Veterinary Parasitology Arthropod Parasites
|
|
|
- Kelly Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Veterinary Parasitology Arthropod Parasites Melanie Buote DVM, DACVP, PhD Candidate Office: 3319 North Annex, Office phone #(902) Cell phone #(902)
2 A little about me BSc, Hon Marine Bio DVM Anatomic Pathology Residency Diagnostic Pathologist PhD Met Husband Got Married Had Babies
3 Bitter Crab Disease
4 Bitter Crab Disease Hematodinium sp. infection: A dinoflagellate (protozoan) parasite of decapod crustacean (arthropod) hemolymph
5 Outline I. Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods (1 lecture) 1. Hemoflagellates Trypanosomes and Leishmania 2. Piroplasms Babesia and Cytauxzoon 3. Malarias Plasmodium and Leucocytozoon II. Arthropods (6 lectures) 1. Arachnids (3 lectures) Ticks and mites 2. Insects (3 lectures) Fleas, lice, flies, and myiasis 3. Crustaceans (0 lectures) Sea lice
6 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods 1. Mechanical Vector Carried by mouthparts/body e.g. Horse flies (Tabanus) transmit Equine Infectious Anemia on their mouthparts 2. Biological Vector Parasite undergoes development within arthropod vector Arthropod can be an intermediate host or the definitive host e.g. Plasmodium undergo sexual reproduction in the Anopholene mosquito (definitive host)
7 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon
8 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods I. Hemoflagellates Genera of veterinary importance: 1. Trypanosoma 2. Leishmania Morphology Elongate with a single flagellum or Rounded with a non-protruding flagellum All possess a kinetoplast Sausage or disc-shaped Found at base of flagellum Contains mitochondrial DNA
9 Stage in arthropod intestine Hemoflagellate Life Cycles Stage in vertebrate blood and/or tissues Chagas Disease Zoonotic disease caused by Trypanosoma cruzi
10 I. Hemoflagellates 1. Trypanosomes Section Salivaria Section Stercoraria* Development in front portion of digestive tract of the arthropod Transmission to vertebrate host via saliva African Trypanosomiasis -Trypanosoma congolense -Trypanosoma vivax -Trypanosoma brucei brucei Development in hind portion of digestive tract of the arthropod Transmission to vertebrate host via feces American Trypanosomiasis -Trypanosoma cruzi *Stercorary = dung repository
11 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes i. African Trypanosomiasis Major species Trypanosoma congolense Cattle, sheep, goats, dogs, pigs, camels, horses, most wild animals Trypanosoma vivax Cattle, sheep, goats, camels, horses, various wild animals Trypanosoma brucei brucei All domestic and various wild animals Most severe in dogs, horses, cats Trypanosoma simiae Domestic and wild pigs, camels Transmission: Tsetse fly (Glossina spp.) (FYI: T. vivax can also be transmitted by biting flies in non-tsetse areas = mechanical transmission)
12 Animals can also host human pathogen parasites Domestic and wild animals = parasite reservoirs T. brucei rhodesiense > T. b. gambiense I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes i. African Trypanosomiasis Bovine trypanosomiasis (Nagana) Sudden death in cattle (T. vivax) Due to secondary infections (i.e., Salmonellosis) Chronic disease in cattle: Anemia, cachexia, chronic ill health, abortion, reduced productivity ~3 million cattle deaths/year Loss in cattle & crop production Nagana many domestic species are susceptible Cattle, equidae, small ruminants, camels, and dogs Horses, dogs - Incoordination and spinal paralysis Dogs - Anterior uveitis (perivascular infections)
13 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis Chagas Disease Dogs and Humans (zoonotic) Animal reservoirs Skunks, cats, pigs, raccoons, opossums, armadillos Cause: Trypanosoma cruzi Transmission: Triatomine bug ( Kissing bug ) Blood transfusions Distribution Endemic in South and Central America Low prevalence in USA (sporadic cases) Southern US States + Virginia/Maryland Potential for expansion of distribution Where there are Triatomine bugs
14 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis Two forms of Chagas Disease in dogs: 1. Acute disease (usually young dogs <2 years old) Lymphadenopathy, pale mucus membranes, lethargy, hepatosplenomegaly, myocarditis, and tachyarrhythmia 2. Chronic disease Congestive heart failure Heart becomes enlarged and flabby After extended asymptomatic period Pathogenesis: Multiplying amastigotes host cell destruction local inflammatory response host cell degeneration and necrosis more inflammation Preference for cardiac and skeletal muscle cells
15 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis Morphology Trypomastigote Slender, um long with a pointed posterior end Found in circulating blood of the vertebrate host Kinetoplast is near the posterior end Flagellum is long & anterior Narrow undulating membrane Amastigote Spheroid, um, lack flagella Develop in clusters Found in muscle and other tissues of vertebrate host Epimastigote Kinetoplast located between the nucleus and the anterior end near the flagellum Found in the posterior portion of a triatomine bug s gut Helpful hints for remembering terms: Trypano = borer or screw-like, A = not, Mastigote = flagellate
16 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease)
17 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis(Chagas Disease) Diagnosis Acute infections Detection of trypomastigotes in blood smear or lymph Within 5 weeks of infection Chronic infections: Culture, Serology (IFA) Xenodiagnosis Naive triatomine bugs feed on host Look for parasites in bug s gut Necropsy with histology Clusters of amastigotes in skeletal and cardiac muscles
