Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011
|
|
|
- Tiffany Riley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance. Parents and children generally have similar eye color, hair texture, height and other characteristics because children inherit genes that control specific characteristics from their parents. Where are genes found in our bodies? Researchers have shown that genes are parts of DNA molecules, and DNA molecules are contained in chromosomes in the nucleus of each cell in our body. How do genes influence our characteristics? Each gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that gives the instructions for making a protein. For example, one gene gives the instructions for making a protein enzyme which helps to make melanin, the pigment which contributes to the color of skin, eyes and hair. Different versions of the gene (called alleles) code for different versions of the protein. One allele of this gene codes for an enzyme that produces melanin, resulting in normally pigmented skin and hair; it is symbolized by A. Another allele of this gene (symbolized by a) codes for an enzyme that cannot produce melanin; this results in very pale skin and hair, which is called albinism. How does a baby inherit genes from his or her mother and father? When we talk about genes being inherited from one generation to the next, we are really talking about how the gene-carrying chromosomes behave during meiosis and fertilization. As you will see in the next section, if you understand how the mother's and father's chromosomes behave during meiosis and fertilization, you can understand why the zygote that becomes a baby has two copies of each gene, one copy from the mother and one copy from the father. In the next section, you will demonstrate this, using model chromosomes. Inheritance of Albinism To learn more about how genetic traits are inherited, you will analyze a specific question: If each parent has one A allele and one a allele (i.e. both parents are Aa), what different combinations of A and/or a alleles would you expect to observe in the children of these parents? To answer this question your group will use four model chromosomes. The pair of homologous chromosomes for each parent will include one model chromosome with an A allele and a second model chromosome with an a allele. 1 Teachers are encouraged to copy this student handout for classroom use. A Word file (which can be used to prepare a modified version if desired), Teacher Preparation Notes, comments, and the complete list of our hands-on activities are available at An alternative version of this activity that does not use model chromosomes is available in the Teacher Preparation Notes for this activity. Additional genetics activities are available at
2 1. One of you should be the mother and use your model chromosomes to demonstrate how meiosis produces different types of eggs, and another should be the father and demonstrate how meiosis produces different types of sperm. In the chart below, write in the genetic makeup of the two types of eggs and the two types of sperm produced by meiosis. 2. Next, model fertilization, using the model chromosome for each type of sperm to fertilize each type of egg. Write the genetic makeup of the resulting zygotes in the chart. To answer the following questions, remember that each zygote undergoes repeated mitosis to become a child, so the child will have the same genetic makeup as the zygote. 3. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to be AA? 4. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to be Aa? 5. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to be aa? The children who have AA alleles will have normal pigmentation, and the children who have aa alleles will have albinism. These children are homozygous for the A allele or the a allele. Homozygous means that both copies of the gene have the same allele. The next question is: Will children who have Aa alleles have normal pigmentation or be albino? This type of combination of two different alleles is called heterozygous. Often, one allele in a heterozygous pair of alleles is dominant and the other allele is recessive; this means that the dominant allele determines the observable characteristic of the heterozygous individual. Typically, the dominant allele is symbolized by a capital letter, in this case A for the allele for normal pigmentation. Thus, heterozygous (Aa) individuals will have normal pigmentation. 6. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to have normal pigmentation? 7. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to have albinism? 2
3 The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual. The phenotype refers to the observable physical and physiological characteristics of an individual. 8. Give an example of two individuals who have the same phenotype, but different genotypes for the albinism gene. Explain how two individuals with the same phenotype can have different genotypes. Biologists frequently express the fractions of different genotypes or phenotypes as ratios. For example, for the mating between two heterozygous parents, the genotype fractions are 1/4 AA, 2/4 Aa, 1/4 aa, which can also be expressed as a 1:2:1 ratio. 9. For the corresponding phenotypes, the fraction with normal pigmentation is and the fraction with albinism is, so the corresponding ratio is. Notice that the chart you completed on page 2 has been very useful in helping you to answer important questions about the inheritance of albinism. Biologists frequently use a simplified version of this chart, called a Punnett Square, to analyze inheritance. The chart below shows a Punnett Square for the example you have been analyzing. A a A AA Aa a Aa aa 10. For this Punnett Square, use arrows to indicate the genetic makeup of each sperm and egg and circle the genetic makeup of each type of zygote. 