma Memories for highly emotionally charged events are often very vivid (precise, detailed). Does intensity correlate with accuracy? Some dramatic changes: People remember being present at events they were not Feel they were more at risk than they were But most often the core memory remains accurate Exceptions tend to involve cases of active imagination fueling memory Flashbacks in drug experiences Most reported among those highly hypnotizable who easily engage in imaginative-fantasy-based activities
9 Memory and Emotion Emotion improves memory for the main features of an experience focusing of attention But not for the details Mood contingent recall: Easier to remember episodes that correspond to one s current mood
10 Kluver-Bucy Syndrome Psychic Blindness or visual agnosia Effects of temporal-lobe lesions on monkeys: the ability to recognize and detect the meaning of objects on visual criteria alone seems to be lost although the animal exhibits no or at least no gross defects in the ability to discriminate visually. also, loss of emotional responsiveness (loss of fear responses) and increased sexual behavior.
11 Hippocampus and Amygdala Adjacent structures with different effects on memory Damasio: conditioning fear response linking an aversive stimulus (noise) with a non-aversive stimulus Patient with amygdala damage failed to develop fear conditioning but remembered the episode Patient with hippocampal damage developed fear response but could not remember the episode Double dissociation Patients with amygdala damage do not show memory enhancement for emotionally charged pictures Connectivity of amygdala to different levels of sensory processing equips it to perform emotional evaluation
12 Recall Failure: Encoding Failure, Retrieval Failure, or Loss of Engram? Which of the following appear on a US penny? The word JUSTICE The words UNITED STATES OF AMERICA The words LEGAL TENDER The word VERITAS The words ONE CENT The date (year of mint) The presidential seal The word COIN The words WASHINGTON, D.C. The left side of Lincoln s face The right side of Lincoln s face The White House An eagle with spread wings The Lincoln memorial The words IN GOD WE TRUST The word LIBERTY Sheaves of wheat The Roman numeral I The words E PLURIBUS UNUM The words MINTED IN USA NO YES NO NO YES YES NO NO NO NO YES NO NO YES YES YES NO NO YES NO
13 Which is the Penny?
14 Memory Exercise Write down where your car is parked Write down where you parked your car the last time you went to that location Write down where you parked your car two times back Write down where you parked your car three times back Write down where you parked your car four time back Write down the topic of our last class Write down the topic of the class before that Write down the topic of two classes back Write down the topic of three classes back
15 Forgetting Forgetting, though often frustrating, is an adaptive feature of our memories. We don t need to remember everything that has ever happened to us; engrams that we never use are probably best forgotten. (Schacter, p. 81) Some things, like memory for words in a foreign language, we retain for a very long time
16 Forgetting and the Engram One of the most recognized features of memory is that we remember less as time goes on. What happens to the engram as we forget Is itself lost (perhaps because of overwriting) Remains undisturbed but becomes less accessible
17 Behavioral Pattern of Forgetting Marigold Linton: self study of the natural history of memories Over 6 years Linton daily wrote down brief descriptions of events from her life (5,500 items) Challenge: to write events down briefly yet retain distinctiveness after first time for event (first trip to Europe) Monthly pairs of items were drawn semi-randomly from the event pool (totaling about 150 items per month) Tried to place them in proper chronological order Tried to reconstruct each item s date Briefly noted her memory search strategy Reevaluated each items salience
18 Forgetting, failing to discriminate, etc. During the forth year, I began to encounter a few old items that simply did not make sense.... [I]tems that I could interpret meaningfully shortly after they were written did not, at the time of the crucial test, permit me to reconstruct a sensible whole. Rate of forgetting: after first year (<1%), flat curve (5-6%) A common way Linton forgot events was by losing the ability to discriminate the memory of one event from another sometimes yielding only a general memory of a type of episode
