The Respiratory System
|
|
|
- Coleen Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
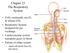
1 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 22 Part 1 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes involved in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of respiratory gases Internal respiration Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System Organs of the Respiratory System Respiratory organs Nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses Pharynx, larynx, and trachea Bronchi and smaller branches s and alveoli Carina of trachea Right main (primary) Right lung Parietal pleura Nasal cavity Nostril Larynx Oral cavity Pharynx Left main (primary) Bronchi Alveoli Left lung Diaphragm Figure 22.1 Organs of the Respiratory System The Nose Divided into Conducting zone Respiratory zone Provides an airway for respiration Moistens and warms air Filters inhaled air Resonating chamber for speech Houses olfactory receptors 1
2 The Nose Size variation due to differences in nasal cartilages Skin is thin contains many sebaceous glands Epicranius, frontal belly Root and bridge of nose Dorsum nasi Ala of nose Apex of nose Naris (nostril) Philtrum Frontal bone Nasal bone Septal cartilage Maxillary bone (frontal process) Lateral process of septal cartilage Minor alar cartilages Dense fibrous connective tissue Major alar cartilages The Nasal Cavity External nares nostrils Divided by nasal septum Continuous with nasopharynx Posterior nasal apertures choanae (a) Surface anatomy (b) External skeletal framework Figure 22.2 Nasal Cavity Two types of mucous membrane Olfactory mucosa Near roof of nasal cavity Houses olfactory (smell) receptors Respiratory mucosa Lines nasal cavity Epithelium is pseudostratified ciliated columnar The Upper Respiratory Tract Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone Sphenoid sinus Posterior nasal aperture Nasopharynx Pharyngeal tonsil Opening of pharyngotympanic tube Uvula Oropharynx Palatine tonsil Isthmus of the fauces Laryngopharynx Esophagus (c) Illustration Frontal sinus Nasal cavity Nasal conchae (superior, middle and inferior) Nasal meatuses (superior, middle, and inferior) Nasal vestibule Nostril Hard palate Soft palate Tongue Lingual tonsil Larynx Hyoid bone Epiglottis Vestibular fold Thyroid cartilage Vocal fold Thyroid gland Figure 22.3c Respiratory Mucosa Nasal Conchae Consists of Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Goblet cells within epithelium Underlying layer of lamina propria Cilia move contaminated mucus posteriorly Superior and middle nasal conchae Part of the ethmoid bone Inferior nasal conchae Separate bone Project medially from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity Particulate matter Deflected to mucus-coated surfaces 2
3 The Pharynx The Nasopharynx Funnel-shaped passageway Connects nasal cavity and mouth Divided into three sections by location Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx Type of mucosal lining changes along its length Superior to the point where food enters Only an air passageway Closed off during swallowing Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) Located on posterior wall Destroys entering pathogens Contains the opening to the pharyngotympanic tube (auditory tube) Tubal tonsil Provides some protection from infection The Oropharynx The Laryngopharynx Arch-like entranceway fauces Extends from soft palate to the epiglottis Epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Two types of tonsils in the oropharynx Palatine tonsils in the lateral walls of the fauces Lingual tonsils covers the posterior surface of the tongue Passageway for both food and air Epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Continuous with the esophagus and larynx The Larynx Nine Cartilages of the Larynx Three functions Voice production Provides an open airway Routes air and food into the proper channels Superior opening is Closed during swallowing Open during breathing Thyroid cartilage Shield-shaped, forms laryngeal prominence (Adam s apple) Three pairs of small cartilages Arytenoid cartilages Corniculate cartilages Cuneiform cartilages Epiglottis Tips inferiorly during swallowing 3