11. Sally and Harry fall in love. They introduce Sally's identical twin, Emily, to Harry's identical twin, Ken. Soon there is a double wedding where Sally marries Harry and Emily marries Ken. Both Sally and Emily get pregnant. They wonder "Will their babies look exactly alike?" Answer their question, and explain your reasoning. (To answer this question, think about the children that could be produced if both pairs of identical twins are heterozygous Aa.) Coin Toss Genetics The way genes behave can easily be simulated using two-sided coins, where tails represent the recessive allele that controls pigment production (a), and heads represent the dominant allele (A). Suppose a parent is heterozygous (Aa). Then, tossing a coin and checking for tails up vs. heads up represents the chance that an egg or sperm produced by the parent will include an a allele or an A allele. To simulate a mating between two heterozygous (Aa) parents, two students will each toss a coin and the result of the pair of coin tosses will indicate the pair of alleles contributed by an egg and a sperm to the baby that results from that mating. 3
4 Find someone to mate with. 1. Each of you will toss your coin, and this pair of coin tosses will indicate the pair of alleles in the first child produced by a mating of two heterozygous (Aa) parents. Make three more pairs of coin tosses to determine the genetic makeup for the second, third and fourth children in this family. Record how many of these 4 children had each of the 3 possible combinations (AA, Aa, or aa) in the row labeled "first family of 4 children" in the table below. 2. Now make 4 more pairs of coin tosses to indicate the alleles in a second family of 4 children. Record these genotypes in the second row in the table below. 3. Do this two more times and record the results in the third and fourth rows of the table below. First family of 4 children Genetic makeup of "children" produced by two heterozygous (Aa) parents AA Aa aa Next family of 4 children Next family of 4 children Next family of 4 children Total Predictions based on Punnett Square (page 3) 1/4 = 25% 2/4 = 50% 1/4 = 25% Class data -- Percents (Total # children = ) 4. Add up your results to determine the total number of children from your coin tosses who had AA, Aa, and aa. Add your numbers to the table of class data. 6. For each family of 4 children produced by your coin toss matings, compare the results with the predictions from the Punnett Square. Are the numbers of AA, Aa, and aa genotypes in your families of 4 children similar to the predicted? Did you get different results in different families? Did any family have no albino (aa) children? Did any family have 2 or more albino children? 4
5 7. Enter the results for the class data in the table on page 4. Are the percents of each genotype in the class data similar to the predictions of the Punnett Square? If there is a difference between the results for the class data and the predictions, is this difference relatively small or large? In many cases, the results for a family of four children will not match the predictions of the Punnett Square. Random variation in which particular sperm fertilizes which particular egg explains why the children in the individual families may differ considerably from the predictions based on the Punnett Square. The random variation observed in small samples usually averages out in large samples. Therefore, the results for a large number of children from multiple pairs of parents with the same genetic makeup are usually close to the predictions of the Punnett Square. Genetics of Sex Determination As you probably know, human males have an X and a Y chromosome (XY), whereas females have two X chromosomes (XX). A zygote must have at least one X chromosome to survive. The gene that causes the development of male anatomy is located on the Y chromosome. This gene is called SRY, which stands for sex-determining region of the Y chromosome. If a zygote has a Y chromosome with the SRY gene, the embryo will develop testes and male anatomy. If a zygote does not have a Y chromosome with the SRY gene, the embryo will develop ovaries and female anatomy. Your understanding of meiosis and fertilization provides the basis for understanding the inheritance of X and Y chromosomes. During meiosis in a female, the two X-chromosomes separate, so each egg has a single X-chromosome. In males, even though the X and the Y- chromosomes are very different, they can nevertheless pair with each other and separate from each other during meiosis. This means that males produce two kinds of sperm; half have an X chromosome and half have a Y chromosome. 1. What will be the sex of a child produced when an egg is fertilized by a sperm that has a Y chromosome? What type of sperm must fertilize an egg to result in a female child? 2. Draw a Punnett Square which shows the inheritance of the sex chromosomes. Use X to indicate an egg or sperm with an X chromosome and Y to indicate a sperm with a Y chromosome. 3. Based on this Punnett Square, what percent of children would you expect to be male? 5
6 4. To test this prediction, begin by writing down the initials of all the children your mother has had. Arrange these initials in order from the oldest to the youngest, indicating whether each was male or female. 5. Complete the following table. Your mother's children Total number of children Number of males % males Children of the mothers of all the students in your class Predicted percent from Punnett square, page 5 6. Next, compare the predicted percent male with the observed percent male for your mother s children, for the children of the mothers of the other members of your group, and for all the children in the class sample. How similar to the prediction are the observed results for individual families and for all the families combined? Notice that the percent male children varies in different families and the percent male children in some families is very different from the predicted. To understand why, remember that each time a sperm fertilizes an egg to form a new zygote, there is random variation in whether the sperm has an X or Y chromosome. Random variation tends to average out in large samples, so the overall percent male children for all the mothers will usually be fairly close to the predicted 1/2. 