ffisffi AIDGA IIou: to use thi^s 4VE.?ntr Equ prncnt BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To At-t-
|
|
|
- Candice Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ffisffi BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To Att The FSC (Field Studies Council) is an independent educational charity committed to raising awareness about the natural world. The organisation works through a network of residential and day Centres throughout the UK providing courses for schools and colleges at all levels. A programme of leisure learning and professional development courses is offered in the UK and overseas. The FSC also provides outreach education, training and consultancy and publishes many titles to support its work. This guide is part of the ADGAP project and will be updated L.# regulariy. ADGAP i aims to produce userfriendly identification guides. We would be grateful 3 for your comments. To make suggestions, or for more information about the FSC, please contact: ESC Publicatiozs, The Annexe, Preston Montford Lane, Shrewsbury Shropshire SY4 1DU & os45 s4s 4072 (01743) & & publications@fie1dstudiescouncil.org S r,vwwfieldstudiescouncil.org ADGA Aids to ldenull6lion in Olffcllt Groups ot Anlmals and Plants 4VE.?ntr ADGAP is supported by FSe, Royal Entomological Society and Lirrnean Society of London f.i"t"a"singvegetableoilbasedinls By Anne Bebbington and John Bebbington ou: to use thi^s This foldout chart aims to describe the basic structure of the plant and the terms most commonly used in identification. t will be particularly useful when used alongside an identification key suitable for your geographical location. t provides a checklist of questions, the answers to which are often required in identification. Parts of the plant and flower are fully illustrated, and the checklist refers the reader to the relevant groups of illustrations. When the chart is being used alongside a flora it is often useful to go through the checklist first, particularly the section dealing with the flower, and to construct a floral formula as described. This will help considerably in the interpretation of the flower and makes passage through the identification key much easier. The chart will also help to clarify points as progress is made through the key. dentification is always best done in the field so that as much information as possible is at hand. However if a flora is not available, the answers to the questions on this chart will provide a good basic description, enabling collection to be kept to an absolute minimum. Additional notes will need to be added with reference to the habitat (e.g. what is the geographical location; what sort of vegetation is it growing in; what is the soil type) and the underlying geology (e.g. how wet is it?). Equ prncnt A good hand lens is an essential tool. A magnification of x10 is probably best although for fine detail x15 or x20 is useful. n order to obtain the maximum advantage from your hand lens it should be held close to the eye. The specimen should be as well lit as possible and brought close to the lens to bring it into focus. Also useful are one or preferably two pairs of very fine watchmaker's forceps. These are extremely helpful in separating the small parts of the flower. A sharp knife or razor blade may also be needed at times. A small rectangular tin lined with a piece of foam rubber will contain these items safely without them rattling. Hold the specimen up to the light
2 pl4rfi': Look at several plants if possible; try to answer the following questions. The general form of the plant (see opposite) 1. s it a tree, shrub or herb? Does it climb or scramble? 2. s it an annual, biennial or perennial? (This may not be easy to determine, but it is useful if you can decide, see Life cycles). 3. Are most of the stems upright or do they lie along the ground? 4. Are the stems solitary or tufted? Are stolons or rhizomes present? 5. What is the main stem like: hairy or hairless; smooth, rough or ridged; hollow or solid; round or square in cross section? 6.f t is a tree, what is the bark like? The inflorescence (see opposite) 1. Are the flowers solitary or in an inflorescence? What sort of in{lorescence is it? Some flowers are tightly packed into a head which resembles a single flower (e.g. daisy) watch out for these. 2. How long are the flower stalks when the plant is in flower and when it is in fruit? 3. Are bracts present? What are they like? (see overleaf L). The flower (see overleaf 13) You will find a floral formula useful here. 1. s the flower actinomorphic or zygomorphic? 2. s the perianth made up of two similar whorls (tepals) or two whorls which differ markedly in size and/or colour (sepals and petals)? 3. How many sepals, petals (or perianth parts) and stamens are there? (f there are more than twelve stamens call them numerous.) Watch out for bifid petals here. 4. Are the perianth parts fused together or are they free (separate)? 5. What is the shape and size of the sepals and petals? 6. Are the stamens joined to each other or to the petals? 7. Are the stamens placed opposite the petals or alternate with them? 8. What is the size of the parts of the stamen (filament and anther) in relation to each other and the other parts of the flower? Do they hang out of the flower? 9. How many carpels make up the gynoecium? (Look at a fruit.) How many styles and stigmas are there? Are the carpels fused? 10. s the ovary superior or inferior? How many loculi are there? What is the placentation? 11. Look for fruits and describe them (see opposite). The leaves (see overleaf 4) 1. How are the leaves arranged? 2. Do the leaves vary markedly in shape and size with position on the plant? f so, describe major types. 3. s the leaf compound or simple? 4. s division or lobing of the leaf pinnate or palmate? 5. What are the leaf veins like? 5. What is the shape and size of the leaves? 7. What are the leaf margins, leaf bases and leaf tips like? 8. Are the leaves hairy? What are the hairs like? 9. s a leaf stalk present? How does the blade (lamina) join the leaf stalk (petiole)? 10. Are stipules present? What are they like? 11. What colour are the leaves? ife cyclcs Plants may have one of three types of life cycle: Annual Completes its life cycle within a yeal Biennial Germinates and grows in its first year. Flowers and completes it growth rycle in the second year. Perennial Lives for more than 2yearc, normally flowering annually but not necessarily in the first year.