4 The Larynx Anatomy of the Larynx Vocal ligaments of the larynx Vocal folds (true vocal cords) Act in sound production Vestibular folds (false vocal cords) No role in sound production Epithelium of the larynx Stratified squamous superior portion Pseudostratified ciliated columnar inferior portion (a) Surface view Body of hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Laryngeal prominence (Adam s apple) Cricothyroid ligament Body of hyoid bone Laryngeal prominence (Adam s apple) Sternal head Clavicular head Sternocleidomastoid Clavicle Jugular notch Epiglottis Thyrohyoid membrane Cricotracheal ligament l cartilages (b) Anterior view Figure 22.5a, b Anatomy of the Larynx Epiglottis Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid membrane Corniculate cartilage Thyroid Arytenoid cartilage cartilage Glottis l cartilages (c) Photograph of cartilaginous framework of the larynx, posterior view Movements of the Vocal Folds Anterior Thyroid cartilage Vocal ligaments of vocal cords Glottis Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle Arytenoid cartilage Corniculate cartilage Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle Posterior Epiglottis Thyrohyoid membrane Cuneiform cartilage Corniculate cartilage Arytenoid cartilage Arytenoid muscle l cartilages Body of hyoid bone Thyrohyoid membrane Fatty pad Vestibular fold (false vocal cord) Thyroid cartilage Vocal fold (true vocal cord) Cricothyroid ligament Cricotracheal ligament Base of tongue Epiglottis Vestibular fold (false vocal cord) Vocal fold (true vocal cord) Glottis Inner lining of trachea Cuneiform cartilage Corniculate cartilage (d) Sagittal section (anterior on the right) Figure 22.5c, d (a) Vocal folds in closed position; closed glottis (b) Vocal folds in open position; open glottis Figure 22.6 The Larynx The Voice production Length of the vocal folds changes with pitch Loudness depends on the force of air across the vocal folds Sphincter function of the larynx Valsalva s maneuver straining Innervation of the larynx Recurrent laryngeal nerves (branch of vagus) Descends into the mediastinum C-shaped cartilage rings keep airway open Carina Marks where trachea divides into two primary bronchi Epithelium Pseudostratified ciliated columnar 4
5 The Bronchi in the Conducting Zone Mucosa Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Lamina propria (connective tissue) Bronchial tree Submucosa Seromucous gland in submucosa Posterior Hyaline cartilage Mucosa Esophagus (b) Photomicrograph of the tracheal wall (250 ) Submucosa lis muscle Lumen of trachea Seromucous gland in submucosa Hyaline cartilage Adventitia Anterior (a) Cross section of the trachea and esophagus Figure 22.7 Bronchi in the Conducting Zone Superior lobe of right lung Extensively branching respiratory passageways Primary bronchi (main bronchi) Largest bronchi Right main bronchi Wider and shorter than the left Bronchi in the Conducting Zone Mucosa Pseudostratified epithelium Lamina propria Superior lobe of left lung Left main (primary) Lobar (secondary) Segmental (tertiary) Inferior lobe of left lung Lumen Cartilage plate Smooth muscle Middle lobe Inferior lobe of right lung of right lung (a) The branching of the bronchial tree Fibromusculocartilaginous layer (b) Photomicrograph of a (13 ) Figure 22.8a Bronchi in the Conducting Zone Changes in Tissue Composition along Conducting Pathways Secondary (lobar) bronchi Supportive connective tissues change Three on the right Two on the left Tertiary (segmental) bronchi Branch into each lung segment Bronchioles Little bronchi, less than 1 mm in diameter Terminal bronchioles Less than 0.5 mm in diameter Figure 22.8b C-shaped rings replaced by cartilage plates Epithelium changes First, pseudostratified ciliated columnar Replaced by simple columnar, then simple cuboidal epithelium Smooth muscle becomes important Airways widen with sympathetic stimulation Airways constrict under parasympathetic direction 5
6 Structures of the Respiratory Zone Structures of the Respiratory Zone Consists of air-exchanging structures Respiratory bronchioles branch from terminal bronchioles Lead to alveolar ducts Lead to alveolar sacs Respiratory bronchioles Terminal bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveoli Alveolar duct Alveolar sac (a) Figure 22.9a Structures of the Respiratory Zone Structures of the Respiratory Zone Respiratory bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveolar pores Alveoli ~300 million alveoli account for tremendous surface area of the lungs Surface area of alveoli is 140 square meters Alveoli (b) Alveolar sac Figure 22.9b Structures of the Respiratory Zone Structures of the Respiratory Zone Structure of alveoli Type I cells single layer of simple squamous epithelial cells Surrounded by basal lamina Alveolar and capillary walls plus their basal lamina form the... Respiratory membrane Structures of alveoli (continued) Type II cells scattered among type I cells Are cuboidal epithelial cells Secrete surfactant Reduces surface tension within alveoli keeps alveoli from collapsing when we exhale Alveolar macrophages 6
