ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CHAPTER 13. Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 1
|
|
|
- Eric Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CHAPTER 13 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 1
2 Endocrine System Overview Endocrine System Consists of ductless glands Secrete hormones directly into bloodstream Affect the function of specific body organs Regulates many intricate body functions Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 2
3 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 3
4 Pituitary Gland Pituitary Gland Referred to as the master gland Secretes hormones that control the functions of other glands Known as the hypophysis Has two distinct lobes with specific functions Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 4
5 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 5
6 Pituitary Gland (continued) Anterior Pituitary Gland = Adenohypophysis Secretes Growth Hormone (GH) Also called Somatotropic Hormone (STH) Regulates growth of bone, muscle, and other body tissues Secretes Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Stimulates normal growth and development of adrenal cortex and secretion of corticosteroids Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 6
7 Pituitary Gland (continued) Anterior Pituitary Gland (continued) Secretes Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Promotes and maintains normal growth and development of the thyroid gland Stimulates secretions of the thyroid hormones Secretes Lactogenic Hormone (LTH) Also called Prolactin Promotes development of breasts during pregnancy Stimulates secretion of milk from breasts after delivery of baby Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 7
8 Pituitary Gland (continued) Anterior Pituitary Gland (continued) Secretes Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Stimulates secretion of estrogen and production of eggs in the female ovaries Stimulates production of sperm in the male testes Secretes Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Stimulates female ovulation and the secretion of testosterone in the male Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH) Controls the intensity of pigmentation in pigmented cells of the skin Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 8
9 Pituitary Gland (continued) Posterior Pituitary Gland = Neurohypophysis Secretes Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Decreases excretion of large amounts of urine from the body Increases reabsorption of water by the renal tubules Secretes Oxytocin (OT) Stimulates contraction of the uterus during childbirth Stimulates the release of milk from the breasts of lactating women in response to the suckling reflex of the infant Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 9
10 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 10
11 Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Tiny, pine cone-shaped gland Located behind dorsal aspect of midbrain region Plays a part in supporting body s biological clock Regulation of patterns of eating, sleeping, and reproduction Secretes melatonin Induces sleep Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 11
12 Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland Located in front of the neck just below the larynx, on either side of the trachea Consists of a right and left lobe Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 12
13 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 13
14 Thyroid Gland (continued) Thyroid Gland (continued) Secretes Triiodothyronine (T3) Helps regulate growth and development of the body Helps control metabolism and body temperature Secretes Thyroxine (T4) Helps maintain normal body metabolism Secretes Calcitonin Helps regulate the level of calcium in the blood Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 14
15 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 15
16 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 16
17 Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid Glands Four tiny rounded bodies located on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland Secrete Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Also known as parathormone Regulates level of calcium in the blood Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 17
18 Thymus Thymus Single gland located in the mediastinum near the middle of the chest, just beneath the sternum Large in fetus and infants, shrinks with age Secretes Thymosin and Thymopoietin Stimulates production of T cells that are involved in the immune response Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 18
19 Adrenal Glands Adrenal Glands Two small glands, one positioned atop each kidney Also known as the suprarenal glands Consists of an adrenal cortex and an adrenal medulla Each has independent functions Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 19
20 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 20
21 Adrenal Glands (continued) Adrenal Cortex secretes Corticosteroids Mineralocorticoids Regulate how mineral salts (electrolytes) are processed in the body Glucocorticoids Influence metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the body Necessary for maintaining normal blood pressure Have an anti-inflammatory effect on the body Increase glucose available during fight-orflight responses by the body Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 21
22 Adrenal Glands (continued) Adrenal Cortex secretes (continued) Gonadocorticoids Sex hormones secreted in small amounts Contribute to secondary sex characteristics in males and females Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 22