19 Effect of frequency of event type on semantic/episodic character of memory Number of trials (or experiences) has contrastive effects on episodic and semantic memories. Increased experience with any particular event class increases semantic (or general) knowledge about the event and its context. Increased experience with similar events, however, makes specific episodic knowledge increasingly confusable, and ultimately episodes cannot be distinguished. (Linton, 1982, p. 79)
20 From semantic to episodic to semantic It seems plausible that a fairly small number of general schemes provide the basic framework for storing episodic information. These schemes organize the event in terms of actors, action, location, and the like. These elements that comprise the building blocks of episodic memories are themselves information from our semantic store.... A specific event is a unique configuration of these elements. As our experience with a particular event type increases, we seem at first to make finer discriminations among related events.... At some point, however, this expansion of elements and configuration ends.... As similar events are repeated, the specific configurations the patterns that link familiar elements to form unique episodes themselves become a well-established potentially confusable part of semantic knowledge. (Linton, 1982, p. 81)
21 Emotion in Linton s self study Evaluated emotional salience at initial writing and each recall Very low correlation between initial emotional salience and later success in recall Change in emotional salience from encoding to recall Habituation of emotional response if event type repeated (including response to memory of initial events) Later changes in judgment depending on what followed: Just as historians must interpret and rewrite history as time passes, so we all rewrite out own personal histories. Few of us are wise enough to be able to predict at the time of their occurrence how significant events will prove to be. (Linton, 1982, p. 88). Did the new person we met become a lover/spouse? Did you accept the job offer or not?
22 Brain regions for episodic encoding
23 Amnesia HM: bilateral resection of hippocampus and surrounding cortex in 1953 at age 29 for intractable epilepsy Hypothesized lesions Actual lesions
24 HM No recurrence of epilepsy No effect on IQ, personality, etc. Graded retrograde amnesia for several years prior to surgery Anterograde amnesia Can learn new skills (such as mirror tracing)
25 HM HM likes detective shows, doing crosswords, and watching TV. However, it is impossible for him to make new friends as he cannot remember a person for any longer than ten minutes. He lives in a world where, for him, Truman is still President. When he is told again of his mother's death evokes the same painful grief for a short period of time, and then, it is gone. He never really knows exactly how old he is, but reckons that he is about 30. When he looks into a mirror, he is shocked by the reflection. He comments on his situation:... what I keep thinking is that possibly I had an operation. And somehow the memory is gone... and I'm trying to figure it out... I think of it all the time. I don't remember this, and why I don't remember that... it isn't worrisome in a way, to me, because I know that if they ever performed an operation on me, they'd learn from it. It would help others.
26 Forgetting and Consolidation Many other patients with medial temporal lobe damage also exhibit pattern of anterograde and partial retrograde amnesia Suggests long-term engram is not laid down all at once Rather, a period during which it is being developed Proposal that medial temporal lobe plays role in consolidating the permanent connections Even that playback during dreaming plays a role
27 Hippocampal Architecture Entorhinal Cortex Subiculum Perforant Pathway CA1 Schaffer Collaterals CA3 Dentate Gyrus Mossy Fibers Convergence of sensory information from rest of cortex Overall loop (EC both input and output center): Autoassociator? McClelland et al., Rolls and Treves Recurrent Connections Recurrent connections esp. in CA3: Autoassociator? Sparse activations (especially in DG): Pattern Separation?