7 Anatomy of Alveoli and the Respiratory Membrane Anatomy of Alveoli and the Respiratory Membrane Red blood cell Nucleus of type I (squamous epithelial) cell Alveolar pores Terminal bronchiole Respiratory bronchiole Capillary O2 Smooth muscle Capillary CO2 Alveolus Macrophage Endothelial cell nucleus Elastic fibers Alveolus Alveolus Respiratory membrane Capillaries (a) Diagrammatic view of capillary-alveoli relationships Red blood cell Type I cell in capillary of alveolar wall Alveoli (gas-filled Type II (surfactantair spaces) secreting) cell Alveolar epithelium Fused basement membranes of the alveolar epithelium and the capillary endothelium Capillary endothelium (c) Detailed anatomy of the respiratory membrane Figure 22.10a, b Figure 22.10c The Respiratory Zone Gross Anatomy of the s Features of alveoli Major landmarks of the lungs Surrounded by elastic fibers Interconnect by way of alveolar pores Internal surfaces A site for free movement of alveolar macrophages Apex, base, hilum, and root Left lung Superior and inferior lobes Fissure oblique Right lung Superior, middle, and inferior lobes Fissures oblique and horizontal Gross Anatomy of the s Bronchopulmonary Segments Right lung Anterior View of Thoracic Structures Right superior lobe (3 segments) Left lung Left superior lobe (4 segments) Intercostal muscle Rib Parietal pleura Pleural cavity Visceral pleura Apex of lung Right superior lobe Horizontal fissure Right middle lobe Oblique fissure Left superior lobe Oblique fissure Left inferior lobe Right inferior lobe Heart (in mediastinum) Diaphragm Cardiac notch Base of lung (a) Anterior view. The lungs flank mediastinal structures laterally. Apex of lung Pulmonary artery Thymus Left superior lobe Left main Oblique fissure Pulmonary vein Impression of heart Oblique fissure Left inferior lobe Hilum Aortic impression Lobules (b) Photograph of medial view of the left lung Figure 22.11a, b Right middle lobe (2 segments) Right inferior lobe (5 segments) Left inferior lobe (5 segments) Figure
8 Blood Supply and Innervation of the s Pulmonary arteries Deliver oxygen-poor blood to the lungs Pulmonary veins Carry oxygenated blood to the heart Bronchial arteries (2 on left, 1 on right) Supply systemic (oxygenated) blood to the lung structures (enter lung s medial surface along with the large pulmonary vessels) Innervation Sympathetic, parasympathetic, and visceral sensory fibers Parasympathetic constrict airways Sympathetic dilate airways Transverse Cut through the Superior Thorax Right lung Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Pleural cavity Pericardial membranes Sternum Vertebra Posterior Esophagus (in mediastinum) Root of lung at hilum Left main Left pulmonary artery Left pulmonary vein Left lung Thoracic wall Pulmonary trunk Heart (in mediastinum) Anterior mediastinum Anterior (d) Transverse section through the thorax, viewed from above. s, pleural membranes, and major organs in the mediastinum are shown. Figure 22.11d The Pleurae Diagram of the Pleurae and Pleural Cavities A double-layered sac surrounding each lung Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Pleural cavity Potential space between the visceral and parietal pleurae Pleurae help divide the thoracic cavity Central mediastinum Two lateral pleural compartments Apex of lung Right superior lobe Horizontal fissure Right middle lobe Oblique fissure Right inferior lobe Thymus Heart (in mediastinum) Diaphragm Cardiac notch Base of lung (a) Anterior view. The lungs flank mediastinal structures laterally. Intercostal muscle Rib Parietal pleura Pleural cavity Visceral pleura Left superior lobe Oblique fissure Left inferior lobe Figure 22.11a Location of s in Thoracic Cavity The Mechanisms of Ventilation Rib 8 9 Clavicle Nipple Rib Two phases of pulmonary ventilation Inspiration inhalation Expiration exhalation (a) Posterior view Parietal pleura 8 Midaxillary line 9 10 Midclavicular line (b) Anterior view Infrasternal angle at the xiphisternal joint Costal margin Parietal pleura Figure
9 Inspiration Inspiration Volume of thoracic cavity increases Decreases internal gas pressure Action of the diaphragm Diaphragm flattens Action of intercostal muscles Contraction raises the ribs Deep inspiration requires Scalenes Sternocleidomastoid Pectoralis minor Erector spinae extends the back Expiration Quiet expiration chiefly a passive process Inspiratory muscles relax Diaphragm moves superiorly Volume of thoracic cavity decreases Forced expiration an active process Produced by contraction of Internal and external oblique muscles Transverse abdominis muscles Changes in Thoracic Volume (a) Inspiration (b) Expiration Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Inspiratory muscles relax (diaphragm rises and contract (diaphragm descends and rib cage descends due to recoil of the costal rib cage rises). Thoracic cavity cartilages). Thoracic cavity volume decreases. volume increases. Ribs are Ribs and elevated and sternum are Changes in sternum flares depressed as superior- as external inferior and intercostals external anterior- contract. intercostals posterior relax. dimensions Diaphragm moves inferiorly during Diaphragm moves contraction. superiorly as it relaxes. Changes in lateral External External dimensions intercostals intercostals (superior contract. relax. view) Figure Changes in Thoracic Volume 1 At rest, no air movement: Air pressure in lungs is equal to atmospheric (air) pressure. Pressure in the pleural cavity is less than pressure in the lungs. This pressure difference keeps the lungs inflated. 