BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
|
|
|
- Janis Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
2 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY
3 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM #4 & FINAL EXAM
4 S PLANT HABIT
5 SOLITARY
6 SOLITARY?
7 SOLITARY T?
8 SOLITARY I TRILLIUM
9 INFLORESCENCE
10 INFLORESCENCE?
11 O? INFLORESCENCE
12 ^ ORCHID INFLORESCENCE
13 INFLORESCENCE MORPHOLOGY
14 INFLORESCENCE 1
15 INFLORESCENCE F 1
16 INFLORESCENCE 2
17 INFLORESCENCE P 2
18 INFLORESCENCE 3 PEDUNCLE
19 INFLORESCENCE R 3 PEDUNCLE
20 INFLORESCENCE 4 RACHIS PEDUNCLE
21 INFLORESCENCE S 4 RACHIS PEDUNCLE
22 INFLORESCENCE 5 SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS RACHIS PEDUNCLE
23 INFLORESCENCE P 5 SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS RACHIS PEDUNCLE
24 INFLORESCENCE 6 PEDICEL SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS RACHIS PEDUNCLE
25 INFLORESCENCE 6 B PEDICEL SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS 6 RACHIS PEDUNCLE
26 INFLORESCENCE BRACT 7 PEDICEL SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS BRACT RACHIS PEDUNCLE
27 S PEDICEL I PEDUNCLE 7 INFLORESCENCE
28 S PEDICEL S PEDUNCLE INVOLUCRE INFLORESCENCE
29 INFLORESCENCE BRACT ^ PEDICEL SUBSUBRACHIS SUBRACHIS BRACT RACHIS PEDUNCLE
30 INFLORESCENCE TYPES
31
32 S
33 SPIKE 4 5
34 R SPIKE 4 5
35 3 RACEME 3 3 SPIKE 4 5
36 P RACEME 3 3 SPIKE 4 5
37 4 RACEME PANICLE SPIKE 4 5
38 U RACEME PANICLE SPIKE 4 5
39 5 RACEME PANICLE SPIKE UMBEL 5
40 C RACEME PANICLE SPIKE UMBEL 5
41 AP RACEME PANICLE SPIKE UMBEL CAPITULUM
42 1 INFLORESCENCE TYPES APPLIED
43 S
44 2 3 SPIKE 2 4
45 R 3 SPIKE 2 4
46 3 3 SPIKE RACEME 4
47 P 3 SPIKE RACEME 4
48 4 PANICLE SPIKE RACEME 4
49 U PANICLE SPIKE RACEME 1 4
50 5 PANICLE SPIKE RACEME 1 UMBEL 5
51 C PANICLE SPIKE RACEME 1 UMBEL 5
52 AP PANICLE SPIKE RACEME 1 UMBEL CAPITULUM
53 INFLORESCENCE TYPES APPLIED
54 R
55 RACEME ^
56 U
57 UMBEL ^
58 C
59 CAPITULUM ^
60 F MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY
61
62 ^
63 SEGMENTS & WHORLS
64 1
65 1 R
66 2 RECEPTACLE
67 S 2 RECEPTACLE
68 C SEPAL RECEPTACLE
69 3 SEPAL / CALYX RECEPTACLE
70 P SEPAL / CALYX 3 RECEPTACLE
71 C SEPAL / CALYX PETAL RECEPTACLE
72 P SEPAL / CALYX PETAL / COROLLA RECEPTACLE
73 ^ PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
74 T PERIANTH TERMS
75 TEPALS
76 S
77 SEPAL P
78 PETAL T
79 TEPALS A
80 A ASEPALOUS VS APETALOUS
81 ASEPALOUS
82 A SEPALS ABSENT
83 A ASEPALOUS
84 APETALOUS
85 A PETALS ABSENT
86 A APETALOUS
87 A APOSEPALOUS VS APOPETALOUS
88 N APOSEPALOUS
89 A NON-FUSED SEPALS
90 A APOSEPALOUS
91 N APOPETALOUS
92 A NON-FUSED PETALS
93 S APOPETALOUS
94 S SYNSEPALOUS VS SYMPETALOUS
95 F SYNSEPALOUS
96 FUSED SEPALS S
97 SYNSEPALOUS S
98 F SYMPETALOUS
99 S FUSED PETALS
100 ^ SYMPETALOUS
101 A PERIANTH SYMMETRY
102 A ACTINOMORPHIC VS ZYGOMORPHIC
103 ACTINOMORPHIC
104
105 ACTINOMORPHIC Z
106 ZYGOMORPHIC
107 ACTINOMORPHIC +
108 AP ACTINOMORPHIC ZYGOMORPHIC
109 PERIANTH SYMMETRY APPLIED
110 Z
111 ZYGOMORPHIC ^
112 A
113 ACTINOMORPHIC ^
114 4 MALE TERMS
115 S 4 PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
116 STAMEN PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
117 LEAF M STAMEN MICROSPORANGIUM
118 MICROSPOROPHYLL 5 STAMEN MICROSPORANGIUM
119 F STAMEN 5 PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
120 6 STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
121 6 A STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
122 ANTHER A STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
123 ANTHER ^ ANDROECIUM STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
124 7 FEMALE TERMS
125 ANTHER P 7 STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
126 ANTHER PISTIL STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
127 LEAF M PISTIL MEGASPORANGIUM / OVULE
128 MEGASPOROPHYLL = PISTIL MEGASPORANGIUM / OVULE
129 CARPEL(S) + PISTIL MEGASPORANGIUM / OVULE
130 ANTHER 8 PISTIL STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
131 ANTHER 8 S STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
132 ANTHER STIGMA 9 STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
133 ANTHER STIGMA S 9 STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
134 ANTHER STIGMA 10 STYLE STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
135 ANTHER STIGMA O STYLE STAMEN 10 FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
136 ANTHER STIGMA! O STYLE STAMEN OVARY FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