7. To answer the following questions, look at your group s lists in question 4 above. If a mother's first child is a son, is the next child necessarily a daughter? If a mother's first child is a daughter, is the next child necessarily a son? If a mother's first two children are sons, is the next child necessarily a daughter? If a mother's first two children are daughters, is the next child necessarily a son? These observations illustrate that you cannot predict the sex of the next child based on the sex of a previous child or children. Each time a sperm fertilizes an egg, the results are independent of any previous fertilizations that resulted in older brothers or sisters. 6
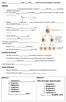
7 Genetics of Sickle Cell Anemia Some alleles of certain genes can cause disease. An example is the gene for hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. One allele codes for normal hemoglobin, while another allele codes for altered hemoglobin, called sickle cell hemoglobin. When a person is homozygous for the sickle cell allele, this causes a serious disease called sickle cell anemia. The sickle cell hemoglobin tends to clump into long rods that cause the red blood cells to assume a sickle shape, in contrast to the normal disk-shaped red blood cell shown on the left in the figure below. 1. What problems might be caused by the sickle-shaped red blood cells? A person who is heterozygous for the sickle cell and normal hemoglobin alleles usually does not have symptoms of sickle cell anemia, so in this respect they are like a person who is homozygous for the normal hemoglobin allele. This is why textbooks usually describe the sickle cell allele as recessive. However, people who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele are not exactly like people who are homozygous for the normal hemoglobin allele. People who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele are less likely to develop severe malaria, an infection of the red blood cells which is transmitted by mosquitoes in many tropical countries. Thus, in areas where malaria is widespread, people who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele are less likely to become seriously ill and die. Because of this advantage, the sickle cell allele became relatively common in regions like West Africa where malaria is common. Since African-Americans are descended from populations in which the sickle cell allele was relatively common, African-Americans have relatively high rates of the sickle cell allele (approximately 8% are heterozygous for this allele and 0.16% are homozygous). 2. Suppose that a person who is heterozygous for the sickle cell allele (Ss) marries a person who is also heterozygous for this allele (Ss). Draw a Punnett Square to show the expected genetic makeup of their children. 3. On average, what fraction of their children will suffer from sickle cell anemia? 4. On average, what fraction of their children will be heterozygous for the sickle cell allele? (These children will not have sickle cell anemia and will be less likely to develop severe malaria.) 7
8 Pedigree Analysis Human geneticists illustrate the inheritance of a gene within a family by using a pedigree chart. On such a chart, males are symbolized by a square ( ) and females are symbolized by a circle ( ). People who are affected by a disease are symbolized by a dark square or circle. The pedigree chart below shows inheritance of albinism. 1 and 2 represent a couple who had five children, including a son who is labeled 3 and a daughter who is labeled 5. Only one of the children, 5, was albino. The son who is labeled 3 and his wife who is labeled 4 had four children, including a son who is labeled In the pedigree below write the genotypes of the individuals who are labeled with numbers, using (A) to represent the dominant allele and (a) to represent the recessive allele. Start by indicating the genotypes of 5 and 6. Next, draw a Punnett Square for parents 3 and 4 and their offspring to figure out what the genotypes for 3 and 4 must be. Next, determine the genotypes of 1 and 2. Finally, determine the genotype of Many other genes have a recessive allele which is inherited in the same manner as the recessive allele for albinism. These include the recessive alleles that cause some genetic diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis (a genetic disease that results in difficulty in breathing and serious illness), and phenylketonuria (a genetic disease that results in mental retardation unless detected at birth and treated with a special diet, etc.). 9
9 Challenge Question Shown below is a pedigree chart for the inheritance of achondroplasia (ay-kon-druh-play-zhuh), a form of dwarfism. Dark circles or squares indicate individuals with achondroplasia. Examine the pedigree chart, and answer the following questions. 1. Is the allele that causes this form of dwarfism recessive or dominant? How do you know? 2. Using D to represent the dominant allele and d to represent the recessive allele, write the genotypes of the indicated individuals. Start by indicating the genotypes of 2, 3 and 7. Next, draw a Punnett Square for parents 5 and 6 and their offspring to figure out what the genotypes for 5 and 6 must be. Next, determine the genotypes of 1 and Based on the frequency of dwarfs among the people you have seen in your lifetime, do you think that the allele for achondroplasia is common or rare in the population? 9
Normal enzyme makes melanin (dark pigment in skin and hair) Defective enzyme does not make melanin
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
2. Circle the genotypes in the table that are homozygous. Explain how the two different homozygous genotypes result in different phenotypes.