23 Adrenal Glands (continued) Adrenal Medulla secretes Catecholamines Epinephrine = adrenaline Sympathiomimetic agent Increases heart rate and force of heart muscle contraction Dilates bronchioles in the lungs Decreases peristalsis in the intestines Raises blood glucose levels by causing the liver to convert glycogen into glucose Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 23
24 Adrenal Glands (continued) Adrenal Medulla secretes (continued) Norepinephrine = noradrenaline Known as a sympathomimetic agent Produces a vasoconstrictor effect on the blood vessels, thereby raising blood pressure Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 24
25 Pancreas Pancreas Elongated gland located in upper left quadrant of the abdomen, behind the stomach Extends horizontally across the body, beginning at the first part of the small intestines and ending at the edge of the spleen Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 25
26 Pancreas (continued) Islets of Langerhans secrete Glucagon Increases blood glucose levels by stimulating liver to convert glycogen into glucose when blood sugar is extremely low Insulin Makes it possible for glucose to pass from blood through cell membranes to be used for energy Promotes conversion of excess glucose into glycogen for storage in the liver for later use Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 26
27 Ovaries Ovaries Female sex glands = female gonads Pair of almond shaped glands Located in upper pelvic cavity, on either side of lateral wall of uterus Near fimbriated ends of the fallopian tubes Responsible for producing mature ova and releasing them at monthly intervals during ovulation Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 27
28 Ovaries (continued) Hormones secreted by the Ovaries Estrogen Promotes the maturation of the ovum in the ovary Stimulates vascularization of the uterine lining each month in preparation for implantation of a fertilized egg Contributes to secondary sex characteristic changes in the female with onset of puberty Progesterone Primarily responsible for changes that occur within the uterus in anticipation of a fertilized ovum Responsible for development of the maternal placenta after implantation of a fertilized ovum Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 28
29 Testes Testes = male gonads = testicles Two small ovoid glands located in the scrotum Primary organs of the male reproductive system Responsible for production of sperm and secretion of androgens (male steroid hormones) Secrete Testosterone Responsible for secondary sex characteristic changes that occur in the male with onset of puberty Responsible for maturation of sperm Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 29
30 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS of the PITUITARY GLAND Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 30
31 Acromegaly Pronounced (ak-roh-meg-ah-lee) Defined Chronic metabolic condition characterized by the gradual, noticeable enlargement and elongation of the bones of the face, jaw, and extremities, due to hypersecretion of the human growth hormone after puberty Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 31
32 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 32
33 Diabetes Insipidus Pronounced (dye-ah-bee-teez in-sip-ih-dus) Defined A condition caused by a deficiency in the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the posterior pituitary gland Characterized by large amounts of urine and sodium being excreted from the body Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 33
34 Dwarfism Pronounced (DWARF-ism) Defined Generalized growth retardation of the body due to the deficiency of the human growth hormone Also known as congenital hypopituitarism or hypopituitarism Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 34
35 Gigantism Pronounced (JYE-gan-tizm) Defined A proportional overgrowth of the body s tissue due to the hypersecretion of the human growth hormone before puberty Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 35
36 Hypopituitarism Pronounced (high-poh-pih-too-ih-tah-rizm) Defined Complex syndrome resulting from the absence or deficiency of the pituitary hormone(s) Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 36
37 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS of the THYROID GLAND Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 37
38 Cancer, Thyroid Gland Pronounced (CAN-sir, THIGH-royd gland) Defined Malignant tumor of the thyroid gland, which leads to dysfunction of the gland and thus inadequate or excessive secretion of the thyroid hormone Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 38
39 Goiter, Simple; Nontoxic Pronounced (GOY-ter Simple; Nontoxic) Defined Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland Results from a deficient amount of iodine in the diet, required for synthesis of T3 and T4, thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 39
40 Graves Disease (Hyperthyroidism) Pronounced (high-per-thigh-royd-izm) Defined Hypertrophy of the thyroid gland resulting in an excessive secretion of the thyroid hormone Causes an extremely high body metabolism, thus creating multisystem changes Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 40
41 Graves Disease Hyperthyroidism (continued) Three Distinguishing Characteristics Hyperthyroidism Thyroid gland enlargement (goiter) Exophthalmia Unnatural protruding of the eyes Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 41
42 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 42
43 Hypothyroidism Pronounced (high-poh-thigh-royd-izm) Defined Condition in which there is a shortage of thyroid hormone causing an extremely low body metabolism due to a reduced usage of oxygen Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 43