137 ANTHER STIGMA! S STYLE STAMEN OVULES FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
138 ANTHER STIGMA F STYLE STAMEN SEEDS FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
139 ANTHER STIGMA G STYLE STAMEN FRUIT FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
140 ANTHER ^ GYNOECIUM STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
141 OVARY ANATOMY
142 ANTHER STIGMA STYLE STAMEN OVARY FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
143 ANTHER STIGMA STYLE STAMEN OVARY FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
144 1 OVARY C.S.
145 CARPEL 1 C CARPEL CARPEL 1 1 OVARY C.S.
146 CARPEL 2 CARPEL CARPEL OVARY C.S.
147 CARPEL L 2 CARPEL CARPEL OVARY C.S.
148 CARPEL 3 LOCULE CARPEL CARPEL OVARY C.S.
149 CARPEL O 3 LOCULE CARPEL CARPEL OVARY C.S.
150 CARPEL ^ OVULE LOCULE CARPEL CARPEL OVARY C.S.
151 H OVARY POSITION
152 HYPOGENOUS
153 H 1 2 3
154 S HYPOGYNOUS 2 3
155 E SUPERIOR 2 3
156 EPIGYNOUS
157 E HYPOGYNOUS 2 3
158 I HYPOGYNOUS EPIGYNOUS 3
159 P HYPOGYNOUS INFERIOR 3
160 PERIGYNOUS
161 P HYPOGYNOUS EPIGYNOUS 3
162 S HYPOGYNOUS EPIGYNOUS PERIGYNOUS
163 ^ HYPOGYNOUS EPIGYNOUS SUPERIOR
164 C GENERAL TERMS
165 C COMPLETE VS INCOMPLETE
166 COMPLETE
167 > C COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
168 C CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
169 A COROLLA CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
170 G COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
171 GYNOECIUM I COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
172 INCOMPLETE
173 A GYNOECIUM COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
174 ^ GYNOECIUM COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE ASEPALOUS INCOMPLETE
175 A GYNOECIUM COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
176 ^ GYNOECIUM COROLLA ANDROECIUM CALYX COMPLETE ANDROECIUM ABSENT INCOMPLETE
177 P SEX CONDITION
178 P PERFECT VS IMPERFECT
179 PERFECT
180 PLANT A
181 ANDROECIUM G PLANT
182 ANDROECIUM GYNOECIUM P PLANT
183 ANDROECIUM GYNOECIUM I PERFECT S PLANT
184 IMPERFECT
185 PLANT G
186 GYNOECIUM ABSENT A PLANT
187 GYNOECIUM ABSENT ANDROECIUM ABSENT I PLANT
188 GYNOECIUM ABSENT ANDROECIUM ABSENT M IMPERFECT S PLANT
189 M MONOECIOUS VS DIOECIOUS VS POLYGAMOUS
190 D MONOECIOUS PLANT
191 P DIOECIOUS PLANT
192 AP POLYGAMOUS PLANT
193 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
194 IF? S PLANT
195 SF IMPERFECT S PLANT
196 STAMINATE PF IMPERFECT S PLANT
197 STAMINATE PISTILATE? IMPERFECT S PLANT
198 M MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
199 M MONOECIOUS PLANT
200 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
201 IF? S PLANT
202 SF IMPERFECT S PLANT
203 STAMINATE SP IMPERFECT S PLANT
204 STAMINATE? STAMINATE PLANT PLANT
205 IF? S PLANT
206 PF IMPERFECT S PLANT
207 PISTILATE PP IMPERFECT S PLANT
208 PISTILATE S SP PISTILATE PLANT PLANT
209 STAMINATE S PP STAMINATE PLANT PLANT
210 PISTILATE? PISTILATE PLANT PLANT
211 D MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
212 M DIOECIOUS PLANT
213 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
214 &? S PLANT
215 ? PERFECT S & IMPERFECT S PLANT
216 P MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
217 ^ POLYGAMOUS PLANT
218 ? MORPHOLOGY REVIEW
219 ? R
220 ? RECEPTACLE
221 S? RECEPTACLE
222 ? SEPAL RECEPTACLE
223 C SEPAL /? RECEPTACLE
224 ? SEPAL / CALYX RECEPTACLE
225 P SEPAL / CALYX? RECEPTACLE
226 ? SEPAL / CALYX PETAL RECEPTACLE
227 C SEPAL / CALYX PETAL /? RECEPTACLE
228 ? SEPAL / CALYX PETAL / COROLLA RECEPTACLE
229 P CALYX /? COROLLA /? RECEPTACLE
230 ? PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
231 S? PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
232 ? STAMEN PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
233 F STAMEN? PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
234 ? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
235 ? A STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
236 ANTHER? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
237 ANTHER A? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
238 ANTHER? ANDROECIUM STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
239 ANTHER P? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
240 ANTHER? PISTIL STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
241 ANTHER? S STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
242 ANTHER STIGMA? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
243 ANTHER STIGMA S? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
244 ANTHER STIGMA? STYLE STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