18 I. Hemoflagellates, 1. Trypanosomes ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease) Treatment & Control Does not respond well to treatment Only extracellular parasites (trypomastigotes) killed Intracellular stages (amastigotes) unaffected by treatment disease recrudescence Symptomatic treatment Medical management of CHF Prevention Insecticides Limit & control exposure to arthropod vectors Avoid contact with reservoir animals Skunks, raccoons, opossums, armadillos Avoid sleeping in a mud, thatch or adobe house. Types of residences more likely to harbor triatomine bugs
19 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon
20 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Leishmania I. Hemoflagellates 1. Trypanosomes i. African Trypanosomiasis ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease) 2. Leishmania
21 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania (Leishmaniasis) Hosts Dogs and Humans (zoonotic) Rodents, wild mammals, rare in cats Horses, mules, donkeys Cause: Leishmania donovani species complex Transmission: Female sandflies Phlebotomus sandflies (Eastern Hemisphere) Lutzomyia sandflies (Western Hemisphere ) Blood transfusion +/- vertical and horizontal transmission
22 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Distribution: Endemic in the tropics: Mediterranean, Middle East, Asia, Central + South America Sporadic reports in North America: English & American Foxhounds in USA, Southern Ontario, & Nova Scotia
23 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Clinical forms of leishmaniasis 1. Cutaneous leishmaniasis Non-specific skin lesions Alopecic or nodular forms (few vs. many organisms in lesions), Often affects the head/face and limbs, +/- chronic ulcers, +/- nail deformites, secondary infections common +/- systemic infection 2. Visceral leishmaniasis Non-specific systemic signs Poor body condition, rough hair coat, chronic wasting, recurrent oculonasal discharge, recurrent diarrhea, mildly enlarged lymph nodes, hepatosplenomegaly with granulomas
24 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Pathogenesis Leishmania organisms are engulfed by macrophages multiply rapidly (binary fission) and destroy the macrophage engulfed by more macrophages formation of granulomas in skin and organs Destruction of cells (i.e., macrophages) from the reticuloendothelial system susceptibility to secondary pathogens
25 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania
26 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Morphology Amastigote Spheroid, lack flagella, um Found in the vertebrate hosts tissue Often found within macrophages Kinetoplast is oriented perpendicular to nucleus (lollipop) Promastigote found in the gut of the sandfly vector forward extending flagellum kinetoplast is located near the anterior end of the body Helpful hints for remembering terms: A = not; Pro = before, earlier, or in favor of; Mastigote = flagellate
27 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Diagnosis Fine needle aspirates (FNAs) of enlarged organs and/or granulomas (liver, spleen, lymph nodes, skin nodules) or bone marrow aspirates Amastigotes within macrophages or free (ruptured host cells) BUT beware of false negative FNAs! Biopsy with histopathology Detect antibodies to parasite in serum Immunofluorescent Antibody test (IFA) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Q-PCR for detection of parasite
28 I. Hemoflagellates 2. Leishmania Treatment and Control Symptomatic medical treatment to reduce the clinical signs of disease (not curative) Meglumine Antimoniate with Allopurinol, Aminosidine & Amphotericin B All drugs require multiple dose regimens Depend on the patient's condition & owner cooperation Relapse is common Weeks, months or years later Vector control is essential Use of insecticide collars, shampoos or sprays Especially in patients under treatment Residual insecticide spraying of houses & animal shelters may help
29 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon
30 Protozoan parasites transmitted by I. Hemoflagellates 1. Trypanosomes arthropods i. African Trypanosomiasis and Nagana ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease) 2. Leishmania i. Leishmaniasis II. Piroplasms 1. Babesia 2. Cytauxzoon 3. Theileria
31 II. Piroplasms Piriform (pear-shaped) intracellular apicomplexan parasites Parasites of blood cells in vertebrates Transmitted by ixodid (hard) tick vectors
32 II. Piroplasms Morphology 1. Babesia spp. Merozoites are found in the erythrocytes of the vertebrate host Piriform to amoeboid 3-5 µm long and 2-4 µm in diameter Size is species dependent Blue cytoplasm with red chromatin mass (Wright-Geimsa) 2. Cytauxzoon felis Signet-ring like merozoites found in erythrocytes µm in diameter Merozoites may be found within monocytes/macrophages (histiocytes) in spleen, lymph nodes, lungs, liver and kidneys
33 Piroplasmosis Human Babesiosis 1. Babesia spp. Schizogony in erythrocytes 2. Cytauxzoon sp. Schizogony in erythrocytes and histiocytes (macrophages) 3. Theileria spp. Schizogony in lymphocytes (+/- macrophages) Schizogony = Merogony (asexual reproduction via fission giving rise to merozoites)
34 II. Piroplasms Pathogenesis 1. Babesia spp. Destruction of parasitized erythrocytes hemolytic anemia lethargy, inappetance, jaundice, dehydration, dark urine Clogging of capillaries in various organs by parasitized cells & free parasites anoxia, accumulation of toxic metabolites, hemorrhaging & organ failure Most characteristic feature of B. bovis infections is a cerebral flush (diffuse reddening of gray matter of brain due to capillary congestion) 2. Cytauxzoon sp. Destruction of parasitized erythrocytes hemolytic anemia lethargy, inappetance, jaundice, dehydration, dark urine Infected histiocytes (macrophages) can clog venules in organs and infiltrate tissues (liver, spleen, lungs, lymph nodes, bone marrow) hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenomegaly +/- liver enzymes & prolonged clotting times Pancytopenia can be seen ( RBCs, WBCs, platelets)