28 Patients with Hippocampal only Deficits RB: damage limited to CA1 fields bilaterally: moderate anterograde but minimal retrograde amnesia GD: damage restricted primarily to the CA1 fields: moderate anterograde but minimal retrograde amnesia LM: damage to all CA fields and dentate gyrus and some cells in entorhinal cortex: moderate anterograde AND graded retrograde amnesia
29 The Aplysia Model Sea slugs exhibit both a short-lasting and a longer-lasting change in its gill retraction response to noxious stimuli The short-lasting response results from even a single stimulation, whereas the longer-lasting response stems from multiple stimulations Short-lasting response involves increases in neurotransmitter release Longer-lasting response involves growth of new synapses Mechanism: long-term potentiation
30 Alternative Hypothesis about Hippocampal Function: Place Memory Two systems for spatial navigation Taxon System: egocentric and governed by local landmarks Locale System: allocentric map
31 Role of Hippocampus in Spatial Navigation Locale memory system lost with hippocampal lesions Evidence of place cells in hippocampus Although these cells may not specify only place Current ongoing attempts to resolve the competing claims about the hippocampus: entry into long term memory versus place memory
32 Long-term storage in cortex Although medial temporal lobe damage does cause graded retrograde amnesia, memories for the far past are retained, indicating that they are stored elsewhere Knowledge of objects depends on inferotemporal cortex Knowledge of faces depends on fusiform gyrus Knowledge of spatial layouts depends on parietal cortex Damasio episodic memory depends on convergence zones (at least until the direct cortico-cortico connections are established.
MEMORY. Announcements. Practice Question 2. Practice Question 1 10/3/2012. Next Quiz available Oct 11
 Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
More dendritic spines, changes in shapes of dendritic spines More NT released by presynaptic membrane
 LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
Henry Molaison. Biography. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Serial model. Amnesia. Amnesia. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras. Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
 Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Serial model Memory terminology based on information processing models e.g., Serial Model Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Serial model Memory terminology based on information processing models e.g., Serial Model Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory
 Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Hippocampus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Systems Neuroscience November 29, Memory
 Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
Theories of memory. Memory & brain Cellular bases of learning & memory. Epileptic patient Temporal lobectomy Amnesia
 Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
to Cues Present at Test
 1st: Matching Cues Present at Study to Cues Present at Test 2nd: Introduction to Consolidation Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 05/03/2018: Lecture 06-4 Note: This Powerpoint
1st: Matching Cues Present at Study to Cues Present at Test 2nd: Introduction to Consolidation Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 05/03/2018: Lecture 06-4 Note: This Powerpoint
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
"False tagging mechanism False Tagging Theory All idea initially believed Doubt occur when prefrontal cortex tags it as false Provides doubt and
 Ventromedial Notes Frontal lobe Prefrontal cortex 1. dorsolateral cortex Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility Planning 2. Orbitofrontal cortex Controls
Ventromedial Notes Frontal lobe Prefrontal cortex 1. dorsolateral cortex Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility Planning 2. Orbitofrontal cortex Controls
MEMORY STORAGE. There are three major kinds of storage:
 MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
Introduction to Long-Term Memory
 Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Consolidation of Memories. Memory in the Real World
 Finish: Consolidation of Memories. Begin: Memory in the Real World Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 05/08/2018: Lecture 07-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain
Finish: Consolidation of Memories. Begin: Memory in the Real World Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 05/08/2018: Lecture 07-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation
 Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1
 Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Mechanisms of Memory: Can we distinguish true from false memories?
