Chapter 2: Biological Bases of Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE
|
|
|
- Anissa Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2: Biological Bases of Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What progressive neurological disorder is characterized by memory loss, personality deterioration, and emotional outbursts? a. Parkinson s disease c. Autism b. Multiple Sclerosis d. Alzheimer s disease ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.1 Introduction, Textbook Video - Alzheimer's Disease, Online Video - Declining Mental Acuity, Online OBJ: LO1 Describe Alzheimer's disease. 2. Charles has Alzheimer s disease. What can Charles and his family expect in the coming years? a. His condition will worsen. b. Charles cognitive function will deteriorate, but his personality should not dramatically change. c. Charles will have to take medication for many months, but it is possible to cure his disease. d. The course of Alzheimer s is difficult to describe. REF: 2.1 Introduction, Textbook Video - Alzheimer's Disease, Online Video - Declining Mental Acuity, Online OBJ: LO1 Describe Alzheimer's disease. 3. Which of the following statements best explains why psychologists should study the nervous system? a. The nervous system is controlled by the mind and psychologists focus on the mind. b. Behavior, both normal and abnormal, has its roots in the nervous system. c. Psychologists can perform brain surgery to cure illnesses such as Alzheimer s. d. It is required for licensing and insurance payments. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.1 Introduction, Textbook OBJ: LO1 Describe Alzheimer's disease. 4. are chains of chemicals arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder. a. Genes c. Opsins b. Neurons d. Neurotransmitters ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 39
2 5. Chromosomes consist of: a. zygotes c. DNA b. sperm d. phenotypes ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 6. A is a specific segment on the long strand of DNA. a. gene c. chromosome b. zygote d. phenotype ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 7. Which statement is most accurate in describing the order from smallest to largest? a. zygote, genes, DNA, chromosomes c. DNA, zygote, genes, chromosomes b. genes, DNA, chromosomes, zygote d. DNA, genes, chromosomes, zygote ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Apply REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 8. The color of your eyes is due to genes. Genes provide instructions for making: a. protein c. DNA b. genomes d. chromosomes REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - "Inheriting Eye Color," Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 9. A gene that has more than one version is called a: a. polymorphic gene c. genome b. zygote d. chromosome ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 10. What type of gene is expressed even if it is paired with a recessive gene? a. polymorphic gene c. genome b. zygote d. dominant ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 40
3 11. The gene for brown eyes is ; the gene for blue eyes is. a. recessive; zygotic c. recessive; dominant b. dominant; recessive d. recessive; phenotypic ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Inheriting Eye Color, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 12. You inherited a gene for brown eyes from your father, but a gene for blue eyes from your mother. What color are your eyes? a. blue c. green b. brown d. impossible to predict ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Apply REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Inheriting Eye Color, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 13. Which statement is not consistent with Darwin s view of evolution? a. Different species arouse from a common ancestor. b. Humans and chimps share at least 98% of their DNA. c. Present day humans descended from a creature that split off from apes. d. Humans belong to their own, unique family tree. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Evaluate REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO3 Articulate the forces believed to be responsible for the evolution of the human brain and describe the relevance of the theory of evolution in how psychologists conduct research today. 14. According to the theory of evolution: a. different species arose from different ancestors b. humans belong to their own, unique family tree c. present day humans descended from a creature related to apes d. humans and chimps share only 1% of their DNA ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO3 Articulate the forces believed to be responsible for the evolution of the human brain and describe the relevance of the theory of evolution in how psychologists conduct research today. 15. From the evolutionary perspective, mutations that improve our survival and functioning are called: a. polymorphic genes c. adaptations b. natural selections d. genome ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook OBJ: LO3 Articulate the forces believed to be responsible for the evolution of the human brain and describe the relevance of the theory of evolution in how psychologists conduct research today. 41
4 16. The two groups of cells in your brain are: a. glial cells and astrocytes c. genes and peripheral cells b. neurons and axons d. neurons and glial cells ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. 17. Which brain cells are responsible for providing insulation around the neuron? a. GABA cells c. axon cells b. curare cells d. glial cells ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. 18. Glial cells are to as neurons are to. a. support; transmit c. support; insulate b. transmit; insulate d. Alzheimer s disease; ADHD OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. 19. The functions of neurons include: a. transmitting and receiving electrical messages b. providing support for glial cells c. insulating axons d. opening sodium gates in glial cells ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 20. Which structures specialize in receiving electrical signals and transmitting electrical signals? a. glial cells c. dendrites b. neurons d. astrocytes ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 42
5 21. What do the two main extensions of a neuron do? a. receive and transmit electrical signals b. wrap around glial cells c. support mature glial cells d. provide the mechanisms by which glial cells repair themselves ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 22. Electrical messages can be transmitted in the neuron up to: a. 2 miles per hour c miles per hour b. 200 miles per hour d. 20,000 miles per hour ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 23. The keeps the neuron in working order and has specialized extensions that arise from it. a. axon c. cell body b. myelin sheath d. synapse ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 24. Consider this scenario: The neuron is dying. All of the structures except the cell body are healthy and undamaged. Why might damage to the cell body be the reason for the neuron s impending death? a. The cell body is responsible for insulating the neuron. b. The nucleus may be damaged. c. The cell body receives nourishment from the glial cells. d. The cell body keeps the neuron in working order. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 25. If the axon is the output structure of the neuron, the input structure is the: a. end bulb c. myelin b. dendrite d. lobe ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 43
6 26. Which part of a neuron carries signals away from the cell body? a. axon c. end bulb b. cell body d. dendrites ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 27. This is a bad television set. We re getting lots of interference from other electrical appliances in our apartment. You remember the structures of the neuron and say, Wish we had a television set covered with a(n)... a. myelin sheath c. dendrite b. axon d. neurotransmitter OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 28. Tiny sacs or vesicles that are filled with neurotransmitters are located in the: a. end bulbs c. dendrites b. axon d. synapse ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 29. A synapse is the: a. part of the dendrite that receives incoming signals b. small space between the end bulb and its neighboring dendrite, muscle fiber, or body organ c. chemical that transmits signals from one neuron to another d. signal that travels from one neuron to another ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 30. End bulbs release neurotransmitters into the: a. cell body c. myelin sheath b. synapse d. axon ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 44
7 31. The membrane of the axon has the unique ability to: a. ionize itself c. open and close its chemical gates b. change its size d. negatively charge the dendrites ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 32. Opposite-charged ions and like-charged ions. a. attract; repel c. have sodium; have protein b. are permeable; are semipermeable d. are positive; are negative REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 33. When a neuron is in a resting state, the majority of the particles in the fluid surrounding the neuron are: a. positive sodium ions b. sodium ions that have yet to pick up a charge c. chloride ions d. chemically inert REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 34. The all-or-none law explains what happens when: a. positively and negatively charged ions meet b. an impulse starts at the beginning of an axon c. electrical impulses spread throughout the body d. your brain gets the idea of a six-pack ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 35. What accounts for the action potential moving down the axon at a constant speed? a. all-or-none law c. snowball effect b. paced resistance principle d. neuronal push rule OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 45
8 36. If the stimulation is strong enough, the neuron s chemical gates and will come into the neuron. a. open; negative sodium ions c. close; positive sodium ions b. open; positive sodium ions d. close; vesicles ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 37. If the positive sodium ions rush inside the axon, the axon will: a. enter the resting state c. change its threshold b. release a neurotransmitter d. experience an action potential ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 38. Which statement is true if there is an action potential at a particular point along the axon? At that point in the axon, the a. inside of the axon is positively charged; the outside is negatively charged b. inside of the axon is negatively charged; the outside is positively charged c. sodium pumps are highly active d. chemical gates are closed to sodium ions ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. MSC: TYPE: Difficult 39. A tiny electrical current generated in the axon is called a(n) a. electropotential c. action potential b. ion wave d. resting potential ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 40. What structure in the neuron helps to speed up the transmission of the action potential? a. axon c. myelin sheath b. dendrites d. end bulb ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 46
9 41. While speeding down an axon, the impulse reaches an incredible speed by jumping at the breaks in the: a. end bulb c. myelin sheath b. dendrite d. synapse ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 42. is/are (a) chemical messenger(s) that transmit(s) information between nerves and body organs. a. Transmitters c. THC b. Ion d. Enzymes ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 43. Neurotransmitters are found in the: a. myelin sheath c. inhibitory sodium b. sodium ions d. end-bulbs ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 44. What substance is found in the end bulbs? a. neurotransmitters c. inhibitory sodium b. sodium ions d. precursors ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 45. If receptors in muscle fibers are thought of as locks, the keys are: a. the action potential of the axon c. the resting state of the axon b. synapses d. neurotransmitters ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 47
10 46. After the release of neurotransmitters in the synapse, neurotransmitters cross the synapse and: a. fit into specially designed axons b. cause the second neuron to open its chemical locks c. cause the process known as reuptake d. fit into specially designed receptors located on the second neuron s dendrites ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 47. If a neurotransmitter key opens the receptor s lock, then the neurotransmitter is said to be: a. at the threshold c. positively charged b. excitatory d. at an action potential ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Apply REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 48. If a neurotransmitter key closes the receptor s lock, then the neurotransmitter is said to be: a. at the threshold c. positively charged b. inhibitory d. at an action potential ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Apply OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 49. Excitatory neurotransmitters: a. open the receptor s lock c. reverse the charge of a sodium ion b. slow down the speed of a nerve impulse d. are released during the resting state OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 50. Inhibitory neurotransmitters: a. close the receptor s lock c. reverse the charge of a sodium ion b. slow down the speed of a nerve impulse d. are released during the resting state OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 48
11 51. The effect of a neurotransmitter on an adjacent neuron, muscle, or organ is: a. excitatory c. either excitatory or inhibitory b. inhibitory d. determined by the all-or-none law ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2,3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 52. Excitatory transmitters chemical locks; inhibitory transmitters chemical locks. a. close; open c. destroy; open b. open; close d. open; destroy ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 53. A child puts her hand on a hot stove. She quickly removes it. This is an example of a(n), and it involves. a. learned response; reflexes c. reflex; involuntary reaction b. activating stimulus; voluntary reaction d. excitatory signal; efferent neurons ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO8 Describe the sequence of the reflex response. 54. Neurons that carry information from the senses to the spinal cord are called neurons. a. spinal c. afferent b. motor d. efferent ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO8 Describe the sequence of the reflex response. 55. If all the efferent neurons were removed from your nervous system, you would be unable to: a. process language c. solve complex problems b. move your body d. control your emotions ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO8 Describe the sequence of the reflex response. 56. Efferent neurons carry information away from the: a. axon c. synapse b. muscles d. spinal cord ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO8 Describe the sequence of the reflex response. 49
12 57. The nerves in the body (excluding the brain and spinal cord) make up the: a. peripheral nervous system c. primary nervous system b. central nervous system d. secondary nervous system REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO10 Classify the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 58. As you re waiting to visit a friend in the hospital, you overhear a physician talking to a patient s parents. You don t hear the entire conversation, but only bits and pieces. There is something about an accident and a question regarding nerves reattaching. The physician replied that the nerves do have the ability to regrow. From your education in psychology, you guess that the nerves were probably part of the: a. spinal cord c. peripheral nervous system b. central nervous system d. limbic system ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO10 Classify the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 59. Afferent is to efferent as is to. a. sensory; motor c. sensory; spinal b. motor; sensory d. spinal; neuron REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 60. The somatic nervous system contains: a. sympathetic division and parasympathetic division b. afferent and efferent fibers c. sensory and afferent fibers d. motor fibers and latent fibers ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 61. Karen was able to live in a coma for several years even when taken off the respirator. This is because parts of the body not under conscious control continue to function. These parts are regulated by the: a. central nervous system c. somatic nervous system b. autonomic nervous system d. forebrain ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 50
13 62. The specific part of the nervous system that is responsible for returning the body to a relaxed state is the: a. parasympathetic nervous system c. autonomic nervous system b. somatic nervous system d. peripheral nervous system ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 63. The two divisions of the nervous system are: a. sympathetic division and parasympathetic division b. somatic nervous system and central nervous system c. autonomic nervous system and central nervous system d. peripheral nervous system and central nervous system ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 64. You re looking at a book entitled Your Autonomic Nervous System. One of the chapter titles is really confusing based upon your knowledge of the autonomic nervous system. Which chapter seems to not fit your knowledge? a. The Sympathetic Division: Activating in Times of Stress b. Relaxing with the Parasympathetic Division c. The Autonomic Nervous System: You CAN Control It All! d. The Autonomic Nervous System: Part of The Peripheral Nervous System ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Evaluate REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Autonomic Nervous System, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 65. What part of your nervous system, which requires deep thought, do you use to correctly answer this question? a. central nervous system c. autonomic nervous system b. somatic nervous system d. parasympathetic division REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 66. Which technique uses radio frequencies to study the structure of the brain? a. MRI scan c. PET scan b. SET scan d. the stereotaxic procedure ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 51
14 67. fmri is to as MRI is to. a. structure; function c. organization; function b. function; structure d. x-ray; gamma ray ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 68. Ivan is having his brain scanned. As the machine is working, he is asked to read words on a screen. He is most likely having a(n): a. MRI scan c. fmri scan b. SET scan d. x-ray scan ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 69. What is the main advantage of fmri over PET scans? a. PET scans can cause brain damage b. cost c. fmri can be done with the person awake d. fmri does not require injection of a radioactive solution ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Evaluate REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 70. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) differs from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in that a PET scan: a. studies the structure of the brain c. uses radio frequencies b. studies activity in the brain d. identifies spinal cord injuries ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 71. Positron emission tomography (PET) is a technique used to: a. transplant fetal brain tissue b. repair damaged neurons in the spinal cord c. study the function of brain areas d. perform a frontal lobotomy ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 52
15 72. Stereotaxic procedures: a. cause a great deal of brain damage b. are used for brain tissue transplants c. have been shown to be ineffective in treating Parkinson s disease d. have only been performed on animals ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO13 Describe experimental procedures to treat the brain. 73. In treating Parkinson s disease with brain stimulation, the patient: a. undergoes painful shock treatment while under general anesthesia b. often develops uncontrollable seizures c. develops unwanted jerky movement d. controls the amount of stimulation ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook Video - A Brain Pacemaker, Online OBJ: LO13 Describe experimental procedures to treat the brain. 74..The three main divisions of the human brain are: a. forebrain, midbrain, and cerebrain c. forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain b. topbrain, midbrain, and hindbrain d. neobrain, lateralbrain, and medialbrain ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 75. The part of the brain that directly allows you to contemplate the answer to this question is the: a. hindbrain c. forebrain b. midbrain d. cerebellum ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 76. Rex is an evil scientist and wants to take away humans ability to use language, plan, and make decisions. What part of the brain should his newly invented Death Ray Gun destroy? a. limbic system c. thalamus b. reticular formation d. forebrain ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 53
16 77. You are listening to a few songs that you really like since they are very relaxing. What part of your brain has a reward or pleasure center that is very active as you listen to the songs? a. Broca s area c. cerebellum b. medulla d. midbrain ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 78. In what brain area do you find the reticular formation? a. midbrain c. occipital lobe b. medulla d. cerebellum REF: 2.6 Brain: Structure and Functions,Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 79. The pons: a. controls vital reflexes such as respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure b. coordinates voluntary movements c. contains Purkinje cells d. connects the spinal cord to the brain and makes chemicals important in sleep ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions,Textbook Video - "Hindbrain Structures," Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 80. The medulla: a. controls vital reflexes such as respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure b. initiates voluntary movements c. regulates the production of speech d. connects the spinal cord to the brain and makes chemicals important in sleep ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - "Hindbrain Structures," Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 81. The cerebellum is an important part of the hindbrain that: a. initiates voluntary movement b. influences social-emotional behavior c. coordinates voluntary movements d. makes humans distinct from all other animals ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Hindbrain Structures, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 54
17 82. Which of the following activities would most likely involve the cerebellum? a. experiencing emotion c. dancing b. long-term memory d. listening to a foreign language ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Hindbrain Structures, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 83. The thin layer of cells that cover the surface of the forebrain is called the: a. cortex c. cerebellum b. myelin sheath d. thalamus ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions,Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 84. The human cortex is wrinkled because: a. it is very old compared to more primitive brains b. wrinkling increases the surface area c. the cell body causes a constriction at the surface d. the axons pull down on certain parts of the cortex ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - The Cortex, Online 85. The forebrain can be divided into lobes. Which of the following is not a lobe? a. frontal c. lateral b. parietal d. occipital ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online 86. Which of the following descriptions of the lobes of the cortex is incorrect? a. frontal involved with personality and emotion b. parietal involved with motor behaviors c. temporal involved with processing auditory experience d. occipital involved with processing visual information ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 55
18 87. The brain area that most distinguishes us from animals is the: a. thyroid c. pons b. cerebellum d. cortex ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - The Cortex, Online 88. The frontal lobe is involved in: a. social-emotional behaviors c. sensory experiences b. reflexive actions d. Wernicke s Aphasia ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - The Cortex, Online 89. After a serious blow to the head, Hector underwent a dramatic personality change. A well-organized, extroverted person before the accident, he no longer could plan, or adjust to new social situations. Hector would also laugh uncontrollably at inappropriate times. What part of Hector s brain appears to have been damaged? a. thalamus c. frontal lobe b. temporal lobe d. hippocampus ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook 90. The story of Phineas Gage demonstrates that: a. the frontal lobe seems to be involved in emotion and decision making b. a person cannot live if the frontal lobe is damaged c. a person cannot walk if the frontal lobe is damaged d. the frontal lobe seems to be a large mass of tissue that does not have any particular function ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook 91. Based upon your textbook, the cognitive functions of the frontal lobe include all but one of the following. Which one is not among the functions found in the frontal lobe? a. attention c. organizing b. decision making d. processing tactile information ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain, Structures and Functions,Textbook 56
19 92. The motor cortex is located in the lobe. a. somatosensory c. temporal b. frontal d. occipital ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 93. The strip of the cortex in the frontal lobe that is involved in the initiation of all voluntary movements is called: a. the somatosensory cortex c. Broca s area b. the sensory homunculus d. the motor cortex ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 94. The motor cortex initiates all voluntary movements and is found in: a. the limbic system c. Broca s area b. the parietal lobe d. the frontal lobe ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 95. The somatosensory cortex is located in the: a. frontal lobe c. motor cortex b. parietal lobe d. occipital lobe ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Parts of the Brain, Online Video - The Cortex, Online 96. If your parietal lobe is damaged, you would have difficulty: a. imitating motor movements b. coordinating movements on the left side and right side of your body c. with visual perception d. recognizing through touch the shape of a telephone in a dark room ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook 57
20 97. Wernicke s area is located in the lobe, whereas Broca s area is located in the lobe. a. occipital; temporal c. parietal; occipital b. temporal; frontal d. frontal; parietal ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Animation - Broca's and Wernicke's Aphasia, Online 98. Wernicke s aphasia and Broca s aphasia are evidence that: a. language abilities are more inherited than acquired b. special areas of the lobes of the cortex control language abilities c. if one area is damaged, the other takes over for it d. human language is so complex that a number of things can go wrong with it ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions,Textbook Animation - "Broca's and Wernicke's Aphasia," Online 99. Which of the following is located in the occipital lobe? a. primary visual c. sensory b. primary auditory d. motor ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook 100. A person with visual agnosia would have problems: a. transmitting electrical messages from the eyes b. recognizing objects or persons they know c. seeing fine parts of a visual stimulus d. seeing objects on a particular side of his or her body ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook 101. What part of the brain do we share in common with the alligator? a. Broca s area c. limbic system b. cortex d. Wernicke s area ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions. 58
21 102. One of the functions of the limbic system is to: a. regulate motivational and emotional behaviors b. moderate pain signals from the muscles c. regulate blood pressure and heart rate d. pass information from one hemisphere of the brain to the other REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions You are watching a really scary movie. The main character is about to be attacked by a monster. You look over to the person sitting next to you and see fear in his face. What part of the limbic system allows you to evaluate his expression? a. hypothalamus c. thalamus b. hippocampus d. amygdala ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions A patient known as H. M., while undergoing brain surgery, suffered accidental brain damage. After the surgery, while he retained all of his old memories, he could no longer make new ones. H. M. could not retain new information for more than about 30 seconds. What part of his limbic system was damaged? a. hypothalamus c. hippocampus b. thalamus d. cortex ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions The hippocampus is involved with: a. receiving sensory information c. regulating sexual behavior b. putting memories into permanent storage d. controlling the secretion of hormones ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions What part of the brain could be compared to a switchboard receiving calls from all over the country and then directing the paths of these incoming calls? a. thalamus c. occipital lobe b. hypothalamus d. cerebellum REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions. 59
22 107. Hormones are secreted from glands located throughout the body. These glands are called the: a. endocrine system c. limbic system b. endorphin system d. pituitary system REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO19 Locate and describe the key elements of the endocrine system The endocrine system and the nervous system are basically: a. similar they are both chemical systems b. similar they both send information throughout the body c. different the nervous system affects the brain and the endocrine system affects the body d. different the nervous system causes positive functioning and the endocrine system causes dysfunctions ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO19 Locate and describe the key elements of the endocrine system are secreted by the glands that make up the endocrine system. a. Gonads c. Rhodopsins b. Hormones d. Pancreas ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO19 Locate and describe the key elements of the endocrine system The structure known as the control center of the endocrine system is the: a. thyroid c. hypothalamus b. adrenal d. parathyroid ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO19 Locate and describe the key elements of the endocrine system Which of the following regulates growth through secretion of growth hormone? a. pancreas c. thyroid b. gonads d. anterior pituitary ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO20 Discuss some ways that hormones regulate behavior. 60
23 112. Hormones that regulate sexual development and the growth of the sex organs are produced by the: a. pancreas c. adrenal glands b. gonads d. posterior pituitary ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.7 The Endocrine System, Textbook OBJ: LO20 Discuss some ways that hormones regulate behavior. TRUE/FALSE 1. A family history of Alzheimer s disease does not affect an individual s risk of Alzheimer s. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.1 Introduction, Textbook OBJ: LO1 Describe Alzheimer's disease. 2. DNA is made up of chromosomes. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 3. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 4. Glial cells are the most numerous brain cells. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neuron's: Structure, Function, and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO4 Identify the main functions of glial cells. 5. The dendrite is the input portion of the neuron. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 61
24 6. The space between neurons is called the synapse. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 7. As the action potential is traveling down the axon, it can increase or decrease in speed. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 8. The nerve impulse is called an action potential. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 9. The action potential occurs when negative sodium ions rush inside the axon. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO6 Describe the sequence of the action potential and neural impulse. 10. Inhibitory neurotransmitters close the chemical locks in the heart muscle. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 11. The relationship between a neurotransmitter and receptor is like a key and lock. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand OBJ: LO7 Describe neurotransmitters and explain how neurons communicate at chemical synapses. 62
25 12. The autonomic nervous system is part of the central nervous system. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online Animation - Autonomic Nervous System, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 13. The sympathetic nervous system returns the body to a calmer state. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook Animation - Nervous Systems, Online OBJ: LO11 Differentiate the functions of the major divisions and subdivisions of the nervous system. 14. MRI scans require an injection of a radioactive material into the patient's blood. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.5 Studying the Living Brain, Textbook OBJ: LO12 Describe the different technologies used to investigate the brain. 15. The cerebellum controls vital reflexes. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Hindbrain Structures, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 16. The frontal lobes govern executive functions. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Cerebral Cortex, Online OBJ: LO14 Identify and locate the major parts of the brain, and state their functions. 17. In Broca's aphasia, the person has difficulty speaking in a fluent way. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Cerebral Cortex, Online Animation - Broca's and Wernicke's Aphasia, Online 18. The primary visual cortex turns visual sensation into a complete, meaningful perception. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Cerebral Cortex, Online 63
26 19. The hippocampus relays sensory information to areas of the cortex. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions. 20. The hypothalamus plays a major role in eating, drinking and other drives. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions. 21. When a child watches violence on TV, there is an increase in the activity of the cerebellum. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO16 Identify and locate key structures in the limbic system, and state their functions. 22. Male and female brains look identical in brain scans during problem solving. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Inside the Female Brain, Online OBJ: LO17 Identify sex differences in the brain. 23. Women have 15-20% more neurons in their brain compared to men. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO17 Identify sex differences in the brain. 24. Women s brains are more effective at solving rotating figures problems men s brains. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook Video - Limbic System, Online OBJ: LO17 Identify sex differences in the brain. 25. The left hemisphere is good at recognizing tone of voice. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO18 Describe lateralization of brain functions. 26. The left hemisphere is good at language functions. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO18 Describe lateralization of brain functions. 64
27 27. The right hemisphere is better at math skills than is the left hemisphere. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO18 Describe lateralization of brain functions. 28. The left hemisphere processes information by examining each separate piece rather than the whole. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.6 Brain: Structures and Functions, Textbook OBJ: LO18 Describe lateralization of brain functions. SHORT ANSWER 1. Why should psychologists study the brain? ANS: Answers may vary, but should note the relationship of the brain to mental functions and behavior. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Analyze REF: 2.1 Introduction, Textbook OBJ: LO1 Describe Alzheimer's disease. 2. What is the relationship between chromosomes, DNA, and genes? ANS: A chromosome is a short, rodlike, microscopic structure that contains tightly coiled strands of the chemical DNA. DNA is made up of four chemicals. The order in which the four different chemicals combine creates a microscopic chemical alphabet. This chemical alphabet is used to write instructions for the development and assembly of the 100 trillion highly specialized cells that make up the brain and body. A gene is a specific segment on the strand of DNA that contains instructions for making proteins. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.2 Genes and Evolution, Textbook Animation - Genes Overview, Online OBJ: LO2 Describe the structures and processes involved in genetic transmission. 3. Briefly explain the function of the neuron cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, and end bulbs. Draw a diagram showing the structures. ANS: The cell body (or soma) is a relatively large, egg-shaped structure that provides fuel, manufactures chemicals, and maintains the entire neuron in working order. Dendrites are branchlike extensions that arise from the cell body; they receive signals from other neurons, muscles, or sense organs and pass these signals to the cell body. The axon is a single threadlike structure that extends from, and carries signals away from, the cell body to neighboring neurons, organs, or muscles. 65
28 The myelin sheath looks like separate tubelike segments composed of fatty material that wraps around and insulates an axon. The myelin sheath prevents interference from electrical signals generated in adjacent axons. End bulbs or terminal bulbs look like tiny bubbles that are located at the extreme ends of the axon s branches. Each end bulb is like a miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters, which are used to communicate with neighboring cells. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function and Communication, Textbook Animation - Neuron and OBJ: LO5 Identify the various parts of the neuron and explain how a neuron functions. 4. What roles do afferent neurons, interneurons, and efferent neurons play in a reflex? ANS: Afferent, or sensory, neurons carry information from the sensors to the spinal cord. An interneuron is a relatively short neuron whose primary task is making connections between other neurons. Efferent, or motor, neurons carry information away from the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Understand REF: 2.3 Neurons: Structure, Function, & Communication, Textbook OBJ: LO8 Describe the sequence of the reflex response. 5. Differentiate between nerves and neurons. ANS: Nerves are stringlike bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue. Nerves carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body s organs to and from the spinal cord. A neuron is a brain cell with two specialized extensions. One extension is for receiving electrical signals, and a second, longer extension is for transmitting electrical signals. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's: Remember REF: 2.4 Nervous System, Textbook OBJ: LO9 Differentiate between nerves and neurons. 6. Describe the major divisions of the nervous system and their subdivisions. ANS: The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. From the bottom of the brain emerges the spinal cord, which is made up of neurons and bundles of axons and dendrites that carry information back and forth between the brain and the body. The peripheral nervous system includes all the nerves that extend from the spinal cord and carry messages to and from various muscles, glands, and sense organs located throughout the body. 66
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
The Nervous System IN DEPTH
 The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Why does the writer above love running so much? One of the reasons. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure. Reader s Guide. Exploring Psychology
 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
 BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
How We Grow & Change
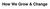 How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system
 Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of
 Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
AP Psychology Ch. 02 The Brain Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System
 AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
35-2 The Nervous System
 1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Neuroscience. Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
 Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
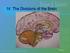 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