3 PY dtr W =*h=. Solitary / ^7 #6 Herb does not develop Tufted persistent woody tissue. Dies at the end of the season or ovenruinters underground Shrubaperennial with muchbranched woody stems. Usually less than 10m tall Organs oil'ffireffiffirproduction Tree a perennial with a single woody trunk. Usually large more than 10m tall Stolon a creeping shortlived stem, usually above the ground Rhizome a horizontal underground stem Corm a swollen stem base Rhizomes and bulbs are also overwintering organs Bulb swollen lea{ bases or bud Spike Raceme (e.9. foxglove) (e.9. lily of the valley) the arrangement of,flornrers,, ',,"t,.', vffi Corymb 4, K% wre aa n Simple monochasial cyme (e.9. houndstongue) Panicle (e.9. meadowsweet) Umbel (e.g candytuft) (e.9. wild garlic) Cymose each flower terminates the growth of the shoot; growth is continued by a lateral shoot Dichasial cyme (e.9. greater stitchwort) Capitulum (e.9. daisy)
4 o.._ t A floral formula provides a very useful shorthand for describing flowers. Look at each part of the flower and coun[ the number of parts. Where the number is too high to count use the symbol. Use the following abbreviations: K: calyx (sepals) C : corolla (petals) p : perianth (where sepals and petals cannot be distinguished) A = androecium (stamens) g : gynoecium (carpels). Further information about the flower is added by using symbols. Brackets shows that the parts are joined: these can either be all the same part g,][lhe flower (e.g. C(5) : 5 joined petals), or it.r,uy U" that two different parts are joined (e.g. es AS : the stamens arise on the petals). A line below the gynoecir n rrrib"r denotes that the ovary is superioq, and a line above it shows that it is inferior. For example: K5 C5 A1O G5 = 5 sepals, 5 petals, 10 stamens, 5 free (not ioined) superior carpels. iolo Otg) = 6 perianth parts (tepals), with 6 stamens arising from them, 3 fused inferior carpels. t<2+2c(4) A G(4 = 2large and 2 smallsepals,4 fused petals, a large number of stamens, 2 fused superior carpels. ^r: 9p : 5 :..:: :::::: _ =: : :::: ^! Q_: E t Pericarp dry m t lndehiscent (usually derived from 1 carpel, 1seeded). ln some species the ovary may split into separate 1seeded compartments * Pericarp membranous Achene i Dehiscent t Pericaro woodv E '.@ Sweet Fruits t lnner 2 layers (mesocarp and endocarp) fleshy ffi:_:@ t Pericarp fleshy lnnermost layer (endocarp) woody dgcherry More than 1 carpel Capsule (several sorts, distinguished by method of opening)!9: : : O o : :_ : '= : N O :: J::::::: o J o o : : : = o_ J: Collection of follicles ffii.m tf, Forricle fl cotumoine Opens along both sides Legume (pod) o o:= N :::::: N _ '= N : N Field Studies Council 1996 Second edition OP 42 SBN: N o
5 te#,u*m*s*iddle,, & * & & " eu,f slrup@ a * a* & * * e s * *, 6 6 s & & * & e' 6 * & & & *' * $ s a * * * * Leaf widcet*@@''rnidd le && subulate sagittate hastate ovate cordate deltoid.,te***#***.. ff#ffiwry oblanceolate obovate spathulate truncate obcordate ff $@#* linear oblong elliptical rhomboid oval & re Yundulate * plain spiny serrate dentate #6 pinnatifid runcinate wavy ry incised #palmate ffi@#w rounded cuneate truncate decurrent ffiffi@ oblique auriculate cordate
6 flower bud bracteole pedicel { bract axillary bud stem leaf (may differ from basal leaves)....:fhe JknCer" enhorls calyxsepals oerianth corolla petals r androecium stamens gynoecium carpels internode Flcnoer Actinomorphic radially symmetrical qfinrnetry. Zygomorphic bilaterally symmetrical t{ l4 (;* Ag,nr J \ P F qby G* ^ \,Sf (hink or a cup and sauce0...the sci.ertffic mw.rrue, This is universal and often provides a description of the plant. Here it is the'comrnon false flower'. The name should be underlined or printed ititalics. naming authority root P s eu doflor n aul aris Bebb. tt generic name 1st letter upper case species or trivial name 1st letter lower case 15il
7 &% f sepals and petals look alike! a s o * e * * * * * ffig perifanth * :.:_1:::T::::','..r* ctndroecfusn. (sepalsandpetals) ss'*** s*****""""'i PeriatMsent.':"W fly'''p M;: nectary flower unisexual e9. Salix qq ;ffir??n""l. stamen filament pollen section of anther carpels joined syncarpous (see ac below) connective To estimate the number of carpels in a syncarpous gynoecium, count the number of: 1. stigmas and styles 2. seams on the ovary wall 3. loculi within the ovary 4. placentae (see opposite) filament filament basifixed dorsifixed iilaments loined "fhe gynoechml (carpels) ww carpels free apocarpous (see df below) 37 stigma [1 a. stamens opposite petals b. stamens alternate with petals (this is more comrnon) free central parietal axile The posi Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology. Station 1. Whole plant structure. Differences between roots, stems, and leaves:
 Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
 BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