245 ANTHER STIGMA O STYLE STAMEN? FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
246 ANTHER STIGMA? STYLE STAMEN OVARY FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
247 ANTHER G? STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
248 ANTHER ^ GYNOECIUM STAMEN FILAMENT PERIANTH PERIANTH RECEPTACLE
249 GENERAL TERMS REVIEW
250 C COMPLETE INCOMPLETE
251 ^ COMPLETE
252 H PERIGYNOUS EPIGYNOUS HYPOGYNOUS
253 ^ HYPOGYNOUS
254 P SEX CONDITION REVIEW
255 PERFECT? VS IMPERFECT
256 PF? S PLANT
257 ? PERFECT S PLANT
258 PP! MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
259 M PERFECT PLANT MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT PERFECT PLANT
260 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
261 IF? S PLANT
262 SF IMPERFECT S PLANT
263 STAMINATE PF IMPERFECT S PLANT
264 STAMINATE PISTILATE? IMPERFECT S PLANT
265 M MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
266 M MONOECIOUS PLANT
267 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
268 IF? S PLANT
269 SF IMPERFECT S PLANT
270 STAMINATE SP IMPERFECT S PLANT
271 STAMINATE? STAMINATE PLANT PLANT
272 IF? S PLANT
273 PF IMPERFECT S PLANT
274 PISTILATE PP IMPERFECT S PLANT
275 PISTILATE S SP PISTILATE PLANT PLANT
276 STAMINATE S PP STAMINATE PLANT PLANT
277 PISTILATE? PISTILATE PLANT PLANT
278 MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
279 M DIOECIOUS PLANT
280 ? MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS APPLIED
281 &? S PLANT
282 ? PERFECT S & IMPERFECT S PLANT
283 P MONOECIOUS DIOECIOUS POLYGAMOUS PLANT
284 ^ POLYGAMOUS PLANT
285 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS +!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM #4 & FINAL EXAM
286 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! POWERPOINT SLIDES WILL BE POSTED ASAP
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Parts of a Flower. Stamen = Pistil = Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel. anther + filament
 Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. E2-4 Flower Anatomy
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers
 WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Review of the previous lecture
 Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Parts of a flower. ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil. petal sepal. petal. ovary PERIANTH. receptacle. peduncle
 THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS
 BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
PREFACE. Best of luck to all the aspirants!
 PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
 In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology. Station 1. Whole plant structure. Differences between roots, stems, and leaves:
 Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations
 ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA
 SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
IB 168 Plant Systematics
 IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of
 ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES
 USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals
 Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Plant Reproduction fertilization
 Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
W.4.1 Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons and information.
 Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process. They will
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the:
 1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday
 Week 2; Monday Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday Plant Morphology - form or structure of a plant and its
Week 2; Monday Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday Plant Morphology - form or structure of a plant and its
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
On the Use of Some Common Botanical Terms
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
GLOSSARY Achene Acidic Soil Actinomorphic Acute Acuminate Aggregate Alkaline Soil Alpine Plants Alternate Leaves Annual Anther Apetalous Apocarpous
 GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
Objectives. Standards (NGSS and Common Core) For state specific standards visit edu.zspace.com/activities. Differentiation
 Dicot Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process.
Dicot Flower Dissection Lesson Overview Flowers use pollination as a mechanism for reproduction and survival. Students will learn about pollination and how each structure plays a role in this process.