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
How do genes influence our characteristics?
 Genetics Supplement 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts:
Genetics Supplement 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts:
Genetics 1. How do genes influence our characteristics?
 Genetics 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts: How do
Genetics 1 This activity will focus on the question: How do genes contribute to the similarities and differences between parents and their children? This question can be divided into two parts: How do
BIOL 109L Laboratory five Fall 2018
 BIOL 109L Laboratory five Fall 2018 Understanding Genetics and Inheritance Student full name: Introduction: Chromosomes are like a set of books that provide instructions for building and operating an individual.
BIOL 109L Laboratory five Fall 2018 Understanding Genetics and Inheritance Student full name: Introduction: Chromosomes are like a set of books that provide instructions for building and operating an individual.
I. Introduction. In this activity you will learn some of the answers to these questions. We will begin by reviewing what chromosomes and genes are.
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization by Drs. Ingrid Waldron, Jennifer Doherty, R. Scott Poethig, and Lori Spindler Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2010 1 I. Introduction When you fall
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization by Drs. Ingrid Waldron, Jennifer Doherty, R. Scott Poethig, and Lori Spindler Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2010 1 I. Introduction When you fall
Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1. Chromosomes and Genes
 Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in a newborn baby? 1b.
Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in a newborn baby? 1b.
Were the babies switched? The Genetics of Blood Typesi
 Were the babies switched? The Genetics of Blood Typesi Two couples had babies on the same day in the same hospital. Denise and Earnest had a girl, Tonja. Danielle and Michael had twins, a boy, Michael,
Were the babies switched? The Genetics of Blood Typesi Two couples had babies on the same day in the same hospital. Denise and Earnest had a girl, Tonja. Danielle and Michael had twins, a boy, Michael,
Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1
 Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in a newborn baby? 1b.
Mitosis How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in a newborn baby? 1b.
Before you learn how new cells are made, we need to briefly review chromosomes and genes.
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in
Before you learn how new cells are made, we need to briefly review chromosomes and genes.
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle How a Single Cell Develops into the Trillions of Cells in a Human Body 1 Every person started as a single cell a fertilized egg. 1a. How many cells do you think there are in
Dragon Genetics -- Independent Assortment and Genetic Linkage
 Dragon Genetics -- Independent Asstment and Genetic Linkage This activity, by Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2008, incpates ideas from Dragon
Dragon Genetics -- Independent Asstment and Genetic Linkage This activity, by Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2008, incpates ideas from Dragon
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
DRAGON GENETICS Understanding Inheritance 1
 DRAGON GENETICS Understanding Inheritance 1 INTRODUCTION In this activity, you and a partner will work together to produce a baby dragon. You will simulate meiosis and fertilization, the biological processes
DRAGON GENETICS Understanding Inheritance 1 INTRODUCTION In this activity, you and a partner will work together to produce a baby dragon. You will simulate meiosis and fertilization, the biological processes
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Inheritance. Children inherit traits from both parents.
 Have you ever been told you have your mother s eyes or your father s smile? Have you ever noticed you share your grandfather s eye color or possibly your grandmother s curly hair, and yet your parents
Have you ever been told you have your mother s eyes or your father s smile? Have you ever noticed you share your grandfather s eye color or possibly your grandmother s curly hair, and yet your parents
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares
 Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Principles of Genetics Biology 204 Marilyn M. Shannon, M.A.