 Mechanisms of Memory: Can we distinguish true from false memories? Lila Davachi D. Cohen (1996) Dept of Psychology & Center for Neural Science New York University AAAS Judicial Seminar on Neuroscience
Mechanisms of Memory: Can we distinguish true from false memories? Lila Davachi D. Cohen (1996) Dept of Psychology & Center for Neural Science New York University AAAS Judicial Seminar on Neuroscience
Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis
 97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior
 Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Memory 2/15/2017. The Three Systems Model of Memory. Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information
 Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION. Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni
 FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
Outline 3/14/2013. Practice question What are the two types of learning we discussed? Example: remembering our ATM PIN. PSYC 120 General Psychology
 Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
Summarized by. Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
Dissociation Explanation
 Dissociation Explanation Introduction: What is Dissociation? Dissociation is the term used to describe a coping mechanism that is used by people to disconnect from some aspect of experience in life. Often
Dissociation Explanation Introduction: What is Dissociation? Dissociation is the term used to describe a coping mechanism that is used by people to disconnect from some aspect of experience in life. Often
Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior. James L. McClelland Stanford University
 Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
BRAIN PLASTICITY. Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
Morris water maze: standard test for spatial memory in rodents
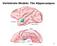 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 34 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 35 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 36 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 37 Animal Models of Learning (Vertebrates) Morris water
Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 34 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 35 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 36 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 37 Animal Models of Learning (Vertebrates) Morris water
Memory. Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith
 Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Importance of Deficits
 Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning
 Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
Systems Neuroscience CISC 3250
 Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved
 Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
How Many Colors Can You Remember? Capacity is about Conscious vs unconscious memories
 Science B44 Lecture 18 Visual Memory Memory 1. Afterimage, persistence, iconic sensory memory 2. Conscious vs unconscious memories 3. Short and long term memories 4. Where are memories seen 5. Flashbulb
Science B44 Lecture 18 Visual Memory Memory 1. Afterimage, persistence, iconic sensory memory 2. Conscious vs unconscious memories 3. Short and long term memories 4. Where are memories seen 5. Flashbulb
NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5)
 NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5) Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition 4 Forms of memory. Neural basis of memory (1): amnesia, the hippocampus Rudolf Cardinal Department of Experimental
NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5) Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition 4 Forms of memory. Neural basis of memory (1): amnesia, the hippocampus Rudolf Cardinal Department of Experimental
Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk.
 chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
October 2, Memory II. 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome. 9 Recent/Remote Distinction. 11 Frontal/Executive Contributions to Memory
 1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
U3A PSYCHOLOGY. How Memory works January 2019
 U3A PSYCHOLOGY How Memory works January 2019 How memory works This session will cover: A definition of memory Different types of memory Some theories of memory Why we forget How to improve your memory?
U3A PSYCHOLOGY How Memory works January 2019 How memory works This session will cover: A definition of memory Different types of memory Some theories of memory Why we forget How to improve your memory?
PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM
 PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M.Phil.) Assistant Professor Physiology Limbic system: (shown in dark pink) Limbic = border Definition: limbic system means the entire neuronal
PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M.Phil.) Assistant Professor Physiology Limbic system: (shown in dark pink) Limbic = border Definition: limbic system means the entire neuronal
PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS
 START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
Memory Disorders. 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc).
 I. Types of memory: A. Declarative memory: Memory Disorders 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc). B. Procedural memory: - examples:
I. Types of memory: A. Declarative memory: Memory Disorders 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc). B. Procedural memory: - examples:
CRISP: Challenging the Standard Framework of Hippocampal Memory Function
 CRISP: Challenging the Standard Framework of Hippocampal Memory Function Laurenz Wiskott Mehdi Bayati Sen Cheng Jan Melchior Torsten Neher supported by: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft - Sonderforschungsbereich
CRISP: Challenging the Standard Framework of Hippocampal Memory Function Laurenz Wiskott Mehdi Bayati Sen Cheng Jan Melchior Torsten Neher supported by: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft - Sonderforschungsbereich
Medicine Review Course Approach to Transient Amnesia
 Medicine Review Course Approach to Transient Amnesia 9 Sept 2012 Dr See Siew Ju Neurology NNI@SGH A Few Questions.. What did you have for breakfast on Friday? How many red lights did you stop at on your
Medicine Review Course Approach to Transient Amnesia 9 Sept 2012 Dr See Siew Ju Neurology NNI@SGH A Few Questions.. What did you have for breakfast on Friday? How many red lights did you stop at on your
Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript
 Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript In class Tuesday we introduced learning disabilities and looked at a couple of different activities that are consistent and representative of
Beattie Learning Disabilities Continued Part 2 - Transcript In class Tuesday we introduced learning disabilities and looked at a couple of different activities that are consistent and representative of
Prof. Greg Francis 5/23/08
 Forgetting IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 20 How accurate is eye-witness testimony? Fundamental fact There is no method other than object physical evidence to verify the accuracy of
Forgetting IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 20 How accurate is eye-witness testimony? Fundamental fact There is no method other than object physical evidence to verify the accuracy of
Why is dispersion of memory important*
 What is memory* It is a web of connections Research has shown that people who lose their memory also lose the ability to connect things to each other in their mind It is these connections that let us understand
What is memory* It is a web of connections Research has shown that people who lose their memory also lose the ability to connect things to each other in their mind It is these connections that let us understand
Which of the following is not an example of a reinforced behavior?
