:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
|
|
|
- Poppy Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information, just as the circulatory system handles blood. :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: There are two major types of cells in the nervous system: glia and neurons. Neurons are cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information. In the human nervous system, the vast majority are interneurons neurons that communicate with other neurons. There are also sensory neurons, which receive signals from outside the nervous system, and motor neurons, which carry messages from the nervous system to the muscles that move the body. The soma, or cell body, contains the cell nucleus and much of the chemical machinery common to most cells. :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 :: The branched structure is called a dendritic tree, and each individual branch is a dendrite. Dendrites are the parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information. The long fiber is the axon. Axons are specialized structures that transmit information to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
2 :: Slide 7 :: :: Slide 8 :: Most human axons are wrapped in a myelin sheath. Myelin is a white, fatty substance that serves as an insulator around the axon and speeds the transmission of signals. In people suffering from multiple sclerosis, some myelin sheaths degenerate, slowing or preventing nerve transmission to certain muscles. The axon ends in a cluster of terminal buttons, which are small knobs that secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals serve as messengers that may activate neighboring neurons. The points at which neurons interconnect are called synapses. A synapse is a junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. :: Slide 9 :: :: Slide 10 :: Glia come in a variety of forms. Their main function is to support the neurons by, among other things, supplying them with nutrients and removing waste material. In the human brain, there are about ten glia cells for every neuron. The neuron at rest is a tiny battery, a store of potential energy. Inside and outside the axon are fluids containing electrically charged atoms and molecules called ions. Positively charged sodium and potassium ions and negatively charged chloride ions are the principal molecules involved in the nerve impulse. :: Slide 11 :: :: Slide 12 :: When the neuron is not conducting an impulse, it is said to be in a resting state. The cell membrane is polarized negatively charged on the inside and positively charged on the outside. The charge difference across the membrane can be measured with a pair of microelectrodes connected to an oscilloscope. In a resting neuron, this difference, called the resting potential, is about 70 millivolts. Click to play animation. Make sure volume is turned up.
3 :: Slide 13 :: :: Slide 14 :: When the neuron is stimulated, channels in its cell membrane open, briefly allowing positively charged ions to rush in. For an instant, the neuron s charge is less negative, or even positive, creating an action potential. Click to play animation. Make sure volume is turned up. An action potential is a very brief shift in the neuron s electrical charge that travels along an axon. :: Slide 15 :: :: Slide 16 :: The size of an action potential is not affected by the strength of the stimulus a weaker stimulus does not produce a weaker action potential. If the neuron receives a stimulus of sufficient strength, it fires, but if it receives a weaker stimulus, it doesn t. This is referred to as the all-or-none law. The neural impulse is a signal that must be transmitted from a neuron to other cells. This transmission takes place at special junctions called synapses, where terminal buttons release chemical messengers. The two neurons are separated by the synaptic cleft, a microscopic gap between the terminal button of one neuron and the cell membrane of another neuron. Signals have to cross this gap for neurons to communicate. :: Slide 17 :: :: Slide 18 :: The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. Click to continue. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Within the buttons, most of these chemicals are stored in small sacs, called synaptic vesicles.
4 :: Slide 19 :: :: Slide 20 :: The neurotransmitters are released when a vesicle fuses with the membrane of the presynaptic cell and its contents spill into the synaptic cleft. After their release, neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the receiving cell. When a neurotransmitter and a receptor molecule combine, reactions in the cell membrane cause a postsynaptic potential, or PSP a voltage change at the receptor site on a postsynaptic cell membrane. After producing postsynaptic potentials, some neurotransmitters either become inactivated by enzymes, or drift away. Most neurotransmitters, however, are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron through reuptake a process in which neurotransmitters are sponged up from the synaptic cleft by the presynaptic membrane. :: Slide 21 :: :: Slide 22 :: Most neurons are interlinked in complex chains, pathways, circuits, and networks. Our perceptions, thoughts, and actions depend on patterns of neural activity in elaborate neural networks. Click to see a video that shows how neural networks work. Specific neurotransmitters work at specific kinds of synapses the study of which has led to interesting findings about how specific neurotransmitters regulate behavior. One example is acetylcholine, which is released by motor neurons controlling skeletal muscles, and contributes to the regulation of attention, arousal, and memory. An inadequate supply of acetylcholine is associated with the memory losses seen in Alzheimer s patients. Here are a few other examples of neurotransmitters, and how their dysregulation is associated with certain disorders. :: Slide 23 :: :: Slide 24 :: The multitudes of neurons in your nervous system have to work together to keep information flowing effectively. The peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord. Nerves are bundles of neuron fibers or axons that are routed together in the peripheral nervous system.
5 :: Slide 25 :: :: Slide 26 :: The peripheral nervous system can be divided into two parts. The somatic nervous system is made up of nerves that connect to voluntary skeletal muscles and sensory receptors. They carry information from receipts in the skin, muscles, and joints to the CNS, and from the CNS to the muscles. The autonomic nervous system is made up of nerves that connect to the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles, and glands. It controls automatic, involuntary, visceral functions that people don t normally think about, such as heart rate, digestions, and perspiration. When a person is autonomically aroused, automatic functions speed up. This speeding up is controlled by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system the sympathetic nervous system mobilizes the body s resources for emergencies and creates the fight-or-flight response. The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, conserves bodily resources to save and store energy. :: Slide 27 :: :: Slide 28 :: The central nervous system, or CNS, consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is protected by enclosing sheaths called meninges, as well as cerebrospinal fluid, which nourishes the brain and provides a protective cushion for it. Neuroscientists use many specialized techniques to investigate connections between the brain and behavior. The spinal cord houses bundles of axons that carry the brain s commands to peripheral. :: Slide 29 :: :: Slide 30 :: Lesioning involves the destruction of a piece of the brain in order to observe what happens. Electrical stimulation of the brain sends a weak electric current into the brain to stimulate it. Brain imaging devices allow neuroscientists to look inside the human brain, such as in a CT (computerized tomography or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan. Another new research tool in neuroscience is transcranial magnetic stimulation, which allows scientists to temporarily enhance or depress activity in a specific area of the brain. This news video shows an example of how TMS may impact patients with depression.
6 :: Slide 31 :: :: Slide 32 :: The hindbrain includes the cerebellum and two structures found in the lower part of the brainstem: the medulla and the pons. The cerebellum is critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium, or physical balance. Damage to the cerebellum disrupts fine motor skills, such as those involved in writing or typing. The pons contains several clusters of cell bodies that contribute to the regulation of sleep and arousal. The midbrain is concerned with certain sensory processes, such as locating where things are in space. The midbrain is the origin of an important system of dopamine-releasing axons. Among other things, this dopamine system is involved in the performance of voluntary movements. The abnormal movements associated with Parkinson s disease are due to the degeneration of neurons in this area. The medulla, which attaches to the spinal cord, has charge of largely unconscious but essential functions, such as regulating breathing, maintaining muscle tone, and regulating circulation. :: Slide 33 :: :: Slide 34 :: Running through both the hindbrain and the midbrain is the reticular formation. Lying at the central core of the brainstem, the reticular formation contributes to the modulation of muscle reflexes, breathing, and the perception of pain. The forebrain is the largest and most complex region of the brain, encompassing a variety of structures, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum. It is best known, however, for its role in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. Activity in the ascending fibers of the reticular formation is essential to maintaining an alert brain. :: Slide 35 :: :: Slide 36 :: The thalamus is a structure in the forebrain through which all sensory information, except smell, must pass to get to the cerebral cortex. This way station is made up of a number of clusters of cell bodies, or nuclei. Each cluster is concerned with relaying sensory information to a particular part of the cortex. The limbic system is a loosely connected network of structures involved in emotion, motivation, memory, and other aspects of behavior. The hypothalamus is made up of a number of distinct nuclei. These nuclei regulate a variety of basic biological drives, including the so-called four Fs fighting, fleeing, feeding, and mating.
7 :: Slide 37 :: :: Slide 38 :: The cerebrum is the largest and most complex part of the human brain. It includes the brain areas that are responsible for our most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness itself. The cerebrum is divided into right and left halves, called cerebral hemispheres. If we pry apart the two halves of the brain, we see that this fissure descends to a structure called the corpus callosum. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided by deep fissures into four parts called lobes. To some extent, each of these lobes is dedicated to specific purposes. The occipital lobe includes the cortical area where most visual signals are sent and visual processing is begun the primary visual cortex. The parietal lobe includes the area that registers the sense of touch the primary somatosensory cortex. The temporal lobe contains an area devoted to auditory processing, the primary auditory cortex. :: Slide 39 :: :: Slide 40 :: In recent decades, an exciting flurry of research has focused on cerebral lateralization the degree to which the left or right hemisphere handles various cognitive and behavioral functions. However, hints of cerebral specialization were found as early as the late 1800s. In 1874, Paul Wernicke discovered that damage to a portion of the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere leads to problems with the comprehension of language. Patients with damage in Wernicke s area can speak normally but have difficulty understanding others. In 1861, Paul Broca, a French surgeon, performed an autopsy on a patient who had been unable to speak. The autopsy revealed a lesion on the left side of the man s frontal lobe. Since then, many similar cases have shown that this area of the brain which came to be known as Broca s area plays an important role in the production of speech. :: Slide 41 :: :: Slide 42 :: Each hemisphere s primary sensory and motor connections are to the opposite side of the body the left hemisphere controls and communicates with the right hand, arm, etc. and the right hemisphere controls and communicates with the left side. Vision is more complex. Stimuli in the right half of the visual field are registered by receptors on the left side of each eye that send signals to the left hemisphere. Roger Sperry and his colleagues found that the ability of split-brain subjects to name and describe objects depended on which side of the visual field the image was flashed in. When pictures of common objects were flashed in the right visual field and thus sent to the left hemisphere, the split-brain subjects were able to name and describe the objects depicted. Similarly, stimuli in the left half of the visual field are registered by receptors on the right side of each eye that send signals to the right hemisphere.
8 :: Slide 43 :: :: Slide 44 :: In another experimental procedure, split-brain subjects were asked to reach under a screen to hold various objects. When objects were placed in the split-brain subjects right hand, which communicates most directly with the left hemisphere, the subjects had no problem naming the objects. Research with split-brain subjects provided the first compelling evidence that the right hemisphere has its own special talents. Based on this research, investigators concluded that the left hemisphere usually handles verbal processing, whereas the right hemisphere usually handles nonverbal processing, such as that required by visual-spatial and musical tasks. When the objects were placed in the subjects left hand, which communicates most directly with the right hemisphere, the subjects had difficulty naming the objects. :: Slide 45 :: :: Slide 46 :: Eventually, researchers wondered whether it was safe to generalize from splitbrain subjects to normal individuals whose corpus callosum was intact. One method of studying cerebral specialization in an intact brain is by looking at perceptual asymmetries left-right imbalances between the cerebral hemispheres in the speed of visual or auditory processing. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemicals known as hormones into the bloodstream that help control bodily functioning. Some hormones are released in response to changing conditions in the body and act to regulate those conditions. Subtle differences in the abilities of the two hemispheres can be detected by precisely measuring how long it takes participants to recognize different types of stimuli. :: Slide 47 :: :: Slide 48 :: Hormones are secreted by the endocrine glands in a pulsatile manner that is, several times per day in brief bursts or pulses. The levels of many hormones increase to a certain level, then signals are sent to the hypothalamus or other endocrine glands to stop secretion of that hormone a negative feedback system. Much of the endocrine system is controlled by the nervous system through the hypothalamus, which also connects with the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland stimulates actions in the other endocrine glands. For example, in the fight or flight response, the hypothalamus sends signals through the pituitary gland and autonomic nervous system to the adrenal glands, which then secrete stress hormones.
9 :: Slide 49 :: :: Slide 50 :: Every cell in your body contains information from your parents, found on the chromosomes that lie within the nucleus of each cell. Each chromosome contains thousands of genes, which also occur in pairs. Sometimes a member of a pair has a louder voice, always expressing itself and masking the other member of the pair this is a dominant gene. A recessive gene is one that is masked when the paired genes are different. When a person has two genes in a specific pair that are the same, the person is homozygous for that trait. If the genes are different, they are heterozygous. Family studies, twin studies, and adoption studies are assess the impact of heredity on behavior. Family studies and twin studies focus on genetic relatedness and how it affects various traits in order to study the influence of nature on behavior. Adoption studies are able to assess the influences of both nature and nurture, as adopted children s traits can be evaluated in relation to both their biological and adoptive parents. :: Slide 51 :: :: Slide XX :: The field of evolutionary psychology is based on the work of Charles Darwin and the ideas of natural selection and reproductive fitness. Left blank Evolutionary theorists study adaptations, or inherited characteristics, that increase in a population because they help solve a problem of survival or reproduction during the time they emerge. :: Slide XX :: :: Slide XX :: Left blank Left blank
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY
 Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
2. When a neuron receives signals, an abrupt, temporary the inside becomes more positive in the polarity is generated (an action potential).
 Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Chapter 3. The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition
 Chapter 3 The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition Communication in the Nervous System Hardware: Glia structural support and insulation Neurons communication Soma cell body Dendrites receive Axon
Chapter 3 The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition Communication in the Nervous System Hardware: Glia structural support and insulation Neurons communication Soma cell body Dendrites receive Axon
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
The Nervous System. B. The Components: 1) Nerve Cells Neurons are the cells of the body and are specialized to carry messages through an process.
 The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurophysiology scripts. Slide 2
 Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
How We Grow & Change
 How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
How We Grow & Change Neural Development What makes up nerves? Neurons! (single cells) Interesting Facts About Neurons: Average brain has approx 100 billion neurons and we only use 10% (10 billion neurons)!
II. Nervous System (NS) Organization: can be organized by location/ structure or by function A. Structural Organization 1. Central N.S.
 Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
35-2 The Nervous System Slide 1 of 38
 1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
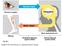 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Structure of the Cortex
 Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s
 Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