 Principles of Genetics Biology 204 Marilyn M. Shannon, M.A. Introduction Nature versus nurture is a topic often informally discussed. Are world-class musicians that good because they inherited the right
Principles of Genetics Biology 204 Marilyn M. Shannon, M.A. Introduction Nature versus nurture is a topic often informally discussed. Are world-class musicians that good because they inherited the right
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders
 Name Date Period Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders Background: Sometimes genetic disorders are caused by mutations to normal genes. When the mutation has been in the population
Name Date Period Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders Background: Sometimes genetic disorders are caused by mutations to normal genes. When the mutation has been in the population
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs:
 Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Biology 501, Summer 2007 Revised Lesson: August 13, 2007
 Biology Lesson: Traits and Inheritance Biology 501, Summer 2007 Revised Lesson: August 13, 2007 Instructors: Dr. Ingrid Waldron Jennifer Doherty TA: Jennifer Tareila Group Members: Theresa Lewis-King,
Biology Lesson: Traits and Inheritance Biology 501, Summer 2007 Revised Lesson: August 13, 2007 Instructors: Dr. Ingrid Waldron Jennifer Doherty TA: Jennifer Tareila Group Members: Theresa Lewis-King,
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE
 Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Name Class Date *PACKET NOTES & WORKSHEETS LAB GRADE MEIOSIS is specialized cell division resulting in cells with the genetic material of the parents Sex cells called have exactly set of chromosomes, this
Unit 5: Genetics Guided Notes
 1 Unit 5: Genetics Guided Notes Basic Mendelian Genetics Before Gregor Mendel 1) When Mendel started his work, most people believed in the blending theory of inheritance. (Inheritance, Heredity, and Genetics
1 Unit 5: Genetics Guided Notes Basic Mendelian Genetics Before Gregor Mendel 1) When Mendel started his work, most people believed in the blending theory of inheritance. (Inheritance, Heredity, and Genetics
11B Crazy Traits. What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? 1. Determining the genotype. 2. Stop and Think. Investigation 11B.
 11B Crazy Traits Investigation 11B What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? Your traits are determined by the genes you inherit from your parents. For each gene, you get at least one allele
11B Crazy Traits Investigation 11B What role does chance play in an organism s heredity? Your traits are determined by the genes you inherit from your parents. For each gene, you get at least one allele
12.1 X-linked Inheritance in Humans. Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12. X-linked Inheritance. X-linked Inheritance
 Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Units of Heredity: Chromosomes and Inheritance Ch. 12 12.1 in Humans X-chromosomes also have non genderspecific genes Called X-linked genes Vision Blood-clotting X-linked conditions Conditions caused by
Genetics Honors NOtes 2017 SHORT p2.notebook. May 26, 2017
 Do Now A man and woman want to predict the chances of their offspring having dimples. The woman is heterozygous for dimples and the man does not have dimples. What is the chance of having a child with
Do Now A man and woman want to predict the chances of their offspring having dimples. The woman is heterozygous for dimples and the man does not have dimples. What is the chance of having a child with
Genes and Inheritance (11-12)
 Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance
 Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Semester 2- Unit 2: Inheritance heredity -characteristics passed from parent to offspring genetics -the scientific study of heredity trait - a specific characteristic of an individual genes -factors passed
Section Objectives: Pedigrees illustrate inheritance. Pedigrees illustrate inheritance
 What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview 14.1 THINK ABOUT IT If you had to pick an ideal organism for the study of genetics, would you choose one that produced lots of offspring, was easy to grow in the lab, and had a short life
Lesson Overview 14.1 THINK ABOUT IT If you had to pick an ideal organism for the study of genetics, would you choose one that produced lots of offspring, was easy to grow in the lab, and had a short life
Patterns in Inheritance. Chapter 10
 Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
GENETICS NOTES. Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16
 GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
GENETICS NOTES Chapters 12, 13, 14, 15 16 DNA contains the genetic code for the production of PROTEINS. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The
REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS
 REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS TEKS 7.14A Define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next generation 7.14B Compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual
REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS TEKS 7.14A Define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next generation 7.14B Compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Human Genetics Notes:
 Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS
 Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
What You ll Learn. Genetics Since Mendel. ! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance
 Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
Meiosis and Genetics
 Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
Meiosis and Genetics Humans have chromosomes in each cell What pattern do you notice in the human karyotype (a technique that organizes chromosomes by type and size)? Humans are diploid 1 Gametes are produced
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes. Lesson Overview. Human Chromosomes
 Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Lesson Overview Karyotypes A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with chromosomes, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS:
 Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
GENETICS - NOTES-
 GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12
 40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
40 Bell Work Week 8 5/12 41 Genetic Notes 5/12 42 Bill Nye Video & Questions 5/12 1. I am available after school on Wed. and Thurs. this week. 2. Quiz Friday over genetic material 3. Last day to turn in
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
REVIEW SHEET: Units 11 Meiosis, Fertilization, & Genetics ACP BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Meiosis & Fertilization (Ch. 11.4, 14.1-2) and Classical Genetics (Ch. 11.1-3) Handouts:! NOTES Meiosis & Fertilization!