 Learning that is not mechanically acquired through reinforcement, void of overt responses, and is gained through paying attention to other's behavior is called learning. 1. observational 2. association
Learning that is not mechanically acquired through reinforcement, void of overt responses, and is gained through paying attention to other's behavior is called learning. 1. observational 2. association
Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why
 Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why do we forget things? Learning Causes Forgetting: Interference
Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why do we forget things? Learning Causes Forgetting: Interference
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL
 MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
A model of the interaction between mood and memory
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING NETWORK: COMPUTATION IN NEURAL SYSTEMS Network: Comput. Neural Syst. 12 (2001) 89 109 www.iop.org/journals/ne PII: S0954-898X(01)22487-7 A model of the interaction between
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING NETWORK: COMPUTATION IN NEURAL SYSTEMS Network: Comput. Neural Syst. 12 (2001) 89 109 www.iop.org/journals/ne PII: S0954-898X(01)22487-7 A model of the interaction between
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
Two ways of assessing recall*
 Recall* Recall or retrieval of memory refers to the subsequent re-accessing of events or information from the past, which have been previously encoded and stored in the brain. In common parlance, it is
Recall* Recall or retrieval of memory refers to the subsequent re-accessing of events or information from the past, which have been previously encoded and stored in the brain. In common parlance, it is
PSY 315 Lecture 13 (3/7/2011) (Learning & Memory Mechanics) Dr. Achtman PSY 215
 PSY 215 Lecture 13 Topic: Learning & Memory- Mechanics Chapter 13.2, pages 393-399 Announcements: Question #37 was removed from Exam 2 and all students will receive an additional point. Average grade on
PSY 215 Lecture 13 Topic: Learning & Memory- Mechanics Chapter 13.2, pages 393-399 Announcements: Question #37 was removed from Exam 2 and all students will receive an additional point. Average grade on
Memory. Chapter 7 Outline. Human Memory: Basic Questions. Memory 10/2/ Prentice Hall 1. Chapter 7. How is pulled back out ( ) from memory?
 Memory Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Outline Basic Processing Encoding Retrieval Systems of Memory Physiology of Memory Your Memory Human Memory: Basic Questions How does get into memory? How is information in memory?
Memory Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Outline Basic Processing Encoding Retrieval Systems of Memory Physiology of Memory Your Memory Human Memory: Basic Questions How does get into memory? How is information in memory?
Singers sometimes find it difficult to recall old song lyrics because of all the new songs they have learned.