44 Hypothyroidism (continued) Hypothyroidism (continued) Most severe form known as myxedema Water retention all over body in connective tissues Person has puffy appearance and thick tongue Reduced metabolic rate Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 44
45 Thyroiditis (Hashimoto s) Pronounced (thigh-royd-eye-tis) (HASH-ee-moh-TOZ) Defined Chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to enlargement of the thyroid gland Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 45
46 Thyrotoxicosis (Thyroid Storm) Pronounced (thigh-roh-toks-ih-koh-sis) Defined An acute, sometimes fatal, incident of overactivity of the thyroid gland resulting in excessive secretion of thyroid hormone Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 46
47 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS of the PARATHYROID GLAND Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 47
48 Hyperparathyroidism (Hypercalcemia) Pronounced (high-per-pair-ah-thigh-royd-izm) (high-per-kal-see-mee-ah) Defined Overactivity of any one of the parathyroid glands, which leads to high levels of calcium in the blood and low levels of calcium in the bones Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 48
49 Hypoparathyroidism Pronounced (high-poh-pair-ah-thigh-royd-izm) Defined Decreased production of parathyroid hormone resulting in hypocalcemia, characterized by nerve and muscle weakness with muscle spasms or tetany Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 49
50 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 50
51 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS of the ADRENAL GLANDS Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 51
52 Addison s Disease Pronounced (AD-ih-sons dih-zeez) Defined A life-threatening disease process due to failure of the adrenal cortex to secrete adequate mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids Resulting from an autoimmune process, a neoplasm, an infection, or a hemorrhage in the gland Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 52
53 Conn s Disease (Primary Aldosteronism) Pronounced (PRYE-mary al-doss-stair-ohn-izm) Defined Condition characterized by excretion of excessive amounts of aldosterone Leads to an increased volume of blood and hypertension Causes the body to retain extra sodium and excrete extra potassium Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 53
54 Cushing s Syndrome Pronounced (CUSH-ings SIN-drom) Defined Condition of the adrenal gland in which there is a cluster of symptoms occurring as a result of an excessive amount of cortisol or ACTH circulating in the blood Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 54
55 Cushing s Syndrome (continued) Cushing s Syndrome Symptoms Central obesity Round moon face Edema Hypertension Supraclavicular fat pads (buffalo hump) Muscular weakness and wasting Skin infection Poor wound healing Low potassium level Emotional changes Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 55
56 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 56
57 Pheochromocytoma Pronounced (fee-oh-kroh-moh-sigh-toh-mah) Defined Vascular tumor of the adrenal medulla that produces extra epinephrine and norepinephrine, leading to persistent or intermittent hypertension and heart palpitations Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 57
58 Virilism Pronounced (VEER-il-izm) Defined Development of male secondary sex characteristics in the female due to the excessive secretion of adrenocortical androgens from the adrenal cortex Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 58
59 Virilism (continued) Virilism Symptoms Excessive hair on the body and face (hirsutism) Absence of menstruation Deepening of the voice Acne Oily skin Muscular hypertrophy Atrophy of the breasts and uterus Ovarian changes Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 59
60 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS of the PANCREAS Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 60
61 Diabetes Mellitus Pronounced (dye-ah-bee-teez MELL-ih-tus) Defined A disorder of the pancreas in which the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas fail to produce an adequate amount of insulin Results in the body s inability to appropriately metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 61
62 Diabetes Mellitus (continued) Classifications Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) Also known as Type I diabetes Usually occurs before the age of 30 Sudden onset Controlled with insulin injections Individuals are prone to developing ketosis Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 62
63 Diabetes Mellitus (continued) Classifications (continued) Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Also known as Type II diabetes Usually appears in adults after the age of 40 Majority of these individuals are obese Usually controlled through diet and exercise Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 63
64 Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 64
65 Pronunciation Diabetic Retinopathy (dye-ah-bet-ik ret-in-op-ah-thee) Defined A disorder of the blood vessels of the retina of the eye in which the capillaries of the retina experience localized areas of bulging (microaneurysms), hemorrhages, and scarring Consequence of an 8-10 year duration of diabetes mellitus Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 65
66 Gestational Diabetes Pronounced (jess-tay-shun-al dye-ah-bee-teez) Defined A disorder in which women who are not diabetic before pregnancy develop diabetes during the pregnancy They develop an inability to metabolize carbohydrates, with resultant hyperglycemia Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 66
67 Pancreatic Cancer Pronounced (pan-kree-at-ik CAN-sir) Defined A life-threatening primary malignant neoplasm typically found in the head of the pancreas Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 67
68 Pancreatitis Pronounced (pan-kree-ah-tye-tis) Defined An acute or chronic destructive inflammatory condition of the pancreas Acute pancreatitis creates symptoms that vary from mild self-limiting pancreatic edema to massive necrotizing hemorrhagic pancreatitis Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 68
69 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures Thyroid Function Tests Tests that measure the blood levels of the hormones T3, T4, and TSH Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Blood Test A test that measures the concentration of TSH in the blood Used to differentiate primary hypothyroidism from secondary hypothyroidism Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 69
70 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures (continued) Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Blood glucose sample taken usually early in the morning after the person has been without food or drink since midnight Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 70
71 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures (continued) Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) A test that evaluates the person s ability to tolerate a concentrated oral glucose load by measuring the glucose levels: Prior to glucose administration 30 minutes after glucose administration 1,2,and 3 hours after glucose administration Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 71
72 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures (continued) Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) Test A thyroid function test that evaluates the function of the thyroid gland by administering a known amount of radioactive iodine and later placing a gamma ray detector over the thyroid gland to determine the percentage or quantity of radioactive iodine absorbed by the gland over specific time periods Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 72
73 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures (continued) Serum Glucose Tests Tests that measure the amount of glucose in the blood at the time the sample was drawn Thyroid Echogram (Ultrasound) An ultrasound examination important in distinguishing solid thyroid nodules from cystic nodules Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 73
74 Diagnostic Techniques and Procedures (continued) Thyroid Scan An examination that determines the position, size, shape, and physiological function of the thyroid gland through the use of radionuclear scanning Copyright 2003 by Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 74
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
Hormones by location
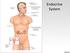 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
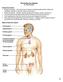 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes?
 Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
54a A&P: Endocrine System
 54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
E - Horton AP Biology
 E - Bio @ Horton AP Biology Unit Anatomy and Physiology Notes Endocrine System A. Categories of Signals 1. Chemical signals are used: between individuals, between body parts, and between cells. 2. Pheromones
E - Bio @ Horton AP Biology Unit Anatomy and Physiology Notes Endocrine System A. Categories of Signals 1. Chemical signals are used: between individuals, between body parts, and between cells. 2. Pheromones
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine Summary 1. Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list of important terms:
 Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System
 Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M
 C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
The Endocrine System - An Overview. 32 Darcy Road, St Osyth, Clacton on Sea, Essex CO16 8QF. Registered Charity Number:
 Last Updated: 23.04.12 Review Date: 25.05.12 Thyroid UK Source materials available on request. If you would like to confirm that this is the latest version of this document please contact: THYROID UK Registered
Last Updated: 23.04.12 Review Date: 25.05.12 Thyroid UK Source materials available on request. If you would like to confirm that this is the latest version of this document please contact: THYROID UK Registered
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 The Endocrine System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Endocrine System The endocrine system interacts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate body activities by means of hormones. Endocrine tissues and
The Endocrine System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Endocrine System The endocrine system interacts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate body activities by means of hormones. Endocrine tissues and
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1. Fill in the Blanks.
 Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
MODULE 6 COURSE MANUAL. CHRISTINA LYNE
 MODULE 6 COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine system has many functions: it works closely with the nervous system and plays an important part in homeostasis,
MODULE 6 COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine system has many functions: it works closely with the nervous system and plays an important part in homeostasis,
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