35 II. Piroplasms Diagnosis 1. Babesia spp. History, clinical signs, serology Observation of merozoites within erythrocytes on stained blood smears Collected blood from ear, tip of the tail, or toe nail as parasites are more common & numerous in capillary blood 2. Cytauxzoon felis History & clinical signs Observation of merozoites within erythrocytes on stained blood smears Intraerythrocytic parasites need to be differentiated from Babesia felis and Mycoplasma haemofelis Observation of merozoites in histiocytes (macrophages) in tissue impression smear (cytology) or histology (biopsies or necropsies) Intrahistiocytic stages = diagnostic
36 II. Piroplasms Treatment & Control 1. Babesia Diaminazene I.M. or phenamide S.C. 2. Cytauxzoon Rapidly fatal disease No treatment has proven effective Prevention Tick control Ticks are rarely seen on cats (grooming behavior)
37 Piroplasmosis Ixodid Tick Vectors (FYI) Disease Causative agent Ixodid Tick Vector Bovine Babesiosis ( Red Water Fever ) Bovine Babesiosis ( Red Water Fever ) Bovine Theleiriosis ( East Coast Fever ) Babesia bigemina Babesia bovis Babesia divergens Babesia argentina Theileria parva Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus (eradicated) Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Rhipicephalus appendiculatus Canine Babesiosis Babesia gibsonii Rhipicephalus sanguinensis (brown dog tick) Feline Cytauxzoonosis Equine Babesiosis Human Babesiosis (Zoonosis) Cytauxzoon felis (bobcat wildlife reservoir) Babesia caballi Theileria (Babesia) equi Babesia microti (parasite of voles and mice) Dermacentor variablis (presumed) Genera: Dermacentor, Hyalomma, and Rhipicephalus Ixodes scapularis
38 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon
39 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods I. Hemoflagellates 1. Trypanosomes i. African Trypanosomiasis and Nagana ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease) 2. Leishmania i. Leishmaniasis II. III. Piroplasms 1. Babesia 2. Cytauxzoon 3. Theileria Malarias 1. Plasmodium 2. Leukocytozoon 3. Haemoproteus
40 III. Malarias 1. Plasmodium spp. Avian Malaria and Human Malaria Transmitted by mosquitoes 2. Leucocytozoon spp. Parasites of domestic & wild birds Over 60 species known to infect birds Transmitted by the black fly, Simlulium spp. 3. Haemoproteus spp. Birds and reptiles Usually an incidental finding (i.e., non-pathogenic) Transmitted by louse flies & biting midges
41 III. Malarias 1. Plasmodium spp. Humans & non-human primates, rodents, birds & reptiles Human Malaria Avian Malaria Transmission Mammals - anopheline mosquito (Anopheles spp.) Birds - culicine mosquito (Culex spp.) Human malaria Between million people are infected/year ~1 million people die from malaria each year 90% of deaths due to Plasmodium falciparum P. knowlesi in macaques = zoonotic
42 FYI: Female mosquitoes use two volatile cues to select and navigate toward hosts: 1. Exhaled CO2 2. Skin odorants Female mosquitoes detect plumes of exhaled CO2 using a class of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) designated cpa. CpA neurons are housed in capitate peg (cp) sensilla on the maxillary palps and express the CO2 receptor, comprising three conserved members of the Gustatory receptor gene family
43 Avian Malaria Numerous species of genus Plasmodium Plasmodium relictum Transmission To birds by culicine mosquito (i.e., Culex spp.) Clinical signs Anemia, lethargy, hepatomegaly, and hepatitis Can be fatal in non-adapted species Penguins (animals in captivity) Hawaiian forest birds Hawaiian crows, honeycreepers (apapane < i iwi)
44 III. Malarias 2. Leucocytozoon spp. Transmitted by the black fly Simulium spp. Parasites of birds Domestic & wild Over 60 species L. simondi Infects ducks & geese (Canadian geese) L. caulleryi Infects chickens L. smithi Infects turkeys
45 III. Malarias 2. Leucocytozoon 1. Black fly transmits sporozoites to vertebrate host Sporozoites disseminate and infect a variety of cell types and undergo shizogony (esp. in liver) cell lysis merozoites released 2. Merozoites infect RBCs, WBCs, and endothelial cells gametocytes Merozoites in RBCs ROUND gametocytes Merozoites in endothelial cells megaloschizonts merozoites invade WBCs ELONGATE gametocytes 3. Gametocytes ingested by black fly sporogony in gut & salivary glands
46 III. Malarias, 2. Leucocytozoon Pathogenesis Destruction (lysis) of infected host cells Ruptured schizonts may induce granulomatous reactions in the surrounding tissues Results in anemia, leukocytosis, splenomegaly, & hepatomegaly Megaloschizonts appear as grey-white nodules Found in the heart, liver, lung or spleen. Megaloszhizonts in endothelial cells occlusion of blood vessels ischemic necrosis and associated inflammation in the heart, brain, spleen, and liver Livers are variably enlarged and pale, may contain nodules (megaloschizonts +/- granulomas), and often contain areas of hemorrhage
47 III. Malarias 2. Leucocytozoon Clinical signs Majority of birds affected with leukocytozoonosis exhibit no signs. Young birds (most susceptible) Acute onset of anorexia, listlessness, laboured breathing, anemia (pallor), diarrhea (with green droppings) Susceptibility to secondary infections is increased. Significant death loss within 24 hours of clinical signs Typically signs appear days post exposure Older birds Chronic infections with low mortality, but can become listless & thin egg production, egg weight & hatchability Recovered birds harbour the parasite in their blood for over a year & often for life