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
ffisffi AIDGA IIou: to use thi^s 4VE.?ntr Equ prncnt BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To At-t-
 ffisffi BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To Att The FSC (Field Studies Council) is an independent educational charity committed to raising awareness about the natural world. The organisation works
ffisffi BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To Att The FSC (Field Studies Council) is an independent educational charity committed to raising awareness about the natural world. The organisation works
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant
 BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations to the
Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations to the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae)
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Taxonomy of Angiosperms
 Taxonomy of Angiosperms Very short Answer Questions 1. What is Omega Taxonomy? A: Besides morphological features, information from other sources viz Embryology, Cytology, Palynology, Phytochemistry, Serology
Taxonomy of Angiosperms Very short Answer Questions 1. What is Omega Taxonomy? A: Besides morphological features, information from other sources viz Embryology, Cytology, Palynology, Phytochemistry, Serology
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae.
 Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae. Principle: Taxonomy deals with identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms. Bentham and Hooker's
Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae. Principle: Taxonomy deals with identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms. Bentham and Hooker's
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
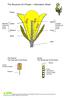 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION?
 LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
Glossary of Botanical Terms
 Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
NCERT. Requirement: Specimens of pea/lentil plant with tendrils, Cactus/Argemone, Pitcher Plant/Utricularia, bulbs of onion/garlic/crocus.
 Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
STAMEN MORPHOLOGY IN FLOWERS OF THE MUSKMELON '
 STAMEN MORPHOLOGY IN FLOWERS OF THE MUSKMELON ' By D. M. MCLEAN Research assistant in plamt pathology, Michigan Agricultural Experimental Station PREVIOUS OBSERVATIONS The morphological interpretation
STAMEN MORPHOLOGY IN FLOWERS OF THE MUSKMELON ' By D. M. MCLEAN Research assistant in plamt pathology, Michigan Agricultural Experimental Station PREVIOUS OBSERVATIONS The morphological interpretation
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38)
 Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
Description: Maximum clade credibility tree from the BEAST analysis of the E series.
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary References Title of file for
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary References Title of file for
CHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS 5.1 THE ROOT
 5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae. Today 4 families
 Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed
 Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus terrestris L.
 ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
Angiosperms * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44650 1 Angiosperms * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m44650 1 Angiosperms * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
table of contents Lesson 1: Introduction to Pollination Lesson 2: What s the Buzz? Lesson 3: Plants and Pollinators...
 lesson packet table of contents Lesson 1: Introduction to Pollination... 3-7 Lesson 2: What s the Buzz?... 8-10 Lesson 3: Plants and Pollinators... 11-13 References... 14 2018 American Farm Bureau Foundation
lesson packet table of contents Lesson 1: Introduction to Pollination... 3-7 Lesson 2: What s the Buzz?... 8-10 Lesson 3: Plants and Pollinators... 11-13 References... 14 2018 American Farm Bureau Foundation
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity. Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara
 Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS THE ROOT In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS THE ROOT In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral
How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI
 How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI Why Study Seeds? o Within the next fi*y years we will need to produce more food than in
How To Make A Seed EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND THE LIFE CYCLE OF ANGIOSPERMS NORA COOPER JAZMIN SAMANO DOMINIC SAADI Why Study Seeds? o Within the next fi*y years we will need to produce more food than in
Reproduction 19/02/2016. Asexual Reproduction. Budding: Types of asexual reproduction: SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL
 Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
PRINCIPLES OF PLANT TAXONOMY II.*
 PRINCIPLES OF PLANT TAXONOMY II.* JOHN H. SCHAFFNER Ohio State University THE EVOLUTION OF THE FLOWER. The views and deductions presented below, as to the general nature of floral evolution, represent
PRINCIPLES OF PLANT TAXONOMY II.* JOHN H. SCHAFFNER Ohio State University THE EVOLUTION OF THE FLOWER. The views and deductions presented below, as to the general nature of floral evolution, represent
UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS. Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
 UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals The description of the diverse
UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals The description of the diverse
Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups
 Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups APPENDIX 1 1. Plants never bearing seeds, but reproducing by spores (FERNS AND FERN ALLIES; /MONILOPHYTA).......................................................KEY
Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups APPENDIX 1 1. Plants never bearing seeds, but reproducing by spores (FERNS AND FERN ALLIES; /MONILOPHYTA).......................................................KEY
not to be republished NCERT Introduction
 Introduction Laboratory is a place where ideas and concepts can be tested through experiments. Biology, like any other discipline of science, is based on experimental work and therefore practical forms
Introduction Laboratory is a place where ideas and concepts can be tested through experiments. Biology, like any other discipline of science, is based on experimental work and therefore practical forms
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