9/25/ Some traits are controlled by a single gene. Selective Breeding: Observing Heredity
 Chapter 7 Learning Outcomes Explain the concept of a single-gene trait Describe Mendel s contributions to the field of genetics Be able to define the terms gene, allele, dominant, recessive, homozygous,
Chapter 7 Learning Outcomes Explain the concept of a single-gene trait Describe Mendel s contributions to the field of genetics Be able to define the terms gene, allele, dominant, recessive, homozygous,
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans
 INTRODUCTION MENDELIAN GENETICS, PROBABILITY, PEDIGREES, AND CHI-SQUARE STATISTICS Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells (RBCs) that transports oxygen throughout the body. The hemoglobin protein
INTRODUCTION MENDELIAN GENETICS, PROBABILITY, PEDIGREES, AND CHI-SQUARE STATISTICS Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells (RBCs) that transports oxygen throughout the body. The hemoglobin protein
Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS
 Name Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS DAY 1: Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary A. Genetics- Study of B. Heredity- The passing on of characteristics (traits) from to C. Trait A particular that can vary from
Name Class *GENETIC NOTES & WORKSHEETS DAY 1: Mendelian Genetics Vocabulary A. Genetics- Study of B. Heredity- The passing on of characteristics (traits) from to C. Trait A particular that can vary from
Mendel. The pea plant was ideal to work with and Mendel s results were so accurate because: 1) Many. Purple versus flowers, yellow versus seeds, etc.
 Mendel A. Mendel: Before Mendel, people believed in the hypothesis. This is analogous to how blue and yellow paints blend to make. Mendel introduced the hypothesis. This deals with discrete units called
Mendel A. Mendel: Before Mendel, people believed in the hypothesis. This is analogous to how blue and yellow paints blend to make. Mendel introduced the hypothesis. This deals with discrete units called
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes
 Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
Meiotic Mistakes and Abnormalities Learning Outcomes 5.6 Explain how nondisjunction can result in whole chromosomal abnormalities. (Module 5.10) 5.7 Describe the inheritance patterns for strict dominant
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg
 14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
14.1 Human Chromosomes pg. 392-397 Lesson Objectives Identify the types of human chromosomes in a karotype. Describe the patterns of the inheritance of human traits. Explain how pedigrees are used to study
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Essential Questions. Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How can genetic patterns be analyzed to determine dominant or recessive inheritance patterns? What are examples of dominant and recessive disorders? How can human pedigrees be constructed
Essential Questions How can genetic patterns be analyzed to determine dominant or recessive inheritance patterns? What are examples of dominant and recessive disorders? How can human pedigrees be constructed
Introduction to Mendelian Genetics
 Introduction to Mendelian Genetics pollen stigma petals anthers Summary of Mendel s First Experiment pollen paintbrush ova ovary Mature male flower A mature pea flower has both male and female parts
Introduction to Mendelian Genetics pollen stigma petals anthers Summary of Mendel s First Experiment pollen paintbrush ova ovary Mature male flower A mature pea flower has both male and female parts
Genetics and Heredity Notes
 Genetics and Heredity Notes I. Introduction A. It was known for 1000s of years that traits were inherited but scientists were unsure about the laws that governed this inheritance. B. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Genetics and Heredity Notes I. Introduction A. It was known for 1000s of years that traits were inherited but scientists were unsure about the laws that governed this inheritance. B. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Science Olympiad Heredity
 Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Genetics Practice Questions:
 Genetics Practice Questions: 1. Define the following Vocabulary Words: Fertilization fusion of a haploid nucleus of an egg cell and a haploid nucleus of a sperm cell haploid-- a nucleus containing a single
Genetics Practice Questions: 1. Define the following Vocabulary Words: Fertilization fusion of a haploid nucleus of an egg cell and a haploid nucleus of a sperm cell haploid-- a nucleus containing a single
Names: Period: Punnett Square for Sex Chromosomes:
 Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Teacher Preparation Notes for Genetics and Genetics Supplement 1
 Teacher Preparation Notes for Genetics and Genetics Supplement 1 The Genetics Student Handout begins with sections that help students to understand basic principles of genetics, including (1) how genotype
Teacher Preparation Notes for Genetics and Genetics Supplement 1 The Genetics Student Handout begins with sections that help students to understand basic principles of genetics, including (1) how genotype
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts
 Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY
 GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel
 Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Genetics Unit Outcomes
 Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
Genetics Unit Outcomes In the cell division unit, you learned that chromosomes come in pairs and that humans have 46 chromosomes in each of their body cells. You receive one of each chromosome from dad
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
Guided Reading and Study. Definition a. The scientific study of heredity. b. Physical characteristics
 Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
Genetics: The Science of Heredity Mendel's Work Guided Reading and Study This section describes how Gregor Mendel identified the method by which characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring.