48 III. Malarias 2. Leucocytozoon Diagnosis Blood smears Microscopic observation of gametocytes in stained thin blood smears Round & elongate gametocytes! Necropsy with histology Identification of schizonts and megaloschizonts in tissue sections New PCR test (research only)
49 III. Malarias, 2. Leucocytozoon Treatment & Control Preventive medication is the norm Sulfadimethoxine & pyrimethamine combinations Clopidol has been approved by the FDA for control of infections in turkeys Prevention Control black fly vector Keep domestic birds separated from wild birds (wildife reservoirs) Simulium black fly
50 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon
51 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Hemoflagellates Trypanosoma Piroplasms Babesia Malarias Plasmodium Trypomastigotes in blood Merozoites in RBCs Merozoites in RBCs Leishmania Cytauxzoon Leucocytozoon Amastigotes in macrophages Merozoites in RBCs (& mø) Merozoites in RBCs, round & elongate gametocytes in blood
52 Protozoan parasites transmitted by 1. Hemoflagellates 1. Trypanosomes arthropods i. African Trypanosomiasis and Nagana (Tsetse fly) ii. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease; Triatomine kissing bug) 2. Leishmania i. Leishmaniasis (Sandflies) 2. Piroplasms 1. Babesia (Ixodid ticks) 2. Cytauxzoon (Ixodid ticks) 3. Malarias 1. Plasmodium (Mosquitoes) 2. Leukocytozoon (Black flies)
53 Protozoan parasites transmitted by arthropods Protozoan Vector Host Disease Trypanosoma congolense, T. vivax, T. brucei brucei Tse tse fly (Glossina sp.) African cattle (etc.) Bovine trypanosomiasis (Nagana) Trypanosoma cruzi Triatomine (kissing) bug (Triatoma sp.) Dogs Chagas Disease Leishmania donovani complex Phlebotomus sandfly Lutzomyia sandfly Dogs Leishmaniasis Babesia bovis Ixodid tick (Rhipicephalus appendiculatus) Cattle Bovine babesiosis Babesia gibsonii Ixodid tick (Rhipicephalus sanguinensis) Dogs Canine babesiosis Cytauxzoon felis Ixodid tick (Dermacentor variabilis) Cats (bobcats) Cytauxzoonosis Plasmodium relictum Culicine mosquito (Culex spp.) Birds Avian malaria Leucocytozoon simondi Simulium black fly (Simulium spp.) Ducks & geese & Chickens & Turkeys Leucocytozoonosis
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
HAEMOFLAGELLATES. Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine
 HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
Blood Smears Only 6 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control 15B-K
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
Morphological forms of hemoflagellates
 Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates
 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Protozoa from tissues. Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp.
 Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Kinetoplastids Handout
 Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Blood Smears Only 07 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control 12B A
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين
 اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
KINETOPLASTIDS. Kinetoplast. Nucleus
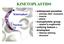 KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
Trypanosomiasis. Introduction. Epidemiology. Global Epidemiology. Trypanosomiasis Risk in UK Travellers
 Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Blood Smears Only 19 May Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 9 May 205 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 9 May 205 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
Blood Smears Only 3 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 3 February 2015 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 3 February 2015 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only
1. Toxoplasma gondii:
 Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Blood Smears Only 20 May Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 20 May 2014 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 20 May 2014 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
 Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
2.Trichomonas vaginalis
 2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
CONTINUED FROM PART 1
 CONTINUED FROM PART 1 1 LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 2 MALARIA
CONTINUED FROM PART 1 1 LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 2 MALARIA
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy
Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear. Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006
 Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006 Pathogens detected in PS Bacteria Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae Staphylococcus sp. Bartonella
Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006 Pathogens detected in PS Bacteria Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae Staphylococcus sp. Bartonella
Trypanosomiasis. By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy
 Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Modified mitochondrion near base of flagellum
 XV. The Flagellates (Chapters 5 & 6) 2011 A. Hemoflagellates 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenozoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma
XV. The Flagellates (Chapters 5 & 6) 2011 A. Hemoflagellates 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenozoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma
XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c.
 XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma (2)
XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma (2)
Entamoeba histolytica
 Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections
 Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged lymph nodes Anaemia Dysentery Parasites causing this clinical presentation How did the parasite produce this presentation
Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged lymph nodes Anaemia Dysentery Parasites causing this clinical presentation How did the parasite produce this presentation
WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
Trypanosomiasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or
EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011
 1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
BLOOD PARASITES. Danka Petrovic
 BLOOD PARASITES Danka Petrovic Parasites Found in Blood Plasmodium species (Malaria) Babesia Trypanosoma spp Microfilariae Leishmania (Visceral) Plasmodium (Malaria) Four species are considered true parasites
BLOOD PARASITES Danka Petrovic Parasites Found in Blood Plasmodium species (Malaria) Babesia Trypanosoma spp Microfilariae Leishmania (Visceral) Plasmodium (Malaria) Four species are considered true parasites
UPDATE ON CANINE AND FELINE BLOOD DONOR SCREENING FOR BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS Wardrop et al, JVIM 2016 Consensus statement
 UPDATE ON CANINE AND FELINE BLOOD DONOR SCREENING FOR BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS Wardrop et al, JVIM 2016 Consensus statement BACKGROUND: 3 types of pathogens: o Vector-borne (testing recommended) o Non-vector-borne
UPDATE ON CANINE AND FELINE BLOOD DONOR SCREENING FOR BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS Wardrop et al, JVIM 2016 Consensus statement BACKGROUND: 3 types of pathogens: o Vector-borne (testing recommended) o Non-vector-borne
Better Training for Safer Food BTSF
 Better Training for Safer Food BTSF Importation of vector-borne infectious diseases Tanguy Marcotty Institute of Tropical Medicine Importation routes Trade Infected live animals (e.g. H5N1 avian influenza)
Better Training for Safer Food BTSF Importation of vector-borne infectious diseases Tanguy Marcotty Institute of Tropical Medicine Importation routes Trade Infected live animals (e.g. H5N1 avian influenza)
EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014
 1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Invest in the future, defeat malaria
 Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Blood Smears Only 5 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control 13B A
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 5 February 2013 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 5 February 2013 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
Blood and Tissue Protozoa
 Blood and Tissue Protozoa Blood and Tissue Protozoa Flagelates Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness (chr, Af) Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness (ac, Af) Trypanosoma cruzi Chagas
Blood and Tissue Protozoa Blood and Tissue Protozoa Flagelates Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness (chr, Af) Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness (ac, Af) Trypanosoma cruzi Chagas
Parasites are found in all groups of organisms
 Parasites are found in all groups of organisms Parasites a very diverse set of eukaryotic pathogens Parasitology as a scientific discipline historically covers a diverse collection of multi- and unicellular
Parasites are found in all groups of organisms Parasites a very diverse set of eukaryotic pathogens Parasitology as a scientific discipline historically covers a diverse collection of multi- and unicellular
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Malaria. Population at Risk. Infectious Disease epidemiology BMTRY 713 (Lecture 23) Epidemiology of Malaria. April 6, Selassie AW (DPHS) 1
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Therapeutic Parasite Reduction or Removal of Harmful Materials. Yanyun Wu, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer
 Therapeutic Parasite Reduction or Removal of Harmful Materials Yanyun Wu, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer None Conflict of Interest Puget Sound Blood Center is now Bloodworks Northwest After 70 years Puget
Therapeutic Parasite Reduction or Removal of Harmful Materials Yanyun Wu, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer None Conflict of Interest Puget Sound Blood Center is now Bloodworks Northwest After 70 years Puget
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
Diseases: If you think about the spread of disease caused by parasites such as blindness, There are several infective causes of blindness :
 Introduction : -The parasites are usually negligible and we don't take it seriously. - They cause diseases in the world. ( morbidity ) - Parasite means الطفيلي somebody who eats at someone else's table!!!!
Introduction : -The parasites are usually negligible and we don't take it seriously. - They cause diseases in the world. ( morbidity ) - Parasite means الطفيلي somebody who eats at someone else's table!!!!
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever)
 Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY
 MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #4 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #4 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 52-year old male presented after complaining of a week of fever and headaches. Other symptoms included malaise and lack of appetite, and
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #4 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 52-year old male presented after complaining of a week of fever and headaches. Other symptoms included malaise and lack of appetite, and
Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
Chagas disease. (American trypanosomiasis)
 Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) Epidemiology 7 to 8 million people worldwide are infected Endemic in Latin America and South America USA, Canada, Europe http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs340/en/index.html
Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) Epidemiology 7 to 8 million people worldwide are infected Endemic in Latin America and South America USA, Canada, Europe http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs340/en/index.html
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Anopheles freeborni. Courtesy
 Anopheles freeborni Courtesy Plasmodia seen with the microscope M. Lontie, MCH, Leuven, 2012 Diagnosis of malaria Thin film (better for species identification). Thick film (more sensitive). QBC (quantitative
Anopheles freeborni Courtesy Plasmodia seen with the microscope M. Lontie, MCH, Leuven, 2012 Diagnosis of malaria Thin film (better for species identification). Thick film (more sensitive). QBC (quantitative
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Malaria. An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture
 Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27
 KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA
 A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA Laura Peachey BVSc BSc MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College Clinical problem Cases of neurological
A RECENT OUTBREAK OF NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE IN THE EQUID POPULATION OF THE CENTRAL RIVER DISTRICT OF THE GAMBIA Laura Peachey BVSc BSc MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College Clinical problem Cases of neurological
The Struggle with Infectious Disease. Lecture 5
 The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
Bloodborne Parasites: A New Perspective on Some Old Nemeses
 Bloodborne Parasites: A New Perspective on Some Old Nemeses Ann Valley- Advanced Microbiologist Tim Monson- Microbiologist Supervisor Communicable Disease Division Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene
Bloodborne Parasites: A New Perspective on Some Old Nemeses Ann Valley- Advanced Microbiologist Tim Monson- Microbiologist Supervisor Communicable Disease Division Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
What is Kala-azar? What are Signs & Symptoms of Kala-Azar?
 What is Kala-azar? Kala-azar is a slow progressing indigenous disease caused by a protozoan parasite of genus Leishmania In India Leishmania donovani is the only parasite causing this disease The parasite
What is Kala-azar? Kala-azar is a slow progressing indigenous disease caused by a protozoan parasite of genus Leishmania In India Leishmania donovani is the only parasite causing this disease The parasite
Intestinal Protozoa 1- Entamoeba Histolytica
 Check NOTES BOXES in sheet 27, just in case 1- Trophozoite Form (Vegetative form / tissue form). 2- Cyst Form (Luminal form), small and circular, can be: a- Immature cyst, which can be either Uninucleate
Check NOTES BOXES in sheet 27, just in case 1- Trophozoite Form (Vegetative form / tissue form). 2- Cyst Form (Luminal form), small and circular, can be: a- Immature cyst, which can be either Uninucleate
Extra-intestinal coccidians
 Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen. Medical Parasitology
 The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
Outline. Origin and Biogeography of Human Infectious Disease. Advantages of virulence. Diseases differ in virulence. Serial passage experiments
 Outline Origin and Biogeography of Human Infectious Disease Alan R. Rogers Evolution of virulence (Ewald 1983) Origin of human infectious diseases (Wolfe et al 2007). Biogeography of human infectious diseases
Outline Origin and Biogeography of Human Infectious Disease Alan R. Rogers Evolution of virulence (Ewald 1983) Origin of human infectious diseases (Wolfe et al 2007). Biogeography of human infectious diseases
(From the Department of Medicine, the Peiping Union Medical College, Peiping, China)
 Published Online: 1 April, 1934 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.59.4.491 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 VIABLE LEISHMANIA DONOVANI IN NASAL AND ORAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS WITH
Published Online: 1 April, 1934 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.59.4.491 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 VIABLE LEISHMANIA DONOVANI IN NASAL AND ORAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS WITH
SUMMARY. Cutaneous leishmaniasis with only skin involvement: single to multiple skin ulcers, satellite lesions and nodular lymphangitis.
 SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Blood and Defense. Chapter 11
 Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby
 Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby 1 2 Onchocerca volvulus (Blinding filariasis; river blindness) Microfilaria of Onchocerca volvulus, from skin snip from a patient seen in Guatemala. Wet preparation 3 Some important
Lecture 5: Dr. Jabar Etaby 1 2 Onchocerca volvulus (Blinding filariasis; river blindness) Microfilaria of Onchocerca volvulus, from skin snip from a patient seen in Guatemala. Wet preparation 3 Some important
GROWING TRYPANOSOMES IN THE LABORATORY
 Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 1 Growing trypanosomes in the laboratory A closer look at the trypanosome lifecycle Cultivating trypanosomes in
Published by the International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Volume 2 Number 1 Growing trypanosomes in the laboratory A closer look at the trypanosome lifecycle Cultivating trypanosomes in
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 6 History of Control Mechanisms 1902 Ford and Dutton, two English physicians working
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 6 History of Control Mechanisms 1902 Ford and Dutton, two English physicians working
Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis
 Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis Xuenan XUAN, DVM, PhD National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Obihiro, Hokkaido 080-8555, Japan Tel.:+81-155-495648;
Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis Xuenan XUAN, DVM, PhD National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Obihiro, Hokkaido 080-8555, Japan Tel.:+81-155-495648;
WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT ANAPLASMOSIS AND BORRELIOSIS AND WHAT WE DO NOT A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DACVP, DABVP
 WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT ANAPLASMOSIS AND BORRELIOSIS AND WHAT WE DO NOT A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DACVP, DABVP Anaplasma phagocytophilum Anaplasma phagocytophilum is an intracellular, gram-negative bacterium
WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT ANAPLASMOSIS AND BORRELIOSIS AND WHAT WE DO NOT A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DACVP, DABVP Anaplasma phagocytophilum Anaplasma phagocytophilum is an intracellular, gram-negative bacterium
Identification of vaccine candidate antigens for a Babesia bovis transmission blocking vaccine
 Identification of vaccine candidate antigens for a Babesia bovis transmission blocking vaccine Carlos E. Suarez Animal Disease Research Unit ARS-USDA Department of Veterinary Microbiology and Pathology
Identification of vaccine candidate antigens for a Babesia bovis transmission blocking vaccine Carlos E. Suarez Animal Disease Research Unit ARS-USDA Department of Veterinary Microbiology and Pathology
BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking Scheme: Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking Scheme: Total marks available
5/11/2009. Information About Malaria. What is Malaria? How many people think Malaria is caused by mosquitoes? Evolution & History
 Information About Malaria Evolution & History Etiology, Host Specific Parasites & Symptoms & Pathology (Human) Treatments (Human) What is Malaria? How many people think Malaria is caused by mosquitoes?
Information About Malaria Evolution & History Etiology, Host Specific Parasites & Symptoms & Pathology (Human) Treatments (Human) What is Malaria? How many people think Malaria is caused by mosquitoes?
University Of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy
 PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
Parasites transmitted by vectors
 Parasites transmitted by vectors Often very specific vector-parasite relationships Biomphalaria sp. - Schistosoma mansoni Anopheles sp. Plasmodium falciparum Simulium sp. Onchocerca volvulis Some more
Parasites transmitted by vectors Often very specific vector-parasite relationships Biomphalaria sp. - Schistosoma mansoni Anopheles sp. Plasmodium falciparum Simulium sp. Onchocerca volvulis Some more
Class Insecta 1. The Latin name of Class insects a) insecta b) arachnida c) chelicerata d) arthropoda 2. The number of pairs of extremities of
 Class Insecta 1. The Latin name of Class insects a) insecta b) arachnida c) chelicerata d) arthropoda 2. The number of pairs of extremities of insects a) 10 b) 3 c) 4 d) 6 3. The body parts of insects
Class Insecta 1. The Latin name of Class insects a) insecta b) arachnida c) chelicerata d) arthropoda 2. The number of pairs of extremities of insects a) 10 b) 3 c) 4 d) 6 3. The body parts of insects
Pathogen prioritisation
 Pathogen prioritisation Comment on Confidence Score: The confidence score has to be given by who compiles the questionnaire. We propose a very simple scoring system, based on 3 classes: 1. based on experience
Pathogen prioritisation Comment on Confidence Score: The confidence score has to be given by who compiles the questionnaire. We propose a very simple scoring system, based on 3 classes: 1. based on experience
African Trypanosomiasis Detection Using Dempster-Shafer Theory Andino Maseleno, 2 Md. Mahmud Hasan
 African Trypanosomiasis Detection Using Dempster-Shafer Theory 1 Andino Maseleno, 2 Md. Mahmud Hasan 1 Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Universiti Brunei Darussalam 2 Jalan Tungku Link,
African Trypanosomiasis Detection Using Dempster-Shafer Theory 1 Andino Maseleno, 2 Md. Mahmud Hasan 1 Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Universiti Brunei Darussalam 2 Jalan Tungku Link,
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar
 Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
Learning Objectives. 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic Morphology 5. Name of diesease 6. Prevention and Control
 Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
HEMOPOIETIC SYSTEM INFECTIONS BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE BLOODSTREAM Reading Assignment: Chapters 50 & 63
 HEMOPOIETIC SYSTEM INFECTIONS BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE BLOODSTREAM Reading Assignment: Chapters 50 & 63 Definitions I. Bacteremia: Viable bacteria in the blood as demonstrated by a positive blood culture
HEMOPOIETIC SYSTEM INFECTIONS BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE BLOODSTREAM Reading Assignment: Chapters 50 & 63 Definitions I. Bacteremia: Viable bacteria in the blood as demonstrated by a positive blood culture
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale. Watersheds of the African Continent
 The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Global Risk By Country-Proportionality Plot P. falciparum P. vivax Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 3 million
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Global Risk By Country-Proportionality Plot P. falciparum P. vivax Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 3 million
Lumpy skin disease and bluetongue training of trainers in FYR of Macedonia Skopje, September 2017
 1 Bluetongue Agent and hosts Epidemiology: Spreading routes and transmission Clinical diagnosis: Clinical sings, Differential diagnosis, post-mortem lesions and findings Tsviatko Alexandrov DVM, PhD, FAO
1 Bluetongue Agent and hosts Epidemiology: Spreading routes and transmission Clinical diagnosis: Clinical sings, Differential diagnosis, post-mortem lesions and findings Tsviatko Alexandrov DVM, PhD, FAO
Amoebas are motile by means of pseudopodia cytoplasmic extensions which allow it to crawl across surfaces.
 Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease. Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP)
 Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP) Lyme Disease Most common vectorborne illness in the United States Caused by the tick-transmitted spirochete
Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP) Lyme Disease Most common vectorborne illness in the United States Caused by the tick-transmitted spirochete
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA K. C. Nayak, Rakesh Meena, *Surendra Kumar, B. K. Gupta, V. B. Singh and Varun Kulkarni Department
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA K. C. Nayak, Rakesh Meena, *Surendra Kumar, B. K. Gupta, V. B. Singh and Varun Kulkarni Department
Lesson 1:Introduction To Malaria INTRODUCTION. Contents. Objectives. From WikiEducator
 Lesson 1:Introduction To Malaria From WikiEducator Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Definition 2.1 The Malaria Life Cycle 2.2 Clinical Classification of Malaria 2.2.1 Conclusion: 2.2.2 Glossary 2.2.3 References
Lesson 1:Introduction To Malaria From WikiEducator Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Definition 2.1 The Malaria Life Cycle 2.2 Clinical Classification of Malaria 2.2.1 Conclusion: 2.2.2 Glossary 2.2.3 References
Protozoal Infections. By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Protozoal Infections By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Classification of Phylum Protozoa 1- According to the organ of locomotion 1- Class Rhizopoda (Amoebae) 2- Class Ciliata (Ciliates) 3- Class Zoomastigophora
Protozoal Infections By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Classification of Phylum Protozoa 1- According to the organ of locomotion 1- Class Rhizopoda (Amoebae) 2- Class Ciliata (Ciliates) 3- Class Zoomastigophora
2015 JUNIOR DISEASES
 2015 JUNIOR DISEASES EASY 2641 (easy) HS47/TH332 Q: What is an acute infection? A: Symptoms appear quickly 2642 (easy) HIH630-1/TH600 Q: What is another name for Equine Infectious Anemia? A: EIA OR swamp
2015 JUNIOR DISEASES EASY 2641 (easy) HS47/TH332 Q: What is an acute infection? A: Symptoms appear quickly 2642 (easy) HIH630-1/TH600 Q: What is another name for Equine Infectious Anemia? A: EIA OR swamp
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale. Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum
 The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 39-year old male traveler developed fever and thrombocytopenia after returning from a trip to the Philippines. The parasitemia was 10,000
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 39-year old male traveler developed fever and thrombocytopenia after returning from a trip to the Philippines. The parasitemia was 10,000
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Spirochaetales 1- Spirochaetaceae Treponema Borrelia 2- Leptospiraceae Leptospira
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Spirochaetales 1- Spirochaetaceae Treponema Borrelia 2- Leptospiraceae Leptospira OS = outer sheath AF = axial fibrils AF Leptospira interrogans Characteristics: Spirochaetaceae
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Spirochaetales 1- Spirochaetaceae Treponema Borrelia 2- Leptospiraceae Leptospira OS = outer sheath AF = axial fibrils AF Leptospira interrogans Characteristics: Spirochaetaceae
THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA
 THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA Imna Malele, Hamisi Nyingilili, Eugen Lyaruu, Winston Kitwika Tsetse & Trypanosomiasis Research Institute Majani Mapana, Off Korogwe
THE ROLE OF LIVESTOCK IN THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SLEEPING SICKNESS IN TANZANIA Imna Malele, Hamisi Nyingilili, Eugen Lyaruu, Winston Kitwika Tsetse & Trypanosomiasis Research Institute Majani Mapana, Off Korogwe
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress LEPTOSPIROSIS Remo Lobetti BVSc MMedVet (Med) PhD Dipl ECVIM (Internal Medicine) Bryanston Veterinary Hospital
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress LEPTOSPIROSIS Remo Lobetti BVSc MMedVet (Med) PhD Dipl ECVIM (Internal Medicine) Bryanston Veterinary Hospital
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Bikaner), V.P.O. Bajor, Dist. Sikar, Rajasthan, India
 REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Malaria, A Widely Prevalent Mosquito-Borne Infection in Humans and Recommended Herbal Therapy Subha Ganguly 1*, Satarupa Roy 2 1 Associate Department of Veterinary
REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijapc.com e-issn 2350-0204 Malaria, A Widely Prevalent Mosquito-Borne Infection in Humans and Recommended Herbal Therapy Subha Ganguly 1*, Satarupa Roy 2 1 Associate Department of Veterinary
Malaria. benign (mild) malaria
 Malaria Caused by the plasmodium protozoa. Four species of plasmodium causes human malaria: Plasmodium falciparum responsible for nearly all serious complications and deaths. P. vivax P. malariae P. ovale
Malaria Caused by the plasmodium protozoa. Four species of plasmodium causes human malaria: Plasmodium falciparum responsible for nearly all serious complications and deaths. P. vivax P. malariae P. ovale
Dengue Virus-Danger from Deadly Little Dragon
 Molecular Medicine Dengue Virus-Danger from Deadly Little Dragon Dr.G.MATHAN Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Science Bharathidasan University Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu Vector (A carrier)
Molecular Medicine Dengue Virus-Danger from Deadly Little Dragon Dr.G.MATHAN Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Science Bharathidasan University Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu Vector (A carrier)