Review of the previous lecture
 Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the:
 1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals
 Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
IB 168 Plant Systematics
 IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
NCERT. Requirement: Specimens of pea/lentil plant with tendrils, Cactus/Argemone, Pitcher Plant/Utricularia, bulbs of onion/garlic/crocus.
 Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
PREFACE. Best of luck to all the aspirants!
 PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Parts of a Flower. Stamen = Pistil = Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel. anther + filament
 Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA
 SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. E2-4 Flower Anatomy
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912)
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912) 1912-02 The Mallows of Ohio Linnell, Mary
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912) 1912-02 The Mallows of Ohio Linnell, Mary
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers
 WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS
 BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
 In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES
 USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Anacardiaceae cashew family
 Anacardiaceae cashew family Mostly tropical, the family includes nearly 600 species; four species are native to Nova Scotia. Leaflets are pinnately or palmately compound. Typical are small, regular flowers,
Anacardiaceae cashew family Mostly tropical, the family includes nearly 600 species; four species are native to Nova Scotia. Leaflets are pinnately or palmately compound. Typical are small, regular flowers,
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of
 ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant
 BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY
 ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY Plant: vines (usually woody), shrubs, or small trees Stem: woody, particularly with age, often with milky or resinous juice (resin ducts in bark) Root: Leaves: simple
ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY Plant: vines (usually woody), shrubs, or small trees Stem: woody, particularly with age, often with milky or resinous juice (resin ducts in bark) Root: Leaves: simple
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Parts of a flower. ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil. petal sepal. petal. ovary PERIANTH. receptacle. peduncle
 THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
Taxonomy of Angiosperms
 Taxonomy of Angiosperms Very short Answer Questions 1. What is Omega Taxonomy? A: Besides morphological features, information from other sources viz Embryology, Cytology, Palynology, Phytochemistry, Serology
Taxonomy of Angiosperms Very short Answer Questions 1. What is Omega Taxonomy? A: Besides morphological features, information from other sources viz Embryology, Cytology, Palynology, Phytochemistry, Serology
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
not to be republished NCERT Introduction
 Introduction Laboratory is a place where ideas and concepts can be tested through experiments. Biology, like any other discipline of science, is based on experimental work and therefore practical forms
Introduction Laboratory is a place where ideas and concepts can be tested through experiments. Biology, like any other discipline of science, is based on experimental work and therefore practical forms
Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations
 ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
GLOSSARY Achene Acidic Soil Actinomorphic Acute Acuminate Aggregate Alkaline Soil Alpine Plants Alternate Leaves Annual Anther Apetalous Apocarpous
 GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
CHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS 5.1 THE ROOT
 5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae. Today 4 families
 Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus terrestris L.
 ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
Glossary of Botanical Terms
 Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS. Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
 UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals The description of the diverse
UNIT 2 STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals The description of the diverse
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS THE ROOT In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS THE ROOT In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. It bears lateral
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower.
 5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae.
 Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae. Principle: Taxonomy deals with identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms. Bentham and Hooker's
Aim: Study and describe flowering plants of families Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae. Principle: Taxonomy deals with identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms. Bentham and Hooker's
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
A guide to eucalypt species identification
 A guide to eucalypt species identification Peter White There are approximately 900 currently recognized species of Eucalyptus, Corymbia and Angophora. On a handful, there can be characters that are so
A guide to eucalypt species identification Peter White There are approximately 900 currently recognized species of Eucalyptus, Corymbia and Angophora. On a handful, there can be characters that are so
Announcements: First lecture exam on Friday; Review session Wednesday at 5:30
 Week 4; Monday Announcements: First lecture exam on Friday; Review session Wednesday at 5:30 Lecture: Rosidae s.l., continued Aceraceae - Maple family (2 gen/113 spp) Aceraceae are included in Sapindaceae
Week 4; Monday Announcements: First lecture exam on Friday; Review session Wednesday at 5:30 Lecture: Rosidae s.l., continued Aceraceae - Maple family (2 gen/113 spp) Aceraceae are included in Sapindaceae
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the Phylum Magnoliophyta Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations to the
Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations to the
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
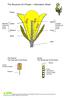 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
E Ebracteate. Without bracts. Eciliate. Without celia. Emarginate. Having a shallow notch at the apex. Glossary
 Glossary Need help identifying native plants? Here is a few definitions to help you from the Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida by Richard P. Wunderlin A Acaulescent. Without a leafy stem; leaves
Glossary Need help identifying native plants? Here is a few definitions to help you from the Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida by Richard P. Wunderlin A Acaulescent. Without a leafy stem; leaves
Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday
 Week 2; Monday Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday Plant Morphology - form or structure of a plant and its
Week 2; Monday Announcements: Arb field trip next week on Th, Fr, Sat; sign up for a time this week or next. First lab quiz next week on Wednesday Plant Morphology - form or structure of a plant and its
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION?
 LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
Phytochemical Investigation and Taxonomic Evaluation of Some Medicinal Plants
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 17 (1): 30-43, 2017 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejaes.2017.30.43 Phytochemical Investigation and Taxonomic Evaluation of Some
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 17 (1): 30-43, 2017 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejaes.2017.30.43 Phytochemical Investigation and Taxonomic Evaluation of Some
Weeds of Importance to Seed Certifiers
 Weeds of Importance to Seed Certifiers Steve F. Schuler Director, Certification Services Kansas Crop Improvement Association 2009 v.2-9-09 FOREWARD This slide set is a work in progress. It will not contain
Weeds of Importance to Seed Certifiers Steve F. Schuler Director, Certification Services Kansas Crop Improvement Association 2009 v.2-9-09 FOREWARD This slide set is a work in progress. It will not contain
Flower Shapes and their function. Describing Flower Shapes
 Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida
 Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity. Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara
 Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae)
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part II, Number 3, May 1979, pp. 183-188, printed in India. Floral organogenesis in Antirrhinum majus (Scrophulariaceae) V SINGH and D K JAIN* Department of Botany,
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
3/6/10. Valerianaceae - valerian family!
 Valerianaceae - valerian family! Family now included with Caprifoliaceae (long-styled genera). Herbaceous plants with opposite or basal leaves. Valeriana edulis - edible valerian Valeriana uliginosa -
Valerianaceae - valerian family! Family now included with Caprifoliaceae (long-styled genera). Herbaceous plants with opposite or basal leaves. Valeriana edulis - edible valerian Valeriana uliginosa -
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]
![W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]](/thumbs/89/98832613.jpg) W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar
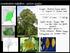 Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar Lauraceae - laurel familiy Umbellularia californica - California bay Sassafras albidum - sassafras Phylogeny of angiosperms! Basal angiosperm! Amborella! Nymphaeales!
Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar Lauraceae - laurel familiy Umbellularia californica - California bay Sassafras albidum - sassafras Phylogeny of angiosperms! Basal angiosperm! Amborella! Nymphaeales!
Lecture Exam 1 Statistics
 Lecture Exam 1 Statistics Average 76.6 Range 54 (42-96) SD: 15.5 Median: 81.5 Skewness: -0.76 Sample size: 28 Field Trip: August 2nd Day-long trip over Grand Park, Mt. Rainier; UW vans for transportation;
Lecture Exam 1 Statistics Average 76.6 Range 54 (42-96) SD: 15.5 Median: 81.5 Skewness: -0.76 Sample size: 28 Field Trip: August 2nd Day-long trip over Grand Park, Mt. Rainier; UW vans for transportation;