Below are the sections of the DNA sequences of a normal hemoglobin gene and the mutated gene that causes sickle cell disease.
 Sickle Cell Analysis Directions: Read the information below to complete the two tables. A person with sickle-cell disease has the genotype: Hb s Hb s. People who have this condition have two abnormal genes,
Sickle Cell Analysis Directions: Read the information below to complete the two tables. A person with sickle-cell disease has the genotype: Hb s Hb s. People who have this condition have two abnormal genes,
Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype.
 UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS
 PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Genetics: CH9 Patterns of Inheritance o o Lecture note Directions Highlight Key information (10-30% of most slides) My Thoughts: Questions, comments, additional information, connections to prior knowledge,
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Goals of Pedigree Analysis Basic Symbols More Symbols Y-Linked Inheritance
 Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3
 Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
Patterns of Heredity - Genetics - Sections: 10.2, 11.1, 11.2, & 11.3 Genetics = the study of heredity by which traits are passed from parents to offspring Page. 227 Heredity = The passing of genes/traits
VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous chromosome sexual reproduction meiosis
 SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans
 MENDELIAN GENETICS, PROBABILITY, PEDIGREES, AND CHI-SQUARE STATISTICS INTRODUCTION Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout the body. The hemoglobin protein consists
MENDELIAN GENETICS, PROBABILITY, PEDIGREES, AND CHI-SQUARE STATISTICS INTRODUCTION Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout the body. The hemoglobin protein consists
Genes and Inheritance
 Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Genes and Inheritance Variation Causes of Variation Variation No two people are exactly the same The differences between people is called VARIATION. This variation comes from two sources: Genetic cause
Codominance. P: H R H R (Red) x H W H W (White) H W H R H W H R H W. F1: All Roan (H R H W x H R H W ) Name: Date: Class:
 Name: Date: Class: (Exceptions to Mendelian Genetics Continued) Codominance Firstly, it is important to understand that the meaning of the prefix "co is "together" (i.e. cooperate = work together, coexist
Name: Date: Class: (Exceptions to Mendelian Genetics Continued) Codominance Firstly, it is important to understand that the meaning of the prefix "co is "together" (i.e. cooperate = work together, coexist
Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y
 Name Date Period Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y Introduction: A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships.
Name Date Period Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y Introduction: A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships.
Bell Work 3/8/18. Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis?
 Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
Bell Work 3/8/18 Mitosis: What occurs during mitosis? What are the products of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Bell Work: 3/9/18 Complete the pre-assessment on your Anchor Activity Unit 6 sheet.
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3
 Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Labrador Coat Color Similar to coat color in mice: Black lab is BxEx Yellow lab is xxee Chocolate lab is bbex Probable pathway:
 Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Honors Genetics 1. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) German monk at the Augustine Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno (today in the Czech Republic). He was a gardener, teacher and priest. Mendel conducted experiments
Name Period. Keystone Vocabulary: genetics fertilization trait hybrid gene allele Principle of dominance segregation gamete probability
 Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Name Period BIO B2 GENETICS (Chapter 11) You should be able to: 1. Describe and/or predict observed patterns of inheritance (dominant, recessive, co- dominant, incomplete dominance, sex- linked, polygenic
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1
 Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Let us test your understanding of Pedigree
Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Let us test your understanding of Pedigree
The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits
 The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits Outcomes: 1. Compare the pattern of inheritance produced by genes on the sex chromosomes to that produced by genes on autosomes, as investigated by Morgan.
The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits Outcomes: 1. Compare the pattern of inheritance produced by genes on the sex chromosomes to that produced by genes on autosomes, as investigated by Morgan.
Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal:
 HUMAN INHERITANCE Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal: 1. Multiple alleles: three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait. 2. Sex chromosomes: these carry genes that determine
HUMAN INHERITANCE Your Vocabulary words-- write into your journal: 1. Multiple alleles: three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait. 2. Sex chromosomes: these carry genes that determine
Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance
 Chapter 3. Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance 1. Mendel s Study of Heredity 2. Applications of Mendel s Principles 3. Formulating and Testing Genetic Hypothesis 4. Mendelian Principles in Human
Chapter 3. Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance 1. Mendel s Study of Heredity 2. Applications of Mendel s Principles 3. Formulating and Testing Genetic Hypothesis 4. Mendelian Principles in Human
Name 9 Patterns of Inheritance Test Date Study Guide You must know: Terms associated with genetics problems: P, F1, F2, dominant, recessive,
 Name 9 Patterns of Inheritance Test Date Study Guide You must know: Terms associated with genetics problems: P, F1, F2, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, phenotypic, and genotypic. How to
Name 9 Patterns of Inheritance Test Date Study Guide You must know: Terms associated with genetics problems: P, F1, F2, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, phenotypic, and genotypic. How to
You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism.
 Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
Unit 6 Genetics 6.1 Genetics You are who you are because of a combination of HEREDITY and ENVIRONMENT. ENVIRONMENT: all outside forces that act on an organism. HEREDITY: traits that are passed from parents
5Which one of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
 Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Practice Questions: 1Humans possess: a. 22 pairs of sex chromosomes and 1 pair of autosomes b. 23 pairs of autosomes c. equal numbers of autosomes and sex chromosomes d. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair
Laws of Inheritance. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The seven characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits. Mendel deduced from his results that each individual had two
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The seven characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits. Mendel deduced from his results that each individual had two
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity
 Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Introduction to Genetics and Heredity Although these dogs have similar characteristics they are each unique! I. Early Ideas About Heredity A. The Theory of Blending Inheritance Each parent contributes
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics
 Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Chapter 28 Modern Mendelian Genetics (I) Gene-Chromosome Theory Genes exist in a linear fashion on chromosomes Two genes associated with a specific characteristic are known as alleles and are located on
Mendel: Understanding Inheritance. 7 th Grade Science Unit 4 NCFE Review
 7 th Grade Science Unit 4 NCFE Review - The DNA Connection Review Inside your cells, you have chromosomes (23 pairs!). Chromosomes are made of long strands of DNA. DNA has a double helix shape (twisted
7 th Grade Science Unit 4 NCFE Review - The DNA Connection Review Inside your cells, you have chromosomes (23 pairs!). Chromosomes are made of long strands of DNA. DNA has a double helix shape (twisted
Lecture 13: May 24, 2004
 Lecture 13: May 24, 2004 CH14: Mendel and the gene idea *particulate inheritance parents pass on discrete heritable units *gene- unit of inheritance which occupies a specific chromosomal location (locus)
Lecture 13: May 24, 2004 CH14: Mendel and the gene idea *particulate inheritance parents pass on discrete heritable units *gene- unit of inheritance which occupies a specific chromosomal location (locus)
UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : Mendelian. (MHR Biology p ) Traits are distinguishing characteristics that make a unique individual.
 1 UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : endelian. (HR Biology p. 526-543) Heredity is the transmission of traits from one generation to another. Traits that are passed on are said to be inherited. Genetics is
1 UNIT III (Notes) : Genetics : endelian. (HR Biology p. 526-543) Heredity is the transmission of traits from one generation to another. Traits that are passed on are said to be inherited. Genetics is
Patterns of Inheritance Review Game Page 1
 Patterns of Inheritance Review Game Page 1 1 The tendency of alleles that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis is called epistasis. codominance. crossing over.
Patterns of Inheritance Review Game Page 1 1 The tendency of alleles that are located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis is called epistasis. codominance. crossing over.
LAB 10 Principles of Genetic Inheritance
 LAB 10 Principles of Genetic Inheritance Objectives 1. Examine the nature of probability. 2. Solve various types of genetics problems. Overview In this laboratory you will learn about the basic principles
LAB 10 Principles of Genetic Inheritance Objectives 1. Examine the nature of probability. 2. Solve various types of genetics problems. Overview In this laboratory you will learn about the basic principles