 PROACTIVE AND RETROACTIVE INTERFERENCE PRACTICE When the aisles of a shopping mart are changed, you may instinctively start walking towards the old shelves instead of the new ones. Singers sometimes find
PROACTIVE AND RETROACTIVE INTERFERENCE PRACTICE When the aisles of a shopping mart are changed, you may instinctively start walking towards the old shelves instead of the new ones. Singers sometimes find
Elizabeth Loftus. Lost in the mall study 1992
 Lost in the mall study 1992 -Subject was told 4 stories from his past, including one that was made up about him being lost in the mall at age 5. -Over the next two weeks, he jotted down whatever memories
Lost in the mall study 1992 -Subject was told 4 stories from his past, including one that was made up about him being lost in the mall at age 5. -Over the next two weeks, he jotted down whatever memories
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Two cortical systems for memoryguided
 Two cortical systems for memoryguided behaviour Charan Ranganath 1,2 and Maureen Ritchey 2 Abstract Although the perirhinal cortex (PRC), parahippocampal cortex (PHC) and retrosplenial cortex (RSC) have
Two cortical systems for memoryguided behaviour Charan Ranganath 1,2 and Maureen Ritchey 2 Abstract Although the perirhinal cortex (PRC), parahippocampal cortex (PHC) and retrosplenial cortex (RSC) have
Announcements. Grade Query Tool Updated with. Exam Scores Aplia Scores Cumulative scores and comparison to class
 Announcements Grade Query Tool Updated with Exam Scores Aplia Scores Cumulative scores and comparison to class Chapter 7 Aplia due Tonight Chapter 8 Aplia due Monday night Earliest Memory still time to
Announcements Grade Query Tool Updated with Exam Scores Aplia Scores Cumulative scores and comparison to class Chapter 7 Aplia due Tonight Chapter 8 Aplia due Monday night Earliest Memory still time to
Announcements. Returning to Memory. V. Stage of processing. V. Stage of Processing Model. What do you recall? 4/9/2014
 Announcements Grade Query Tool Updated with Exam Scores Aplia Scores Cumulative scores and comparison to class Chapter 7 Aplia due Tonight Chapter 8 Aplia due Monday night Earliest Memory still time to
Announcements Grade Query Tool Updated with Exam Scores Aplia Scores Cumulative scores and comparison to class Chapter 7 Aplia due Tonight Chapter 8 Aplia due Monday night Earliest Memory still time to
Cerebral Cortex. Edmund T. Rolls. Principles of Operation. Presubiculum. Subiculum F S D. Neocortex. PHG & Perirhinal. CA1 Fornix CA3 S D
 Cerebral Cortex Principles of Operation Edmund T. Rolls F S D Neocortex S D PHG & Perirhinal 2 3 5 pp Ento rhinal DG Subiculum Presubiculum mf CA3 CA1 Fornix Appendix 4 Simulation software for neuronal
Cerebral Cortex Principles of Operation Edmund T. Rolls F S D Neocortex S D PHG & Perirhinal 2 3 5 pp Ento rhinal DG Subiculum Presubiculum mf CA3 CA1 Fornix Appendix 4 Simulation software for neuronal
Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine. University of Split
 Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine University of Split Nonassociative? Associative? Nonassociative learning when an animal or a person is exposed once or repeatedly
Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine University of Split Nonassociative? Associative? Nonassociative learning when an animal or a person is exposed once or repeatedly
memory Examples: Obama is president, PSYC 2 is in Price Center Theater, my 21st birthday was a disaster
 PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Cognition 2 Version: 11/18/12 - original version Memory Classifications A note on memory classifications Definitions developed from
PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Cognition 2 Version: 11/18/12 - original version Memory Classifications A note on memory classifications Definitions developed from
Acetylcholine again! - thought to be involved in learning and memory - thought to be involved dementia (Alzheimer's disease)
 Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Patient education : The Effects of Epilepsy on Memory Function
 Patient education : The Effects of Epilepsy on Memory Function Patricia G. Banks, RN, MSNEd, CCRP, VHACM Program Coordinator National office of Neurology Louis Stoke Cleveland VAMC Thursday, June 6, 2013
Patient education : The Effects of Epilepsy on Memory Function Patricia G. Banks, RN, MSNEd, CCRP, VHACM Program Coordinator National office of Neurology Louis Stoke Cleveland VAMC Thursday, June 6, 2013
Butter Food Eat Sandwich Rye Jam Milk Flour Jelly Dough Crust Slice Wine Loaf Toast
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Comments on your comments Thank you! Some things that I can change NOW: Slow
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Comments on your comments Thank you! Some things that I can change NOW: Slow
The Learning Process. Learning is a Process. Behavioral Learning Theories. Chapter 3 Learning and Memory. How many of these do you remind?
 Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
The motor regulator. 2) The cerebellum
 The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Feed-back and feed-forward control circuits By
The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Feed-back and feed-forward control circuits By
Cronicon EC NEUROLOGY. Mini Review. Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain. Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA *Corresponding Author: Caron Leid, Aspen University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA *Corresponding Author: Caron Leid, Aspen University,
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
How attract your dream clients
 How attract your dream clients Would you like to bring healing where it's truly needed to people who appreciate what you do? Or would prefer to stagger back home after a treatment feeling tired and drained?
How attract your dream clients Would you like to bring healing where it's truly needed to people who appreciate what you do? Or would prefer to stagger back home after a treatment feeling tired and drained?
Dissociative Experiences Scale-II (DES-II) DIRECTIONS
 Dissociative Experiences Scale-II (DES-II) Eve Bernstein Carlson, Ph.D. & Frank W. Putnam, M.D. DIRECTIONS This questionnaire consists of twenty-eight questions about experiences that you may have in your
Dissociative Experiences Scale-II (DES-II) Eve Bernstein Carlson, Ph.D. & Frank W. Putnam, M.D. DIRECTIONS This questionnaire consists of twenty-eight questions about experiences that you may have in your
PSY 215 Lecture 13 (3/7/11) Learning & Memory Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 13 Topic: Mechanisms of Learning and Memory Chapter 13, section 13.
 PSY 215 Lecture 13 Topic: Mechanisms of Learning and Memory Chapter 13, section 13.2 Corrections: No corrections Announcements: Question # 37 was thrown out on the last test because it was confusing the
PSY 215 Lecture 13 Topic: Mechanisms of Learning and Memory Chapter 13, section 13.2 Corrections: No corrections Announcements: Question # 37 was thrown out on the last test because it was confusing the
Autobiographical Memory. Chapter 8 (p )
 Autobiographical Memory Chapter 8 (p202-213) Autobiographical Memory (AM) Mental time travel Field perspective vs. observer perspective Episodic and semantic memory components Multidimensional: verbal,
Autobiographical Memory Chapter 8 (p202-213) Autobiographical Memory (AM) Mental time travel Field perspective vs. observer perspective Episodic and semantic memory components Multidimensional: verbal,
Emotional Quotient. Andrew Doe. Test Job Acme Acme Test Slogan Acme Company N. Pacesetter Way
 Emotional Quotient Test Job Acme 2-16-2018 Acme Test Slogan test@reportengine.com Introduction The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
Emotional Quotient Test Job Acme 2-16-2018 Acme Test Slogan test@reportengine.com Introduction The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
Synap&c Plas&city. long-term plasticity (~30 min to lifetime) Long-term potentiation (LTP) / Long-term depression (LTD)
 Synap&c Plas&city synaptic connectivity constantly changes in response to activity and other factors During development: provides the basic wiring of the brain s circuits Throughout rest of life: basis
Synap&c Plas&city synaptic connectivity constantly changes in response to activity and other factors During development: provides the basic wiring of the brain s circuits Throughout rest of life: basis
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Visual Memory Any neural or behavioural phenomenon implying storage of a past visual experience. E n c o d i n g. Individual exemplars:
 Long-term Memory Short-term Memory Unconscious / Procedural Conscious / Declarative Working Memory Iconic Memory Visual Memory Any neural or behavioural phenomenon implying storage of a past visual experience.
Long-term Memory Short-term Memory Unconscious / Procedural Conscious / Declarative Working Memory Iconic Memory Visual Memory Any neural or behavioural phenomenon implying storage of a past visual experience.
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015
 Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Learning and Memory. The Case of H.M.
 Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Spatial View Cells and the Representation of Place in the Primate Hippocampus
 Spatial View Cells and the Representation of Place in the Primate Hippocampus Edmund T. Rolls* Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford, Oxford, England HIPPOCAMPUS 9:467 480 (1999)
Spatial View Cells and the Representation of Place in the Primate Hippocampus Edmund T. Rolls* Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford, Oxford, England HIPPOCAMPUS 9:467 480 (1999)
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience. Nov. 28, The limbic system. Daniel C. Kiper
 Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
A systems neuroscience approach to memory
 A systems neuroscience approach to memory Critical brain structures for declarative memory Relational memory vs. item memory Recollection vs. familiarity Recall vs. recognition What about PDs? R-K paradigm
A systems neuroscience approach to memory Critical brain structures for declarative memory Relational memory vs. item memory Recollection vs. familiarity Recall vs. recognition What about PDs? R-K paradigm
Introduction to Cognitive Neuroscience fmri results in context. Doug Schultz
 Introduction to Cognitive Neuroscience fmri results in context Doug Schultz 3-2-2017 Overview In-depth look at some examples of fmri results Fusiform face area (Kanwisher et al., 1997) Subsequent memory
Introduction to Cognitive Neuroscience fmri results in context Doug Schultz 3-2-2017 Overview In-depth look at some examples of fmri results Fusiform face area (Kanwisher et al., 1997) Subsequent memory
?Pass Out? vs.?blackout?: How Alcohol Can Affect Memory (And Why It Matters)
 Published on Voice For The Defense Online (https://www.voiceforthedefenseonline.com) Home > Printer-friendly PDF?Pass Out? vs.?blackout?: How Alcohol Can Affect Memory (And Why It Matters) [1]Features
Published on Voice For The Defense Online (https://www.voiceforthedefenseonline.com) Home > Printer-friendly PDF?Pass Out? vs.?blackout?: How Alcohol Can Affect Memory (And Why It Matters) [1]Features
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II
 THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
Interplay of Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex in Memory
 Current Biology 23, R764 R773, September 9, 2013 ª2013 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.041 Interplay of Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex in Memory Review Alison
Current Biology 23, R764 R773, September 9, 2013 ª2013 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.041 Interplay of Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex in Memory Review Alison
4/15/2018. Neuroplasticity: Is it for Real? Neuroplasticity Research. Neuroplasticity Research. You can wire and re-wire your brain!
 Neuroplasticity: Is it for Real? Sandra Petersen, DNP, APRN, FNP/GNP-BC, PMHNP-BE, FAANP Neuroplasticity Research You can wire and re-wire your brain! Our brain is a dynamic system that has the capability
Neuroplasticity: Is it for Real? Sandra Petersen, DNP, APRN, FNP/GNP-BC, PMHNP-BE, FAANP Neuroplasticity Research You can wire and re-wire your brain! Our brain is a dynamic system that has the capability
There are often questions and, sometimes, confusion when looking at services to a child who is deaf or hard of hearing. Because very young children
 There are often questions and, sometimes, confusion when looking at services to a child who is deaf or hard of hearing. Because very young children are not yet ready to work on specific strategies for
There are often questions and, sometimes, confusion when looking at services to a child who is deaf or hard of hearing. Because very young children are not yet ready to work on specific strategies for
Thank you for your time and dedication to our industry and community.
 secti To: AFP International Fundraising Conference Speakers From: Troy P. Coalman, Board Member, AFP Advancement Northwest, and Member, AFP International Committee for Diversity & Inclusion Date: February
secti To: AFP International Fundraising Conference Speakers From: Troy P. Coalman, Board Member, AFP Advancement Northwest, and Member, AFP International Committee for Diversity & Inclusion Date: February
Marketing Religion DAIANA KAPLAN
 2015 Marketing Religion DAIANA KAPLAN Marketing Religion Abstract Religion has been marketed since the beginning of its existence and simply by considering how many different religions there are today
2015 Marketing Religion DAIANA KAPLAN Marketing Religion Abstract Religion has been marketed since the beginning of its existence and simply by considering how many different religions there are today