2 Inspiration: Inspiratory muscles contract and increase the volume of the thoracic and pleural cavities. Pleural fluid in the pleural cavity holds the parietal and visceral pleura close together, causing the lungs to expand. As volume increases, pressure decreases and air flows into the lungs. Main bronchi Diaphragm Air Air Thoracic wall Pleural cavity At rest Expanded V P Parietal Visceral pleura pleura Air flows in Pleural cavity V P Thoracic wall Neural Control of Ventilation Most important respiratory center VRG ventral respiratory group Located in reticular formation in the medulla oblongata Neurons generate respiratory rhythm 3 Expiration: Inspiratory muscles relax, reducing thoracic volume, and the lungs recoil. Simultaneously, volumes of the pleural cavity and the lungs decrease, causing pressure to increase in the lungs, and air flows out. Resting state is reestablished. V V P P Air flows out Figure
10 Respiratory Centers in the Brain Stem Neural Control of Ventilation Ventral respiratory group (VRG) contains rhythm generators whose output drives respiration. Pons Medulla Pons Medulla To inspiratory muscles Pontine respiratory centers interact with the medullary respiratory centers to smooth the respiratory pattern. Dorsal respiratory group (DRG) integrates peripheral sensory input and modifies the rhythms generated by the VRG. Respiratory center Generates baseline respiration rate In the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata Chemoreceptors Sensitive to rising and falling oxygen levels Central chemoreceptors located in medulla Peripheral chemoreceptors Aortic bodies Carotid bodies External intercostal muscles Diaphragm Figure Location of Peripheral Chemoreceptors Disorders of Lower Respiratory Structures Brain Sensory nerve fiber in cranial nerve IX (pharyngeal branch of glossopharyngeal) External carotid artery Internal carotid artery Carotid body Common carotid artery Cranial nerve X (vagus nerve) Sensory nerve fiber in cranial nerve X Aortic bodies in aortic arch Aorta Bronchial asthma A type of allergic inflammation Hypersensitivity to irritants in the air or to stress Asthma attacks characterized by Contraction of bronchiole smooth muscle Secretion of mucus in airways Heart Figure Disorders of Lower Respiratory Structures Disorders of Lower Respiratory Structures Cystic fibrosis (CF) inherited disease Exocrine gland function is disrupted Respiratory system affected by Oversecretion of viscous mucus Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Airflow into and out of the lungs is difficult Obstructive emphysema Chronic bronchitis History of smoking 10
11 Disorders of Lower Respiratory Structures Alveolar Changes in Emphysema Figure Figure Disorders of Upper Respiratory Structures Epistaxis nosebleed The Respiratory System Throughout Life By week 4 of development Olfactory placodes appear Invaginate to form olfactory pits Laryngotracheal bud Forms trachea, bronchi, and bronchi subdivisions Reaches functional maturity late in development At birth, only one-sixth of alveoli are present Those who begin smoking as teenagers s never fully develop Additional alveoli never form The Respiratory System Throughout Life Aging of the Respiratory System (a) 4 weeks: anterior superficial view of the embryo s head Frontonasal elevation Olfactory placode Stomodeum (future mouth) Laryngotracheal bud Future mouth Eye Bronchial buds (b) 5 weeks: left lateral view of the developing lower respiratory passageway mucosae Pharynx Foregut Olfactory placode Esophagus Liver Number of glands in the nasal mucosa declines Nose dries Produces thickened mucus Thoracic wall becomes more rigid s lose elasticity Oxygen levels in the blood may fall Figure
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System:
 The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
CHAPTER 24. Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
Respiratory System Structures and Gas Exchange
 A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Read Me. We are the Learning Lab. to look
 Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
The RESPIRATORY System
 The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed.
 Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p.731) 1. The cardiovascular system and the respiratory system cooperate in order to: i. supply oxygen which is required by cells
Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p.731) 1. The cardiovascular system and the respiratory system cooperate in order to: i. supply oxygen which is required by cells
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Respiratory System. Ling Shucai
 Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
RESPIRATORY LAB. Introduction: trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
 RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
THE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 42790_01_ch01_001-052.qxd 7/6/07 12:23 PM Page 1 CHAPTER ONE THE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM O B J E C T I V E S By the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. List
42790_01_ch01_001-052.qxd 7/6/07 12:23 PM Page 1 CHAPTER ONE THE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM O B J E C T I V E S By the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. List
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
GROSS ANATOMY - OVERVIEW
 K. KOZEKA, Ph.D. GROSS ANATOMY - OVERVIEW Respiratory System Nasal cavity Nostril Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Carina of trachea Right main (primary) bronchus Right lung Left main (primary) bronchus
K. KOZEKA, Ph.D. GROSS ANATOMY - OVERVIEW Respiratory System Nasal cavity Nostril Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Carina of trachea Right main (primary) bronchus Right lung Left main (primary) bronchus
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System
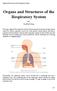 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System
 Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Four processes = pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; gas transport; internal respiration. I. Functional Anatomy Conduction zones lead into respiratory zones.
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1
 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
The Respiratory System
 23 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Respiratory System Learning Outcomes 23-1 Describe the primary
23 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Respiratory System Learning Outcomes 23-1 Describe the primary
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Unit 13: The Respiratory System
 Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
Unit 13: The Respiratory System I. Organs of the Respiratory System A. Nose B. Pharynx C. Larynx D. Trachea E. Bronchi F. Lungs alveoli II. Functions of the Respiratory System A. Gas exchanges between
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Anatomy Sheet #5. In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura.
 Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiration is a term used to refer to ventilation of the lungs (breathing) In other contexts it can be used to refer to part of cellular metabolism Functions of respiration
Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiration is a term used to refer to ventilation of the lungs (breathing) In other contexts it can be used to refer to part of cellular metabolism Functions of respiration
Upper Respiratory Tract
 Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Respiratory System
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Respiratory System I. Overview of the Respiratory System A. The respiratory system functions as an air distributor and gas exchanger supplying oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Respiratory System I. Overview of the Respiratory System A. The respiratory system functions as an air distributor and gas exchanger supplying oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Respiratory System 13PART A Organs of the Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi
Development of the nasal cavity :
 Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
otorhinolaryngology -the study of the structure, function, and disorders of the ears, nose, and throat
 89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46548 1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46548 1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
22 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1033 22 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Figure 22.1 Mountain Climbers bortescristian /flickr.com) The thin air at high elevations can strain the human respiratory system. (credit:
Chapter 22 The Respiratory System 1033 22 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Figure 22.1 Mountain Climbers bortescristian /flickr.com) The thin air at high elevations can strain the human respiratory system. (credit:
